iris & pupil
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
what is the major role of the iris?
to dynamically react to ambient lighting conditions and adjust retinal illumination. the pupil also plays a role in the accommodative reflex.
more light =
close pupils
less light =
open pupils
Light from a distant object or infinity is parallel and can fall on the image plane or retina of an ______ eye.
emmetropic
for an object at near, the lens accommodates (_____ in power, _____ the focal length) to focus the object onto the retina
increases power, reduces focal length
when focused on a certain plane, objects in front of, or behind that plane will be out of focus generating a _______.
blur circle
a hole limiting the amount of light passing along an optical pathway placed near or at the lens
this hole is an aperture stop
has less effect on the field of view (this is because light rays coming from oblique sources can still pass through the lens)
aperture stop
a hole limiting somewhat the amount of light passing along an optical pathway placed at a distance from the lens
this hole is a field stop
has less effect on the amount of light passing through the lens
field stop
limits the field of view because light rays from oblique sources cannot pass through the hole in the stop to reach the lens
field stop
what limits the amount of light, but does not reduce the field of view?
an aperture stop
what has a very large effect on the field of view, but has little effect on limiting the amount of light?
a field stop (large effect on field of view)
what structure acts like an aperture stop?
the iris
the range of distance in object space within which an acceptable focus can be achieved
depth of field
the corresponding range of distance in image space inside the eye within which focus is acceptable
refers specifically to retinal image and perceived image clarity (absence of blur).
depth of focus
smaller pupil leads to ____ depth of field and depth of focus. (and vice versa)
larger
bending of light waves at the edges of an aperture (like pinhole or pupil)
diffraction of light
changes in focal points for light rays entering off-axis in a lens
spherical aberration
light of different wavelengths (colors) is refracted (bent) differently by a lens, thus focal point varies with color
chromatic aberration
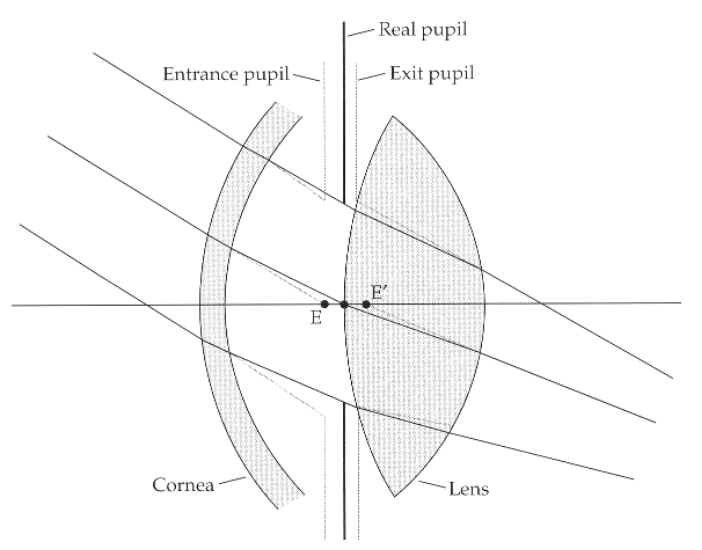
Because of refraction by the cornea, when light rays passing through the center or grazing the edges of the real pupil are projected back into object space towards an observer, the rays will appear to arise from a slightly larger pupil (1.13 times larger) that lies in a plane in front (0.5 mm in front) of the real pupil. This apparent pupil is the entrance pupil! It has a center E in the diagram
entrance pupil, 1.13 times larger
A similar construction taking refraction by the lens into account shows the exit pupil (1.03 times larger than the real pupil) and behind the real pupil (0.8 mm behind the real pupil) It has a center E’ in the diagram.
