Module 3: Reproductive System
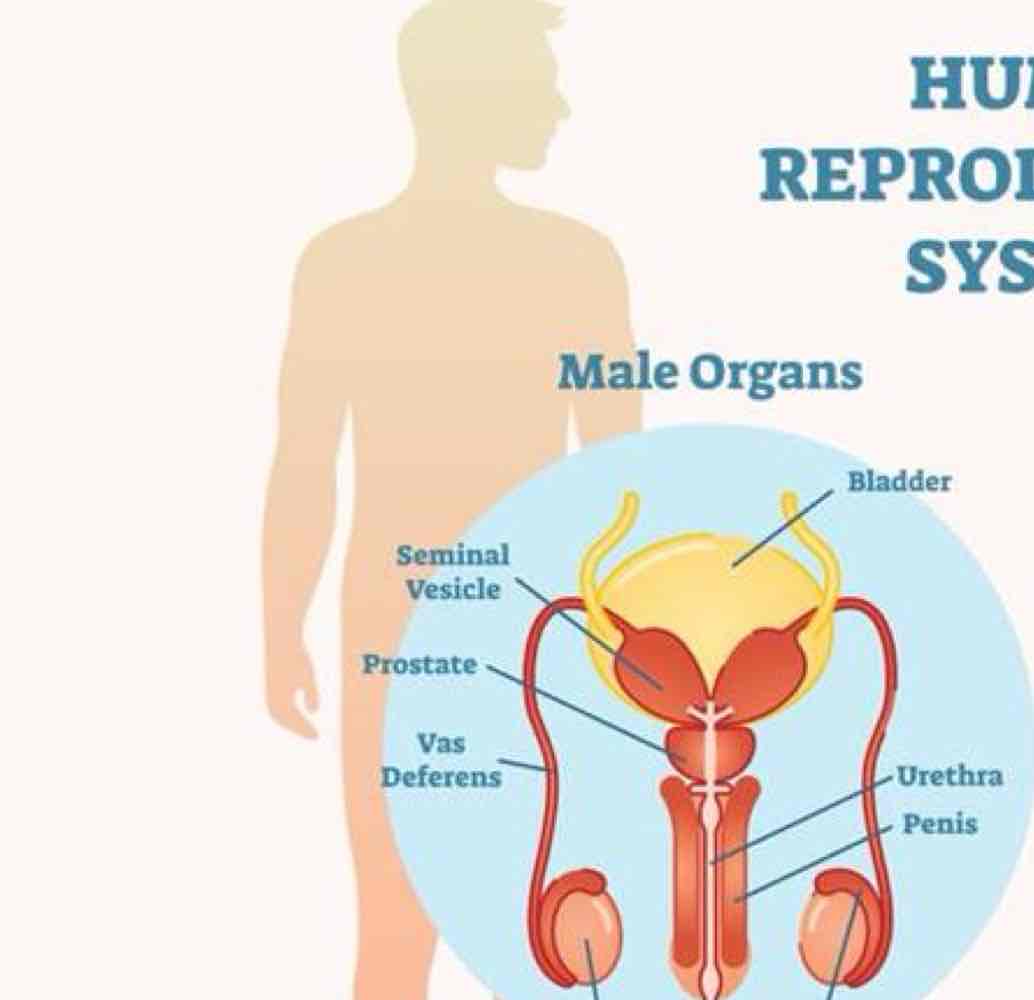
In regards to male organs…
testes secrete what 2 things?
prostate gland produces and expels what?
vas deferens for transport of semen from where?
