medical embryology - development of CNS
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
to what is the ventriuclar system (aka all brain ventricles) connected
the central canal of the spinal chord
what do the brain ventricles contain
cerebrospinal fluid
what structures are formed by the cephalic end of the neural tube (simultaneously with brain vesicle development)
2 flexures:
flexura cranialis
flexura cervicais (cervicle flexure)
when is the third flexure formed and what is the name and position
the flexura pontina is formed when the secondary brain vesicles are established and marks the boundary between meten en myelencephalon
what is the beginning of development of the CNS
it starts with neural plate induction form ectoderm stimulated by the primitive node
what seperates the mesen and metencephalon
the midbrain-hindbrain border, ookwle isthmus (=sharp bend)
during cytodifferentiation, neuroepethelial cells differentiate into:
neurblast cells (form neurons, glia cells & ependymall cells)
how are the mantle layer and marginal zone established
neurons migrate peripherally
describe the orientation of mantle and marginal zone
the central canal is surrounded by ependymal cells, surrounded by mantle zone, surrounded by marginal zone
what is the mantle zone, and what the marginal zone
mantle zone is the presumptive grey matter
marginal zone is the presumptive white matter
white matter always surrounds grey matter behalve in cerebral cortex
what is formed by the further divisions of mantle layer
the ventral and dorsal sides of neural tube thicken and form the dorsal alar plates (become sensory neurons) and the ventral basal plates (become motor neurons)
what sperates the two dorsal alar plates from e/o, what the two ventral basal plates. and what sperates the alar from basal plates
roof plate separates the dorsal alar plates
floor plate separates the ventral basal plates
The alar and basal plates are separated by the sulcus limitans
how are the lateral ventricles connected to the 3rd ventricle
Foramen of Mono = interventriculum foramen
the telencephalon can be divided into a ventral and dorsal region, what structures develop from each
the ventral region: subpallium = striatal rigde → corpus striatum → caudate nulecus & lentiform nucleus
dorsal region: pallium → hippocampus, cerebral cortex, commissures, olfactory bulbc & tracts
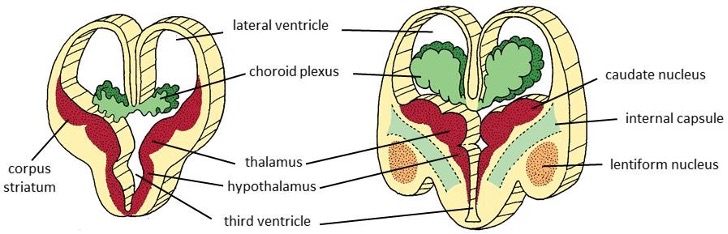
fill in: the ependymal wall only grows when its attached to … to form the ..
attached to the diencephalon roof plate to form the choroid fissure (waaruit choroid plexus ontstaan)
what are the two the surface structure of the cerebral cortec called
sulci (grooves) & convolutions (gyri)
what is the function of the olfactory tract
to connect the olfactory bulb to other brain sensory regions
Name of the groove that seperates sensory areas from motor ares
central sulcus
What type of plates does the diencephalon contain
