Stem cells + differentiation T3 W3
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
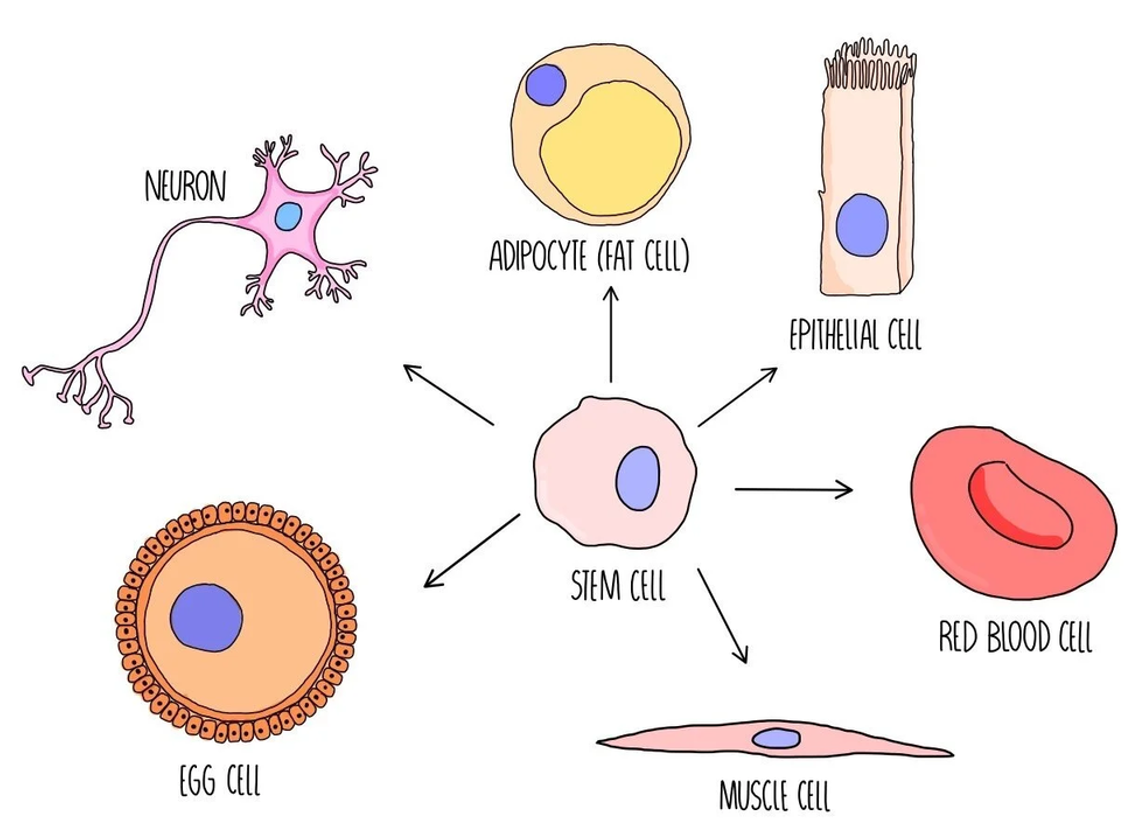
2 classifications of cells
Stem cells or specialised cells. Specialised cells being cells with a specific function with is structure modified to help carry out that function
