IT IS THE ULTIMATE ORTHO REVIEW
1/751
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
752 Terms
what population is most likely to seek care for neck pain?
younger females are more likely to seak treatment
age and male were negatively associated with PT use
Which imaging modality does not use radiation?
Diagnostic ultrasound tests
VINDICATE
vascular
infection
neoplasm
drugs
idiopathic/ inflammatory
congenital
autoimmune
trauma
endocrine/ metabolic
"Do not have to memorize"
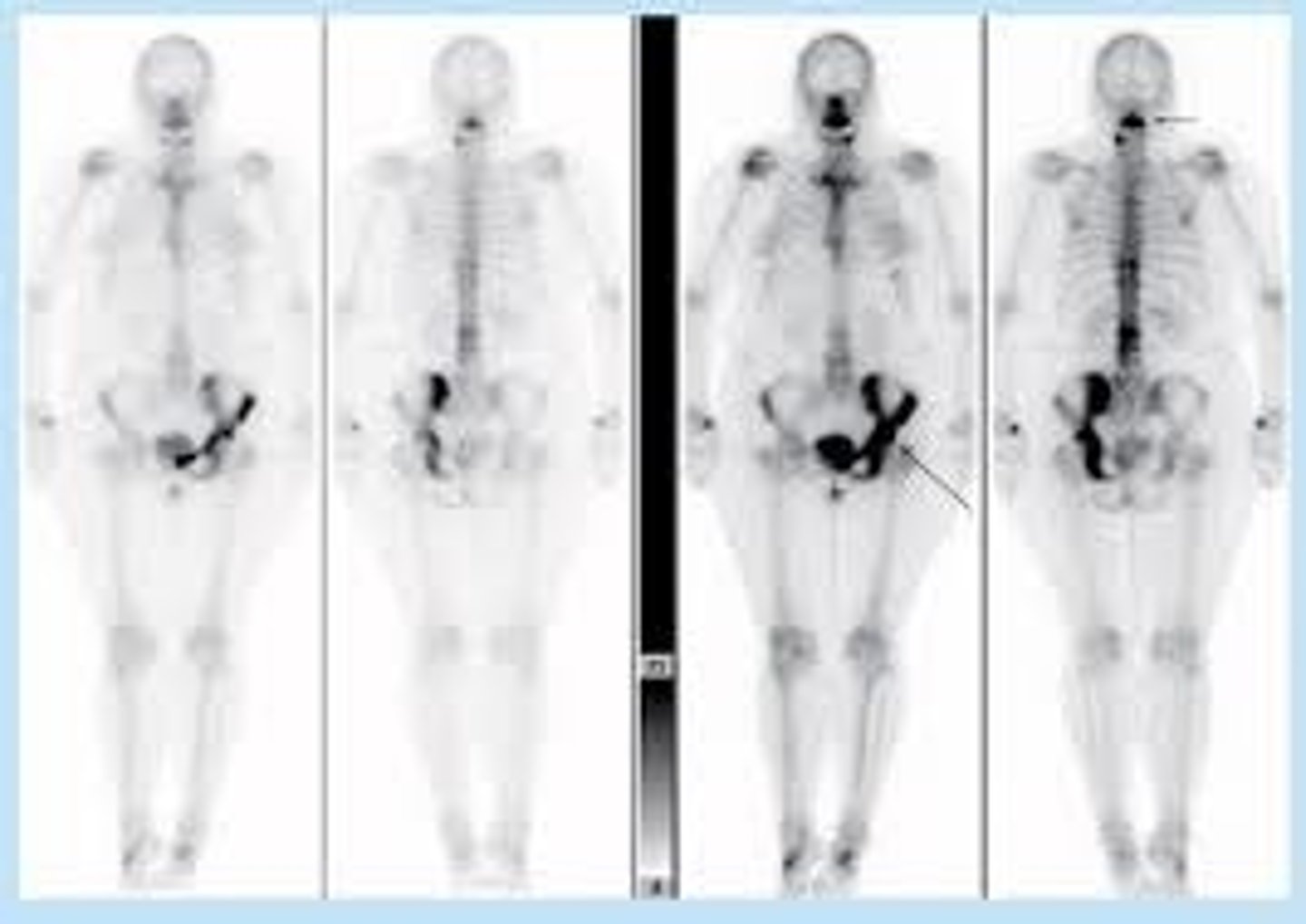
pagets disease
a condition of unknown cause affecting about 3% of population over 40years, characterized by excessive and abnormal remodeling of bone
radiographic findings of Paget's disease
enlargement of an affected bone, increased opacity of involved bone, along with disorganized and coarsened trabecular pattern
Wi law for ordering x-rays
DPT degree or specialist certification
board approved residency or fellowship
formal training with ordering X-rays
What does Wi X ray ordering law require?