secondary sex characteristics
metabolic support
testosterone and sperm
fluid for semen
testicles
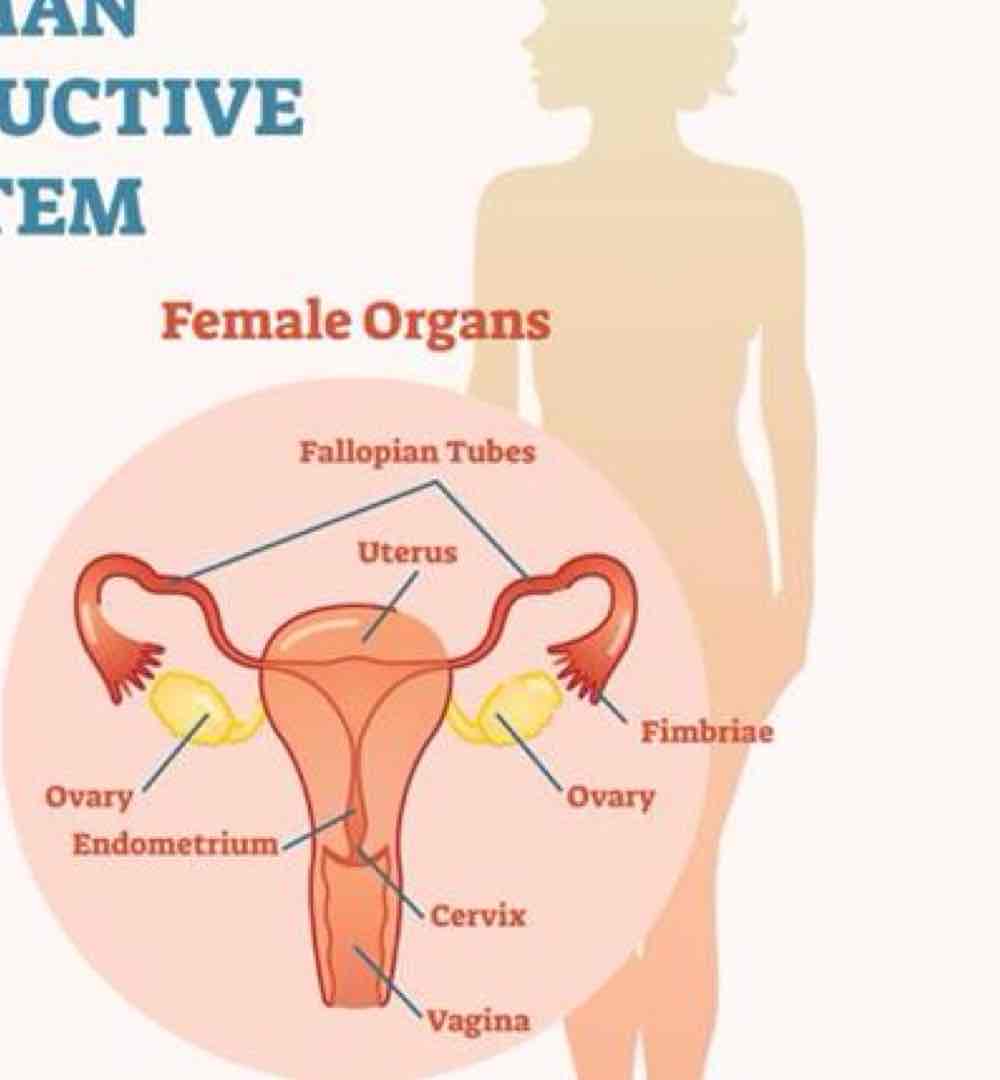
In regards to female organs..
ovaries secrete what two things?
uterus houses fetus during ?
fallopian tubes transport what?
breasts contain ?
ovulation, pregnancy, secondary sex characteristics
metabolic and bone/CV/brain health
estrogen and progesterone
pregnancy
ovum
mammary glands
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms

In regards to male organs…
testes secrete what 2 things?
prostate gland produces and expels what?
vas deferens for transport of semen from where?
secondary sex characteristics
metabolic support
testosterone and sperm
fluid for semen
testicles

In regards to female organs..
ovaries secrete what two things?
uterus houses fetus during ?
fallopian tubes transport what?
breasts contain ?
ovulation, pregnancy, secondary sex characteristics
metabolic and bone/CV/brain health
estrogen and progesterone
pregnancy
ovum
mammary glands
what is the prevalence of erectile dysfunction?