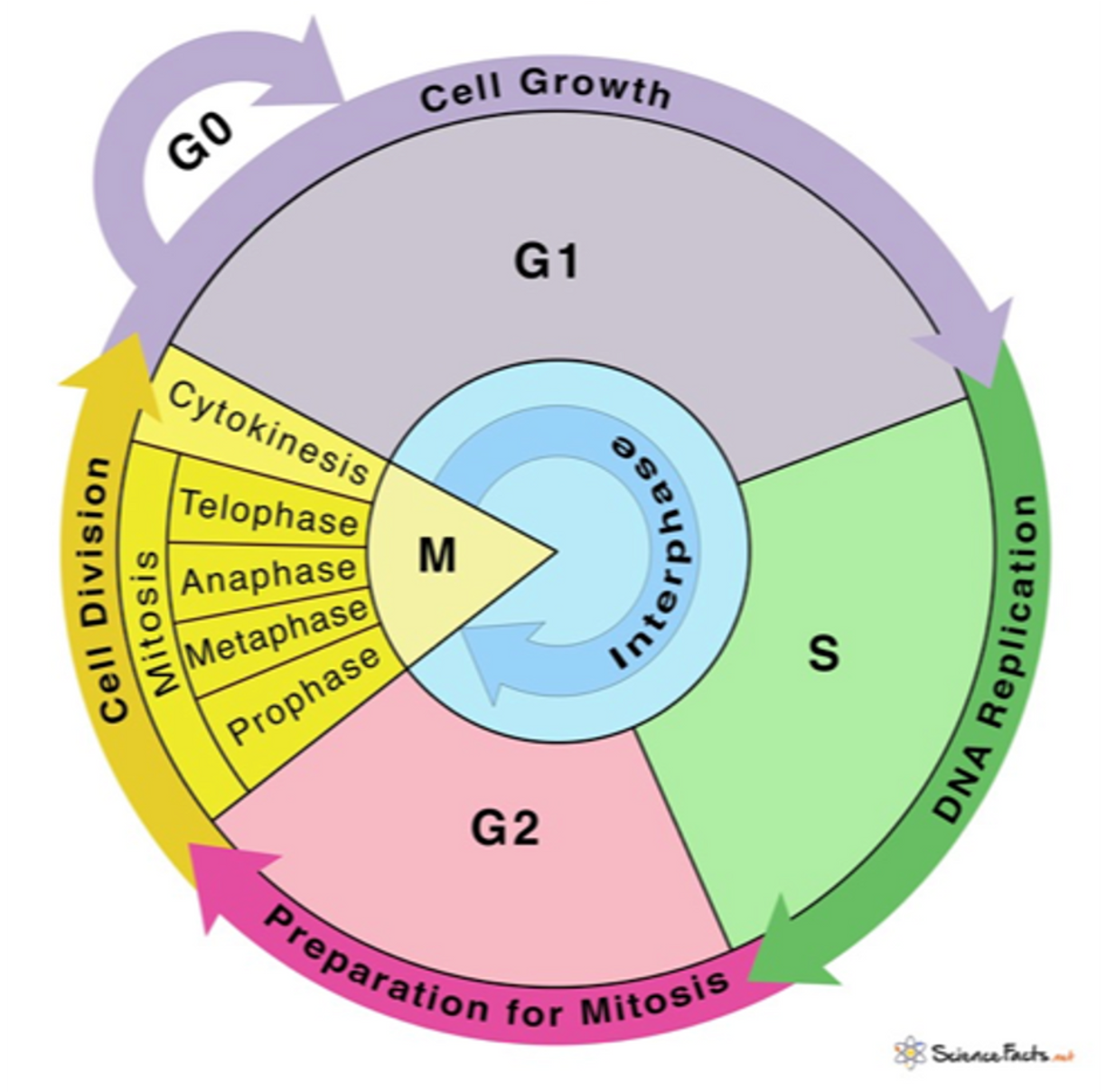
What phase are specialised cells stuck at
In general, highly specialised cells are unable to divide – they enter the G0 phase of the cell cycle and stay there.
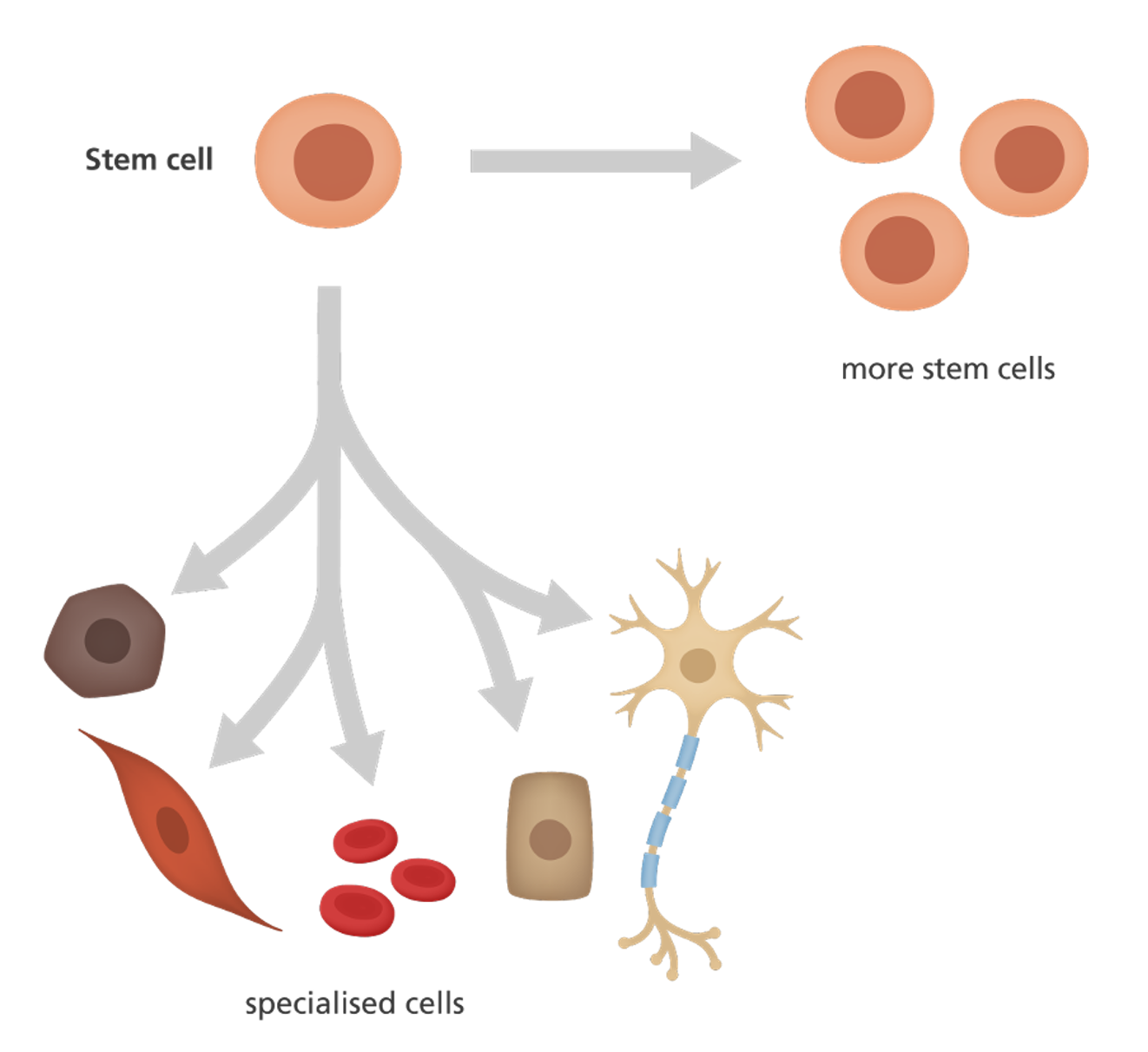
Stem cell defintion
An unspecialised cell:
•Stem cells undergo cell division.
