UNIT 4 (Part 1) - Muscle Types, the Sarcomere, NMJ, Steps of Contraction
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
actin
thin filaments (red, labelled C)
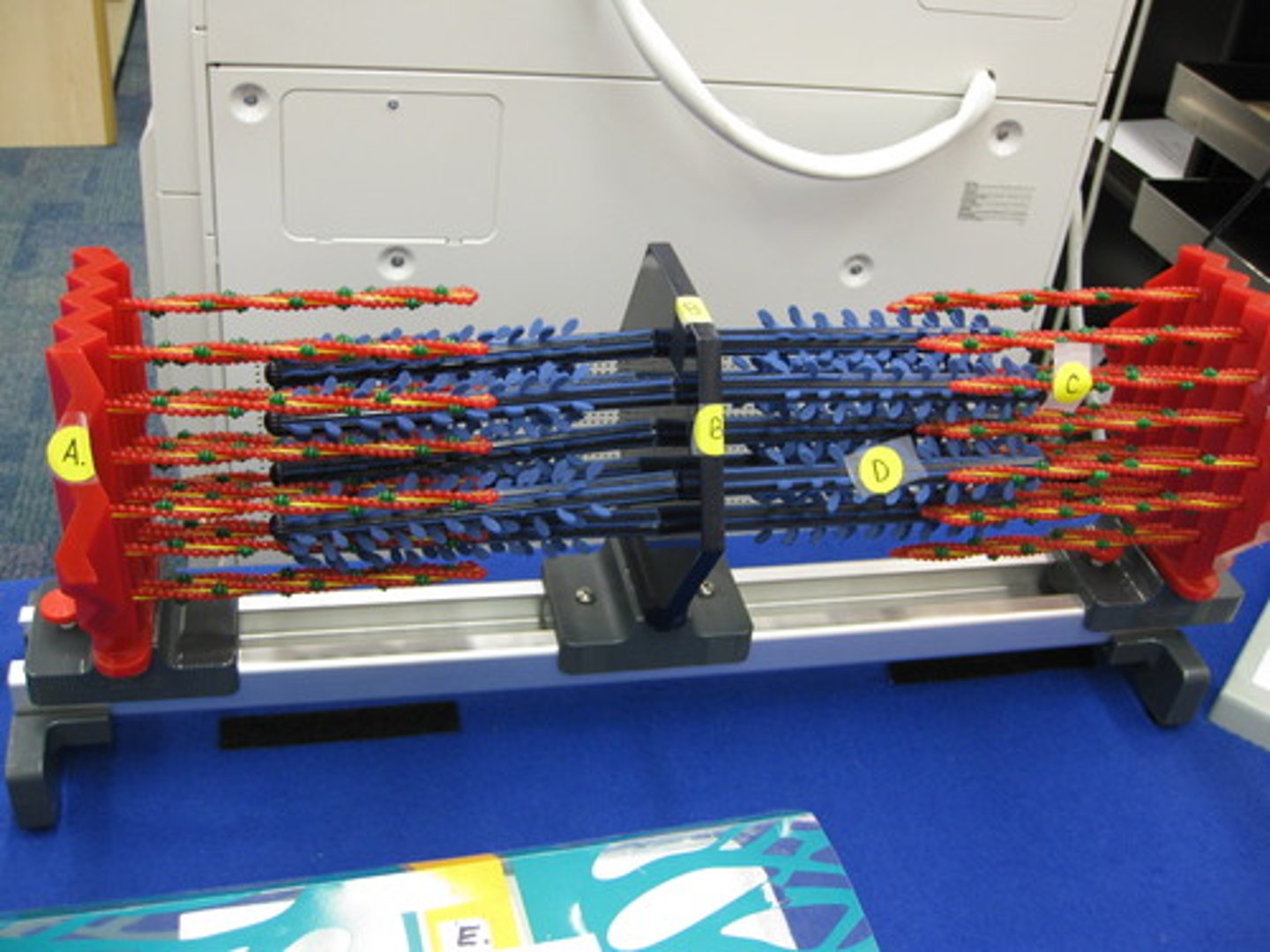
myosin
thick filaments (blue, labelled D)
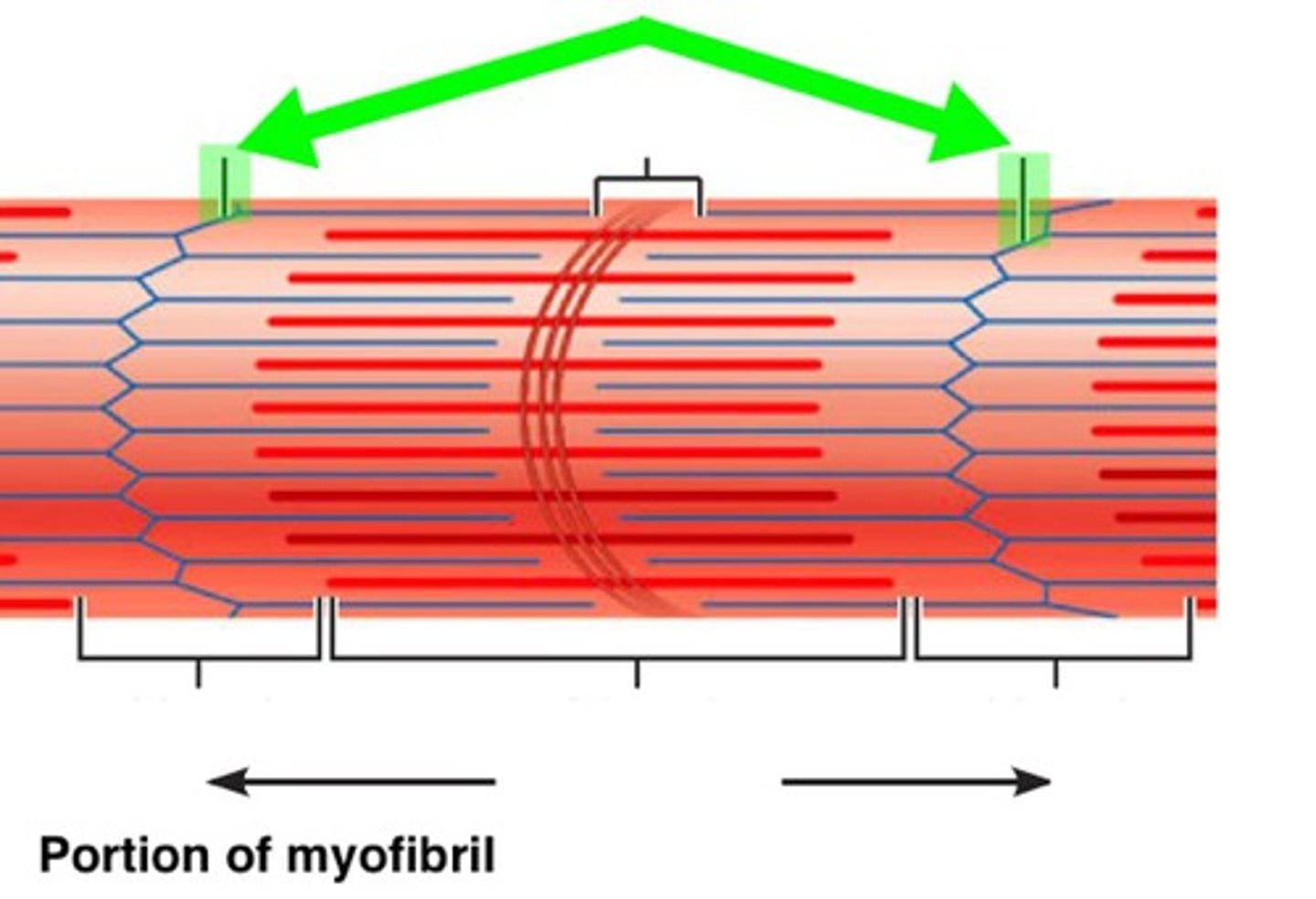
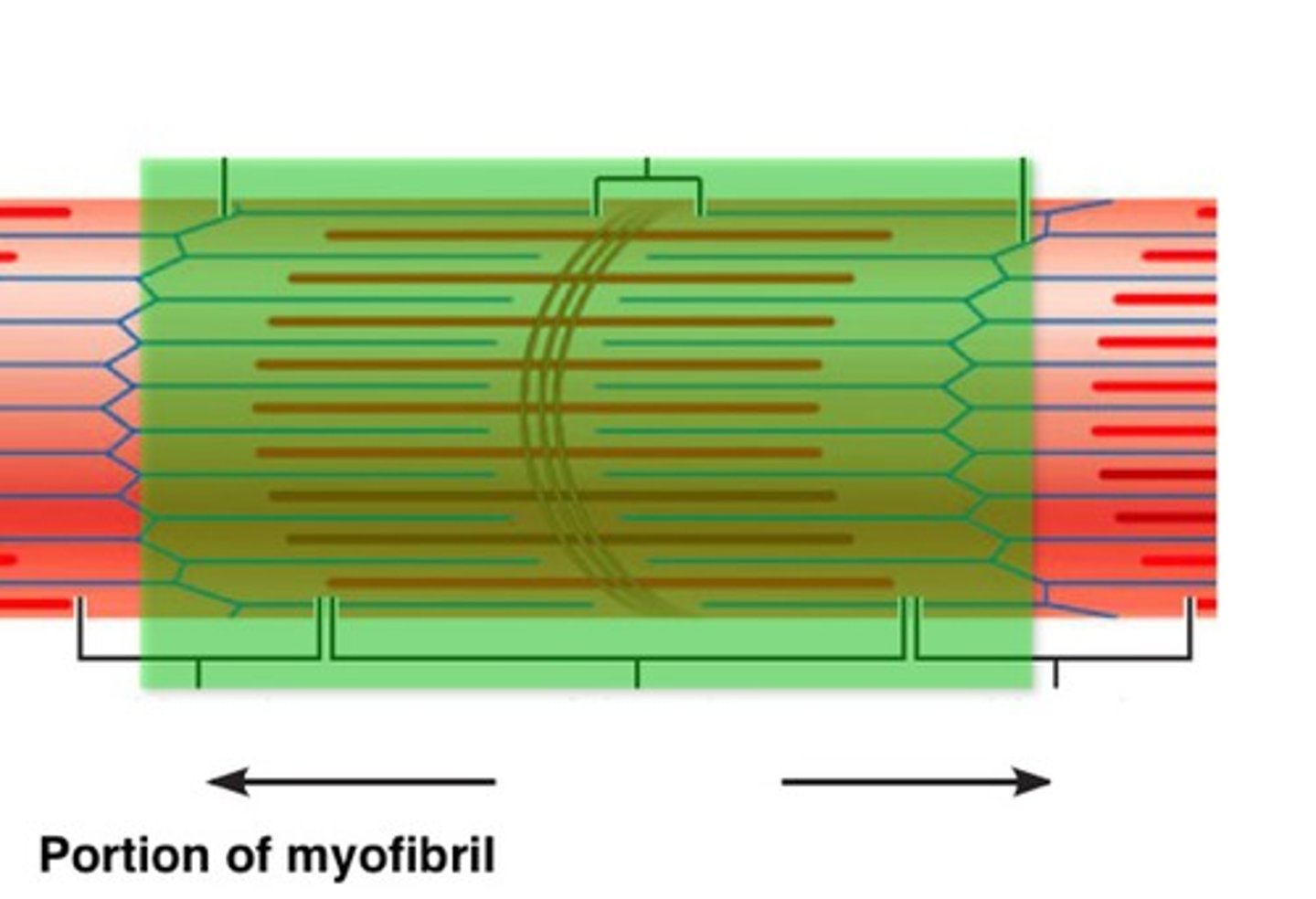
Z-disc
Separates the sarcomeres from each other, anchors filaments and forms each end of the sarcomere
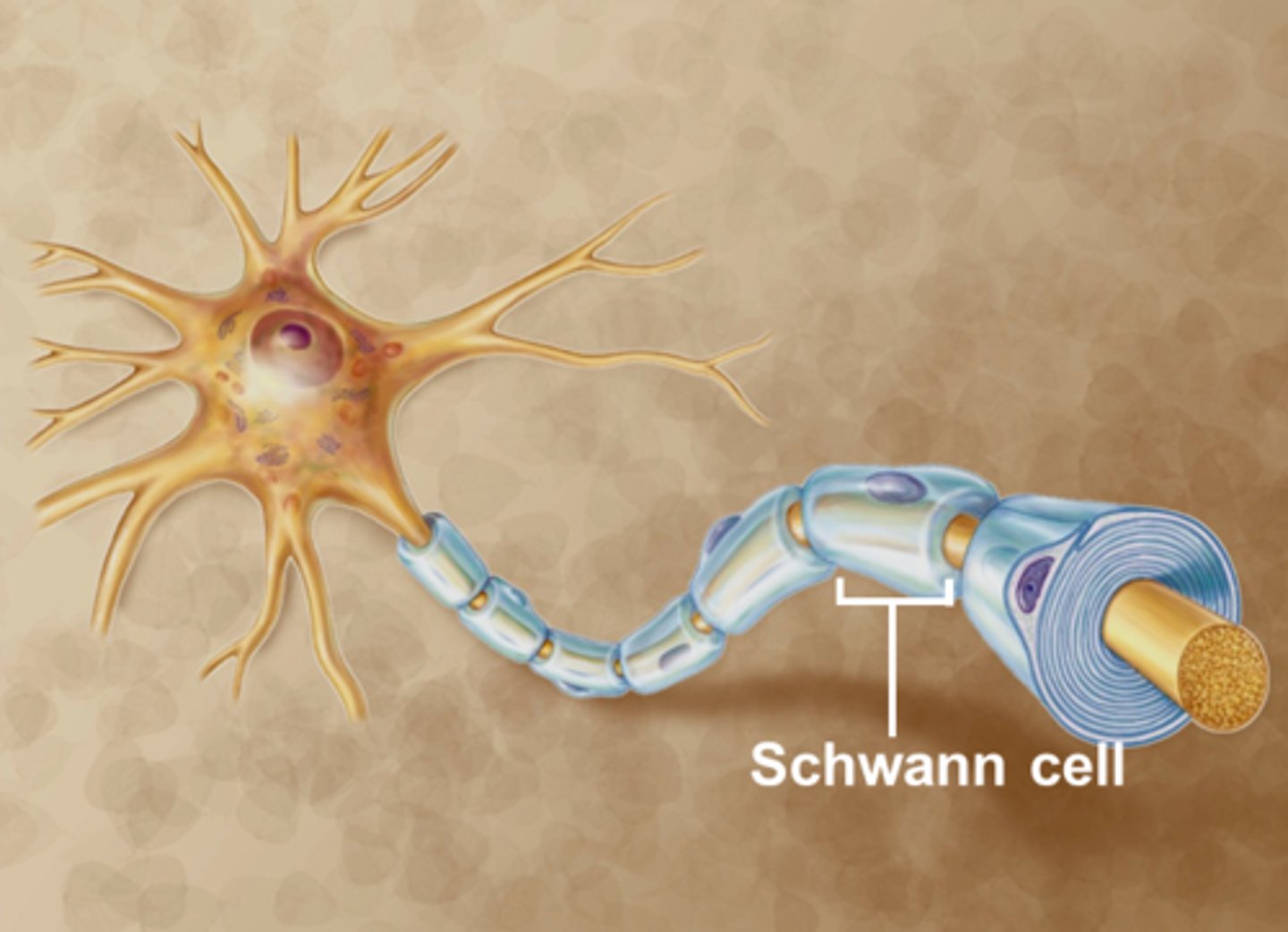
Schwann cell
cell that forms insulation and wraps itself around nerve axons
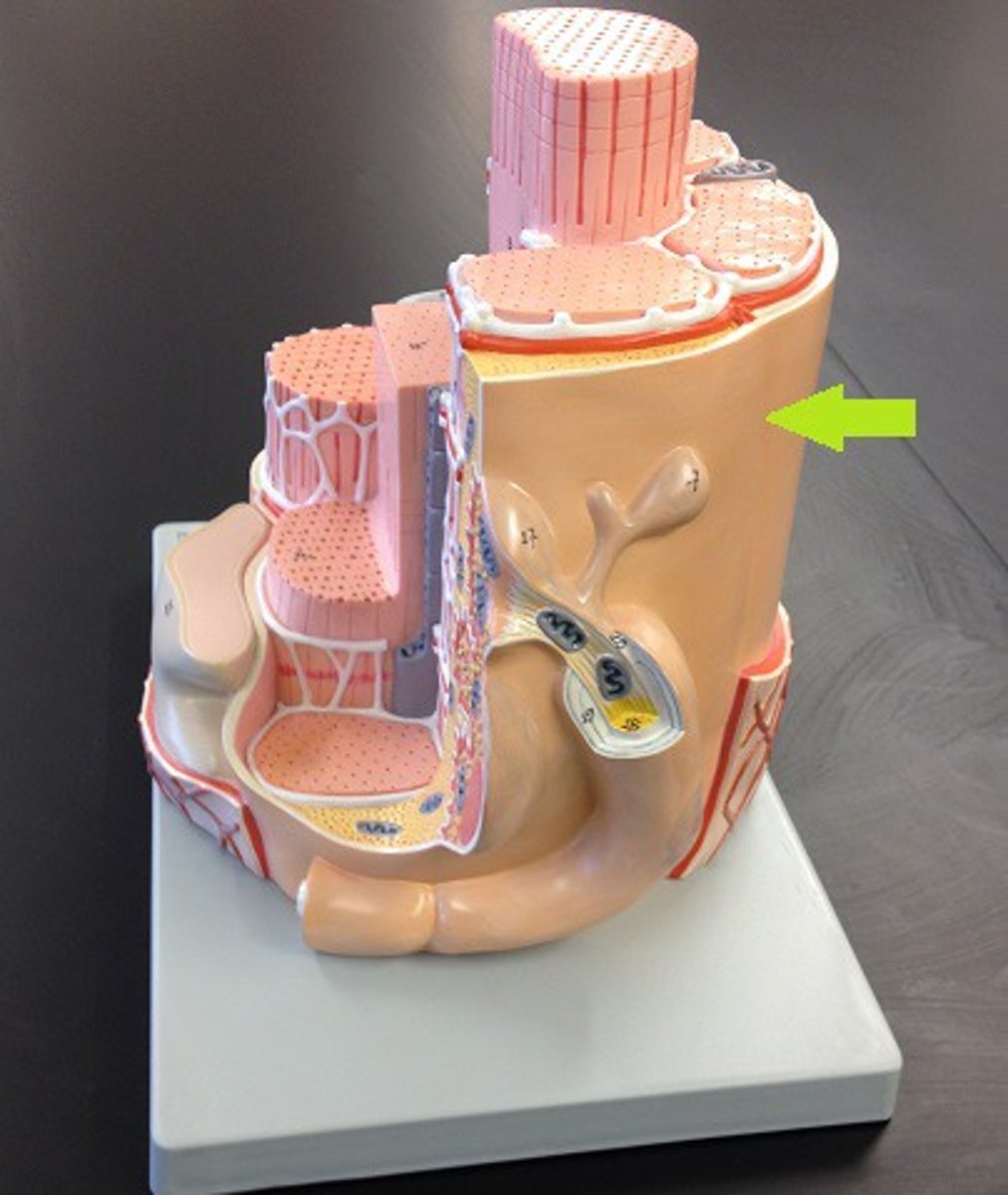
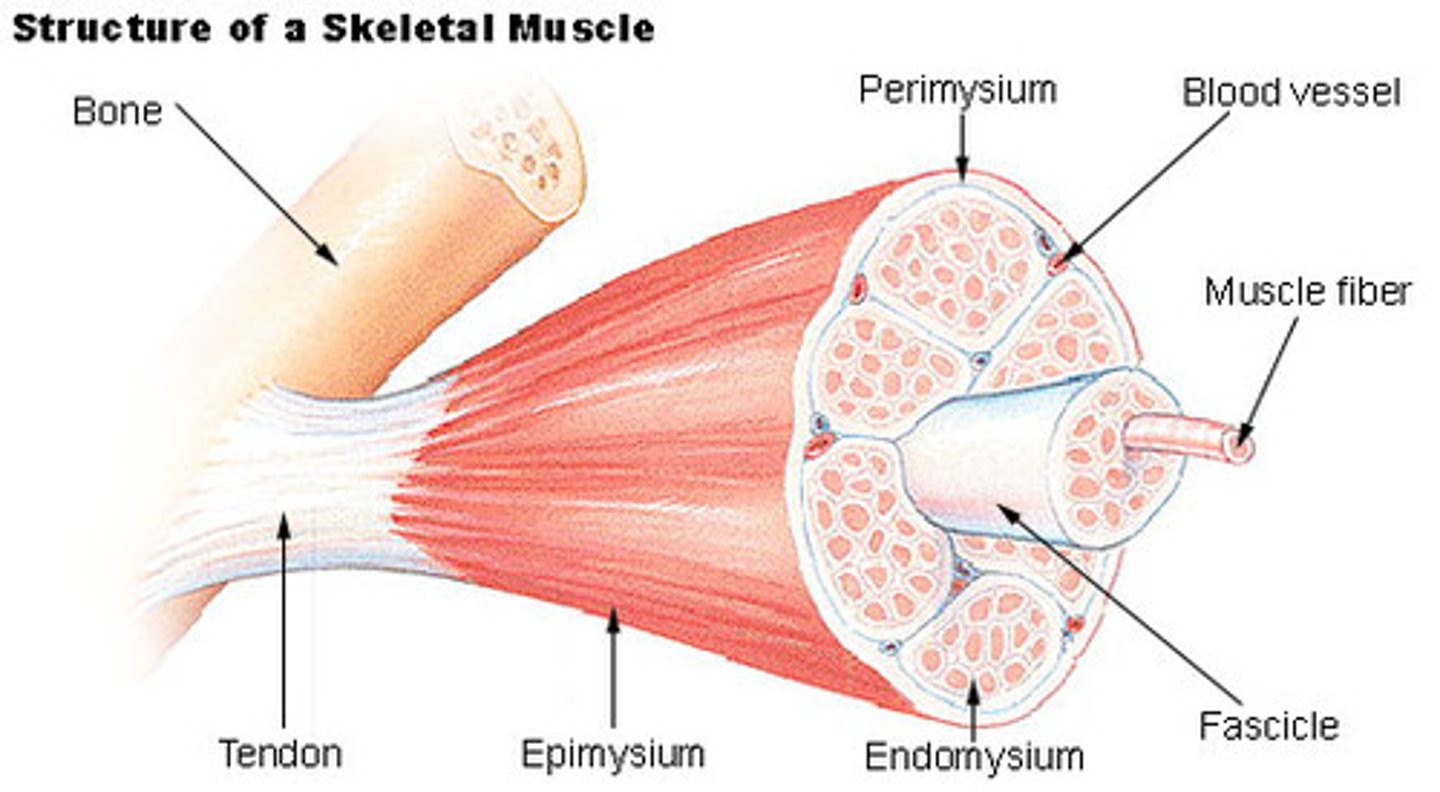
Endomysium
