The Skull (Cranium and Face)
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What is the neurocranium?
the bones that support or protect the brain
What is the viscerocranium?
the bones that support the soft tissues of the face and aid in eating, drinking, chewing, speaking
How many bones make up the cranium and what are they?
8, the frontal bone, occipital bone, temporal bones (two), parietal bones (2), sphenoid and ethmoid
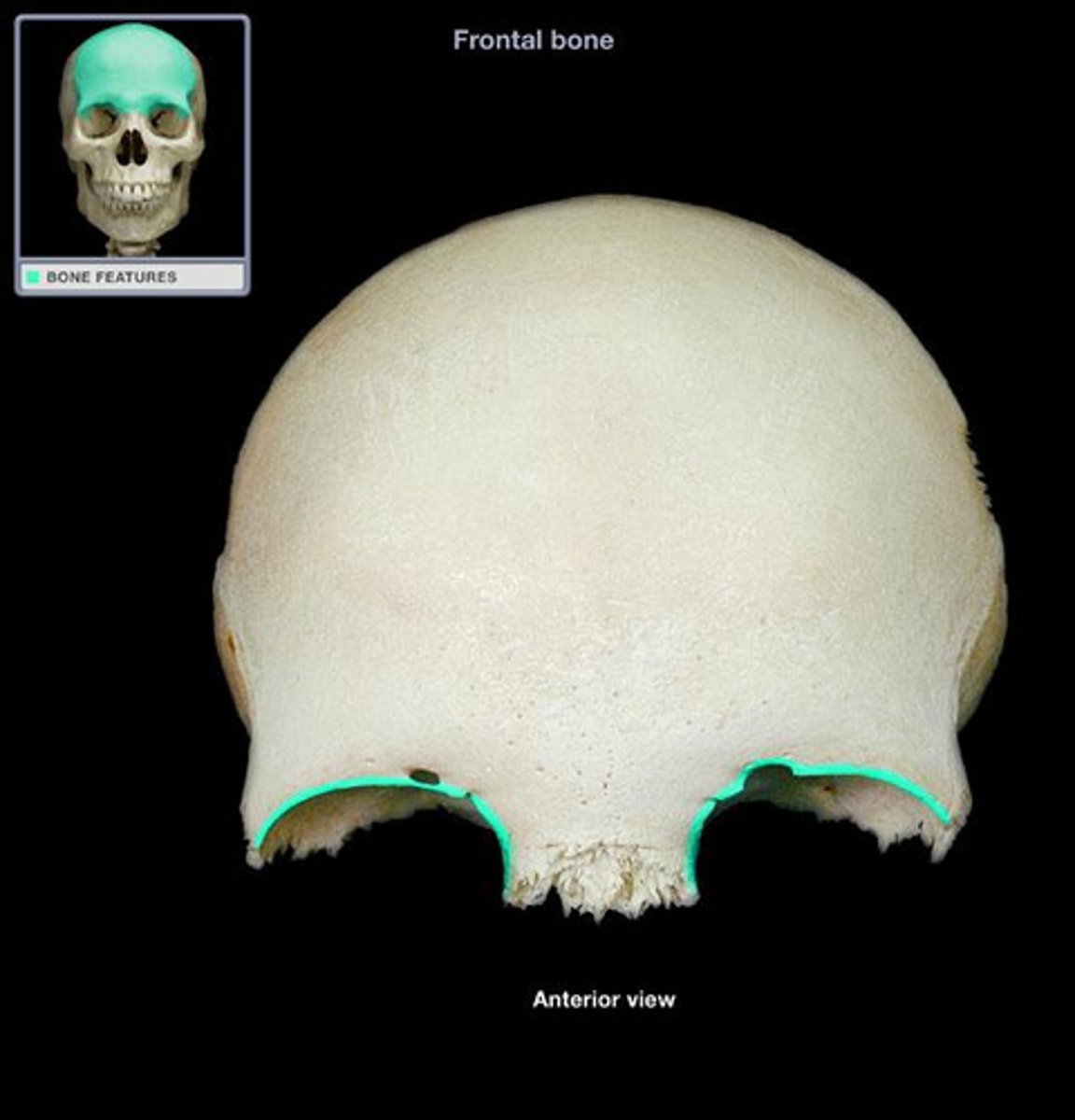
Supraorbital margin of frontal bone
the sharp ridge that forms the border between the forehead and inside of the orbit
supraorbital foramen of frontal bone
opening above each orbit allowing blood vessels and a small branch of CN V1 nerve to pass
frontal sinus of frontal bone
Cavity within the bone that is lined with muscosa and open to the exterior. It lightens the skull and alters vocal quality
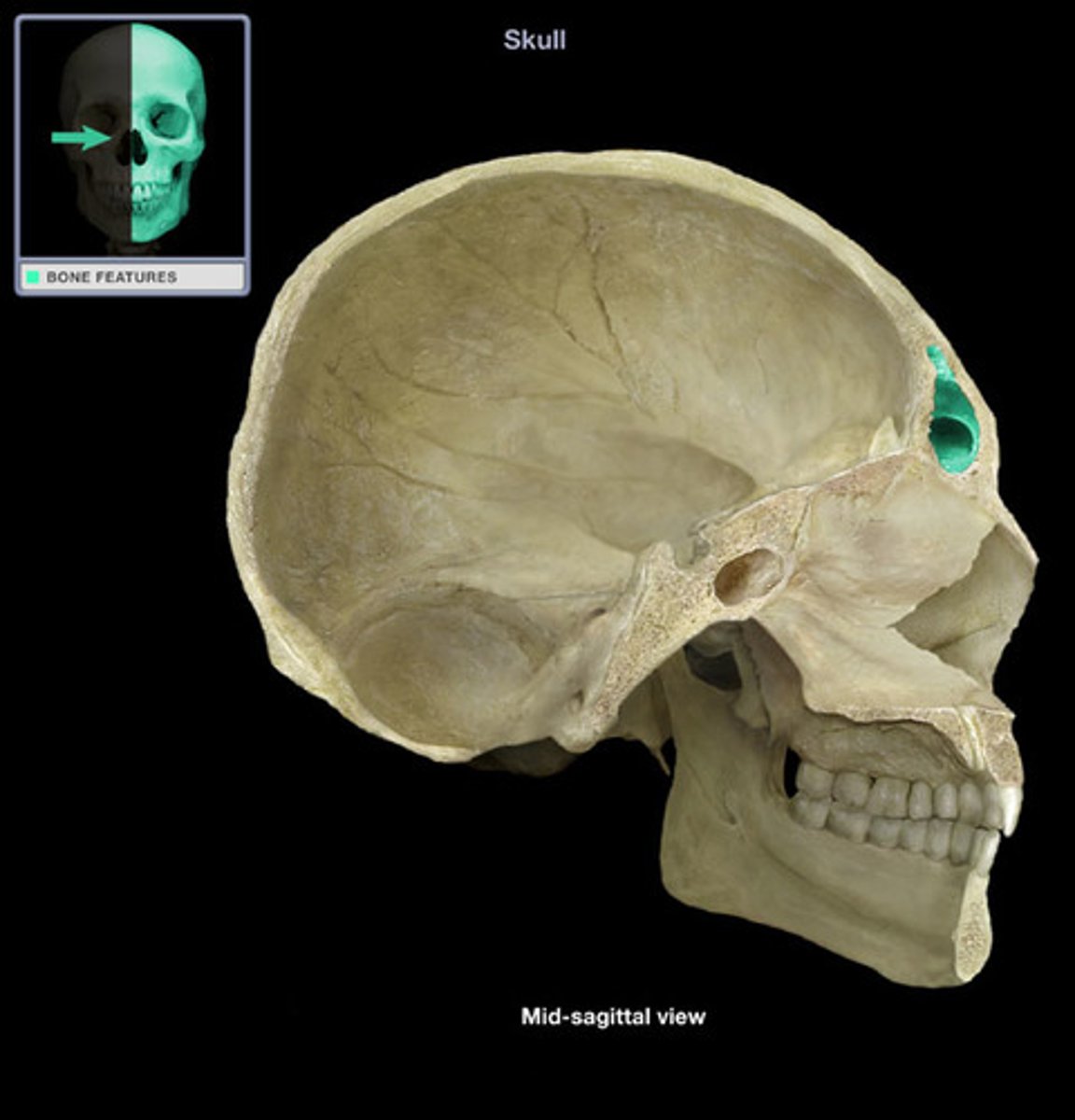
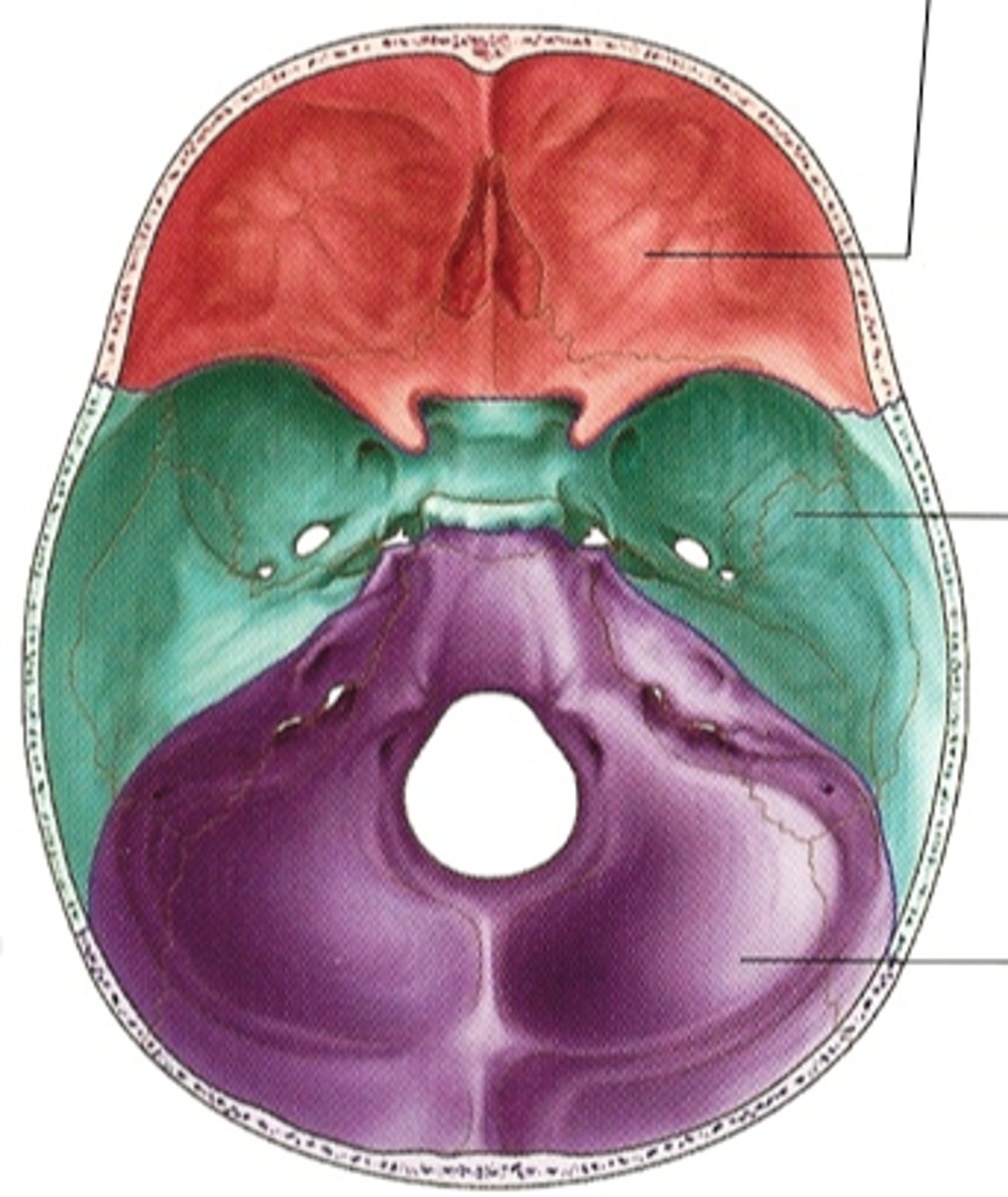
anterior cranial fossa
the portion of the cranial cavity formed by the frontal bone

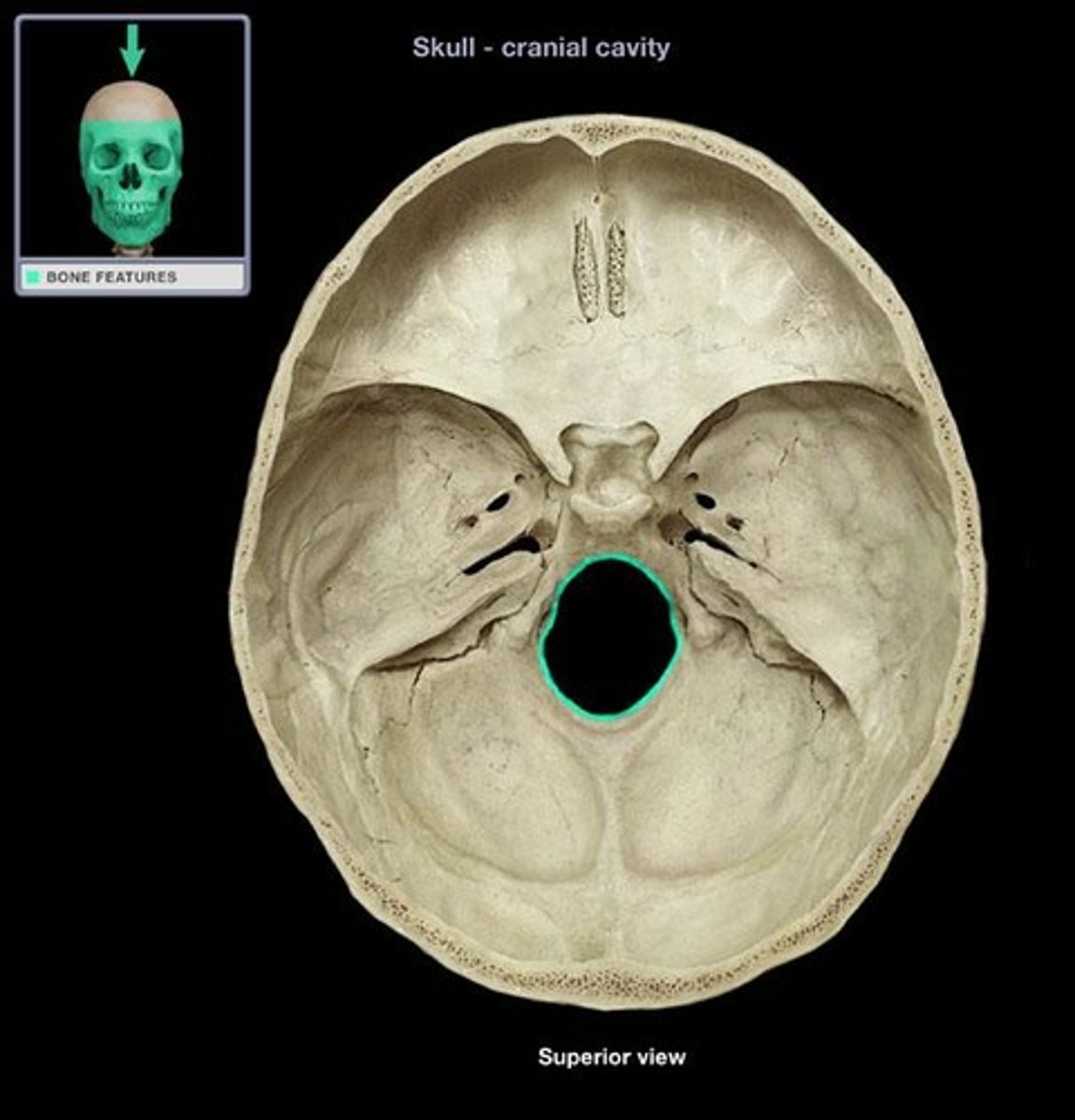
foramen magnum of occipital bone
opening through which spinal cord connects to lower brain
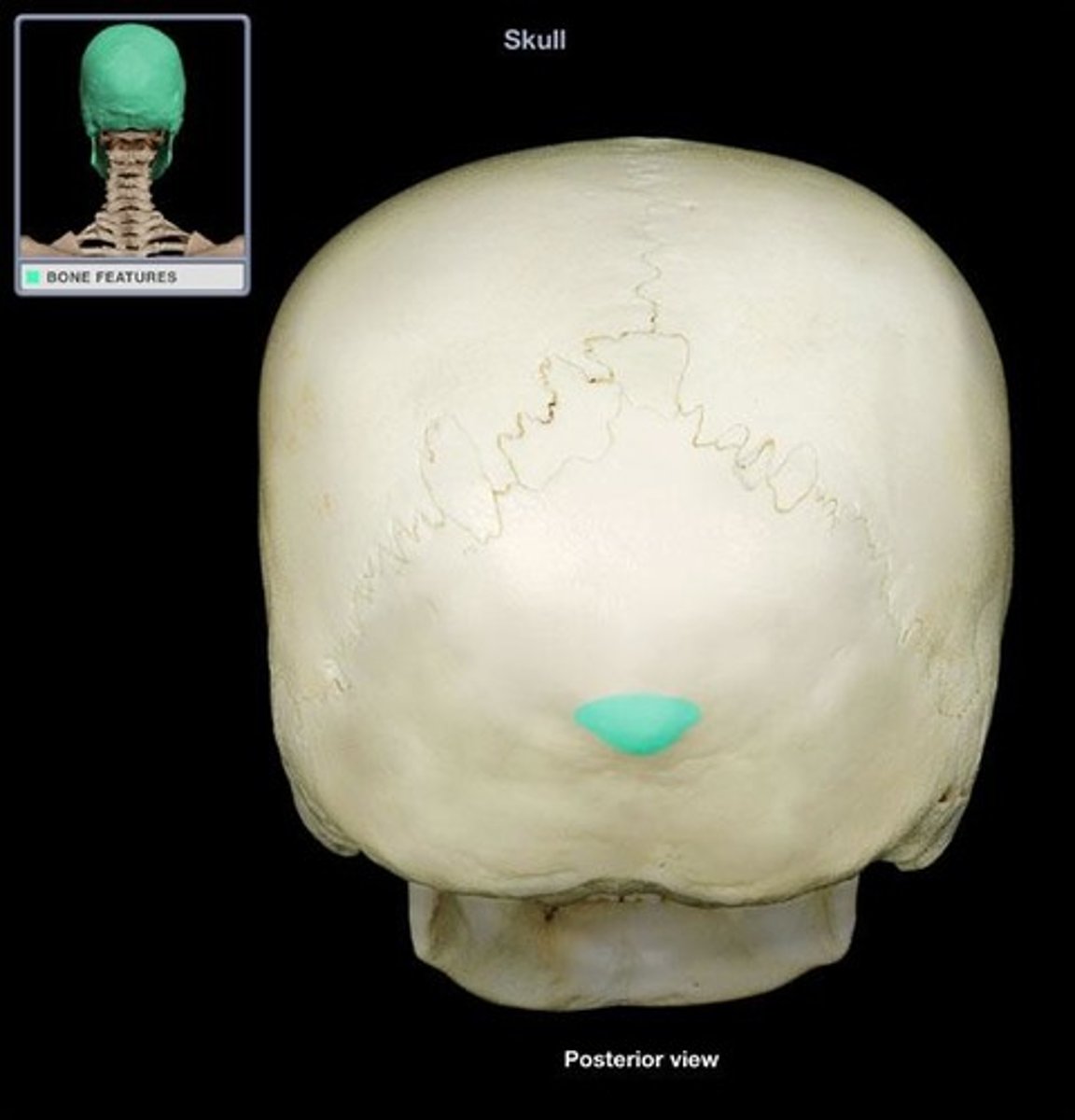
external occipital protuberance
bump on back of head where the trapezius and ligmentum nuchae attach
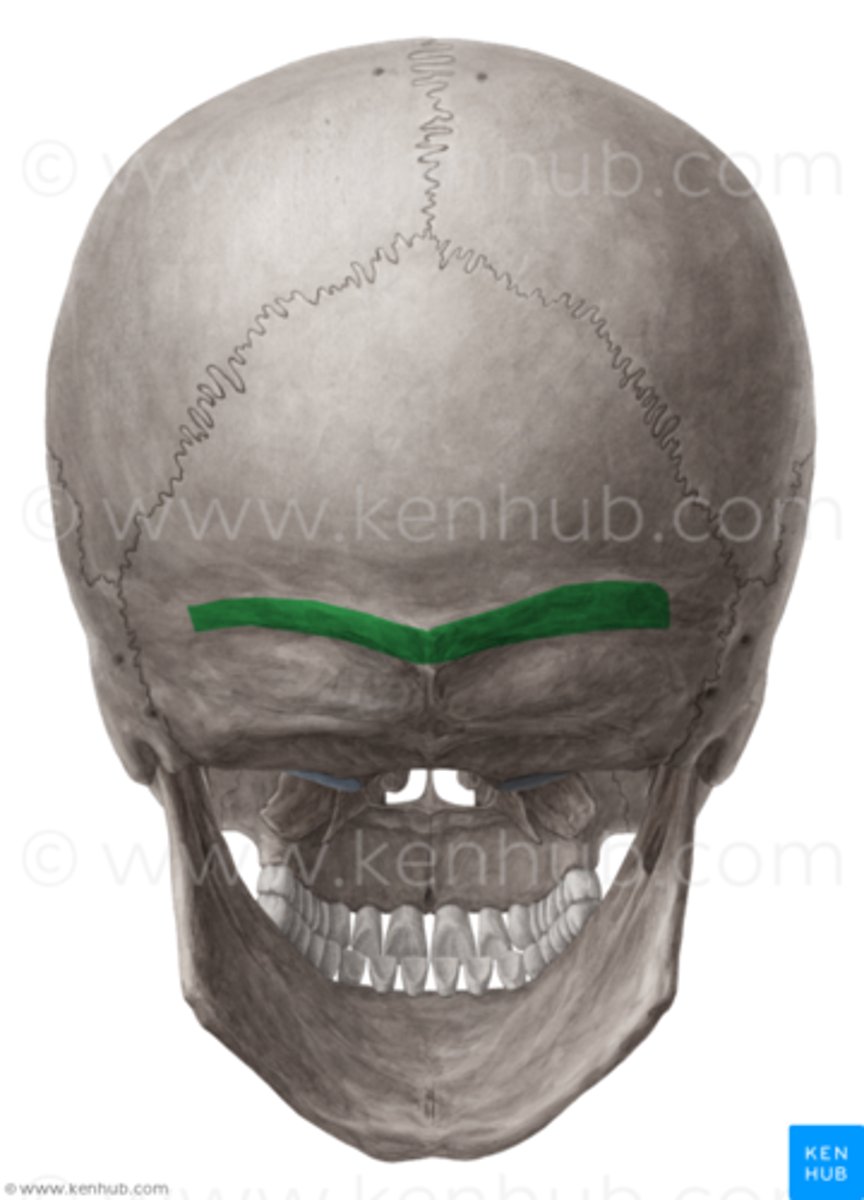
superior nuchal line of occipital bone
site of muscle attachment for trapezius, occipitalis, and splenius capitis muscles
inferior nuchal line of occipital bone
site of muscle attachment for obliquus capitis superior muscle, rectus capitis posterior major muscle, and rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