52% of men generally >40 y.o , increases by age group
what are the risk factors and etiology of erectile dysfunction? (7)
diabetes is #1
coronary heart dz / vessel dz
HTN
anxiety/depression or other mental health disorder
excessive alcohol consumption
pelvic floor dysfunction
what are some presentation/subjective characteristics of erectile dysfunction? (5)
difficulty/inability to establish and/or maintain erection
premature ejaculation
pain w ejaculation
pain w intercourse
DDx/comorbid peyronie’s dz (trauma-induced curvature); prostate dysfunction
what is the tx for erectile dysfunction?
lifestyle changes
pharmacological intervention
PT implications:
primary intervention can be your ability to perform tailored education
rapport w pt
what is endometriosis?
endometrial tissue growth outside the uterus, commonly on ovaries, fallopian tubes, or other pelvic organs but sometimes far away from pelvic area
what is the average amount of years from onset of symptoms to get a diagnosis endometriosis via laparoscopy?
7-12 yrs
US/MRI not yet fully diagnostic
what is the common presentation and associated comorbidities/DDx (inflammatory responses) of endometriosis? (part 1 - 6 symptoms)
abdominal/LBP, often patterned w menstrual cycle
dysmenorrhea, excessive bleeding during menses, intermenstrual bleeding
SIBO/IBS, severe bloating or abdominal distention
interstitial cystitis
constipation/bowel dysfunction, hemorrhoids/fissures, diarrhea, nausea
pelvic floor dysfunction
what is the common presentation and associated comorbidities/DDx (inflammatory responses) of endometriosis? (part 2 - 7 symptoms)
pain with intercourse
infertility
central sensitization/widespread pain/ hyperalgesia
fibroids, adenomyosis, PCOS, fibromyalgia, pelvic inflammatory dz
higher risk of autoimmune conditions (Hashimoto’s, celiac, sjogren’s, MS, eczema, RA, systemic lupus)
anxiety/depression
jt pain/ stiffness upon walking
what are the risk factors for endometriosis? part 1 (6 factors)
family hx of endometriosis
toxin exposure in utero
infertility/never giving birth
early menses (12 or younger)
late menopause
short menstrual cycles (<27 days)
what are the risk factors for endometriosis? part 2 (5 factors)
higher levels of estrogen, poor estrogen metabolism (liver)
lower BMI
any condition that prevents normal menstrual flow
reproductive tract abnormalities
long-term use of birth control? (controversial)
what is the typical management of endometriosis?
dietary considerations (i.e. FODMAPs)
lifestyle modifications
physical activity
how does PT manage endometriosis?
typically within pelvic floor speciality
focused on CNS down-regulation
myofascial release
pelvic floor muscle coordination
scar tissue mobility
in regards to endometriosis, what is the gold standard for surgical intervention?
excision (removal of endometrial tissue)
what two ways do surgeons perform surgery on endometriosis pt’s?
excision (removal) and ablation (cauterizing)
why is ablation a less favorable treatment for endometriosis?
less effective for deeper endometrial tissue
poses risk of thermal damage to neighboring tissue
presents high rate of recurrence
disables biopsy for analysis
what 4 things are still pretty controversial in factors relating to endometriosis?
