when things go wrong in the kidney
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from physio lecture
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
one of the kidney’s main functions is hormonal control of other systems including the release of calcitriol. what happens as a result of high serum Ca2+?
calcitonin from thyroid signals kidney to decrease Ca2+ reabsorption, promoting it’s excretion
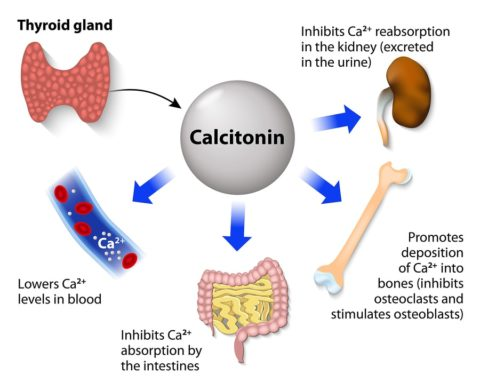
one of the kidney’s main functions is hormonal control of other systems including the release of calcitriol. what happens as a result of low serum Ca2+
the kidney responds to PTH by increasing Ca2+ reabsorption from urine and making calcitriol to increase Ca2+ GI absorption.
a decrease in circulating volume (like one of the effects of ANP/BNP), does this to blood pressure
decreases it
diuresis (like one of the effects of ANP/BNP), does this to blood pressure
decreases it
in kidney failure, low calcitriol can lead to low serum Ca2 due to these conditions
secondary hyperparathyroidism, increased bone breakdown
what happens when pH is not in it’s normal range (7.35-7.45)
enzymes denature and can’t perform catalytic function
excess serum ammonia can be toxic. it is caused by liver disease. it is termed
hyperammonemia
unexplained vomiting and mental status changes may be indicative of liver disease and thus,
hyperammonemia
tx for hyperammonemia that allows it to increase stool water content, and eliminate ammonia through colon instead of as urea in the kidney
lactulose

common site for abdominal aortic aneurysms due to many branches
infrarenal aorta
region located on the floor of the bladder characterized by two openings (where the ureters enter the bladder) and the single opening of the urethra (where the urine exits) often site for infections
trigone
short urethra (3-4 cm) in females makes women more susceptible for these
UTIs
compress to prevent reflux of urine back to kidneys
distal ureters
in this situation, there is a temporary decrease in GFR, to increase blood volume, blood pressure, and blood to vital organs
fight or flight, sympathetic stimulation
vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles has this affect on renal filtration
decreases renal blood flow and filtration, helps dilute higher Na+ conc
if these neural receptors signal a drop in arterial BP, afferent arterioles are signaled to vasoconstrict
aortic arch and carotid sinus (baroreceptor reflex)
vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles reduces GFR and thus water and sodium excretion, helping maintain blood volume and eventually increase it. explains this reflex
baroreceptor reflex
in severe hypoxemia, signals from chemoreceptors act to alter GFR how?
decreases it
higher than normal serum creatinine indicates this about the kidneys
poor ability of kidneys to filter waste effectively
elevated BUN effect on kidney
can impair kidney function
high levels of creatinine may be caused by these conditions
hyperthyroidism or rhabdo (muscle breakdown)
low levels of creatinine may be caused by these conditions
malnutrition or muscle wasting (bed-bound pts)
low levels of BUN may be caused by these conditions
