Religions - Intro to AP World
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
monotheism
Belief in one god

polytheism
Belief in many gods

universalizing religions
Religions that follow beliefs which are not culture-specific; can spread across cultures, and encourages the spreading of the religion

ethnic religions
Cultural religions which create strong bonds among people, but do not encourage the diffusions or conversion of outsiders

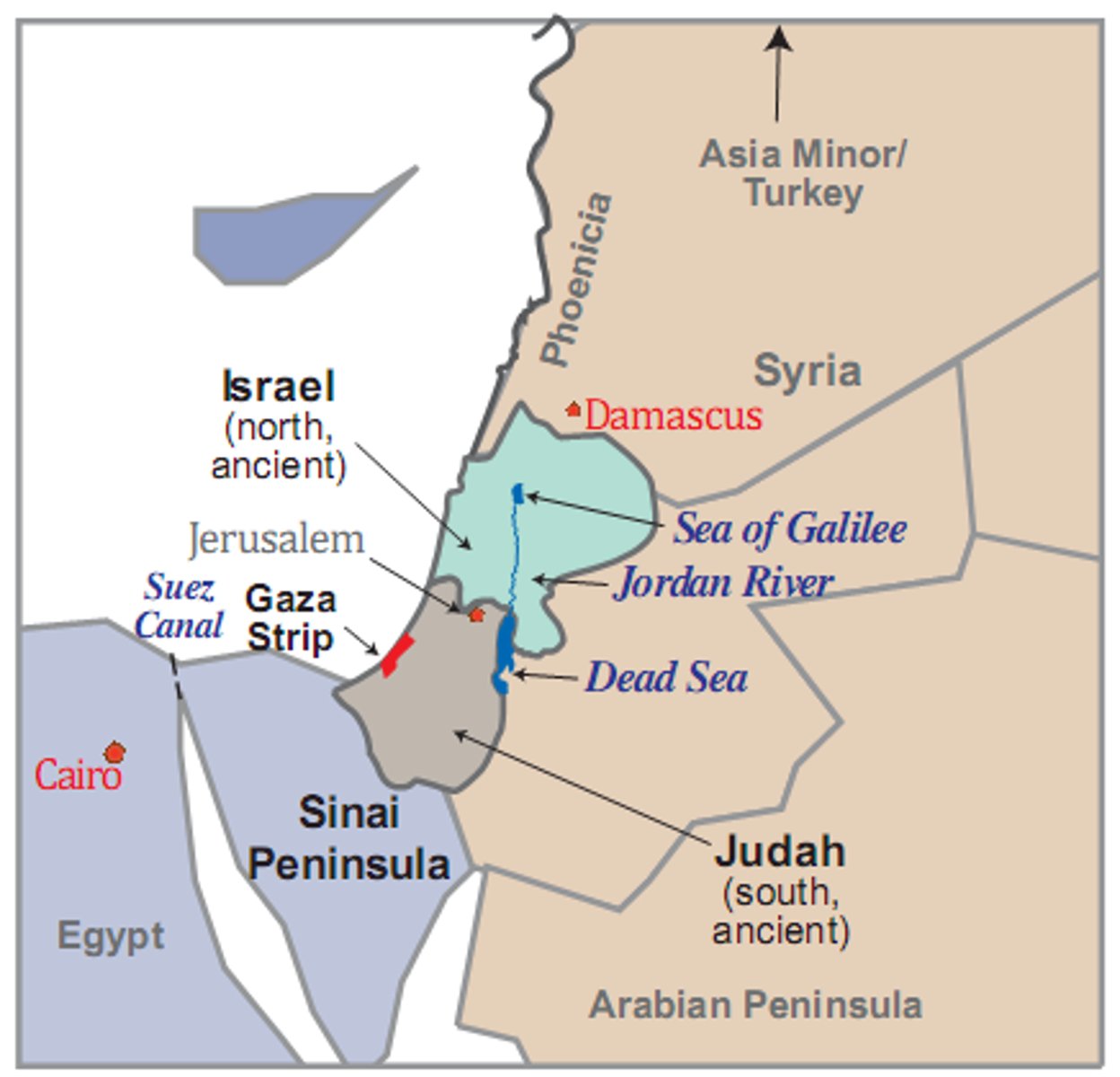
Judaism
Monotheistic religion of ancient Hebrews