exit pupil, 1.03 times larger
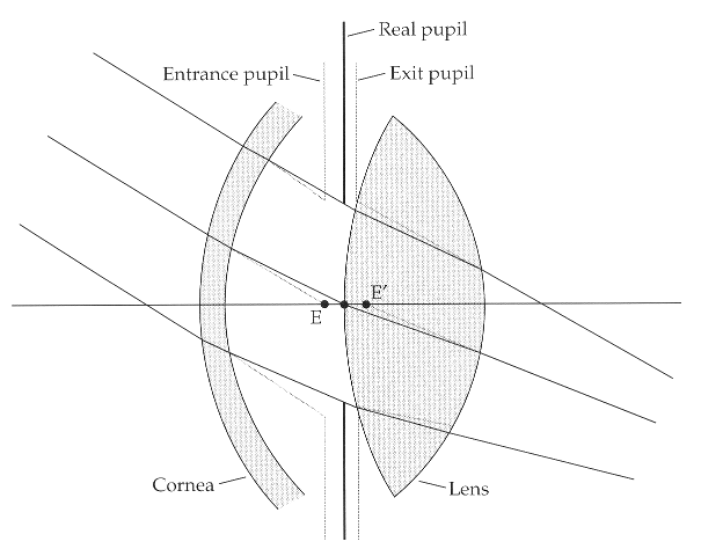
which pupil size is measured in the clinic? what is the size range?
entrance pupil size, 2-8 mm in young healthy adults depending on ambient illumination
if there is over a 100,000 fold change in lighting, the retina only sees about a 10,000 fold change . . .
why? what does this demonstrate?
because the pupil diameter will change! this shows how the iris dynamically responds to ambient lighting conditions.
when you change your point of focus from a distant to a near object, what 3 things will occur? **triad of the near response**
1) increase lens curvature by accommodation
2) convergence (eyes rotate inward nasally to align a target on the fovea-extraocular muscle)
3) pupil constricts
how does the convergence of the near response change over the range of accommodative responsiveness? what is the slope called?
increases linearly. slope = Accommodative Convergence/Accommodation ratio (AC/A)
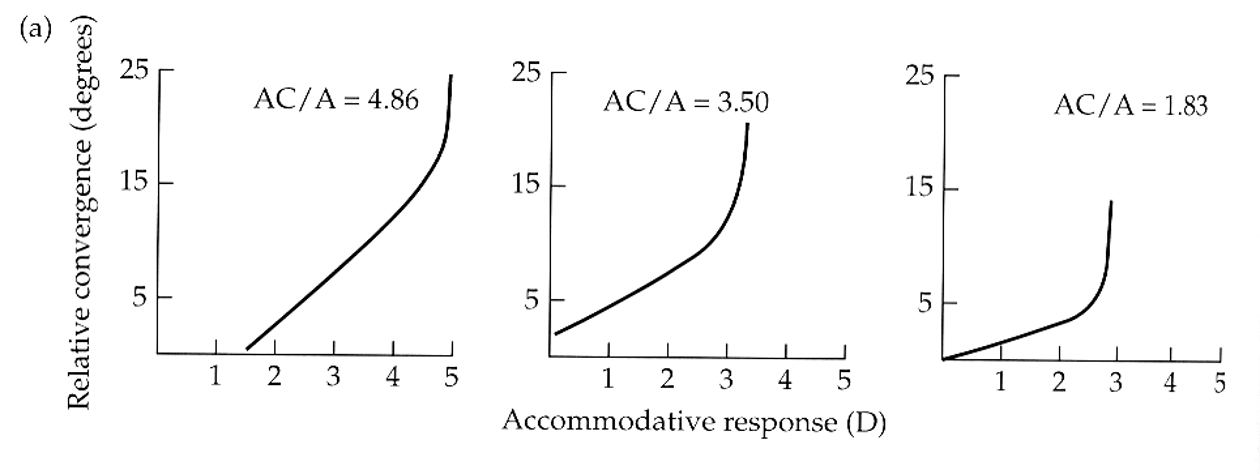
during the near response, how does the pupil size change with accommodative response? what is the slope called?