Therapist communication of the order to the patient's PCP or HCP
When is communication not required for X ray orders?
Patient does not have a PCP
Patient was not referred by another practitioner
Or if radiologist does not identify a significant finding
How are radiographic views named?
by beam entry and exit
ex: AP- entered anterior exit posterior
ex: PA - Chest/hand
plain film radiograph... Accuracy? Cost? Distortion type? What is it best for? Converts what to what?
accuracy to less than mm
cheapest (with exception of diagnostic US)
point source distortion
3D info turned into 2D
best for bone
What shows up as black on an X-ray? Type of residences?
least radiodense (air)
more radiolucent
What shows up as white on an X-ray? Type of residences?
most residence (bone)
more radiopaque
What is magnification of x- rays? Close vs far? Resolution impact?
structures that are closes to the beam source are enlarged and have less resolution
structures farther are less enlarged and more resolution
What are contrast enhanced studies? What do mediums do?
medium injected into body
improve visualization of areas with minimal inherent contrast
What is an arthrogram? Where can it be injected? What are limitations of this? What can it be combined with?
contrast media study of a joint and soft tissue
shows abnormalities of synovium articular cartilage, capsule and soft tissue
limitations- not multiplanar, invasive
can be combined with advanced imaging to get more info
What is a myelogram? What are some abnormal results?
contrast media of spinal cord maters and nerve roots
abnormal results: ruptured disc, spinal stenosis, nerve root injury, intravertebral tumor
What is a fluoroscopy? What are they used for? What is another term for it?
real time/ open shutter x ray
used for angiography, catheter placement, arthrography, myelography, facet joint injection
"Open-shutter" X-ray
What are the ABCs of reading radiographs?
Alignment, Bones, Cartilage, Soft tissue
What are the A's (alignment) for radiographs?
subluxation, dislocation, diastasis
What is subluxation?
A displacement of a bone in relation to apposing bone at the joint
results in partial loss on continuity of joint surfaces
What is dislocation
a displacement of a bone in relation to the apposing bones at the joint, resulting in A COMPLETE LOSS OF CONTINUITY OF THE JOINT SURFACES
What is diastasis?
A displacement of bone in relation to the apposing bone in a slightly movable or synathrodial joint
What are the 3 abnormalities that the "B" (bones) fall into?
1) abnormal contour
2) abnormal size and shape
3) abnormal opacity
-decreased opacity (lucency)
-increased opacity (sclerosis)
In normal bone what are osteoclasts? Osteoblasts?
They are in equilibrium
Osteoclasts: Bone removers
Osteoblasts: bone formers
What happens when osteoclasts are stimulated in normal bone? What does this cause for bone mass and opacity?
Osteoclasts have the capability to reabsorb bone 20x faster than osteoblasts lay it down
Causes net bone loss and decrease opacity (increased lucency)
What are other causes of decreased opacity?
Lucent line (fracture)
Focal lucency (tumor and infection/Osteomyelitis)
Diffuse lucency (drugs, endocrine/metabolic, tumor)
What is diffuse lucency? Most common metabolic disorder?
A global process
Osteoporosis
What are causes of increased opacity? (sclerosis)
bone impaction or rotation (fracture)
bone production fracture-> callus, tumor-> tumor bone, infection-> periosteal reaction, osteoarthritis-> subchondral sclerosis
What is a fracture callus? Why can't they be seen?
