Sedatives & Alcohol
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIOM 3090
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What is anxiety, and what feelings are associated with it?
Anxiety is defined as feelings of apprehension, tension, uncertainty, dissatisfaction, and fear
What are the 5 main types of anxiety disorders?
PD (panic disorder): frequent, spontaneous attacks + avoidance
GAD (generalized anxiety disorder): constant worry & physical symptoms
OCD (obsessive compulsive disorder): excessive, repetitive thoughts & behaviours
SP (social phobia): embarrassment & humiliation in social situations
PTSD (Post traumatic stress disorder): thoughts and experiences of a horrible event
Common symptoms of a panic attack
Palpitations
Sweting
Trembling
Shortness of breath
Choking
Chest pain
Nausea
Dizziness
Fear of losing control, fear of dying
Paresthesias (pins/needles)
Hot/cold flashes
What are the main treatments for anxiety disorders?
Medication
Psychotherapy
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT)
How is anxiety secondary to other disorders like psychosis or depression best treated?
By treating the primary illness causing the anxiety
What are the main types of sedative-hypnotics used to treat anxiety?
Benzodiazepines and barbiturates
What is an anxiolytic?
An anxiolytic is a sedative drug that produces a calming effect and relief of anxiety with little or no effect on motor or mental function
What is a hypnotic?
A hypnotic is a drug that produces drowsiness and induces sleep
According to the dose-response curve, which drug has the highest risk of respiratory death with increasing dose?
Barbiturates - their curve continues steeply to respiratory depression and death
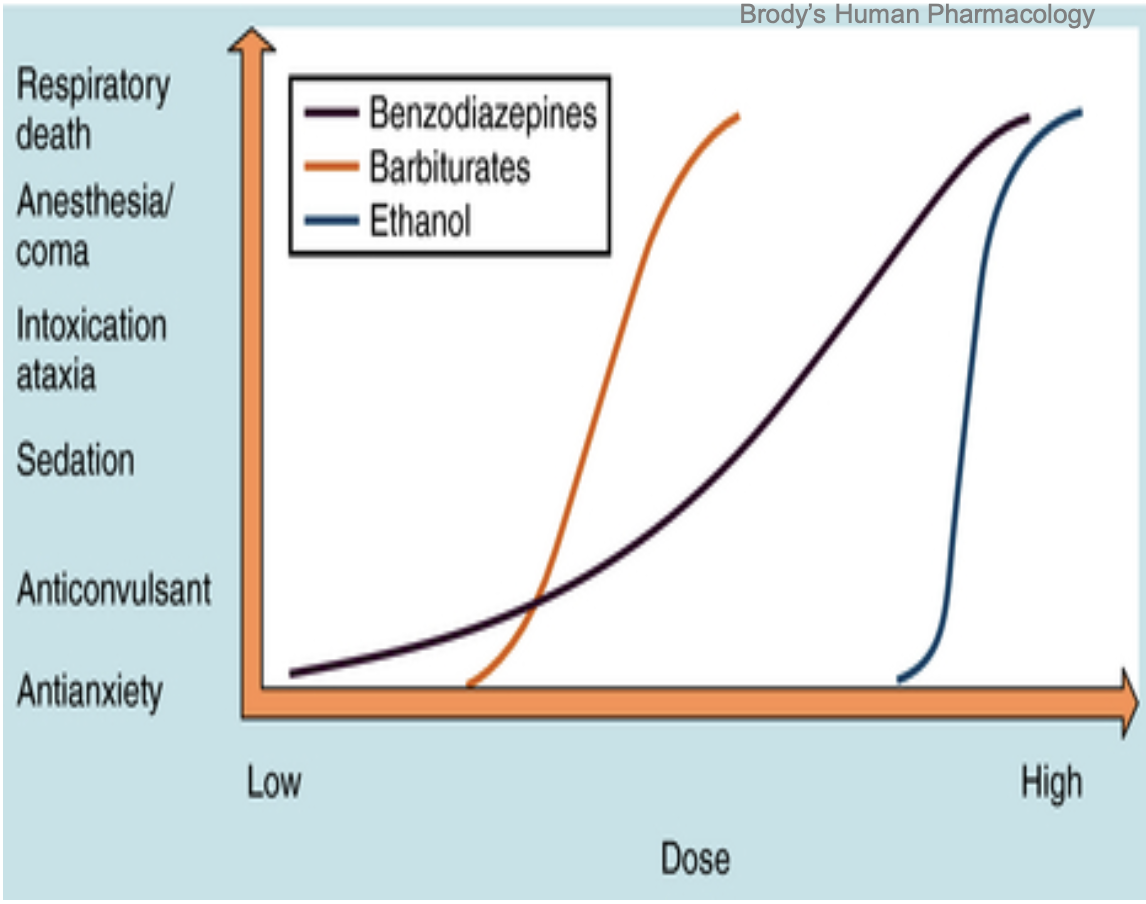
What does the graph indicate about benzodiazepines compared to barbiturates and ethanol in terms of safety?