Surrounds individual muscle fibers
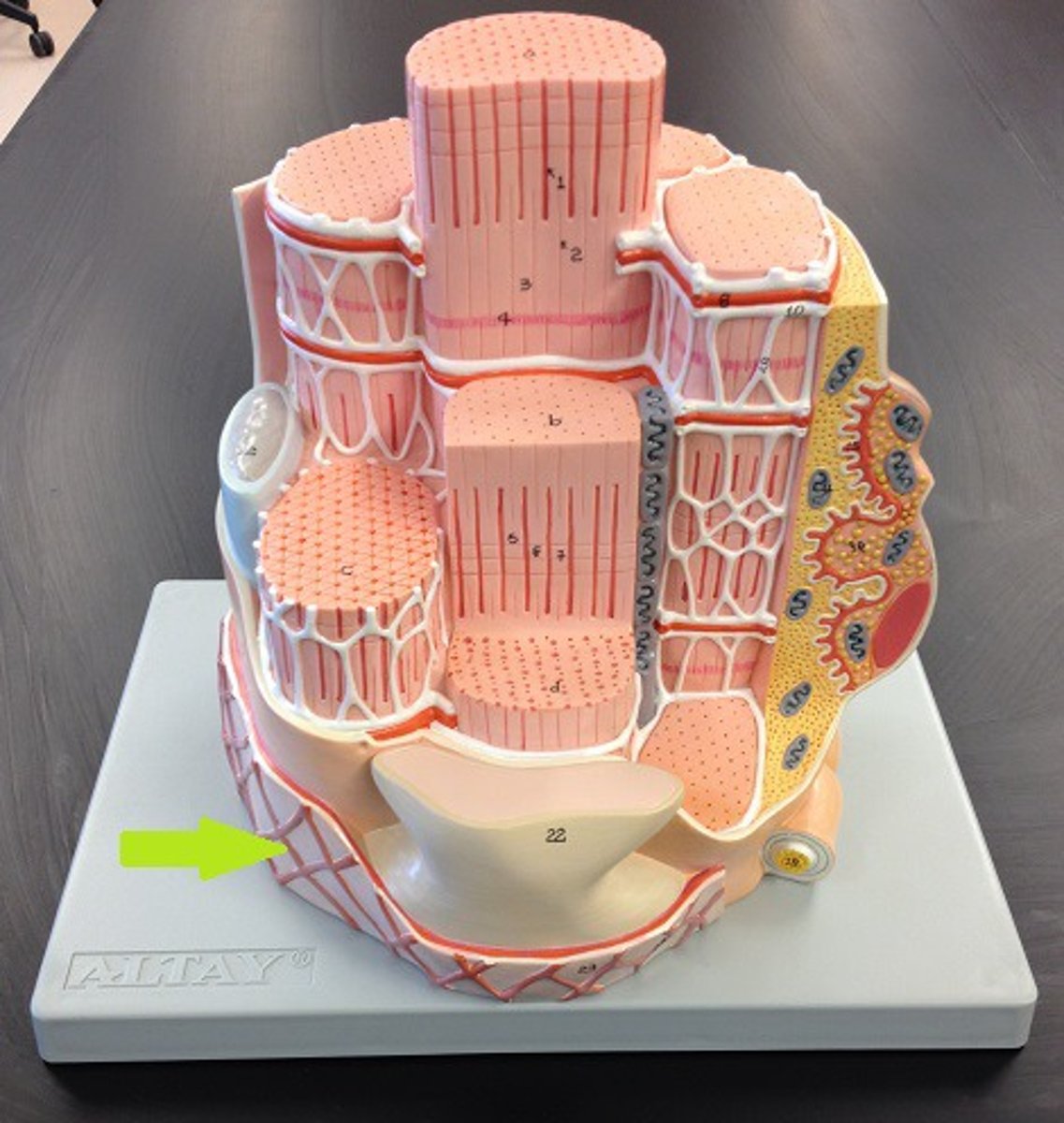

Sarcolemma
T-tubules (transverse tubules)
spread the action potential into the interior of the muscle fiber
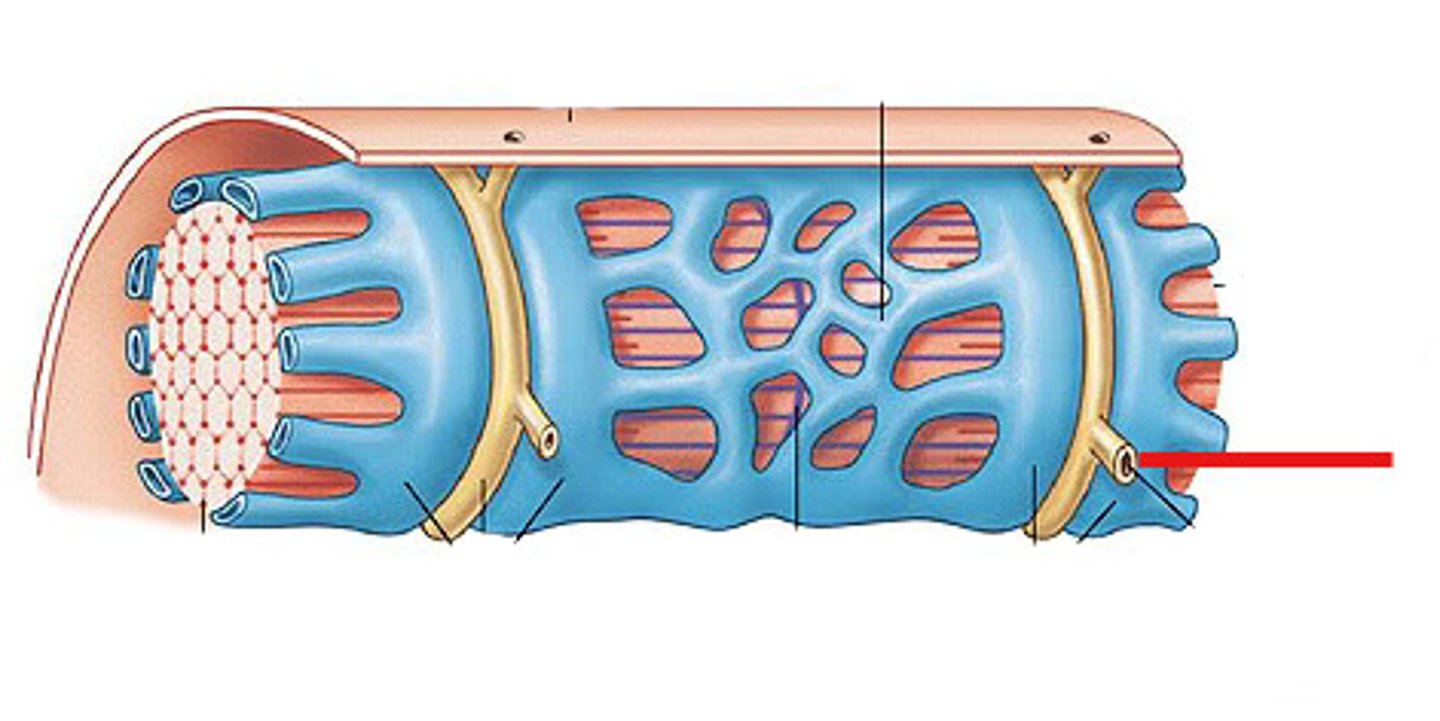
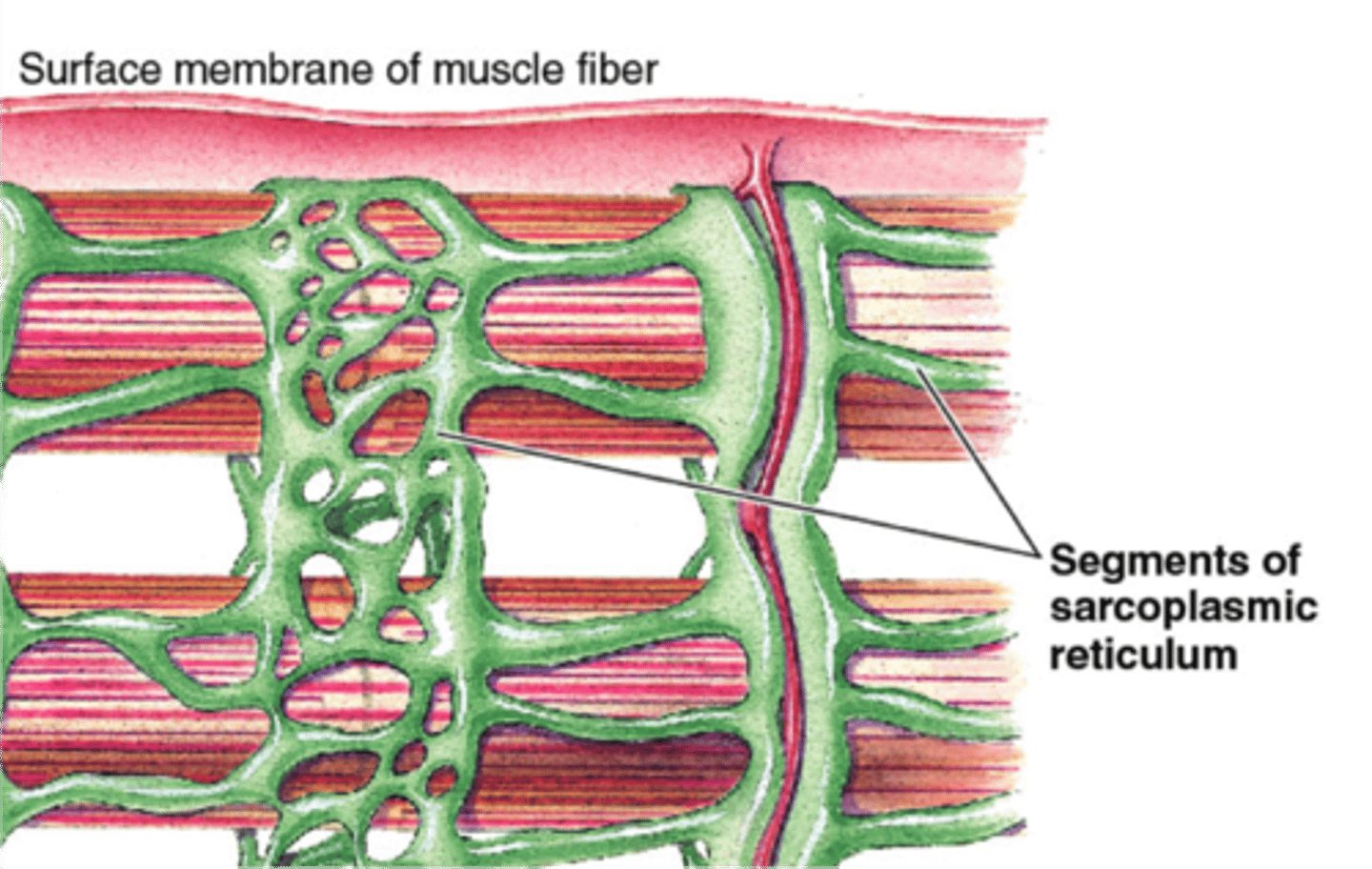
sarcoplasmic reticulum
specialized endoplasmic reticulum of muscle cells that stores calcium
mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
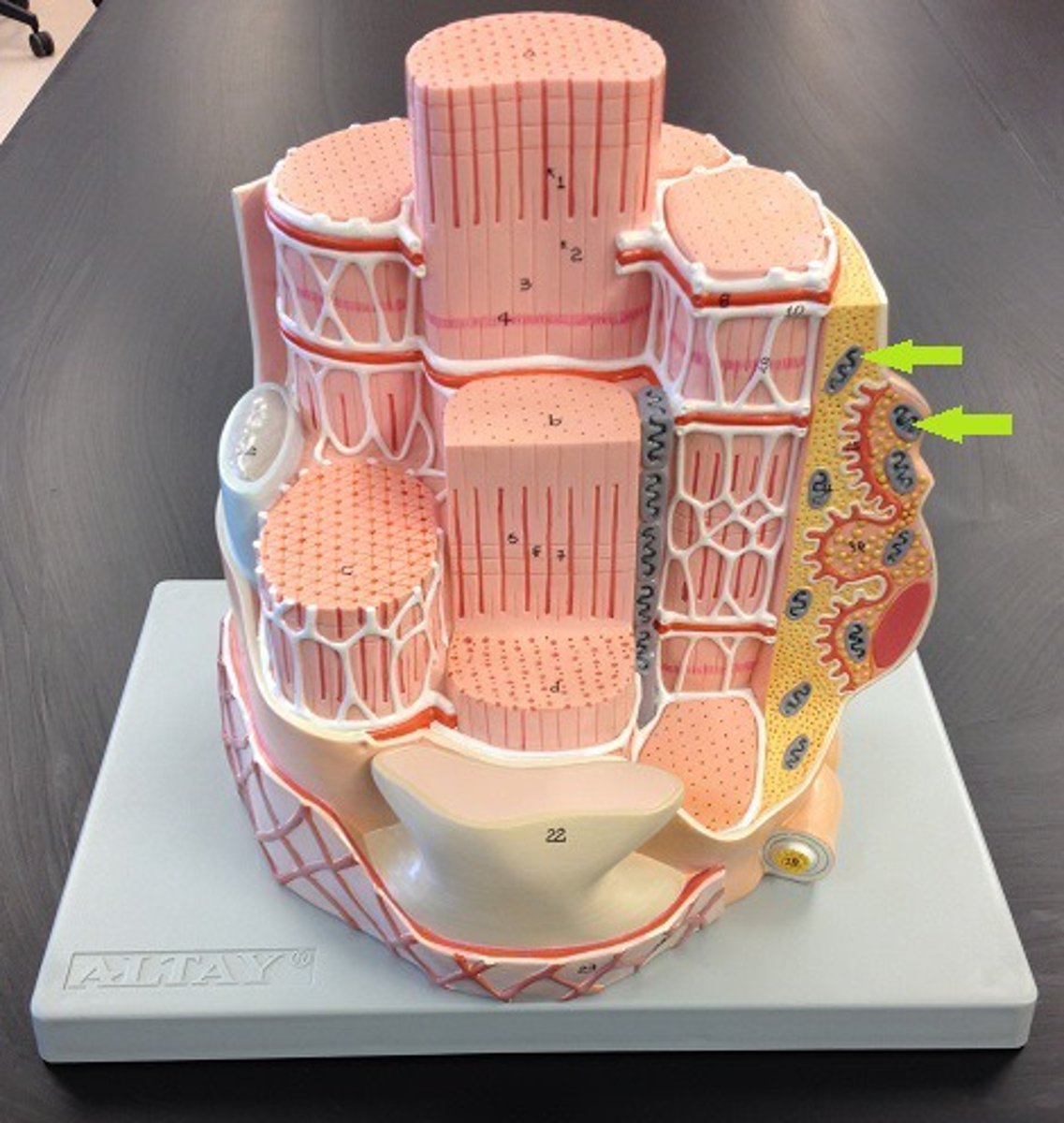

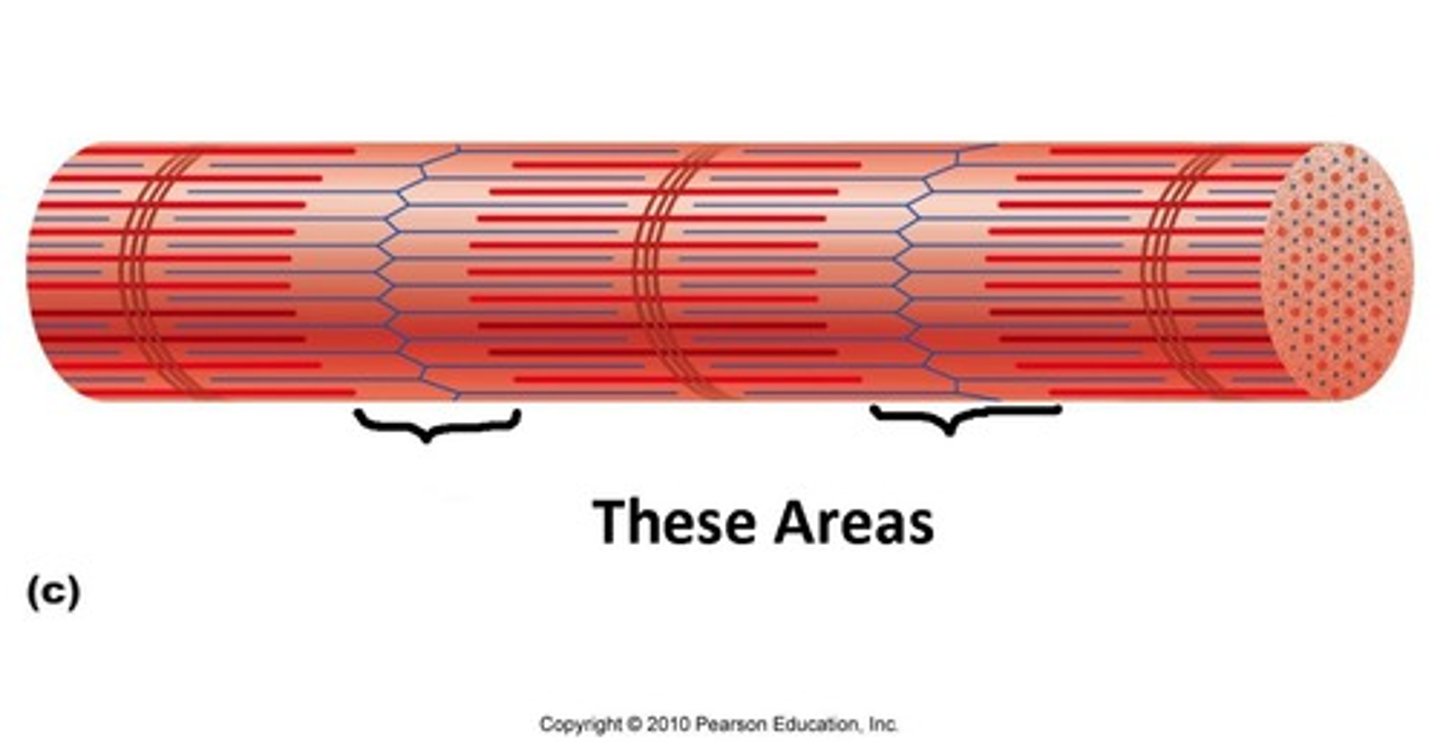
A-bands
dark bands on skeletal muscle
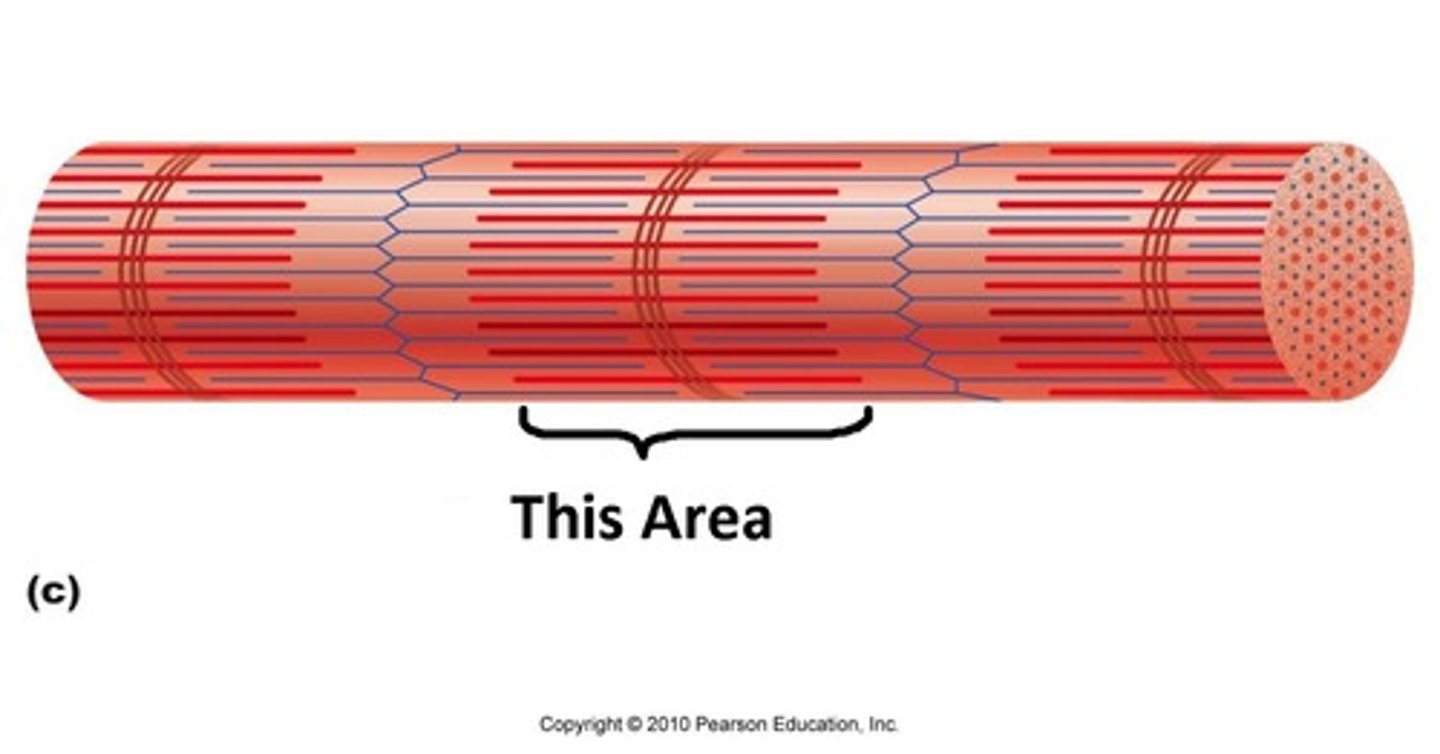
I-bands
light bands because they contain only thin filaments
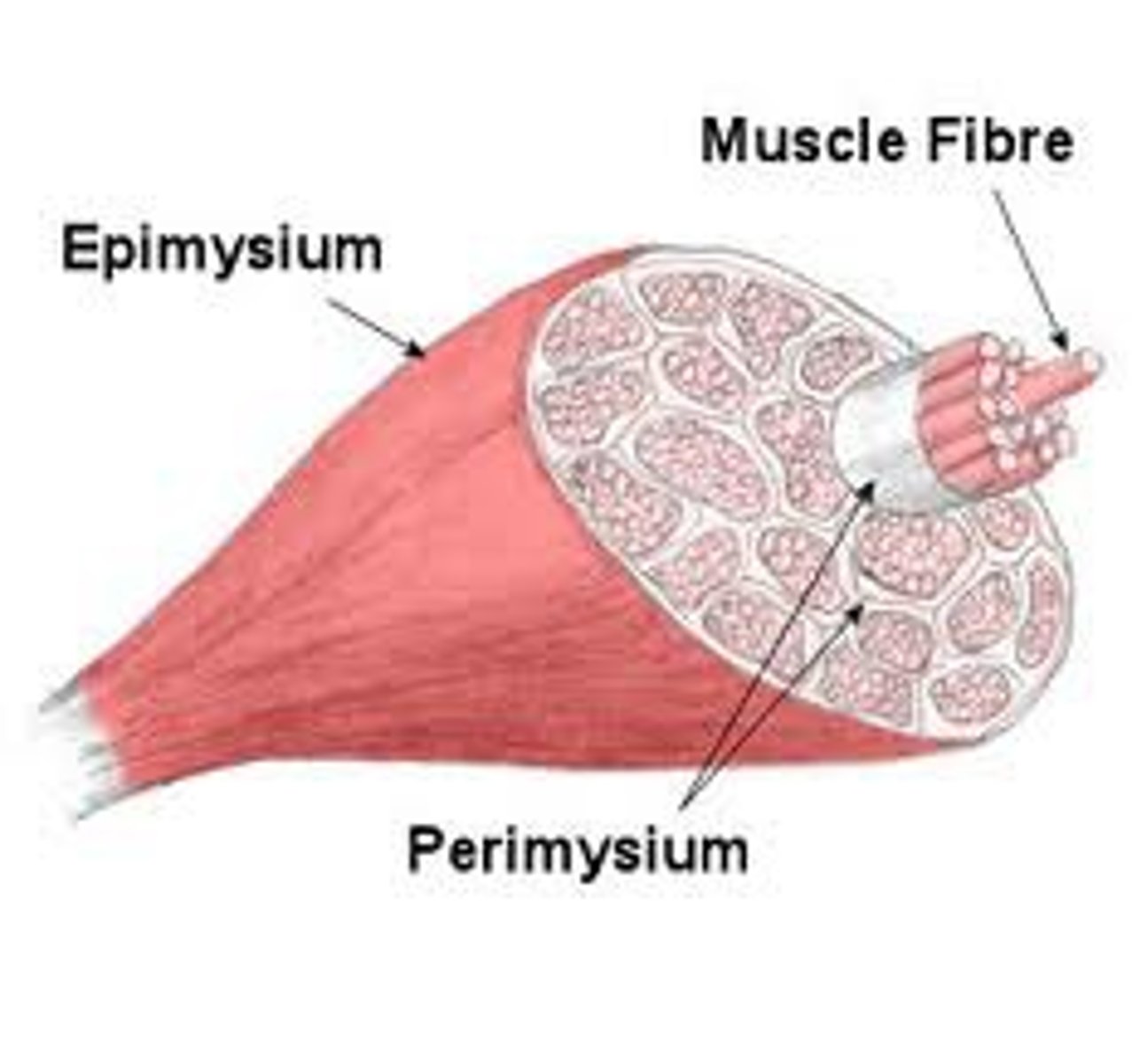