Hebrews
Nomadic herders whose beliefs eventually developed into Judaism
Hebrew Bible (Torah)
Jewish religious scriptures

Abraham
Hebrew prophet and founder to Judaism; made a covenant with God. He is also known as a forefather to Christianity and Islam as well.

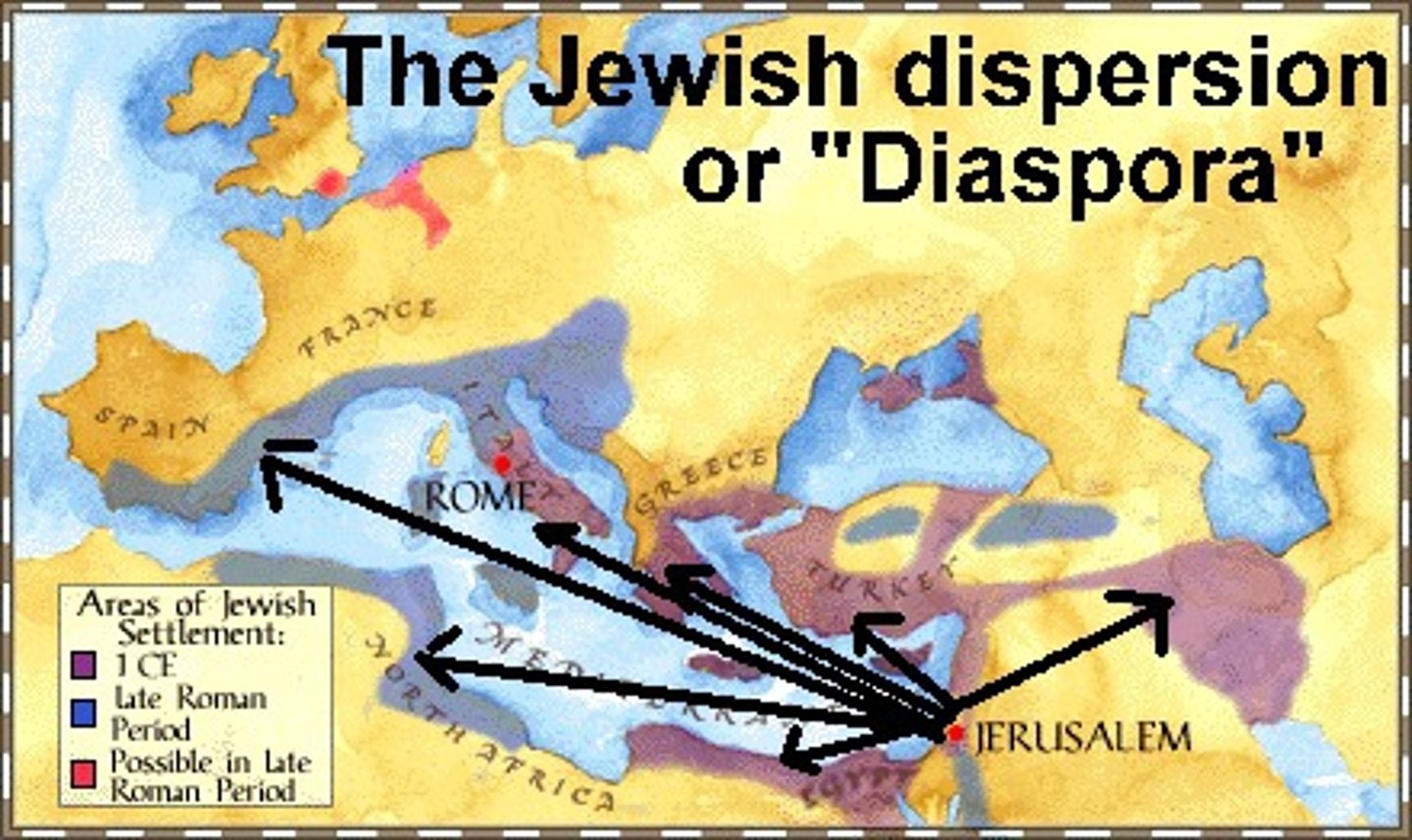
diaspora
Scattering of people; an example is when Jews were forced to flee Canaan during the Roman Empire
Zoroastrianism
Monotheistic religion developed in Persia (modern day Iran) around the time of Judaism

