2.2.3 - Ethiopia case study
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Where is Ethiopia
east-central Africa
What countries border Ethiopia
bordered on the west by Sudan and South Sudan, the east by Somalia and Djibouti, the south by Kenya, and the northeast by Eritrea.
What is the landscape of Ethiopia like
several high mountains, the highest of which is Ras Dashan at 4,620 m.
What is the river going through Ethiopia like?
The Blue Nile, or Abbai, rises in the northwest and flows in a great semicircle before entering Sudan. Its main reservoir, Lake Tana, lies in the northwest.
How has location affected Ethiopia’s development
Ethiopia is a landlocked and mountainous country which means that it has no access to the coast. Therefore any trade by sea requires access via its neighbouring countries which can be difficult at times. It is also more expensive to trade by land and air rather than sea.
Trade generates income for a country and if you spend a lot to export and import goods due to the landscape and location of a country, the country will not make any capital to spend on developing its own infrastructure such as roads.
Ethiopia’s neighbours are also LIDC’s which mean that infrastructure is also limited and unreliable
Ethiopia has a trade deficit as exports value US$3 billion but imports value US$11 billion.
The location of Ethiopia is a factor in causing this deficit.
How do Mountainous landscapes affect development
Mountainous land (up to 4500m) has steep slopes and thin soils.
This means that few crops can be grown so farming is subsistence and no capital is made.
Coffee, cotton and grains can be grown in lower valleys and used to export.
Coffee, cotton and grains are exported in its raw form and are low value cash crops.
Therefore Ethiopia does not make much capital to invest in its infrastructure which is essential to develop and to manufacture its own goods from the raw materials.
how do lowland landscapes affect development
Lowlands contain both livestock grazing and agriculture due to the flat more fertile land. The lowlands do however suffer from mosquitoes and malaria and unreliable rainfall.
This means that the lowlands are overgrazed and over cultivated which can lead to soil erosion and desertification (formation of desert like land).
Malaria can cause severe illness and loss of workforce and earnings.
how does climate affect development?
Western highlands are milder and wetter and coffee, cotton and grains can be grown in lower valleys.
Unreliable rainfall occurs and climate change is altering the monsoon and dry climates.
This can result in drought, soil erosion and desertification which leads to widespread famine.
Cattle do not have enough food due to the drought and they die.
This affects Ethiopia’s development as people do not have food and water which are essential to survive and therefore develop. Poverty is high and famine results meaning that workforces are lost.
How do natural resources affect development
Ethiopia has small reserves of natural minerals such as gold, platinum and copper as well as reserves of natural gas.
There is only one large-scale gold mine in operation but there are plans to develop more and to develop the potential of oil and gas reserves.
Mining contributes to more than 19% of Ethiopia’s exports (2012) but the natural resources are not able to be manufactured in Ethiopia so the resources are of a low value.
If mining is developed and managed sustainably it could positively impact Ethiopia’s development by creating an income that can help to develop infrastructure and a manufacturing base. This means raw materials can be manufactured and exported at a higher cost.
How has politics affected Ethiopia’s development
The independence of Eritrea has caused Ethiopia to become landlocked which means they have tense relationships with Somalia because they have to use Somalia's ports for trade. This makes trading difficult.
military coup evicted the government from 1974-87 and a civil war resulted killing 1.4 million people.
In 1984 drought/famine led to BAND AID. International aid provided US$2000 million worth of food and water. This drought and famine was worse than it needed to be due to the civil war meaning the government could not help the people.
This resulted in many potential workers being lost and Ethiopia’s funds are spent on war rather than into basics such as the provision of food and water. The country cannot develop and remains a ‘traditional’ society.
A stable government is essential for Ethiopia to develop and currently Ethiopia is developing trade links with the USA.
The government are also investing in training programmes for farmers which aim to increase soil fertility and productivity. This will help the country to develop in the long term as the population will be able to move from subsistence farming to commercial farming.
How has trade affected Ethiopia’s development
Ethiopia has a trade deficit, with a export value US$3 billion but imports vale US$11 billion. They export products in their raw form (like coffee beans) -> low income
Ethiopia cannot earn profit from trade -> debt remains
Because of the trade deficit, there is less government income to development.
The trade deficit reduces government income -> less investment in infrastructure and education -> less productive workforce -> hinders development
Climate is very unreliable in Ethiopia. There can be periods of large droughts, which can sometimes lead to desertification. When this happens, soil becomes loose like sand and blows away. This means crops and flowers can’t grow as there aren't any available nutrients and that there's less trade
If more people are living in poverty it means that more people aren’t able to go out and wok. This means that the government cannot tax people and therefore don’t have money to invest in infrastructure like hospitals and school can be improved. School improvements mean that children that do go to school can receive better education and can then have better and higher earning jobs.
how has international investment affected Ethiopia’s development
Ethiopia has improving international links and global support from TNCs.
This means that Ethiopia is now making more money from trade of manufactured goods like clothes and electrical equipment – but sometimes working conditions are poor.
A range of TNCs like Hilton Hotels (company providing leisure and recreation services) have been investing in Ethiopia.
Growth of tourism creates more jobs in tourism – these may not seem well-paid by AC standards but are better than average for Ethiopia.
Therefore, Ethiopia is beginning to make a little more profit from tourists and manufactured goods.
Workers in hotels are often paid a fair wage and have access to the facilities out of hours.
H&M (They manufacture textiles and do university education in textiles) have been manufacturing clothes and Siemens ( They manufacture telecommunications, electrical items and medical technology.) have been manufacturing electrical equipment.
However, this can come at the cost of fair treatment of workers.
How has population affected Ethiopia’s development
Ethiopia has a population of over 94 million, making the 13th most populous nation in the world. There is a high birth rate and a slowly falling death rate.