Epimyseum
connective tissue covering ENTIRE muscle
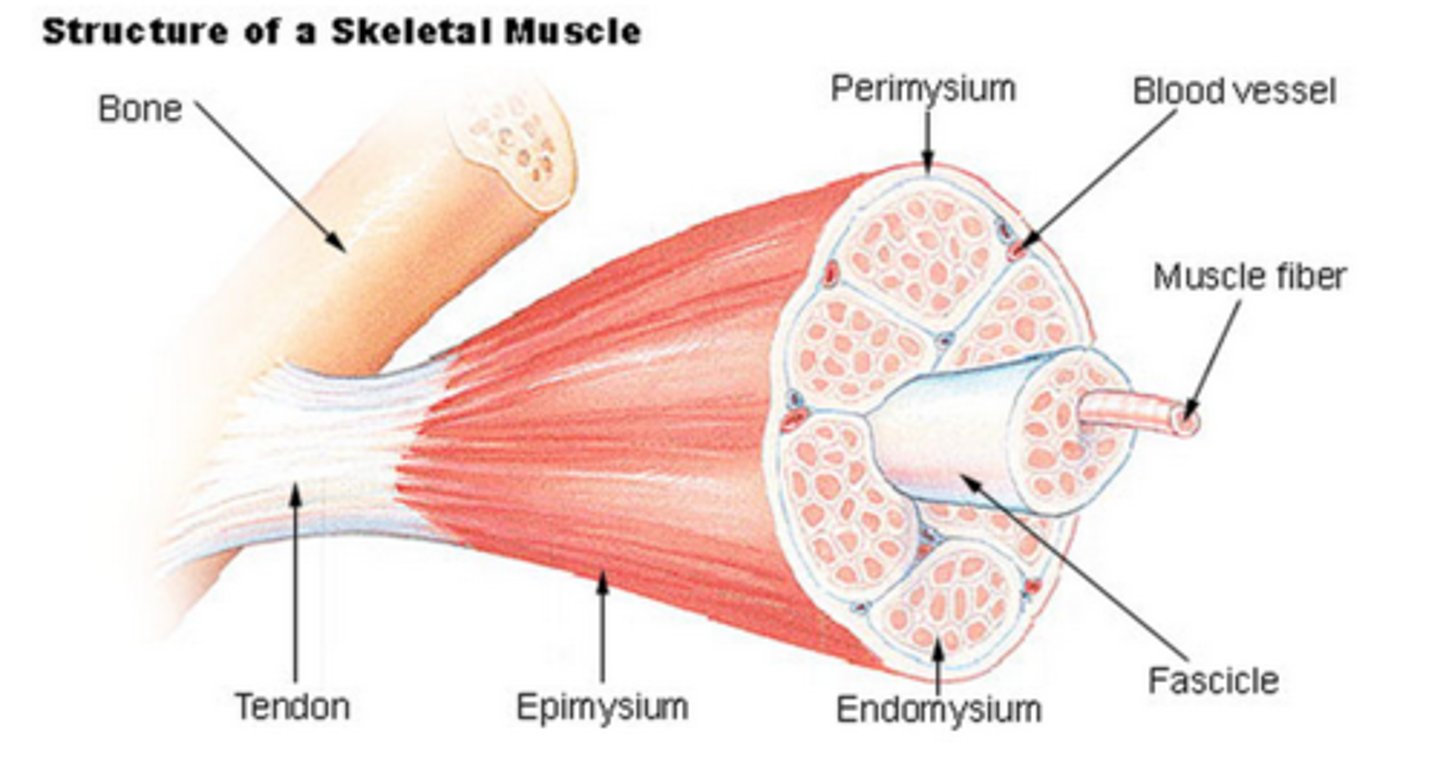
perimysium
connective tissue surrounding fascicule of muscle
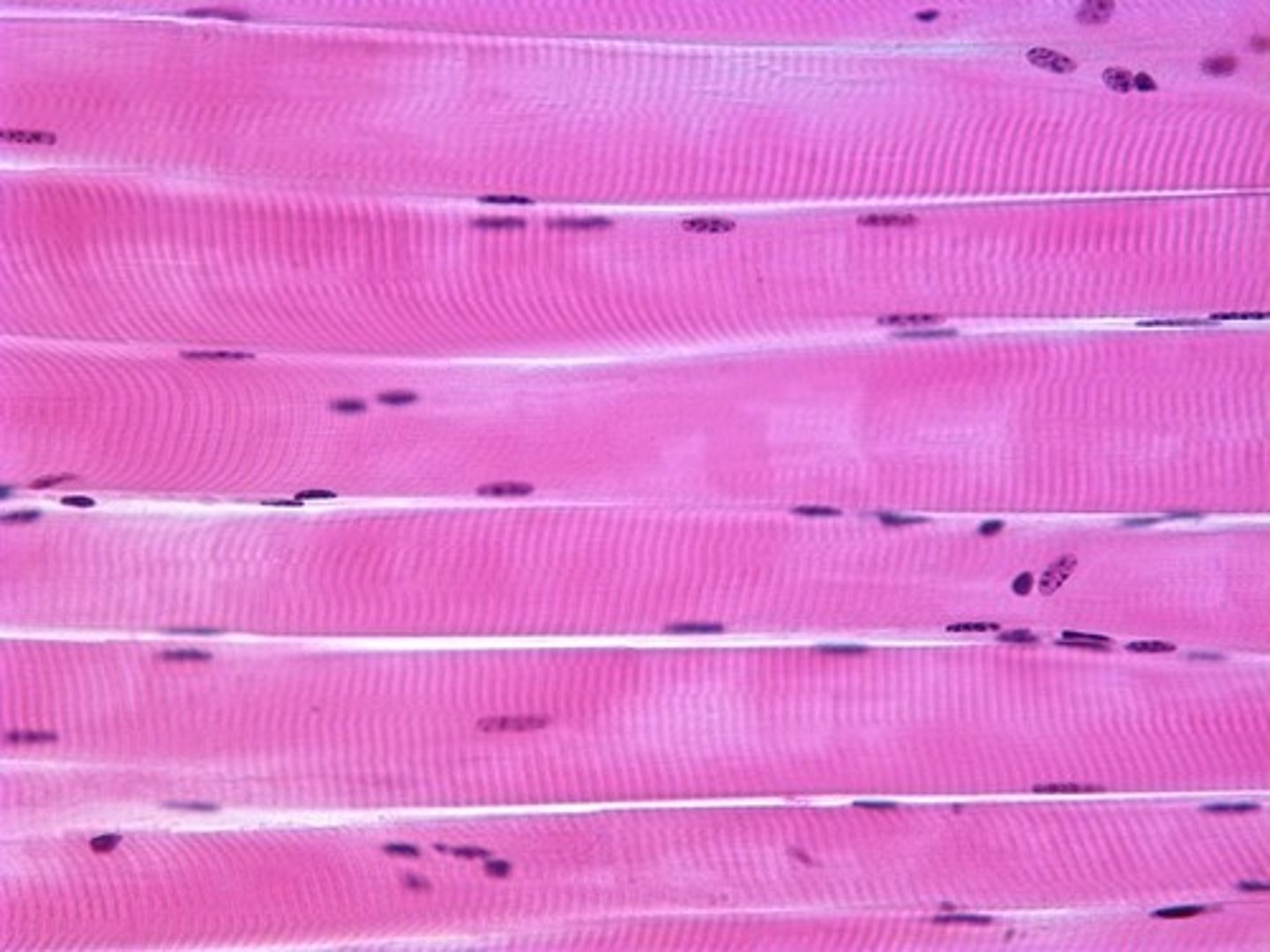
skeletal muscle
striated, long and cylindrical, voluntary, multi-nucleated (more than 1 nucleus per cell)
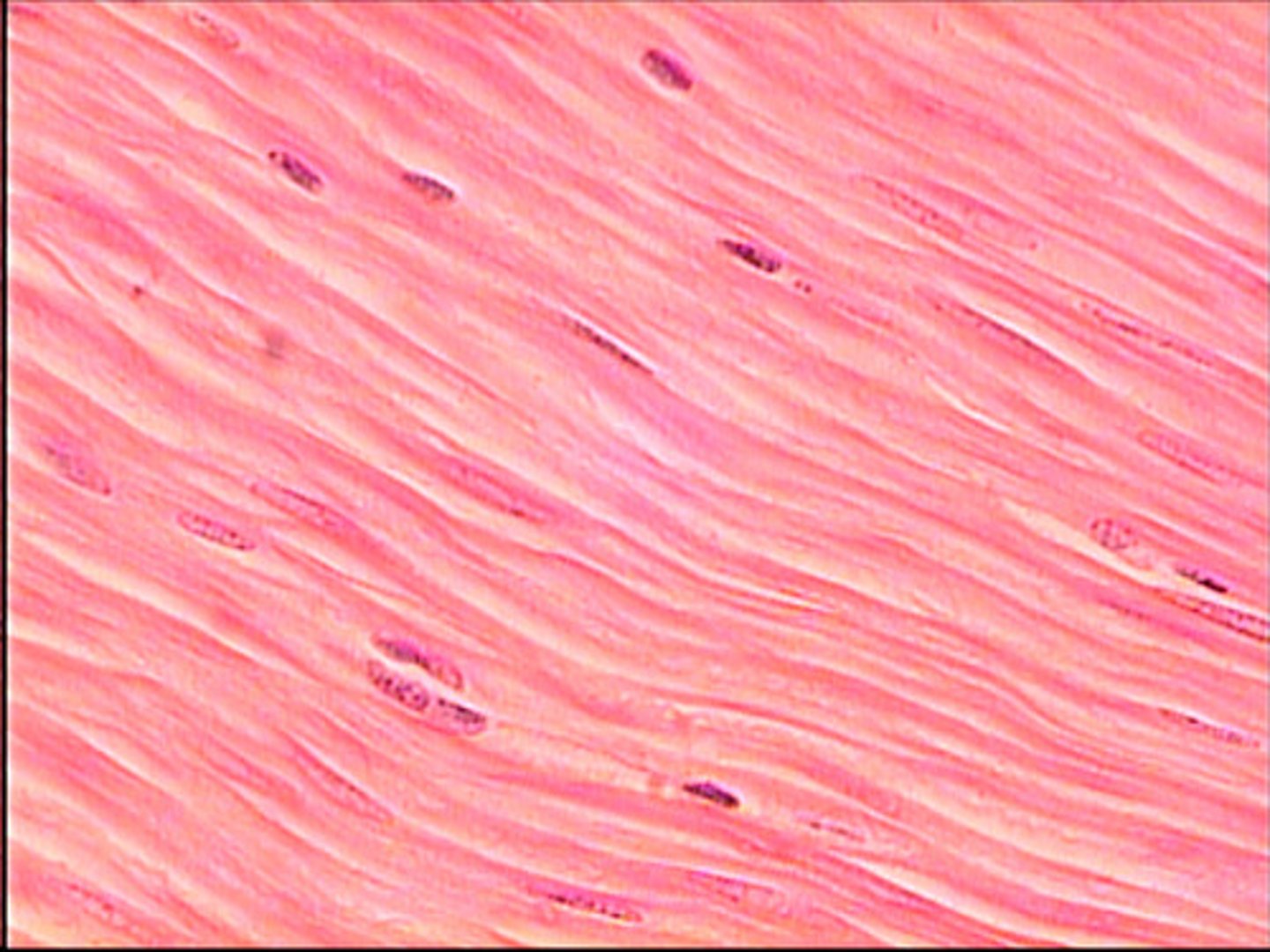
smooth muscel
spindle--shaped, not striated, one nucleus, involuntary
cardiac muscle
striated, Y-shaped, involuntary, 1 or two nuclei, intercalated discs
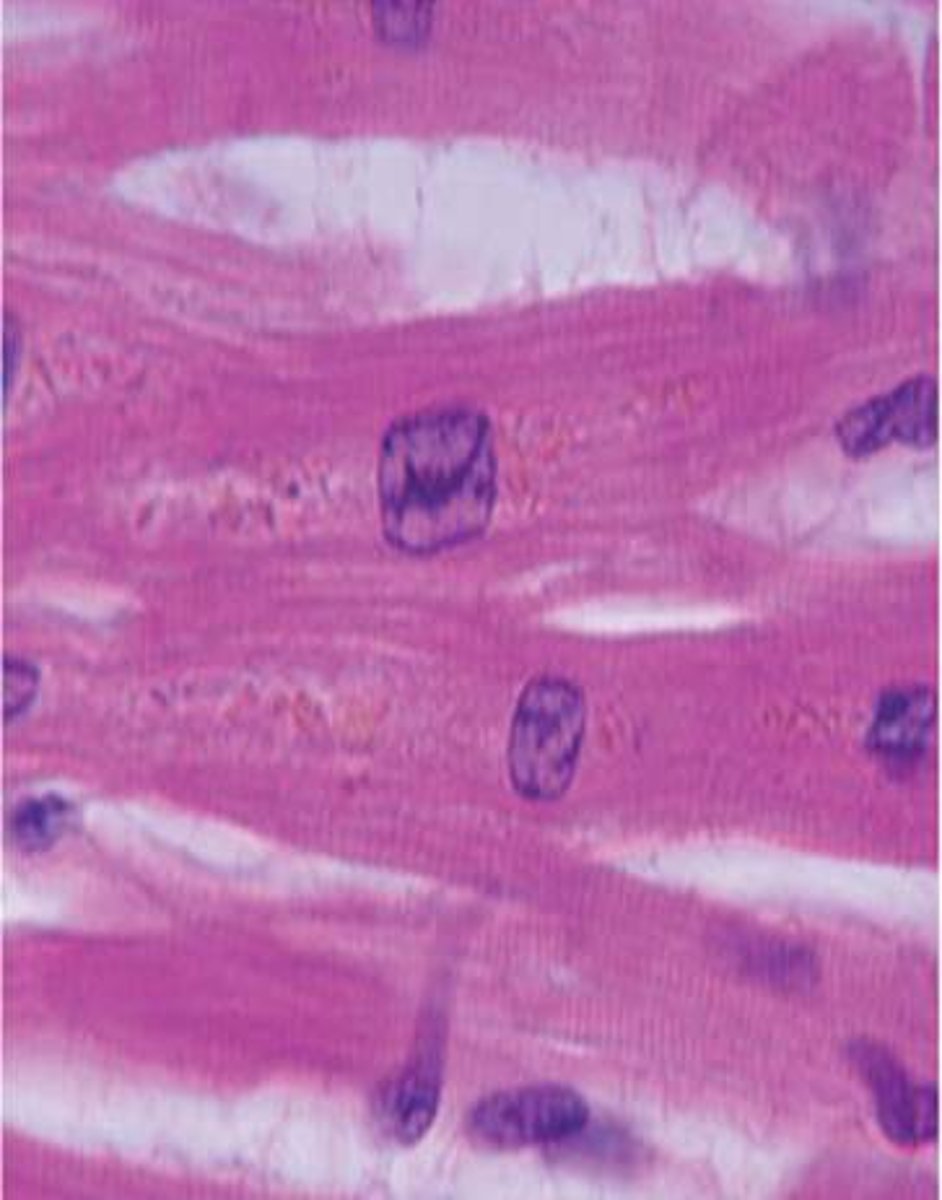
muscle fiber
a single muscle cell
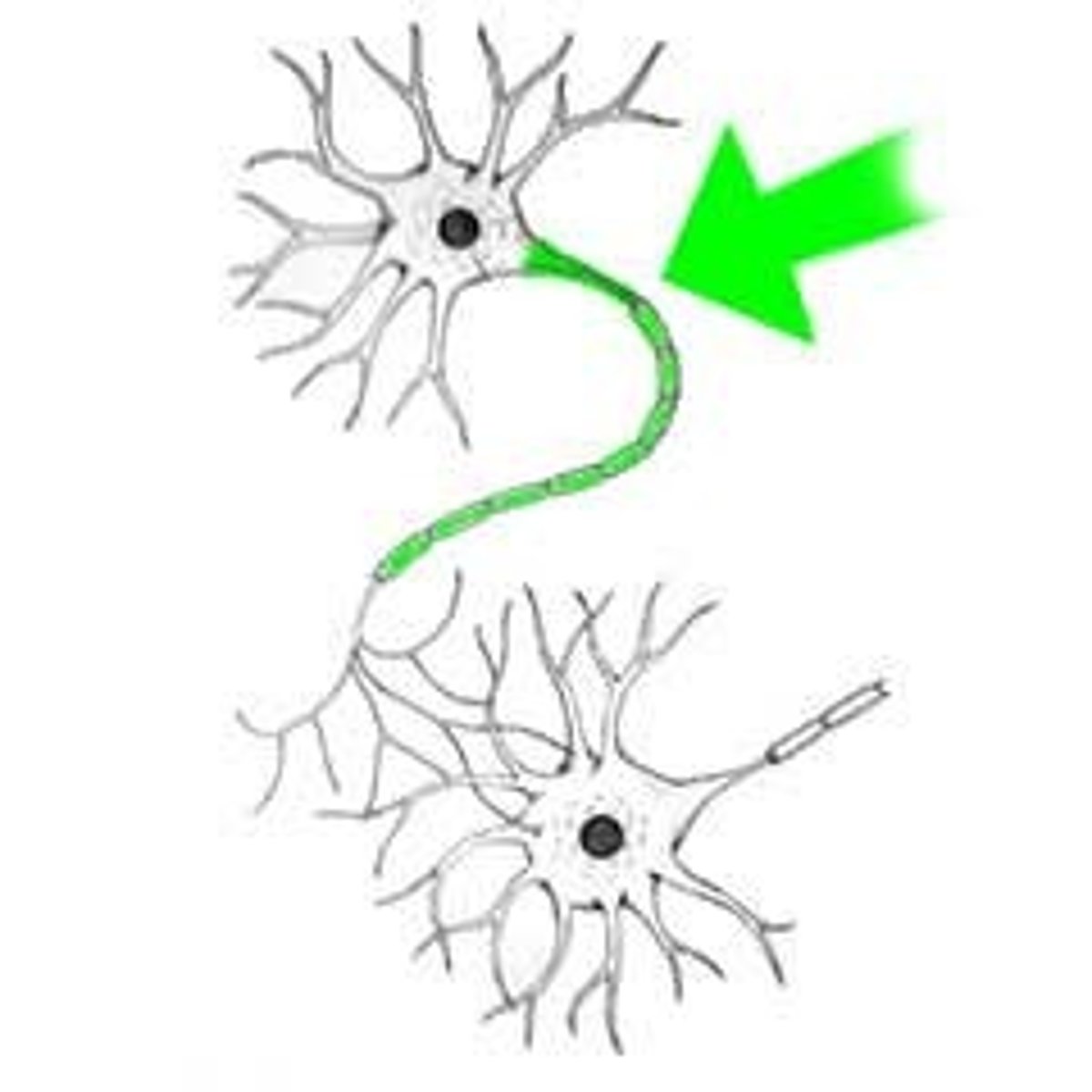
nerve fiber
axon of a neuron (the long process of a nerve cell)