pregnancy
birth control
hysterectomy
Rx- induced menopause
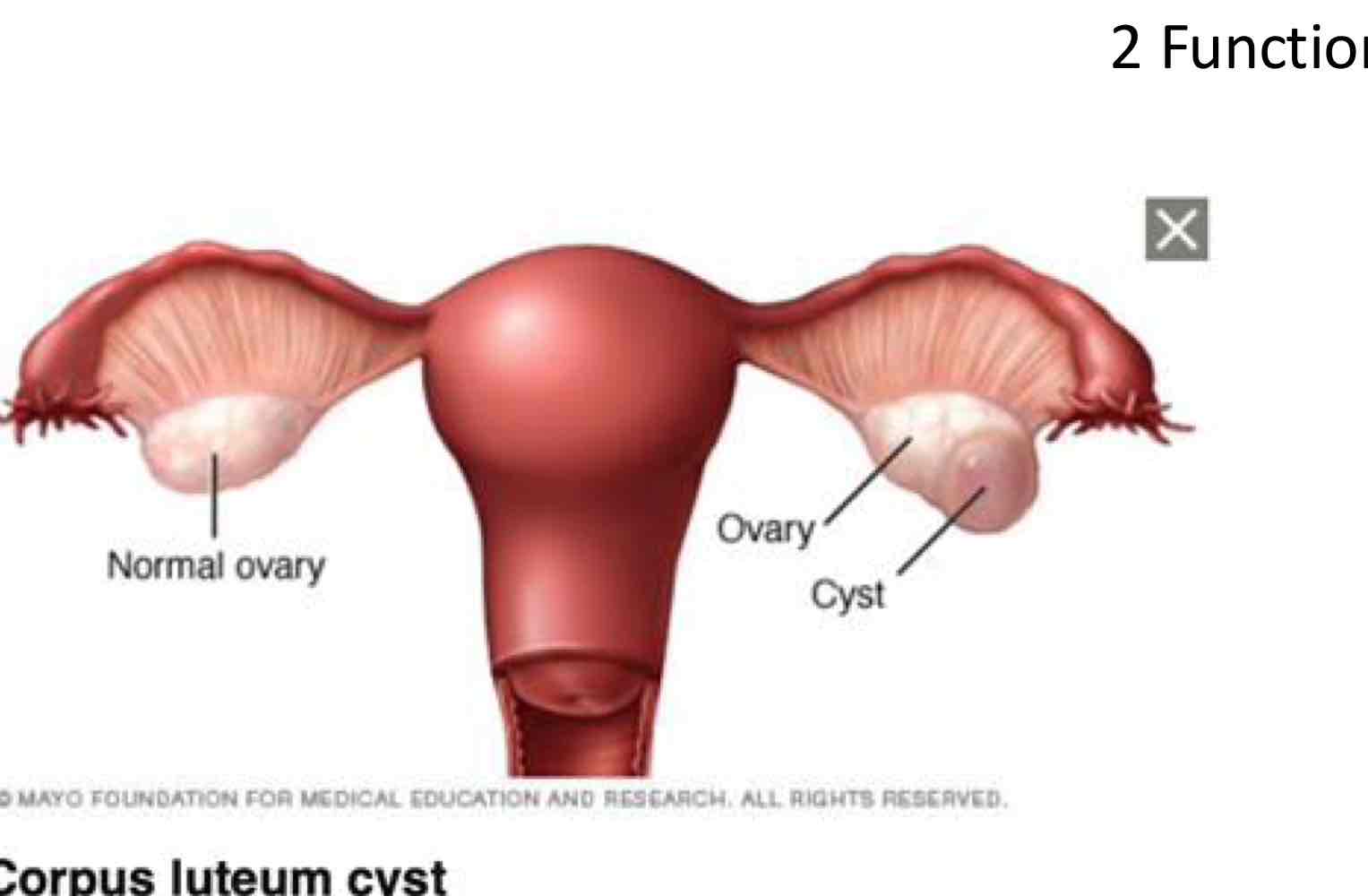
Corpus Luteum Cyst:
Abnormal changes in the ____ of the ovary after an egg has been released
Can cause what?
Where does fluid accumulate?
Follicles
Cause the egg’s escape opening to seal off.
Fluid accumulates inside the follicle
a corpus luteum cyst develops.
