Chapter 15
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
ocean currents
masses of water that flow from one place to another
surface currents
develop from friction btw. ocean and wind that blows across surface
Coriolis effect
The effect of Earth's rotation on the direction of winds and currents.
Gyres
Huge circular moving current systems dominate the surfaces of the oceans.
Where is each gyre located
Thermohaline circulation
ocean currents that occur due to differences in density due to temperature and salinity
Shore
area between lowest tidal level and highest areas affected by storm waves
Shoreline
contact between land and sea
coastline
seaward edge of the coast
beach
accumulation of sediment along landward margin of ocean
crest
top of the wave
trough
bottom of the wave
wave height
vertical distance btw trough and crest
amplitude
amplitude vertical distance from midpoint to crest or midpoint to trough
Wavelength
Horizontal distance between midpoint to crest or midpoint to trough
wave period
time it takes for one full wave to occur
wave base
negligible water movement below 1/2 wavelength
Fetch
distance wind travels
Beach drift
sediment moves in a zigzag pattern along beach face due to waves and gravity
Longshore currents
current in surf zone that flows parallel to shore
wave refraction
bending of waves
headland
land that sticks out into the sea
wave cut platform
flat area along a shore cut by wave erosion
marine terraces
when platform is no longer under water
sea stack
when sea arch has eroded away leaving rock detached from the rock shore
sea arch
rocks make an arch created as headland is eroded more from the sides
spit
ride of sand extending from land into mouth of an adjacent bay with an end that often hooks landward
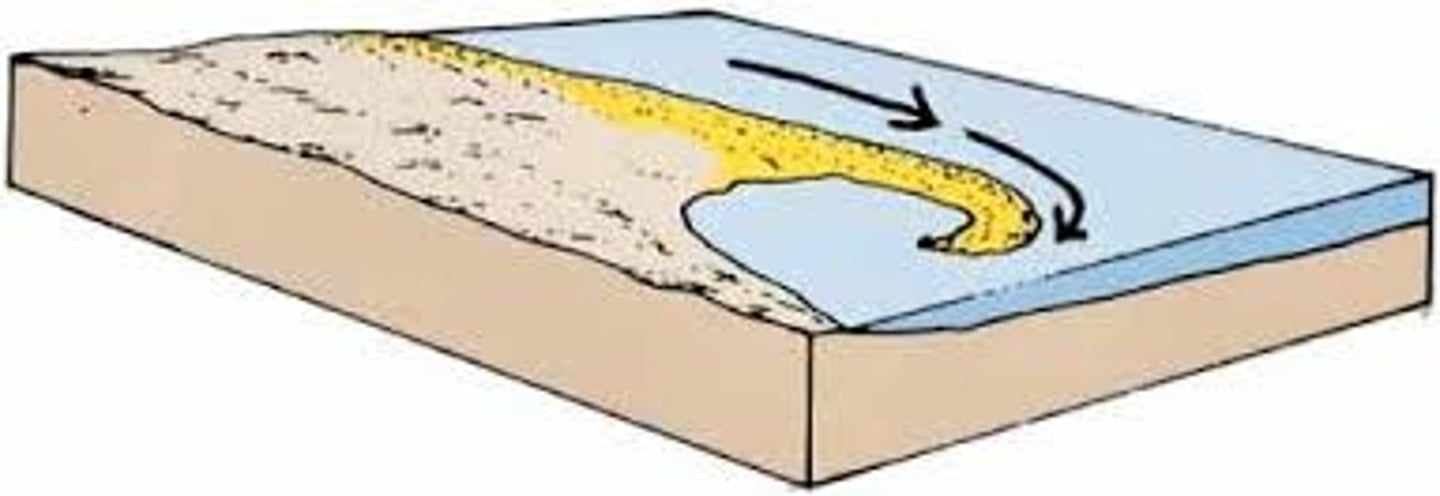
baymouth bar
sand bar that completely crosses a bay. can have a river exiting through it
tombolo
a ridge of sand that connects an island to the mainland
Barrier islands
ridge of sand parallel to the shore but offshore
seawall
armors coast against force of breaking waves
breakwater
barriers built offshore parallel to coast to protect boats from breaking waves
Groins
barriers built at a right angle to the beach that are designed to trap sand
beach nourishment
by adding sand to the beach system
Where are the five gyres located
North pacific gyre, south pacific gyre, north atlantic gyre, south atlantic gyre, indian ocean gyre
How does ocean water circulate at the surface?
Formation by wind, Gyres, Coriolis Effect, Temperature, Warm currents, Cold currents
how does ocean water circulate at depth (vertical currents)
Density differences known as thermohaline circulation
How do ocean currents affect global and local temperatures
Heat transfer, Coastal Climate Modification (Waters take longer to heat up and cool off causing regulation)
How are waves generated?
Wind
What affects the size of a wave?
long fetch = bigger waves
What are the shoreline features that are produced from erosion?
Headland, wave-cut cliff, wave-cut platform, marine terraces, sea arch, sea stack
How does sediment move relative to the shoreline?
longshore current causes the sand too be dragged down the coast, gravity pulls the sand away = Beach drift makes a zigzag motion.
What are the depositional features of the shoreline
Baymouth bar, tombolo, barrier islands, spit
What methods can be used to stabilize shorelines and reduce erosion?
Jetties, groins, breakwaters, seawalls, beach nourishment