decreases linearly until the accommodative response can no longer respond. slope = pupil size/accommodation ratio (P/A)
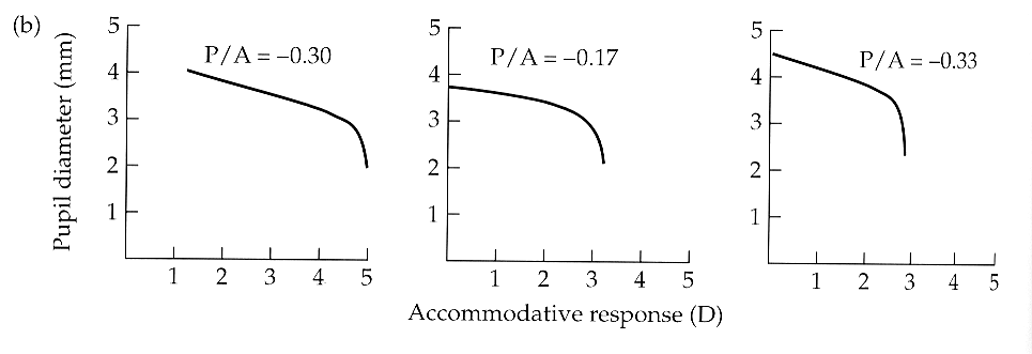
for the same three subjects, pupil diameter _____ with convergence angle.
reduces linearly
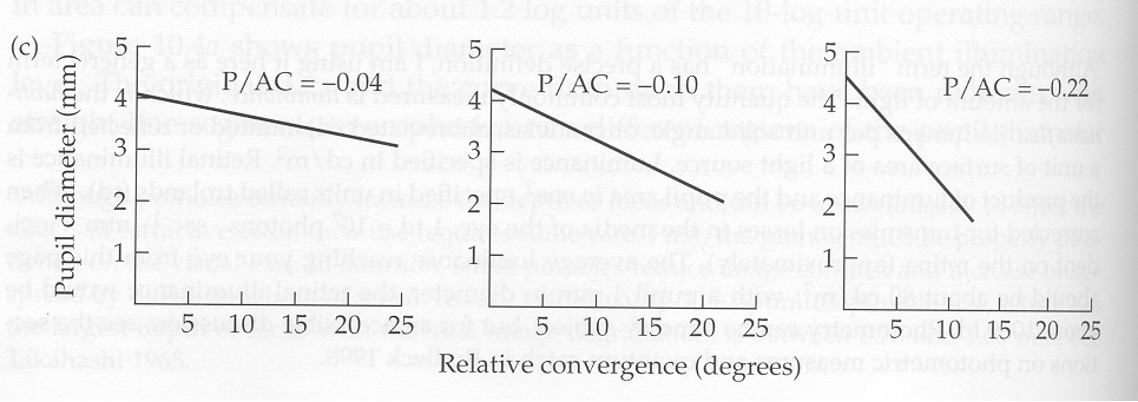
does the P/A ratio change with age? how?
yes, the P/A ratio changes more as we age. it gets more negative overtime.
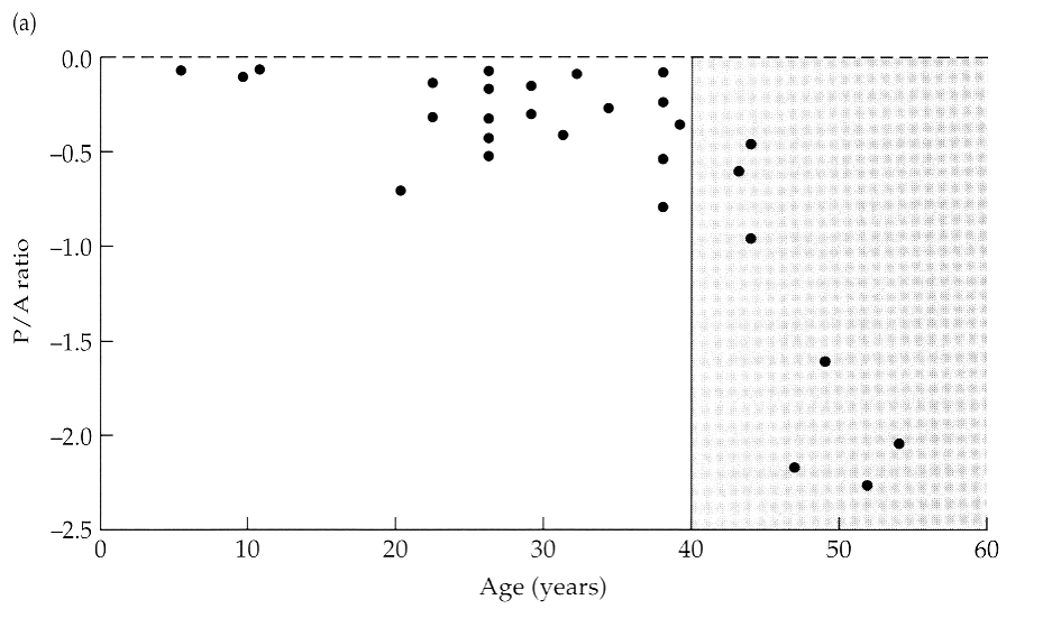
mismatched iris color
heterochromia
condition where a person has different colored eyes
caused by a variation in the amount of melanin, the pigment that gives iris its color
can be genetic, congenital or acquired (via trauma, eye disease or certain medications)
heterochromia
an arc or ring of white or gray coloration around the outer edge of the iris denotes deposition of fat or cholesterol within the cornea. this usually age-related, and may indicate ______.
hyperlipidemia
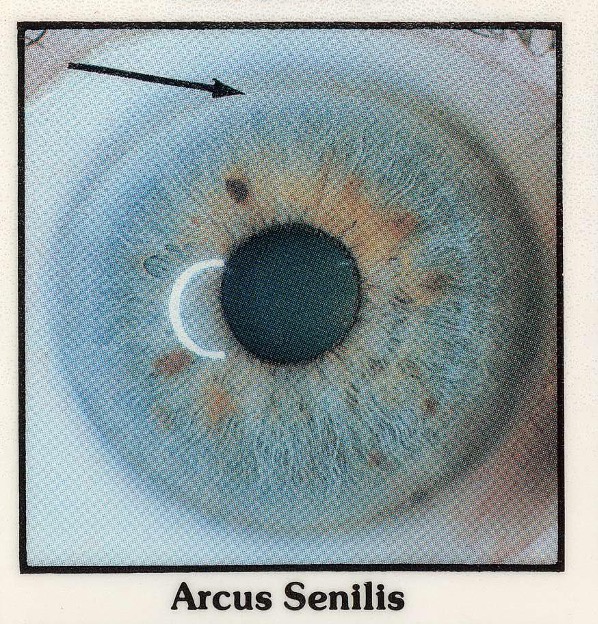
what is the arrow pointing to?
a ring of white/gray coloration, indicating cholesterol/fat deposition within the cornea (could be hyperlipidemia)