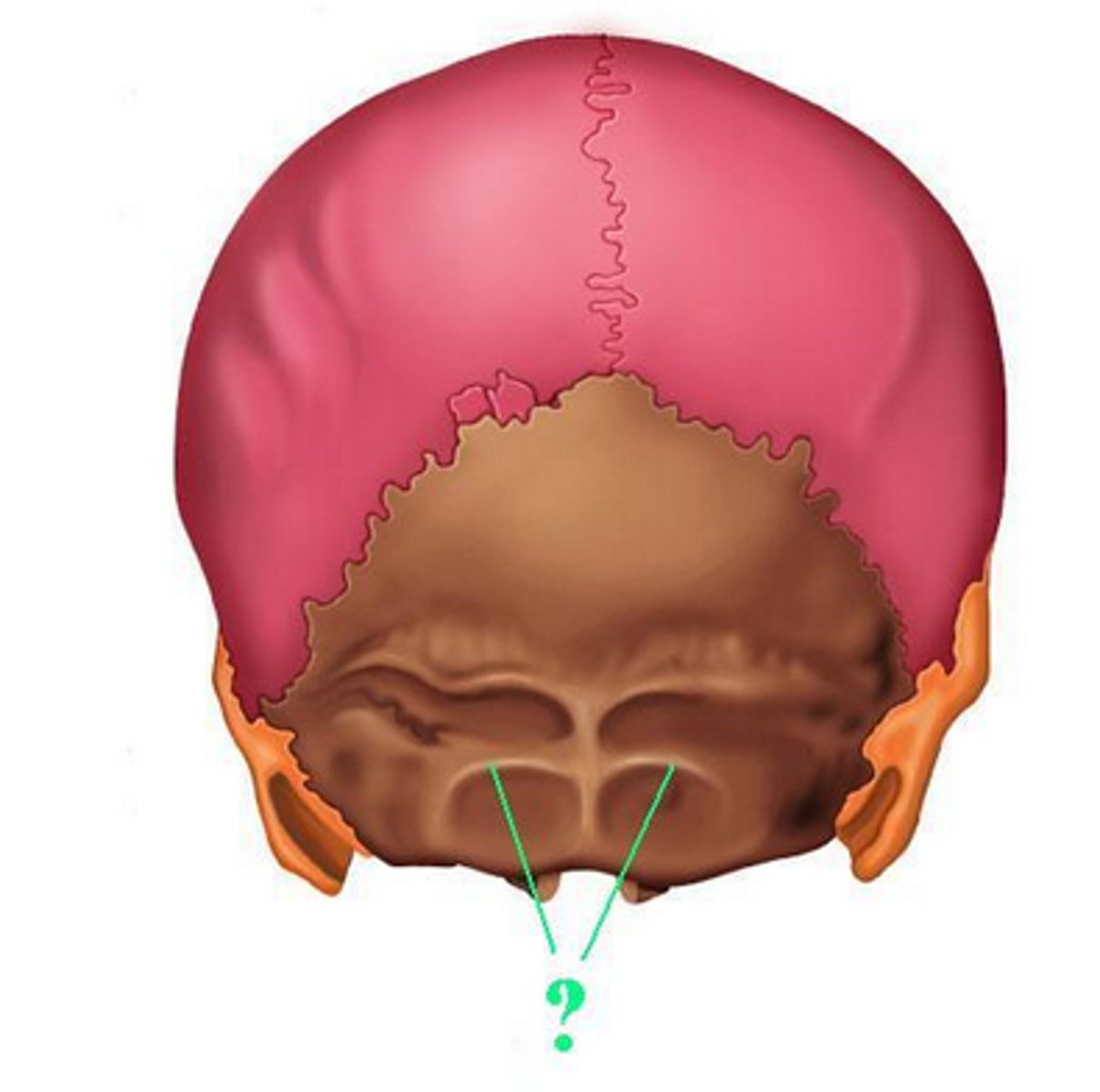
occipital condyles of occipital bone
rounded processes that articulate with the atlas (C1)
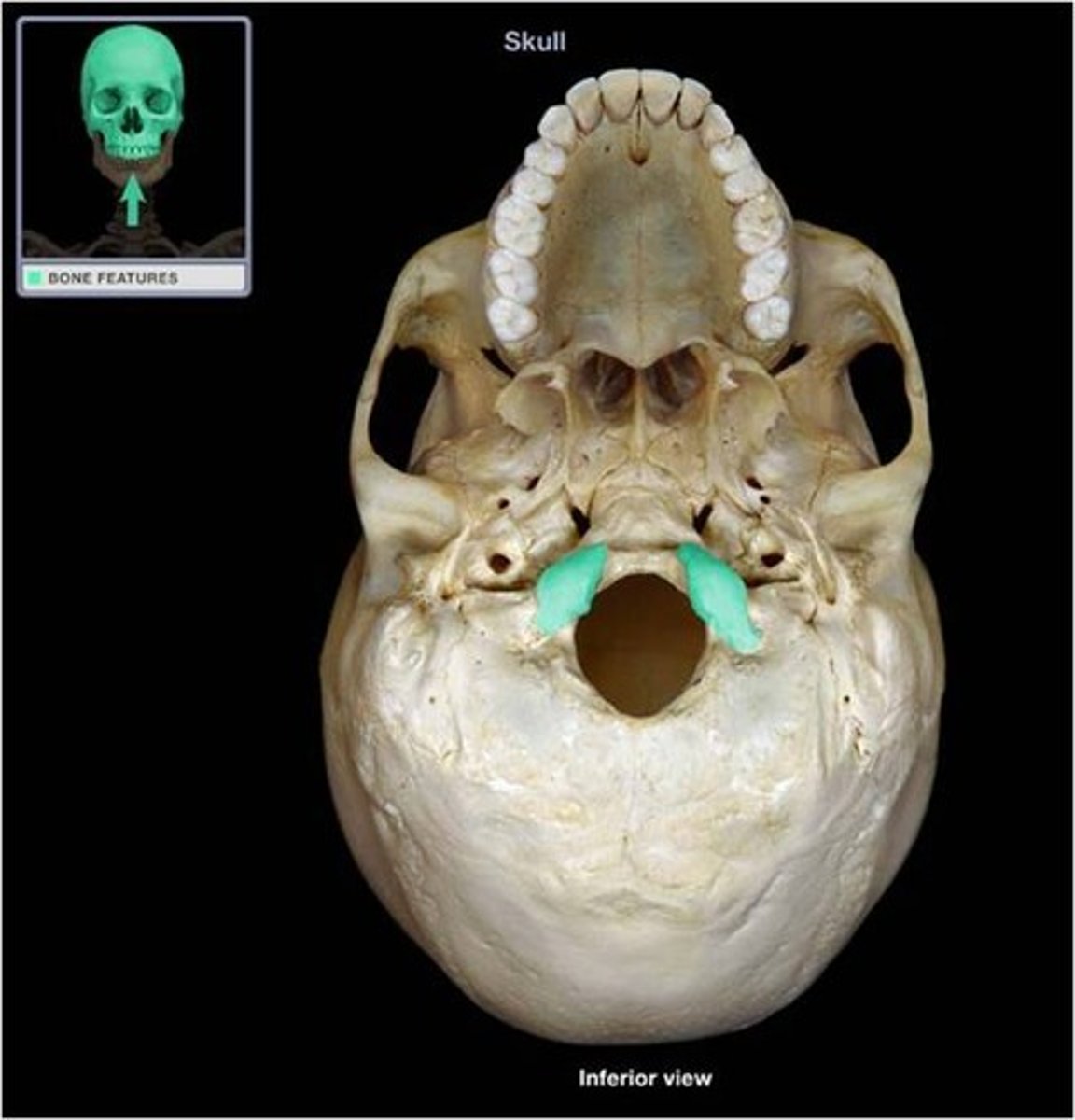
hypoglossal canal of occipital bone
Hypoglossal (CN XII) runs through, inner aspect of occipital condyle
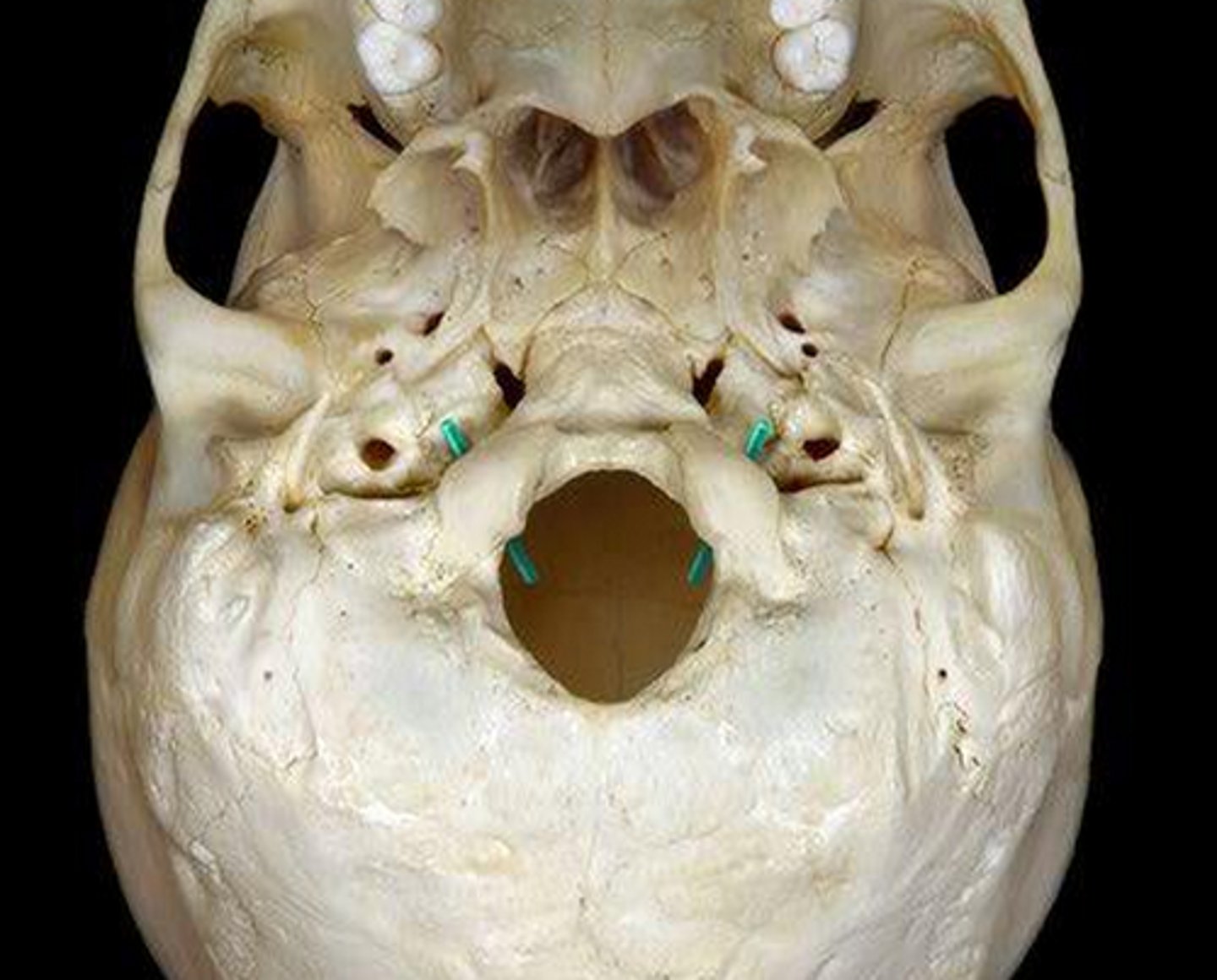
groove for transverse sinus
occipital bone depression
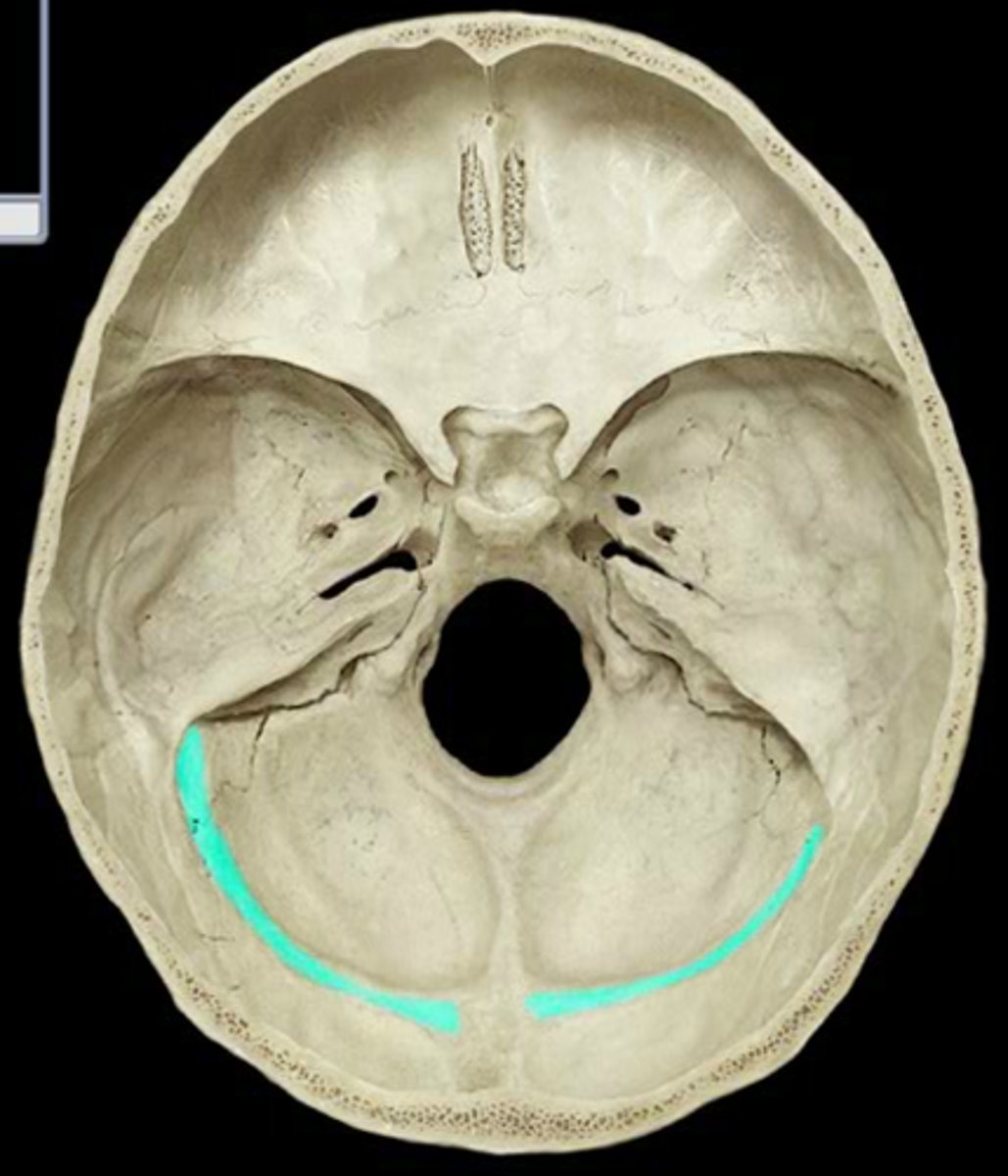
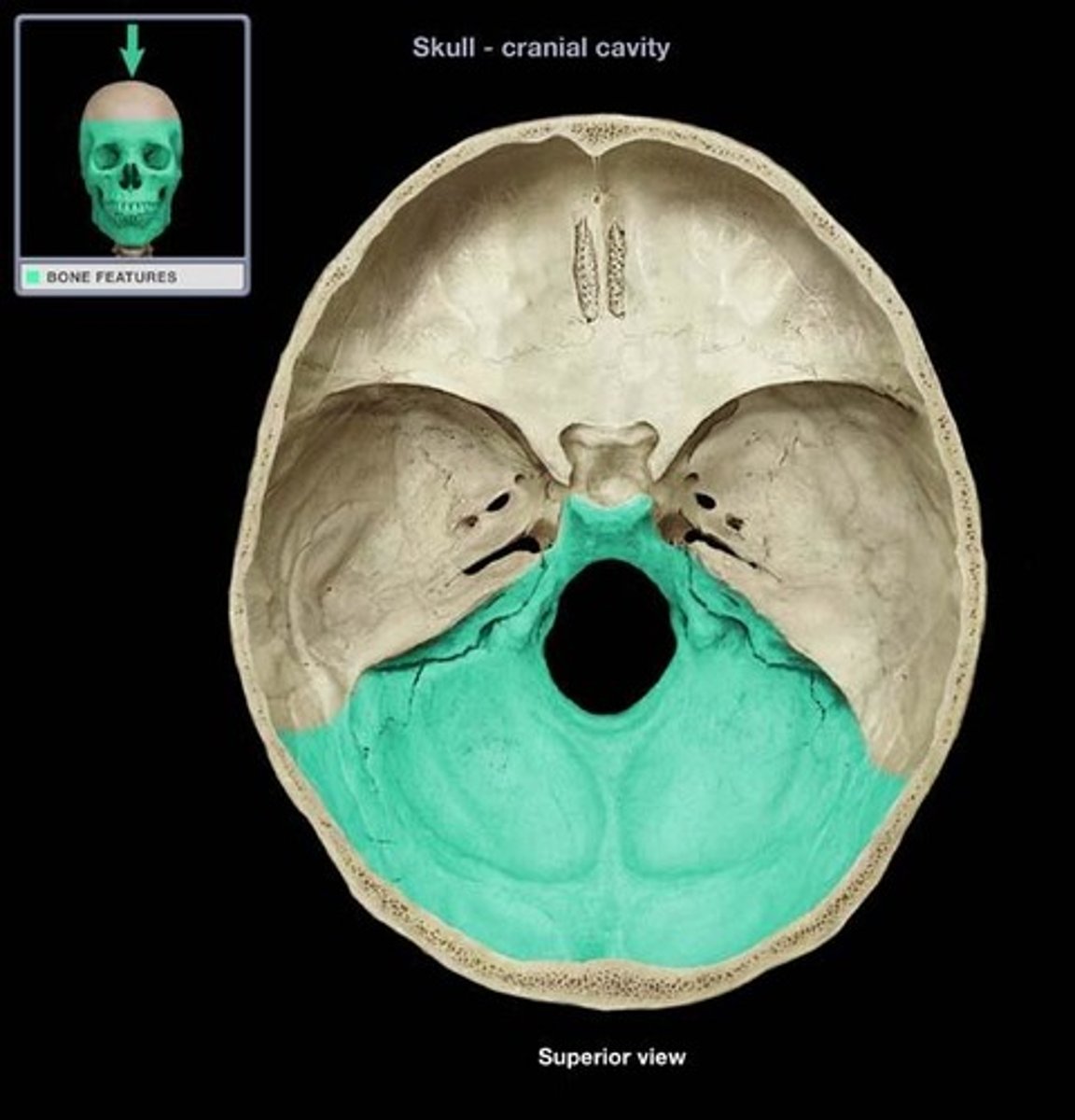
posterior cranial fossa
portion of cranial canal formed by the occipital
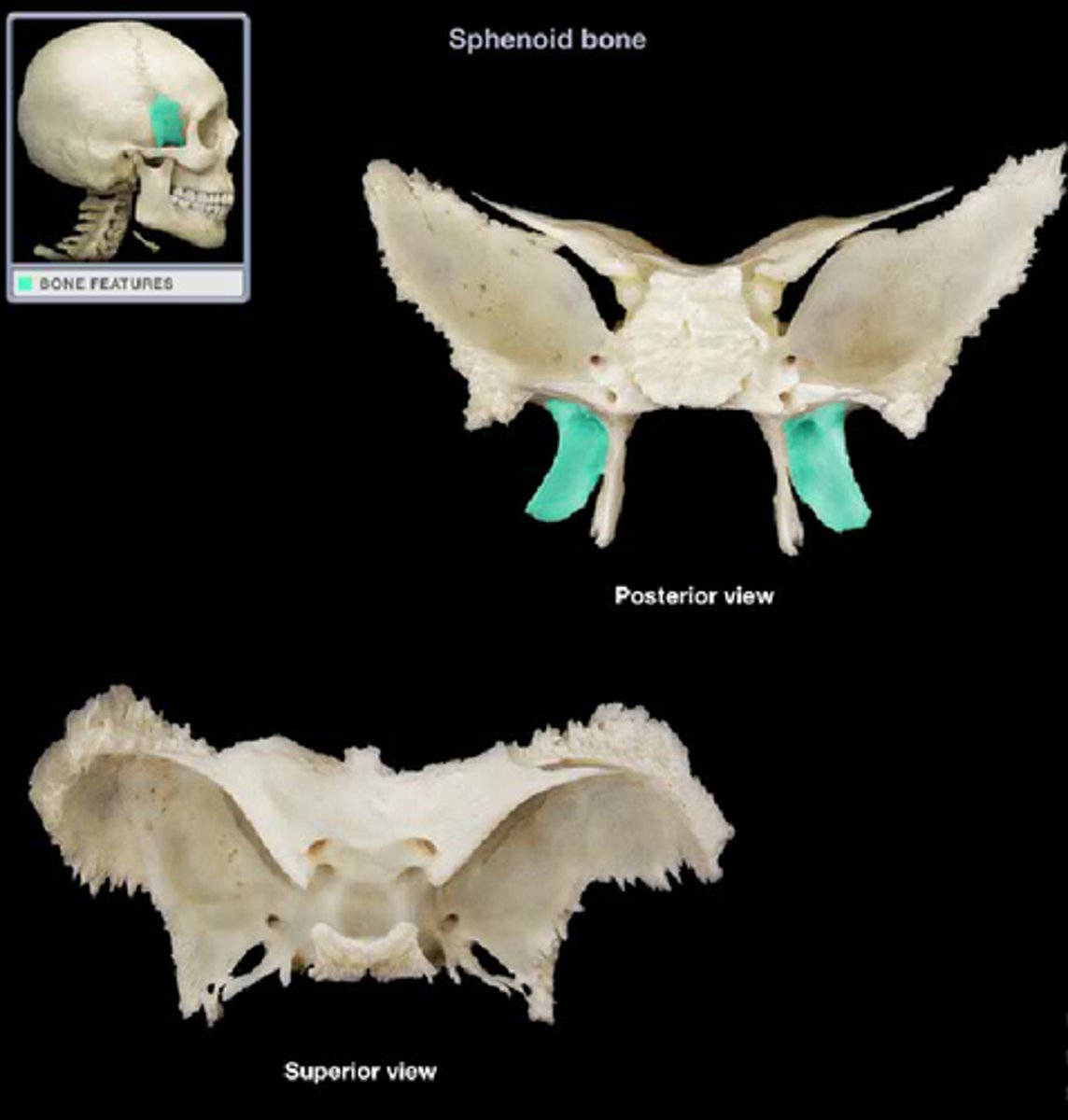
sphenoid bone
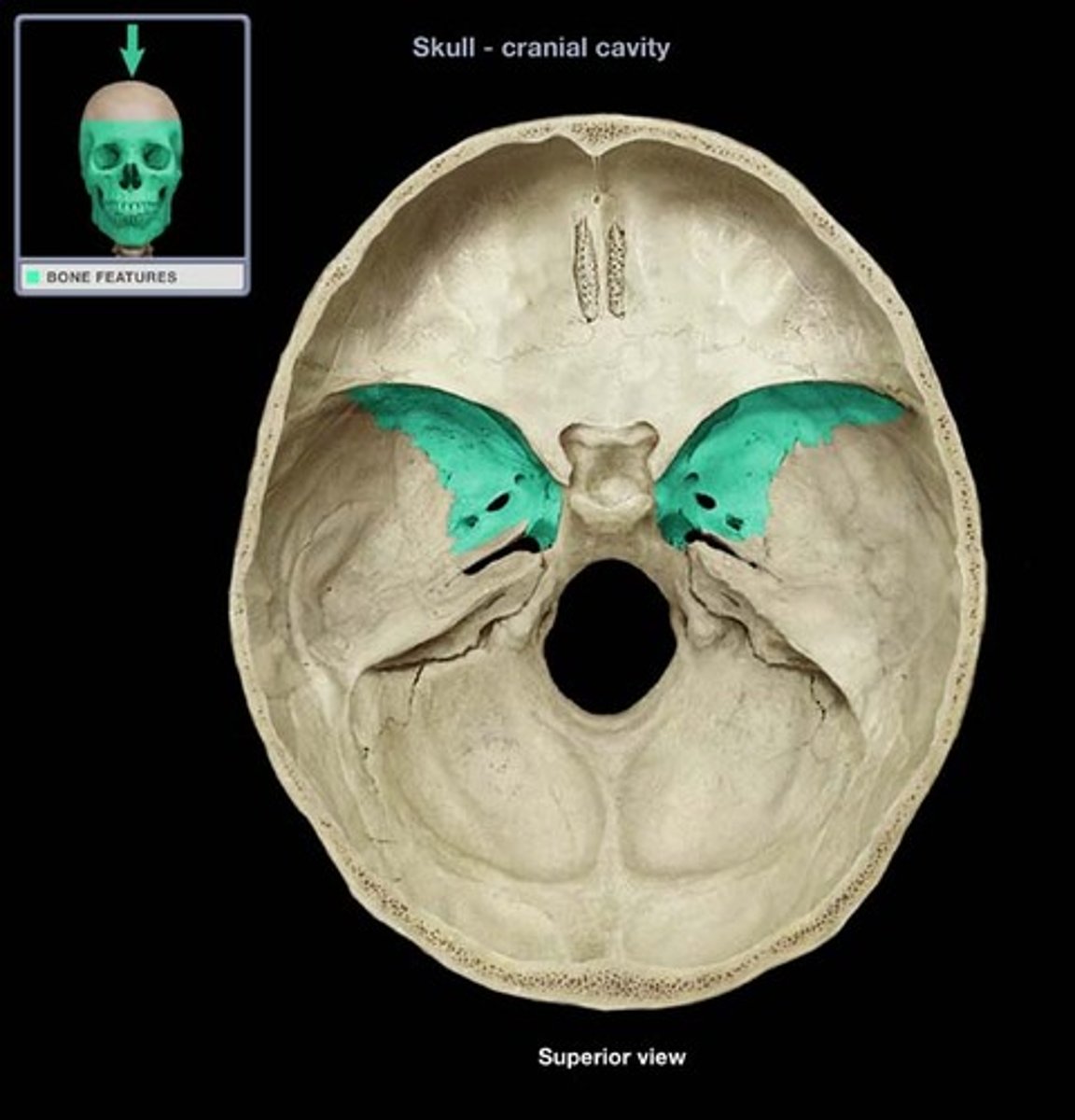
greater wing of sphenoid bone
posterior and inferior to lesser wing on the interior of the skull, also visible in the posterior orbit and lateral side of the skull
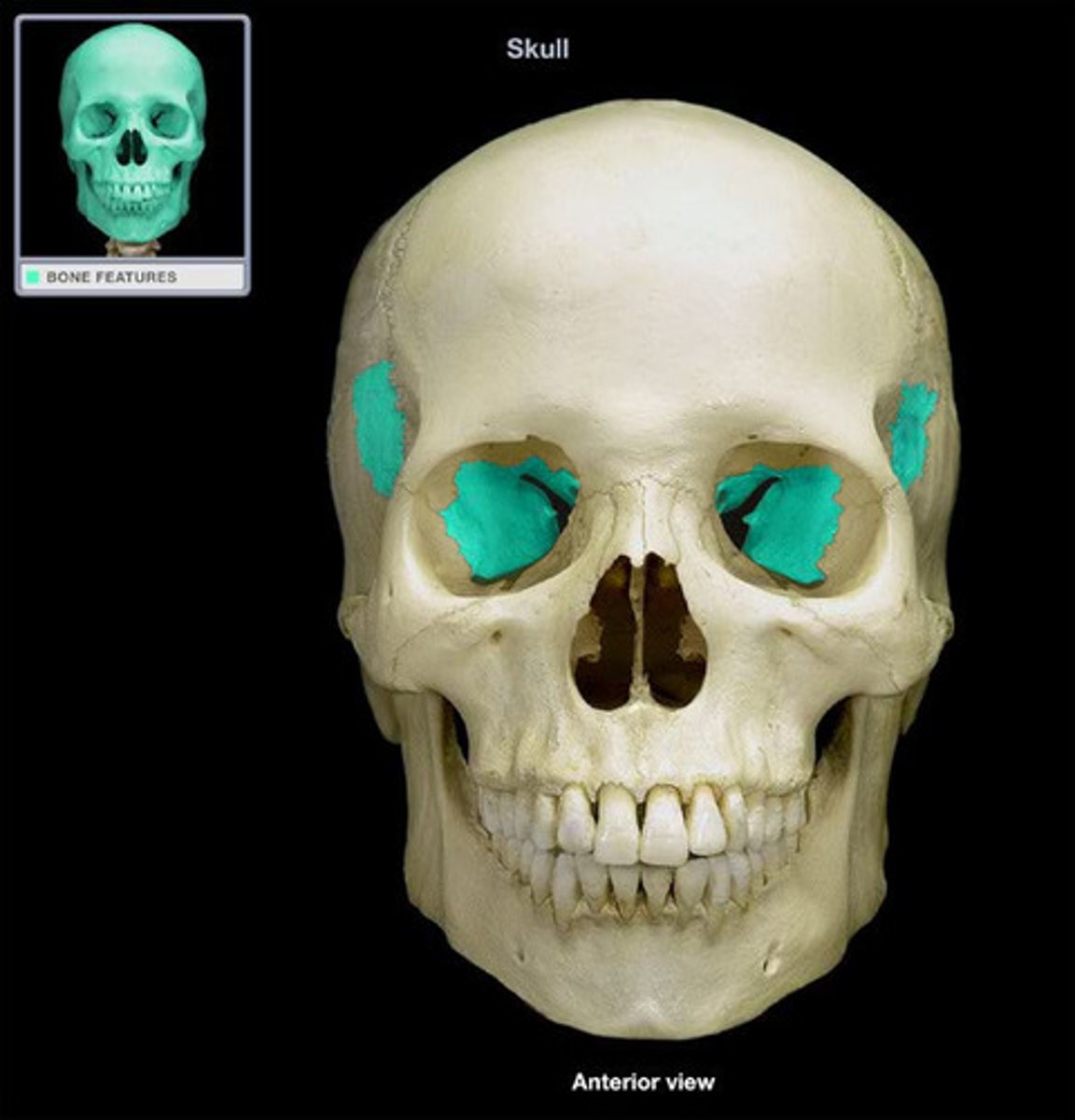
lesser wing of sphenoid bone
One of two side wings extending from the body of the sphenoid bone
medial pterygoid plate of sphenoid bone
site for tendon attachment, articulates with vomer and palatine processes of sphenoid
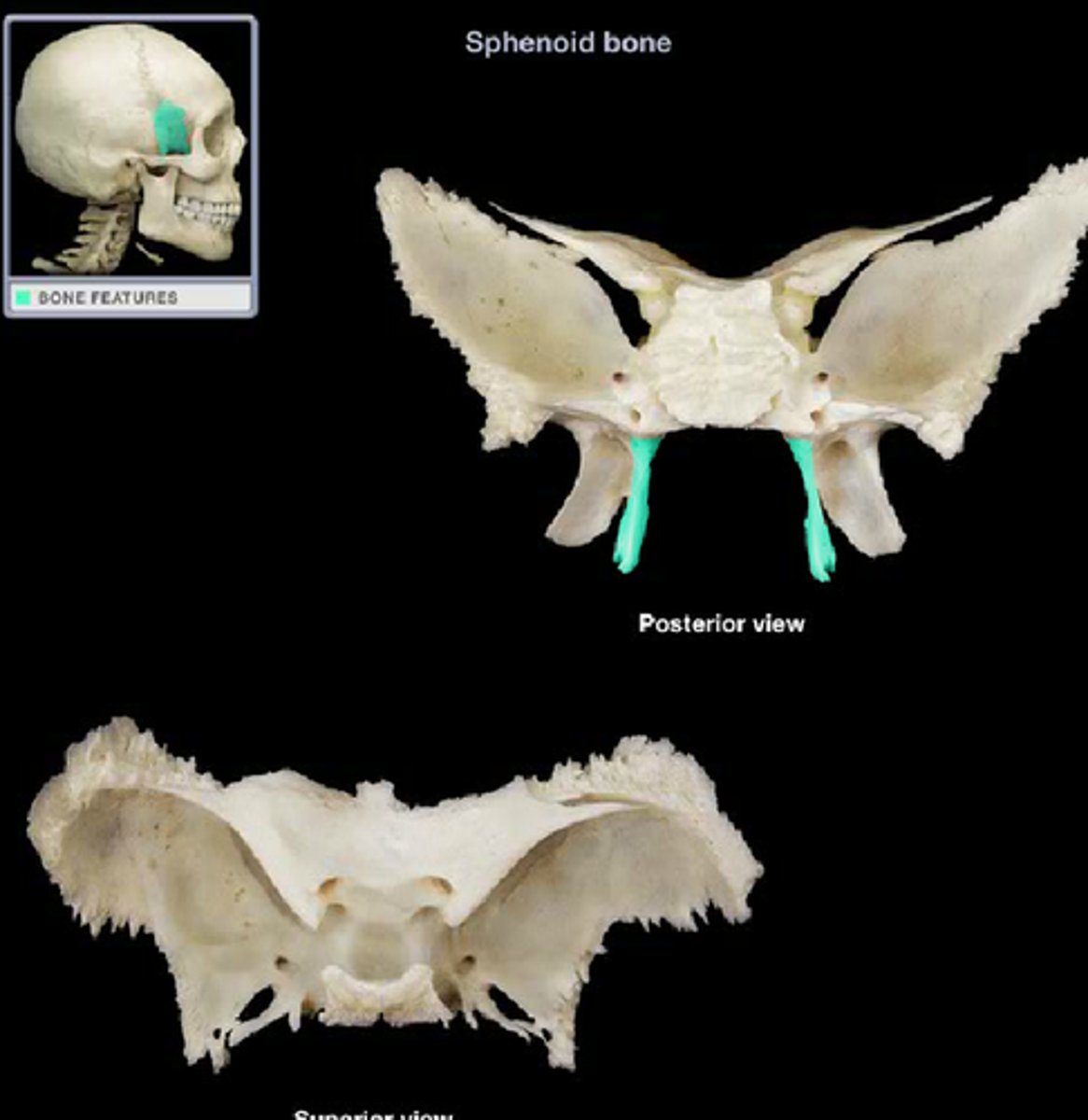
lateral pterygoid plate of sphenoid bone
sharp process that laterally and inferiorly projects from the sphenoid, attachment for lateral pterygoid muscle
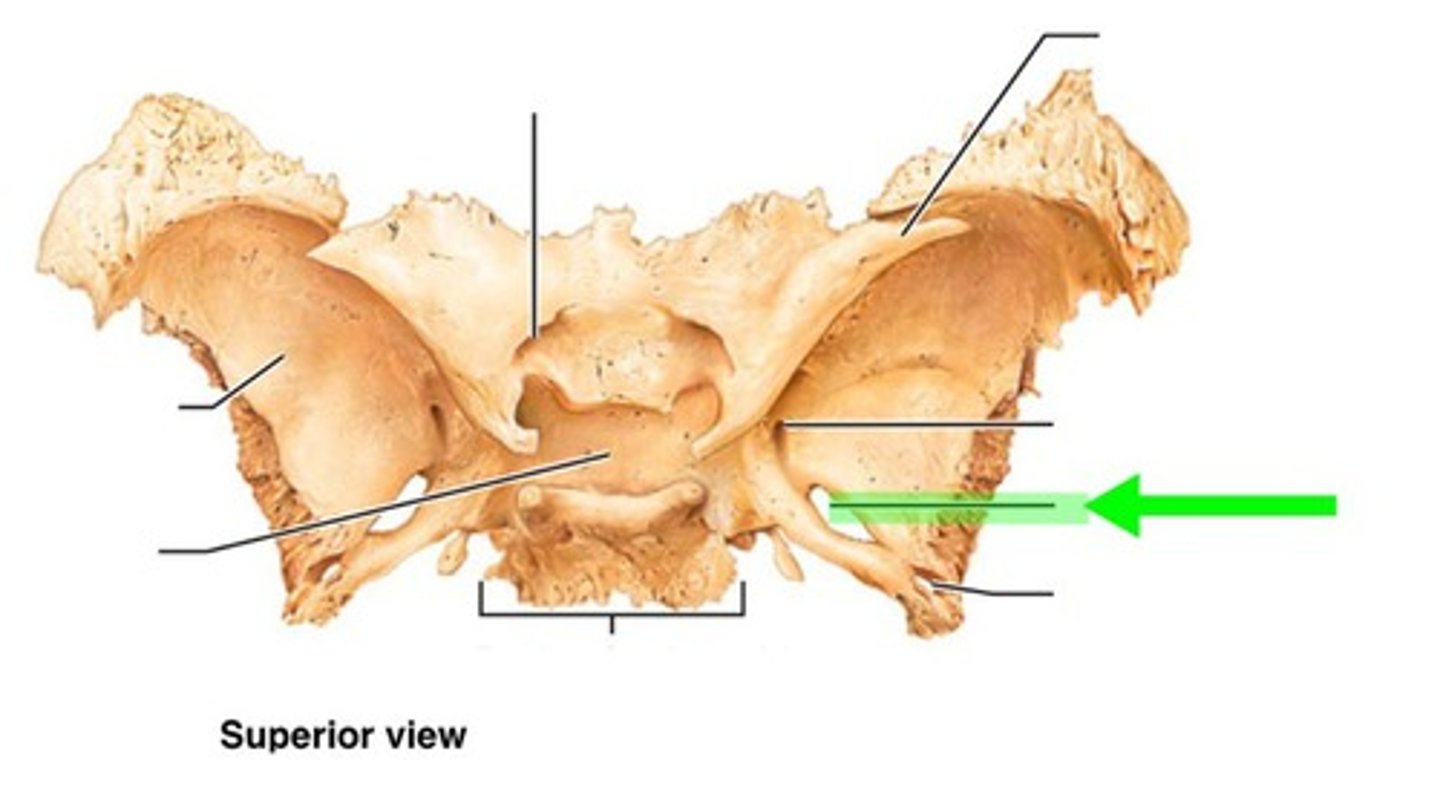
foramen ovale of sphenoid bone
mandibular branch CN V3 (of trigem) passes through
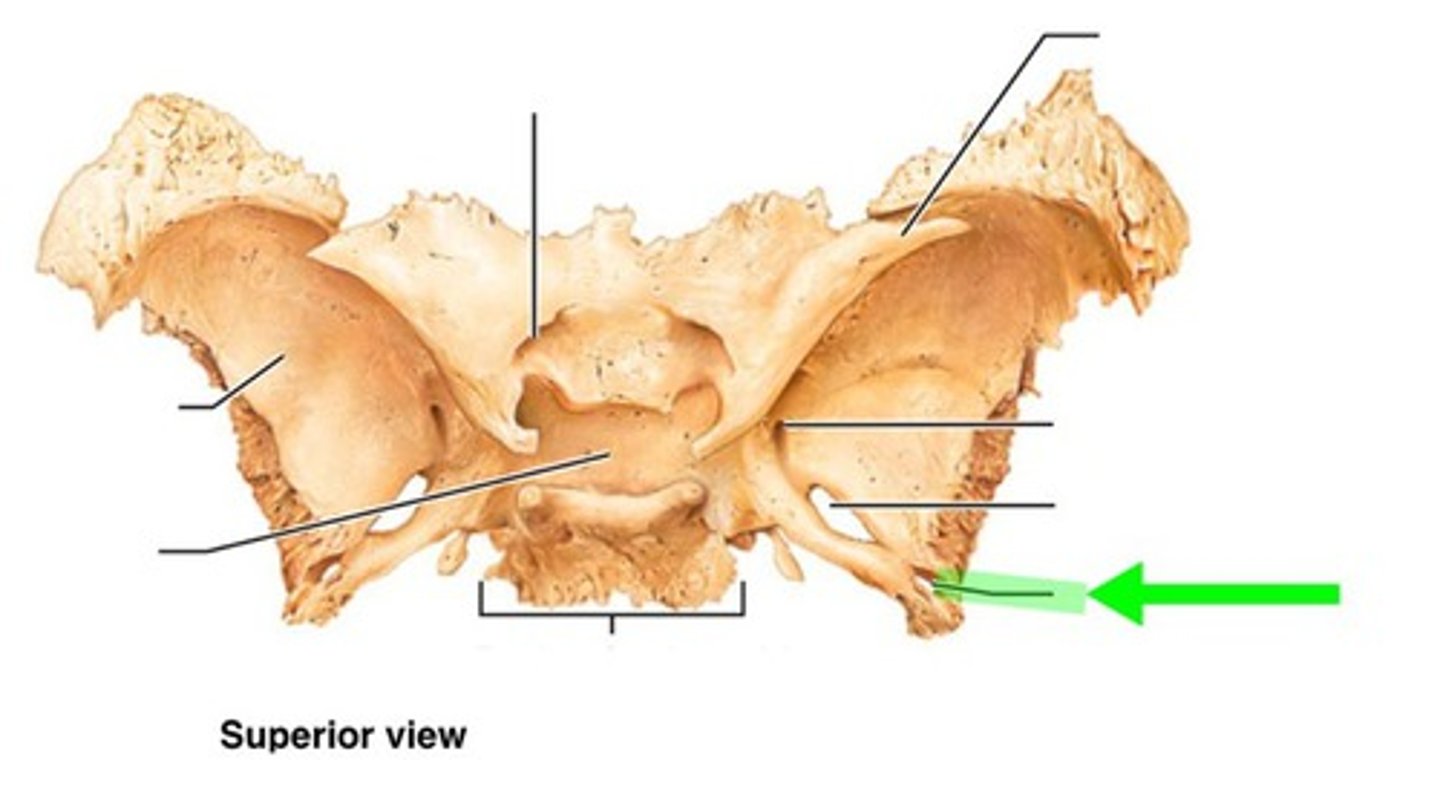
foramen spinosum of sphenoid bone
surrounded by grooves for middle meningeal vessels and meningeal branch of mandibular nerve
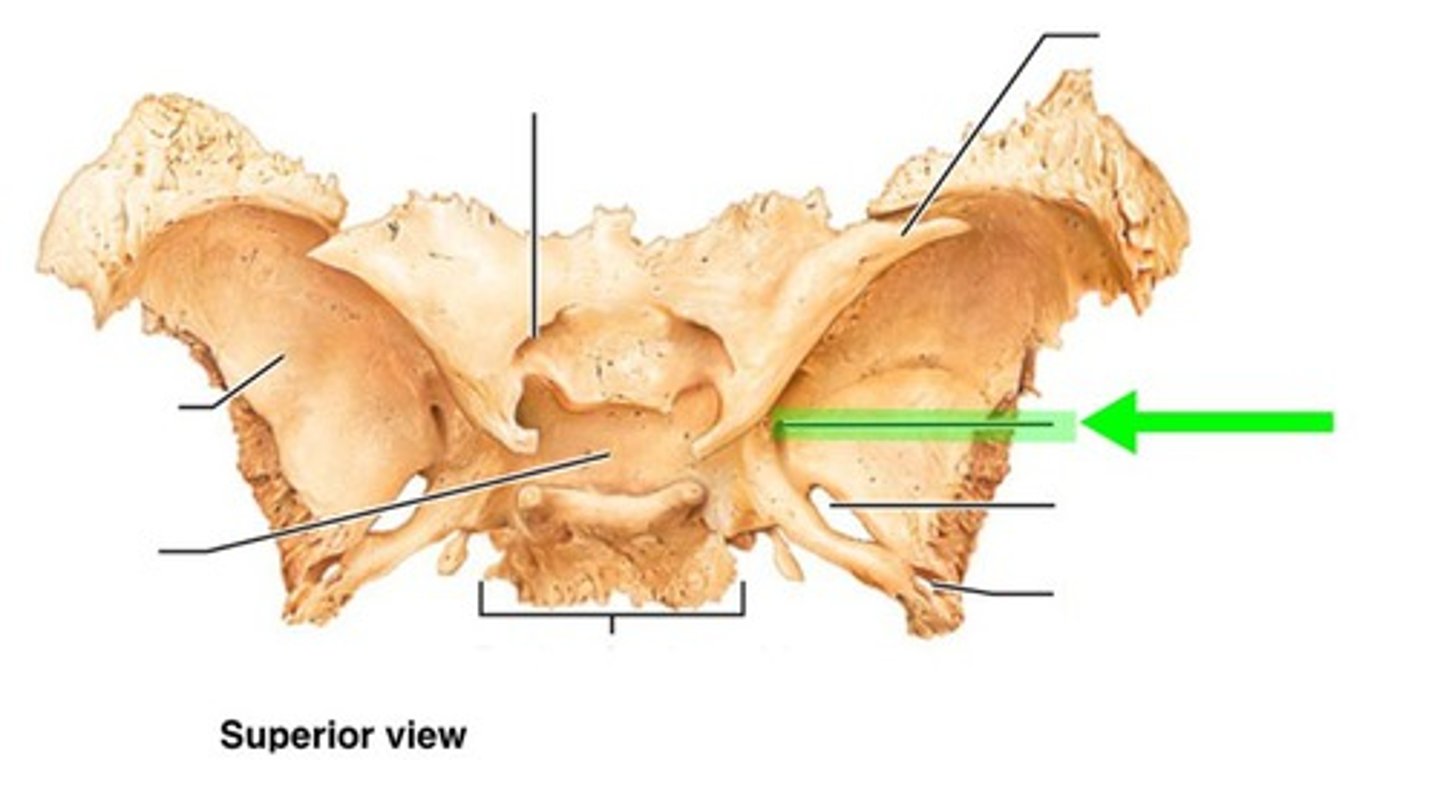