Christianity
Monotheistic religion based on teachings of Jesus; believed Jesus as messiah

Jesus of Nazareth
Jewish man in Roman Empire, claimed to be messiah or "son of God"

messiah
Savior, "son of God", Christos in Greek meaning "anointed one"

Emperor Constantine
Roman emperor who legalized Christianity in 313 CE with the Edict of Milan.

Hinduism
Religion developed in India in ancient times with many deities incarnate of Brahma.

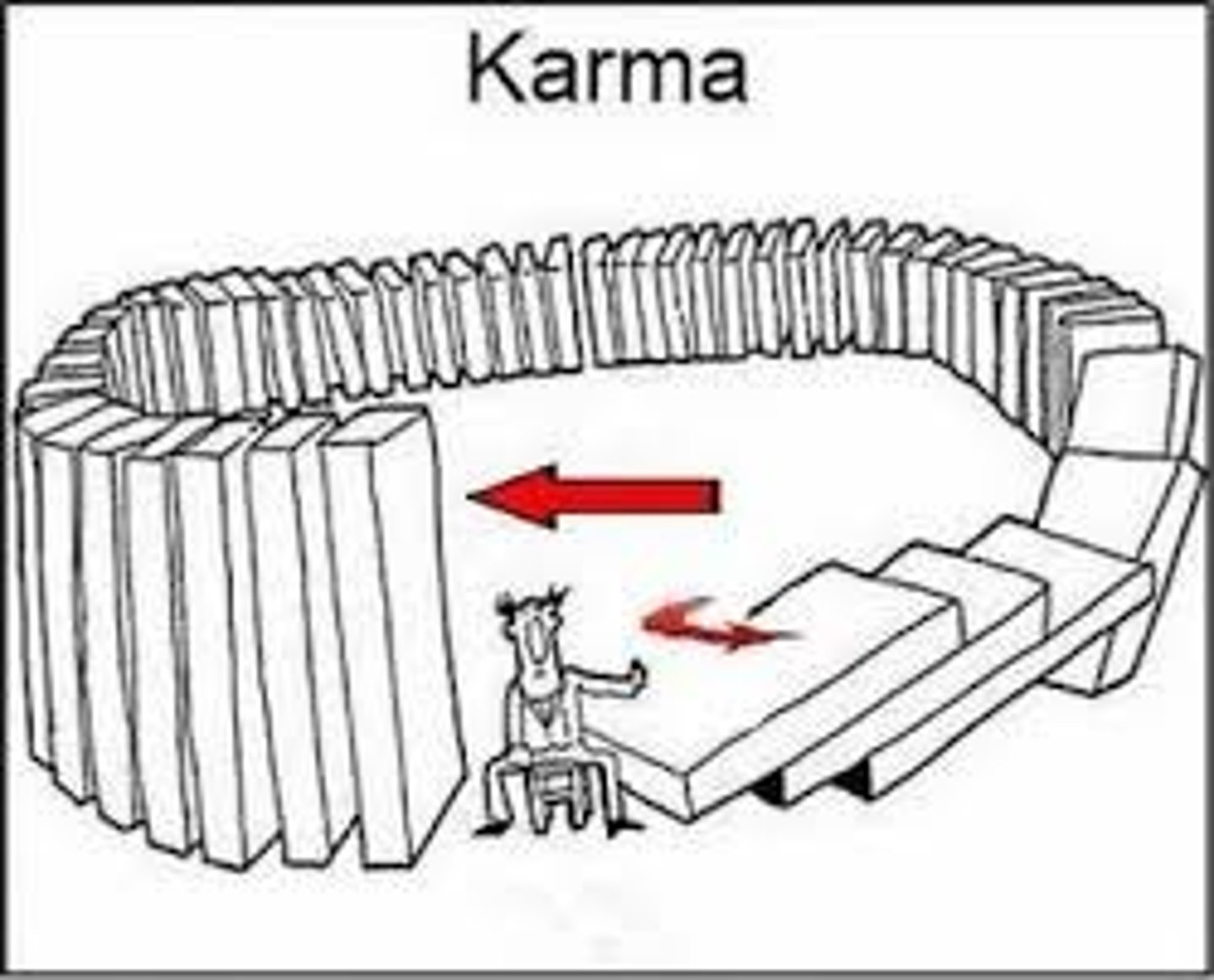
karma
Fortune or destiny determined by actions in life, which will impact the next life
dharma
Set of duties that must be fulfilled in life
moksha
Final resting place for a Hindu soul where the soul becomes united with Brahma

