Ch9: The Science of Biomechanics
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
biomechanics
study of internal and external forces acting on the human body and effects
quantitative analysis
research based
based on quantity
qualitative analysis
information that can be readily obtain to asses performance
kinematics
describes spatial and timing characteristics of motion of the human body without reference to the forces that cause the motion eg time, distance, velocity, acceleration
kinetics
describes forces leading to motion
they can be internal or external
internal forces
happens inside the body
external forces
acts outside the body
mass
the amount of matter in an object
inertia
the reluctance to change motion unless by an external force
moment of inertia
the more the mass the more the inertia
movement of inertia is rotation
gravity
force of attraction between 2 bodies
difference between mass and weight
mass is the measure of inertia
weight is the measure of the force of gravity
types of motion
linear motion/translation
angular motion/rotation
general motions
linear motion/translation
all body parts move in a straight line
angular motion/rotation
moves on circular parts in the same direction
general motions
combination of linear and angular
force
any action that causes an object to change its course of motion
causes of linear motion
forces that act through a bodies force of mass
torque (moment of force)
when a force causes angular motion
components of lever system
axis of rotation
fulcrum (pivot)
lever attached to fulcrum
types of levers
first class
second class
third class
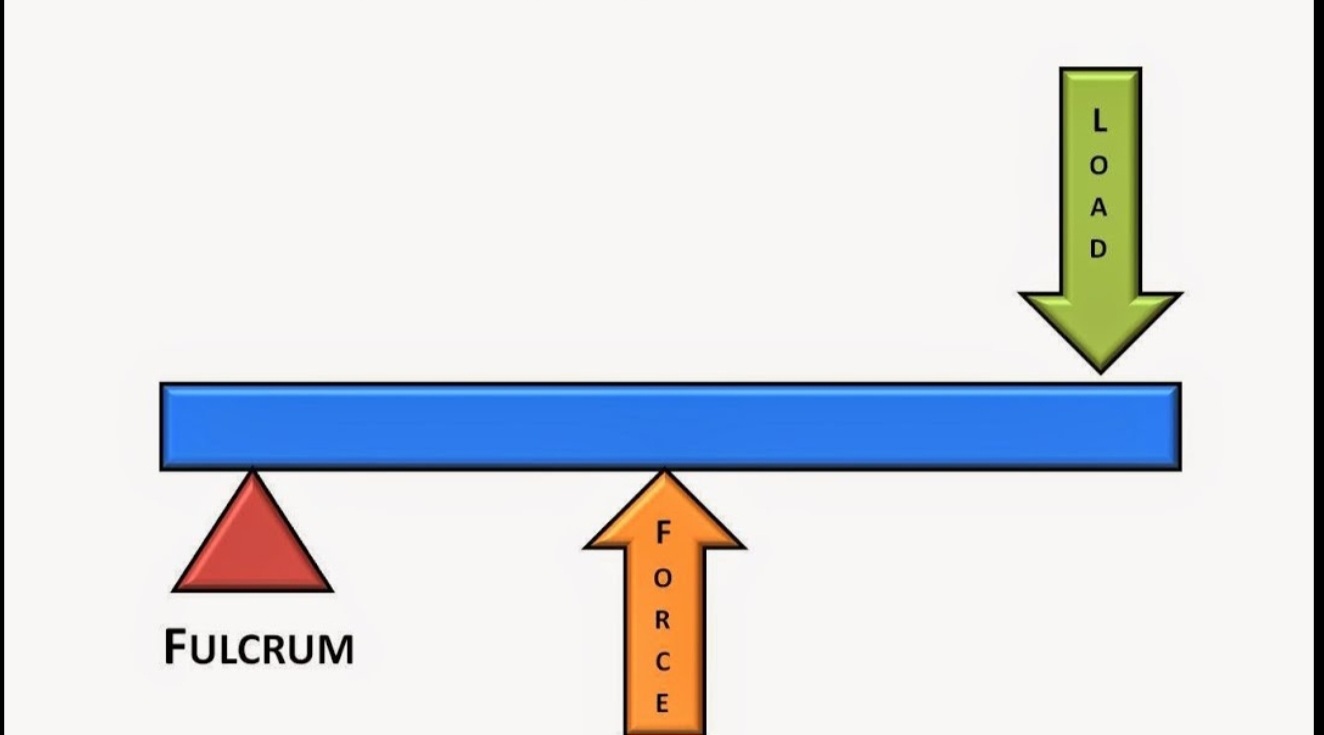
first class levers
applied force and resistance are located on opposite sides eg crowbar, seesaw, neck region
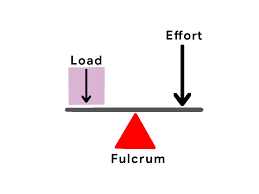
second class lever
force and resistance are on the same side
force acts far away from axis (fulcrum)
eg wheelbarrow
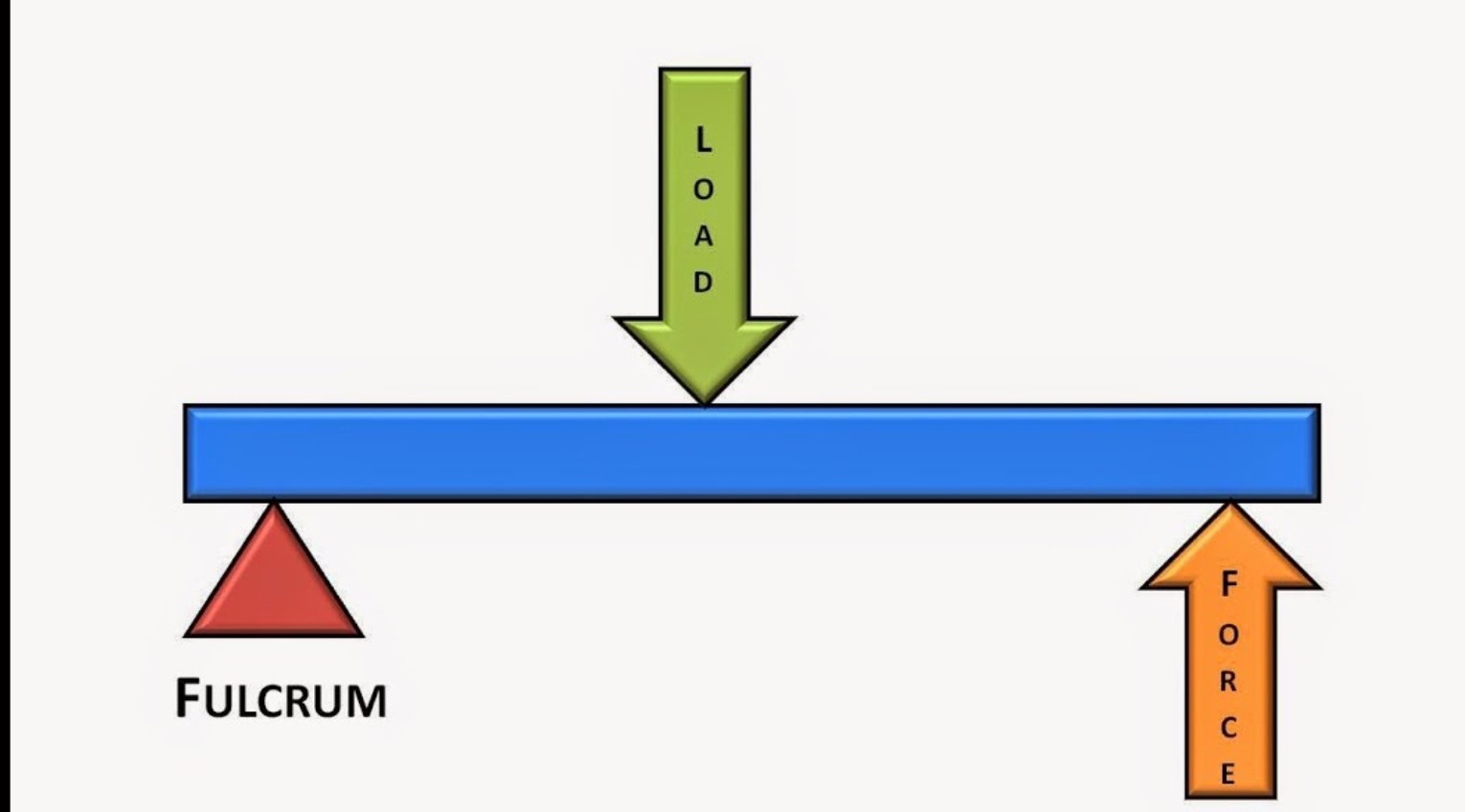
third class lever
force and resistance on the same side
applied force closer to the axis
human body consists of mainly third class levers, due to this we are at a biological disadvantage
make humans faster
newtons 1st law
law of inertia: objects will not change state of motion unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force
newtons 2nd law
law of acceleration: objects experience change in velocity proportional to the external unbalanced force
newtons 3rd law
law of action-reaction: for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
fluid environments
water
air
water + air
drag
type of fluid force that acts opposite to the bodys direction and works to slow you down
profile drag
caused by an objects size and shape
surface drag
caused by an objects roughness
the faster you go-
the more drag you experience
body size and surface roughness
surface drag
boundary layer
a thin layer of fluid that is carried with the body
laminar flow
very little disruption, the air around you moves smoothly
turbulent flow