foramen rotundum of sphenoid bone
passage for maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve (V2)
sphenoid sinuses
in body of sphenoid
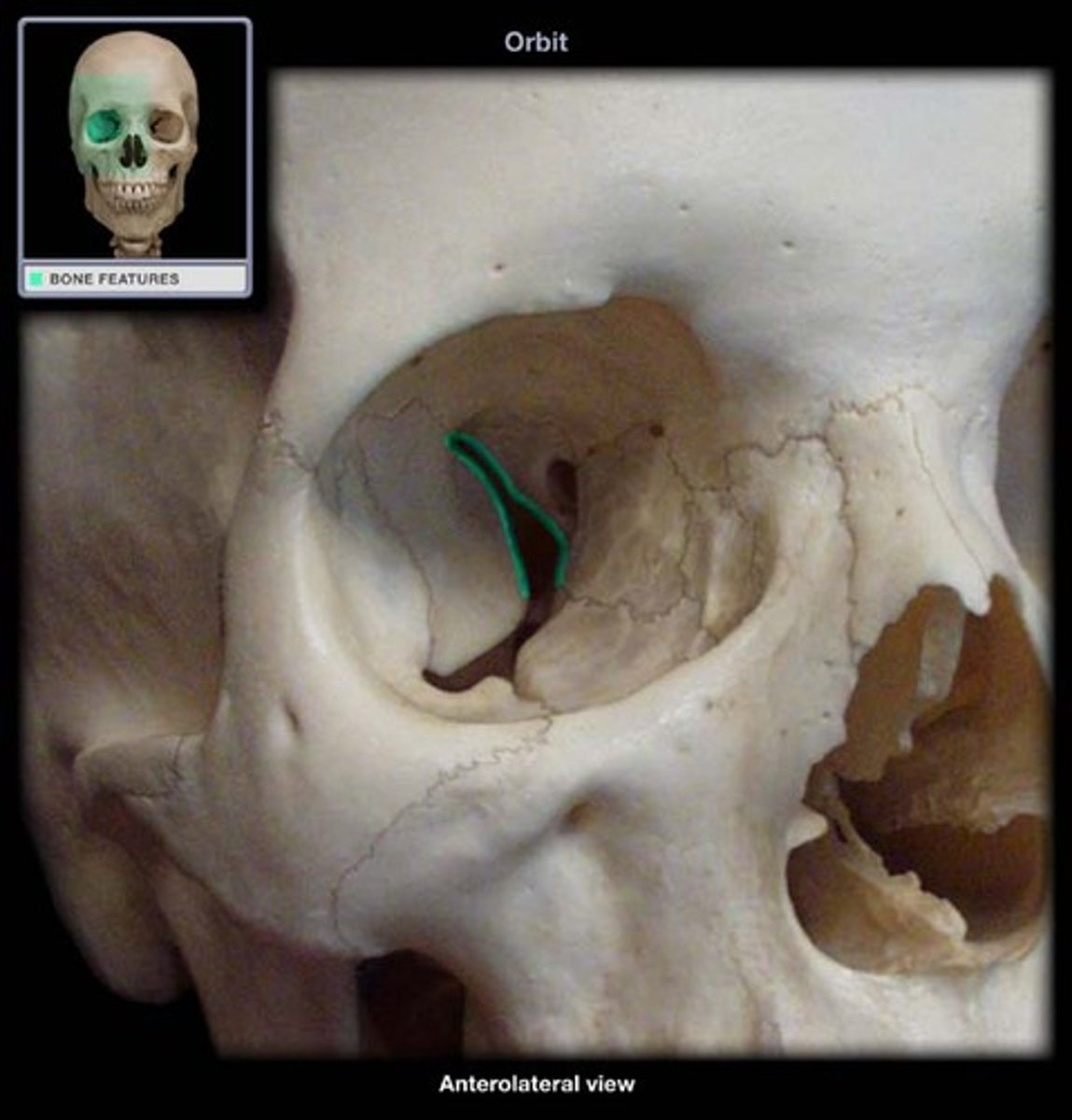
superior orbital fissure of sphenoid bone
Between greater and lesser wing on the sphenoid bone, transmits oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens nerves. Also a branch of opthalmic CN V1
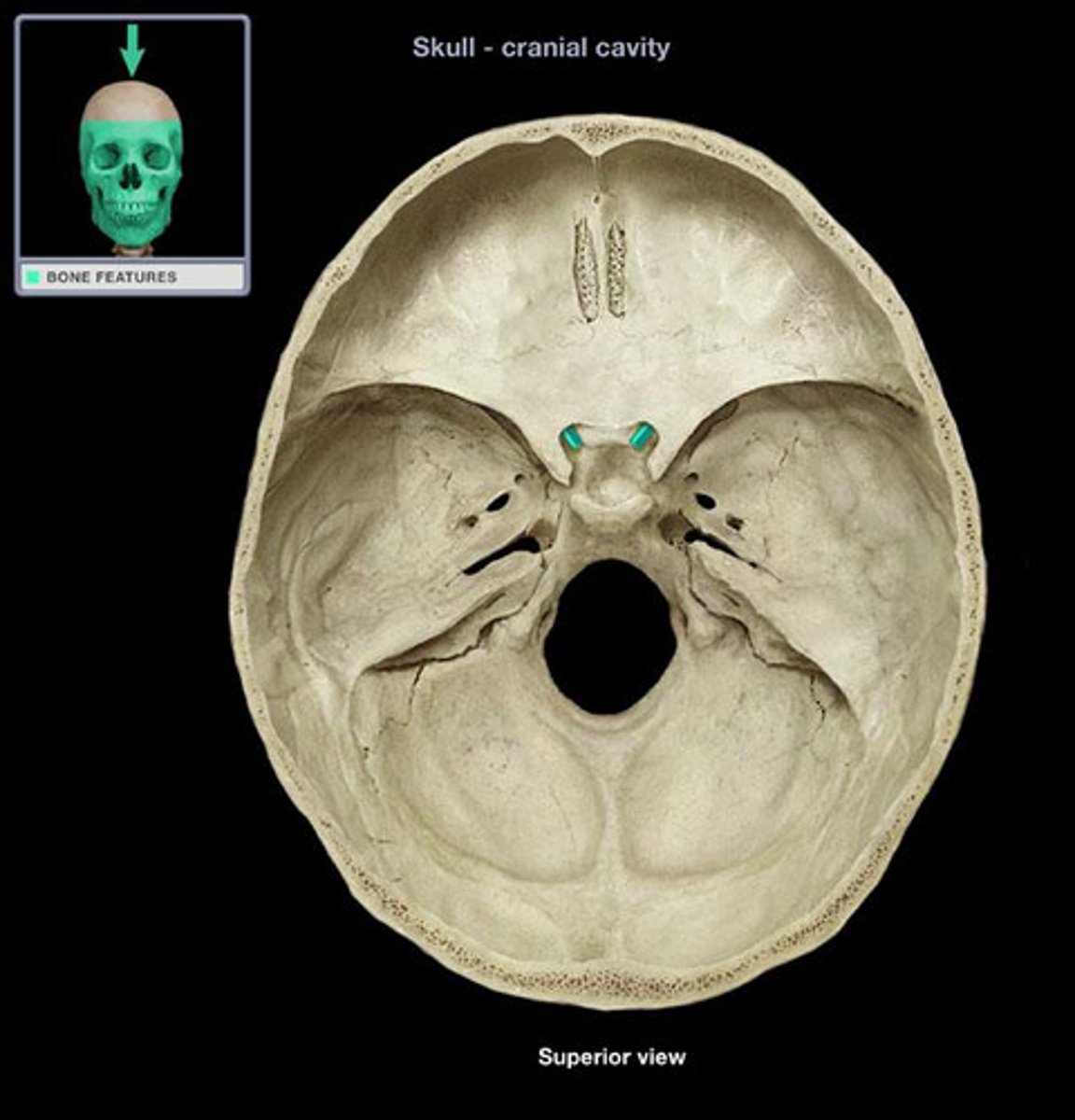
optic canal of sphenoid bone
passage of the optic nerve (CN II) and ophthalmic artery
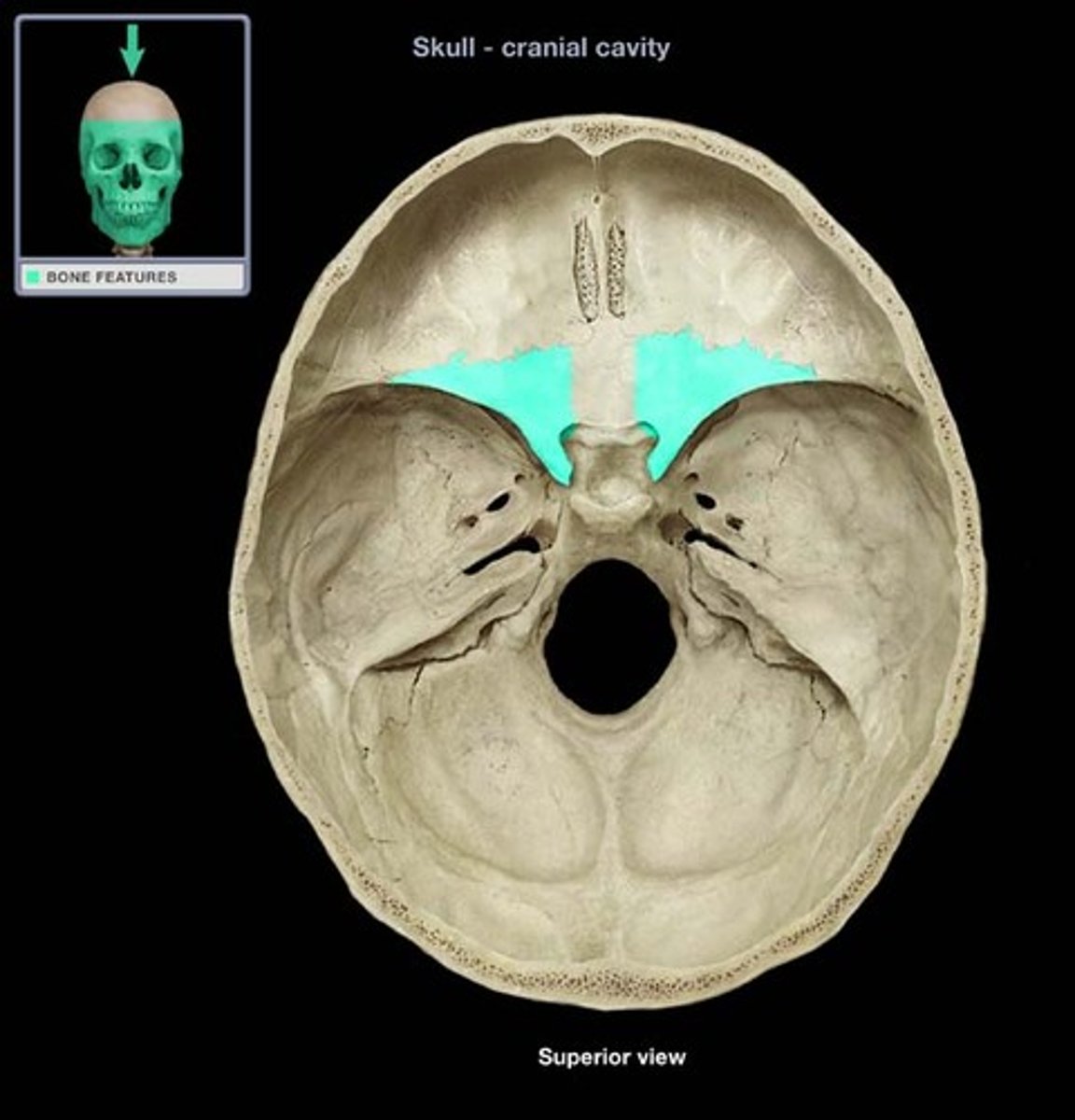
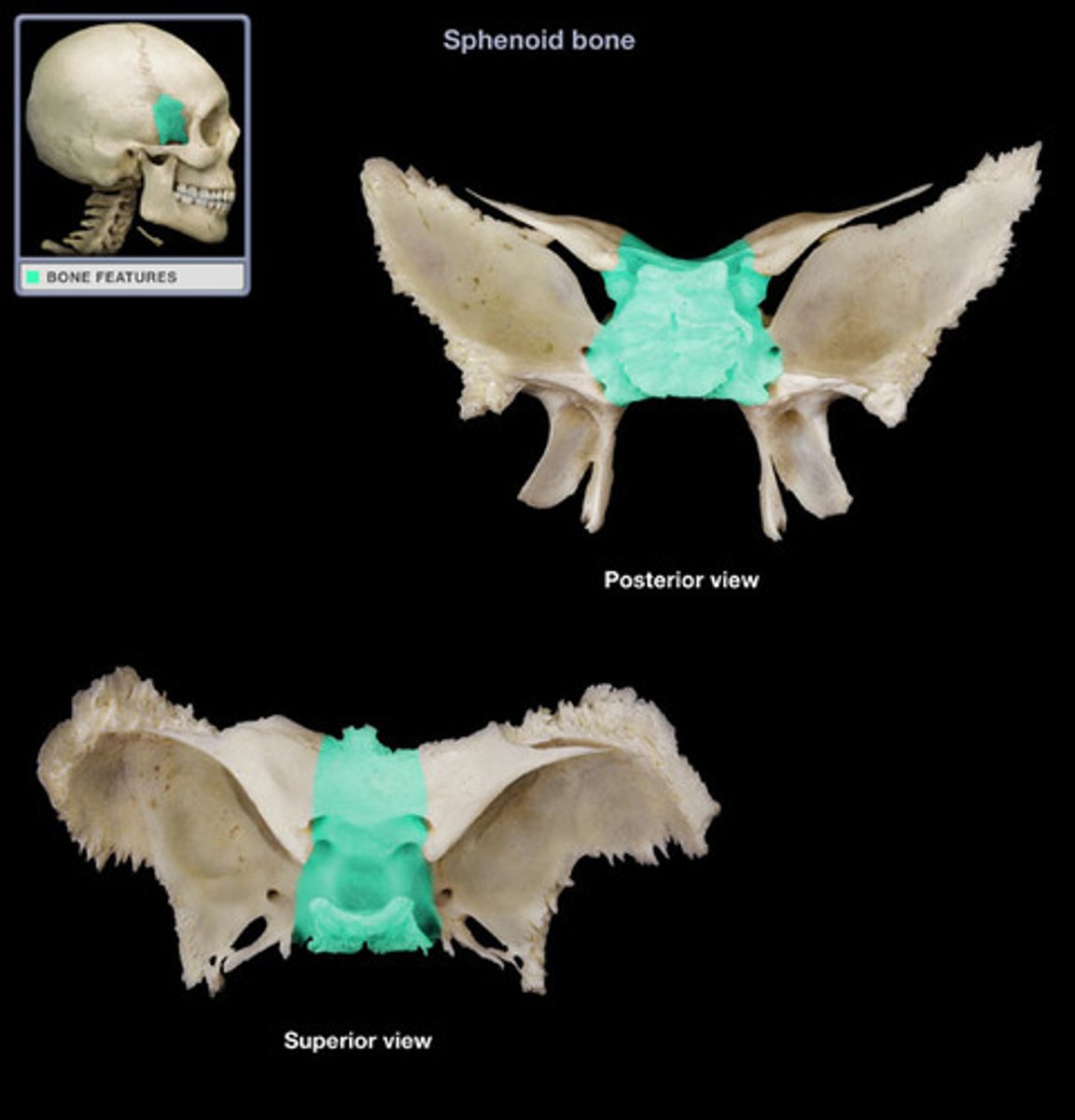
body of sphenoid bone
central section of sphenoid
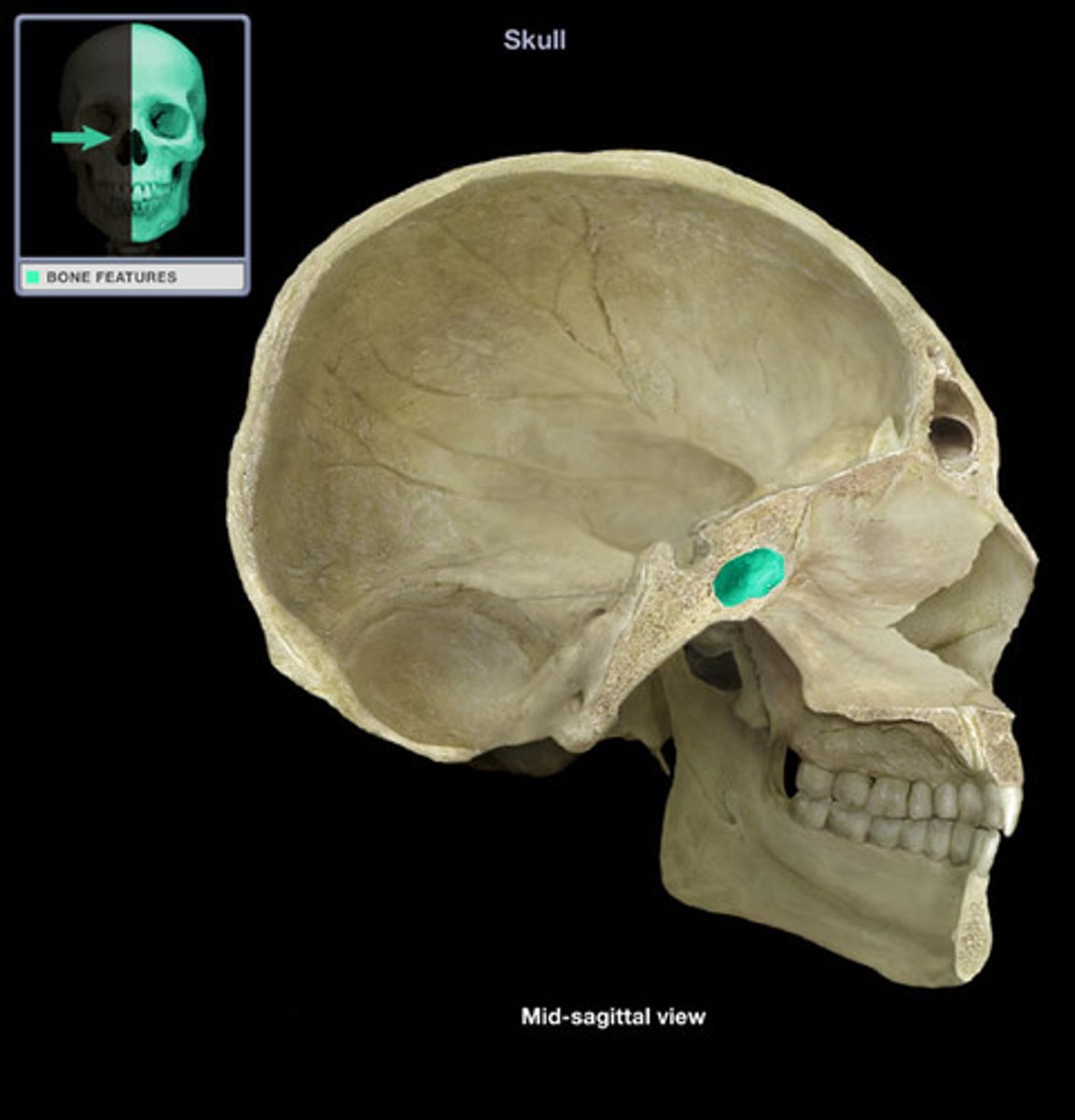
sella turcica of sphenoid bone
houses the pituitary gland
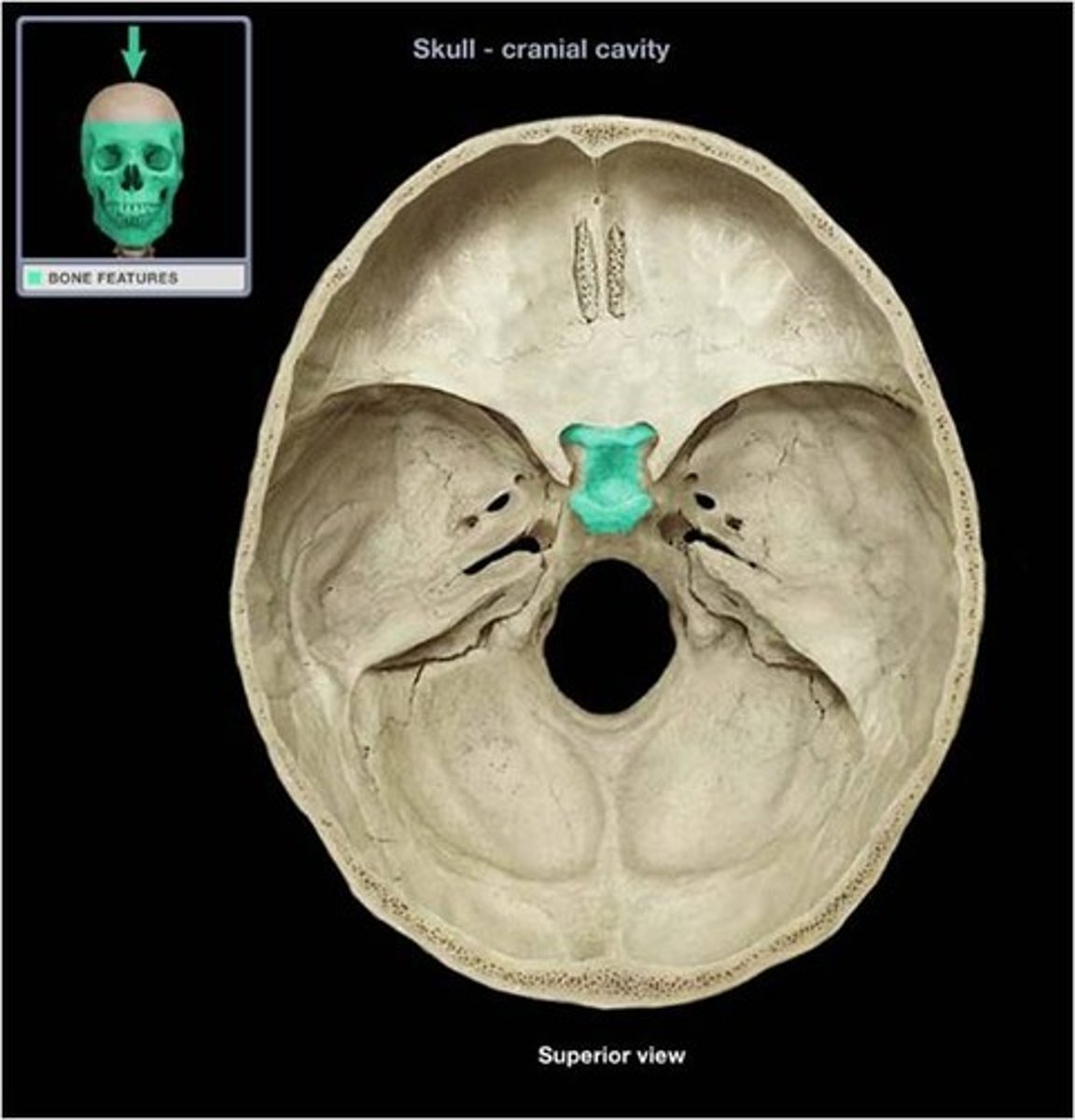
ethmoid bone
Light spongy bone between the eye sockets; forms part of the nasal cavities.
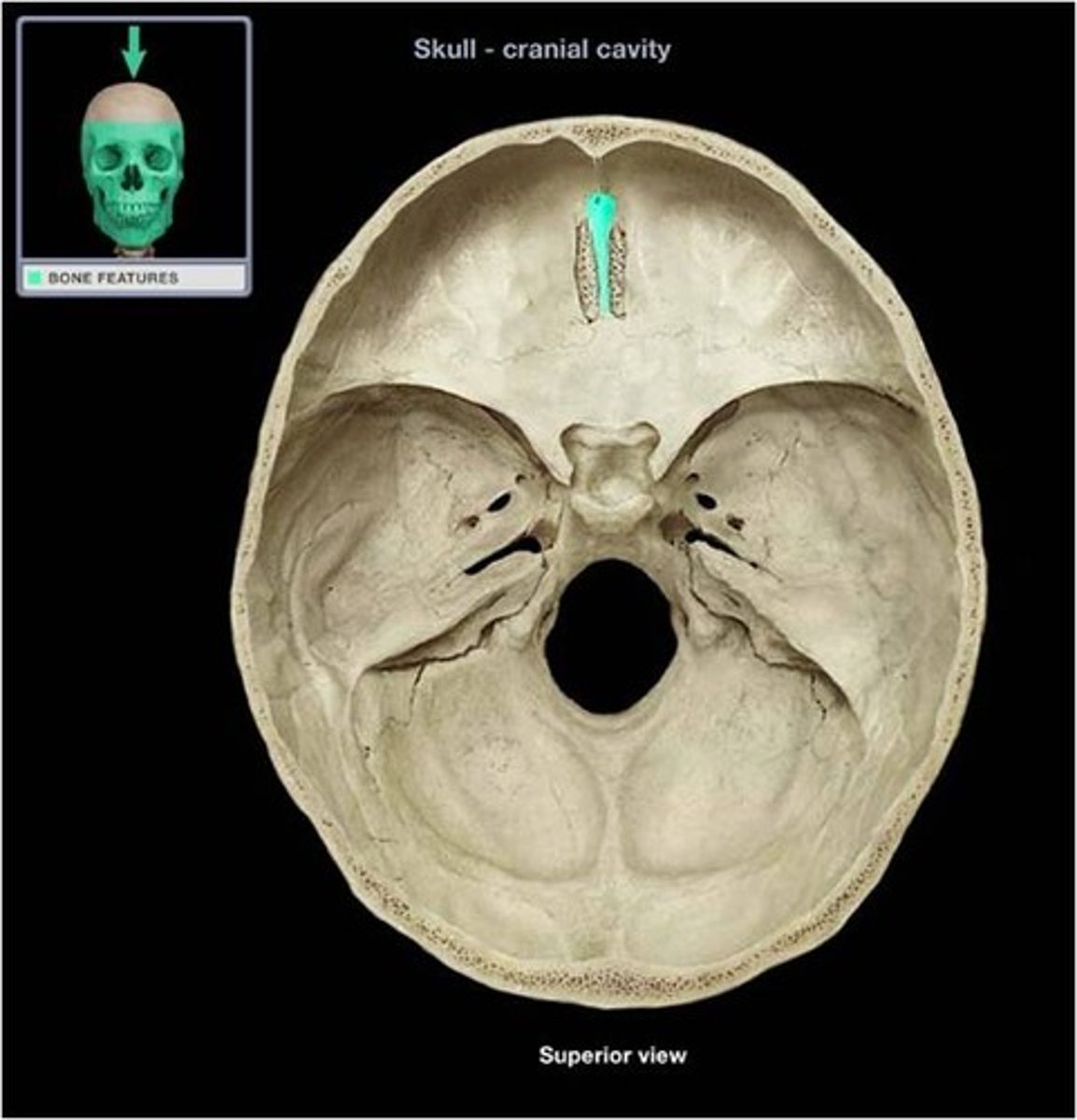
crista galli of ethmoid bone
superior projection in the middle of the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone; providing a point of attachment for the dura mater, helping to secure the brain within the skull
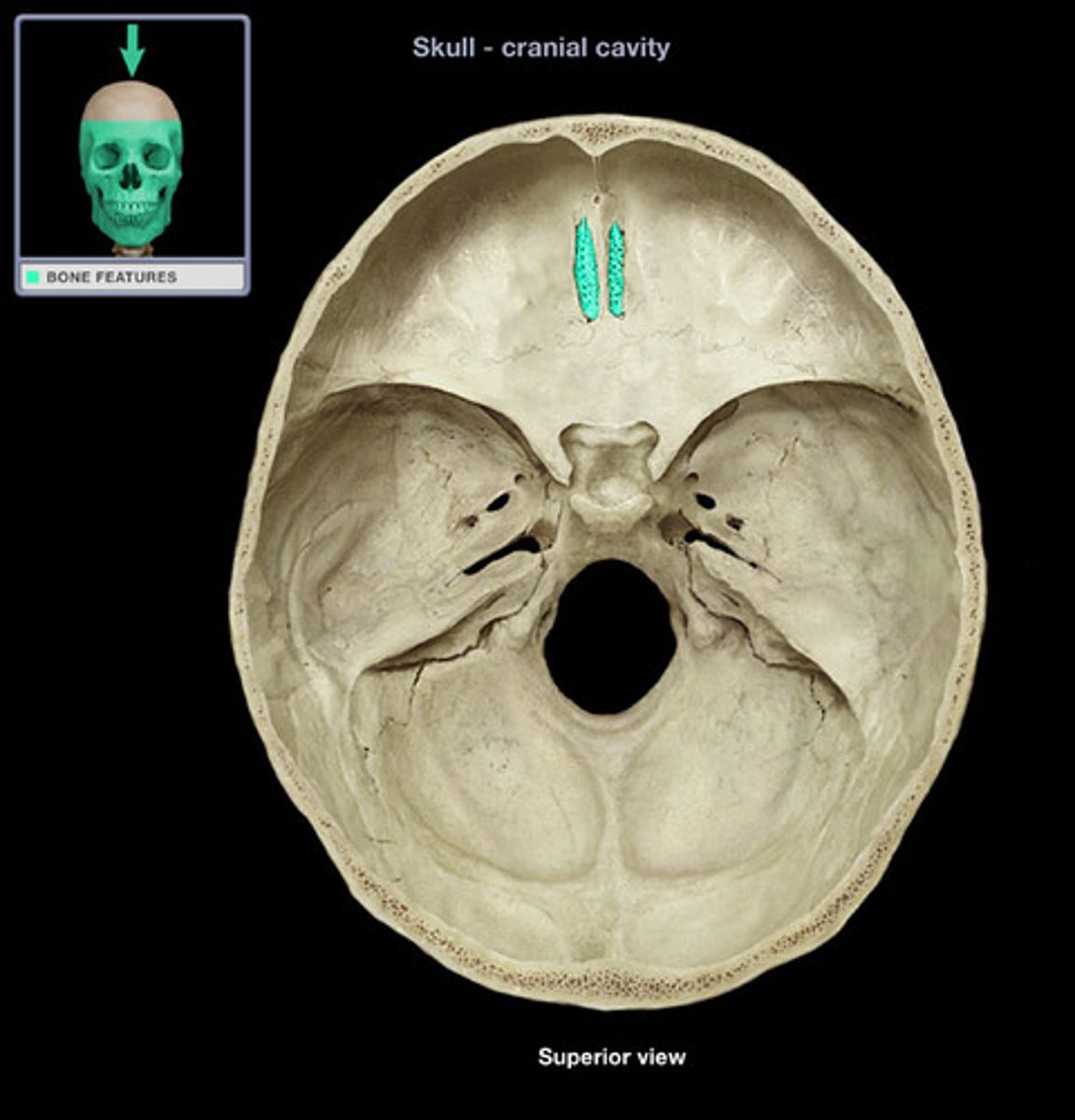
cribriform plate of ethmoid bone
The horizontal plate of the ethmoid bone separating the cranial cavity from the nasal cavity. Where the olfactory bulb sits and CN I synapses
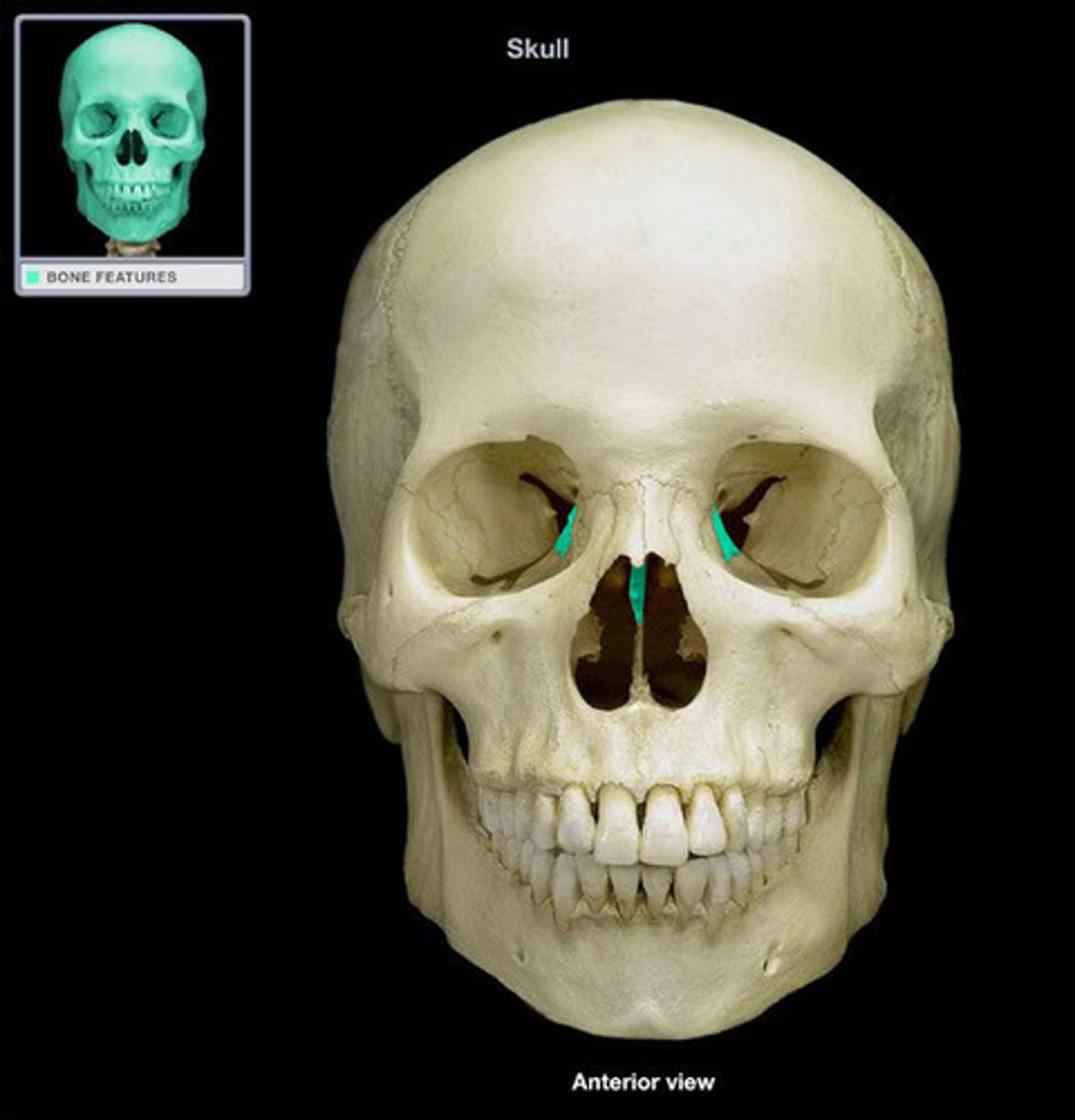
perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
superior portion of the bony nasal septum
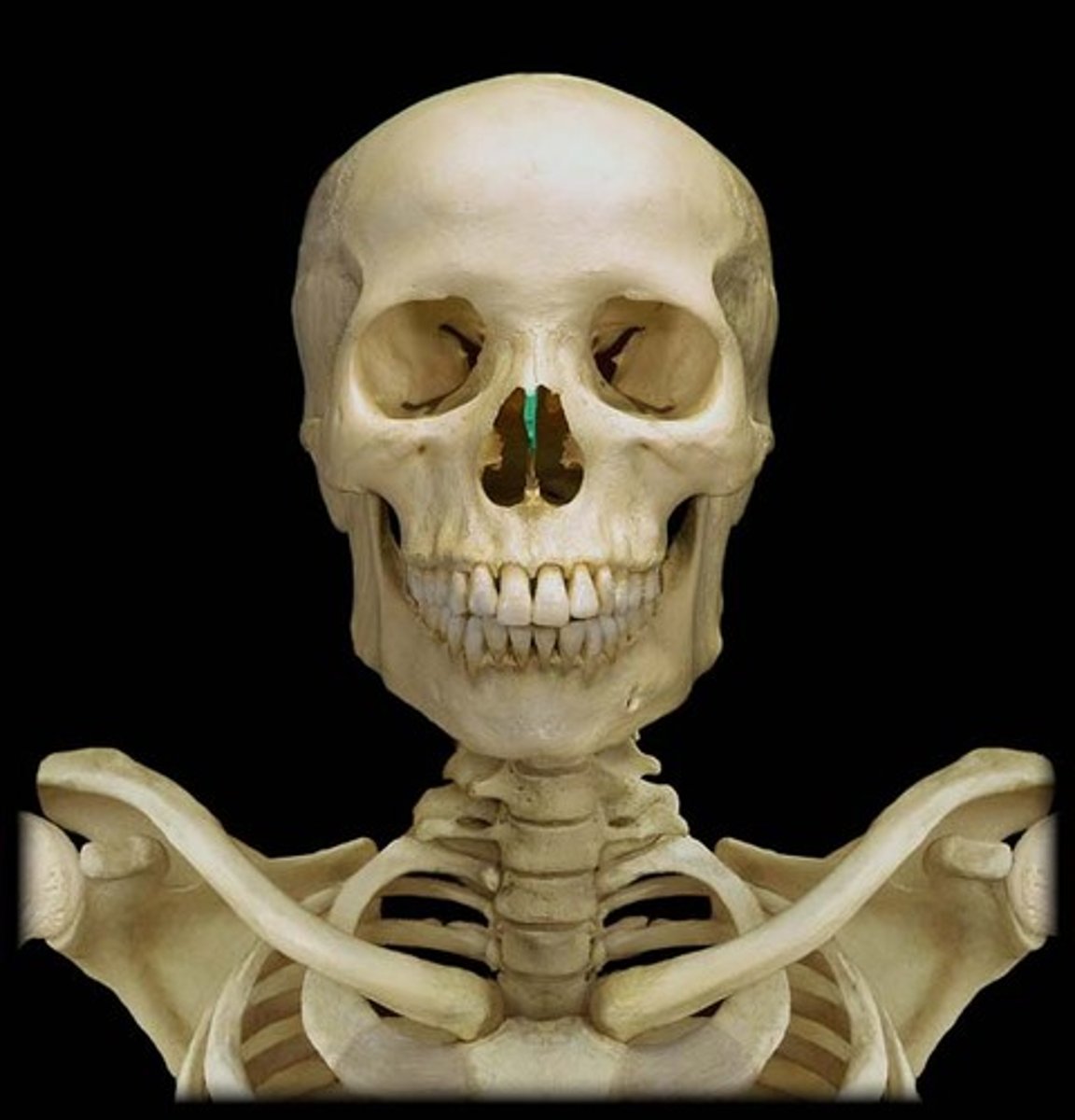
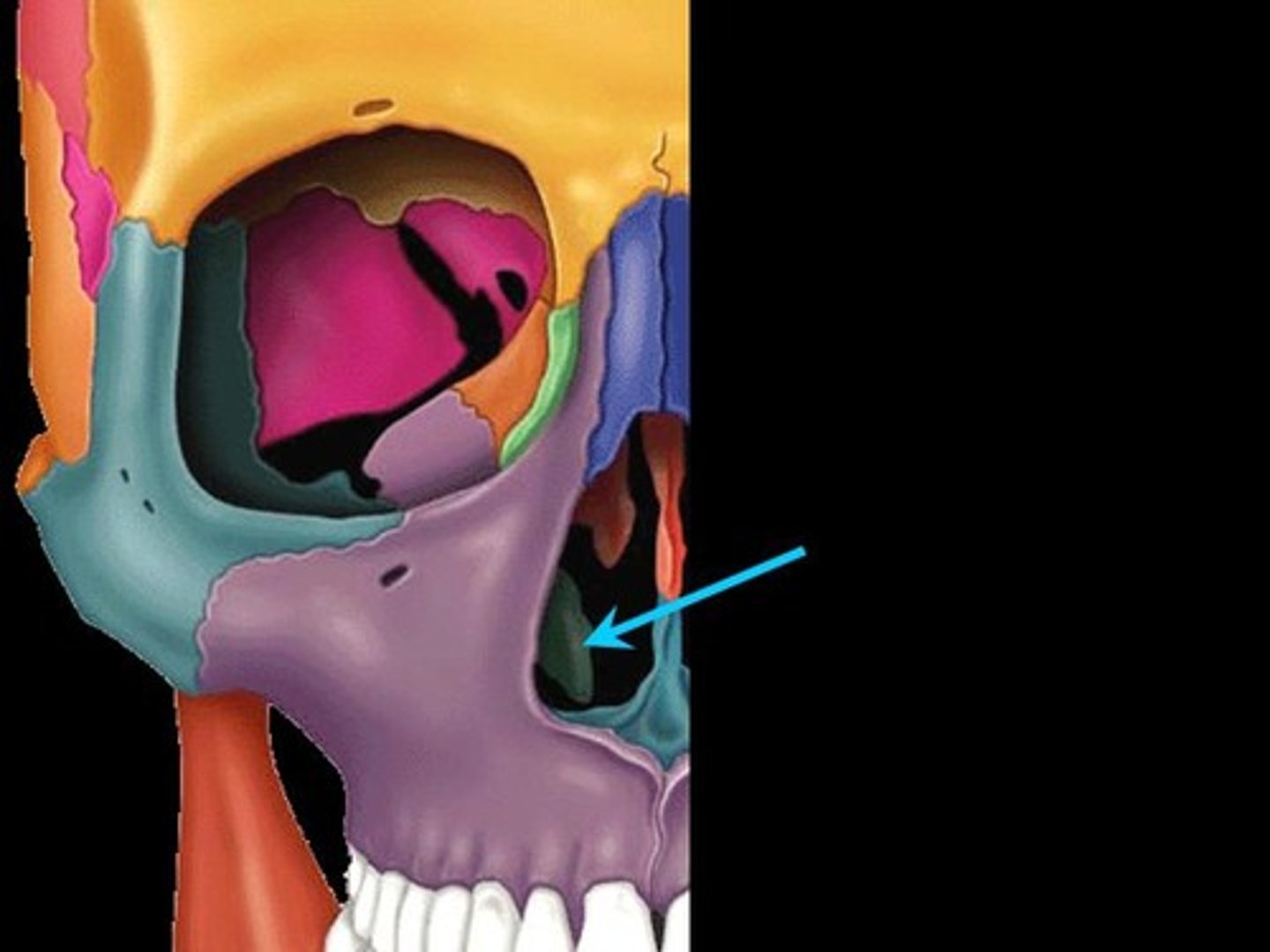
Inferior nasal conchae
