The Motor Effect
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
What is the motor effect
How does it work → process of how it is created?
definition: the magnetic force (F=BIL sinθ) a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field experience due to the interaction between the magnetic field created by the current and the existing magnetic field.
Current = the flow of charge per unit of time acts as the direction of motion (aka velocity) for the charges
process:
The current consists of moving charges that are perpendicular to the magnetic field.
Thus, each charge experiences a force F=qvBsin𝜃.
Hence, the entire conductor experiences a force in the magnetic field as the sum of these forces, and this is called the motor effect
Ampere’s Force Law
Applies to Parallel Current Carrying Conductors
A current produces a magnetic field ∴ current carrying conductors experience a force when they interact with the magnetic fields of other current carrying conductors
Current in same direction (in parallel) = opposite B fields = attract
Current in opposite direction (in series) = like B fields = repel
Due to N3L, the forces on each of the wires are equal and opposite:
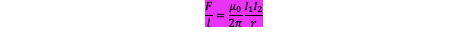
Parallel Current Carrying Conductors experiment
Two wires are connected to a current/one current and a magnet
Different currents are run through one of the wires/current wire is run infront or behind of the magnet
A balance is used to record the ‘mass’ of a rod/magnet
This balance reading is not actually the mass of the rod, but the net force
For top wire
Balance reading decrease = repulsive force that is making it move upwards (↓ Fnet)
Balance reading increase = attractive force that is pulling it down (↑ Fnet)
For bottom wire
Balance reading decrease = attractive force that is making it move upwards ((↓ Fnet)
Balance reading increase = repulsive force that is pulling it down (↑ Fnet)
You graph the information
Find the gradient of the line and its significance: either F=BIL or or ampere’s force law
Insert the gradient into the equation and rearrange for unknown value
How to change the direction vs the magnitude of force (F=BIL)
Magnitude | direction |
Increase θ to 90° = increase F
Increase magnitude of the current = increase F
Include more length of wire in the field = increase F Increase strength of the magnetic field = increase F |
|