Sociological Perspectives on Inequality
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Anishinaabek
Indigenous peoples in North America, primarily in Canada.
Haudenosaunee
Confederacy of six Native American nations.
Lūnaapéewak
Indigenous people from the Delaware Valley region.
Chonnonton
Indigenous group historically located in southwestern Ontario.
London Township Treaty
1796 agreement involving land rights in Ontario.
Sombra Treaties
1796 treaties concerning land use in Ontario.
Dish with One Spoon Covenant
Agreement for shared resource management among tribes.
Social Inequality
Unequal distribution of resources and opportunities in society.
Meritocracy
Belief that success is based on individual merit.
Sociological Imagination
Understanding personal experiences within broader social contexts.
Social Facts
Patterns of behavior that influence social life.
Equity
Fairness in treatment and opportunity for all individuals.
Equality
Equal status and rights for all individuals.
Social Life
Interactions and relationships among individuals in society.
Myths of Meritocracy
False beliefs about equal opportunity and success.
Testable Statement
Hypothesis that can be empirically verified.
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals
Global objectives for sustainable development (2015-2030).

Collective Behaviour
Actions taken by a group in response to social situations.
Moral Values
Principles that guide behavior regarding right and wrong.
Cynicism
Distrust in the motives of others.
Capitulation
Acceptance of a situation without resistance.
Empirical Challenge
Questioning beliefs based on observed evidence.
Meritocracy
Distribution of roles based on individual traits.
Key Assumptions
Inequalities arise from talent, effort, and choices.
Individual Blame
Meritocracy blames individuals for their circumstances.
Hockey Success
Success in hockey is theoretically based on merit.

Talent
Natural ability contributing to success in sports.
Hard Work
Individual effort necessary for achieving success.
Toughness & Determination
Moral virtues essential for overcoming challenges.
Roger Barnsley
Researcher who studied hockey success patterns.
Statistical Pattern
Most successful players born January to June.
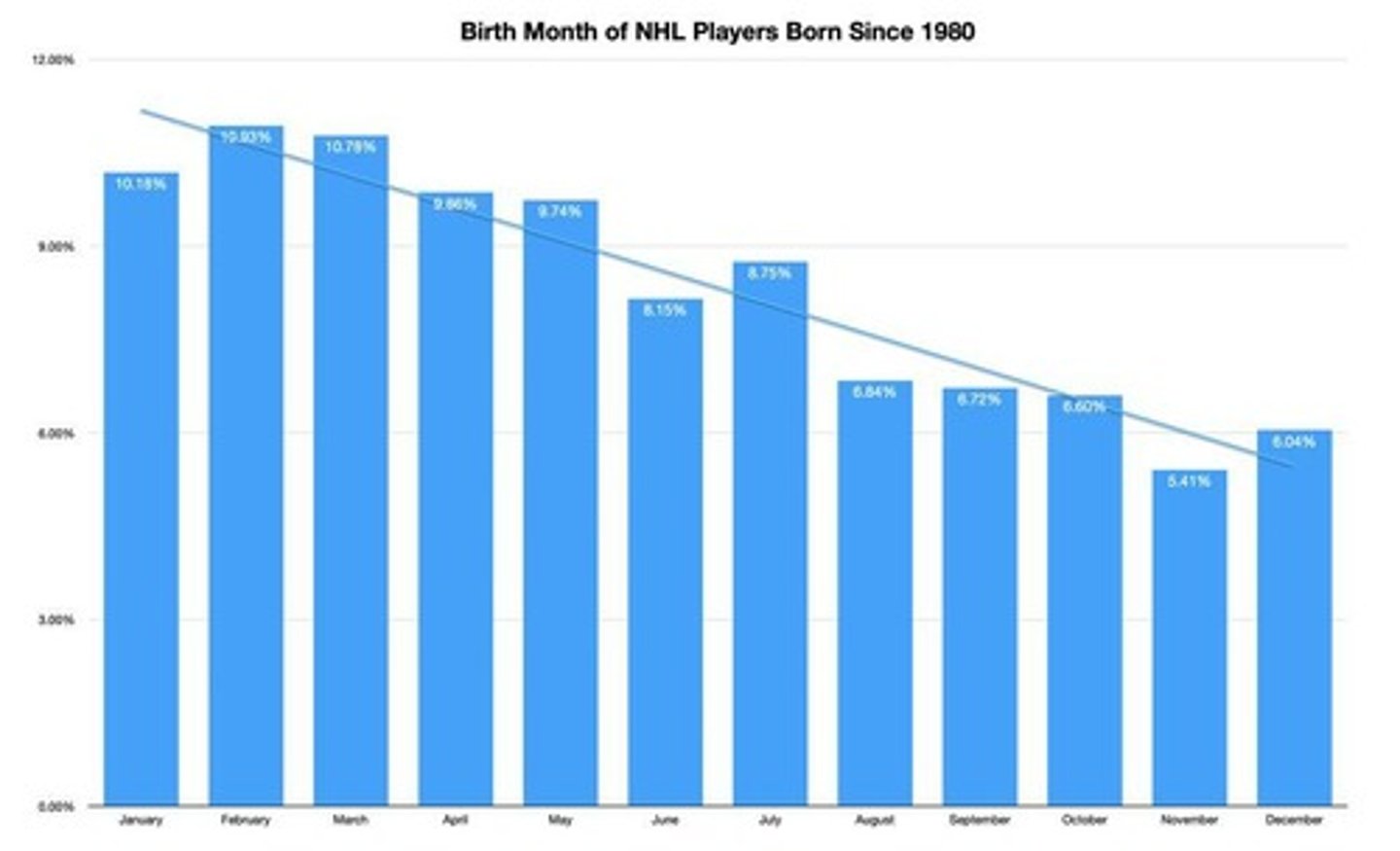
Relative Age Advantage
Early birth dates lead to physical advantages.