two bones that help to complete the nasal cavity by forming the side and lower wall (superior and middle portions are from the ethmoid)
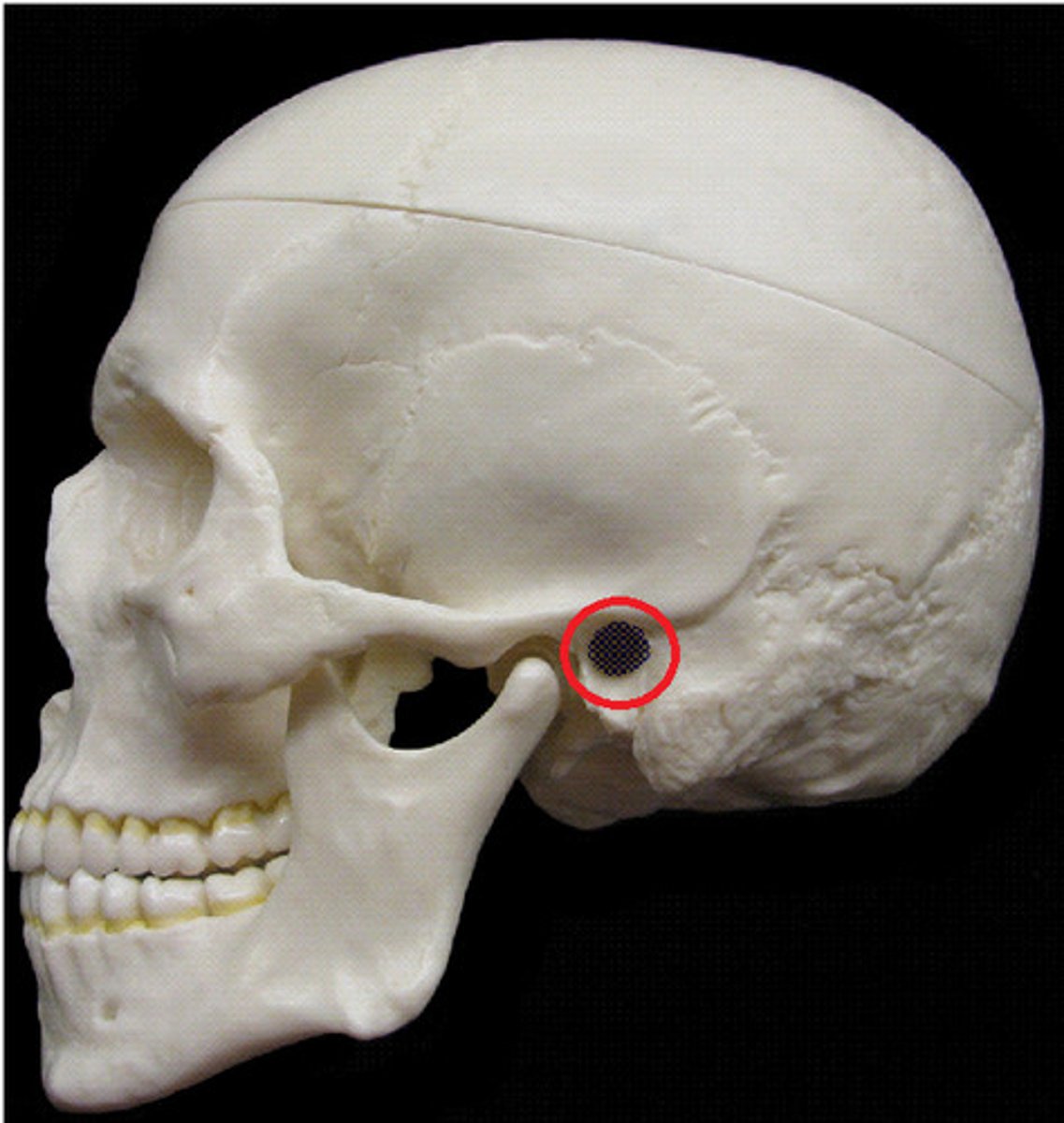
external auditory meatus of temporal bone
tube-like opening for the ear canal
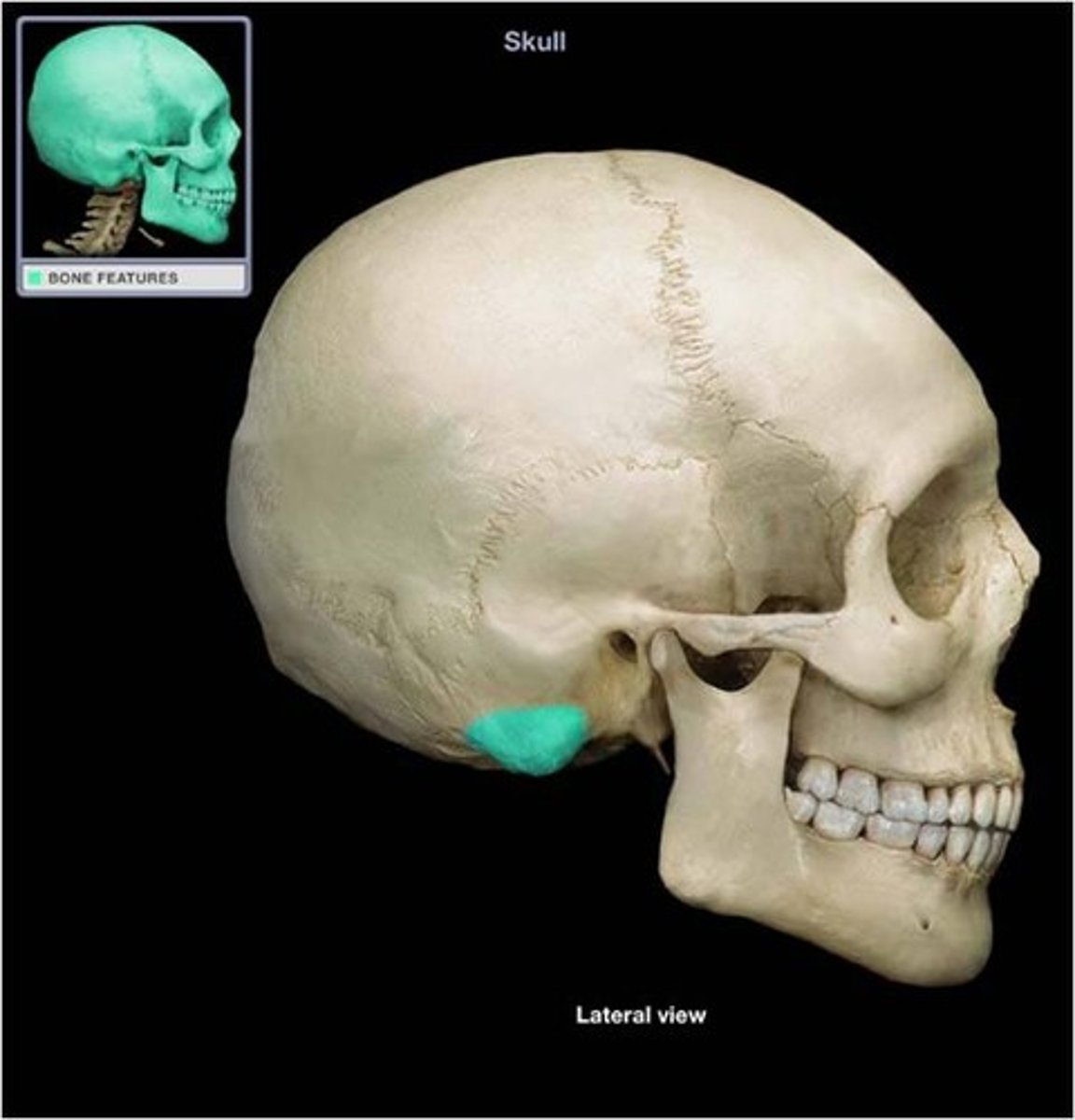
mastoid process of temporal bone
insertion of sternocleidomastoid
styloid process of temporal bone
attachment for stylohyoid ligament,
stylomandibular ligament, styloglossus muscle (innervated by the hypoglossal nerve)
stylohyoid muscle (innervated by the facial nerve)
stylopharyngeus muscle (innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve)
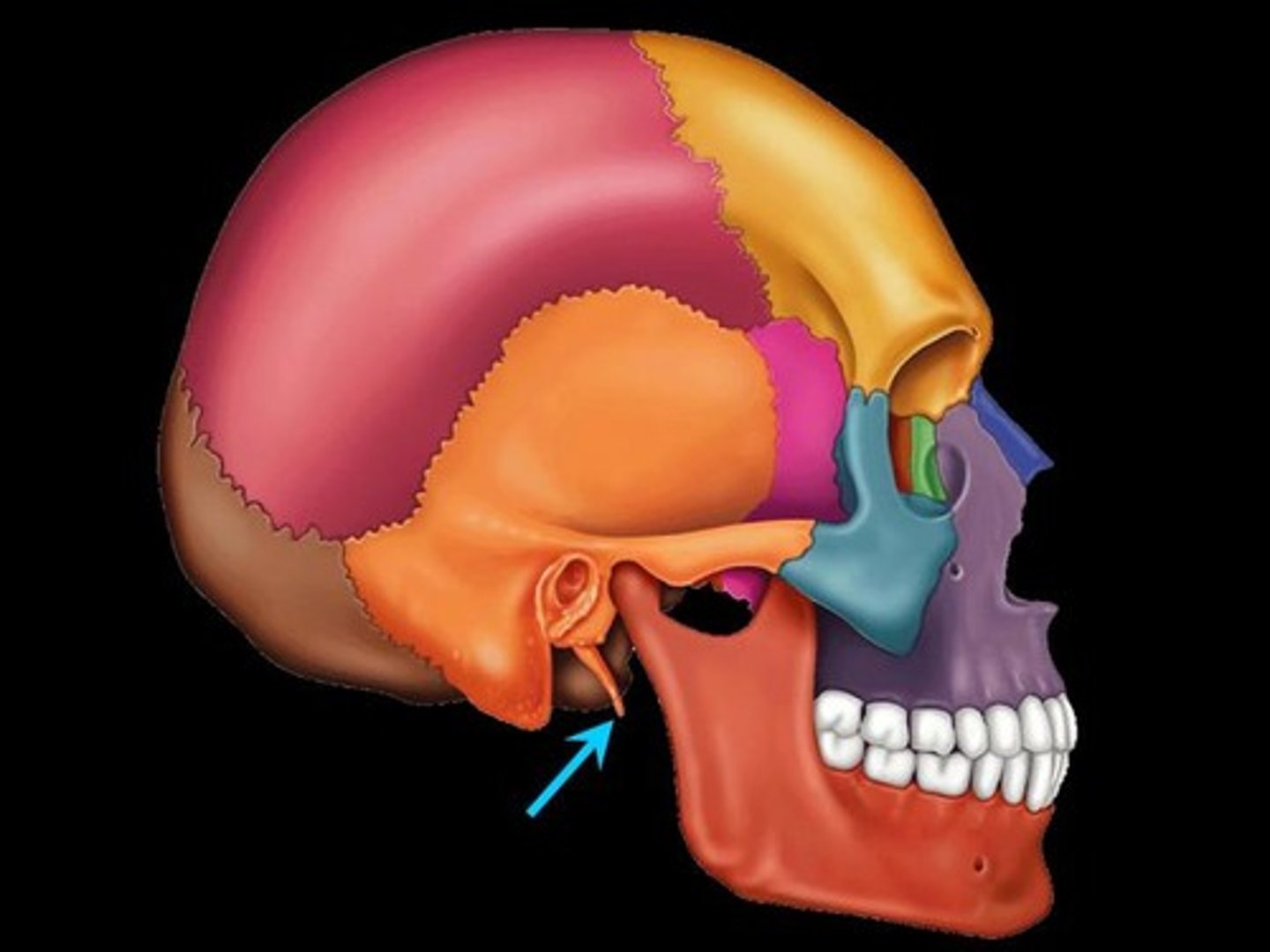
mandibular fossa of temporal bone
Articulates with the head (condoloid process) of the mandible to form the temporomandibular joint. The mandible (lower jaw) joins with the skull at this site.
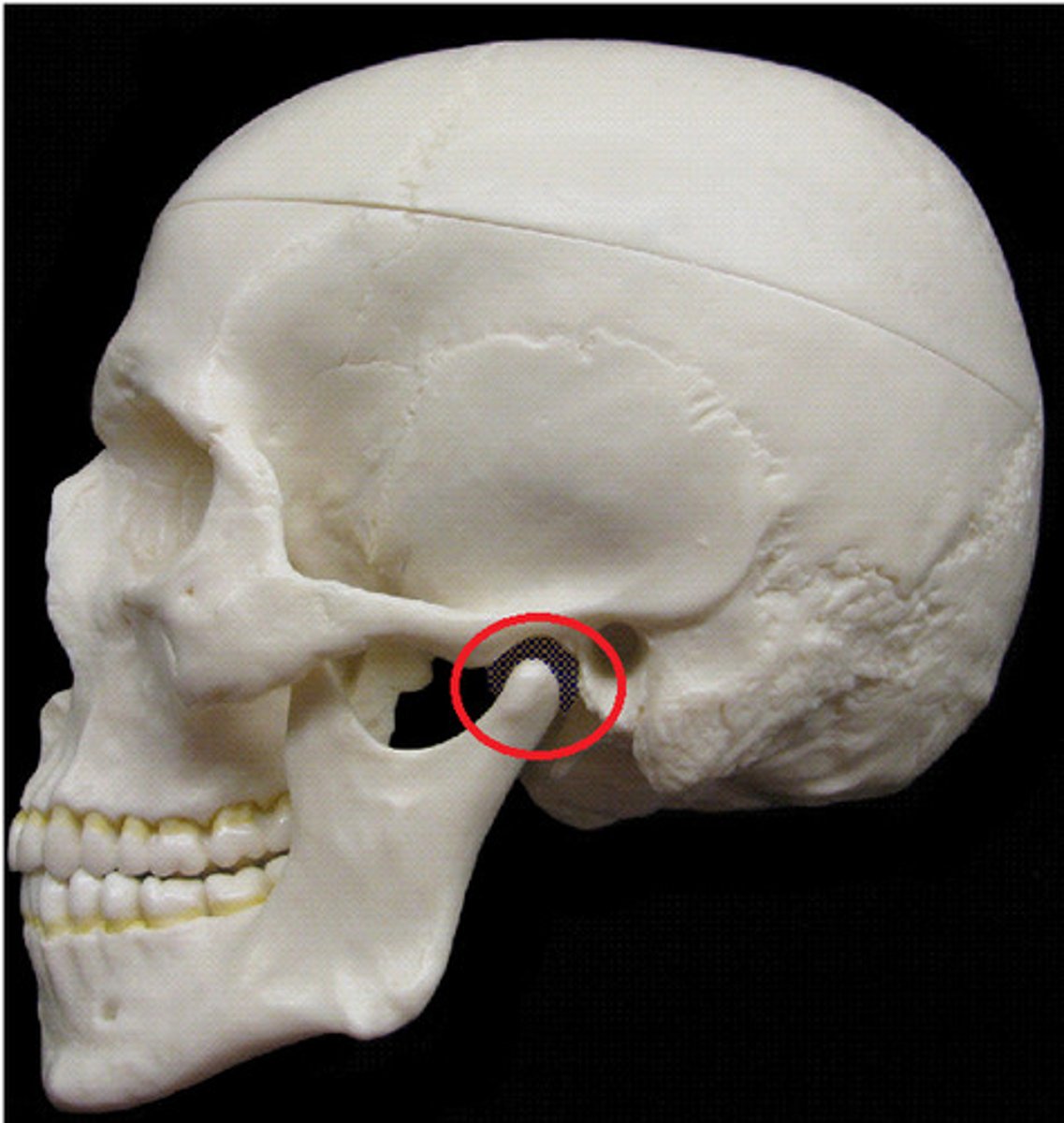
zygomatic process of temporal bone
extension from the temporal bone that forms the posterior portion of the zygomatic arch, attachment point for temporal fascia
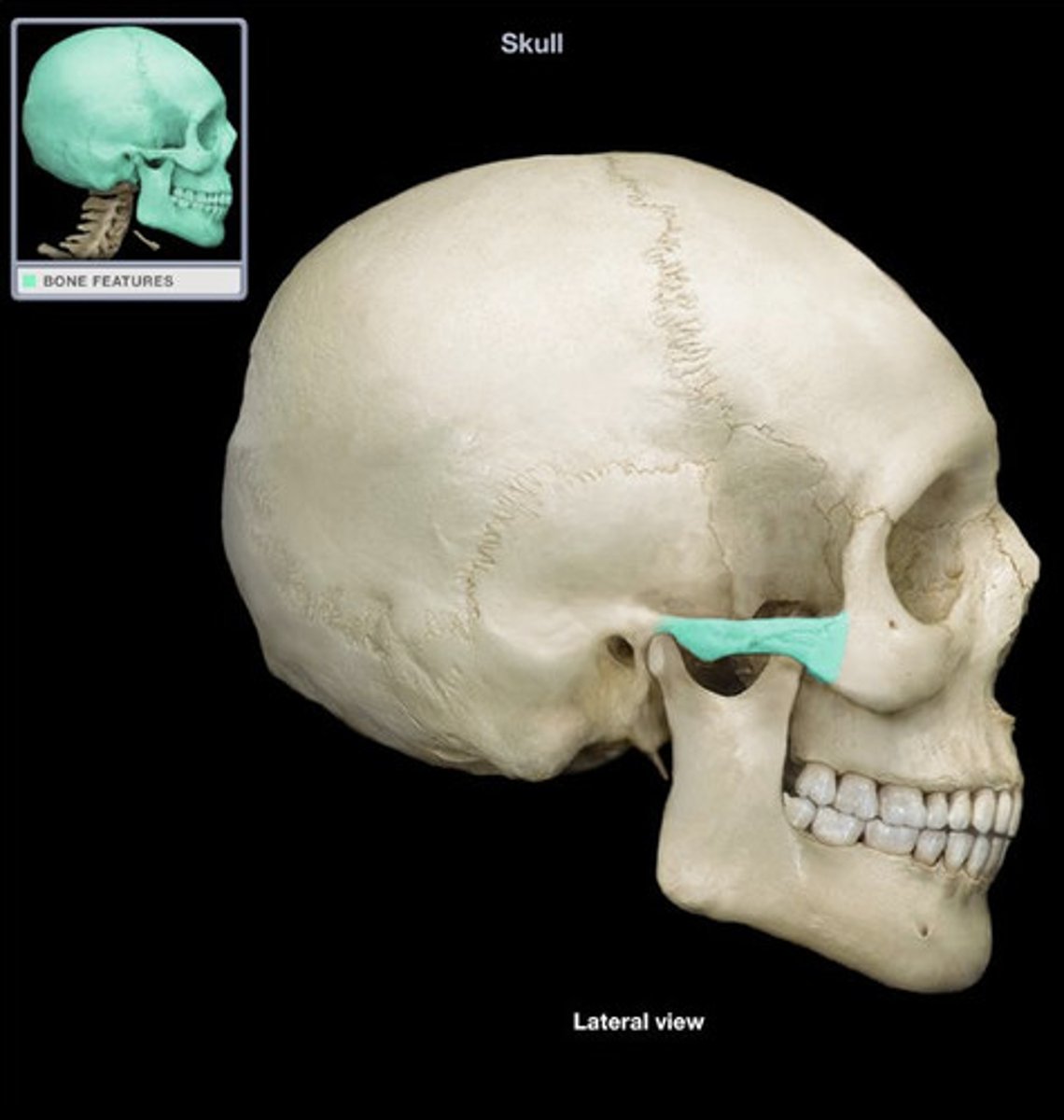
squamous part of temporal bone
large flat bone posterior to the sphenoid bone and inferior to the parietal bone, very thin
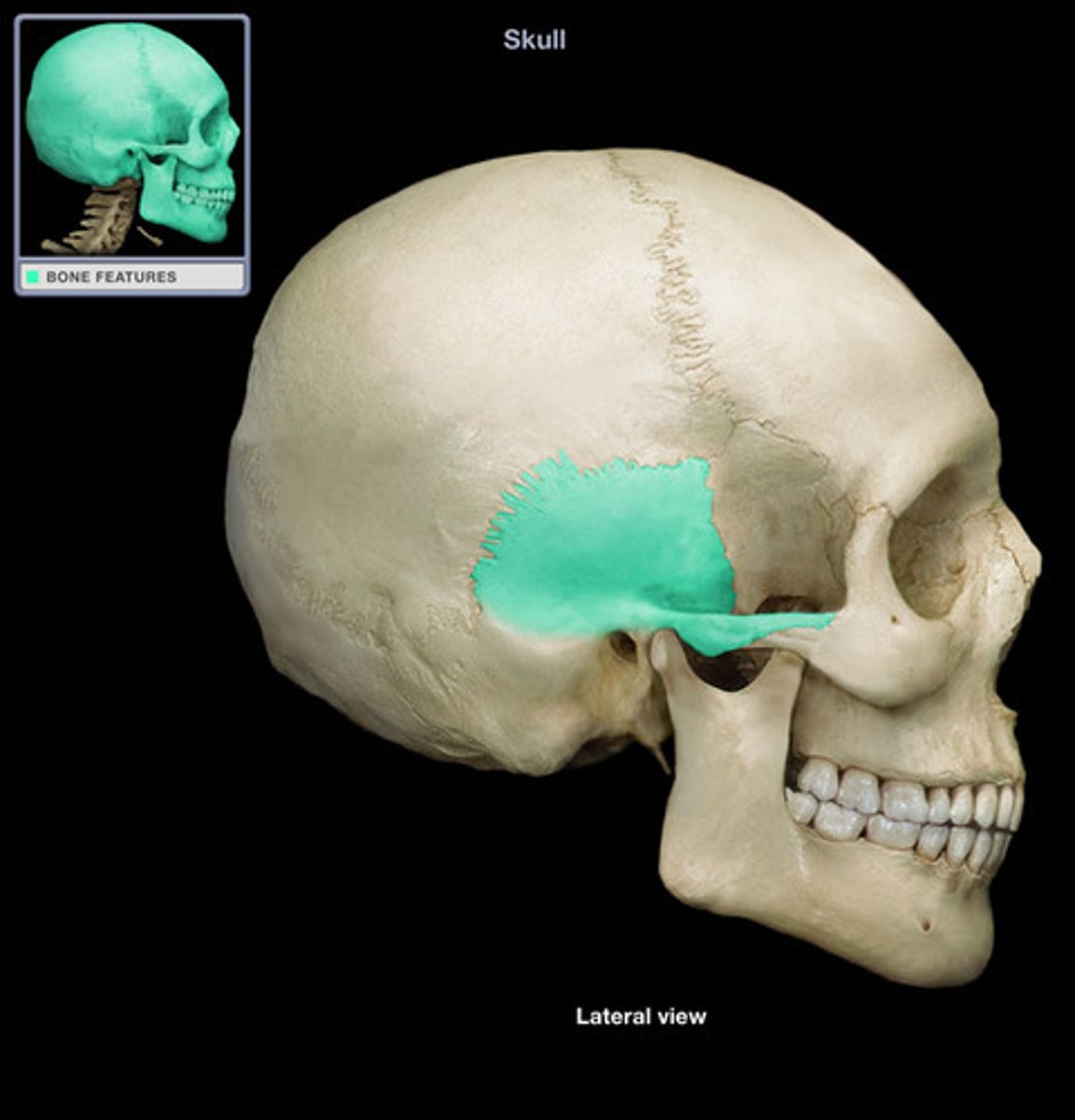
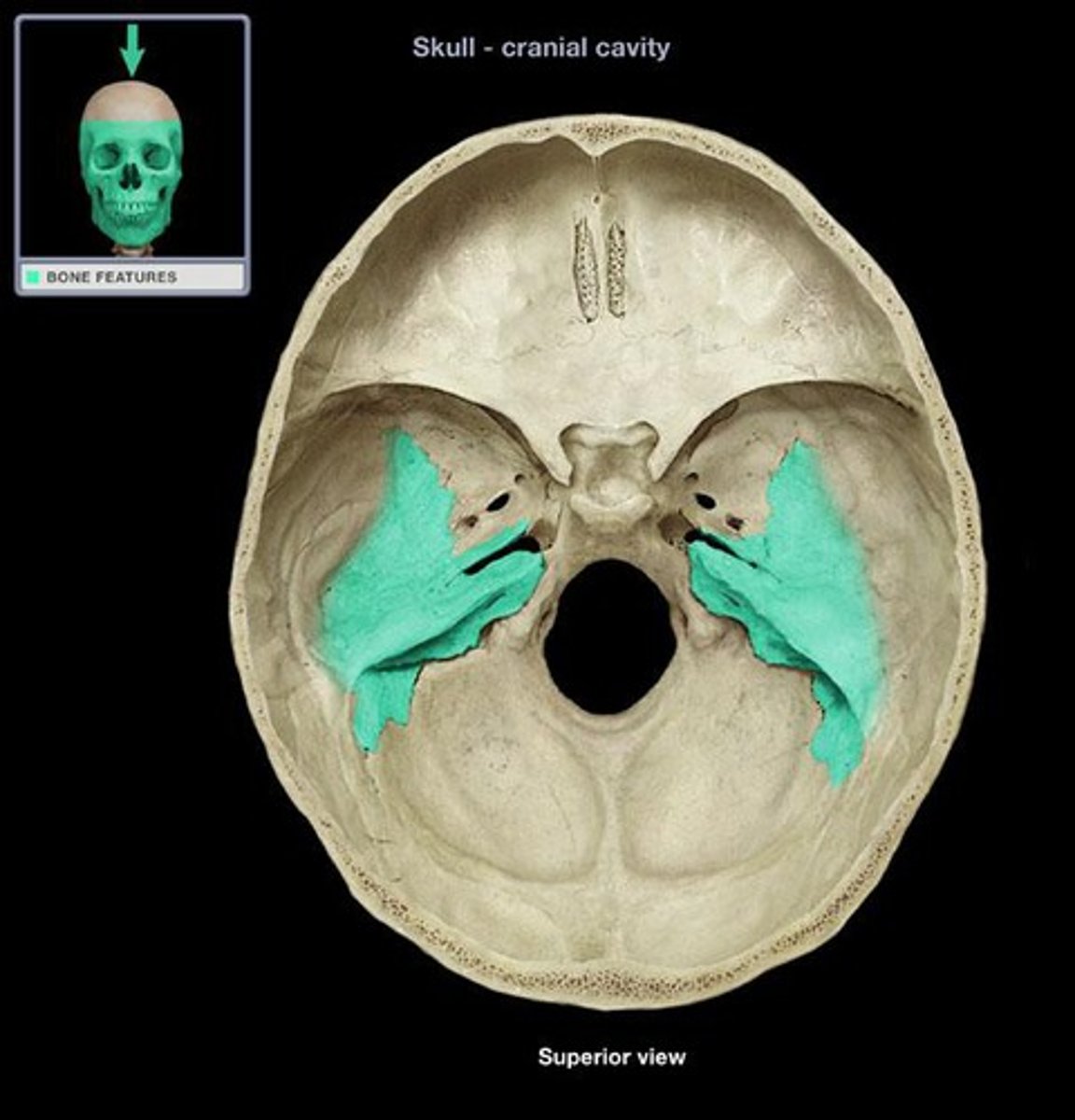
petrous portion of temporal bone
Thick portion of the temporal bone; hearing and balance are housed here
foramen lacerum
jagged opening filled with cartilage in a living person, formed by space between the borders of the temporal, occipital and sphenoid bones, transmits multiple blood vessels
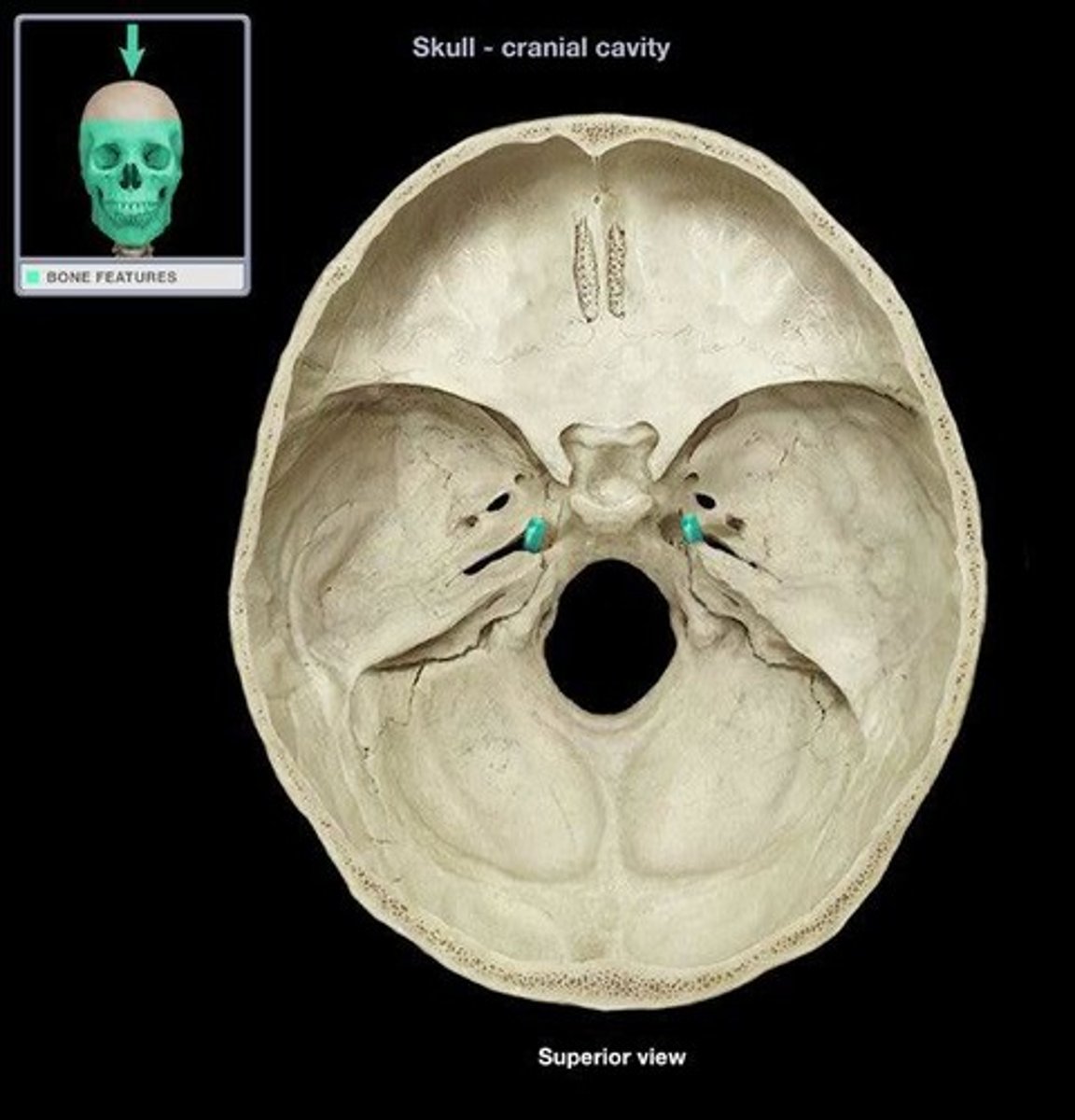