caste system
Strict social hierarchy followed by Hindus
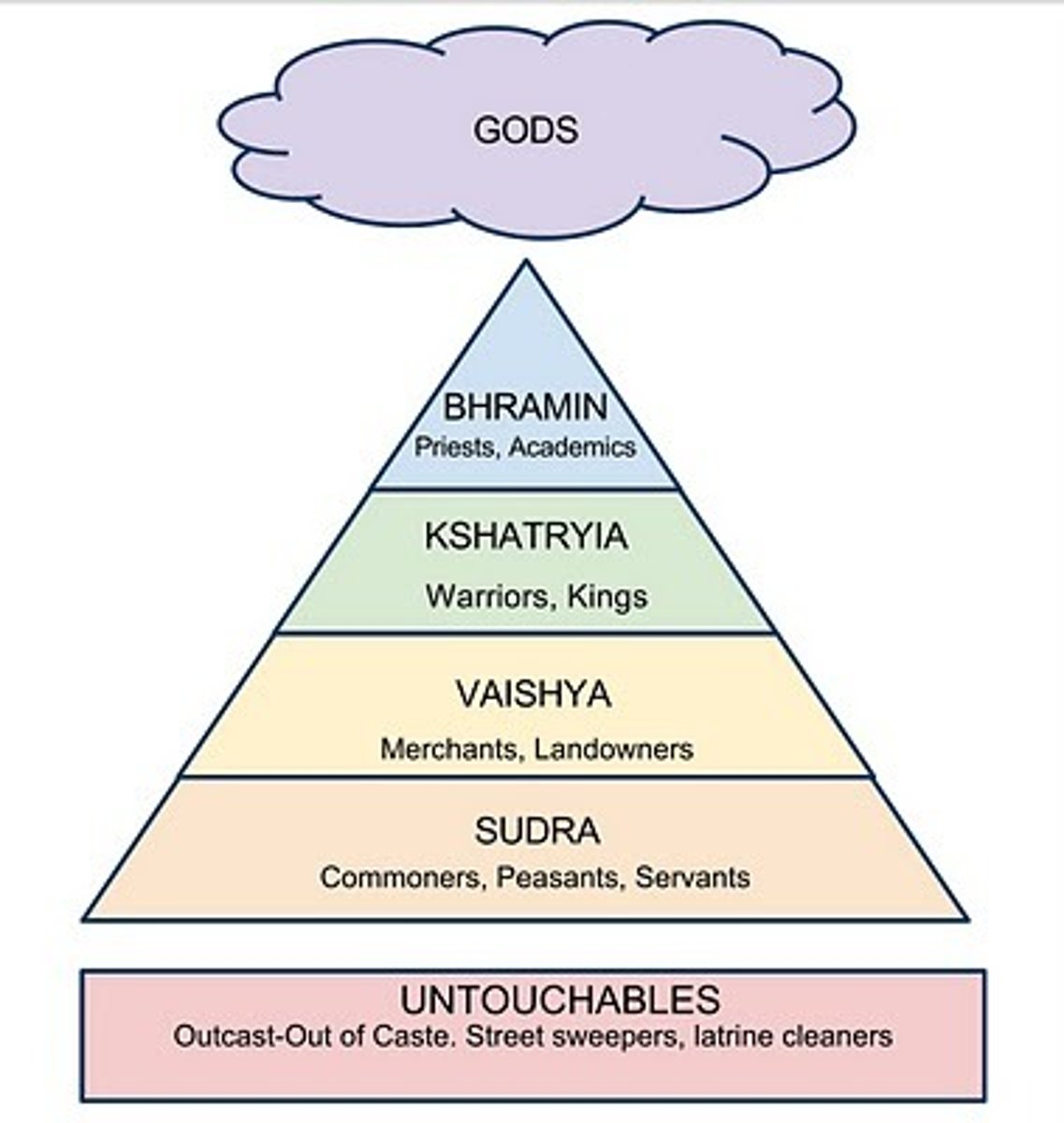
Brahma
Universal spirit, creator of the universe in Hinduism. All other deities stem from God, and the levels of the caste stem from his parts.