disruption in the air flow
profile drag
resistive drag against an object and it is characterized by turbulent flow
profile drag reducing strategies
decrease frontal surface area
decrease source of turbulence
drafting
taking advantage of the region of air shielded by another athletes body
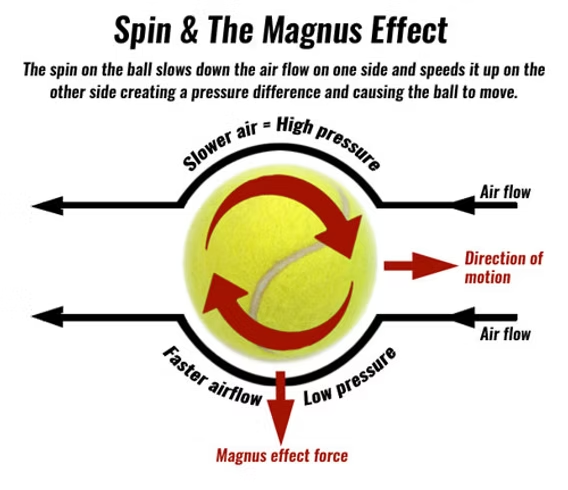
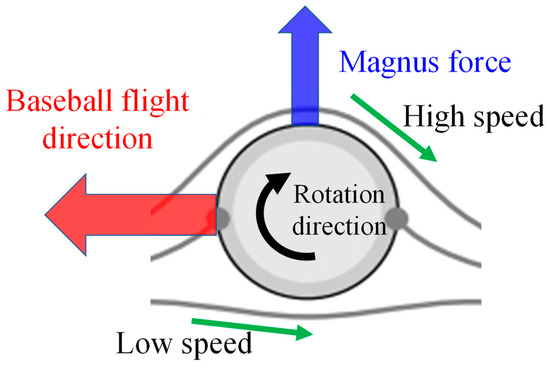
magnus force
net difference in pressure on opposite sides of a rotating object
topspin
downwards magnus force
boundary layer flows opposite to relative airflow
air is slowed by friction
zone of increased pressure created
backspin
upwards magnus force
boundary layer flow same as relative airflow
air is not slowed down
zone of decreased pressure created
equilibrium
not experiencing change in direction of speed
static equilibrium
no movement
dynamic equilibrium
movement at a constant speed
balance
ability to maintain equilibrium
balance is affected by two factors
base of support: larger your base of support the better your balance
location of line of gravity: best at the centre of your base of support
stability
measurement of how hard it is to disrupt your equilibrium
increase in stability: static equilibrium
increase in base size
increase in body size
lower centre of gravity
increase distance between gravity line intersecting base and outside base
increase in stability: dynamic equilibrium
widen base
move centre of gravity towards the edge
shift centre of gravity towards oncoming force
use reflex to regain loss of balance