KIN 111 final
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
dermatomycosis
fungal infection of the skin or scalp
what are typical symptoms after a seizure?
sleepy/fatigue
problems with vision, speech, or writing
headache
body aches
Loss of bladder/bowel control.
Lack of consciousness.
Confusion.
Fear and anxiety.
What are the 3 stages of labor?
dilation stage
expulsion stage
placental stage/afterbirth
dilation stage
first stage of labor
begins with uterine contractions and ends when cervical dilation is complete
expulsion stage
second stage of labor
starts with complete cervical dilation and ends with birth of the baby
placental stage/afterbirth
third stage of childbirth
begins after birth of baby and ends once uterus had discharged placenta
what is the difference between a suffix and a prefix
suffixes are found at the end of medical terms while prefixes are found at the beginning
protrate
to lay flat or to be overcome by physical weakness and exhaustion
pulmonary respiration
the process by which O2 is taken from air and carried to body cells for their use, and VO2 and water, waste generated by cells, is carries to lungs and returned to environment
what are the four processes of respiration
pulmonary ventilation
external respiration
transport of respiratory gases
internal respiration
pulmonary ventilation
breathing
large involuntary actions that moves are in and out of the lungs in response to blood o2 and co2 levels
external respiration
the exchange of O2 and CO2 between the alveoli and the blood in the pulmonary capillaries
transport of respitory gases
the movement of O2 to body cells and CO2 to the lungs by means of the cardiovascular system
internal respiration
the exchange of O2 and CO2 between body cells and the blood in systemic capillaries
-emesis
vomiting
cranial bones
bones that make up the skull
how many cranial bones are there and what are they called?
8 bone structures
occipital bone
temporal bone—>2
parietal bone—>2
frontal bone
ethmoid bone
sphenoid bone
Thyromegaly/goiter
enlargement of thyroid glands
etiology
to establish the cause of a disease
priapism
painful erection of the penis
radical prostatectomy
removal of the entire prostate, seminal vesicles, and surrounding lymph nodes
infra-
below, underneath
arthroscopy
visual examination of a joint using flexible scope
phlebostenosis
narrowing of a vein
homo-
same, alike
peritonsillar
abscess that consists of a collection of infected material in the area around the tonsils
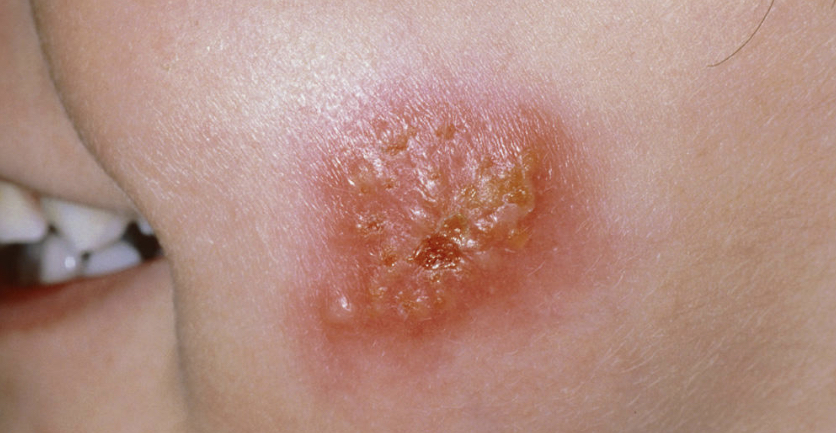
impetigo
bacterial skin infection categorized by isolated pustules that become crusted and rupture
lobectomy
surgical procedure where an entire lobe of your lung is removed
occlusion
the blockage of a blood vessel
sebum
sticky, oily substance that body produces in order to keep the skin moisturized
made up of fat molecules, waxes, and squalene
aorta
largest artery in the body
supplying oxygenated blood to the circulatory system
right and left ventricle
pump blood from the heart
right does pulmonary—>blood to lungs
left does systemic—>blood to entire body
right and left atrium
upper chambers that collect blood
what does left atrium do?
receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle.
what does right atrium do?