•They have the ability to continue to cycle through the cell cycle.
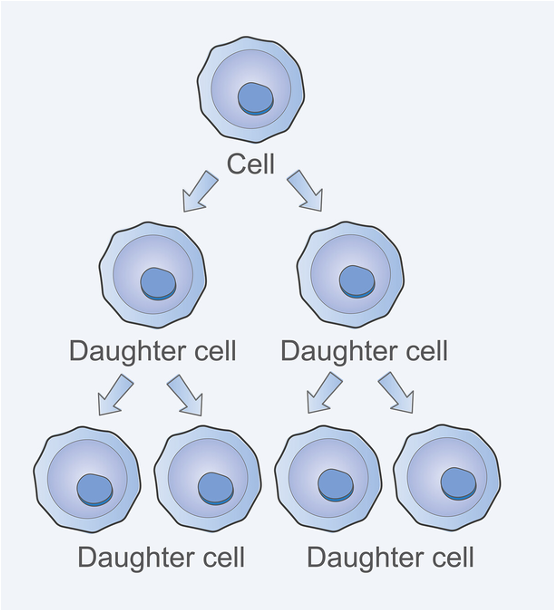
Stem cells 2 properties
⚬The ability to proliferate
⚬The ability to differentiate
Proliferation
Stem cells can continue to enter the cell cycle through many cycles, i.e., they repeatedly divide to create new cells. Thus, this means that stem cells can self-renew.
Differentiation
Process of making specialised cells
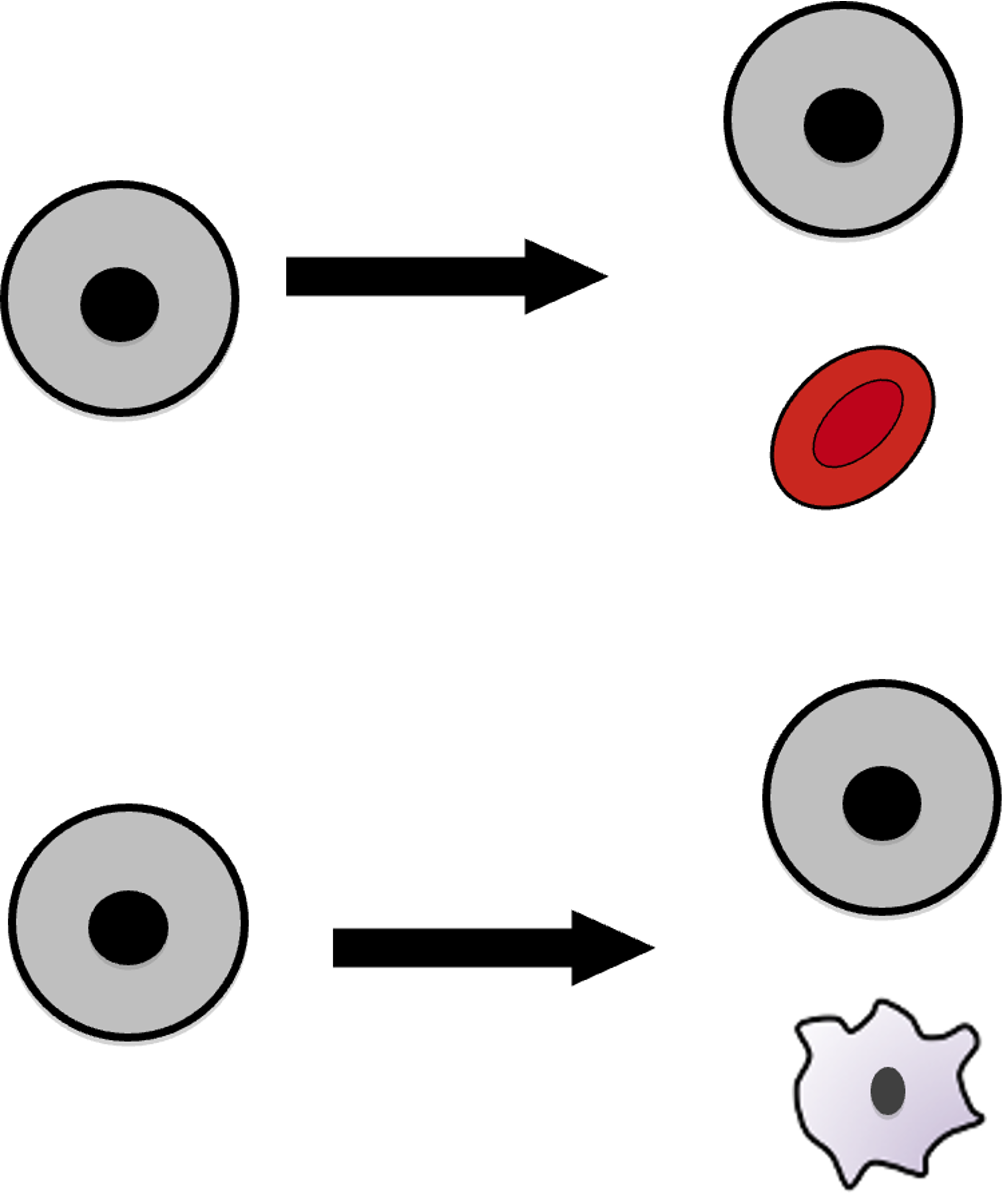
Proliferation + differentiation example
Completes the cell cycle and enters G0 – can re-enter the cell cycle when required. As this cell is unspecialised it is called a stem cell.