Benzodiazepines have a plateau in their dose-response curve, indicating a lower risk of fatal respiratory depression at high doses compared to barbiturates and ethanol
What is the brand name of diazepam?
Valium
Describe the phase I metabolism of Diazepam
Phase I involves oxidation by cytochrome P450 enzymes, and all metabolites produced are active
What happens during phase II metabolism of diazepam?
Oxazepam undergoes conjugation with glucuronide to become more water-soluble for excretion
What are the active metabolites of diazepam?
Nordazepam, Temazepam, oxazepam
What is a key pharmacokinetic feature of many benzodiazepines, including Diazepam?
They undergo first-pass metabolism where oxidation leads to active metabolites
What is the primary action of benzodiazepines on neurotransmission?
They enhance GABA neurotransmission
How do benzodiazepines enhance GABA neurotransmission?
They bind to a subset of GABAA receptors at a site distinct from GABA (GABA binds to the same receptor but at a different part, making the receptor more responsive to GABA)
What effect does benzodiazepine binding have on GABAA receptors?
It increases the frequency of GABA-mediated Cl- channel opening
Can benzodiazepines activate GABAA receptors by themselves?
No- they require GABA to be present in order to exert their effect
What happens to Cl- influx when benzodiazepines and GABA both bind?
Cl- channels open more frequently, increasing inhibitory effects
What is an example of a barbiturate?
Phenobarbital
How does the safety margin of barbiturates compare to benzodiazepines?
Barbiturates have a smaller margin of safety than benzodiazepines
Describe the pharmacokinetics of barbiturates
Phase I: Oxidation by cytochrome P450
Phase II: conjugation with glucuronide (body prepares it for removal)
Are barbiturate metabolites active?
Metabolites are generally not active
What is the unique pharmacokinetic property of barbiturates regarding liver enzymes?
Barbiturates increase the expression of cytochrome P450 enzymes
What is the mechanism of action of barbiturates?
Enhance GABA neurotransmission
How do barbiturates interact with GABAA receptors?
Bind to all GABAA receptors at a site distinct from both GABA and benzodiazepine binding sites
What affect does barbiturate binding have on GABAA receptors?
Increases the duration of opening of the GABA-mediated Cl- channel
What can barbiturates do at high doses?
Directly activate GABAA receptors
Inhibit glutamate receptors
Inhibit some sodium and calcium channels
What is the overall effect of enhancing Cl- conductance in neurons?
Increased inhibition of many neurons in many brain regions
What is the effect of GABA binding to GABAA receptors?
Opens Cl- channels, causing Cl- influx and hyperpolarization of the neuron
What is the structural composition of the GABAA receptor?
It is a chloride ion channel composed of five subunits (alpha, beta, gamma) forming a central pore
What do benzodiazepines and barbiturates bind on the GABAA receptor?
Benzodiazepines bind at a site between the alpha and gamma subunits
Barbiturates bind at a different allosteric site on the receptor
What are sedative-hypnotics commonly used to treat in psychiatric conditions?
Anxiety and psychosis (initial management)
How are sedative-hypnotics used in the treatment of sleep disorders?
They are used to treat insomnia
What is the role of sedative-hypnotics in surgical settings?
