Pathokinesiology of the Spine
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
effects of aging on the spine
1. decreased fluid in disc
2. decreased height of disc
3. changes in facet relationship
4. increased compressive forces on joints
5. PLL slack
6. increased neutral zone causing decreased stability
7. osteophytes
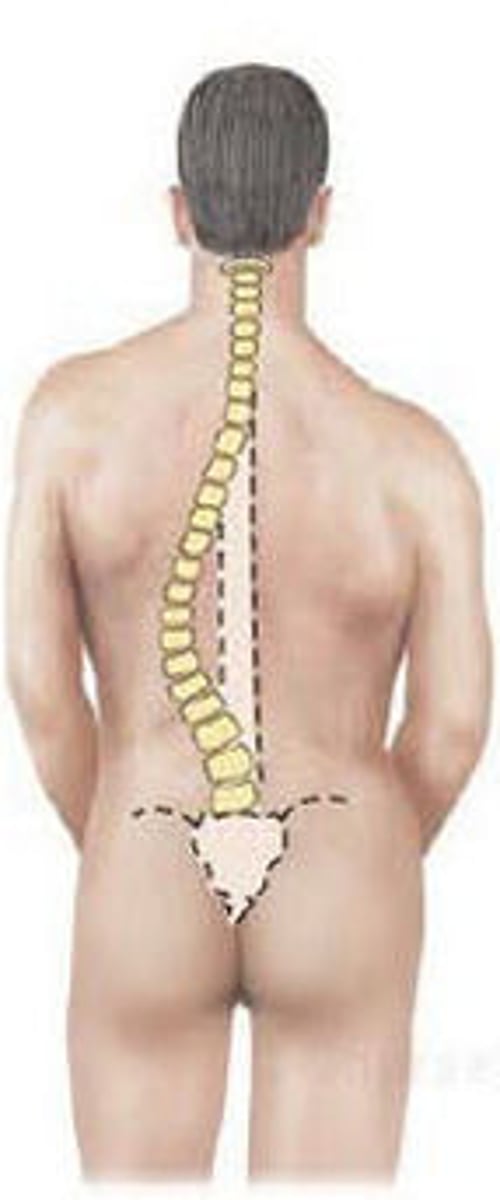
scoliosis
abnormal lateral curvature of the spine in the frontal plane with vertebral rotation
