19. Affinity of hemoglobin for respiratory gases
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
what is affinity and how does the O2-hemoglobin dissociation curves help us understand this?
affinity is how easy it is for the hemoglobins to grab onto oxygens
a shift to the right means the O2 partial pressure needed to saturate is higher, and O2 affinity is lower
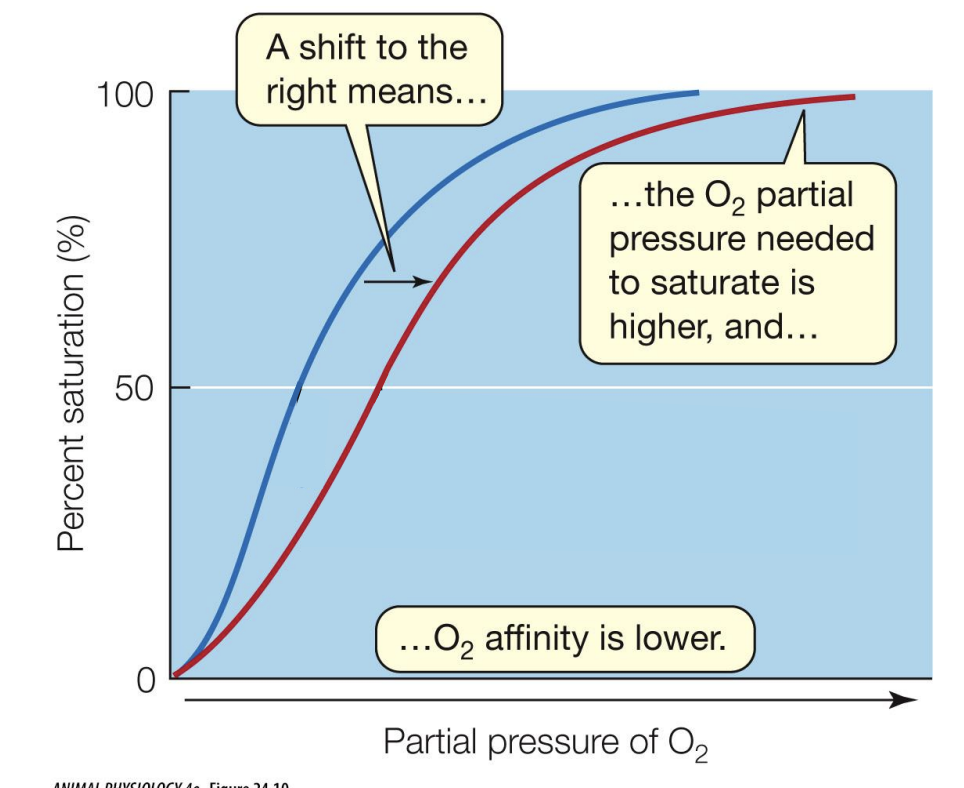
acute, chronic, developmental, and evolutionary changes in blood O2 affinity can be demonstrated in humans and other animals
yes, it is good to have better O2 affinity, but if it has very good O2 affinity, what can happen?
good affinity is good at loading the hemoglobin with oxygen, but once it is time to unload the oxygen in the systemic capillaries, the hemogloblin might not want to let go of the oxygen