This means that the natural increase is occurring, and the population is growing by 2.6% per year.
Therefore in Ethiopia, there will be a lot of pressure on the economy as there is an overpopulation and there are locals already struggling with food insecurities and lack of resources.
The Life Expectancy is at 63 years, lower than the world's average.
Therefore, this reduces the amount of people in work-forces, as famine and disease also contribute to the number of deaths.
This means that the government have less money for taxes, meaning that they cannot invest and therefore development is hindered.
How has Employment structure (primary, secondary, tertiary jobs) affected Ethiopia’s development ?
History of famine, drought, poor healthcare, disease, poverty and conflict
This leads to one of the lowest levels of development with an HDI of 0.435, also with the life expectancy being 63 even though it has been increasing it is lower than the world average of 72
The landscape is mainly rural and large-scale argiculture has only recently begun to develop
The country is reliant on agriculture making up 89% of all exports and 80% of all jobs.
Therefore other sources of income is needed to develop (other than primary) - over 2.5 million workers are required in tertiary
SUCH AS TOURISM – potential – due to landscape but is still lacking hotels and services – however investment is increasing.
TNCs are encouraged to invest + Secondary manufacturing is increasing
How has healthcare affected ethiopia’s development
One doctor shared by 3333 people
This means that doctors are going to be able to treat less people and more likely people will have to wait longer for healthcare
Eighty percent of the population live within 10km of a doctor
Diarrhoea and Malaria as the biggest killers of children yearly
Child mortality used to be 97/1000
This means that the Infant mortality rate is low
Mortality rate is now 45/1000 because more investment in child health care and maternal care however some more rural areas are still struggle with infant mortality rate
How has education affected ethiopia’s development
Ethiopia used to have quite a poor Educaton rate for people who lived there, just 43% of girls were in schools in 2000 a very low number showing that the education gap had still not closed in Ethiopia.
It means that there is a gender gap between male and females when it comes to education
Therefore, the government have put in place several plans such as the national Education Development plan which ensures that 96 percent of children join a primary school. This has risen by 50% since 1990 showing this plan has helped development in Ethiopia.
How has technology and innovation affected Ethiopia’s development
Ethiopia is behind other African countries in terms of technology and innovation. Ethiopia is one of the last African countries to have a state-owned monopoly, operated by ethio telecom (ETC).
This means that there is a lack of competition which had led to
slow technological developments
despite the market for mobile phones increasing
the network coverage is poor.
There are no credit cards and no international banking systems which makes online purchasing inaccessible
Therefore, less than 4% of Ethiopia's population in 2015 were connected to the internet.
In 2024 60% of the population in Ethiopia use mobile phones.
Difficult for small technology start-ups to develop and less interest for other businesses.
In other African countries such as South Africa and Morocco have improved their economics and social development by developing the communication technology. With these successful examples, Ethiopia may learn from them.
In 2013, technology has developed so that people could use phones to send money and pay in shops. This makes payment easier, so people buy goods and spend money more. Therefore promoting the country's economy.
How has Aid affected Ethiopia’s development
Oxfam provides goat aid in Ethiopia (goats provide resources to sell like milk, cheese etc)
this provides better health and allows then to sell the produce allowing them to invest in education, food and clothing, due to them being able to sell the produce and clothing. The goat can then be re-bred making more goats and repeating the process.
Therefore girls receiving goat aid are less likely to be subject to arranged/ forced marriage, prostitution and disease and poverty. This in turn, improves development, providing a goat support equalities and reduce birth rate
International development support through aid and debt relief has benefited Ethiopia
The debt relief and support from international communities. Ethiopia's economy was in debt by 155%
By 2012 the debt declined to 21% of the national economy meaning the government were able to invest in services.
5 million people receive food aid each year
Providing people with food decreases health issues (e.g. malnutrition)
Less money needed to be spent on medical treatment.
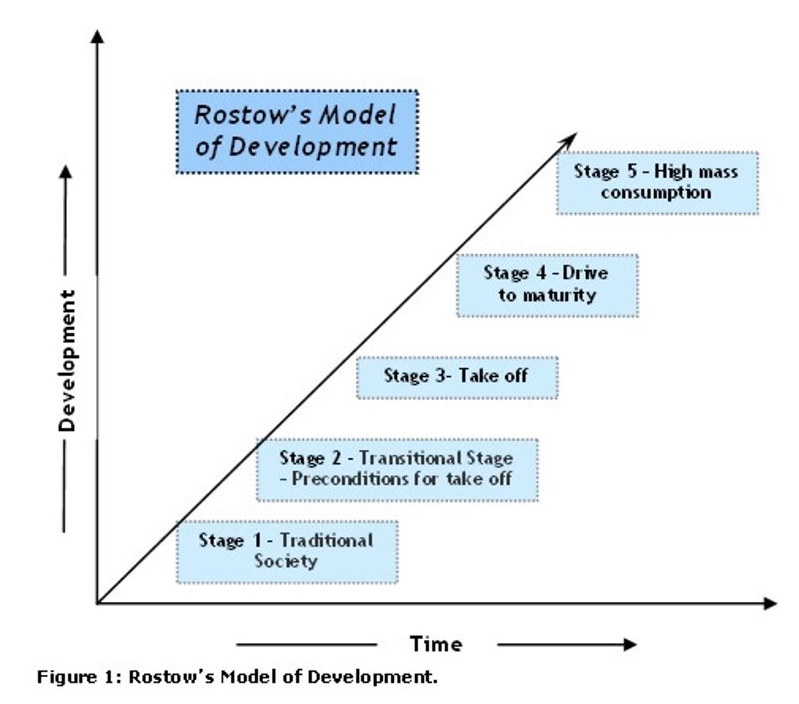
describe the Rostow model