Callus's can only be seen once they have started to heal
What is cartilage? What are 3 things you can see with cartilage?
cant really see on plain radiograph
can infer how cartilage is doing by looking at joint space
1. Decreased joint space, most common, Infers arthritis (OA commonly followed by RA)
2. Increased joint space, acromegaly or joint effusion
3. Chondrocalcinosis
What is chondrocalcinosis?
most commonly due to calcium deposition in the joints (knee, wrist, pubic symphysis
What are examples of S? (soft tissue)
swelliing
- most common, usually not diagnostically helpful
gas
- pentrating injuries, following surgery, soft tissue infections infections due to gas-forming organisms
calcification (non specific)
- non-specific
mass (hematoma, absess, tumor)
- MRI more helpful imaging choice for most masses
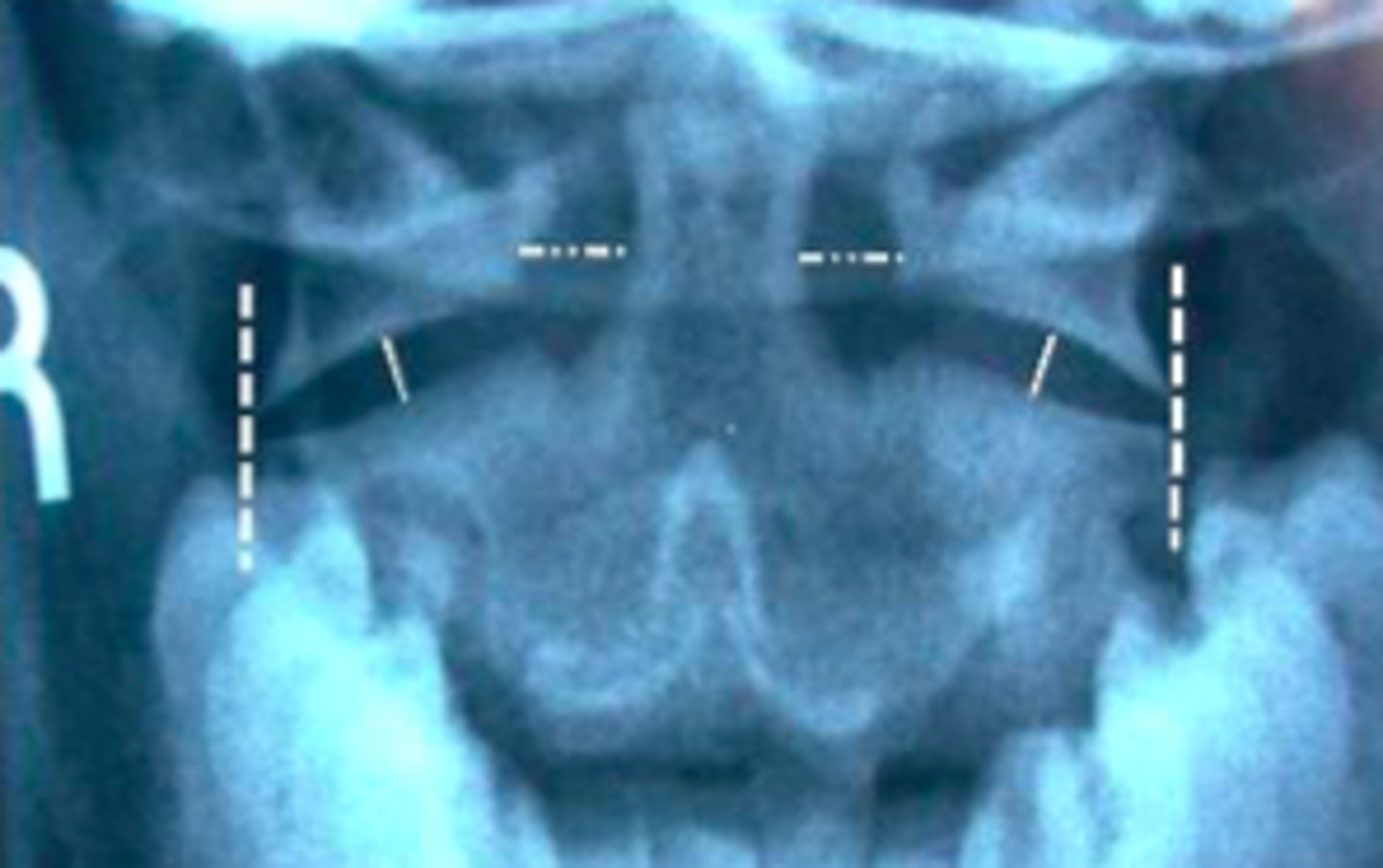
When would we use an open mouth view? (AP, lateral)
When there is a basic C-spine injury? (cervical) (AP, lateral)
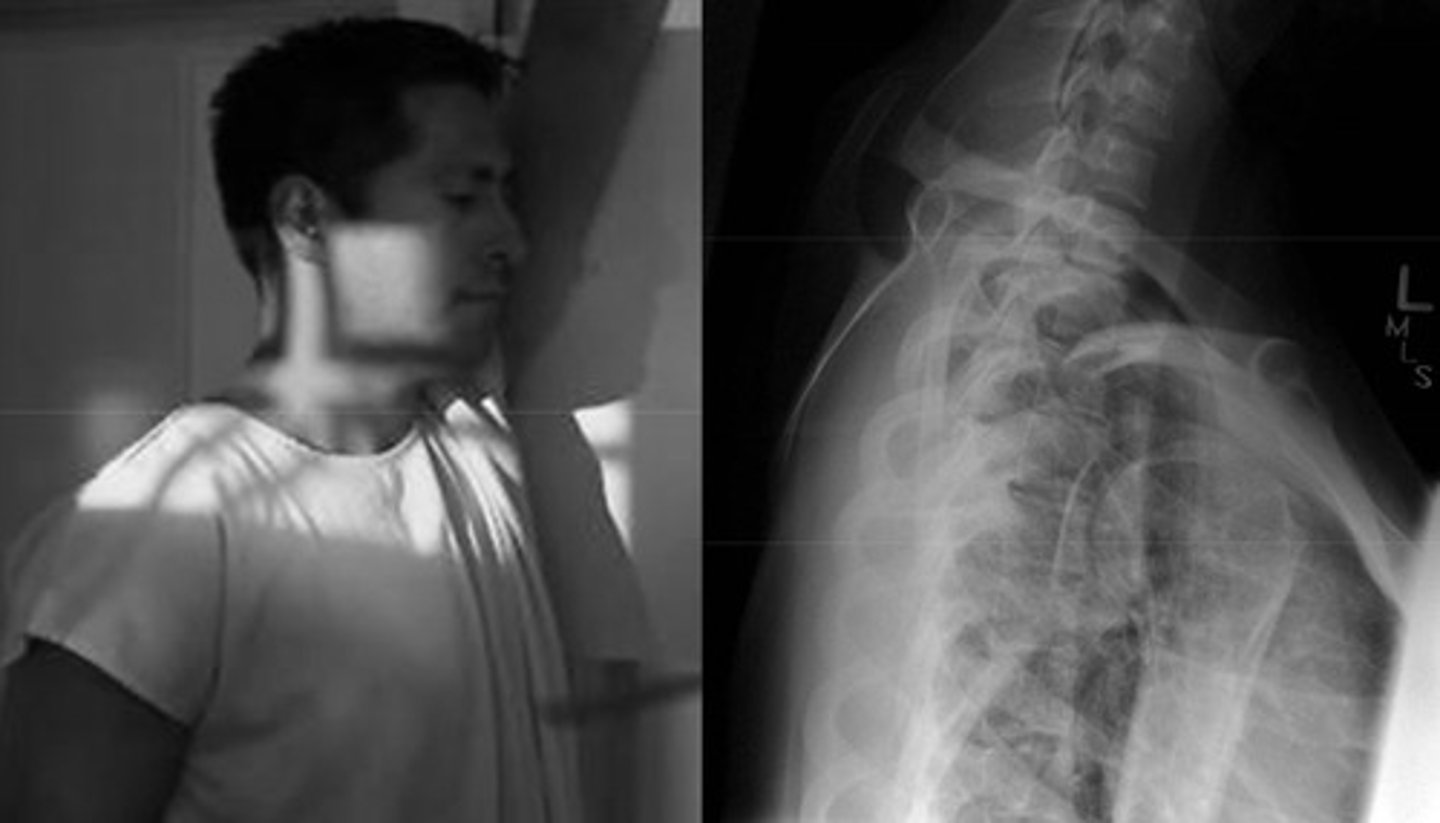
When would you use swimmers view?