Vedas (Rig Veda)
Hindu holy scriptures

Mahabharata, Ramayana
Epic poems which reflect Hindu values

Buddhism
Religion which rejected the Hindu caste system, developed by Siddhartha Gautama

Siddhartha Gautama
Nepalese prince who rejected the Hindu caste system and founded Buddhism

Buddha
Meaning "the enlightened one"

nirvana
Final resting place of the Buddhist soul

Four Noble Truths
Four understandings on what causes pain and suffering in life

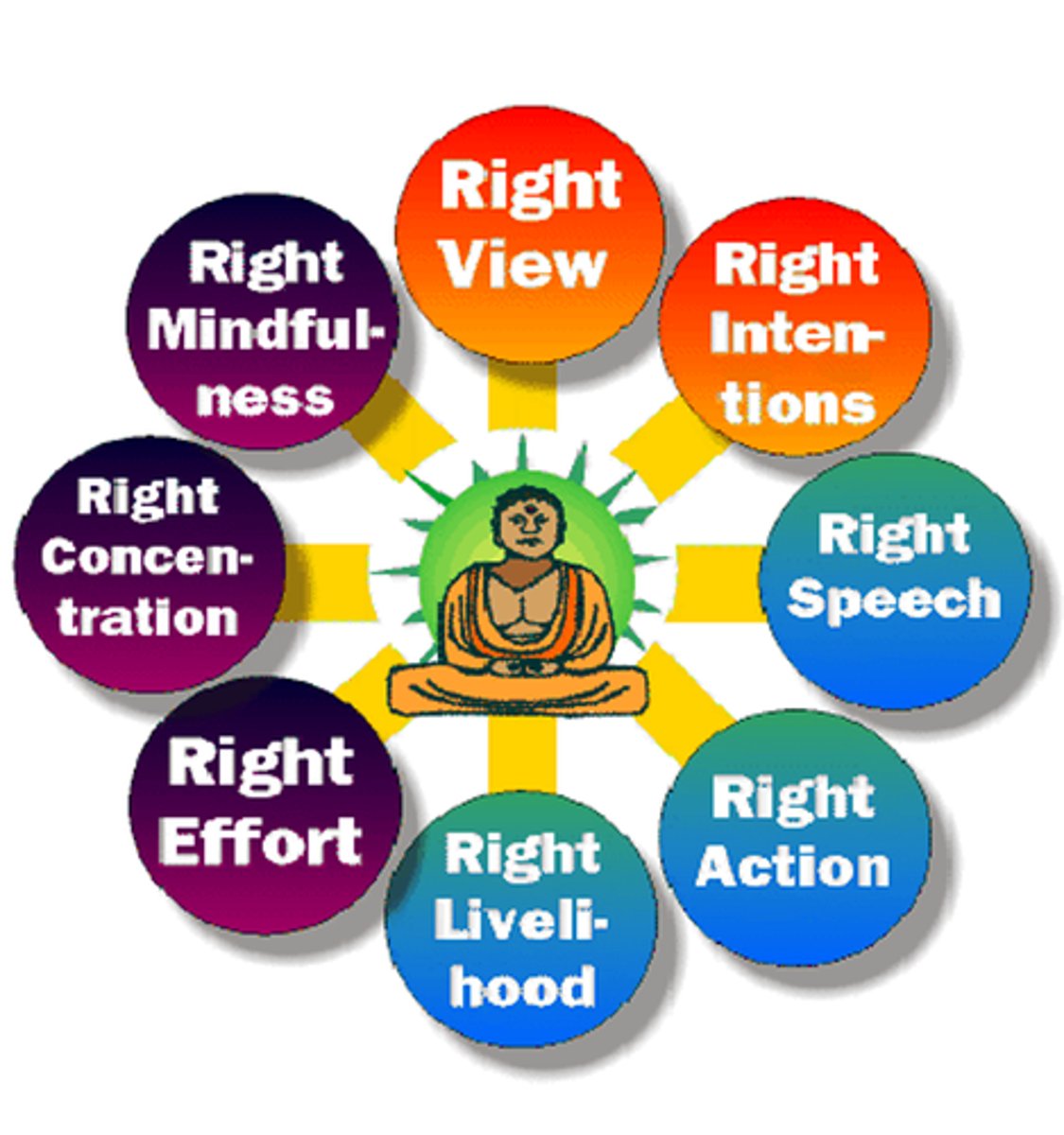
Eightfold Path
Rules Buddhists must follow to end pain and suffering
Ashoka
Mauryan ruler who spread Buddhist ideals throughout India by building pillars and stupas

Theravada
Sect of Buddhism, believes you MUST reach enlightenment in order to achieve nirvana

Mahayana
Sect of Buddhism, believes you don't have to reach enlightenment to achieve nirvana

Confucianism
Chinese philosophy based on filial piety and the five key relationships

Confucius
Ancient Chinese philosopher who founded Confucianism

Analects
Scriptures containing Confucian ideas, written by Confucius' students

Filial Piety (Xiao)
Devotion to the family, respect for elders in society. Common in Confucianism, this is a popular societal order in Han China.

Li (reciprocity)
Respect and reciprocity within the five key relationships

Daoism
Chinese philosophy/religion based on the balance of forces in nature known as yin and yang

Laozi
Chinese Daoist philosopher; taught that governments were of secondary importance and recommended retreat from society into nature.