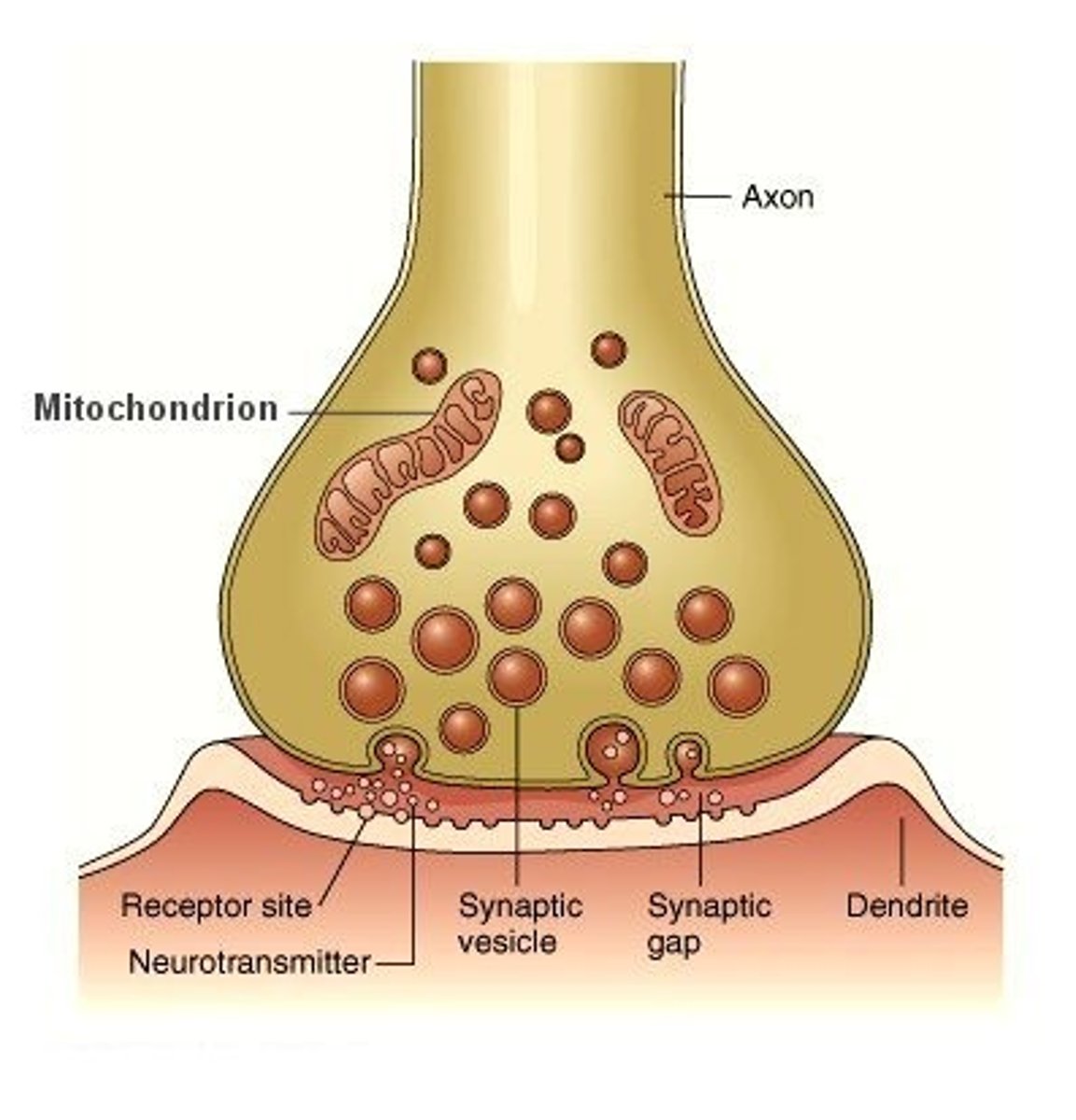
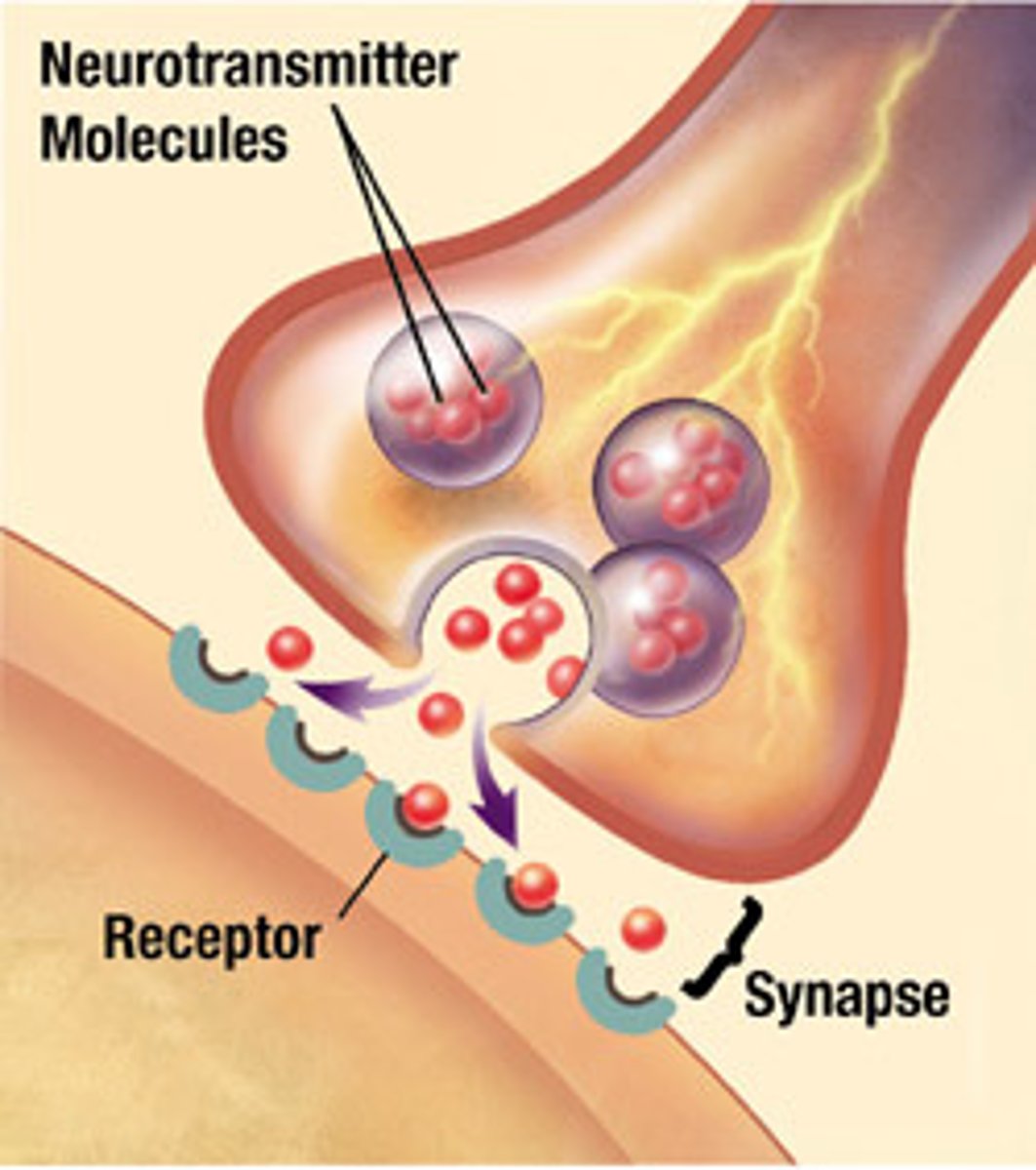
synaptic end bulb
A swollen area at the end of a nerve axon--it stores and releases neurotransmitter molecules onto a target cell across a synapse
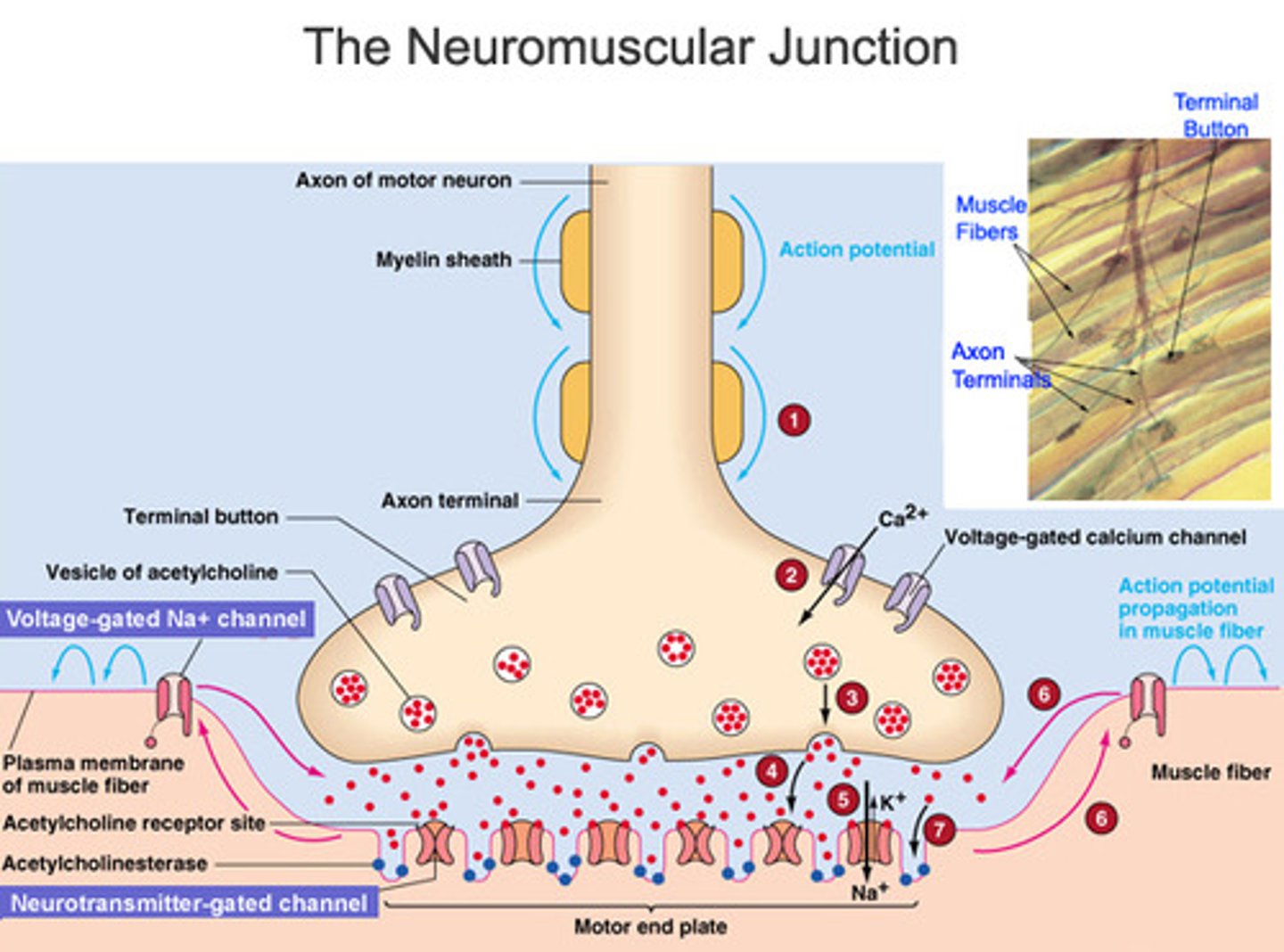
nueromuscular junction (NMJ)
a synapse between a motor neuron axon and a muscle cell (=muscle fiber)
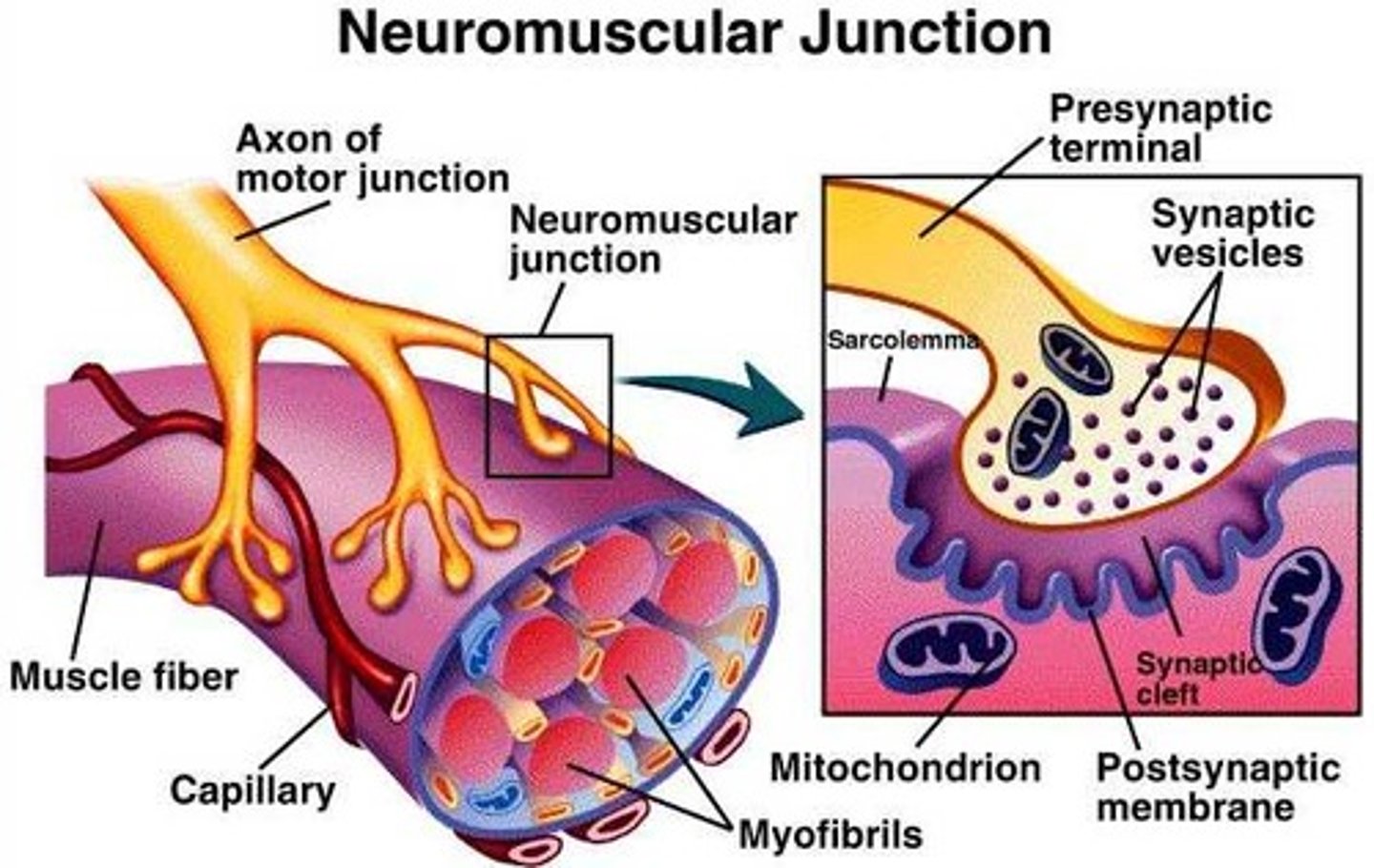
motor end plate
the flattened end under the synaptic bulb of a motor neuron that transmits neural impulses to a muscle, usually by releasing neurotransmitter molecules across the synaptic cleft
4 functions of the muscular system