can be seen in severe liver disease, malnutrition, nephrotic syndrome

high levels of BUN may be caused by these conditions
dehydration (concentrates urea), high protein diet, or GI hemorrhage (increased protein load from digested blood)
originates from vascular endothelium. causes vasodilation
c-type natriuretic peptide
released from DCT and CTs, causes vasoDILATION, natriuretic effects, and diuretic effects (increasing sodium and water excretion from the kidneys to lower blood pressure and volume)
urodilatin
when levels of this are high, it signals kidney to increase Ca++ excretion
calcitonin from thyroid gland
secrete renin
JG cells
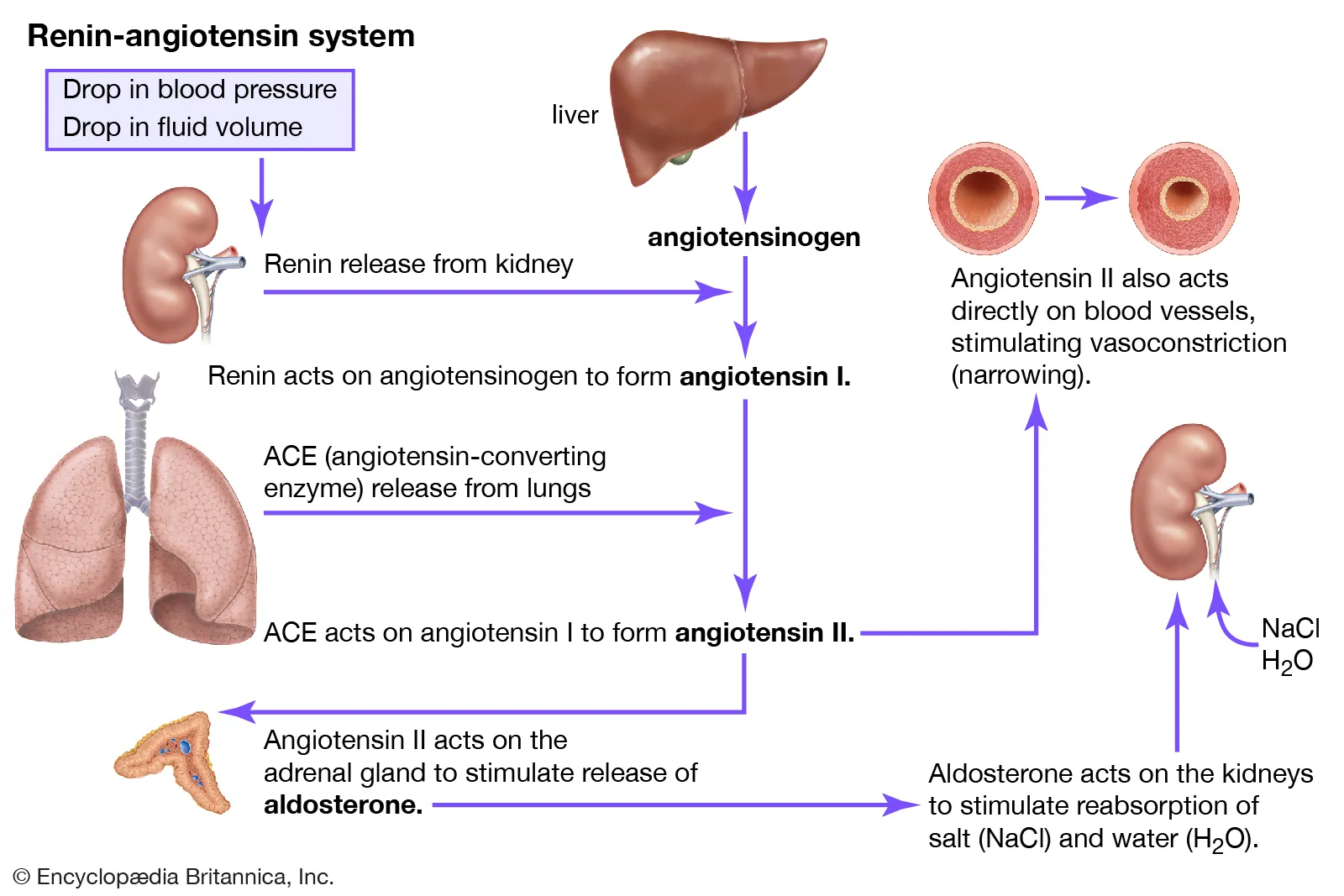
potent vasoconstrictor of RAAS system
angiotensin II
angiotensin II role on kidneys
increase Na+ reabsorption → K+ secretion → water retention → increased BP
angiotensin II effect on adrenal cortex
secrete aldosterone
angiotensin II effect on thirst
increases thirst, encourages water intake
lead to increased diuresis. decrease circulating volume by promoting sodium and water loss. increased urine formation (diuresis)
ANP/BNP
these cells are especially useful in low hydration to conserve water.
JG cells
ANP/BNP trigger:
elevated ANP/BNP levels indicate increased circulating volume
ANP/BNP mechansims:
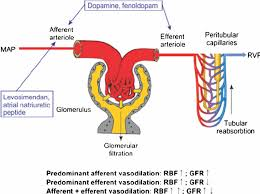
glomerular filtration: anp/bnp vasodilate afferent arterioles and constrict efferent arterioles. more GFR
decrease reabsorption of Na+ and H2O
block renin and aldosterone secretion
all ANP/BNP wants to do is stop this
stop further increases in circulating volume (lower BP)
every hormone/substance that can be released to cause afferent arteriole vasoconstriction
macula densa cells (in response to high serum Na+)
sympathetic stimulation (fight or flight)
angiotensin II
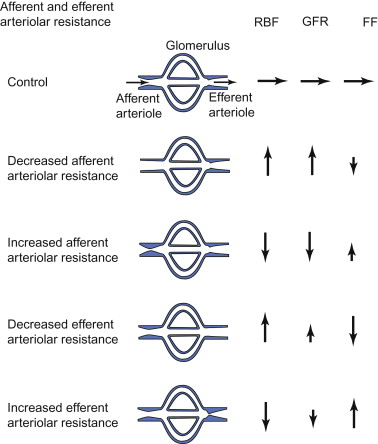
the main effect of vasoconstriction of the afferent arterioles with respect to blood flow
decreased renal flow, GFR
the main effect of vasoconstriction of the afferent arterioles with respect to blood pressure
increases it
the main effect of vasodilation of the afferent arterioles with respect to blood flow
increases renal blood flow, GFR
the main effect of vasodilation of the afferent arterioles with respect to blood pressure
lowers it
every hormone/substance that can be released to cause afferent arteriole vasodilation
macula densa cells (in response to low Na+ serum)
c-type natriuretic peptide
urodilatin
ANP/BNP
less pressure on afferent arterioles (vasodilation) does this to GFR
increases it
GFR and blood pressure have this relationship
inverse
high GFR (from vasodilation) = lowers BP
low GFR (from vasoconstriction) = increases BP
how does a high GFR lower BP?
increases urine output: increased GFR means the kidneys filter more blood, which leads to a greater volume of urine being produced.
decreases blood volume: excreting more fluid through urine reduces the total volume of blood in the circulatory system.
lowers blood pressure: a lower blood volume leads to a lower overall blood pressure.
both diuretics and natriuretic peptides lower ________ by reducing __________
blood pressure
reducing fluid volume