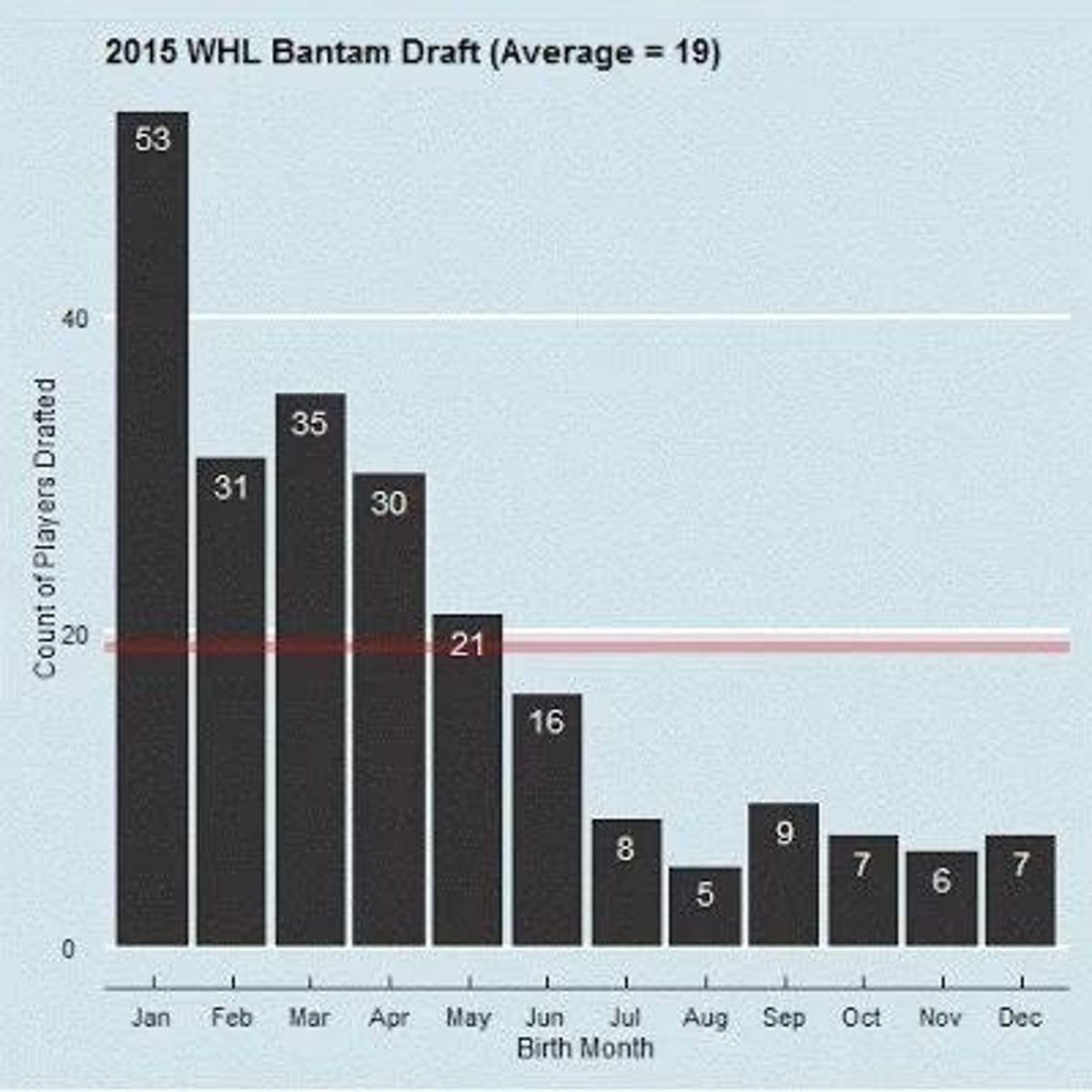
Eligibility Cut-off
Age-class hockey cutoff is January 1.