Undergoes differentiation to specialise into a red blood cell.
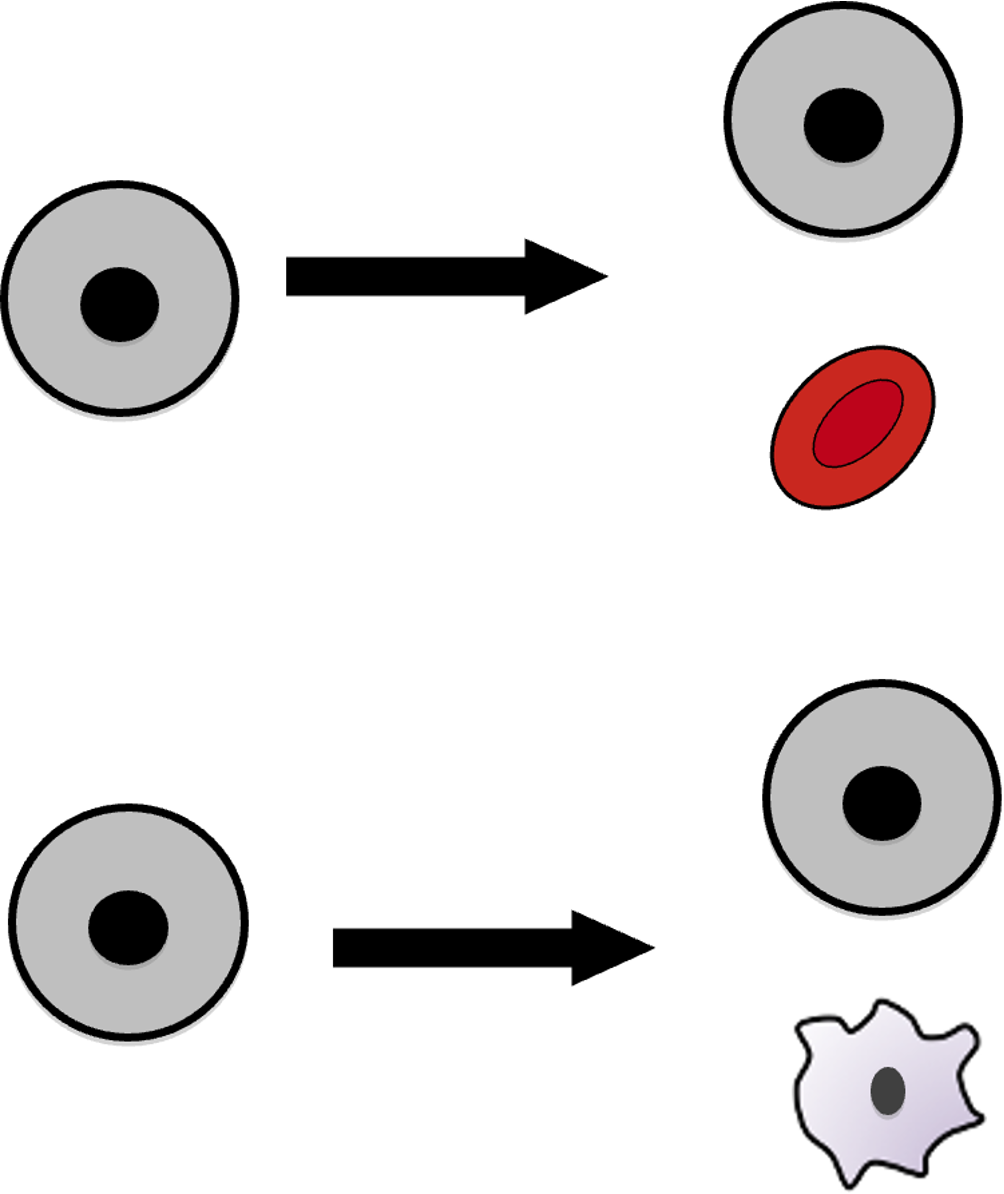
Why is self-renewal important
Self-renewal is required to maintain a pool of stem cells. If they don’t copy themselves, stem cells would run out.