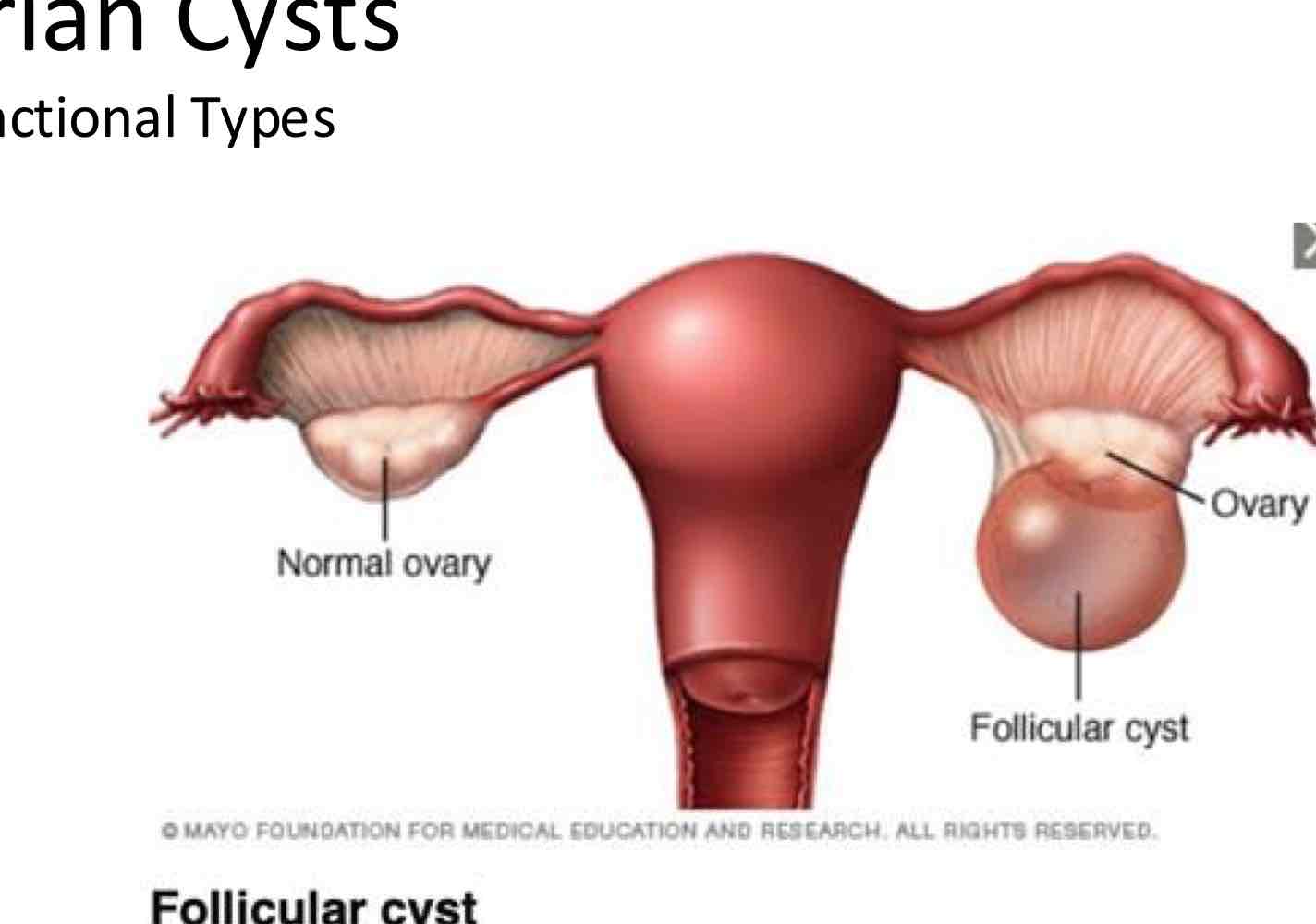
what is a follicular cyst?
When does it occur?
What happens instead
Occurs when the follicle of the ovary doesn’t rupture or release its egg.