TYPES:
1. non-structural
2. structural
non-structural scoliosis
a reversible lateral curvature of spine without a rotational component
*straightening as individual flexes the spine
NOT a boney abnormality
ex. leg length difference
structural scoliosis
BONEY ABNORMALITY
*fixed lateral deformity that does not correct with bending
1. congenital
2. neuromuscular
3. idiopathic
infantile--> under 3
juvenile--> 3-10 yrs
adolescent--> 10-skeletal maturity
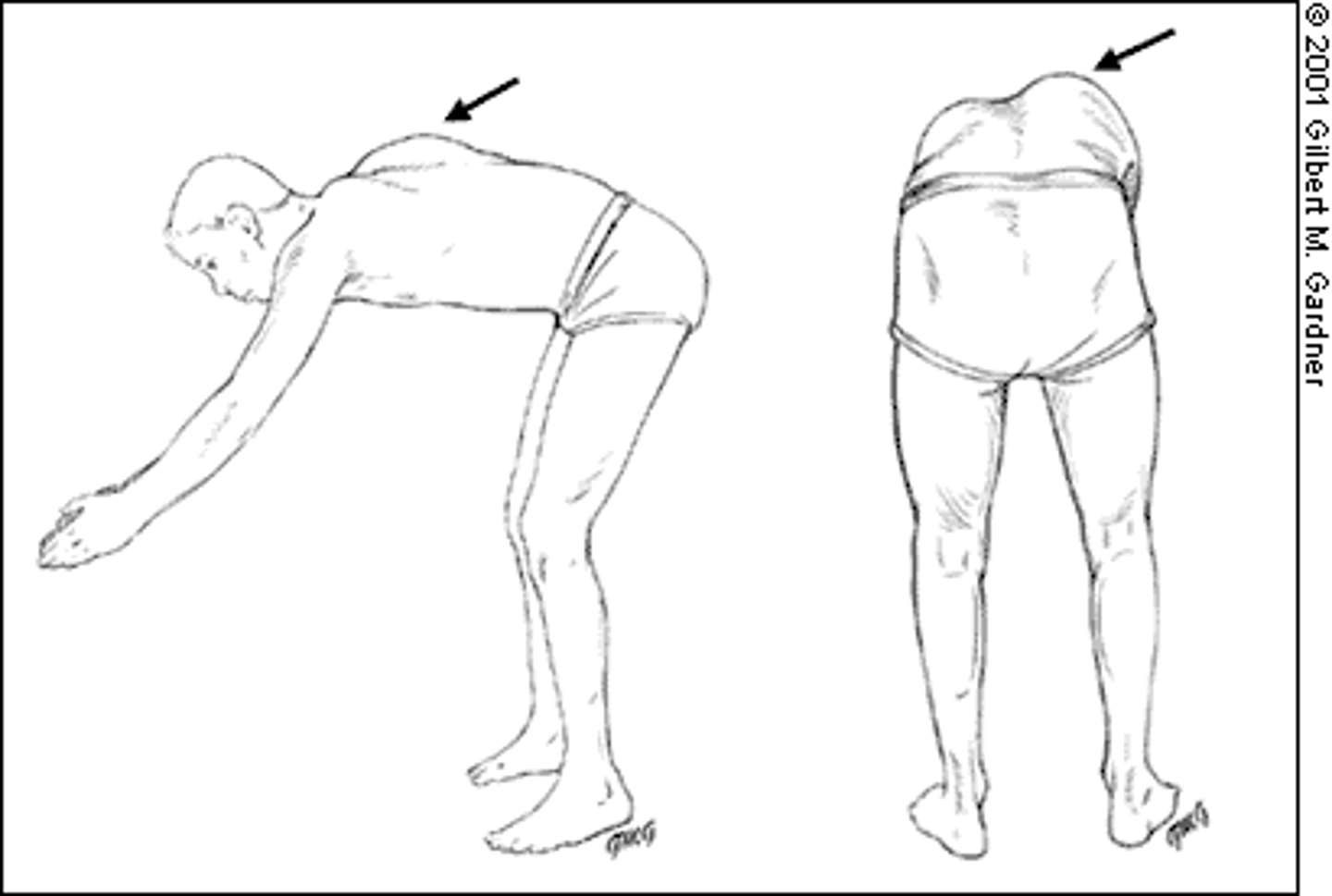
forward bending test
test for scoliosis
*positive if rib cage elevated on one side (rib hump)
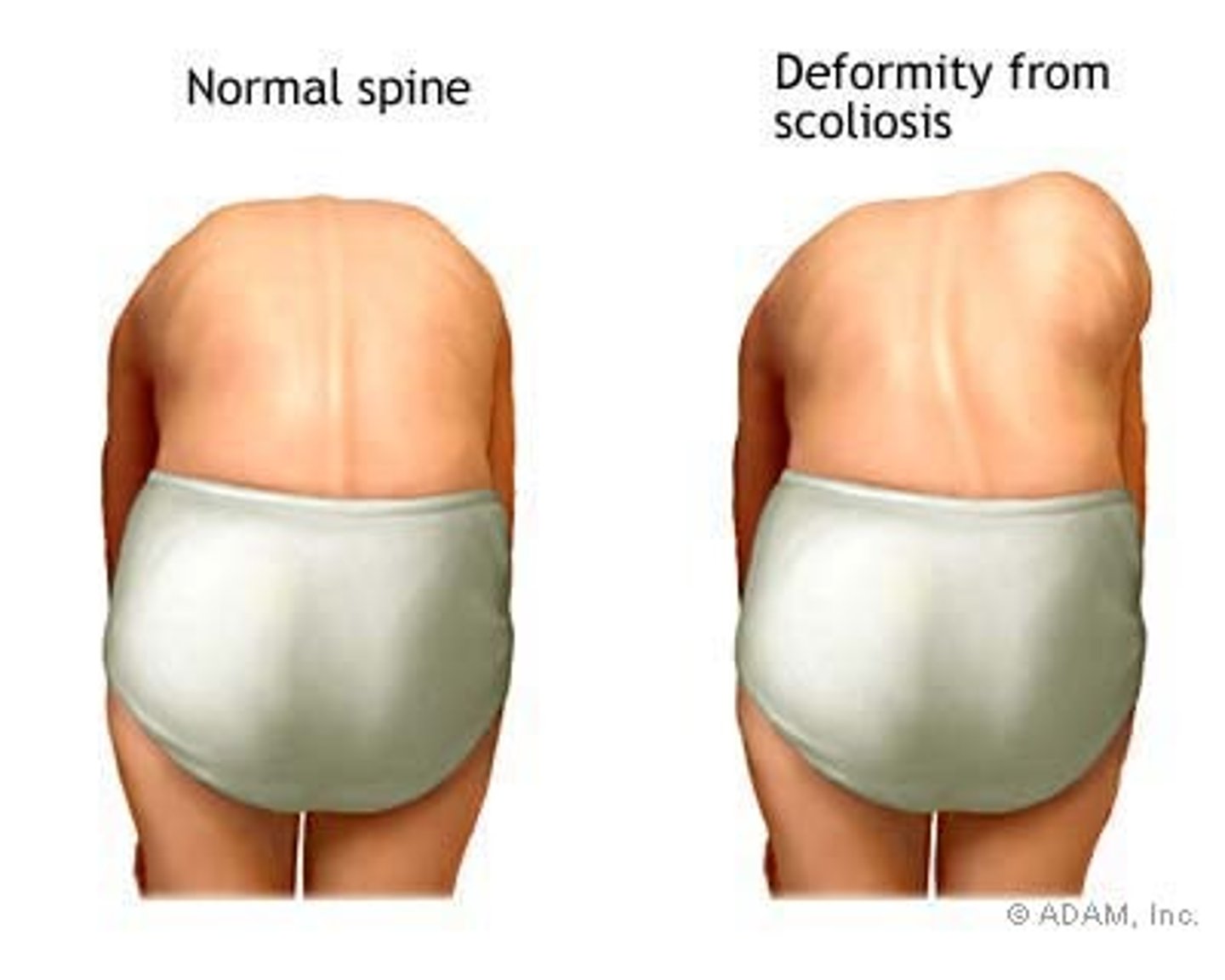
rib hump
positive finding in forward bending test for scoliosis
convexity
Scoliosis is named based on the side of _________________.
ex. R scoliosis in image
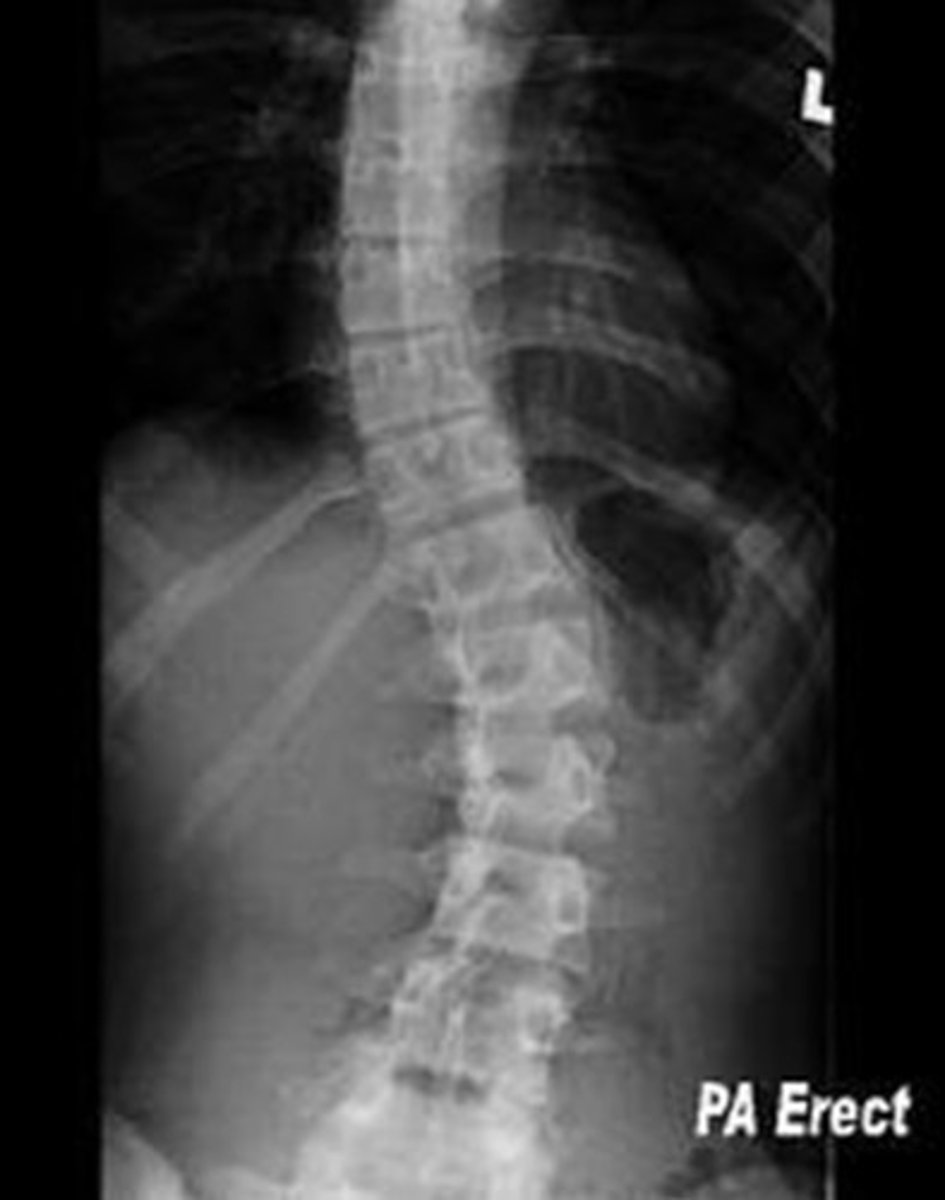
left, right