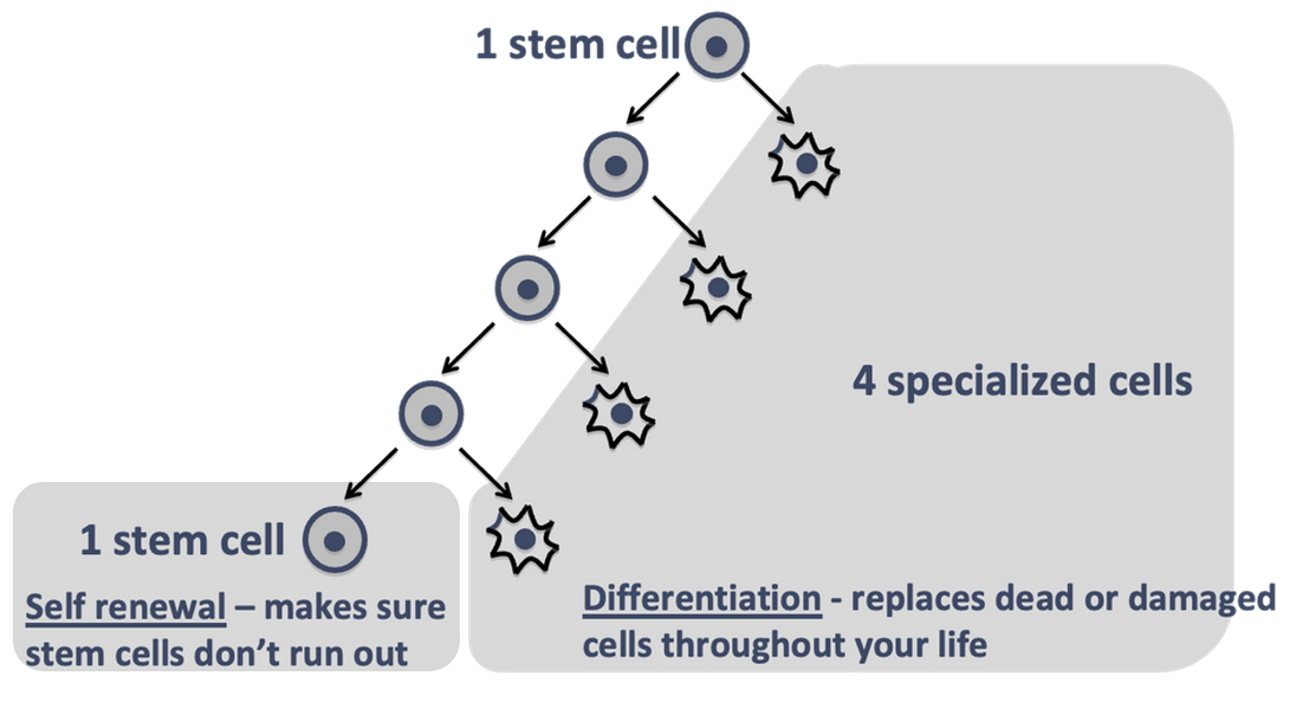
Why is differentiation important
Differentiation is important because specialised cells are used up, damaged or die all the time during life. Specialised cells cannot make copies of themselves, but they need to be replaced for your body to carry of functioning and working.
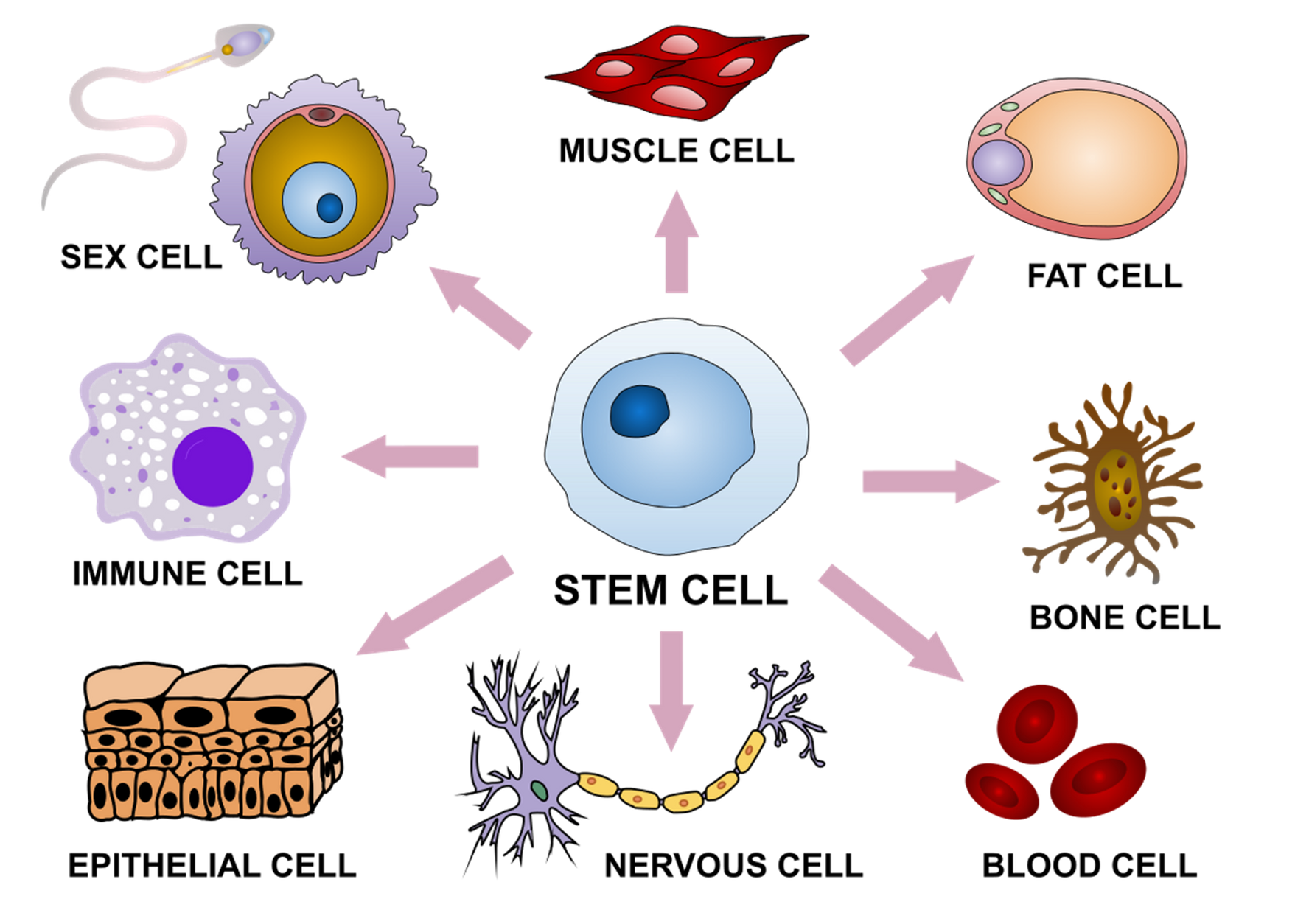
How differentiation is triggered
•chemicals signals in the microenvironment around the cell.
How do the chemical signals cause differentiation
Activate certain genes and cause gene expression of particular genes in each cell type.