Lower C-spine injury
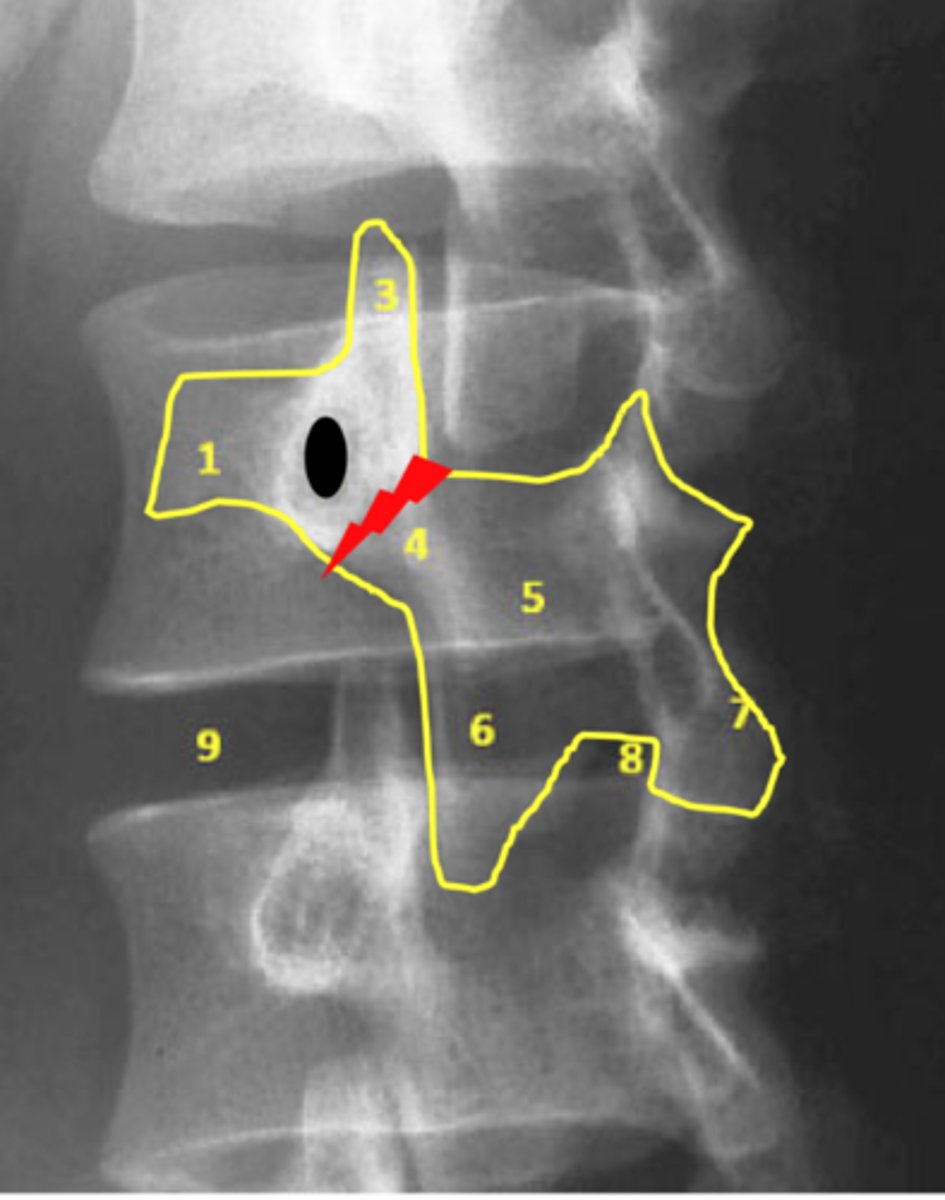
When would you use a coned view image?
L-spine basic injury
What are each of the items labeled 1-9?
Slide 39 in first powerpoint
What is an ultrasound?
imaging using sound
diagnostic and therapeutic
considered cheapest and safest imaging modality
rugged and portable
real time
Radiation free
What are the uses of ultrasound?
lesions to muscles, tendons and ligaments
detection of cyst
measure blood flow
can be dynamic
What are some limitations of ultrasound?
operator dependent
does not penetrate bone
does not cross air
does not work well in obese
What is nuclear imaging?
tracer is absorbed by specific tissues in varying amounts based on metabolic activity within that tissue
pathologies can be identified by variation in uptake
Gamma rays are emitted from body
What are the SPECT and PET imaging tools and info do they provide?
neuclear medicine imaging techniques which provide metabolic and functional info when combined with CT and MRI
What is PET positron emission tomography? Characteristics?
expensive
uses position emitting radiosisotope
better contrast and spatial resolution
What is SPECT single photon emission computed tomography? Characteristics?
lower cost
uses gamma emitting radiosotope
What is a Bone Scan?
early indicator of increased bone activity
abnormal conditions show increased uptake of tracer (technetium
What do you want to do first when imaging bone? Which X-ray modality?