what is the general histology of the iris?
very spongy sheet with strong pigmentation
a circular blackout curtain
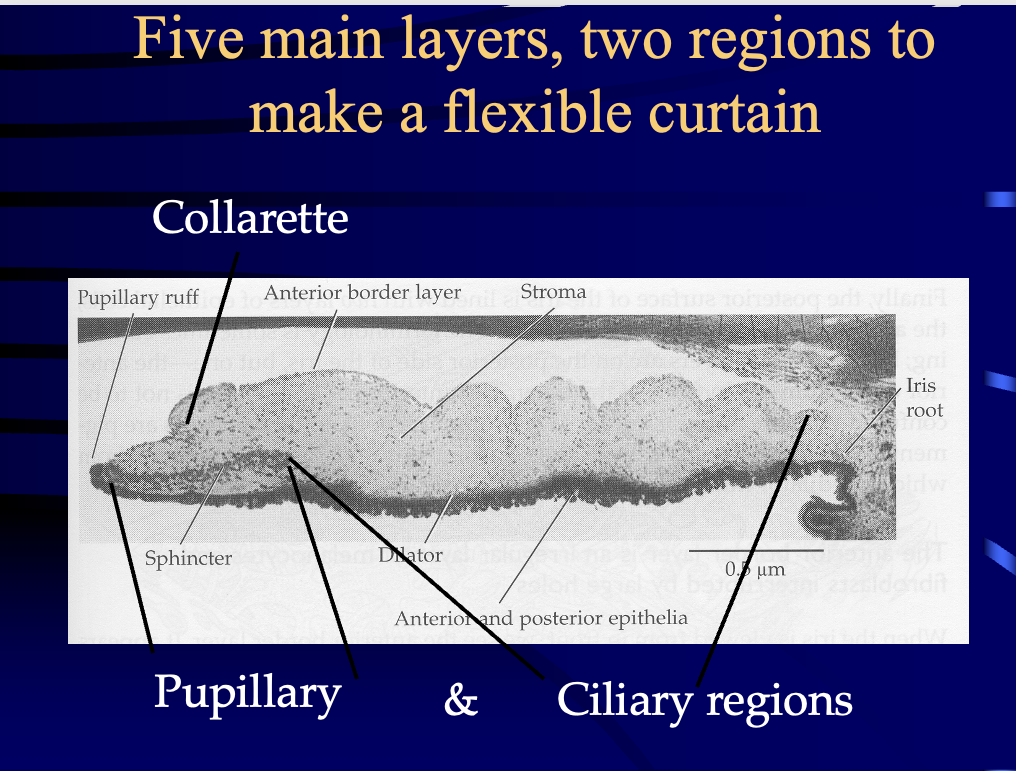
what are the 5 layers of the iris?
1) anterior border
2) stroma
3) muscular layer (sphincter & dilator)
4) anterior iris epithelium layer **really near the posterior wall of the iris
5) posterior iris epithelium layer **this is the posterior wall of the iris
attachment site (weakest area of tissue)
fibrils attached to trabecular meshwork and scleral spur
iris root / iris processes
anatomical border
thickest region of the iris
collarette
the collarette is a border between what 2 regions?
pupillary region (thick central region contains sphincter muscle)
ciliary region (contains dilator muscle)
the collarette is the site of the _______.
minor arterial circle
what provides the blood supply for the iris derived from the major** arterial circle MAC?
minor* arterial circle
the MAC is formed by anastomoses of what?
anterior ciliary arteries & long posterior ciliary arteries (LPCAs)
anatomy of the layers
which layer has melanocytes, fibroblasts, and lot of holes?
anterior border layer. this is the brown/blue color that you see in someone’s eyes.
what are the holes in the anterior border layer called?
crypts of Fuchs
the anterior border layer has ______ that appear during dilation.
contraction folds
in the anterior border layer, contraction folds during dilation can block the anterior chamber and _____ intraocular pressure (beware of angle closure)
increase
in the anterior border layer, the Crypts of Fuchs (holes) allow ____ to enter the ____.
aqueous into the stroma
what serves as the “iris fingerprint”?
Crytpts of Fuchs in the anterior border layer
what is the function of the anterior border layer?
1st pigmented cells to block light helping the iris to serve as effective aperture stop, and to determine eye color
true or false. the structure of the iris (Crypts of Fuchs) is so anatomically unique, it is used to establish identity.
true
what are the shape of the cells of the anterior border layer?