movement, posture, joint stability, heat production
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that travel from the nerve cell synaptic bulb to receptors on the muscle cell membrane (sarcolemma). In muscular system, neurotransmitter = ACh (Acetylcholine)
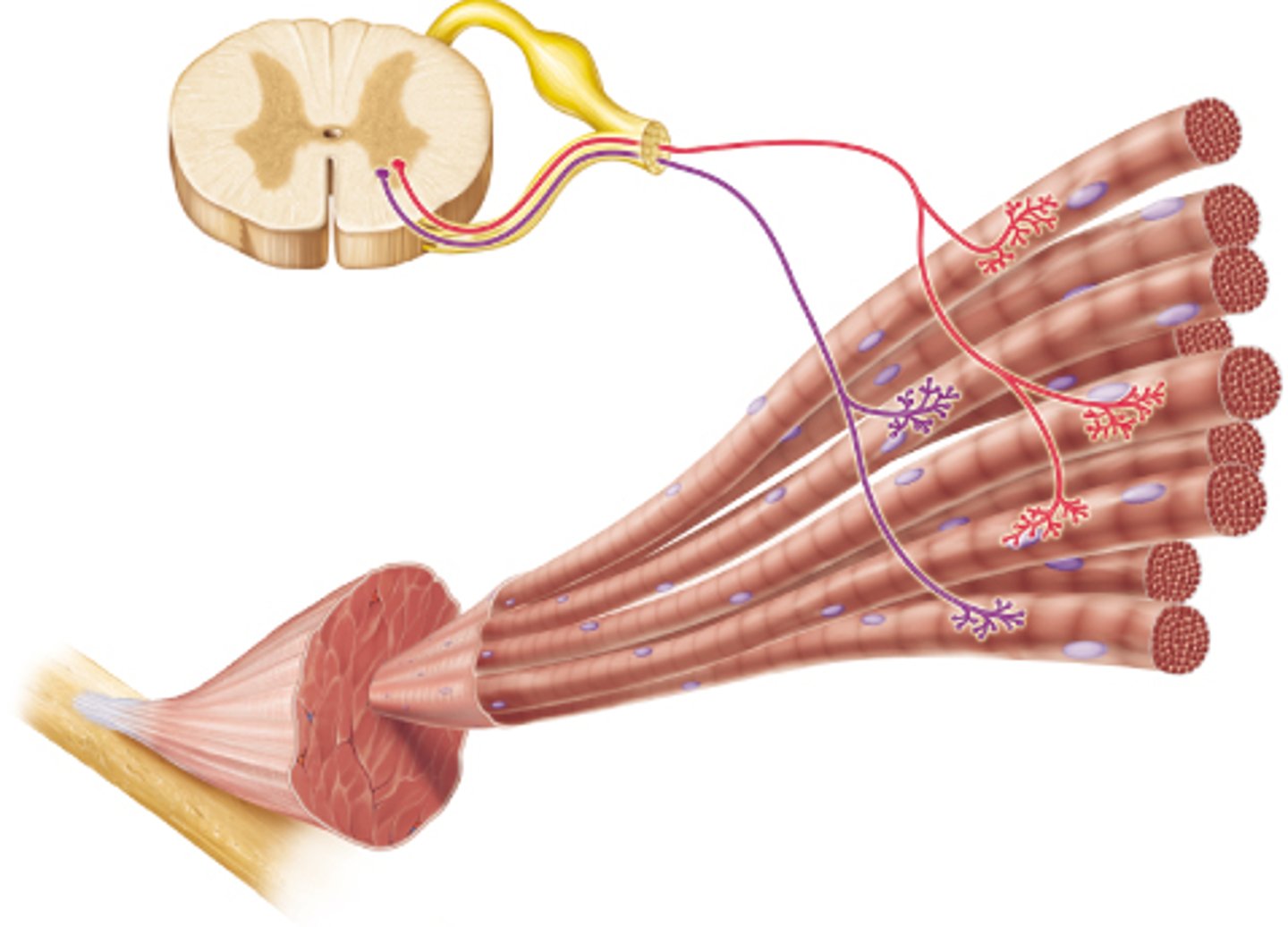
motor unit
A motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
isotonic contraction
muscles contract and SHORTEN, produces body movement, like a biceps curl
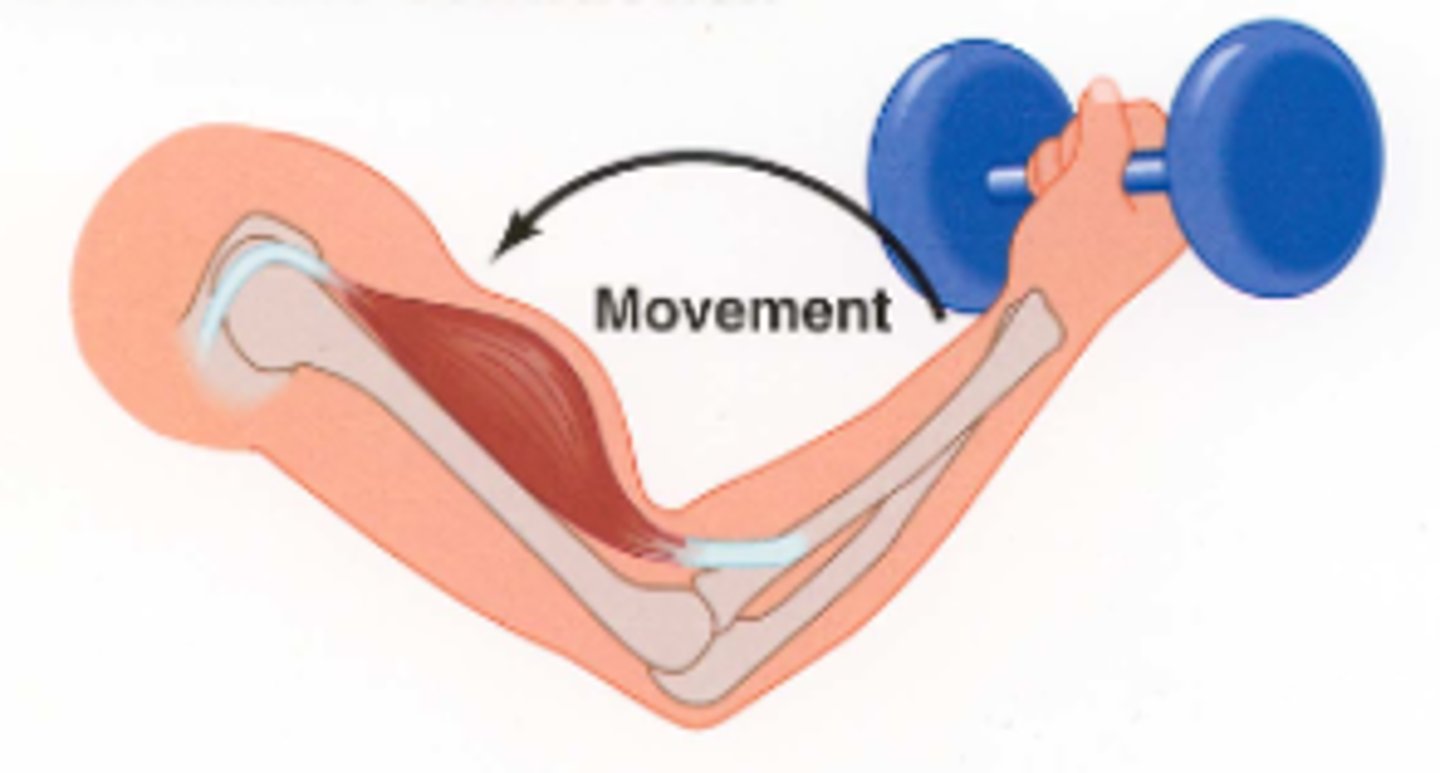
isometric contraction
Muscle contracts but there is NO MOVEMENT, muscle stays the same length (like doing a plank)

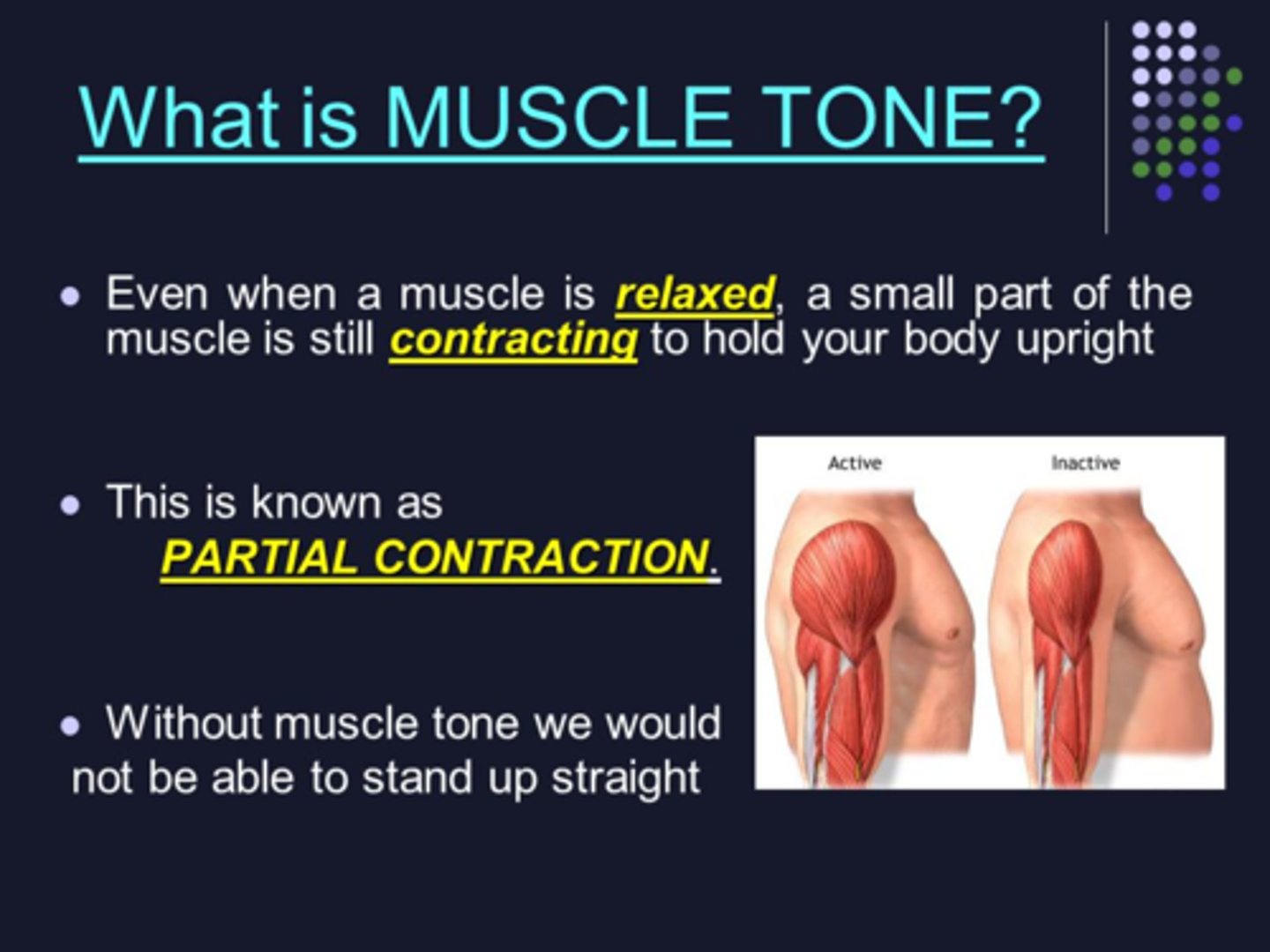