The right atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from the body and pumps it to the right ventricle
veins
return blood to the heart
formed from smaller vessels called venues
artery
major type of blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to all cells of the body
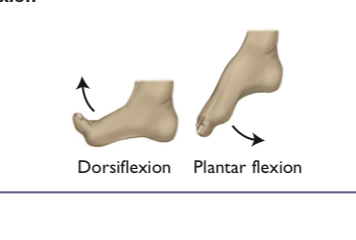
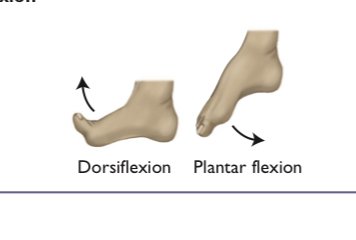
dorsiflexion
the backward bending and contracting of your hand or foot
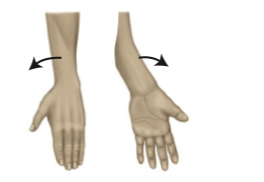
pronation
to turn the palm downwards
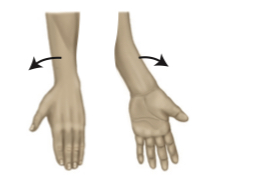
supination
to turn the palm upwards
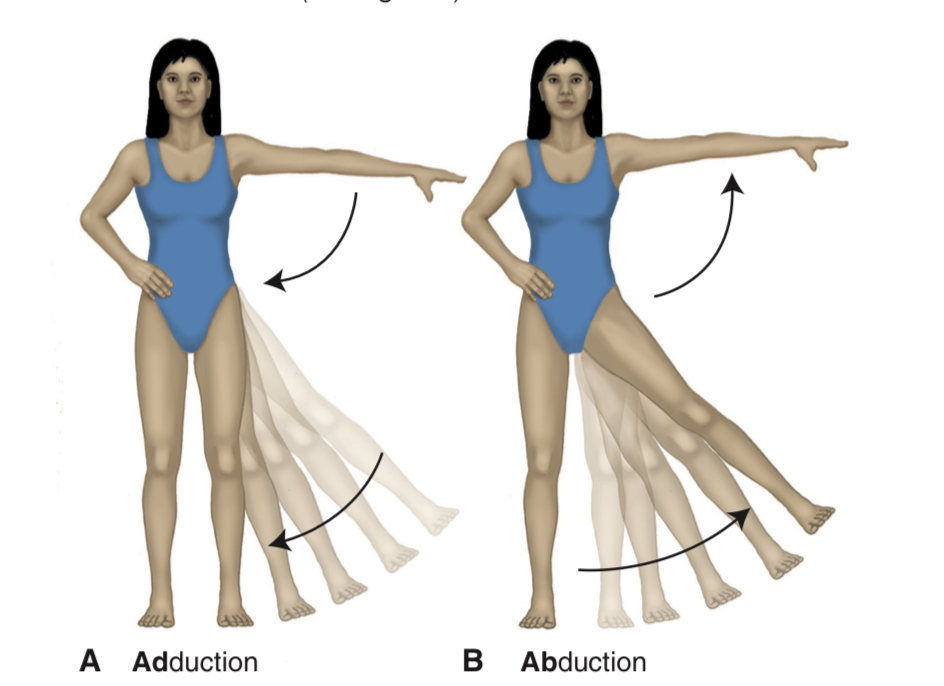
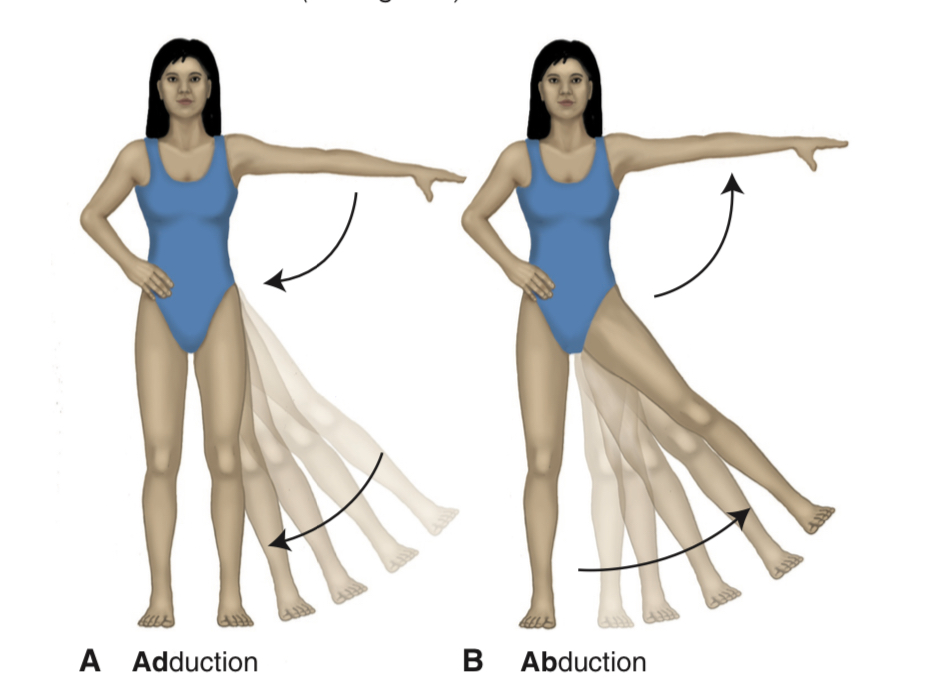
adduction
movement of a limb towards the body
plantar flexion
lowering the foot, pointing the toes
abduction
movement of limb away from the body
bile
bitter greenish-brown alkaline fluid that aids in digestion and is secreted by the liver and is stored in the gallbladder
chyme
semiliquid form of bolus that slowly leaves the stomach through the pyloric sphincter to enter the duodenum
vas deferens
also called seminal duct or ductus deferens
narrow tube that transports sperm from the testicle to the urethrat
epididymis
highly coiled duct behind the testicle, sperm passes along it to the vans deferent
protrate
debridement
the removal of damaged tissue or foreign objects from a wound
anosmia
loss, usually partial, of the sense of smell. It can be temporary or permanent
consolidation
when lung tissue loses its spongy texture and becomes swollen and engorged
fontanelles
soft spot on baby’s head before the skull is fully formed in infancy
hyponatremia
lower than normal level of sodium in the blood
suprarenal
another term for adrenal
adrenal/suprarenal glands
homeostasis
The state of balance within all physical systems needed for a body to function properly and survive
erythropenia
abnormal deficiency in the number of red blood cells in body
subluxation
partial or incomplete dislocation of one or more vertebrae
phimosis
narrowing of foreskin so that it cannot be retracted over the tip of the penis
What can happen when there is an excess of Co2 in the blood?
Excess CO2 can build up and cause Hypercapnia, shortness of breath (dyspnea) and fatigue
hypercapnia
having high levels of CO2 in the blood
dyspnea
shortness of breath