however, mario is right about this: advantage of loading oxygen outweighs the disadvantage of unloading
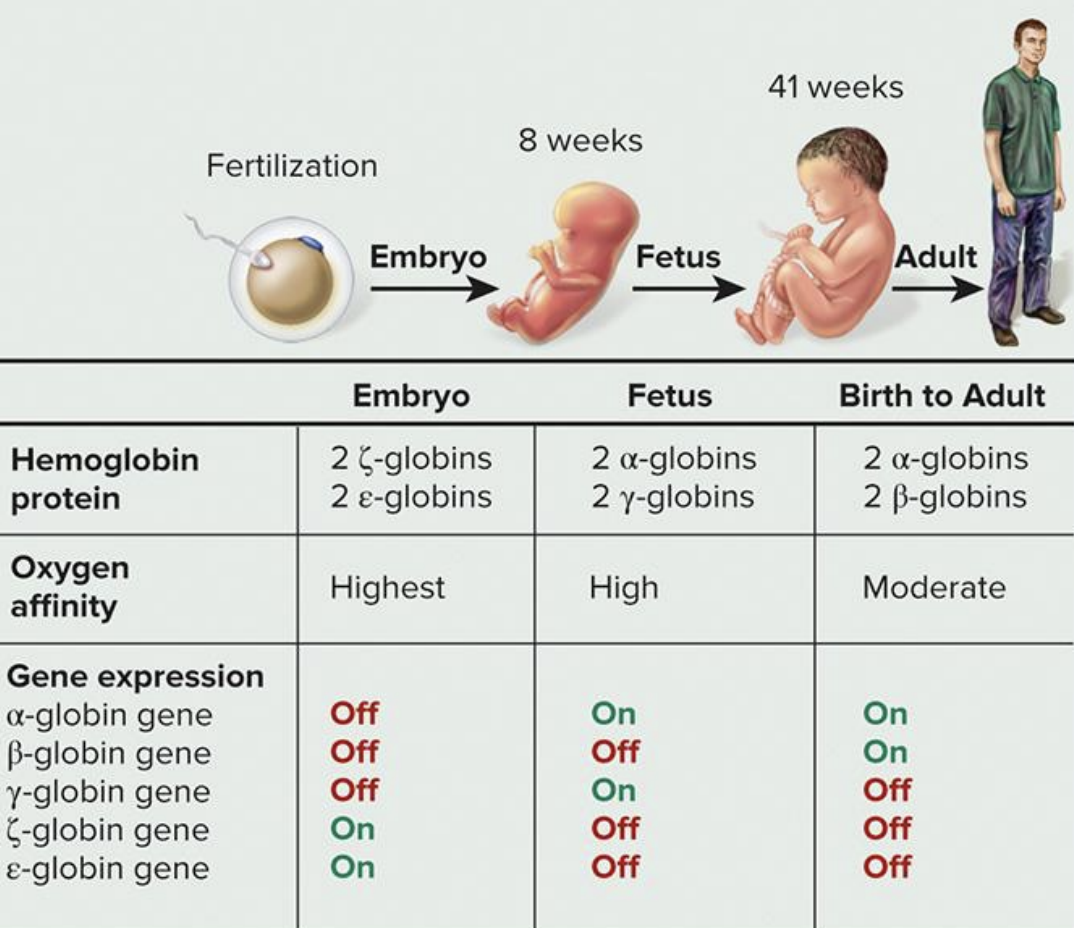
how does developmental changes in globin gene expression affect hemoglobin binding affinity?
embryo → highest oxygen affinity
fetus → high oxygen affinity
birth to adult → moderate oxygen affinity
what is the bohr effect?
O2 affinity decreases as pH decreases (more acidic or when CO2 partial pressure increases to drive reaction to the right to make more protons)
this is because CO2 makes pH change which will affect how well the hemoglobin affinity works
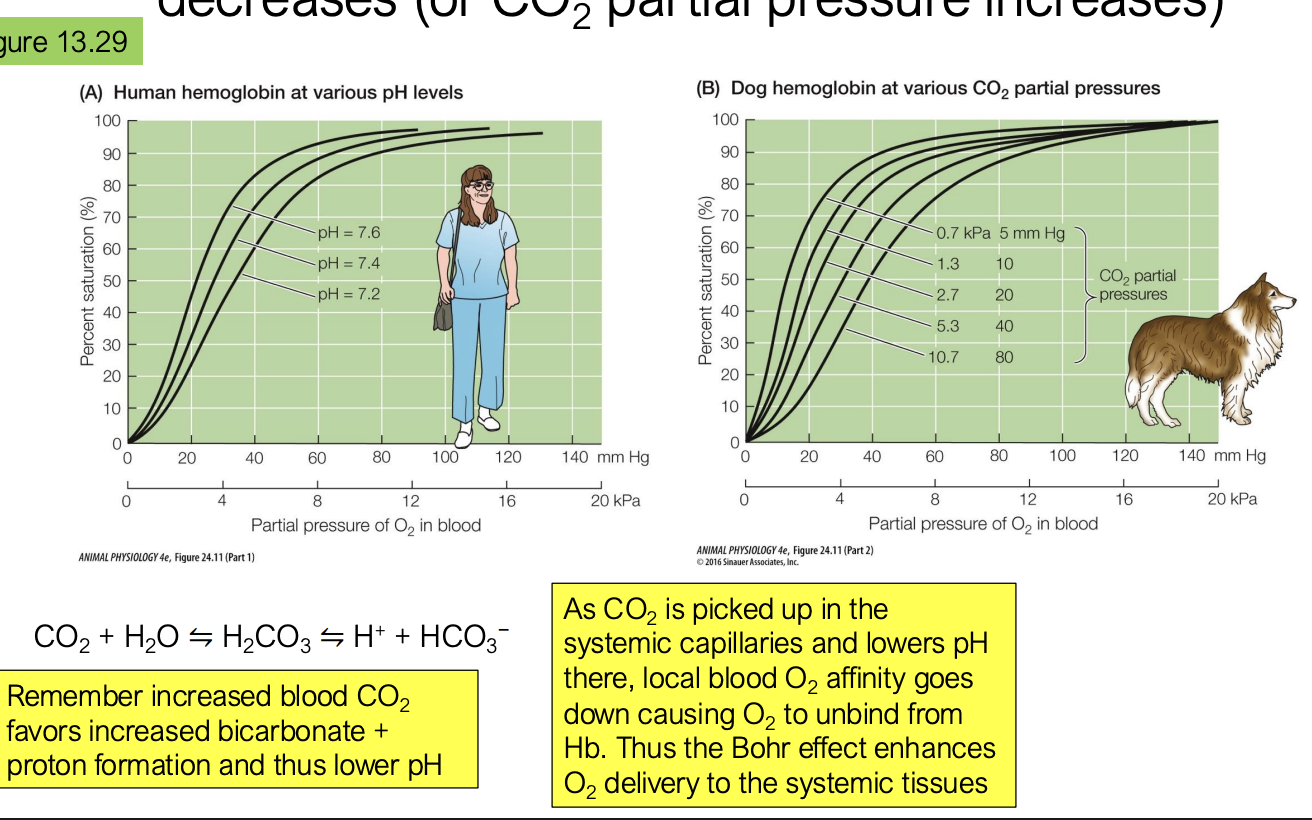
how can the bohr effect enhance O2 delivery to the systemic tissues?