muscle tone
A state in which your muscles are partially contracted (even when you are at rest)
aerobic exercise benefits
increases muscle endurance, benefits heart, also helps with attention, memory, goal-directed thinking and behavior, creativity

resistance training
training designed to increase STRENGTH, power, and MUSCLE ENDURANCE

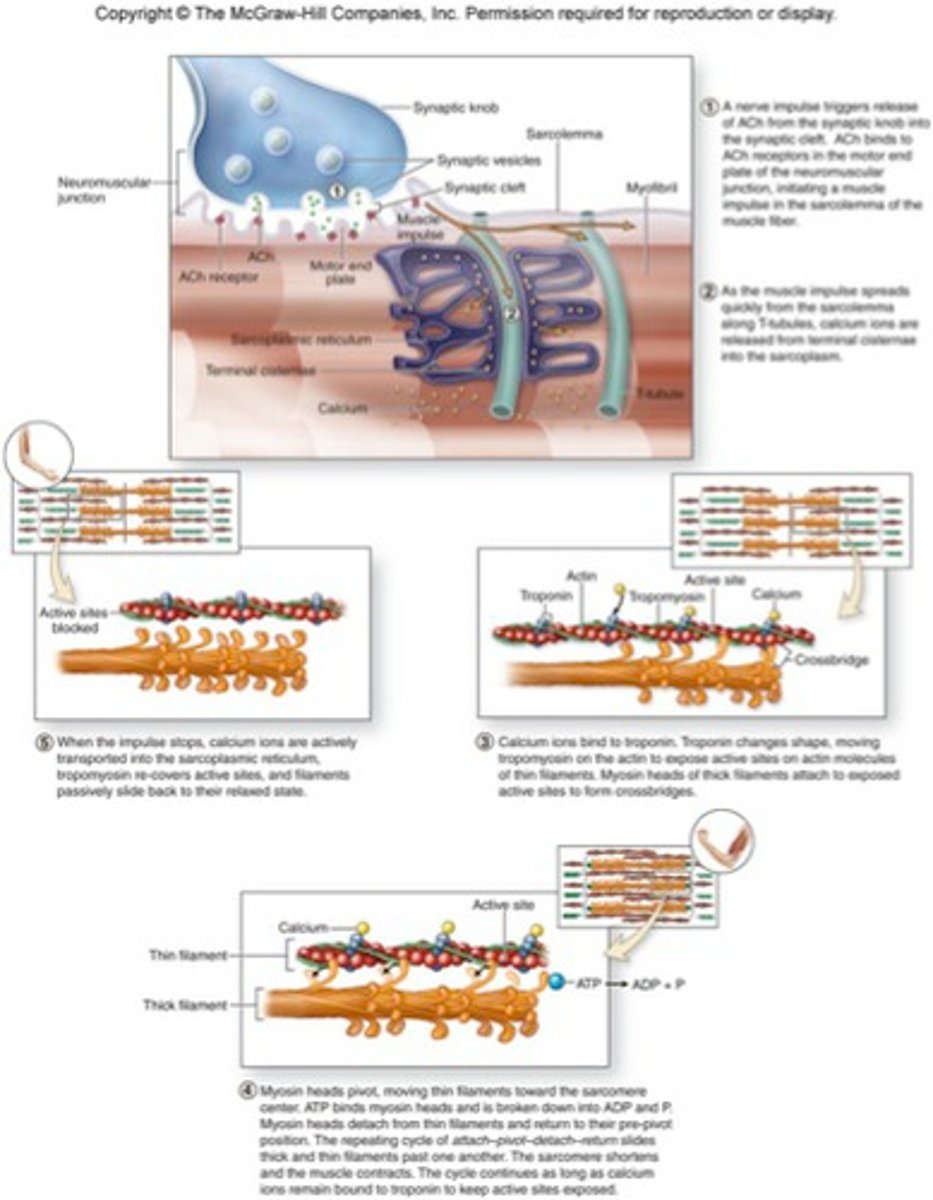
The first step in a muscle contraction is _________.
a nerve impulse reaches the neuromuscular junction
When the neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the muscle cell membrane, the muscle cell _______.
is stimulated to contract