roof plate, floor plate, 2 alar plates (no basal plates)
what seperates the diencephalon
the hypothalamic sulcus
what lies dorsal (above) the hypothalamic sulcus
thalamus (relays sensory and motor signals to the cortex) and and the epithalamus (includes pineal gland)
What lies ventral (above) the hypothalamic sulcus
hypothalamus, controls body temp, hormone release & hunger
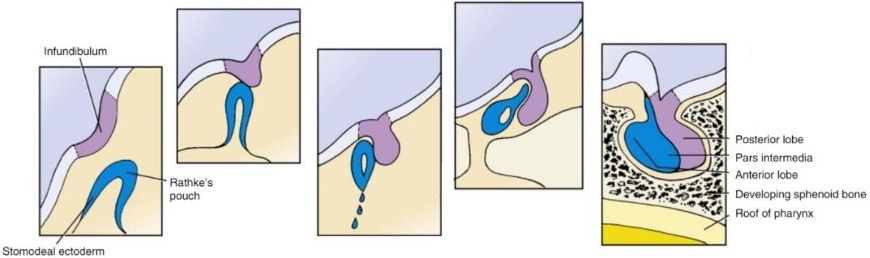
describe formation of the hypophysis (pituitrary gland) in 4 steps
the Rathke’s pouch grows upward from the stomodeum (oral ectoderm) and the infundibulum grows as invagination of diencephalon
they meet
Rathke’s pouch loses its connection to the stomodeum and starts forming around the infundibulum
they fuse together to form the hypohysis (Rathkes pouch forms anterior, and infundibulum posterior)
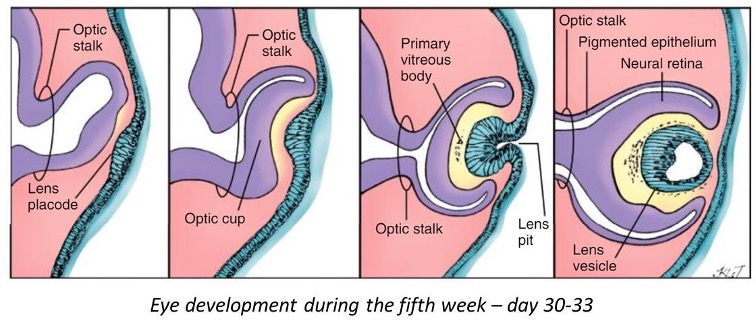
shortly describe eye development (beschreven in 5 stappen)
optic vesicles form as invagination of lateral diencephalon
they invaginate to form the optic cup (gives rise to the neural retina and pigmented retina)
invagination of the surface extoderm forms the lens placode, this develops into the lens pit
lens pit pinches off and is now enclosed by the optic cup
posterior cells of lens vesicle elongate to form long primary fibers, these reach the les vesicle and form the lens.
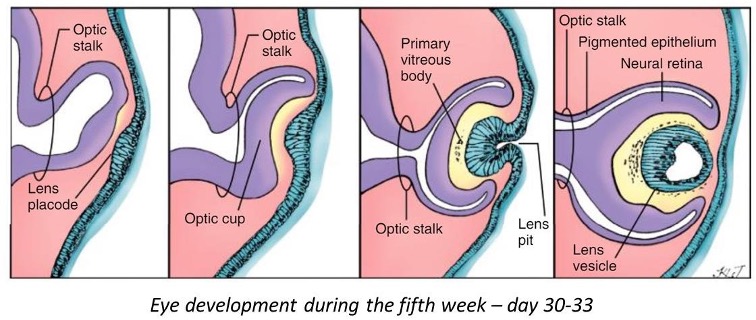
As what structure do developing eyes first appear and how are optic cups connected to the 3rd ventricle
eyes first form as shallow grooves on side of fore brain called optic sulci
optic cups are connected to the 3rd ventricle through th eoptic stalk
what plates does the mesencephalon contain and what develops from them
dorsal alar plates (sensory tract) develop into tectum (2+2 colliculi)
ventral basal plates (motor tract) develops into tegmentum
What role does the mesencephalon play in connecting the cerebral cortex to the pons in the brainstem
the marginal layer of the mesencephalon enlarges and becomes the crus cerebri (cerebral peduncle) and this connect the pons and cerebral cortex
What does the metencephalon develop into
pons (ventral) & cerebellum
What does the myelencephalon develop into
medulla oblongata
Meten en Myelencephalon follow the fundamental pattern of alar and basal plates, but what is different about them
the expansion of the roof plate = ependymal roof plate (spans the fourth ventricle and is where the choroid plexus develops)
what are nuclei and how are they related to the meten/myelencephalon
nuclei are aggregations of cell bodies, the basal and alar plates are evntually organized into columns of nuclei, both visceral and somatic afferent (to the brain) and efferent (away from the brain)
What do the rhombic lips develop into and what is the function
Cerebellum, functions in coordinating sensory input wuth motor funcions (dus balans, posture, smoothness of movement)
what is the proces of neural plate formation called
neural induction