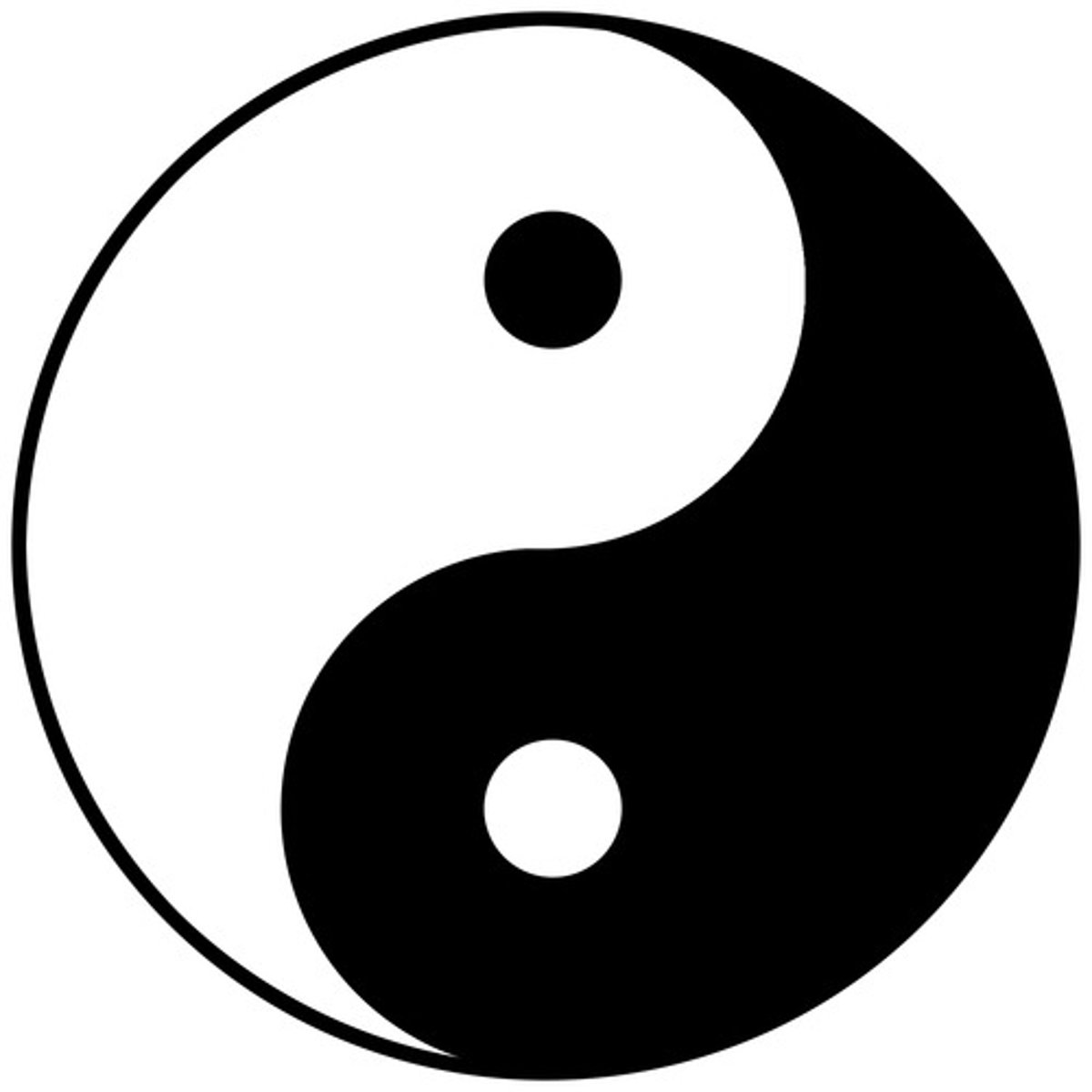
yin and yang
Two opposing forces in nature that must be in balance in order for society to be properly organized and peaceful

wuwei
Non-action or inactivity in nature, which allows the forces of nature to govern society

Laozi
Chinese philosopher who founded Daoism

Islam
A religion based on the teachings of the prophet Mohammed which stresses belief in one god (Allah), and a body of law written in the Quran. Followers are called Muslims.