starfish shaped cells (fibroblasts over melanocytes)
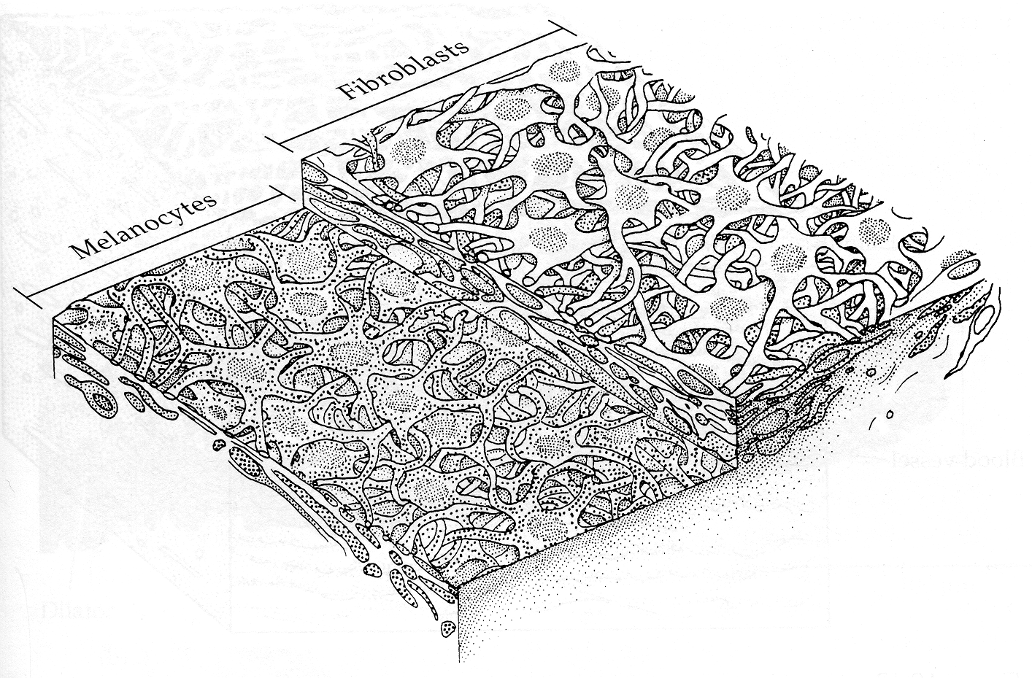
which layer is a spongy mixture of melanocytes, fibroblasts, collagen, and blood vessels?
stroma
where do clump cells appear?
near the sphincter muscle
what do clump cells do?
they clean up “spilled” pigment from melanocytes or pigmented epithelium
in the arterial circles, the blood vessels are very tight with no fluid leaks. what contributes to this tightness?
tight junctions (lots of zonule occludens)
overlapping endothelial
secondary covering of pericytes and collagen
the iris is like a folding blackout curtain. how does this impact the blood supply?
the blood supply must go on as the tissue expands to cover a large area, or it will be compacted by pupil dilation
minor arterial circle is about ___ of the way from root to the pupil.
2/3
where is the minor arterial circle positioned?
at the collarette
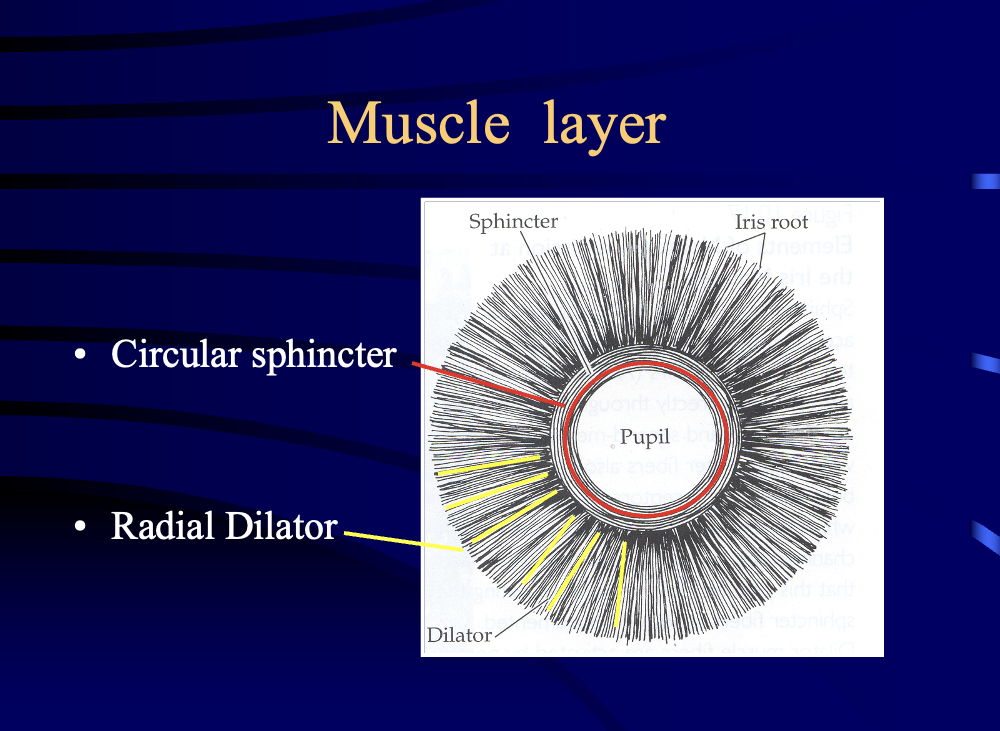
what layer has the sphincter (of the pupillary region, defines the collarette)?