carotid canal of temporal bone (within petrous part)
Opens into Foramen Lacerum, transmits internal carotid artery
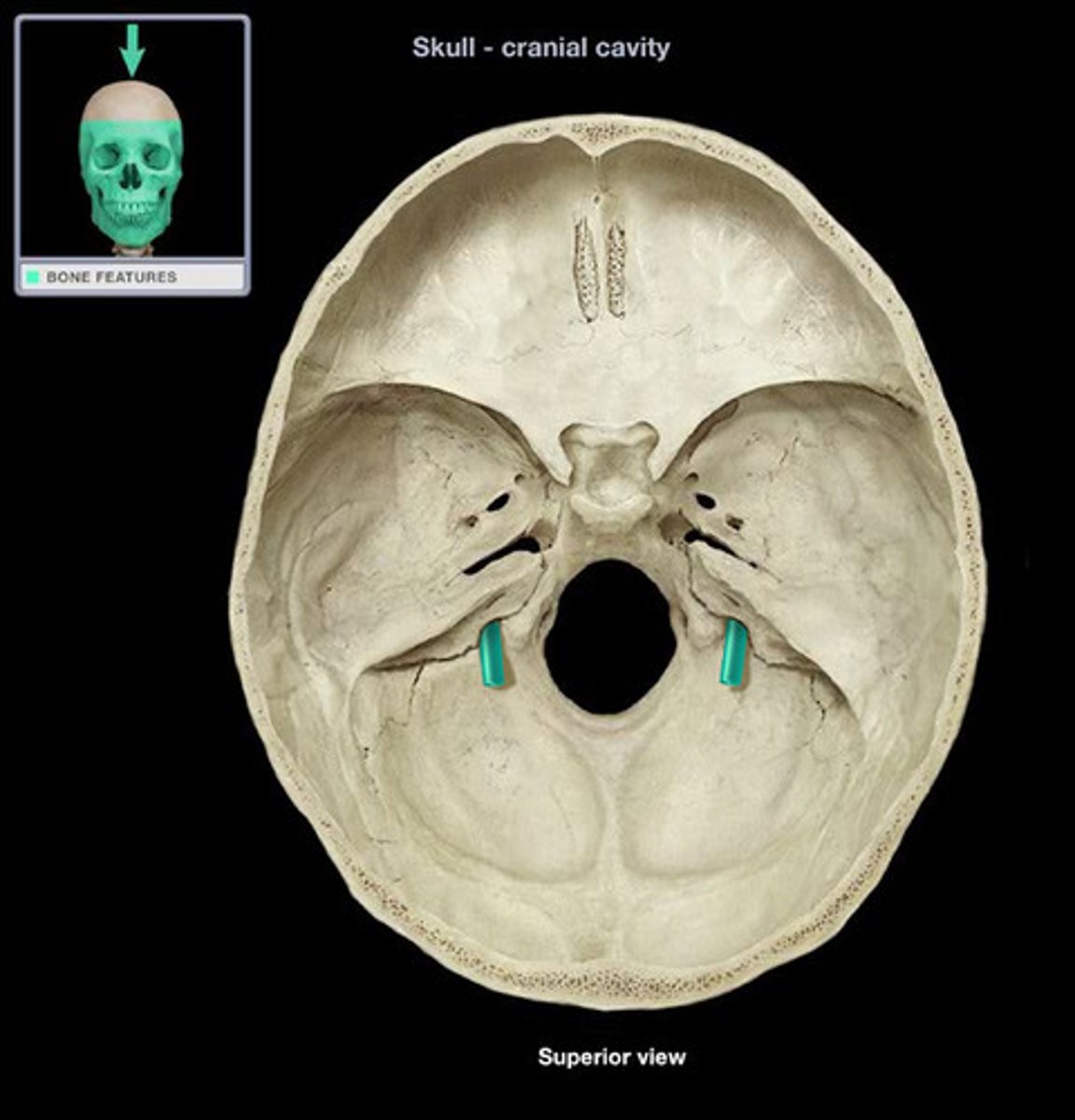
jugular foramen
a large opening at the inferior surface that transmits the jugular vein, glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), vagus nerve (CN X), and spinal accessory (CN XI) and some blood vessels
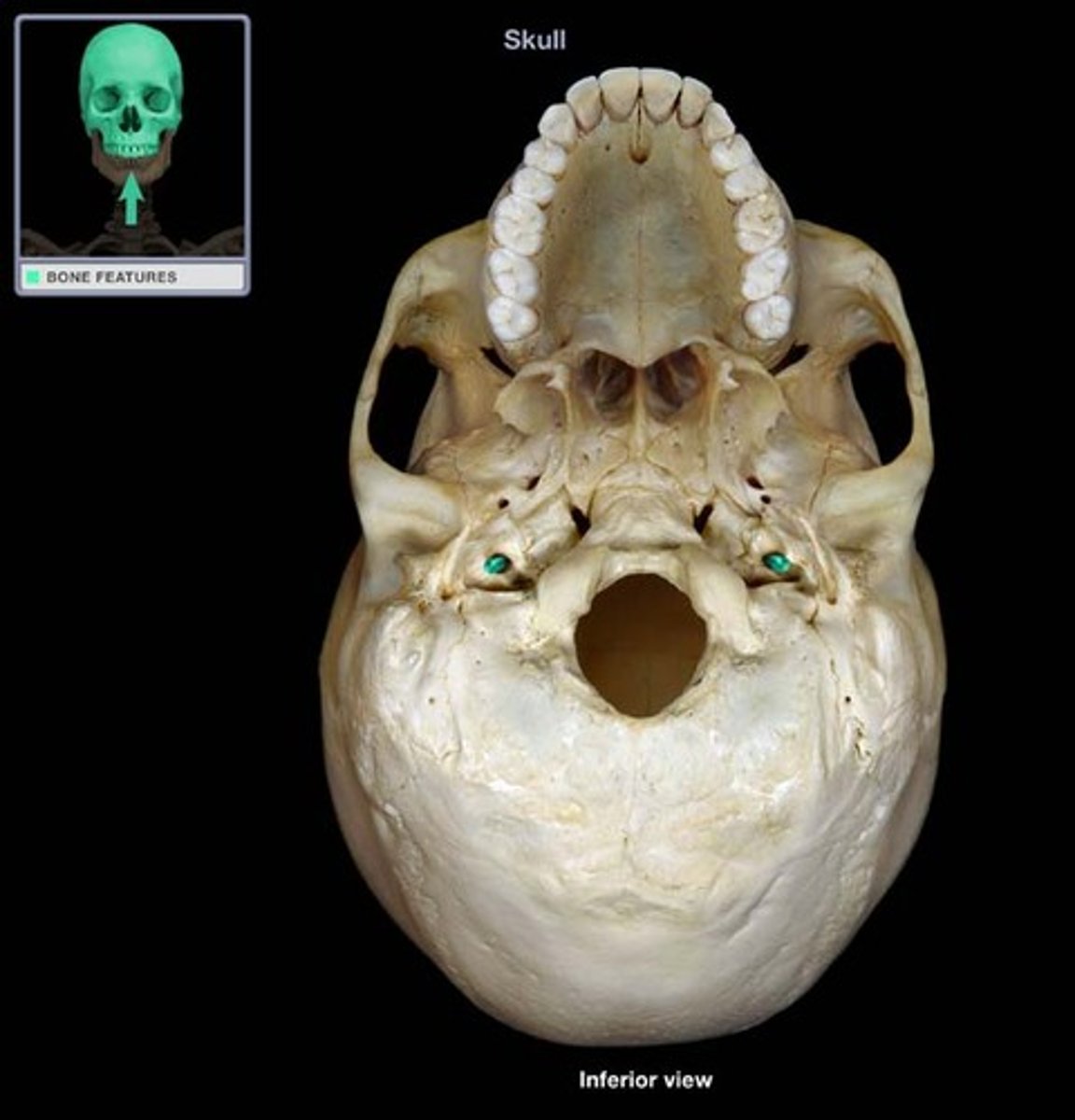
stylomastoid foramen of temporal bone
opening for an artery and cranial nerve VII (facial)
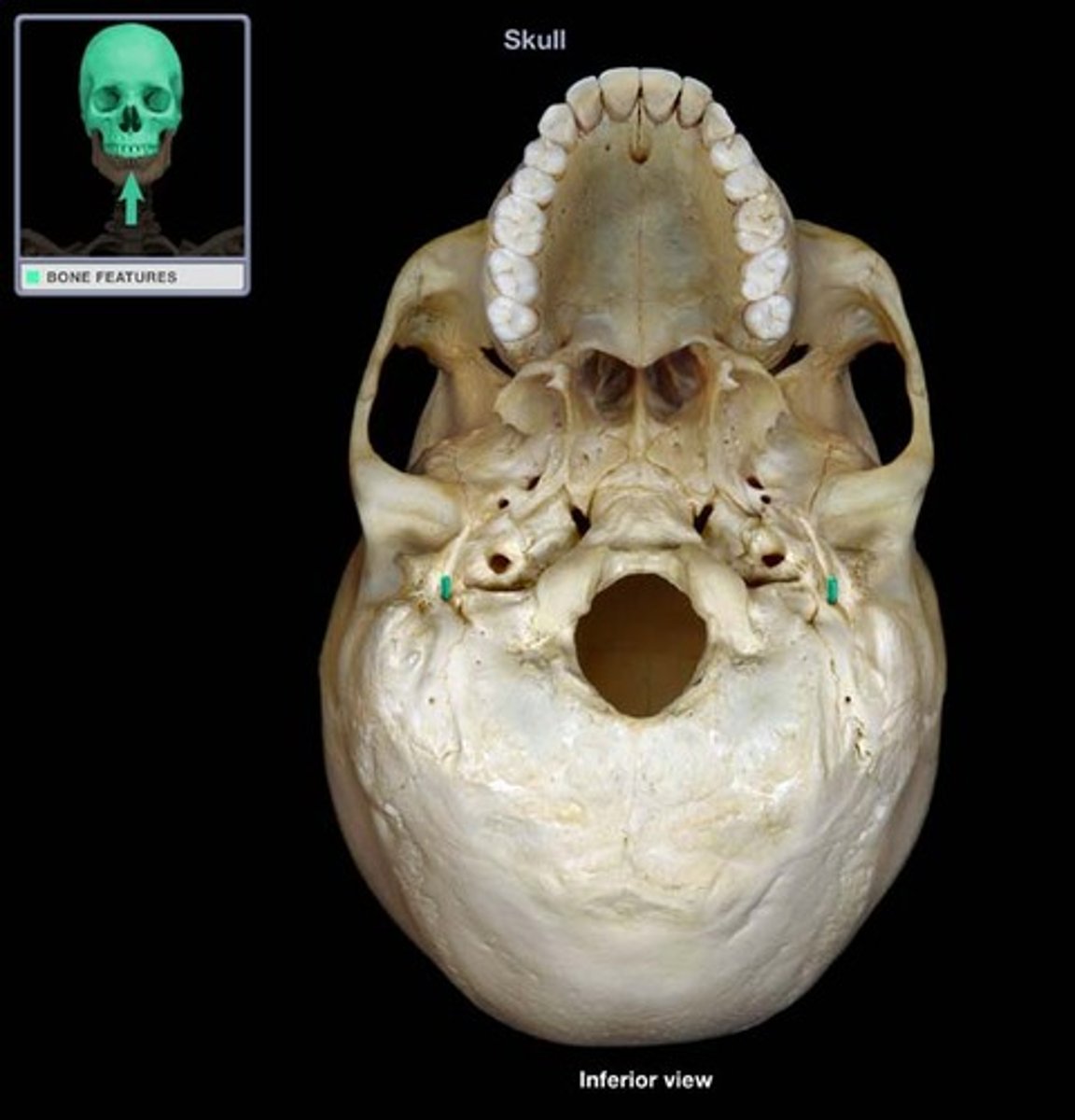
internal auditory meatus of temporal bone
Passageway for nerves and vessels that supply the ear (CN VIII, vestibulocochlear, and CN VII, facial)
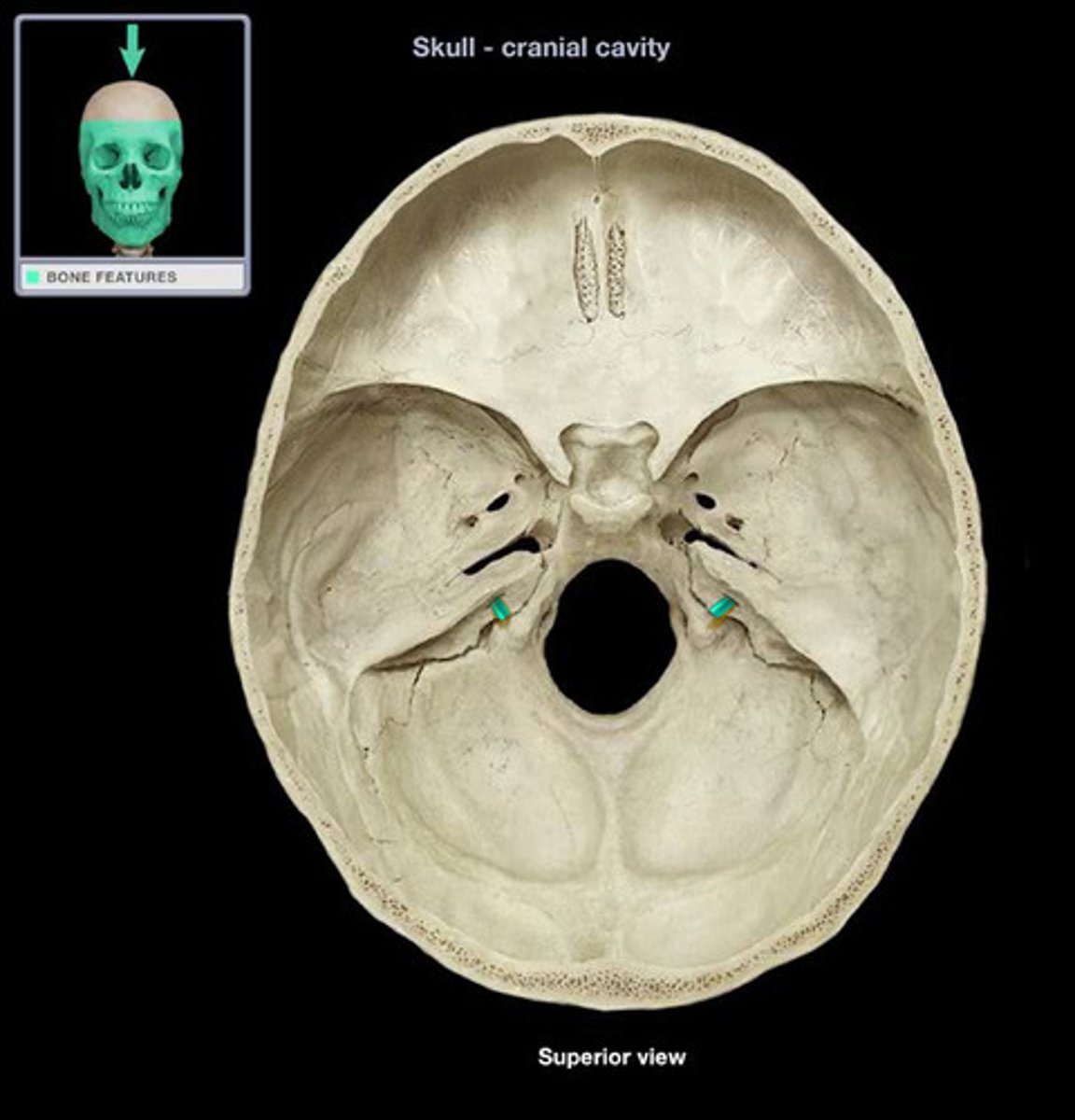
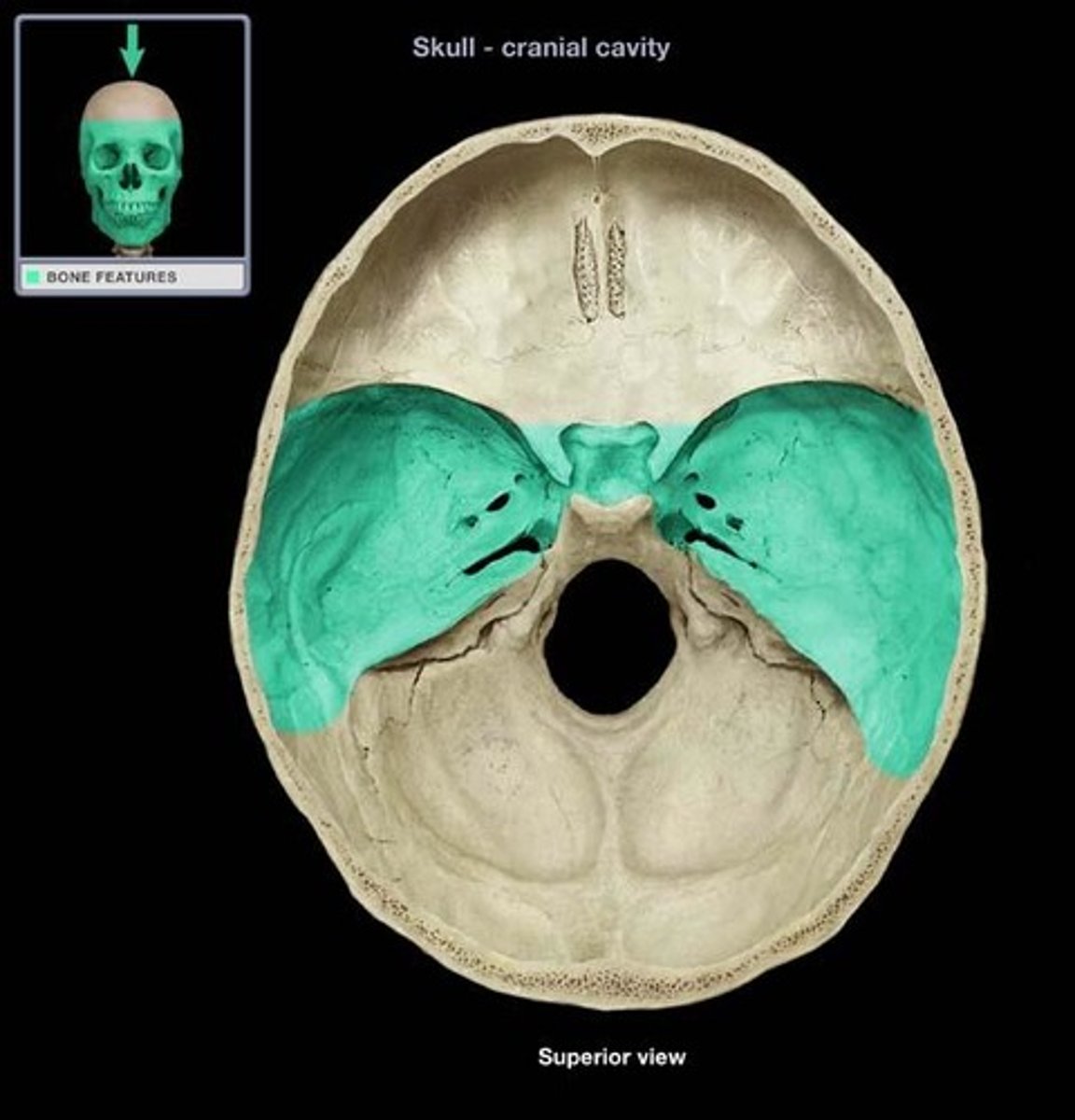
middle cranial fossa
holds the temporal lobes of the brain
grooves for middle meningeal vessels of parietal bones
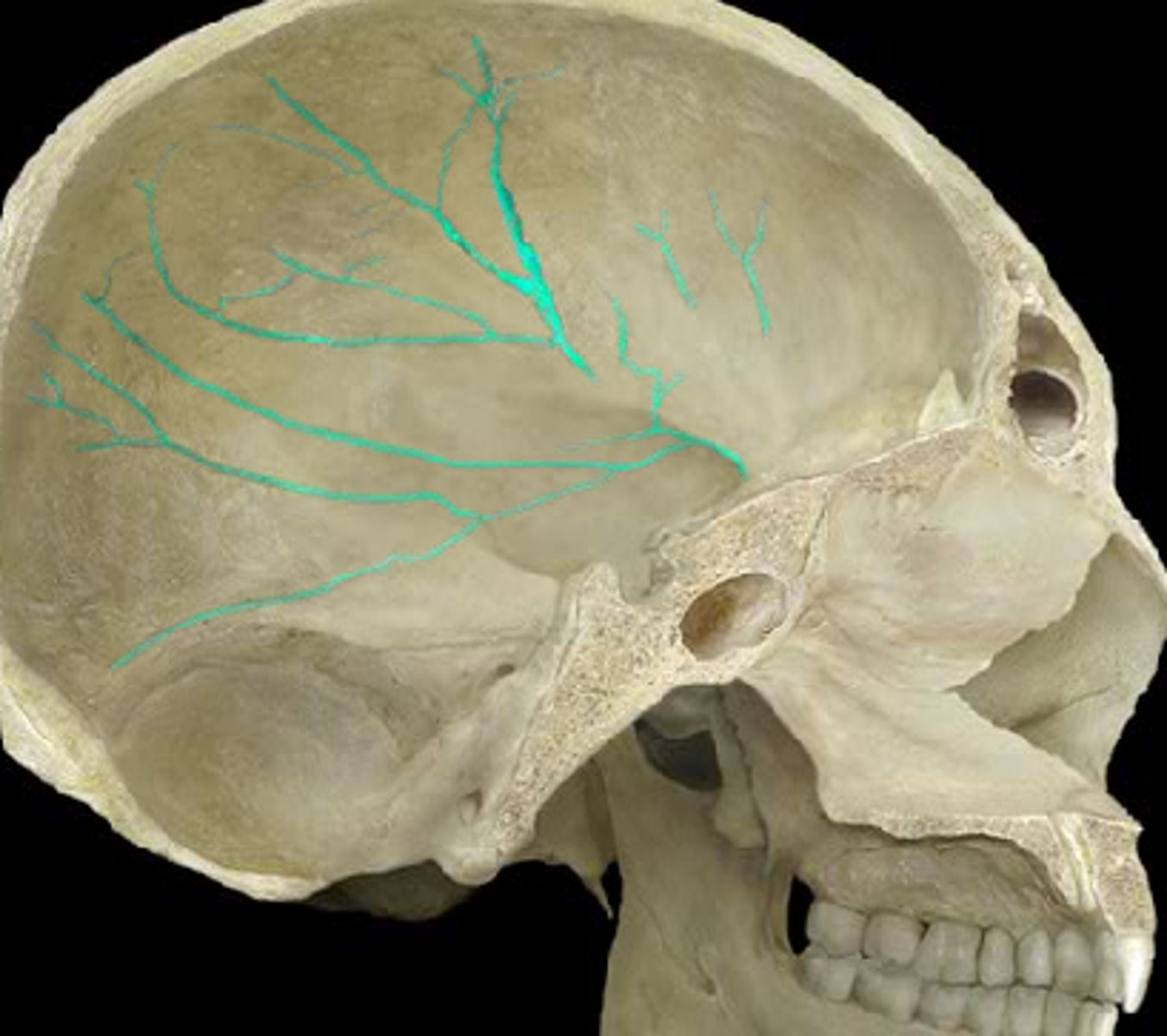
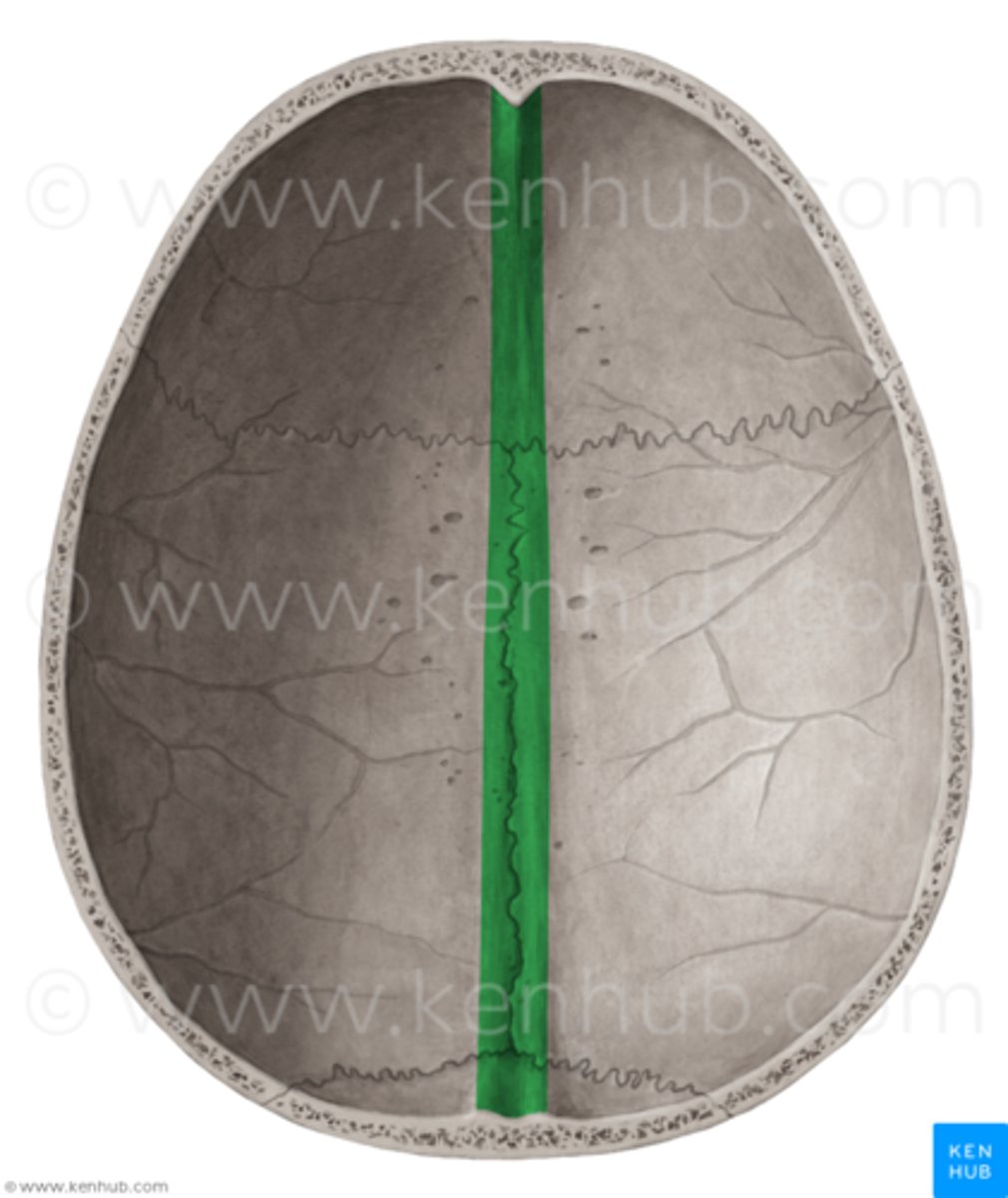
groove for superior sagittal sinus of parietal bone
right down the two hemispheres this groove exists
How many bones make up the face and what are they?
vomer, hyoid, mandible, and pairs of : maxillae, nasal bones, inferior nasal conchae, zygomatics, palatines, and lacrimals
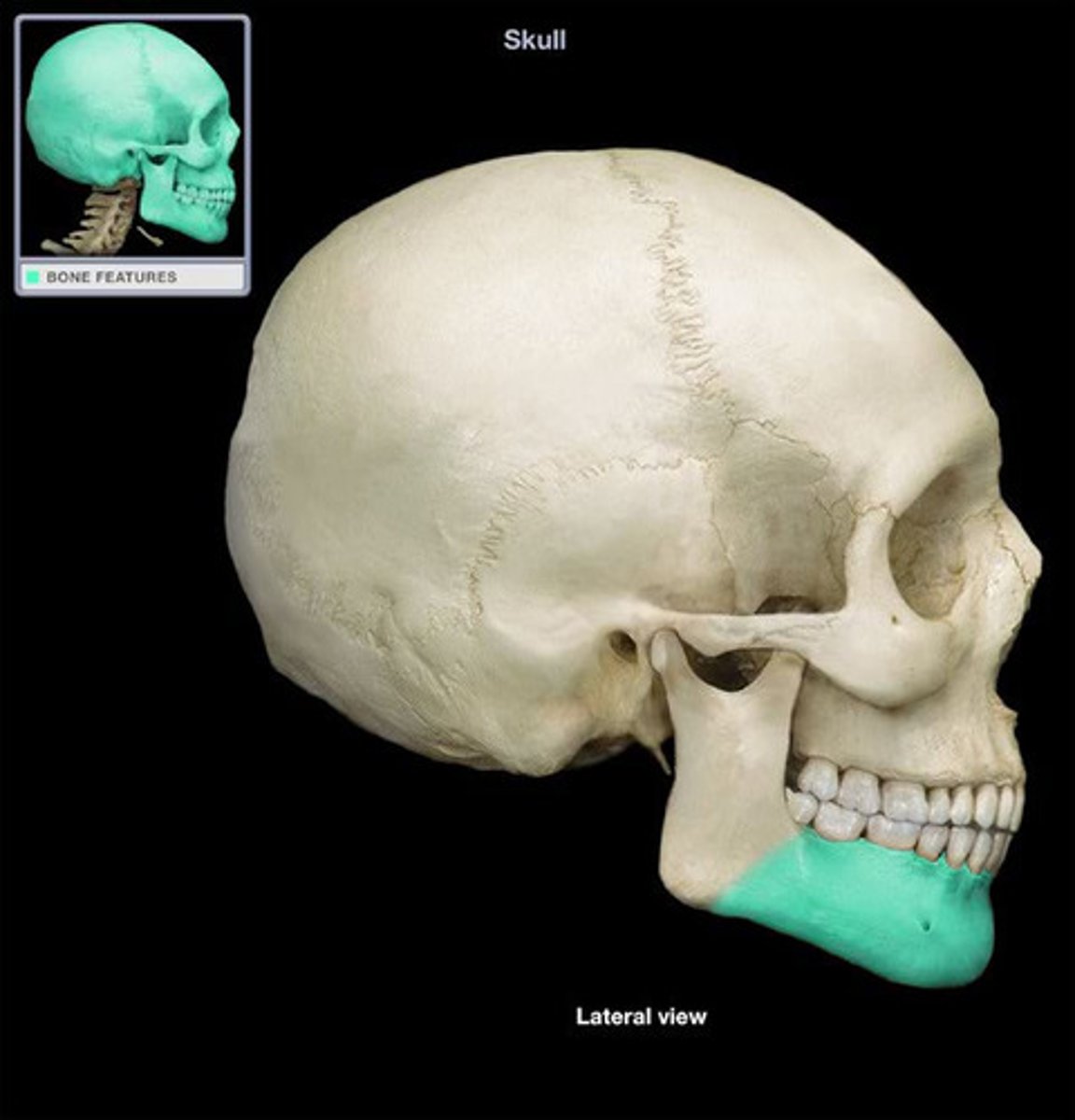
Mandible Body (Mandible)
horizontal portion of the mandible
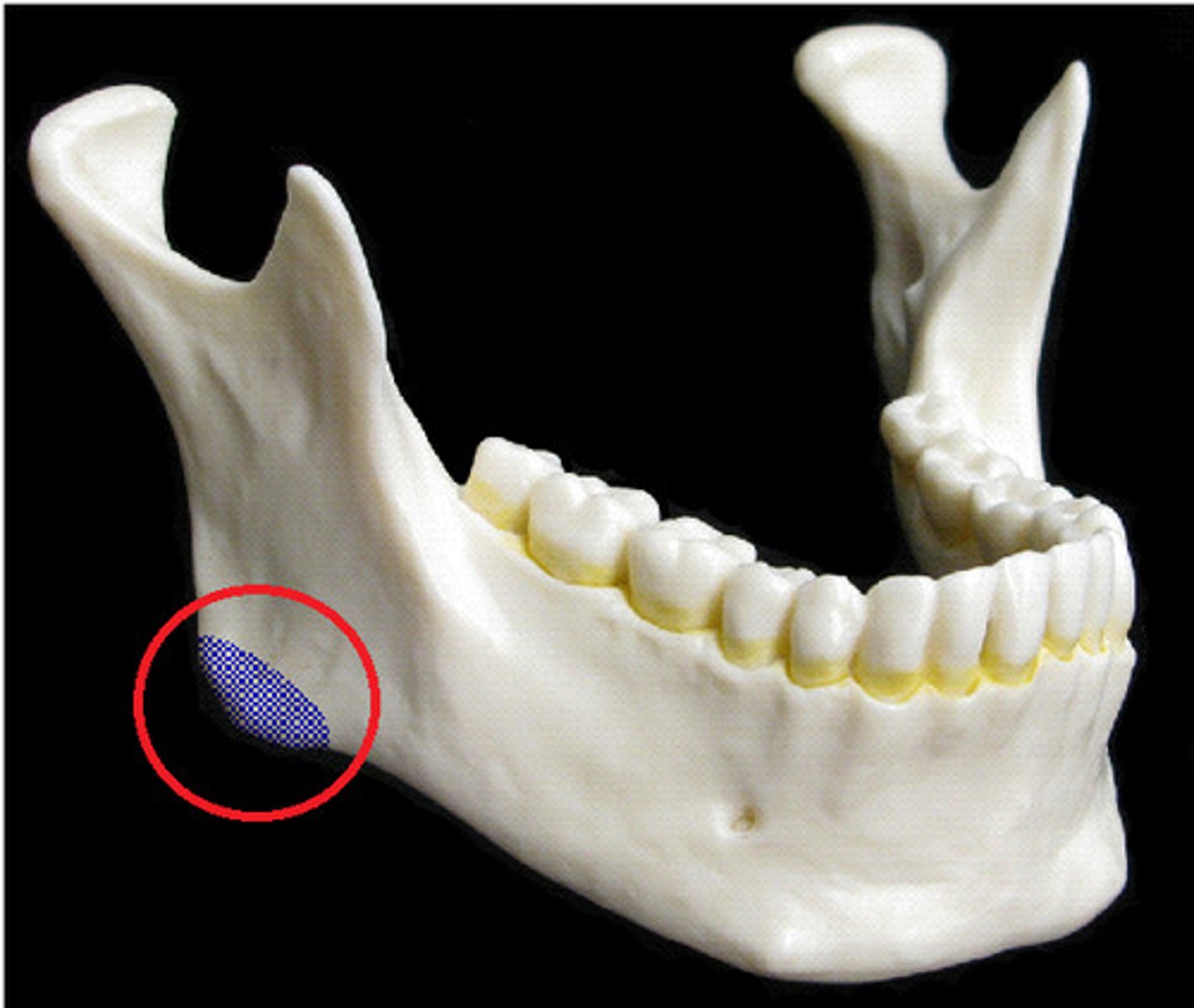
mandible angle
where the body and ramus of the mandible meet, attachment of the masseter laterally, and the pterygoideus internus (medial pterygoid muscle) medially; the stylomandibular ligament is attached to the angle between these muscles.