what is an extreme, life-threatening response to an allergen called?
Anaphylaxis
What term means an excessive growth of body hair, especially in women?
hirsutism
The procedure to incise and remove a pancreatic stone is called
pancreatolithotomy
the CF home/o means
same, alike
the suffix -emia means
blood condition
which of the following substances act as an electrolyte? thyroxine, cortisol, glucagon, insulin, sodium
sodium
which structure joins the two hemispheres of the brain?
corpus callosum
a sudden, violent contraction of one or more voluntary muscles is called a(n)
convulsion
Which structure supports and connects the cells of the nervous system?
neuroglia
Neurological symptoms that occur shortly after a seizure are a(n)
postical event
removal of a ganglion is called a
gangliectomy
The CF scot/o means
darkness
downward displacement of the eyelid is called
blepharoptosis
untreated otitis media can lead to a bone infection called
mastoiditis
optic nerve and blood vessels enter the eye at the
optic disk
lazy-eye syndrome is a type of strabismus called
amblyopia
the suffix -prandial means
meal
which medical specialty is involved with digestive disorders?
gastroenterology
an accumulation of serous fluid in the abdominal cavity is called
ascites
The CF chol/e means
bile, gall
the suffix -orexia means
appetite
the suffix -globin means
protein
The CF thym/o means
thymus gland
Destruction of old RBCs is a function of the
spleen
Which type of blood cell is responsible for the immune response?
lymphocyte
which type of bone marrow transplant is prepared from a compatible donor?
homologous
an abnormal, inward curvature of the lower portion of the spine is called
lordosis
A type of elastic connective tissue that provides a smooth surface for movement of the joints is called the
articular cartilage
what is the CF for bones of the fingers and toes
phalang/o
bone-forming cells are called
osteoblasts
The CF arthr/o means
joint
Which laboratory test identifies the bacteria obtained from a body specimen and determines effective antibiotics for treatment?
culture and sensitivity
what glands produce sweat?
sudoriferous
the prefix an- means
without, not
a wheal is also called a(n)
hive
the CF cutane/o means
skin
the CF spir/o means
breathe
removal of a lobe of the lung is called
lobectomy
the structure that covers the larynx is called the
epiglottis