Instead, it grows until it becomes a cyst
Ovarian Cysts:
What are the 3 main S/S of Ovarian Cysts?
Unilateral sharp or dull pain
Fullness or heaviness in abdomen
Bloating
Ovarian Cysts:
What 3 S/S is considered as an EMERGENCY for pts w Ovarian Cysts?
Sudden onset of severe abdominal or pelvic pain
Pain w fever or vomiting
Signs of Shock:
Clammy Skin
Rapid Breathing
Lightheadedness or Weakness
If a pt presents w S/S EVERY month due to their period, what organ can be the issue?
Id a pt presents w S/S every OTHER month due to their period, what organ can be the issue?
EVERY = Uterus
Central Structure
OTHER:
Ovaries and Fallopian Tube
Women alternate ovulation to L and R every month
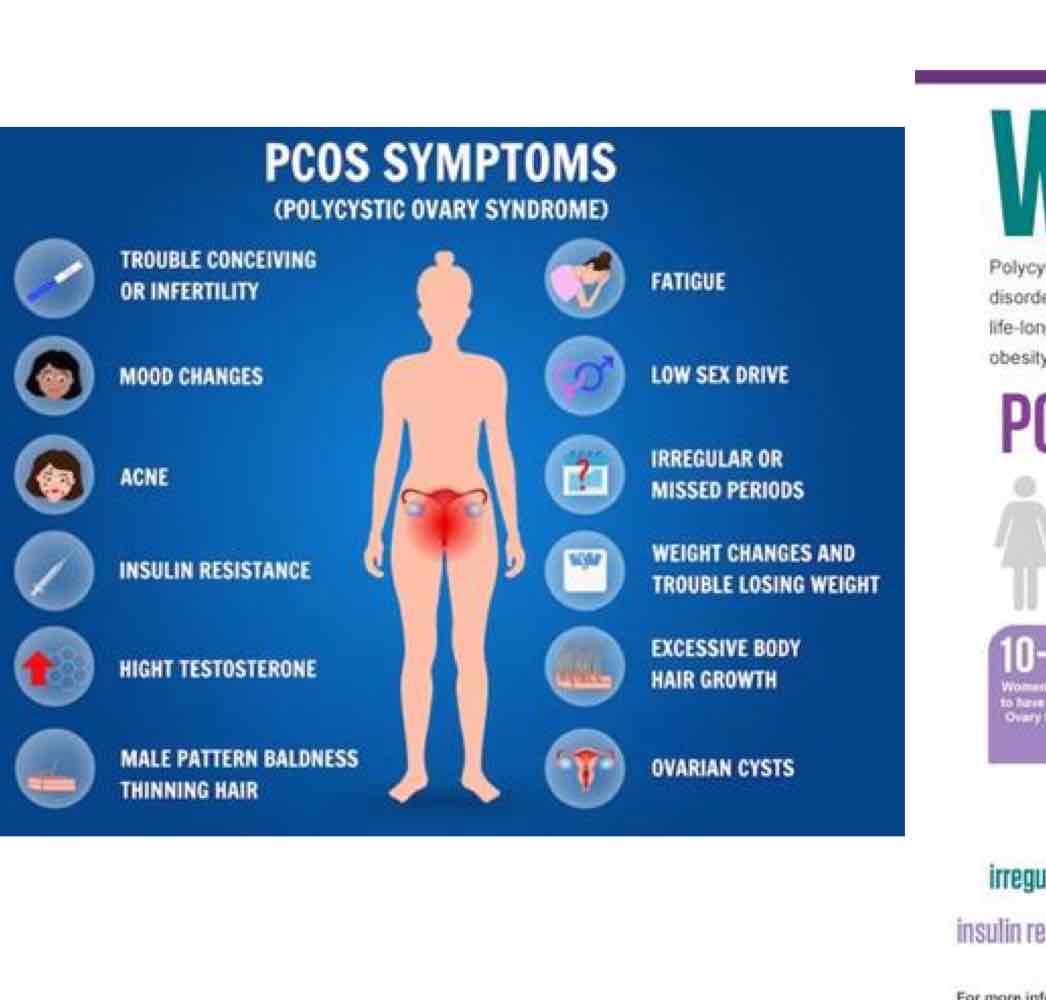
what is PCOS?