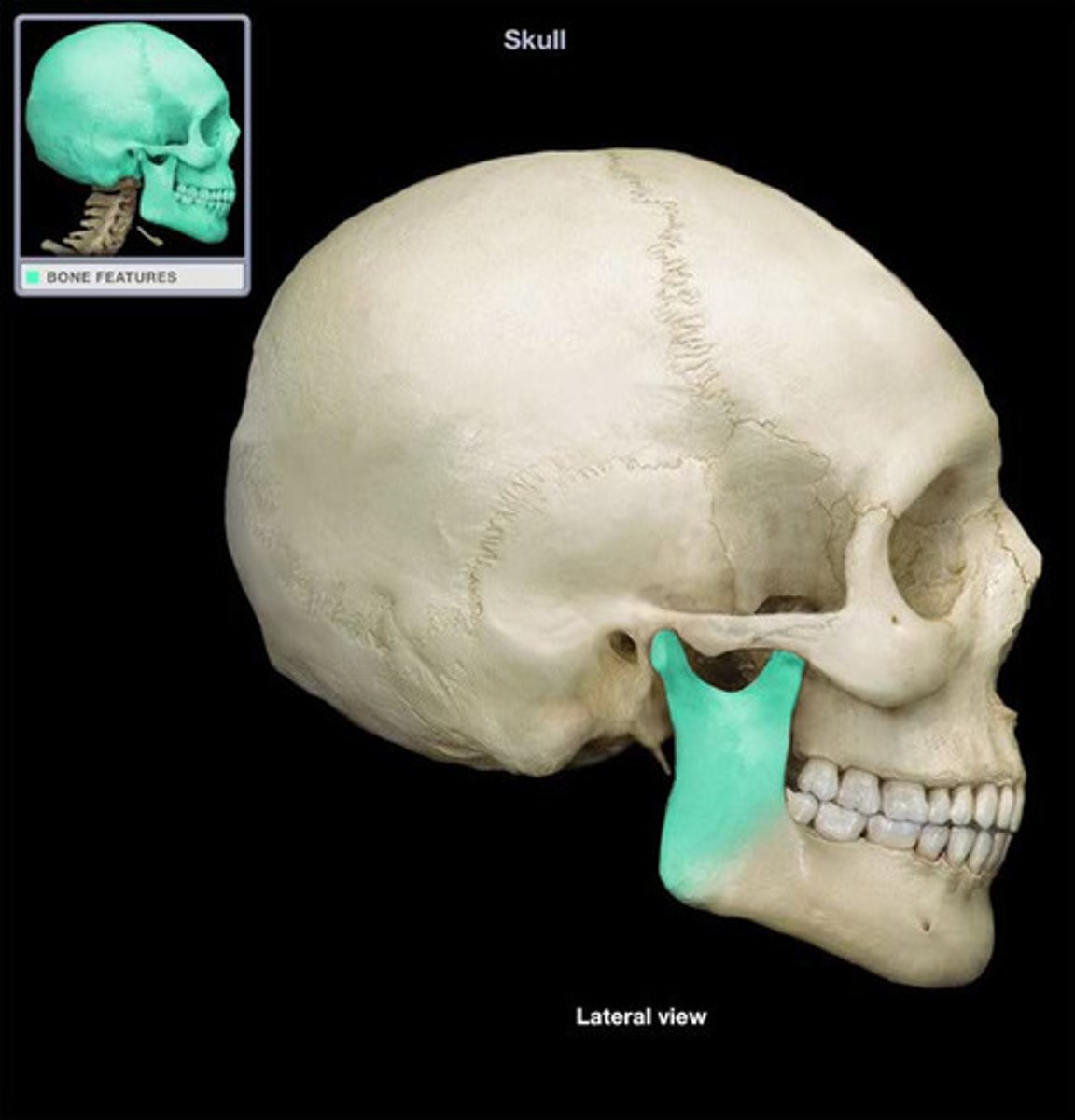
mandible ramus
vertical extension of the body on either side
coronoid process of mandible
insertion of temporalis
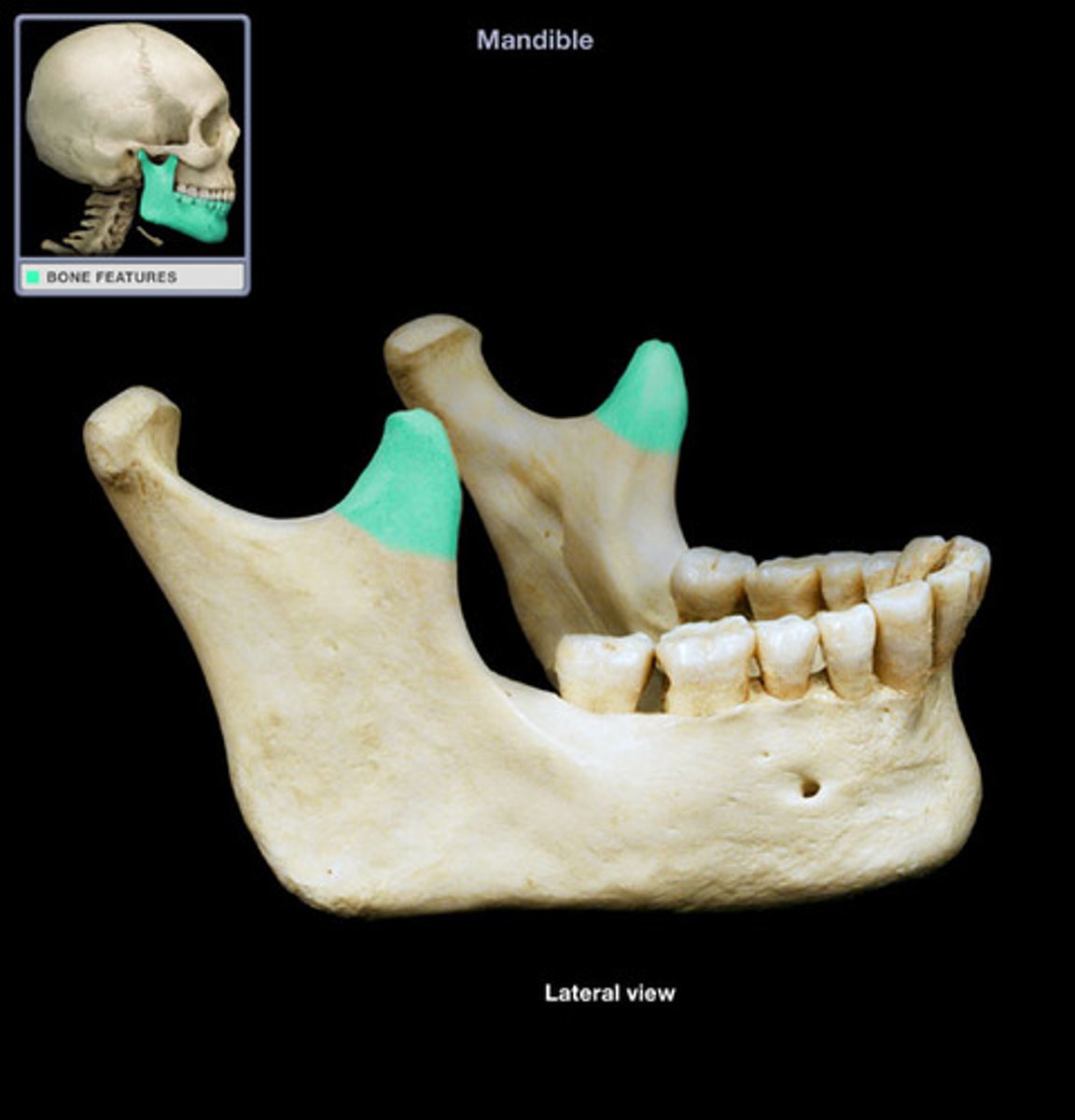
head of mandible
round portion at the top of the condylar process; articulates with temporal mandibular fossa
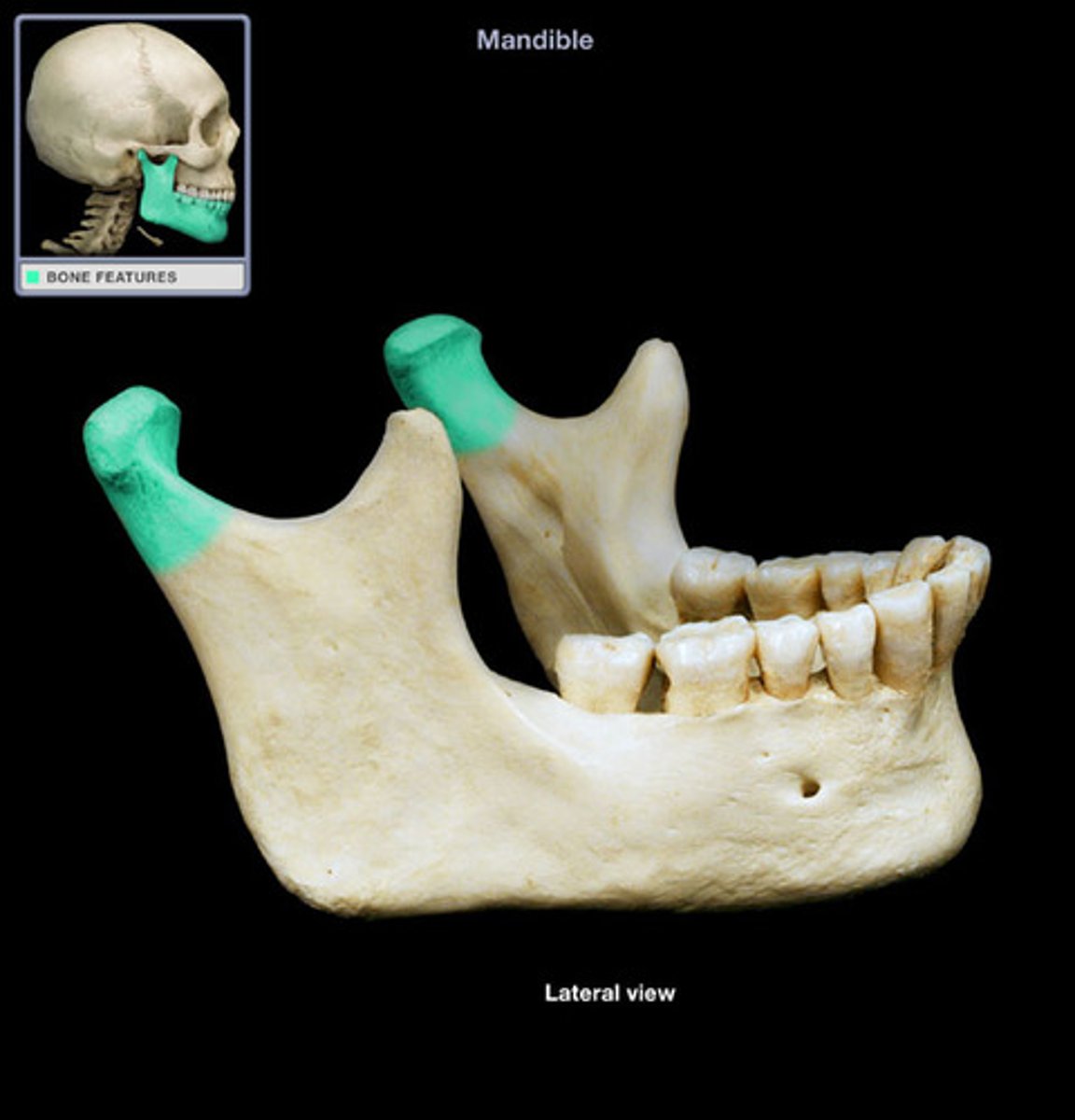
alveolar part of mandible
houses the teeth in dental alveoli (sacs)
frontal process of maxilla
the ascending part of the upper jaw which gradually protrudes as it rises beside the nasal bone to meet the frontal bone; the ascending process of the upper jaw.
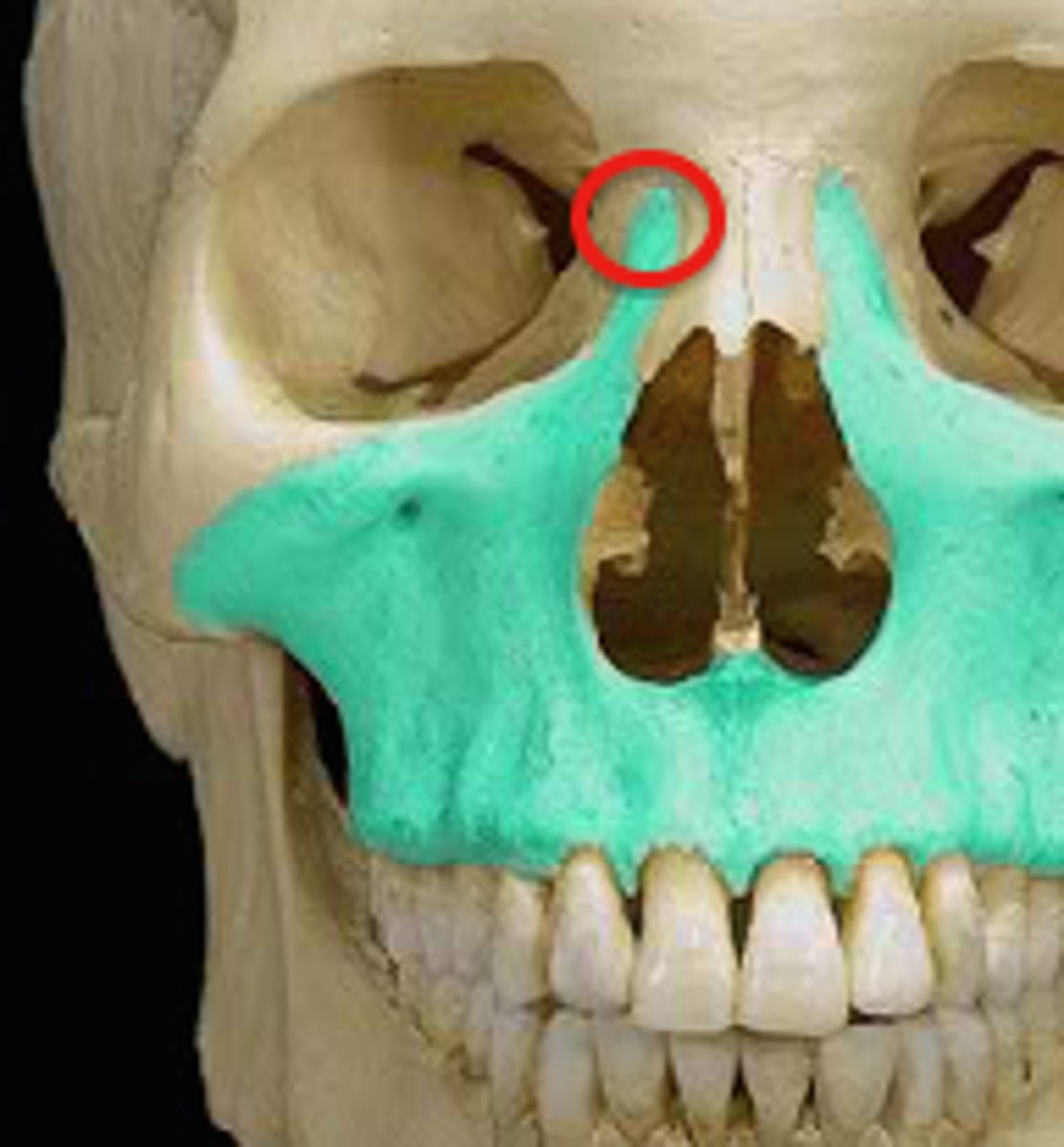
body of maxilla
Horizontal part of upper jaw superior to teeth
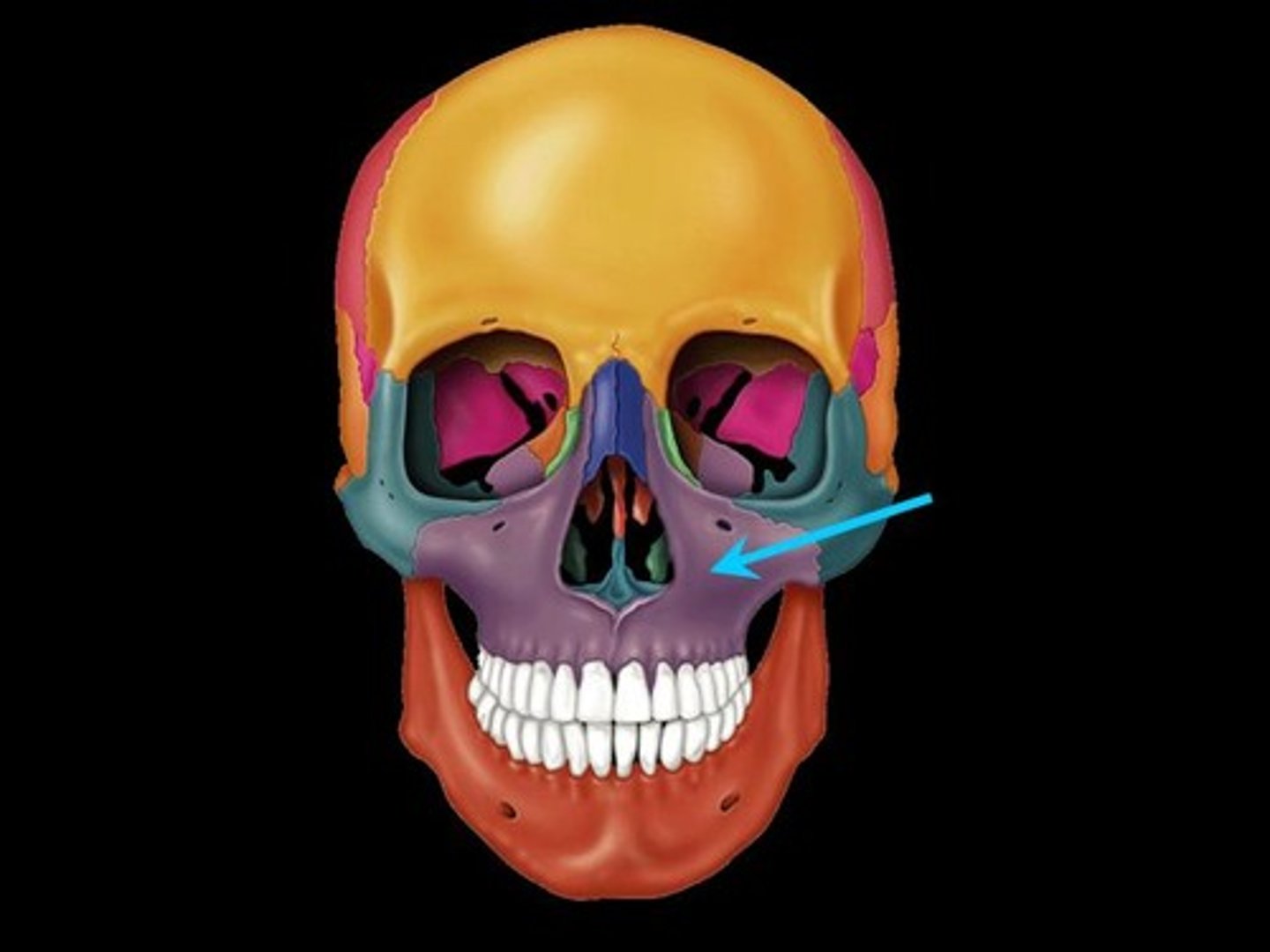
zygomatic process of maxilla
articulates with zygomatic bone
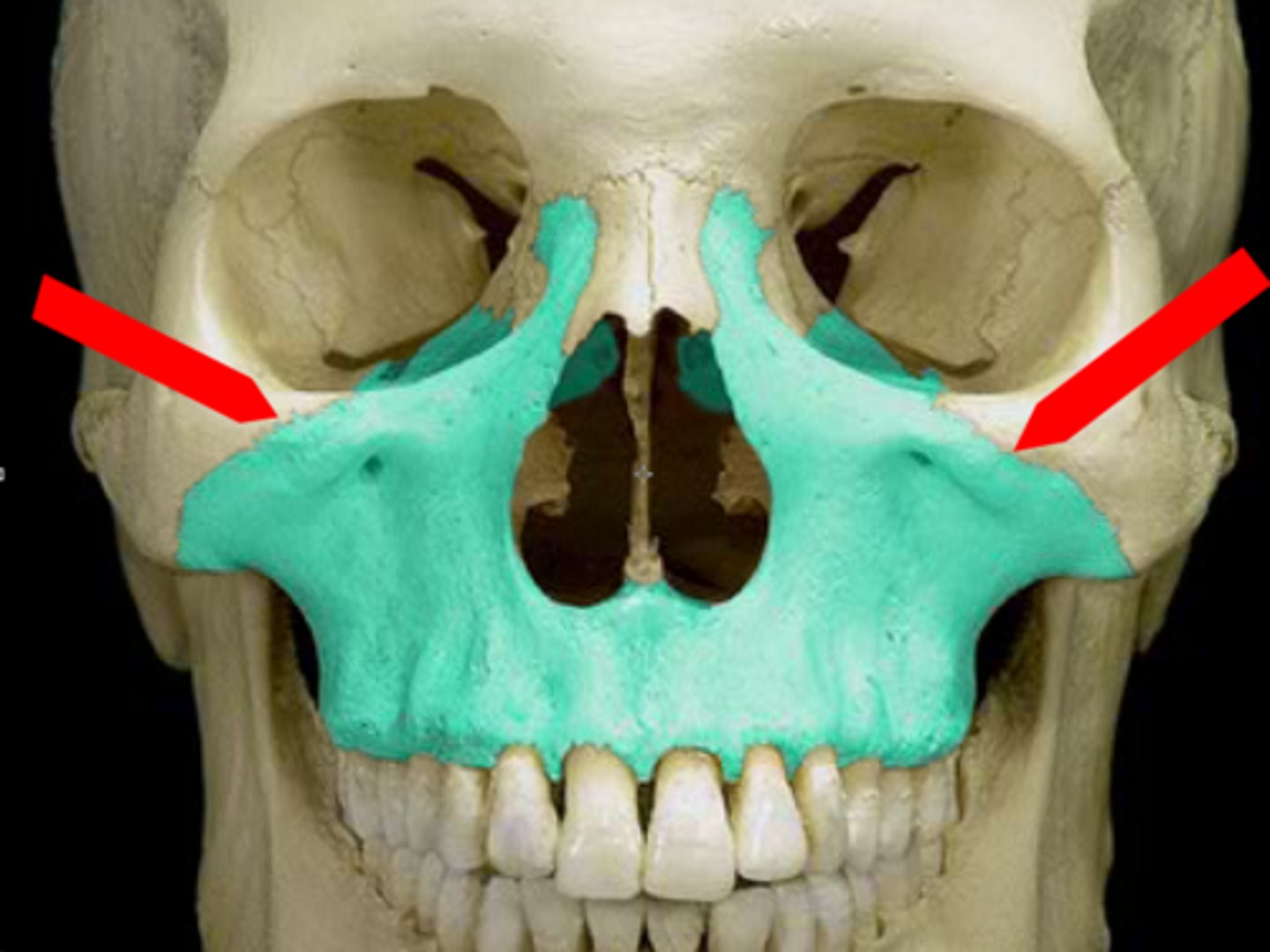
alveolar process of maxilla
curved, inferior margin of the maxilla that supports and anchors the upper teeth
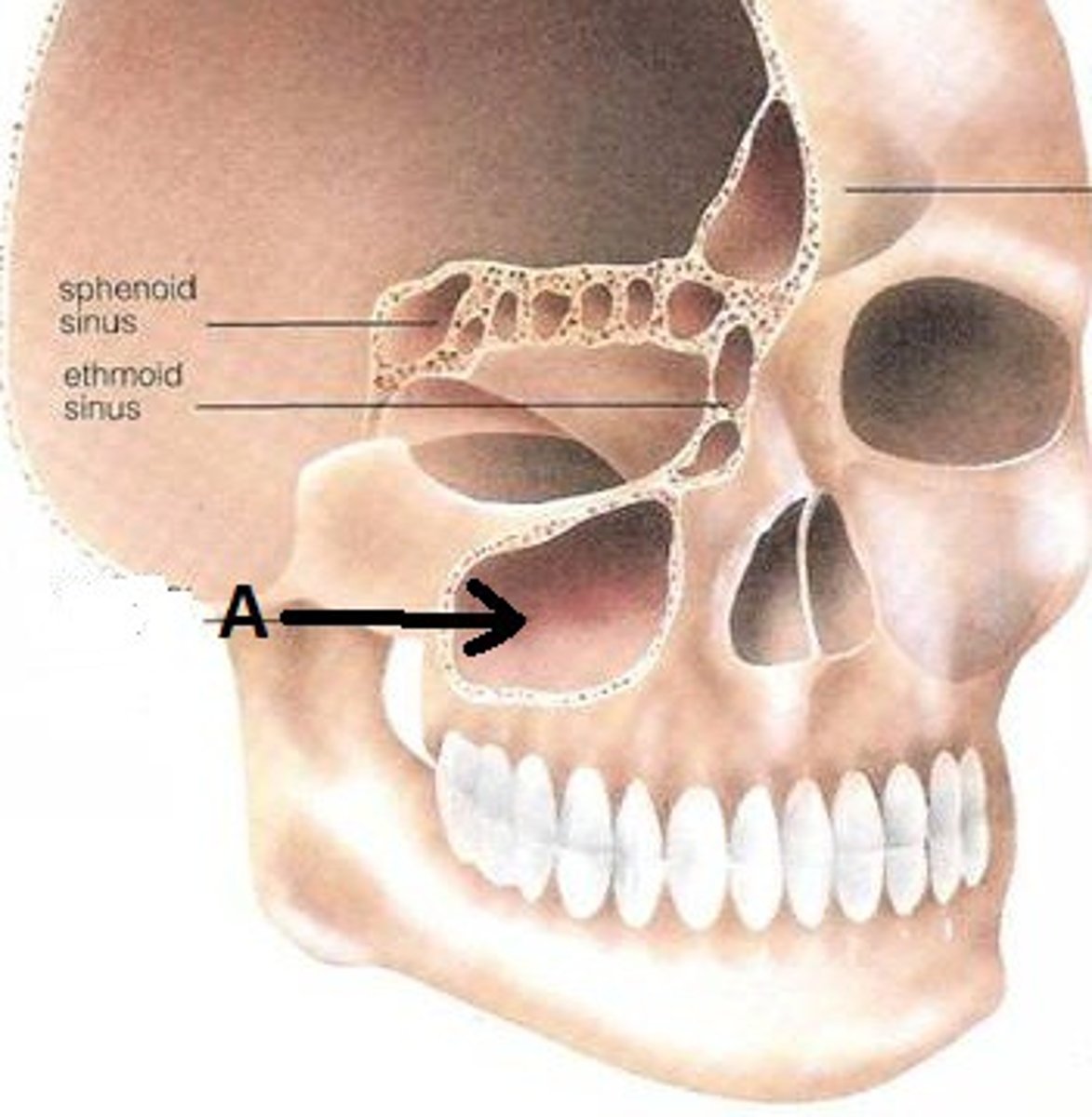
maxillary sinus
sinus on either side of the nasal cavity below the eyes
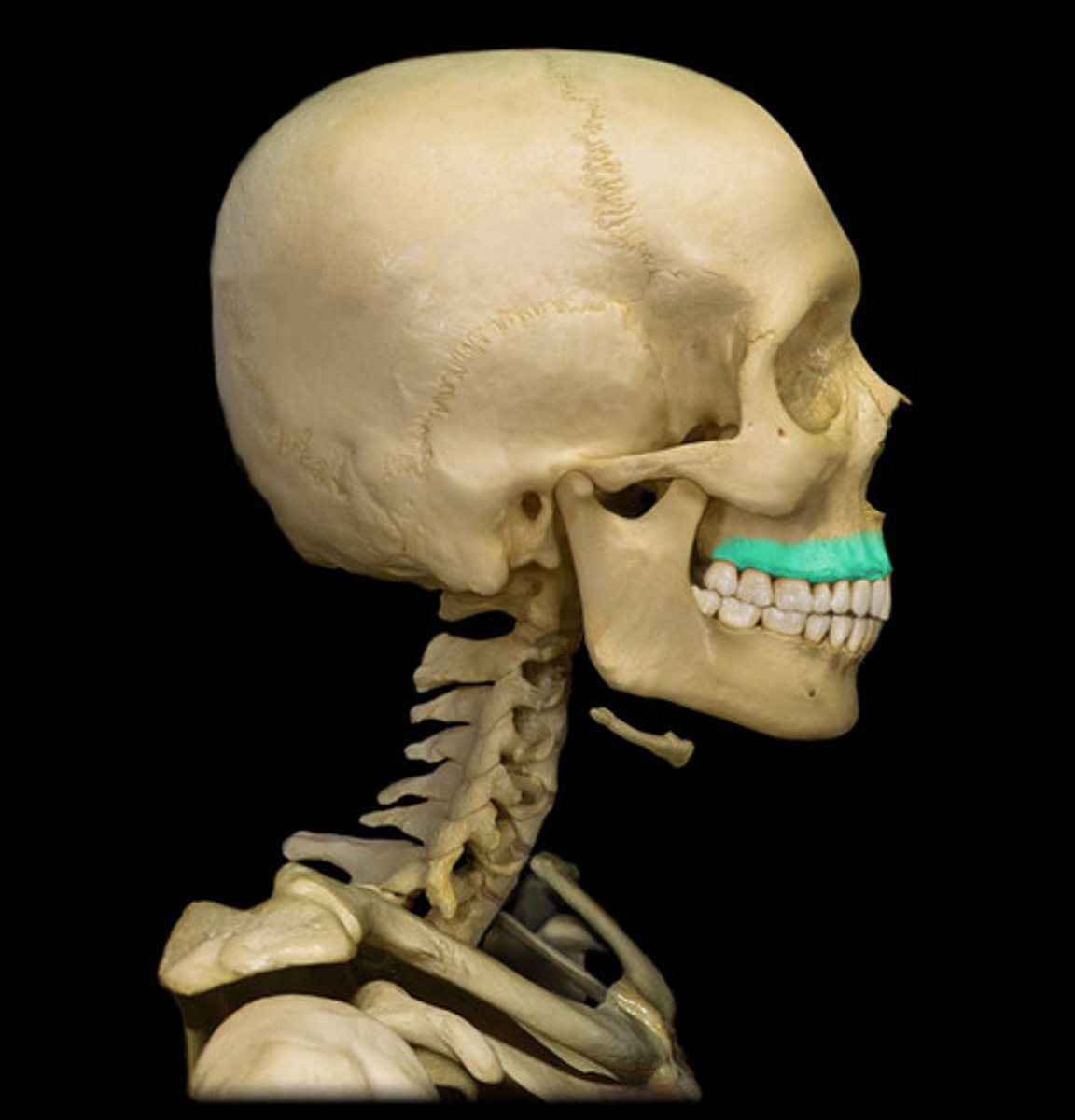
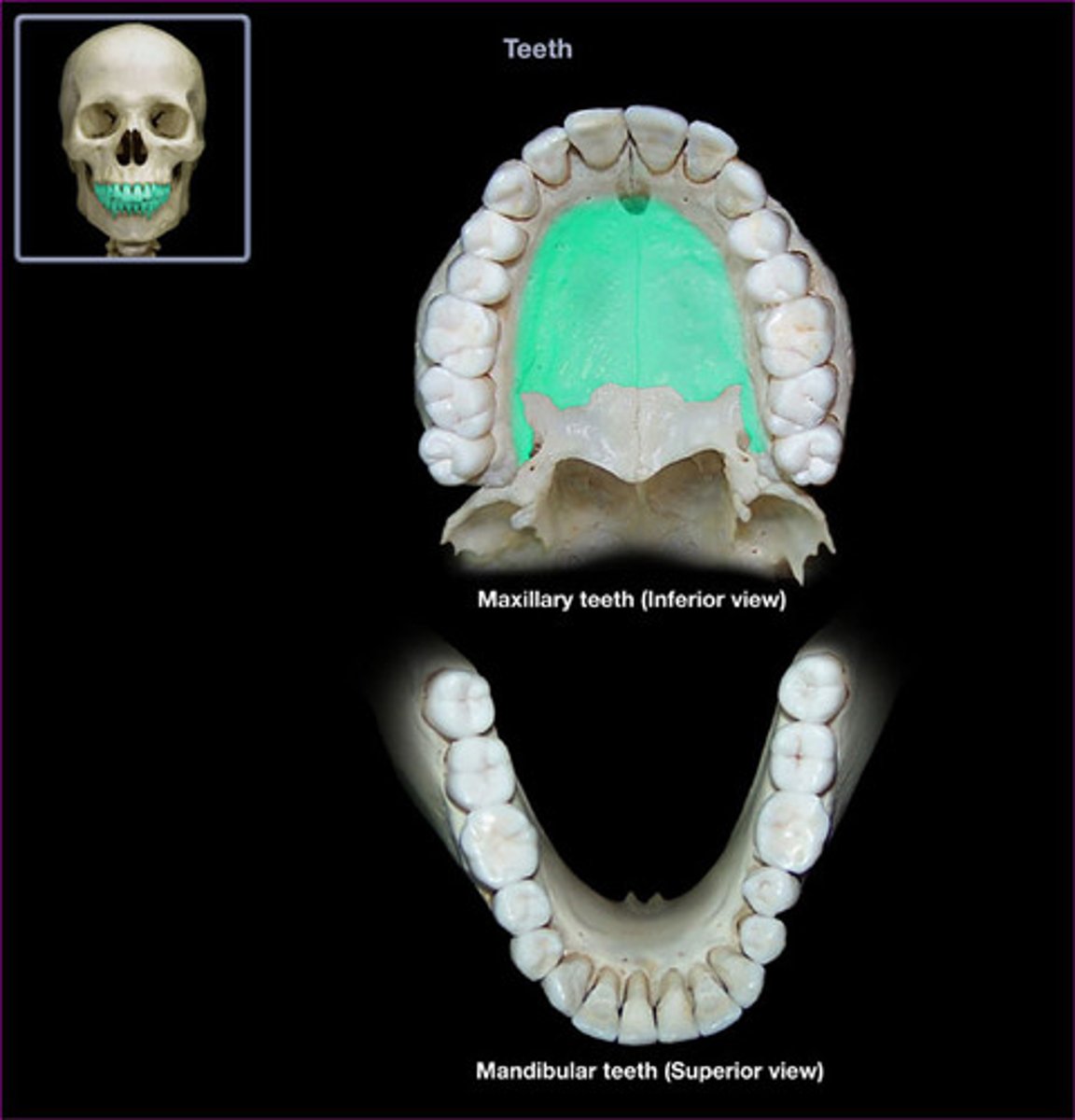
palatine process of maxilla
forms hard palate
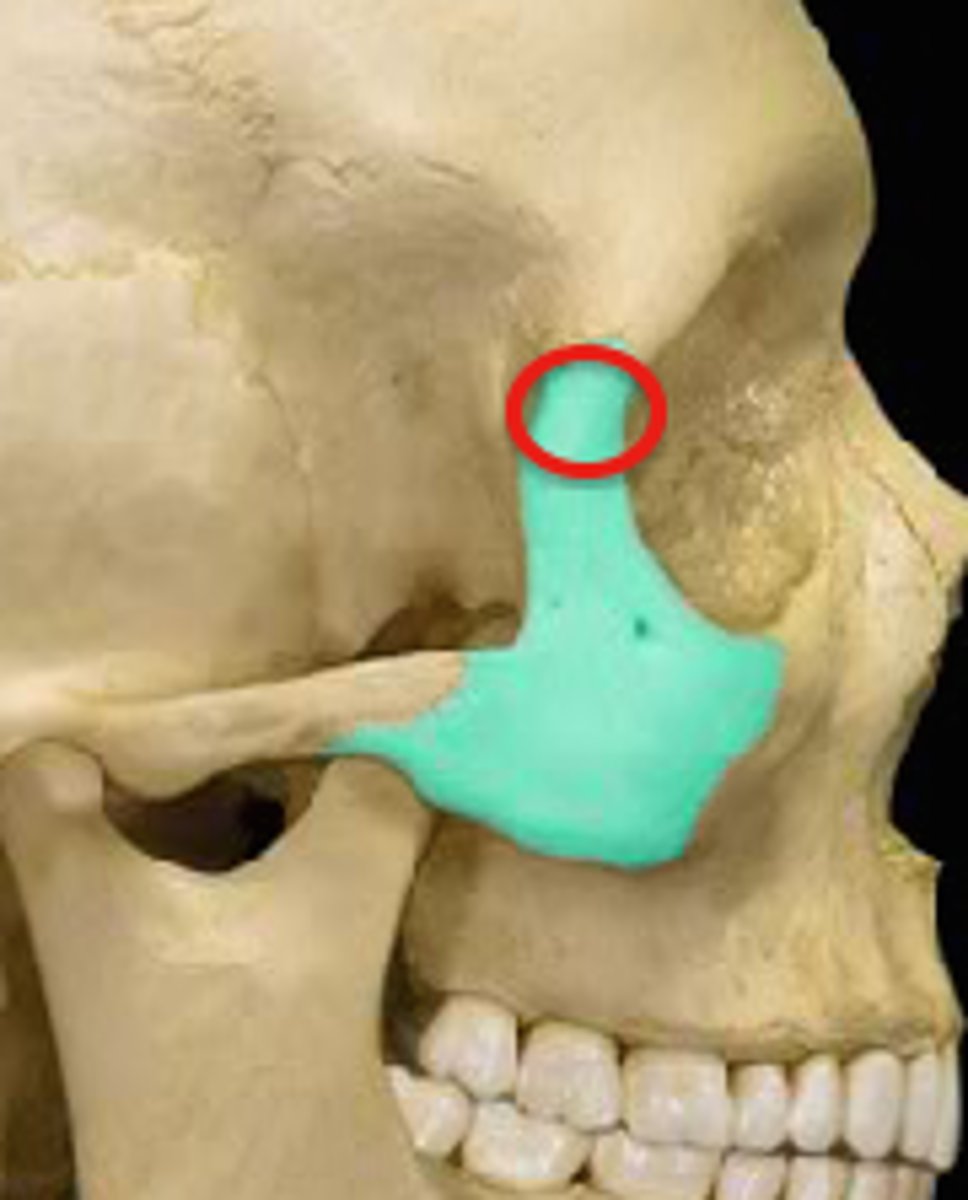
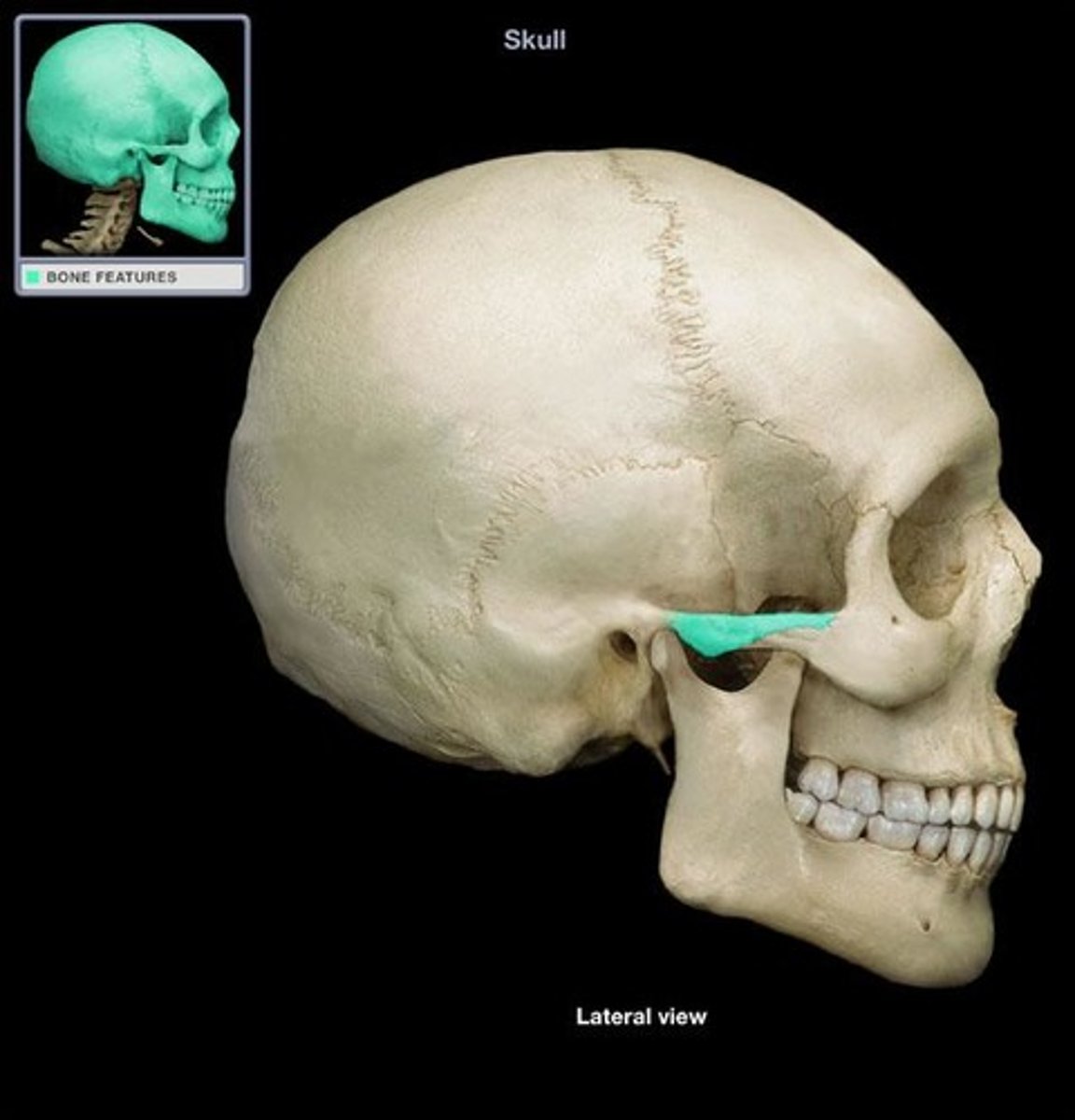
zygomatic frontal process
The lateral rim of the eye socket formed by a process of the frontal bone and a process of the zygomatic bone.