Plain film radiographs
CT scan would be second
What are some principles of CT?
merges x rays and computer technology
provides detailed x sectional images
same imaging principles as radiology
reflect radiodensity
Some software can reformat into 3D images
Free from superimposition
What does "free from superimposition" mean in a CT scan?
Radiodense structures appear white
Less dense structures appear dark
Air < Fat < Water < bone
It is opposite from an MR image
What are the principles of an MRI?
uses magnetic field and radiofrequency signals
What is an MRI best for seeing? (6)
Bone marrow changes (tumor, AV)
Soft tissue
Disk herniations
Nerve root impingement
Neoplasms
Bone METS (more sensitive than bone scan, as those are used for screening)
CT vs MRI
usually MRI except osteomyelitis and stress fractures
CT= complicated fractures
What is the difference between a T1 and T2 MRI?
- T1 (anatomical)- fast to acquire, excellent structural detail, fluid is dark
- T2 (pathological)- slower to acquire, fluid appears bright
What is a CT scan best for? (5)
Loose bodies in a joint
Subtle or complex fractures
Degenerative changes
Serious trauma
Spinal stenosis
If someone has osteomyelitis, which diagnostic imaging test should be used? MRI, CT, or NM?
1a. NM, 1b. MRI
If someone has a complicated fracture, which imaging test should be used?
A CT scan
If someone has suspected stress or an occult fracture which diagnostic imaging test should be used? (MRI, CT, or NM)
NM
Which two modalities cost the most to use? (MRI, CT, Ultrasound, PET, SPECT)
MRI
PET
what region of the spine is the most mobile and why? (examples of what it can be used for?)
The cervical spine is the most mobile
Needed for vision and balance, allows for rapid head motions
why does cervical spine need stability
The cervical spines uses the "Sense organs"
needs protection for the vital "tubes"
In the upper cervical spine; what is the "craniovertebral complex" made up of?
occiput, atlas, axis
OA and AA joints
What are C7, T1, T2?
transitional segments
what is the lower cervical spine made up of? what motions occur here?
C3-7
motion occurs in all planes (primarily the sagittal)
What is a transitional vertebral segment? what vertebrae make up the transitional segments?
The vertebrae has characteristics of both regions
C7, T1, T2
how is epidemiology data useful in patient care
needed for clinical reasoning and likelihood ratios (ex: most patients with neck pain will have a musculoskeletal neck disorder)
what is the difference between incidence and prevalence?
Incidence: # of new cases in a time period / population at risk
Prevalence = # of existing cases at point in time / population at risk
Lots of new cases but ending in death over a short duration would be an example of what kind of incidence and prevalence
this would e an example of high incidence but low prevalence (high incidence due to the large number of deaths; low prevalence due to the short duration)
high prevalence example: OA
low prevalence example: common cold
On a global scale, what is the ranking of neck pain as a global disability and overall burden disability (two rankings)
4th greatest global disability
21stgreatest of overall disability burden
what is the ranking in the US for neck pain as the most common MS disorder associated with injury and disability claims
Neck pain is 2nd only to LBP as the most common MSK disorder
who is at the highest risk for neck pain? (gender, age, cultures)
greater in women
increases with age (peaking in 35-49)
cultural risk- head carrying cultures (Africa)
what happens after someone experiences neck pain (turns into? what kind of pain? how long will it last?)
44% will go to develop chronic conditions
32% moderate residual pain
50-85% will report neck pain 1-5years later
what are some common risk factors for cervical spine neck pain? (Gender? age? job type? physical activity?)
female
45-59
heavy labor
office/ computer jobs
health care
unemployed
sedentary work
repetitive work
smoking
previous neck pain
depression
job strain
low co worker social support
what is mechanical neck pain? what is the most common cause of mechanical neck pain?
Neck pain that behave mechanically (pain is influenced by movement, position); serious pathology (fracture, disease) have been ruled out
this is a type of musculoskeletal cause
What are some common causes of musculoskeletal neck pain? are PT's better at figuring out these issues?
soft tissue injury (ligament, muscle, capsule)
degenerative changes in zygapophyseal joint
joint pain
fracture
dislocation
PT's should be better at treating this one compared to non-musculoskeletal causes
non msk causes of neck pain
infection
tumor
cardiac
endocrine
GI
neurological
pulmonary
systemic disease
Do most patients with neck pain have a specific cause? what is the is called?