polycystic ovary syndrome
what are some common signs and symptoms of PCOS? (9)
irregular periods
excess facial and body hair
severe acne
small cysts in ovaries
insulin resistance
anxiety and depression
infertility
wt gain
male pattern hair loss
define perimenopause
2-8 years while body is transitioning to menopause (~40 yo)
what are some symptoms of menopause? (5)
none?
hot flashes, night sweats
irregular periods
mood changes
trouble sleeping
define menopause (2)
Permanent cessation of menstrual periods (1 yr)
Depletion of estrogen, progesterone, testosterone (avg 51 y.o)
women after menopause have an increased risk of developing/getting? (4)
osteoporosis
cardiac events
brain changes - Alz/Dementia
infection/UTI
what are some things to consider with menopause pts? (2)
HRT (hormone replacement)
Education on strengthening MSK and maintaining CV health
Menopause:
HRT:
Vary in…
Vary in…
Vary in…
___/Indirect
vary in types - systemic, local
vary in ingredients - horse urine, bioidentical
vary in application - cream, suppository, Rx
DHEA/ indirect
what can cause pelvic girdle pain? (3)
SIJ hypermobility
pubic symphysis (SPD)
relaxin hormone peaks mid-pregnancy and persists for months following delivery, longer with breastfeeding
what are some DDx that can occur with pregnancy and postpartum that are MSK? (8)
sciatica, piriformis syndrome
round ligament pain
coccydynia
diastasis recti
postural dysfunction
stress urinary incontinence
de quervain’s tenosynovitis
dyspareunia
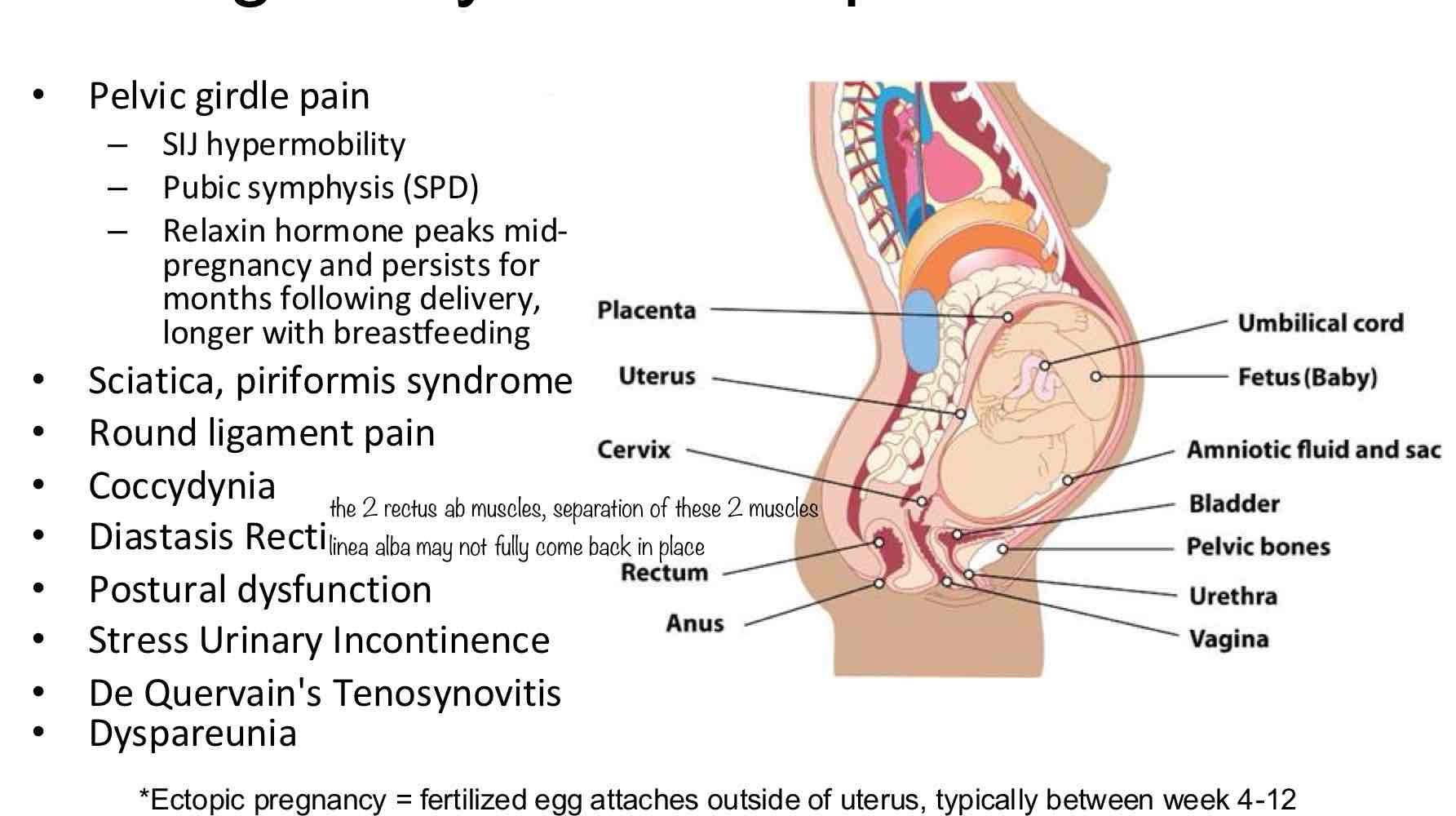
Ectopic Pregnancy:
What is it?
When does it typically occur during preg?
What is":
Fertilized egg attaches outside of uterus
Typically btwn weeks 4-12
this is LIFE THREATENING for mother
Ectopic Pregnancy:
5 main S/S