Calcium ions are released into the muscle cell and bind to ________.
troponin-tropomyosin (blocks the myosin binding sites)
As long as calcium is present in the muscle cell, the muscle will continue to _________.
contract
The method that regenerates the most ATP during muscle activity is ________.
aerobic pathway
The motion in which you move your arms and/or legs laterally away from your body is termed ___________.
abduction
What condition results if muscles are not used, such as when immobilized in a cast for healing a broken bone?
atrophy
What is the main function of the quadriceps group?
Knee Extension (rectus femoris also flexes hip)
During skeletal muscle contraction, myosin heads bind actin filaments to form ________.
cross bridges
How are calcium ions removed from the muscle cell cytoplasm?
active transport
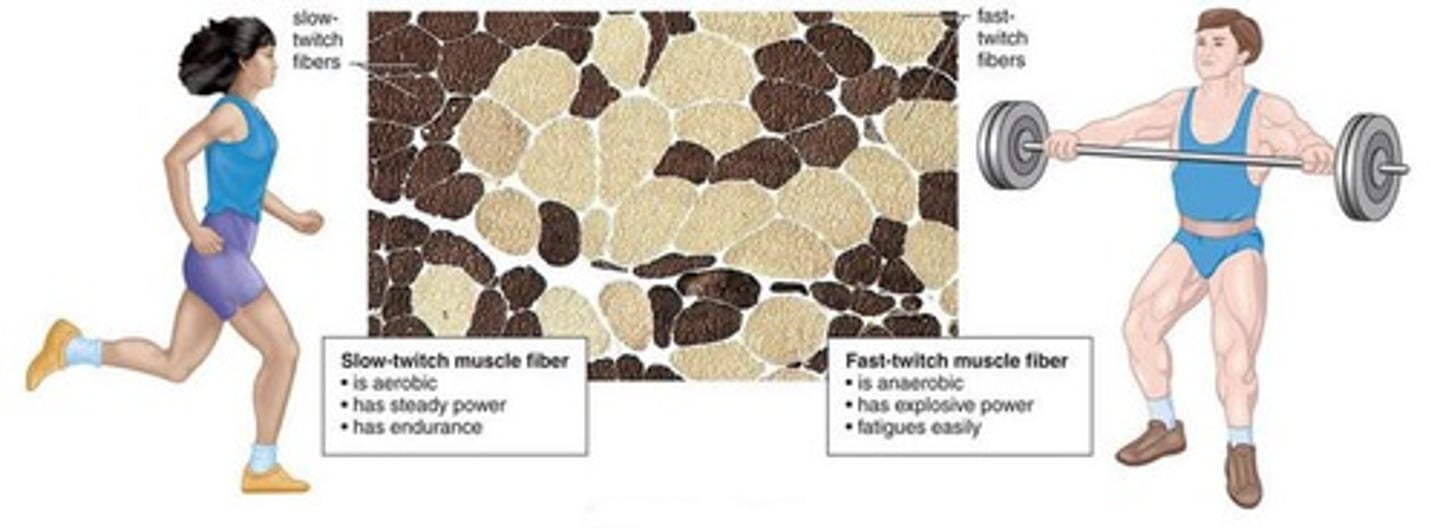
white muscle fibers
fast twitch muscle fibers--little blood supply, good for bursts of speed (such as sprinting)

red muscle fibers
slow-twitch muscle fibers--have good blood supply, great for activities that require stamina (such as running a marathon)
Steps of muscle contraction
Know the order and general process
sarcomere
functional contractile unit of muscle
ACh (Acetylcholine)
the neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction--causes muscles to contract