A patient with RIGHT scoliosis with present with lateral flexion to the __________ and rotation to the ___________.
dislocations/subluxations
traumatic
- may cause cord compression
- requires surgical stabilization
- unilateral versus bilateral (superior subluxation or dislocation due to forced flexion)
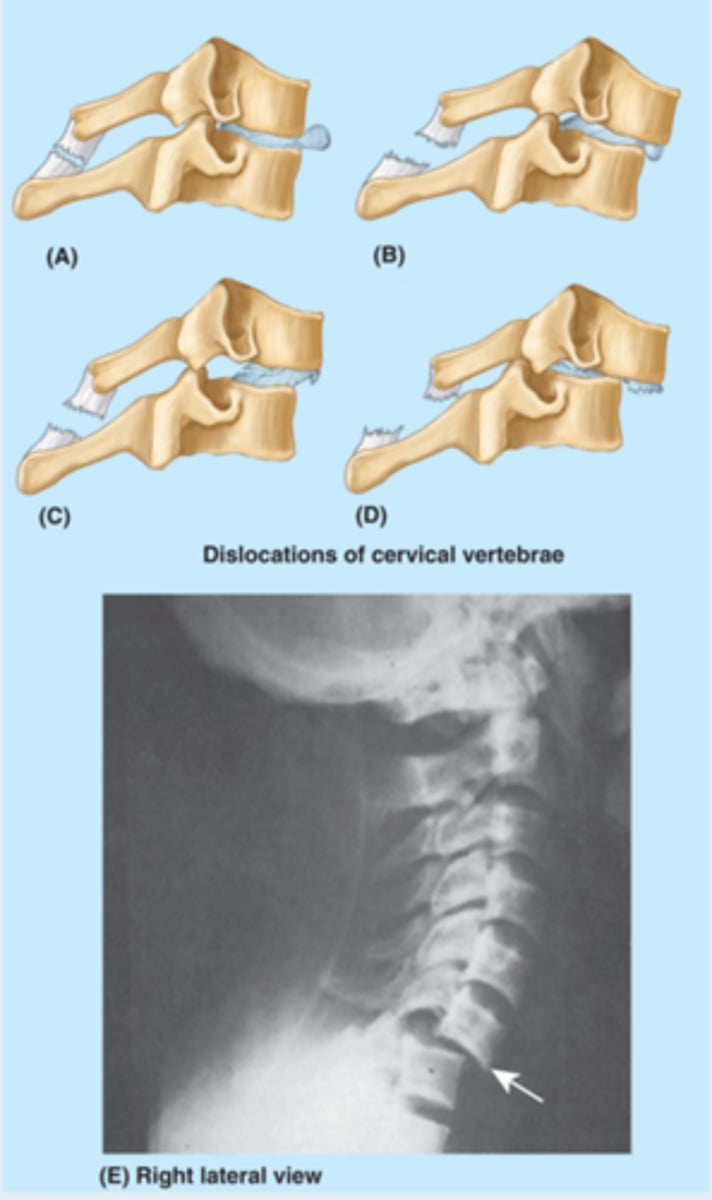
bilateral
A patient with cord compression caused by a dislocation/subluxation will present with what type of symptoms?