muscle layer
in the muscle layer
sphincter =
dilator =
sphincter = pupillary region
dilator = ciliary region (very thin)
the nerves that control the muscle layer function are _____, which means they are NOT voluntary.
autonomic
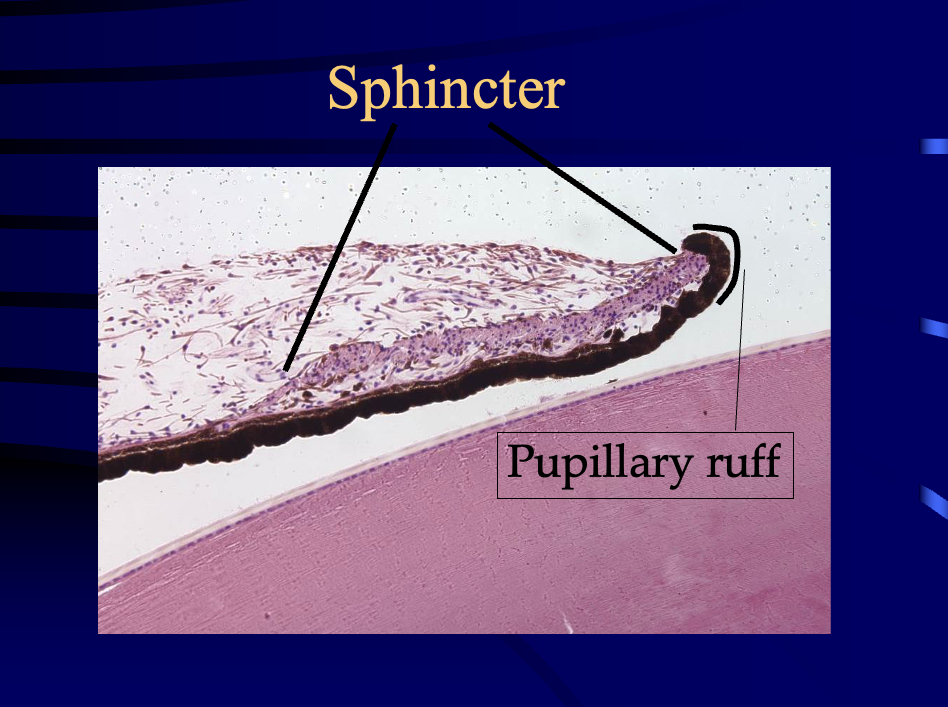
sphincter vs pupillary ruff
circular sphincter vs radial dilator
parasympathetic of ANS
neurotransmitter?
stimulates what muscle?
neurotransmitter is Acetylcholine
stimulates the sphincter, smaller pupil
sympathetic of ANS
neurotransmitter?
stimulates what muscle?
neurotransmitter is norepinephrine
excites the dilator, causing mydriasis (larger/dilated pupil)
chemical packaged and ready for release at synaptic endings
neurotransmitter
what is the function of a neurotransmitter?
to depolarize (excite) or hyperpolarize (inhibit) the post synaptic cell
neurotransmitters are important sites for drug actions.
agonist _____ transmitter function
antagonist _____ transmitter function
agonist mimics
antagonist blocks
synapses are communication sites. during transmitter action, what do all actions require?