temporal process of zygomatic bone
short extension from the zygomatic bone that forms the anterior portion of the zygomatic arch
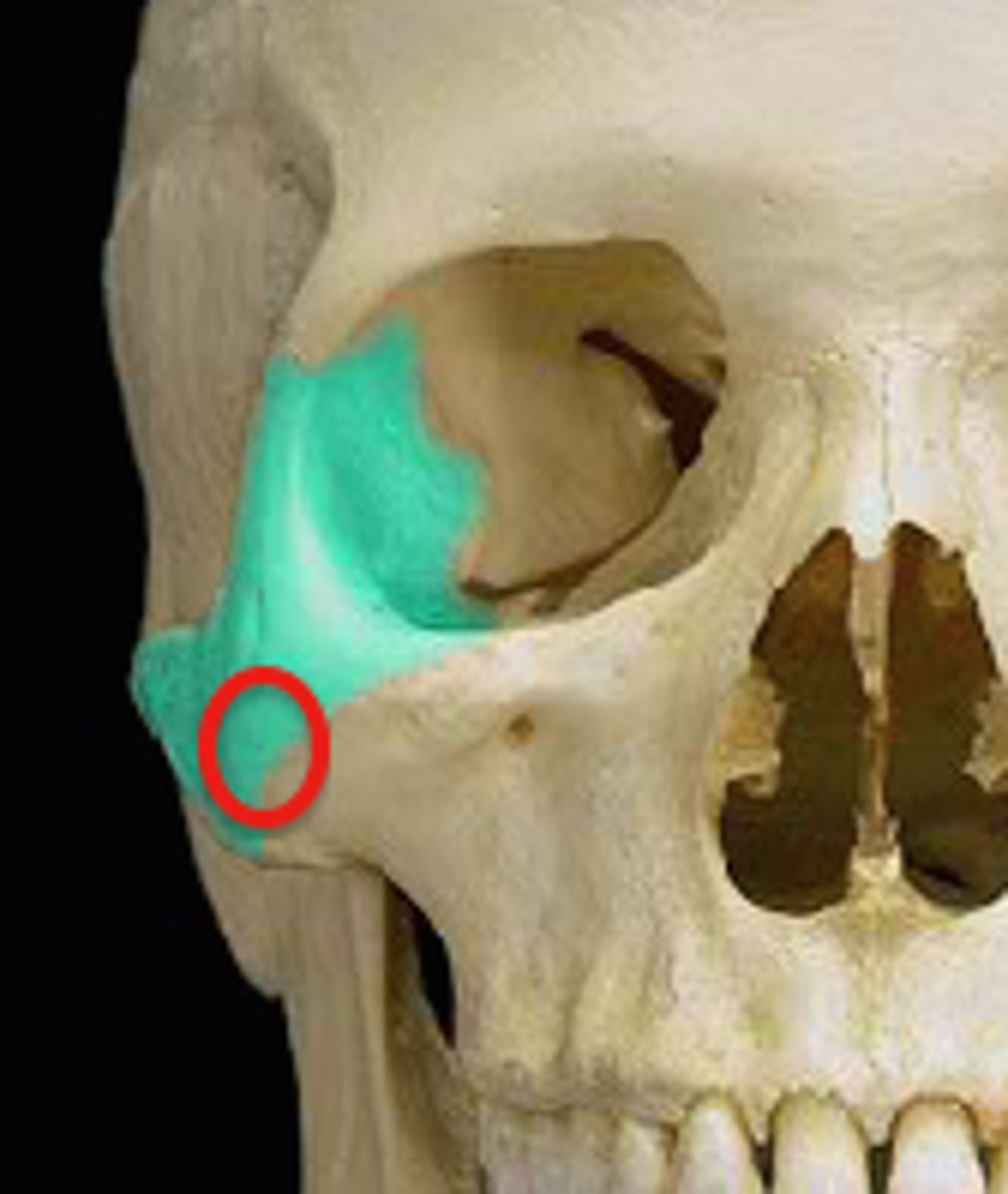
maxillary process of zygomatic bone
the part of the zygomatic bone that joins with the maxilla
horizontal plate of palatine bone
forms posterior part of hard palate

palatine bones
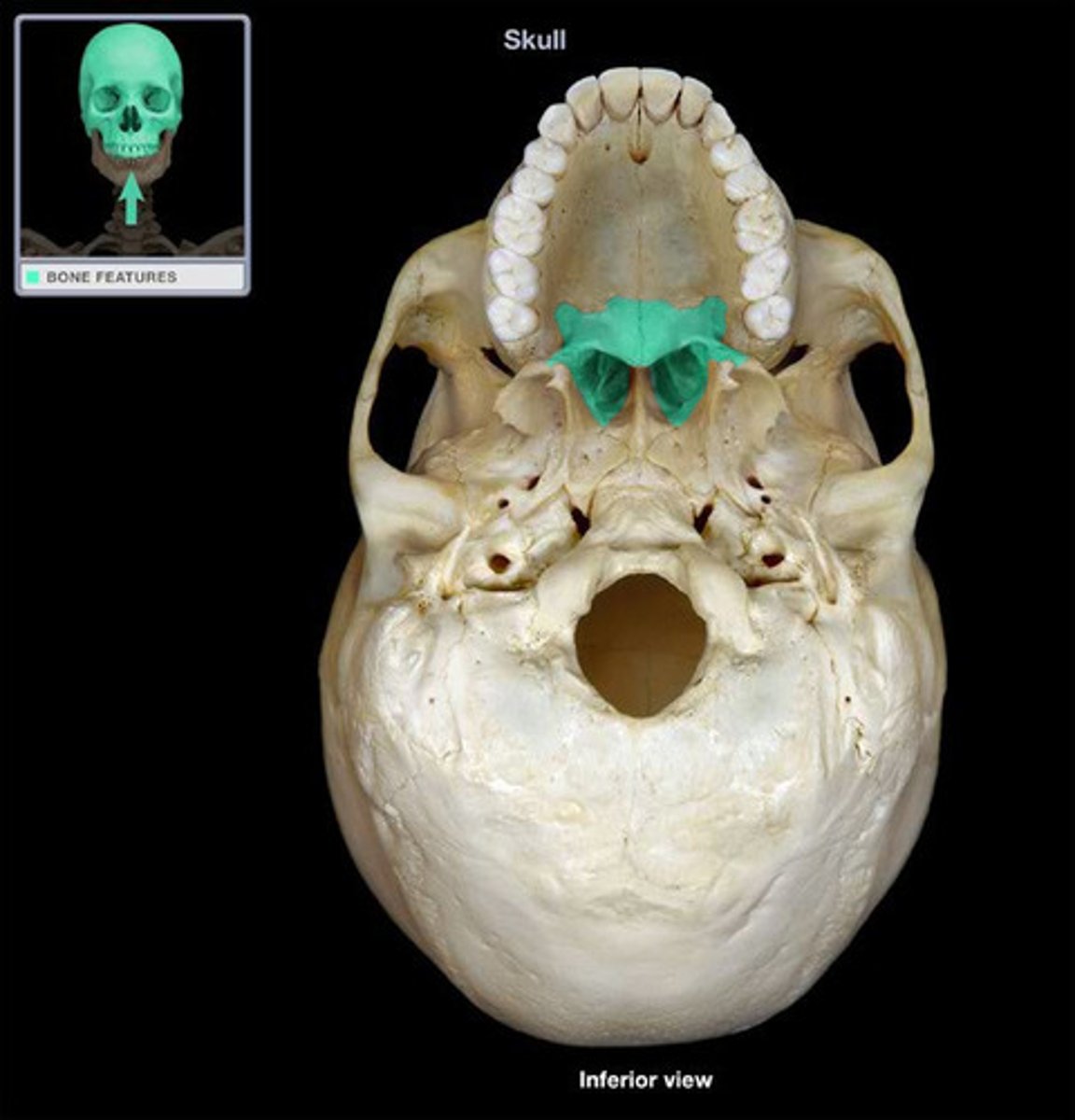
vomer bone
forms the base for the nasal septum
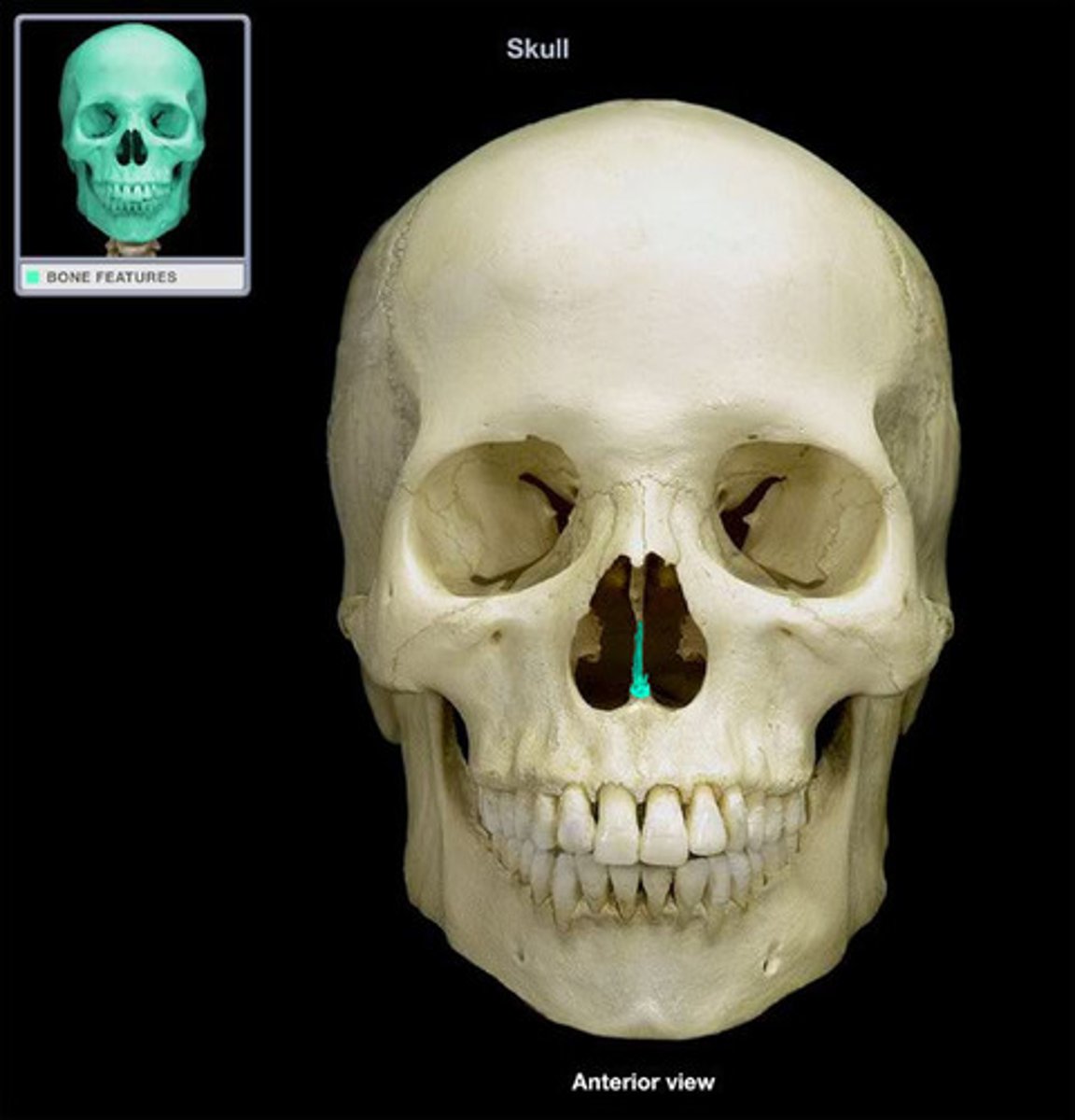
hyoid bone
a U-shaped bone in the neck that supports the tongue.
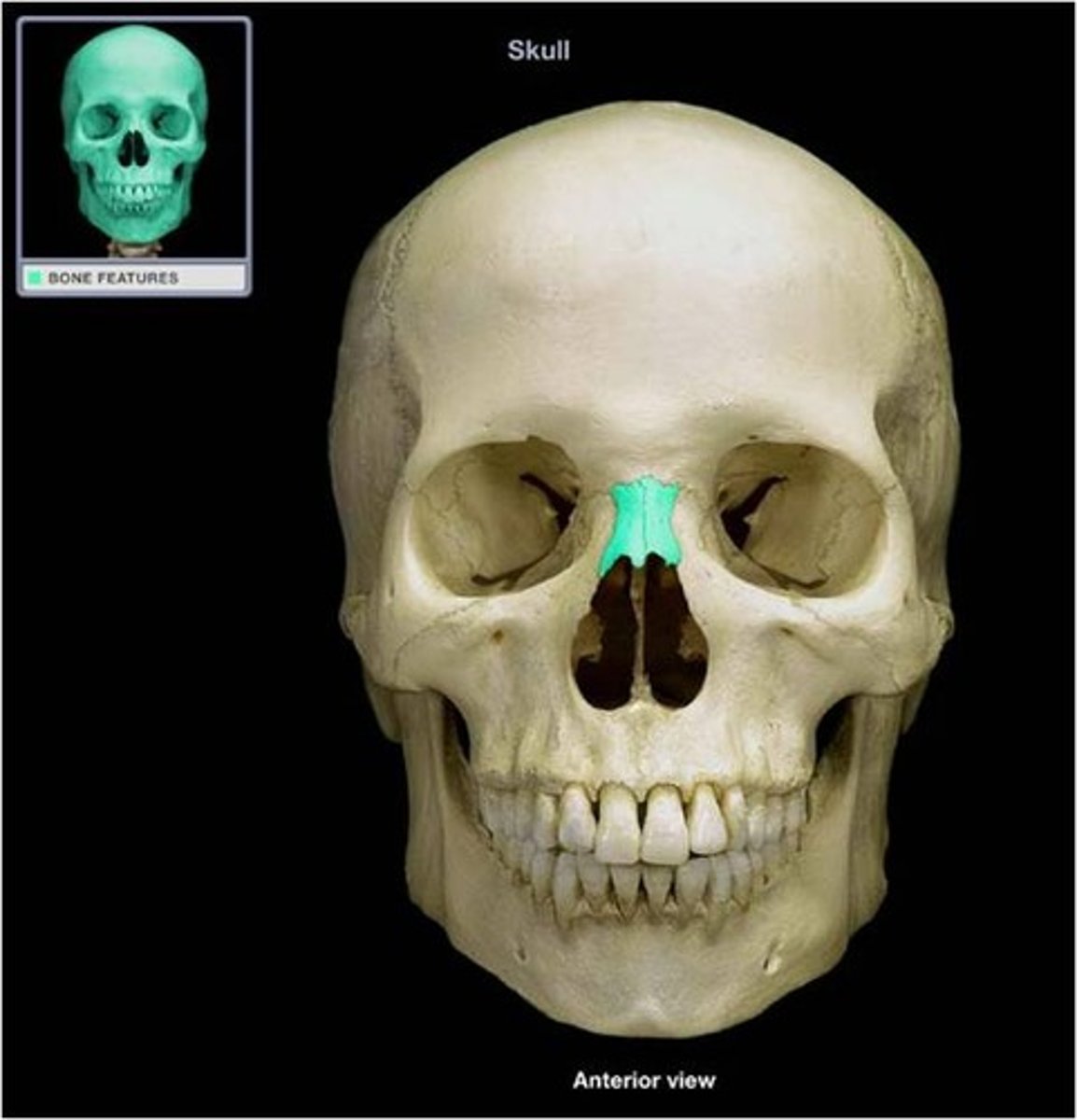
nasal bones
form the bridge of the nose
inferior nasal conchae
The lowermost scroll-shaped bones on the sidewalls of the nasal cavity.
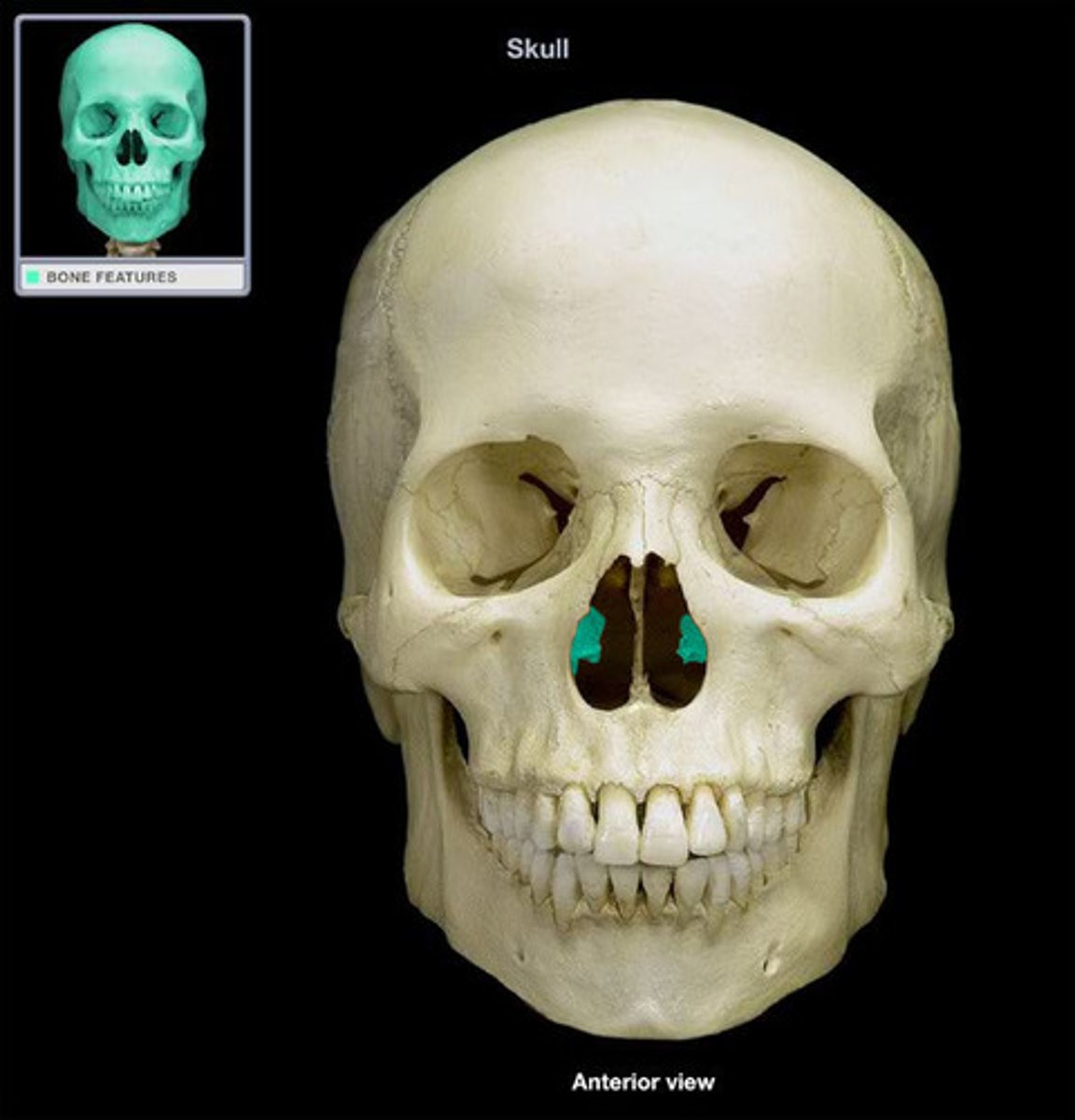
lacrimal bones
make up part of the orbit at the inner angle of the eye
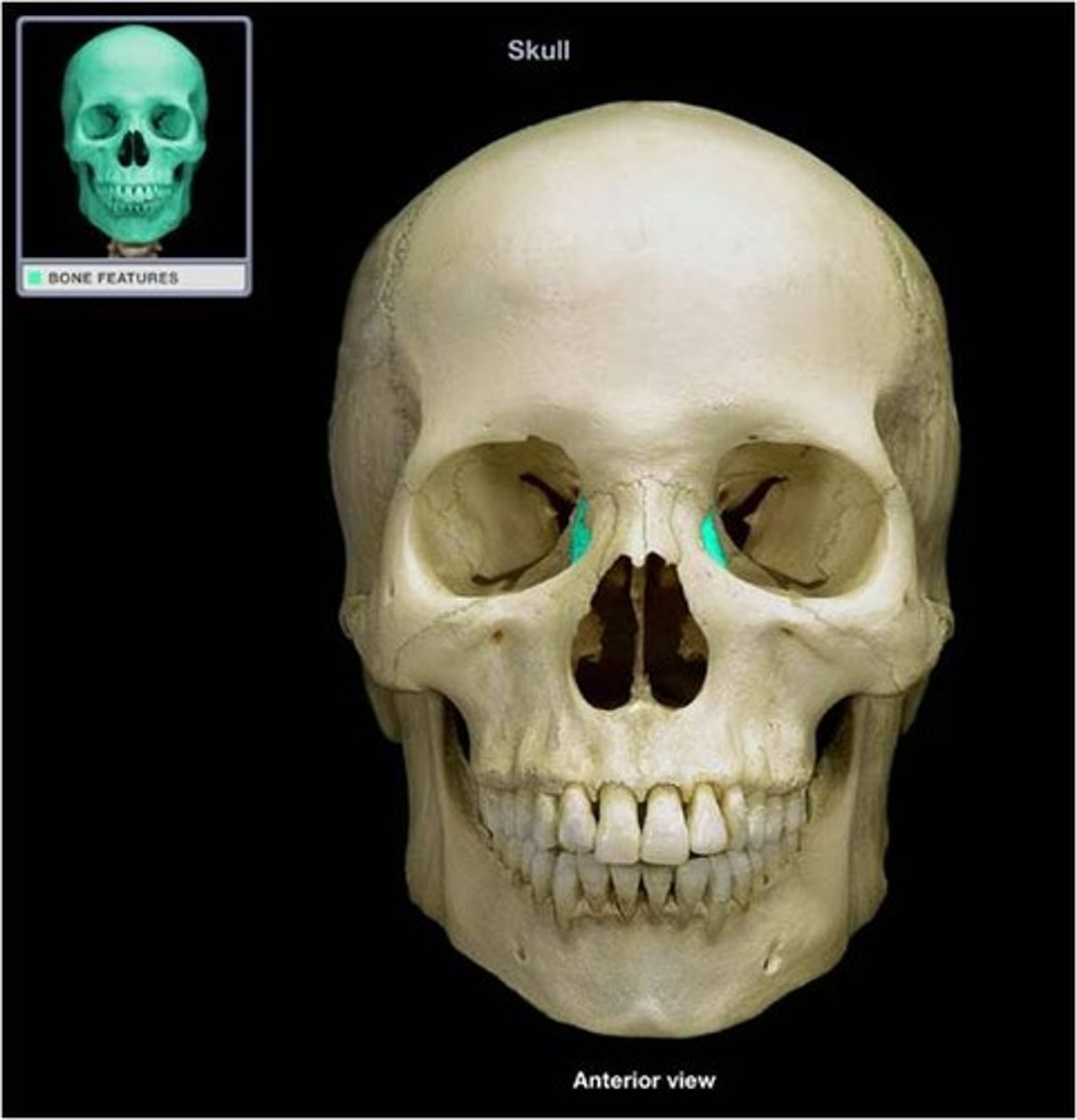
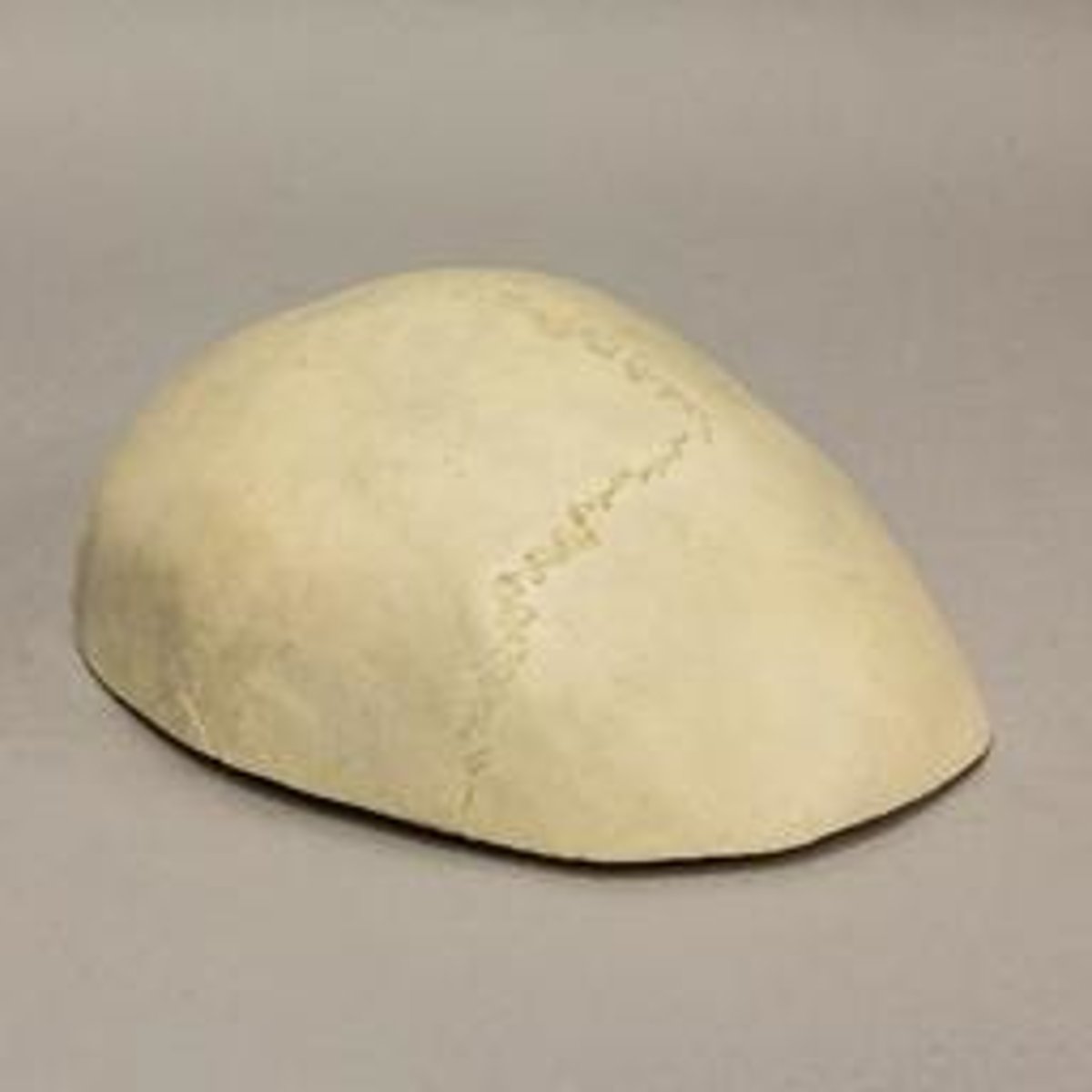
What is the calvarium?
skull cap, portion of neurocranium consisting of the frontal, parietal and occipital bones

What is the cranial base?
floor of the neurocranium, consisting of all the neurocranial bones
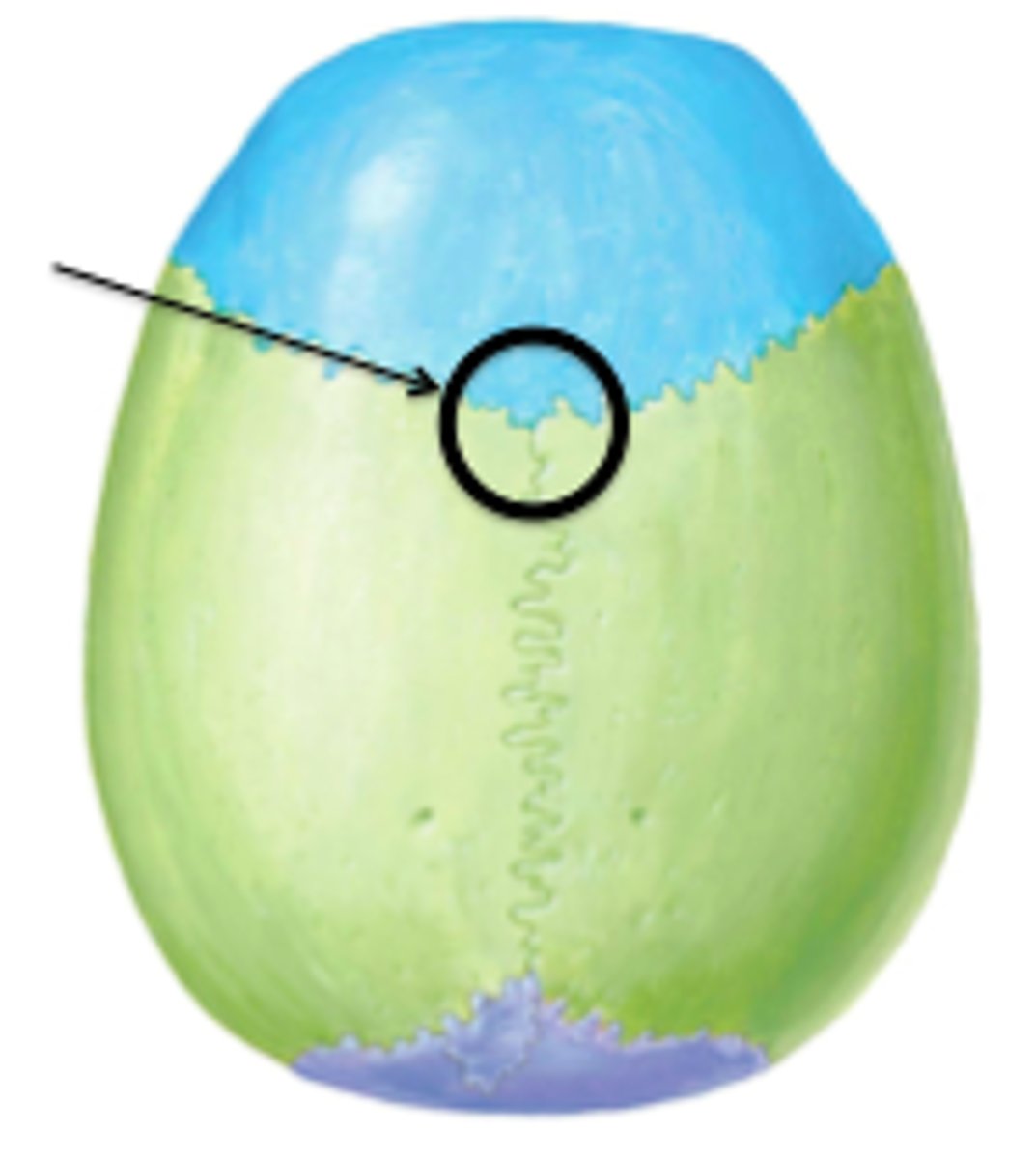
Why don't the cranial sutures fuse until age 25?
