Intracellular accumulations
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Intracellular accumulation of Lipids: Foamy cells/cholesterol deposits
xanthomas: foamy cell accum in sub-epithelial connective tissue of. skin/tendon
foamy cells/streaks (cholesterol laden microphages0
atherosclerosis
cholesterosis (gallbladder)
Lysosomal storage diseases
group of inherited genetic disorders that affect the body’s lysozomes
Neimann-pick disease type c
autosomal recessive
mutation in an enzyme involved in cholesterol trafficking (many organs: brain, liver, spleen)
Fatty liver (abnormal metabolism)
Intracellular accumulation of Proteins: proteinuria
reabsorption of protein droplets in renal tubules
elevated protein level in urine
symptom of other disease/condition
not a disorder but happens when you have a specific disease
Intracellular accumulation of Proteins: Alpha-1 Antitrypsin deficiency
A1A (produced in liver) usually coats lungs, protecting them from neutrophil elastase (produced by WBCs, used to destroy harmful bacteria)
Lack of A1A leaves lungs susceptible to damage from enzyme (often mimics COPD)
also begins to build up in liver (causing damage) neurofibrillary tangles found in alzheimers
Intracellular accumulation of Glycogen/carbon
glycogen: energy source stored int he cytoplasm of healthy cells
excessive deposits when patients have abnormality in either glucose or glycogen metabolism
diabetes mellitus
glycogen storage disorder
Intracellular accumulation of Pigments: Exogenous
exogenous: originated from outside the body
carbon
inhaled carbon: anthracosis, coal miners pneumonconiosis
tattoos
Intracellular accumulation of Pigments: Endogenous
endogeneous: originated from inside the body
lipofuscin: free radical injuries, lipid perioxidation, and normal aging causes build-up in liver and heart
pigment that builds up in the skin, or deposited inside organs start to build up when you age (especially in highly vascular areas)
melanin
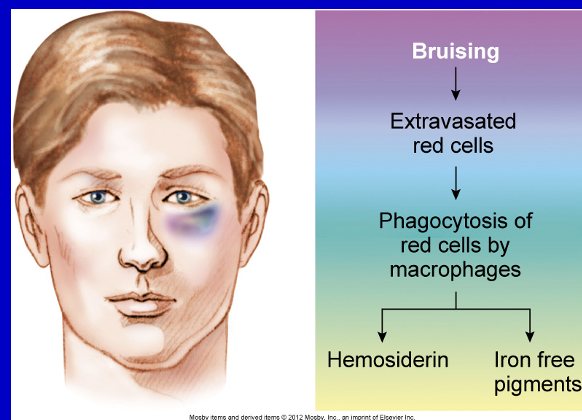
homosiderin: hemoglobin derived from iron
normal bruising, or systemic overload (yellow/brown pigment)
ion containing pigment inside RBC, spills out when there is cell damage and as it gets broken down its inner components turn into different colors (bruise)
bilirubin: not breaking down blood cells which is a by product from something else
Bruising pathway
Manifestations of cellular injury
cellular accumulations (endogenous infiltrations)
urate/uric acid
calcium
this can occur from protein breakdown, muscle damage, excess protein
can be metabolic or from an injury
contributes to gout (accumulation of uric acid crystals in joint) and can aggravate arthritis, UTI, kidney stones
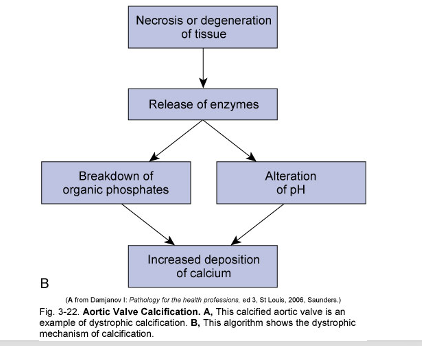
Intracellular accumulation of Calcium: Pathologic calcification
abnormal tissue deposition of calcium salts plus iron, magnesium, and other mineral salts
Intracellular accumulation of Calcium: Dystrophic calcification
occurs locally in dying tissue (more localized than metastatic calcification
serum levels of Ca are normal
causes fine white granular clumps
Intracellular accumulation of Calcium: Metastatic calcification
deposits of Ca salts in otherwise normal tissue
results from hypercalcemia (too much Ca in blood)
secondary to some disturbance in Ca metabolism
increased secretion of PTH
resorption of bone tissue (from tumors of bone marrow: multiple myeloma, leukemia, etc.)