G-protein 2nd messenger
true or false. both epithelial layers of the iris line the posterior chamber.
true. they both line it.
flatter, less pigmented
forms the dilator muscle (it is the myoepithelium from which the dilator muscle arises)
anterior epithelial layer
heavy pigmentation
most central tissue wraps around the pupil margin, forming the pupillary ruff
posterior epithelial layer
columnar heavy pigmentation tight junctions
posterior epithelium
how does the pupillary light reflex work? is it important?
it is very important!!
direct reflex = light strikes one eye & constricts pupil
consensual light reflex = light strikes one eye & effects both pupils
Agonists: Pilocarpine
stimulate Sphincter (pilocarpine)
parasympathetic
constriction
Agonists: Physostigmine
stimulate Sphincter
parasympathetic
constriction
Antagonists: Dapiprozole
inhibit / block Dilator
sympathetic
constriction
Antagonists: Tropicamide
inhibit Sphincter
parasympathetic
dilation
Agonists: Phenylephrine
stimulate Dilator
sympathetic
dilation
what is the iris a barrier for?
aqueous humor circulation
Which epithelium in the iris has columnar heavy pigmentation & tight junctions?
posterior epithelium
synechia
touching
iris Bombé
bulging iris
what is the solution for synechia & iris Bombé?
make a hole or several holes through the iris to shunt the aqueous directly into the anterior chamber
what happens in the 2nd wave of neural crest cell migration?
The 2nd wave forms a thin line of tissue which forms the iris stroma. The cells in this layer will differentiate & proliferate to become fibroblasts and melanocytes for the iris & anterior border. They have NOTHING to do with the sphincter or dilator. The stroma blood vessels are mesodermal.
what structures are formed from the Neural Crest?
Corneal stroma
Corneal Endothelium
Sclera
Trabecular structures
Uveal pigment cells
Ciliary muscle
Ganglia of Autonomic nervous system
Iris stroma***
what structures are formed from the Neural ectoderm? (tube/rim of the optic cup)
RPE & retina
Fibers of optic nerve
Neuroglia
Epithelium of ciliary body
Epithelium of iris***
Iris muscles***
Oculomotor nerves
What is the last anatomical structure of the iris to form?
Pupil
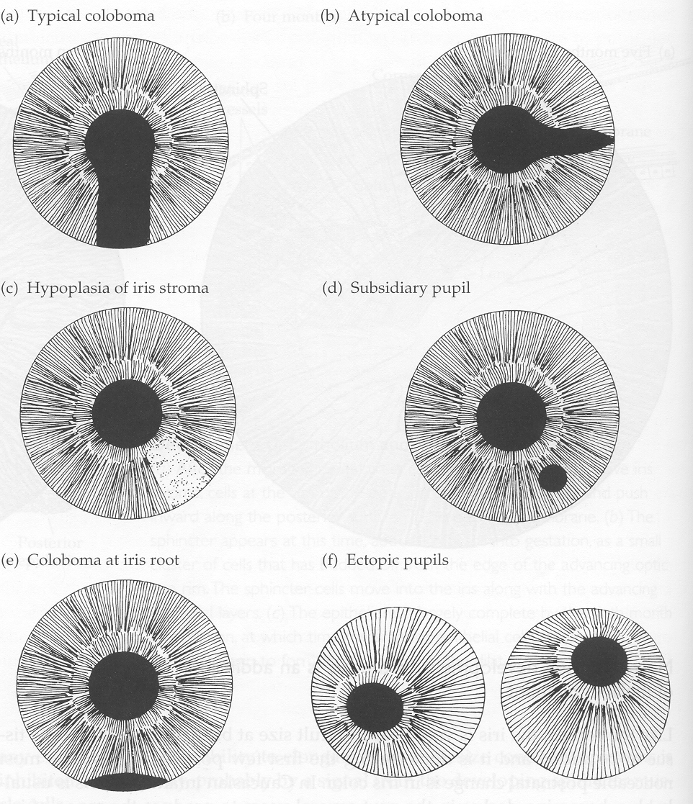
The pupil is the last structure to form in the iris, so early or late development can cause problems. What is a Coloboma?
part of the iris is missing