unfused sutures can move as the fetus passes through the birth canal and there are multiple periods of rapid brain growth through adolescence
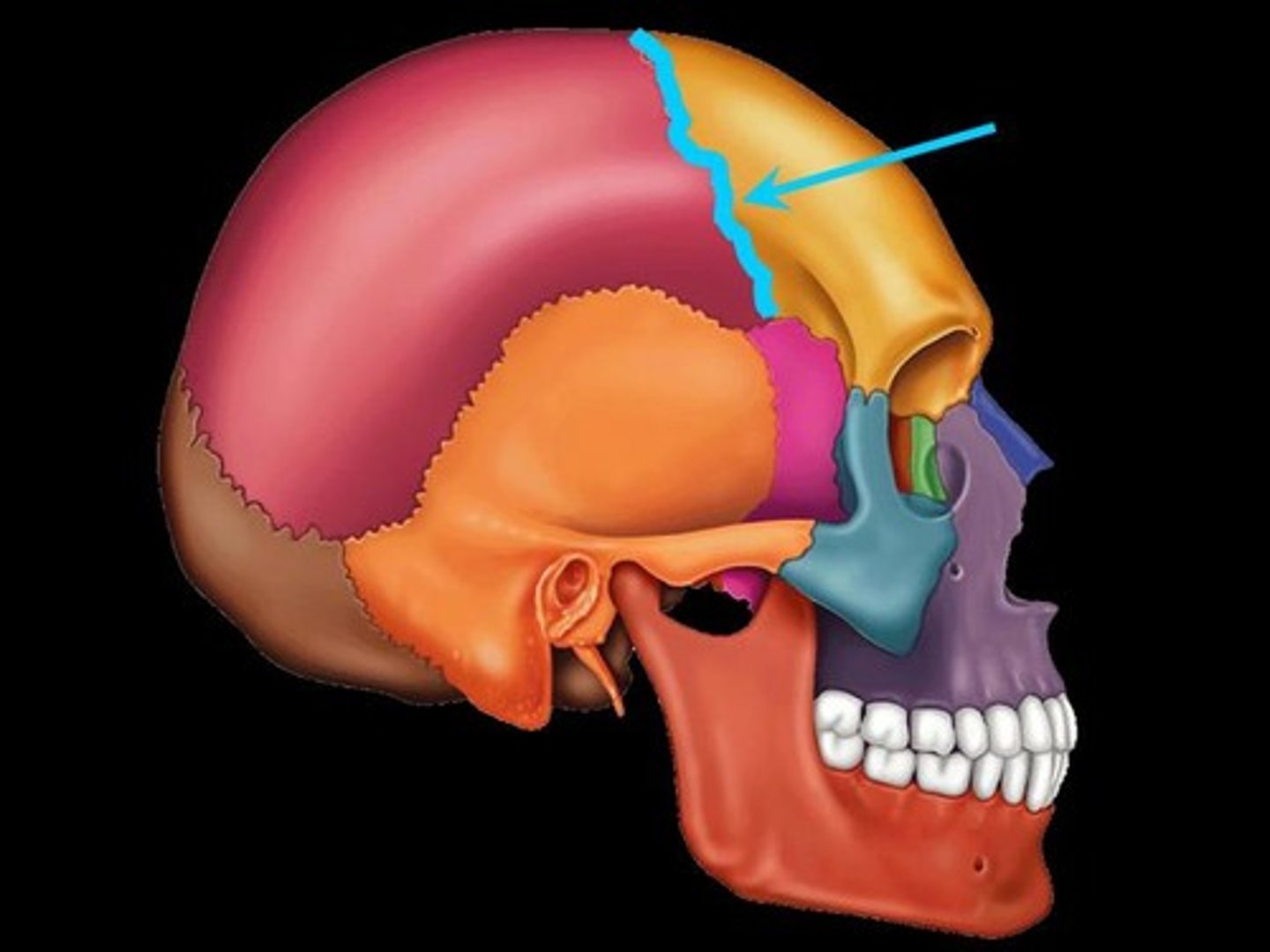
coronal suture
the suture between the parietal and frontal bones of the skull
Bregma
junction of coronal and sagittal sutures

sagittal suture
between the two parietal bones
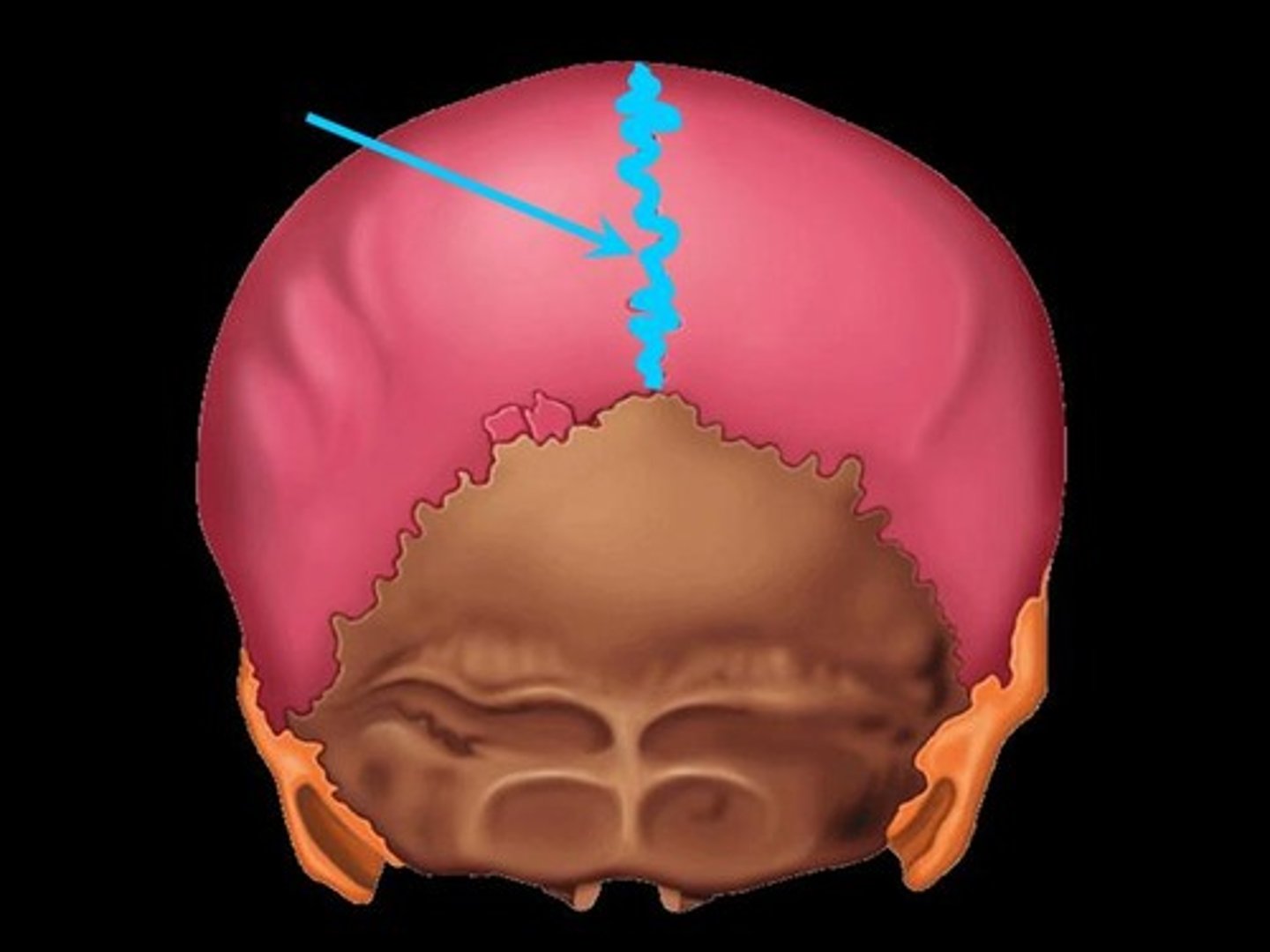
lambdoid suture
between parietal bones and occipital bone
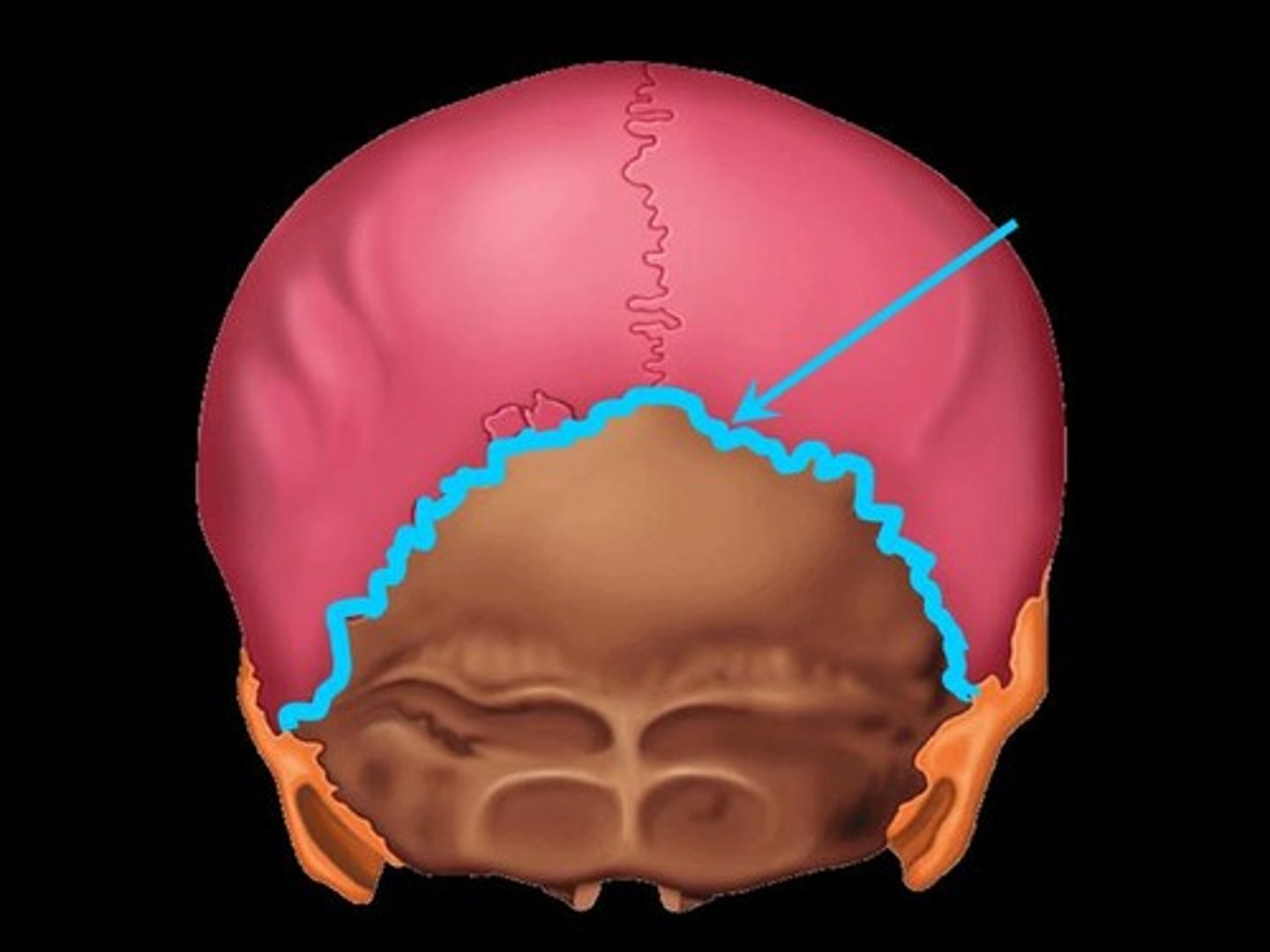
lambda
junction of sagittal and lambdoidal sutures
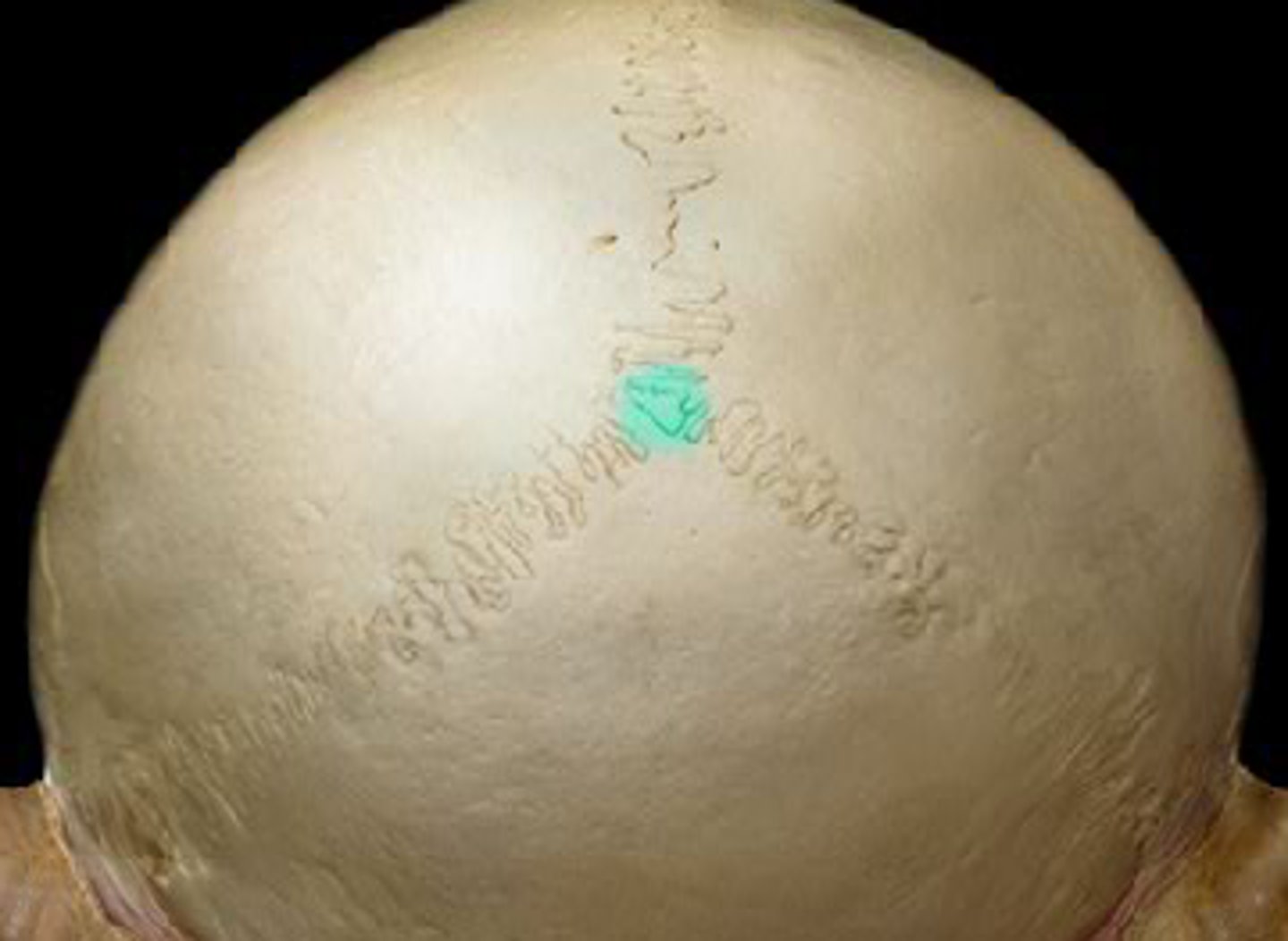
parietal foramen
parietal emissary vein passage
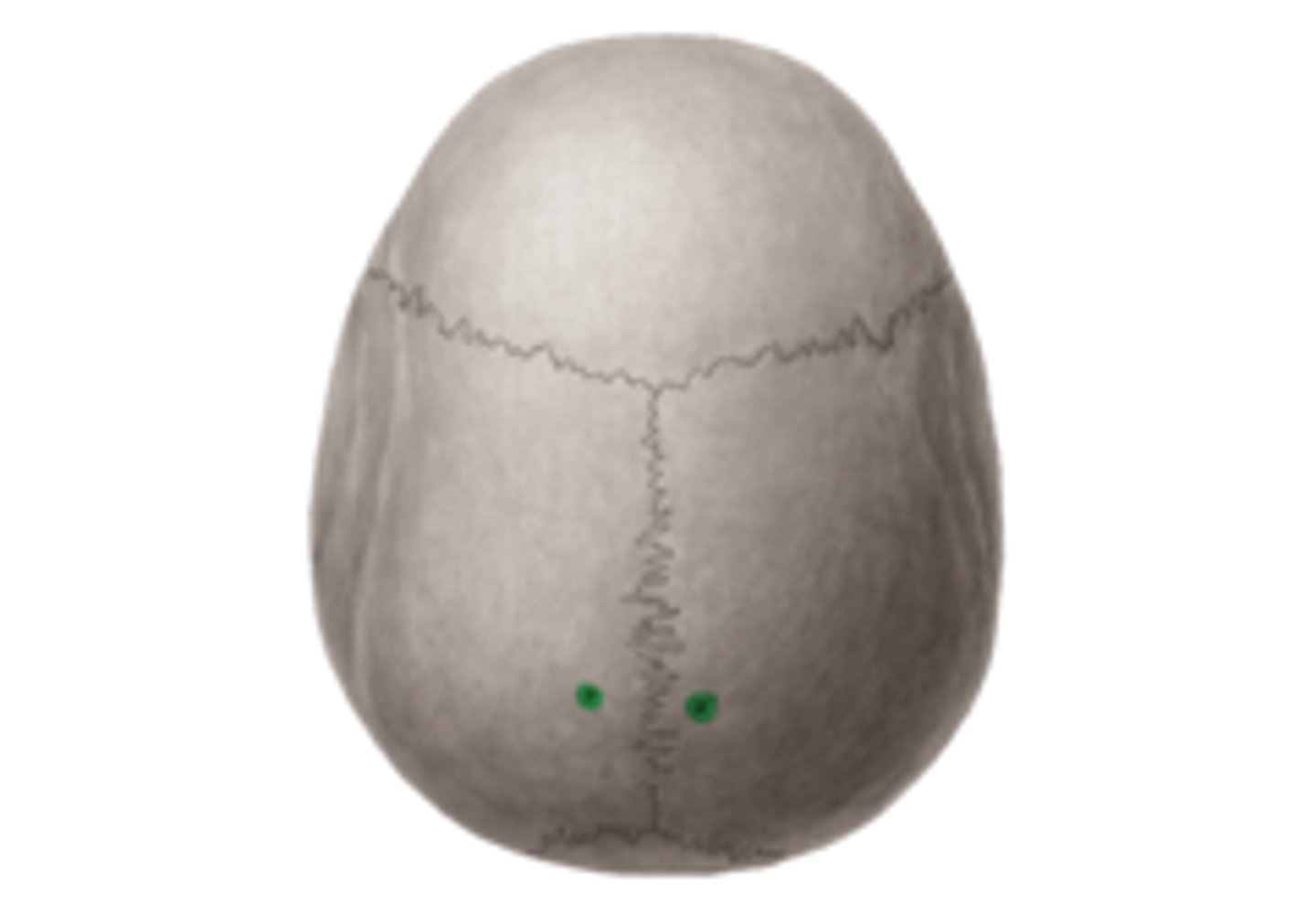
What are craniometric points (pterion, bregma, lambda) used for?
anatomical landmarks during surgeries
pterion
Junction of frontal, parietal, sphenoid, and temporal bones. Structural vulnerability as it is thin and middle meningeal artery is just deep, so hard head blow can result in subdural hematoma
What is different about the way the flat bones of the skull form and what is this process called?
intermembranous ossification, they don't have an intermediate cartilaginous stage
What is the diploe of a flat bone?
the spongy area between layers of compact bone
What are sinuses?
air pockets in the bones of the skull (pneumatized)
What makes sinuses vulnerable to infection?
They are continuous with the nasal cavity
What are the paranasal sinuses?
frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, maxillary
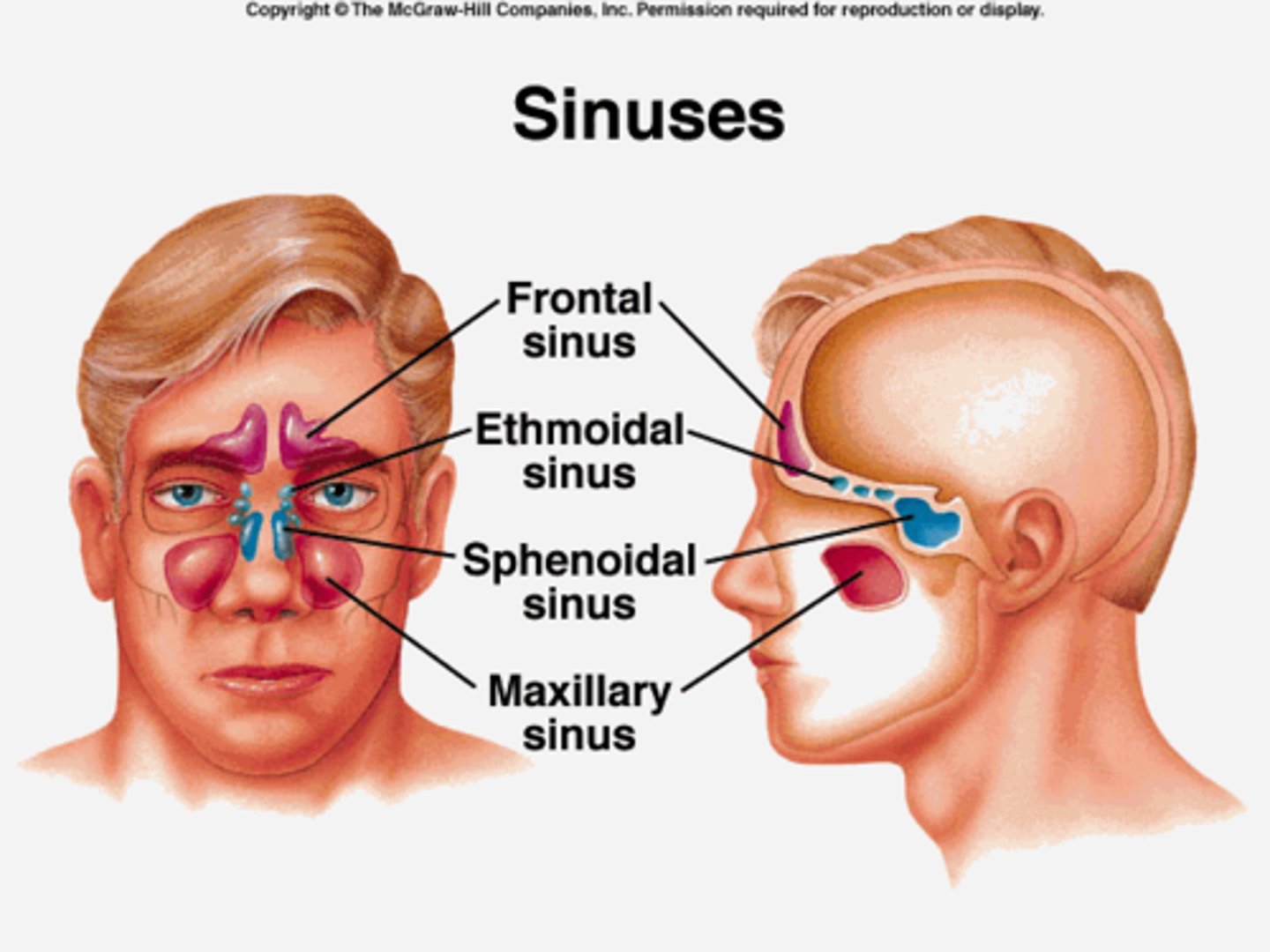
What is the purpose of having sinuses?
1. reduce weight of skull
2. humidify and heat inhaled air
3. increase resonance of speech
4. protect vital structures during facial trauma
What are the features of the neonate skull?
large cranium and small face, mandibular division that fuses into mandibular symphysis, prominent fontanelles
What are fontanelles?
fibrous membranes connecting the cranial bones, anterior, posterior, sphenoid and mastoid
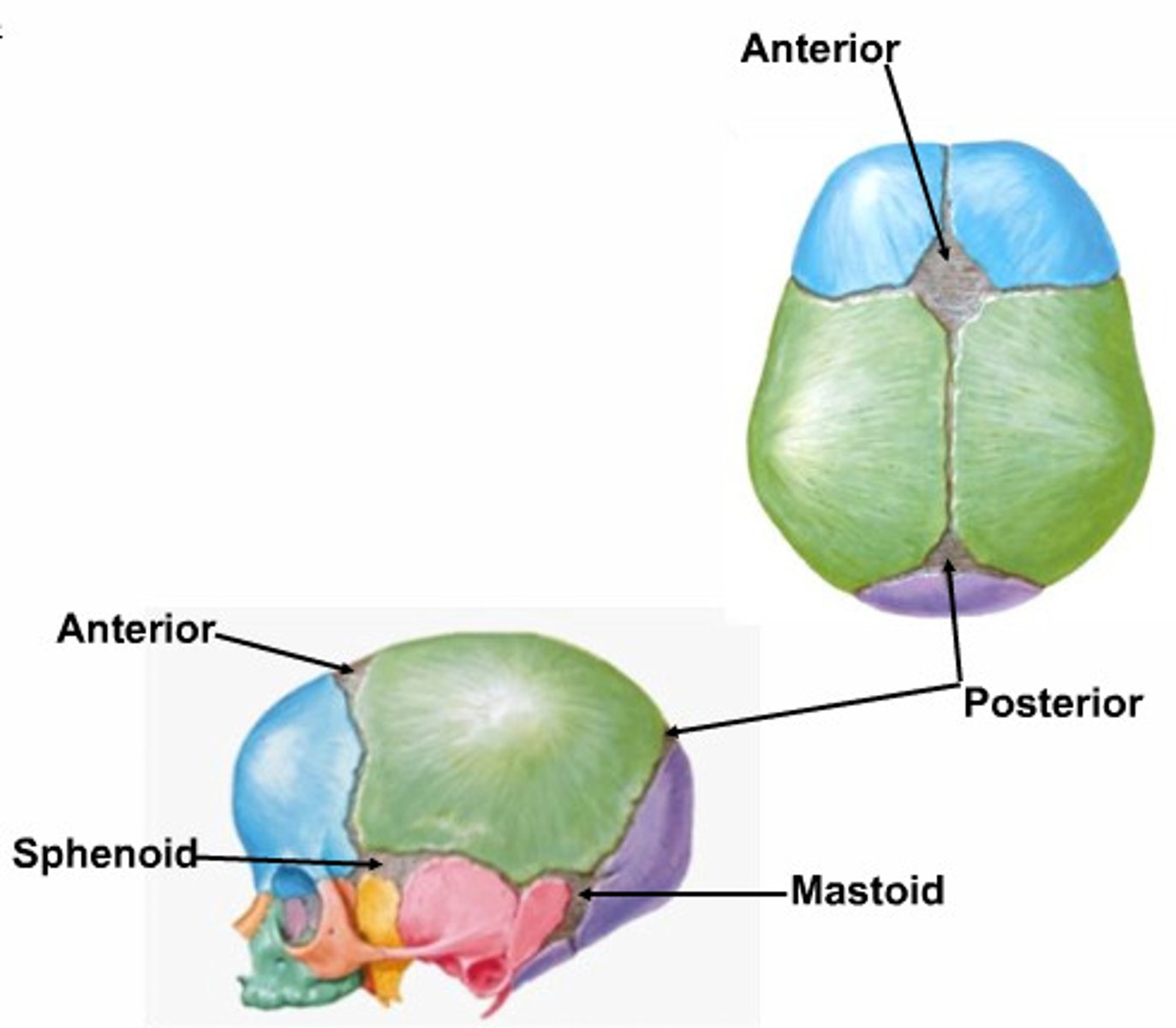
What might a raised anterior fontanelle mean?
brain inflammation
What might a sunken fontanelle mean?
dehydration
What is craniosynostosis and how is it corrected?
the premature ossification of 1 or more sutures resulting in bulging at the fontanelle at the contralateral side. Treated by helmets and or surgery
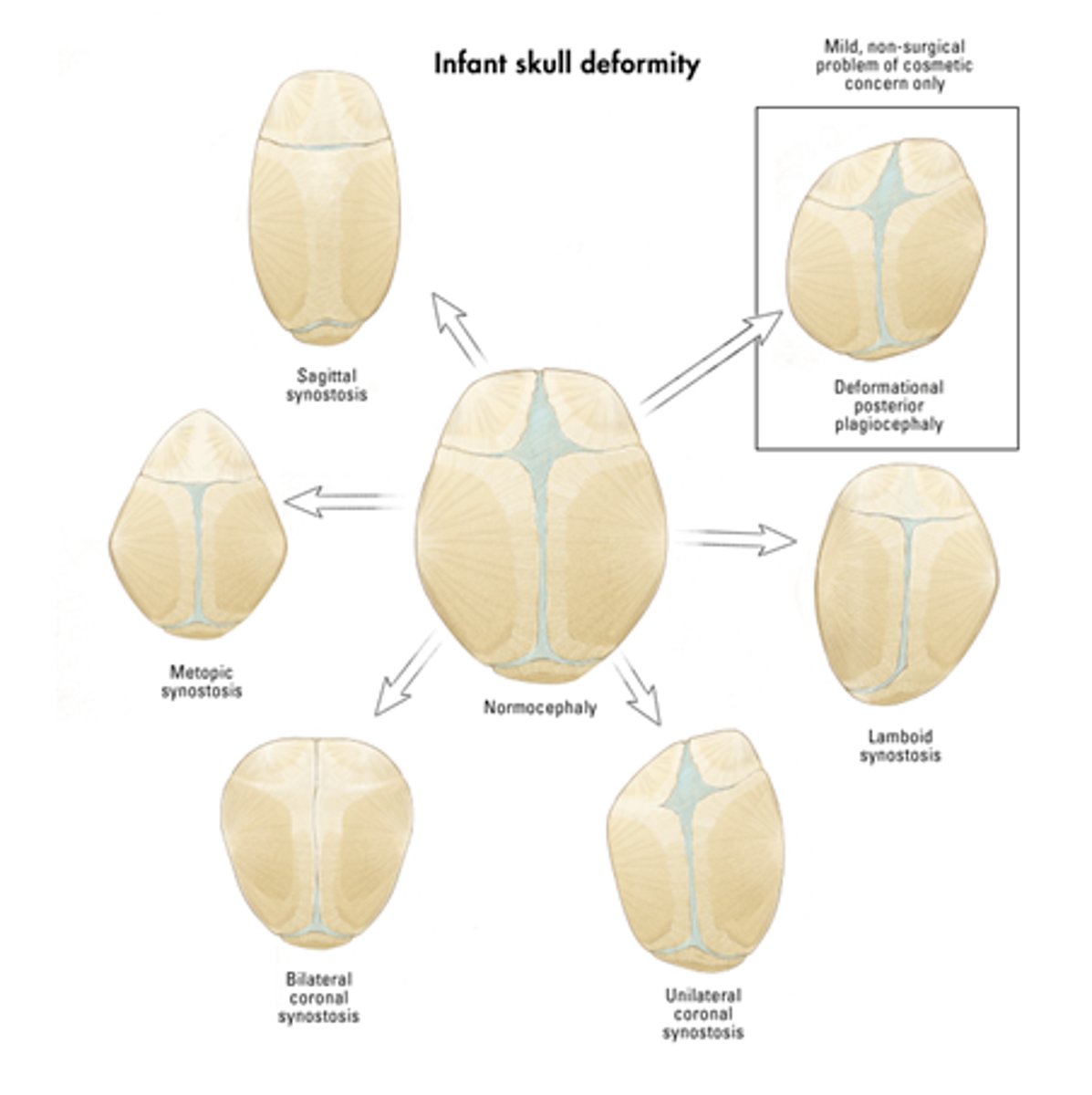
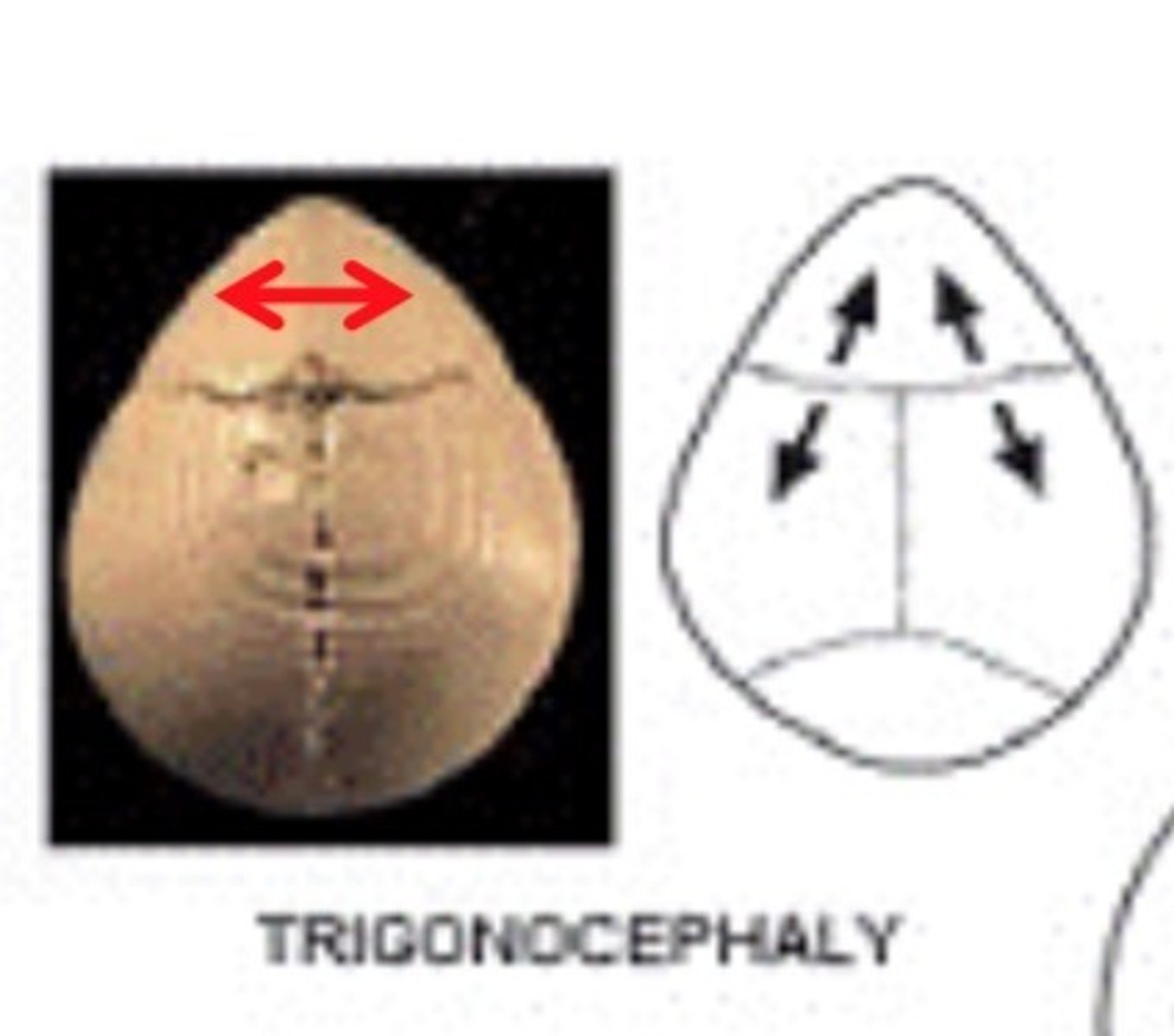
metopic craniosynostosis
fusion of the frontal suture resulting in elongation at the forehead
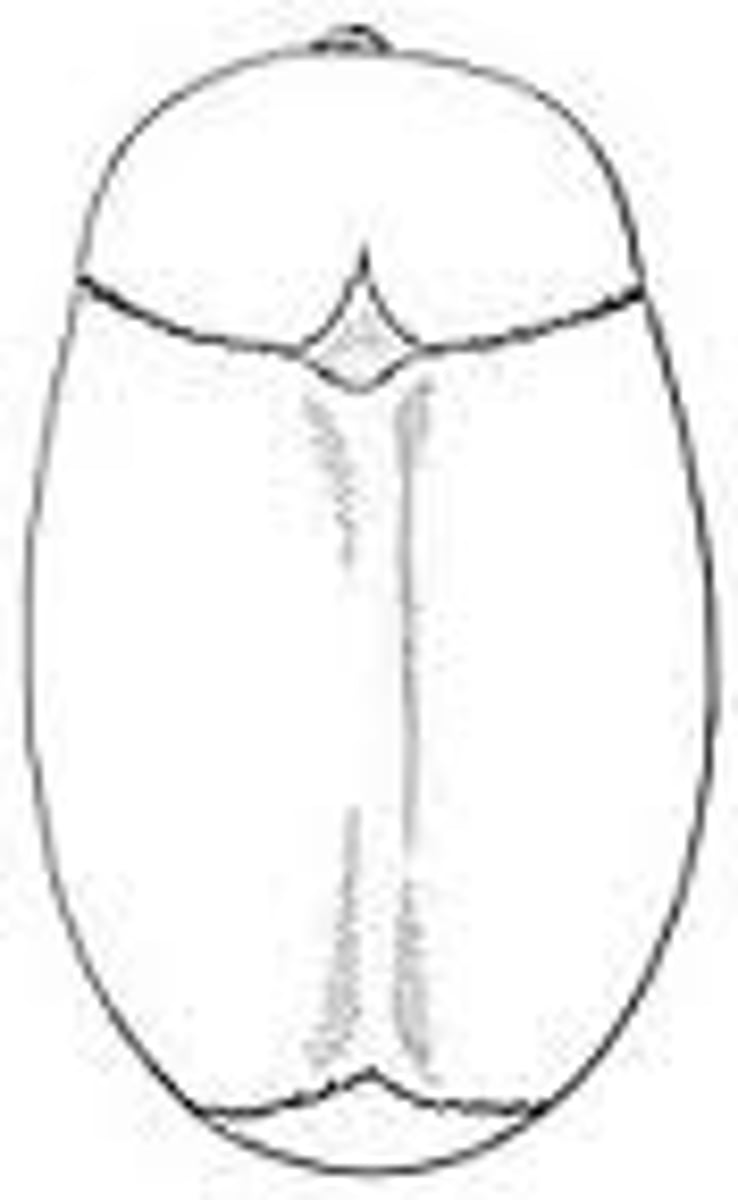
Sagittal Craniosynostosis
premature closure of sagittal suture resulting in posterior elongation
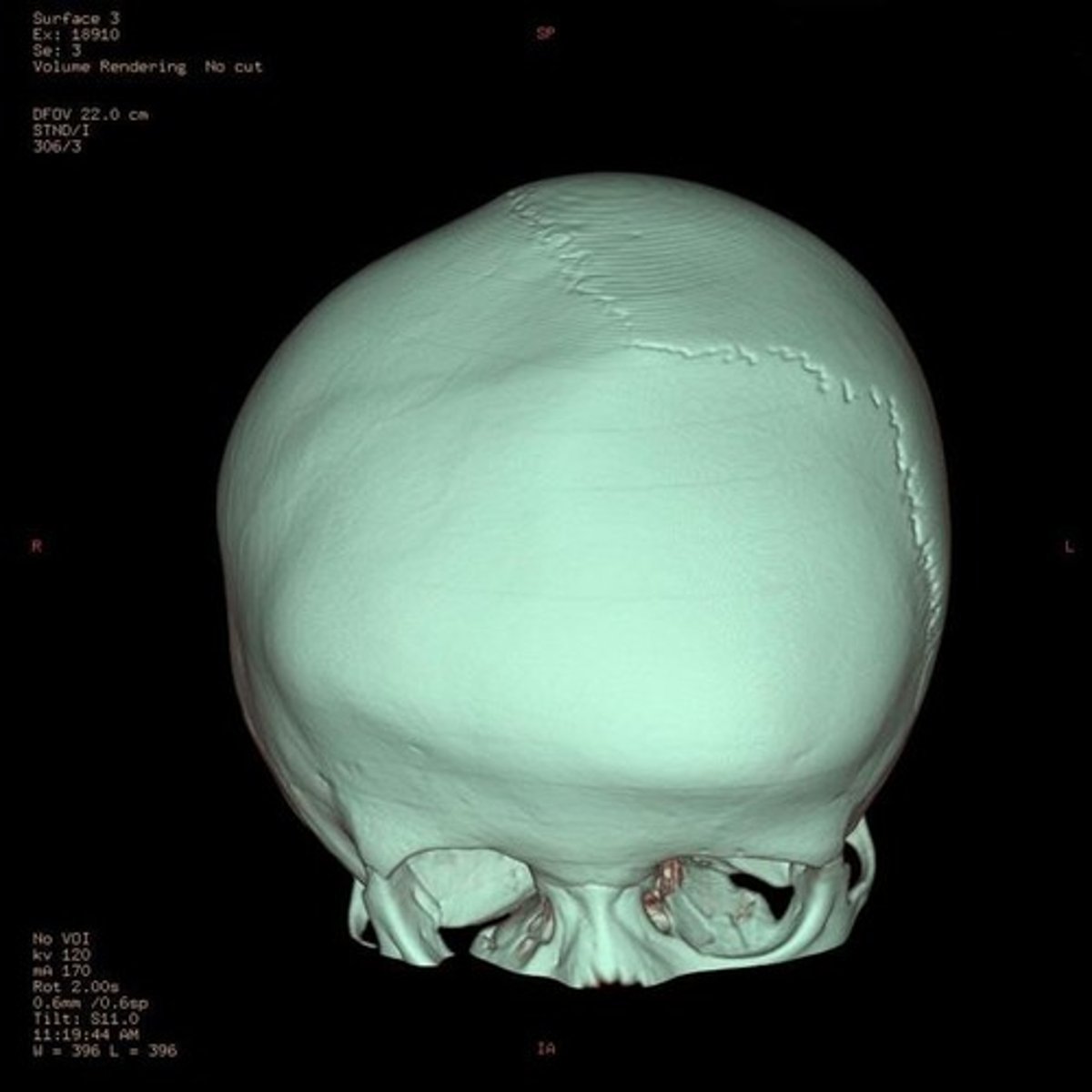
unicoronal craniosynostosis
one-sided closure of the coronal suture resulting in bulging at the contralateral forehead
lambdoid craniosynostosis
closing of one side of the lambdoid suture resulting in posterior bulging at the contralateral side