Stems cells are classified based on
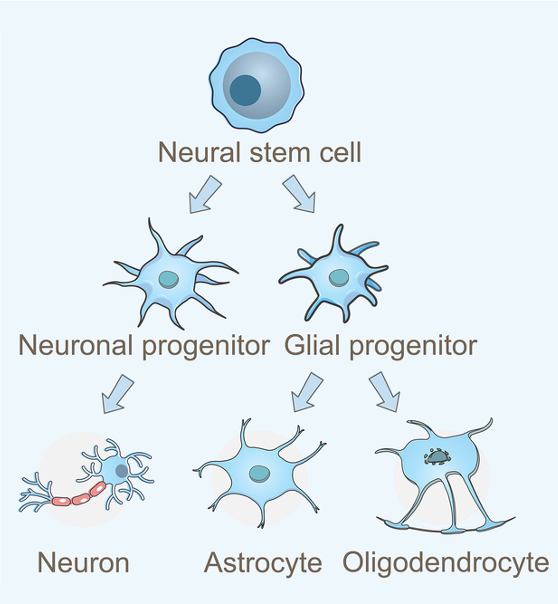
⚬The number of different types of cells that they can form - potency
⚬Where they originate (their source) - embryonic, somatic
What does ‘The potential of a stem cell’ mean
How many different types of cells the stem cell can differentiate into.
3 types of stem cells based on which types they can differentiate in to:
Totipotent stem cells
Pluripotent stem cells
Multipotent stem cells
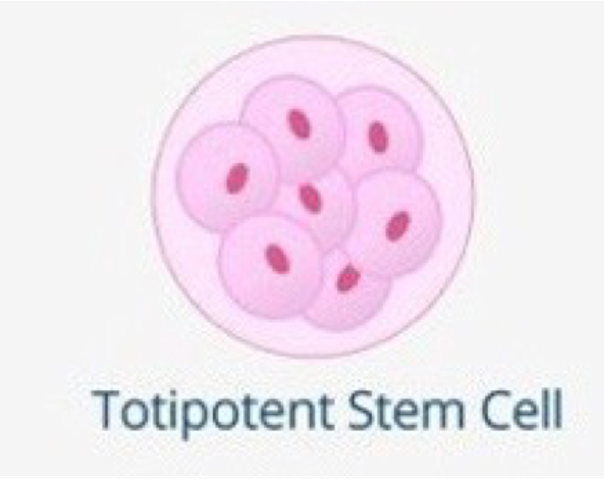
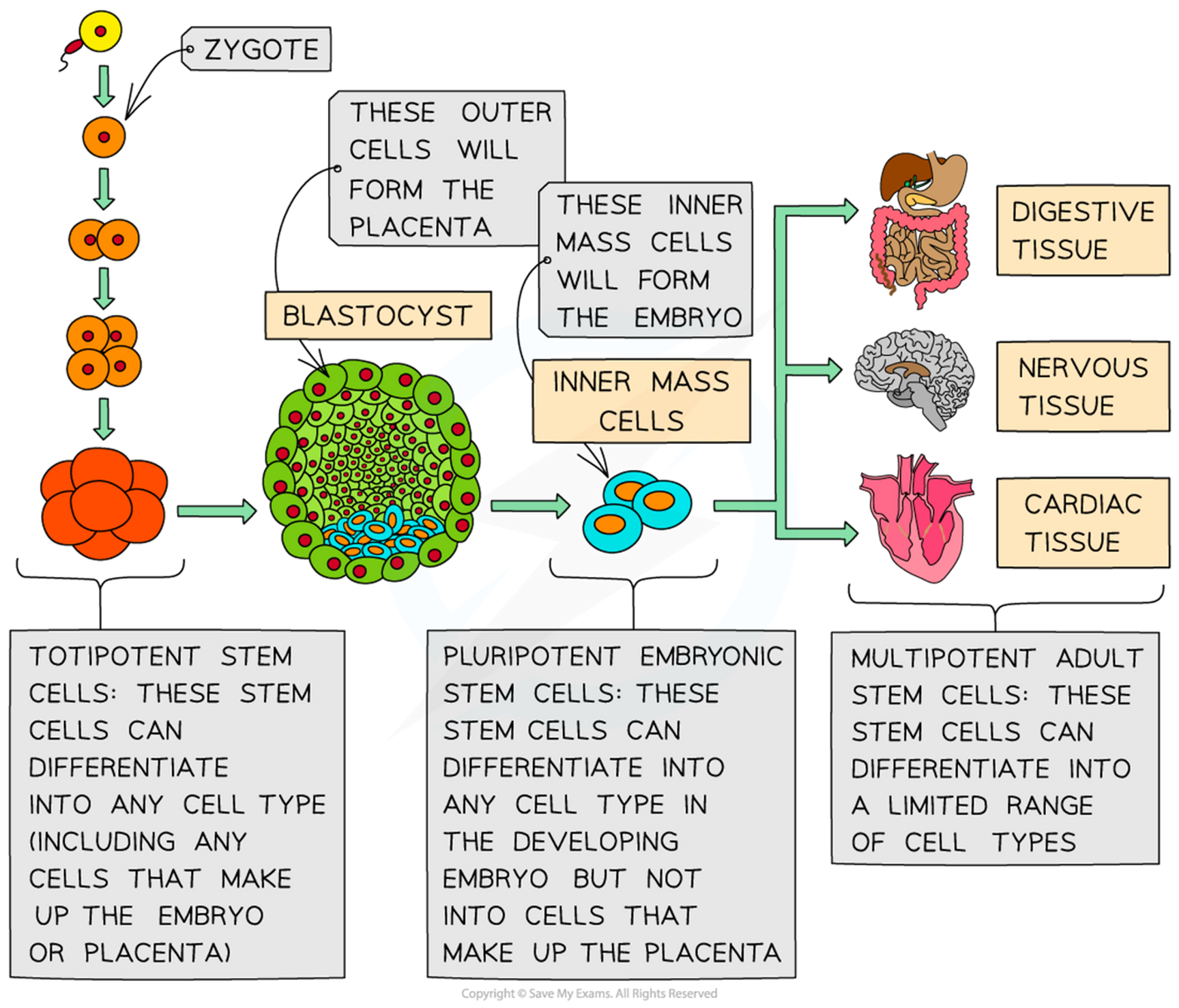
Totipotent stem cells