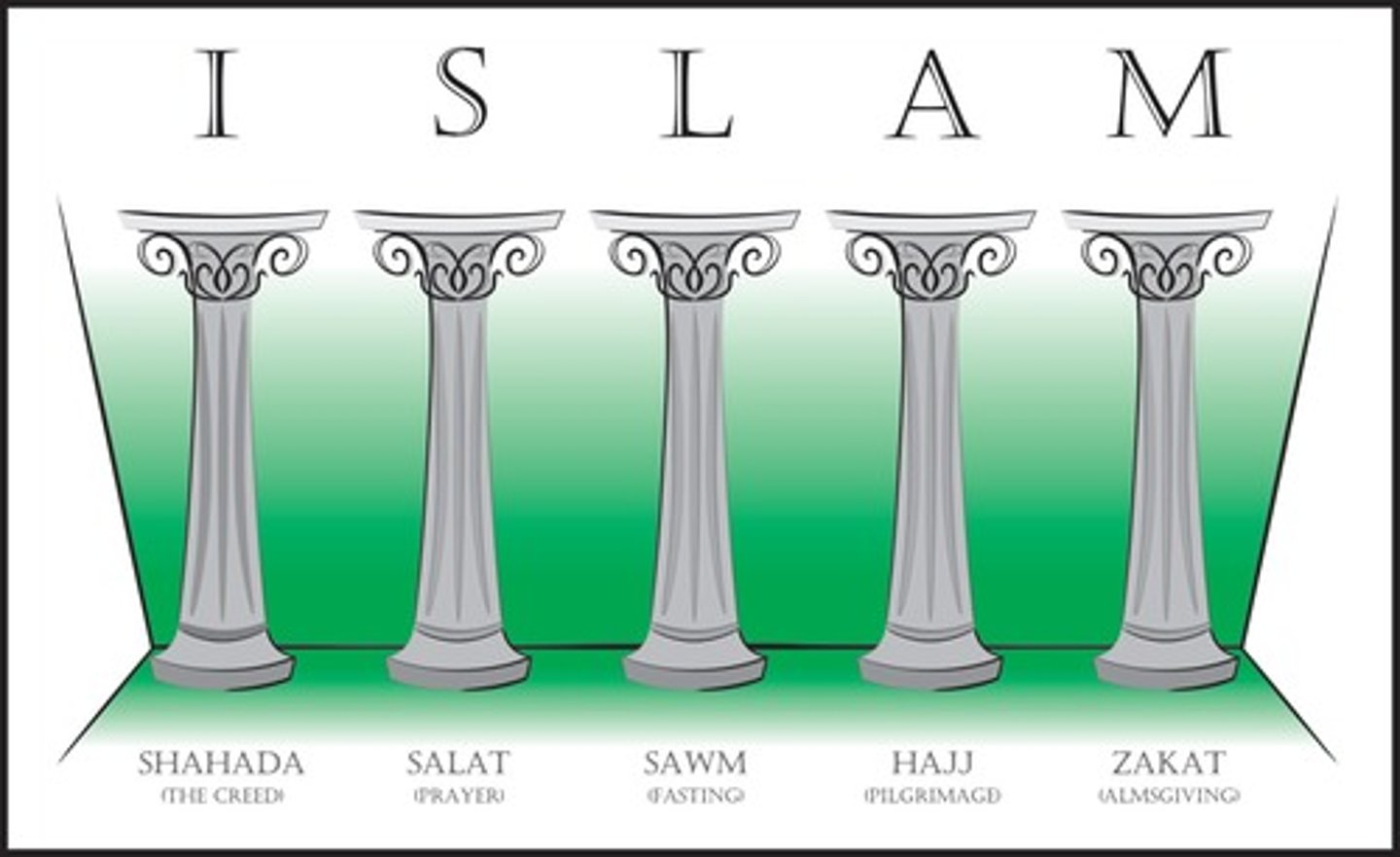
5 Pillars of Faith
5 mandatory practices which guide the lives of Muslims; these include belief in God, praying 5x/day toward Mecca, observing Ramadan, the Hajj pilgrimage, and giving to charity.
Place of worship
name of a site where followers worship - a church (Christianity), a synagogue (Judaism), a mosque (Islam), a temple (Hinduism, Buddhism) or at home.

Muhammad
Arab prophet; founder of religion of Islam. He was also a merchant, so he spread the religion to new areas.

Quran
Holy Book of Islam - sacred writings of Islam revealed by God to the prophet Muhammad during his life at Mecca and Medina