severe sharp/dull/cramping pain
shoulder pain
abnormal bleeding
GI distress
dizziness/fainting
in regards to exercise during pregnancy…. what are some relative contraindications (precautions) (9)
severe anemia (thready pulse, spacey, weak)
chronic respiratory dysfunction (O2 to baby and mom.. not MSK)
poorly controlled T1DM
extreme morbid obesity
extreme underweight
hx of extremely sedentary lifestyle
intrauterine growth restriction
poorly controlled HTN, seizure disorder, or hyperthyroidism
heavy smoker
what are some absolute contraindications to exercise during pregnancy? (9)
significant heart dz that is impacting hemodynamics
restrictive lung dz
incompetent cervix
multiples: in late second and into 3rd trimester, risk of early labor
persistent bleeding in second or third trimester
placenta previa after 26 wks
premature labor in current pregnancy (that has been stabilized)
ruptured membranes
preeclampsia/pregnancy induced HTN
in regards to PT, what are some considerations we need to be aware of if our patient is pregnant and doing exercise/PT? (positions)
avoid prolonged flat supine after 1st trimester due to decreased cardiac output, compression
in regards to PT, what are some considerations we need to be aware of if our patient is pregnant and doing exercise/PT? (activity dosage)(4)
decreased O2 availability,
earlier fatigue/pain limiting point of activity,
SOB
COM and BOS shift
in regards to PT, what are some considerations we need to be aware of if our patient is pregnant and doing exercise/PT? (exercise directives)
trunk/postural stabilization
IAP management
breathing (diaphragmatic, birth prep)
pelvic floor muscle coordination with abdominals and breathing
pelvic alignment and stabilization
functional movements - bending, lifting, carrying