•Can become ANY cell of the BODY and/or the embryonic MEMBRANES.
•The ONLY totipotent stem cells are the cells of the embryo within the first couple of mitotic divisions after fertilisation.
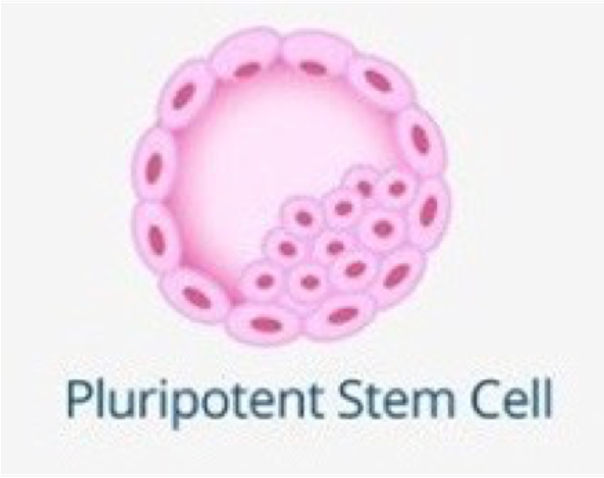
Pluripotent stem cells
•Can become ANY cell of the body but NOT the embryonic membranes.
•These stem cells are ONLY found in blastocysts; these are early embryos.
•The inner cell mass is what becomes an embryo and is made of pluripotent stem cells.
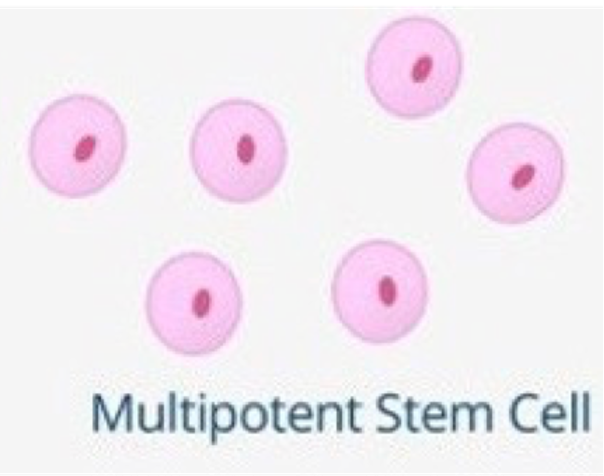
Multipotent stem cells
•Can become SOME cells of the body ONLY.