Induce sedation and amnesia prior to surgery
Used as a component of total anesthesia
How are sedative-hypnotics useful in neurobiological conditions?
Epilepsy: control seizures
Muscle relaxation: reduce muscle spasms or rigidity
What role do sedative-hypnotics play in substance use disorders?
They are used in the management of alcohol withdrawal
What is the dose-dependent effect of sedative-hypnotics on the CNS?
They can cause impaired judgment/motor skills → amnesia → coma → death
Why should sedative-hypnotics not be combined with other CNS depressants (eg. opioids, alcohol, antihistamines)?
They can cause additive CNS depression, increasing the risk of severe side effect like respiratory depression or death
What occurs with prolonged use of sedative-hypnotics?
Withdrawal symptoms may develop when the medication is stopped
Who is at increased risk of adverse effects from sedative-hypnotics?
Individuals with impaired liver function (due to impaired drug metabolism)
What is meant by tolerance in the context of sedative-hypnotics?
Over time, higher doses are needed to achieve the same effect
How do barbiturates affect drug metabolism?
They alter metabolism of both themselves and other drugs via induction of cytochrome P450 enzymes
What role does the endocannabinoid system play in anxiety regulation?
It regulates anxiety and stress response by dampening excitatory signals that involve the neurotransmitter glutamate
How do exogenous cannabinoids from marijuana affect anxiety?
They can reduce anxiety initially
What happens with chronic use of marijuana?
Chronic use down-regulates cannabinoid receptors (highly expressed in the amygdala), which paradoxically increases anxiety
What vicious cycle can chronic marijuana use create in anxiety?
It can lead to increased marijuana use to relieve the now-heightened anxiety, sometimes resulting in addiction
Define endocannabinoids and where they are produced
They are lipid neuromodulators
Produced on-demand in the postsynaptic neuron
How do endocannabinoids regulate neurotransmitter release?
Act retrogradely: released from postsynaptic neuron and bind to CB1 receptors on presynaptic terminal
Cause inhibition of transmitter release (GABA or glutaamate)
Supress excitatory signaling
How does Marijuanna affect CB1 receptors
Compounds in marijuana (like THC) activate CB1 receptors
mimic endocannabinoid activity
can reduce neurotransmitter release (initial anxiolytic effect)
What happens to endocannabinoids after release?
Rapidly metabolized by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH)
helps limit duration of their effect
What are the acute effects of ethanol on the CNS?
Dose dependent CNS depression:
decreases membrane excitability
Increases GABAA activation
decreases NMDA activation
Results in decreased anxiety, slurred speech, impaired judgement
What are other acute effects of ethanol beyond the CNS depression?
Diuresis (increased urine)
Initial increase followed by decreased in myocardial contractility (muscular heart tissue)
Toxic doses lead to CNS and respiratory depression
What are the chronic effects of ethanol on the body?
Fatty liver → hepatitis → cirrhosis → liver failure
Pancreatitis & gastritis
Malnutrition
How is ethanol primarily metabolized in the body?
Over 90% is metabolized by the liver via oxidation
Major pathway: alcohol dehydrogenase
Minor pathway: Cytochrome P450 (MEOS = microsomal ethanol oxidizing system)
How much ethanol is excreted unchanged, and by which organs?
less than 10% excreted unchanged
via kidney and lung
What type of kinetics does ethanol elimination follow and what does it imply?
Zero-order kinetics
Clearance rate is constant, regardless of concentration
So, blood ethanol levels continue to rise if consumption exceeds elimination
Why is ingesting hand sanitizer dangerous, and what type of poisoning can it cause?
Ingesting alcohol-based hand sanitizer can cause methanol poisoning
methanol is toxic and can lead to impaired vision, seizures, hospitalization or death
It should never be ingested
What makes methanol toxic and how is methanol poisoning treated?
methanol has CNS depressant effects similar to ethanol
metabolized to formic acid, which accumulates in the retina leading to optic nerve damage which can lead to blindness
Treatment: ethanol
Why is ethanol used as a treatment for methanol poisoning?
Ethanol competes with methanol for alcohol dehydrogenase and has a higher affinity for it
Slows methanol metabolism which reduces the production of toxic formic acid