Selection
External factors influencing individual life circumstances.
Streaming
Placement in social situations affecting advantages.
Differentiated Experiences
Unequal outcomes from social processes.
Malcolm Gladwell
Author of Outliers discussing social advantages.
Correlation vs. Causation
Statistical relationship does not imply direct cause.
Family Influence
Family background significantly affects life chances.
Educational Streaming
Early advantages affect schooling types and courses.
Unequal Educational Outcomes
Disparities in suspensions and university admissions.
Carl Philips
Discussed environment's role in opportunity access.
Life Chances
Social factors shaping success and hardship.
Sociological Reflection
Consider personal experiences with selection and streaming.
Correlation
Relationship between two variables; not causation.
Causation
One event directly influences another event.
Social Advantage
Favorable conditions improving life outcomes.
Social Disadvantage
Unfavorable conditions hindering life outcomes.
Equality
All individuals have the same status and opportunities.
Equity
Fair treatment addressing historical social oppressions.
Social Inequality
Gap between advantaged and disadvantaged groups.
Consequential Differences
Differences impacting rights and opportunities.
Preferential Access
Unequal distribution of resources and opportunities.
Human Differences
Socially significant traits affecting life outcomes.
C. Wright Mills
Sociologist emphasizing connections between personal lives and history.
Traps of Private Life
Feeling of being stuck in personal troubles.
Historical Change
Transformations in society affecting individual experiences.
Institutional Contradiction
Conflicts within societal structures impacting individuals.
Age of Fact
Era dominated by overwhelming information availability.
Skills of Reason
Ability to process and analyze information critically.
Moral Energy
Emotional and ethical capacity to engage in struggles.
Nonomura et al. 2020
Source discussing equality and equity definitions.
Augie & Fleras
Authors defining social inequality in detail.
IS, p. 11
Textbook reference for inequality definition.
Email Requirement
Use UWO email for iClicker account creation.
Full Name Requirement
Use complete name, no initials for registration.
Social Inequality
Disparities in wealth, status, and opportunities.
Common Sense
Understanding based on popular wisdom and beliefs.
Biological Determinism
Genetic differences explain social group disparities.
Cultural Differences
Inequalities arise from perceived inferior values.
Psychological Explanations
Focus on mental processes affecting behavior.
Social Facts
External structures influencing individual actions.
Structural Analysis
Examines how social structures shape behavior.
Social Privilege
Unseen advantages benefiting certain groups.
Sociological Explanations
Scientific analysis of social forces and inequalities.
C. Wright Mills
Sociologist emphasizing connection between personal and societal issues.
The Sociological Imagination
Understanding individual lives within broader social contexts.
Empirical Observation
Systematic collection of data to study phenomena.
Theories
Broad conceptual models explaining social behavior.
Norms
Social rules guiding behavior in society.
Values
Beliefs that shape societal standards and behaviors.
Social Structures
Organized patterns of relationships within society.
Prejudice
Preconceived opinion not based on reason.
Social Forces
Influences that shape societal behavior and outcomes.
Individual Choice
Decisions made by individuals based on circumstances.
Invisible Aspects
Societal elements not easily perceived or recognized.
Unequal Distribution
Disparity in access to resources and opportunities.
Lucid Summations
Clear understanding of complex social phenomena.
Sociological Imagination
Understanding personal troubles and public issues together.
Personal Troubles
Individual problems faced by a person.
Public Issues
Social problems affecting large groups.
Example of Unemployment
Individual unemployment vs. national unemployment rates.
Economic Institutions
Organizations influencing economic policies and practices.
Political Institutions
Structures governing political behavior and decisions.
Survival Trauma
Psychological impact of survival situations.
Binge Drinking
Excessive alcohol consumption in short time.
Social Relations
Connections between individuals in society.
Social Structure
Organized patterns of relationships in society.
Inequality
Disparities in resources and opportunities.
C. Wright Mills
Sociologist known for the concept of sociological imagination.