vitamin D related disorders (sarcoidosis, williams syndrome)
renal failure
serum calcium levels are elevated
pull minerals from bone, tells digestive tract to absorb more Ca from food so Ca concentration in blood will be through the roof
calcium deposition can be due to
acid production from dying or injured cells
Necrosis or degeneration of tissue pathway
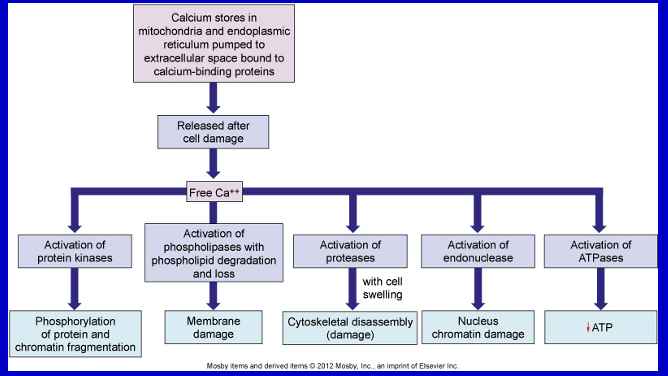
Calcium infiltration (from an injured cell)
free floating Ca ions in the cytoplasm (can be from inside or out of the cell)
this is the point of no return and cell is going to die
Calcium inside cell is no longer bound to the places where it is supposed to be (not on top of calcium binding proteins)
Necrosis
Spectrum of morphologic changes that follows cell death in living tissues
affects groups of cells
evoked by non-physiological events (viruses, ischemia, toxins, etc.)
inflammation
swelling of cytoplasm and mitochondria
loss of plasma membrane integrity
no energy requirement; passive process
calcium overload a key feature
Necrosis vs Apoptosis
necrosis:
During necrosis, cell swelling causes organelles to become vacuolated as the cell tries to retain excess fluid.
Eventually, the swollen cytoplasm and organelles crowd the cell, leading to rupture of the plasma membrane.
apoptosis:
decrease cytoplasm and package things up very neatly and so that they are nice packaged for macrophages to engulf
apoptosis
controlled cell death of individual cells
induced by physiological stimuli
no inflammation
shrinking of cytoplasm and condensation of nucleus
blebbing of plasma membrane with no loss of integrity
energy (ATP)-dependent; active process; functional mitochondria
cell death pathway activation
pathogenesis of necrosis
denaturation od intracellular proteins
enzymatic digestion of the cell
Coagulative necrosis
preservation of general tissue architecture-tombstone appearance of the cells
affected tissue is firm
denaturation of structural proteins and enzymatic digestion of cells
ex. heart, kidney, spleen, adrenal gland
looks like it is being turned to stone
Liquefactive necrosis
neurons and glial cells of the brain
hydrolytic enzymes
bacterial infection
staphylococci, streptococci, and e. coli
tissue becomes liquid viscous mass
material is creamy yellow in color
seen in brain, abscess
caseous necrosis
combination of coagulative and liquefactive necrosis
seen in tuberculous infections **** know for exam
tissue is cheesy white in appearance
the tissue architecture is preserved
For tb, it is only seen in the lungs
Fat necrosis
seen in pancreas, breast, and other abdominal organs
in acute pancreatitis, activated lipase causes fat necrosis
grossly visible chalky white areas
(broken down triglycerides-FA combine with salts = soap=saponification
fatty acid + salt = soap
presence of shadowy outlines of necrotic cells
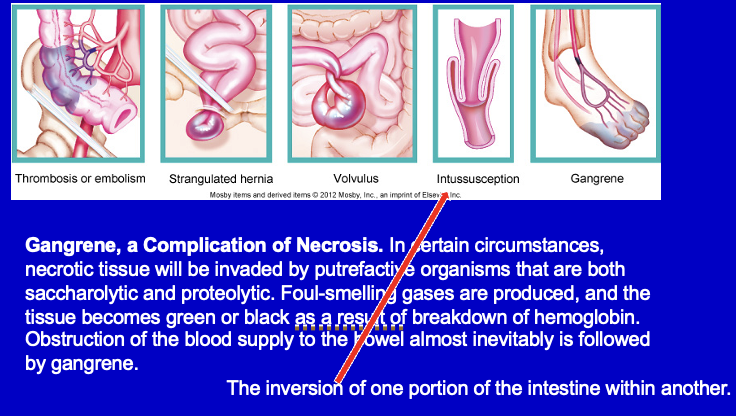
gangrenous necrosis
not a type of necrosis but happens as a result of them
end stage of other types of necrosis
deahth of tissue from severe hypoxic injury (dry vs wet)
gas gangrene: clostridium
Wet vs Dry va Gas Gangrene
Wet
occurs in moist tissues like mouth, bowel, lung, cervix
diabetic foot
bed sores
Dry (due to blockage of blood supply to an area)
toes and feet due to arteriosclerosis
raynauds disease
trauma
Gas
wet gangrene caused by gram positive anaerobic bacteria
seen in muscle and in colon
Various inductions of necrosis