Chemistry: Chemical Reactions Test
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Difference between mass and matter?
Mass: The amount of matter in an object
Matter: Anything that has mass and takes up space
Different between atoms, elements, and compounds?
Atoms: basic units of matter, similar to a particle of an element
Elements: Substances made of only one type of atom (pure substance)
Compounds: substances made of two or more different types of atoms in a bond (pure substance
What is an intensive physical property?
Doesn’t depend on the amount of substance present
ex. Temperature, density, color are intensive because they’re a characteristic of the substance itself
What is an extensive physical property?
Depends on the amount of substance present
ex. Mass and volume
Difference between physical properties and physical changes?
Physical properties: describe characteristics of a substance (color, shape, density, etc.)
Physical changes: Alter the form or appearance of the substance without changing its chemical composition (melting ice, breaking a pencil, cutting a piece of paper, etc.)
7 signs of chemical change
Change in color
Change in smell
Change in temperature
Production of light
Production of sound
Production of gas
Formation of a precipitate (A solid formed from 2 liquids)
What is a reactant and a product?
Reactants: Substances that undergo a chemical reaction (left side of equation)
Products: Substances formed as a result of the reaction (right side of equation)
What is a pure substance?
A substance composed of only one type of particle with the same chemical and physical properties throughout
What is a mixture?
Combination of two or more substances that are physically combined, but not chemically bonded
what is a homogeneous mixture?
A mixture where its components are uniform throughout, also called a solution (soda, coffee, milk).
What is a heterogeneous mixture?
A mixture where its components are not uniform throughout (pizza, salad, sandwich).
What are the diatomic elements?
Br - Bromine
I - Iodine
N - Nitrogen
Cl - Chloride
H - Hydrogen
O - Oxygen
F - Flourine
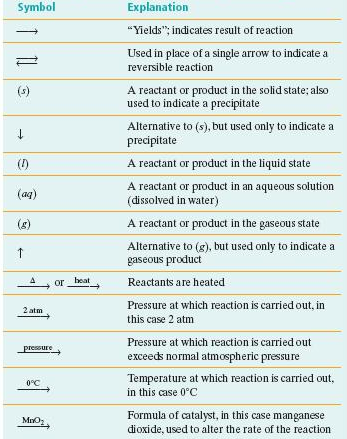
Common symbols used in chemical reactions
.
How to tell if an element is reactive based on location on the periodic table and why?
Elements on left side of periodic table are more reactive (Group 1 - Alkali metals, Group 2 - Alkaline metals)
They are reactive due to their lack of valence electrons, making them prone to lose electrons in a bond, especially when paired with halogens.
What does it mean when an element/compound is oxidized?
Loss of electrons (Increase in oxidization number)
What does it mean when an element/compound is reduced?
Gains electrons (Decrease in oxidization number)
metal + acid
ex. 2Na + 2HCl
single replacement
compound + H2
2NaCl + H2
compound + compound
Ca(NO)3 + 2LiBr
double replacement
compound + compound (switch fronts)
CaBr2 + 5LiNO3
nonmetal (F2, Cl2, Br2, I2) + compound
NaCl + 2F2
single replacement
compound + nonmetal (Br2, Cl2, I2)
NaF + Cl2
active metal + water
group I & group II
2Na + 2H2O
single replacement
metal hydroxide + hydrogen gas
2NaOH + H2
metal compound
FeCl3 + 3Li
single replacement
metal + compound (weaker metal gets kicked out)
Fe + 3LiCl
hydrocarbon (C&H + Oxygen)
C3H8 + 5O2
combustion
always yields CO2 + H2O
3CO2 + 4H20
acid
H2SO4
decomposition
always yields nonmetaloxide + H2O
H2O + SO3
*write water first, then balance
metallic chlorate
Zn(ClO)3
decomposition
always yields metal chloride + O2
ZnCl2 + 3O2
*watch for tm
metallic hydroxide
Pb(OH)4
decomposition
metal oxide + H20
PbO2 + 2H2O
*watch for tm
metallic carbonate
BaCO3
decomposition
metal oxide + CO2
BaO + CO2
*watch for tm
binary compound
2FeO
decomposition
element + element
2Fe + O2
*watch for tm and BrINClHOFS
nonmetaloxide + water
N2O5 + H2O
synthesis acid
2HNO3
element + element
4Al + 3O2
synthesis compound
2Al2O3
metaloxide + water
MgO + H20
synthesis metalhydroxide
Mg(OH)2
Oxidization number of F?
-1
Oxidization number of H UNLESS paired with a metal?
+1
with metal: -1
Oxidization number of Oxygen UNLESS paired with F?
-2
Paired with F: +2
Oxidization number of elements with no charge?
0