Specific PATHOANATOMIC cause is not known in musculoskeletal causes
what are pain characteristics associated with nonmusculoskeletal symptoms (location, chronology)
location: deep, non specific
chronology: constant, unrelated to movement, night
what are red flag symptoms of neck pain associated with nonmusculoskeletal symptoms
insidious onset with no mechanical association
symptoms unchanged by movement or position
not proportionate to injury
unexplained swelling, paresthesia, weakness, tone changes
unintended weight loss
visual changes
growing mass
changes in skin or nails
pain associated with exertion/ exercise
bowel/ bladder changes
dyspnea, shortness of breath or dysphagia
changes in skin or nail condition
constitutional symptoms: fatigue, fever, dizziness/fainting
What are the signs and symptoms of tracheobronchial conditions
Signs: inflammation, viral and bacterial infection, tumor
symptoms: referred neck pain, dyspnea, dysphagia, persistent cough, fever/chills, hemoptysis
what are the types of tumors associated with the neck? how common are they? what are some symptoms
-Bone: overall uncommon; more common in young adults
-spinal cord: less common than intracranial CNS tumor
-esophageal, thyroid
Symptoms: neck pain, sore throat, dysphagia, growing mass, UMN signs (if spinal cord is involved)
What is a pancoast tumor? what are some common symptoms
Pancoast tumor: Lung cancer in the upper lobe that invades the lower brachial plexus
symptoms:
-extrapulmonary: pain in shoulder and scapula and referred pain down the arm
-pulmonary (uncommon): cough, chest pain
What is Honer's syndrome?
if the tumor invades the sympathetic chain
what is osteomyelitis in the neck and common symptoms?
Osteomyelitis: bone inflammation that is secondary to an acute or chronic infection
Symptoms: neck pain, stiffness, fever
what is discitis
disc inflammation that can be infectious, disc narrowing
causes neck pain, stiffness, and fever
what are some cardiovascular conditions that refer pain to the neck?
acute myocardial infarction (neck and jaw)
acute coronary insufficiency
carotodynia (painful carotid artery)
what are some GI conditions that refer pain to the neck?
esophageal infection, tumor, varices
symptoms: dysphasia ant neck pain
what are some other conditions that can refer pain to the neck?
lymes
RA
ankylosing spondylitis
fibromyalgia
klippel- fiel
thyroid
-hyper/hypo-thyroidism
what is klippel- fiel syndrome?
congenital fusion of cervical vertebrae
Occam's Razor (Law of Parsimony)
the simplest solution tends to be the simples one
what is the atlantoaxial joint / what does it pivot around?
bony ring pivoting around dens
What are the 5 ligaments that support the AA joint?
alar
cruciform (includes the transverse ligament which hold the dens to the arch)
accessory
apical
anterior atlanto- dental ligament
anterior atlanto- dens interval instability occurs after how many mm's? (AADI)
if > 3.5mm, instability occurs
sings and symptoms of upper cervical instability (could involve deficits in?)
deficits of ligamentous/bony/muscular support causing...
C2 pain
bilateral UE/ LE paresthesia
clumsiness
nystagmus
headaches
blurred visions
UMN (hyperreflexia, spasticity, abnormal gait, Clumsiness, Babinski)
what are some of the main causes of atlantoaxila instability?
congential bony malformation
down syndrome
inflammatory
trauma
chronic corticosteroid use
how does down's syndrome affect atlantoaxial instability?
causes AAI incidence, ligamentous laxity, special Olympics position statement
inflammatory causes of Atlantoaxial instability?
RA
psoriatic arthritis
anklyosing spondylitis
osteomyelitis
Trauma causes of atlantoaxial instability?
MVA: head striking windshield
football: spearing
What is radiculopathy?
nerve root impingement
causes sensory and motor changes
how do nerve roots exit at a level?
nerve roots exit above the named level
two common sequences of impingement of the nerve?
radiculopathy: nerve root and sensory/motor changes
myelopathy: spinal cord; UMN signs
during the standard orthopedic patient interview (history portion) what is included
demographic
employment
condition
medical care
functional status
social history
current health status
personal health history
family health history
what is the self-report instrument tool used for the neck?
Neck disability index (NDI)