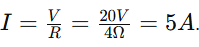Physics: Variable resistors
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What does the term “Variable Resistor” mean?
A component that can change its resistance to obstruct current flow in an electric circuit.
What is a “Circuit Diagram”?
A visual representation of an electric circuit using standard symbols to denote components.
What is an “Ammeter”?
An instrument used to measure the flow of electric current in a circuit.
What is a “Bulb”?
A device that produces light by passing electric current through a filament or gas.
What is a “Current”?
The flow of electric charge in a circuit, measured in amperes.
What does the term “Resistance” mean?
The opposition to the flow of electric current in a circuit, measured in ohms.
What is graphite and what sots of properties does it have?
A material used in the demonstration of variable resistance due to its conductive properties.
What is “pencil lead”?
A common form of graphite used in the experiment to demonstrate variable resistance.
What is a “sliding contact”?
A movable part that alters the amount of resistance in a circuit by changing the length of conductive material.
What is a resistor?
A resistor is a component in an electrical circuit that limits or controls the flow of electric current.
What is a variable resistor?
A variable resistor is a resistor whose resistance can be adjusted to different levels.
Why would you use a variable resistor?
To control the amount of current or voltage in a circuit, allowing you to adjust things like the brightness of a light or the speed of a motor.
What are two common types of variable resistors?
Potentiometers and rheostats.
How does a potentiometer work?
A potentiometer has a rotating or sliding knob that changes the resistance as you turn it.
What’s a simple example of a potentiometer?
The volume control on many radios and speakers is a type of potentiometer.
How is a rheostat different from a potentiometer?
A rheostat is usually used to control higher currents and has only two connection points, while a potentiometer has three.
In what kind of devices are variable resistors commonly found?
They’re found in devices like dimmer switches, volume controls, and speed controls for motors.
What material is commonly used in the track of a variable resistor?
Carbon or a thin strip of metal is often used as the track where resistance is varied.
How does a variable resistor affect brightness in a circuit with a light bulb?
By increasing resistance, less current flows, making the bulb dimmer; decreasing resistance allows more current, making it brighter.
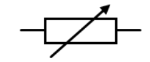
What is the symbol for a variable resistor in circuit diagrams?
A rectangle with an arrow across it.
What happens to the resistance when you turn a potentiometer’s knob clockwise?
It usually increases, causing the current to decrease.
Why is it important to be able to change the resistance in a circuit?
Changing resistance lets you control the amount of energy going to different parts of the circuit.
True or False: A variable resistor can only reduce current, not increase it.
False. A variable resistor can be adjusted to either increase or decrease current, depending on the setting.
Name a place where you might find a rheostat in everyday life.
In a dimmer switch used to adjust room lighting.
In a simple circuit with a 12V battery and a variable resistor, the resistor is set to 4 ohms. What is the current in the circuit (in amps)?
Using Ohm's Law (V = I × R). The answer is 3A
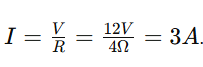
If a voltmeter is placed across a variable resistor set to 3 ohms in a circuit with a 9V battery, what would the voltmeter read?
Since the resistor is the only component, it takes the full voltage of the battery. So, the voltmeter would read 9V.
In a circuit with a 10V battery and a variable resistor set to 5 ohms, what would the voltmeter reading be if connected across the resistor?
Since the resistor is the only component, the voltmeter would read the full battery voltage, which is 10V.
A circuit has a 15V battery and a variable resistor set to 10 ohms. What is the current through the resistor?
1.5 amps
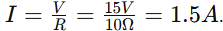
A 6V battery is connected to a variable resistor, which is set to 2 ohms. What does the voltmeter read across the resistor?
The resistor takes the full voltage of the battery, so the voltmeter reads 6V.
In a circuit with a 9V battery and a variable resistor set to 3 ohms, calculate the current in the circuit.
3 amps
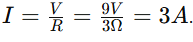
A 12V battery is connected in a circuit with a variable resistor set to 6 ohms. What is the reading on the voltmeter if placed across the resistor?
Since the resistor takes the full battery voltage, the voltmeter reads 12V.
If the variable resistor is set to 8 ohms in a circuit with a 16V battery, what is the current?
2 amps
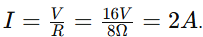
In a circuit with a 5V battery, a variable resistor is set to 1 ohm. What does the voltmeter read across the resistor?
The resistor takes the full 5V from the battery, so the voltmeter reads 5V.
A circuit has a 20V battery and a variable resistor set to 4 ohms. What is the current in the circuit, and what would the voltmeter read across the resistor?
The current is 5 amps, and the voltmeter would read the full 20V.