as CO2 is picked up in the systemic capillaries, and lowers pH there, local blood O2 affinity goes down causing O2 to unbind from the hemoglobin, enhancing O2 delivery to the systemic tissues
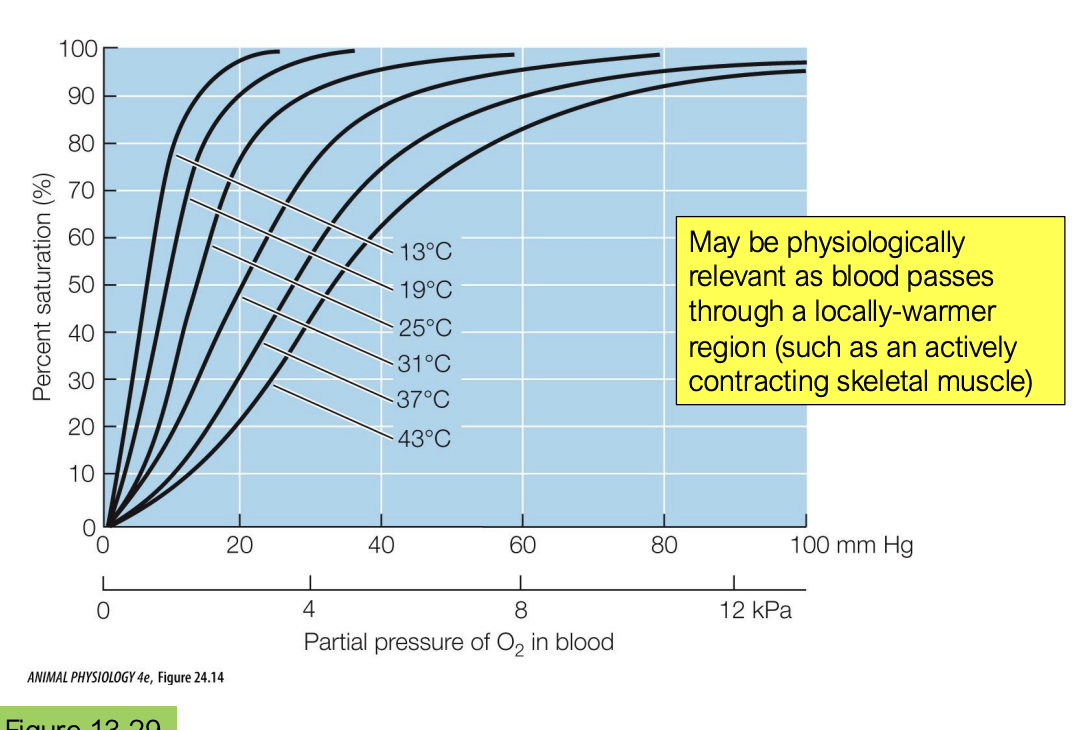
what is the effect of temperature on hemoglobin O2 affinity? is our body temperature always the same? how can this be helpful?
an increase in temperature also causes a decrease in hemoglobin O2 affinity
although we regulate our body temperature, it is not always the same throughout our body. for example, if we are exercising, our legs would get warmer and this is good because warmer temp leads to lower O2 hemoglobin affinity, which allows O2 to unbind and go into the necessary tissues