•I.e., can develop in to more than one type of cell, but not all cell types.
⚬E.g. a blood stem cell in bone marrow can give rise to RBCs, WBCs & platelets, but not any other kind of cell.
•Multipotent stem cells are found in different locations in the human body depending on what they specialise into.
Stem cell types diagram
What are embryonic stem cells come
Are derived from embryos – the inner cell mass of the blastocyst.
Where do embryonic stem cells come from
•Most embryonic stem cells come from excess embryos donated from IVF clinics.
What type of stem cell are embryonic stem cells
•These stem cells are pluripotent.
Where are adult stem cells found
•Also called tissue stem cells and somatic stem cells.
•Occur in tissues such as bone marrow, muscles and the brain, derived from the foetus, baby, and all your life.
Adult stem cells use and what type of stem cell they are
•Able to produce new cells to replace those that are worn out, injured or diseased.
•These stem cells are multipotent.
Cord blood + placenta stem cells use
•Umbilical cord blood and placental stem cells are collected at birth and are particularly a rich source of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs).
•HSCs are responsible for producing all blood and immune cells throughout a person’s life.
•These stem cells are multipotent.
What type of stem cells are cord blood + placenta stem cells
These stem cells are multipotent.
What can stem cells be used for
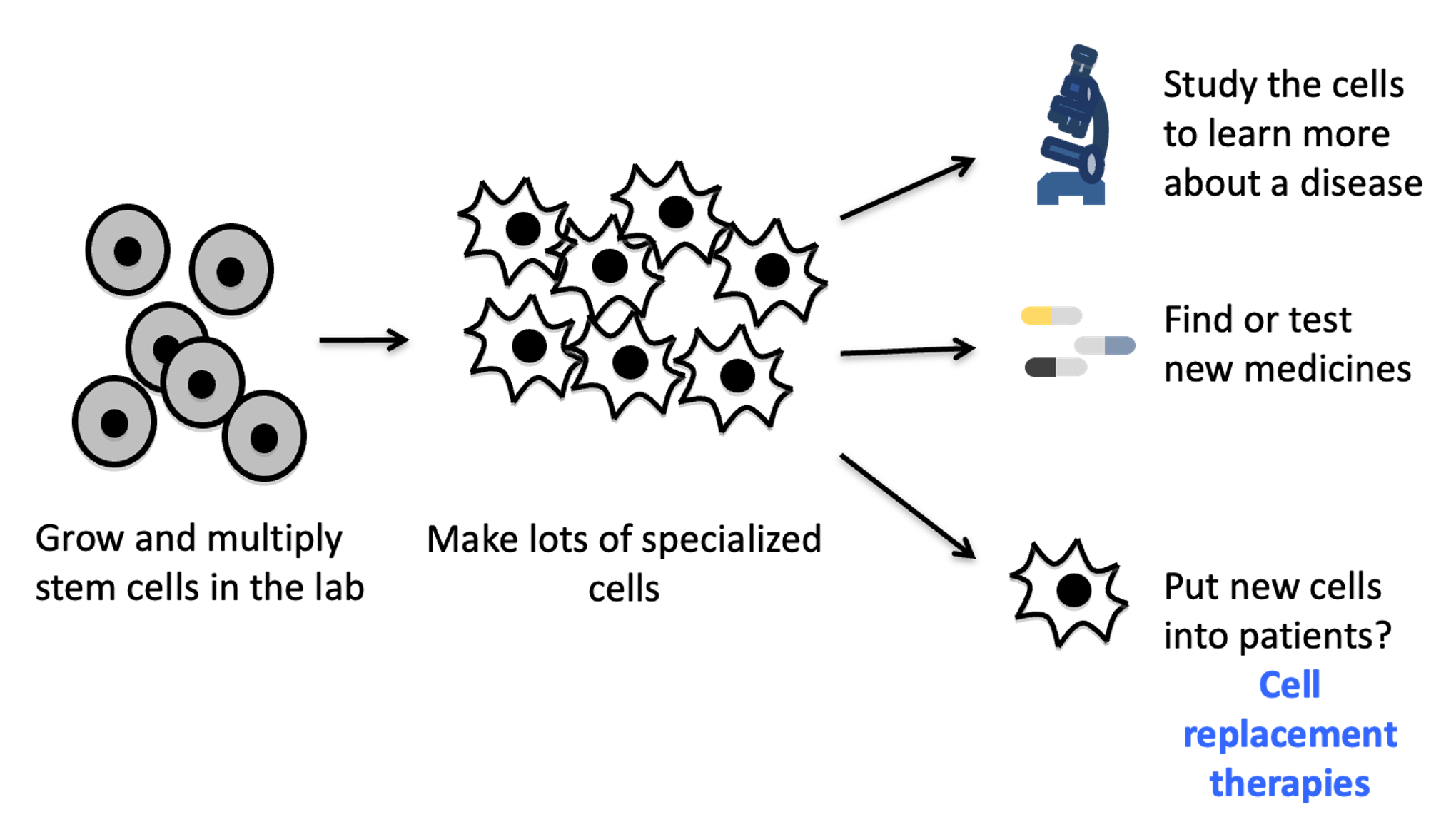
types of cell replacement therapies
Bone marrow transplants for blood diseases
Skin grafts for very bad burns
Grow a new cornea for damaged eyes