cervical degeneration
cervical spine appears very straight with a variance in disc space & body size
*calcifications (degenerative) also common
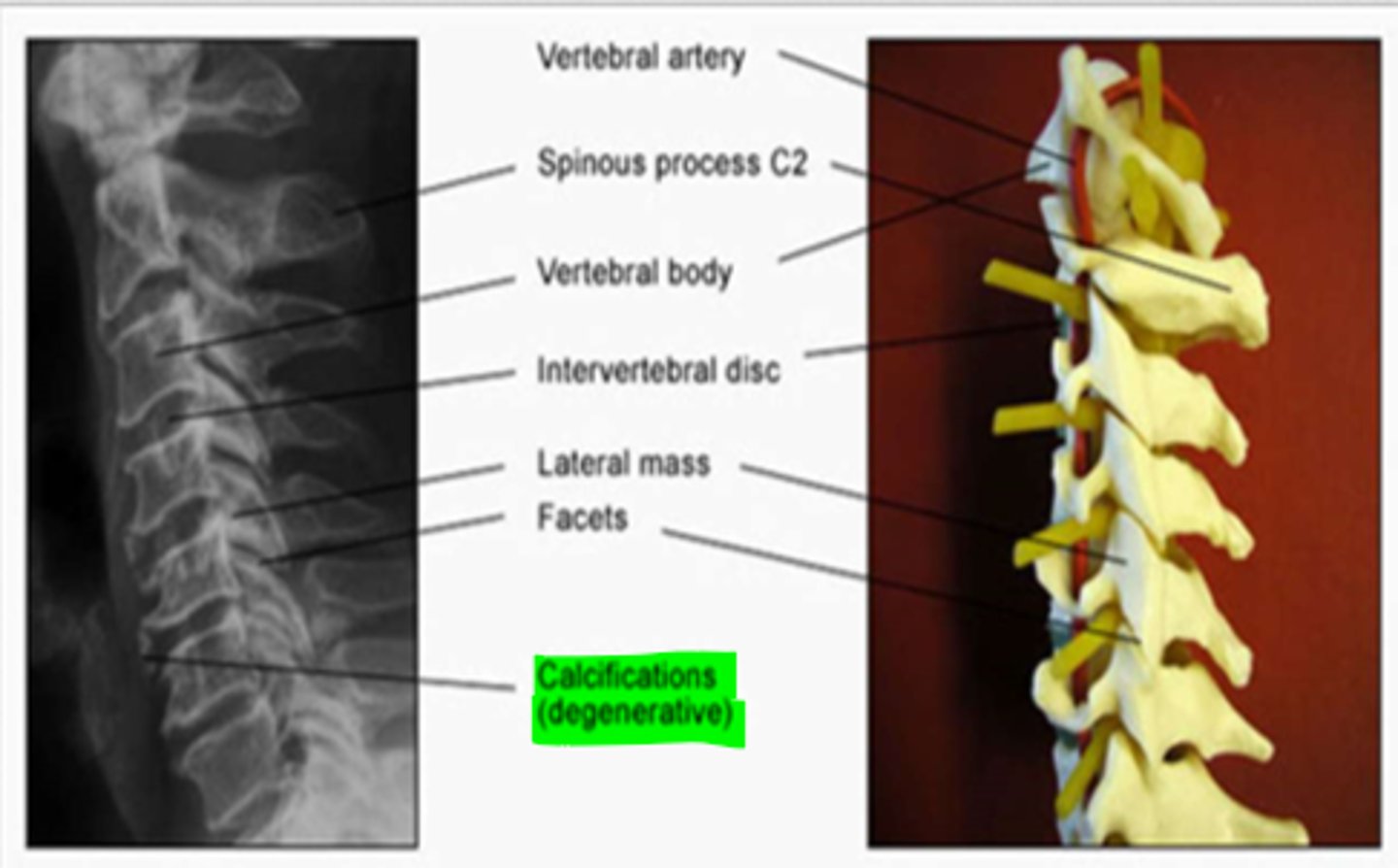
whiplash injuries
stress and strain on soft tissues of the cervical spine
1. hyperextension injury
2. hyperflexion injury

hyperextension injuries
MVA hit from behind OR rebound flexion injury
*results in ligament strains/muscle sprains
MUSCLES INVOLVED:
1. SCM
2. longus colli
3. scalenes
**facets are forced closed and cause compression
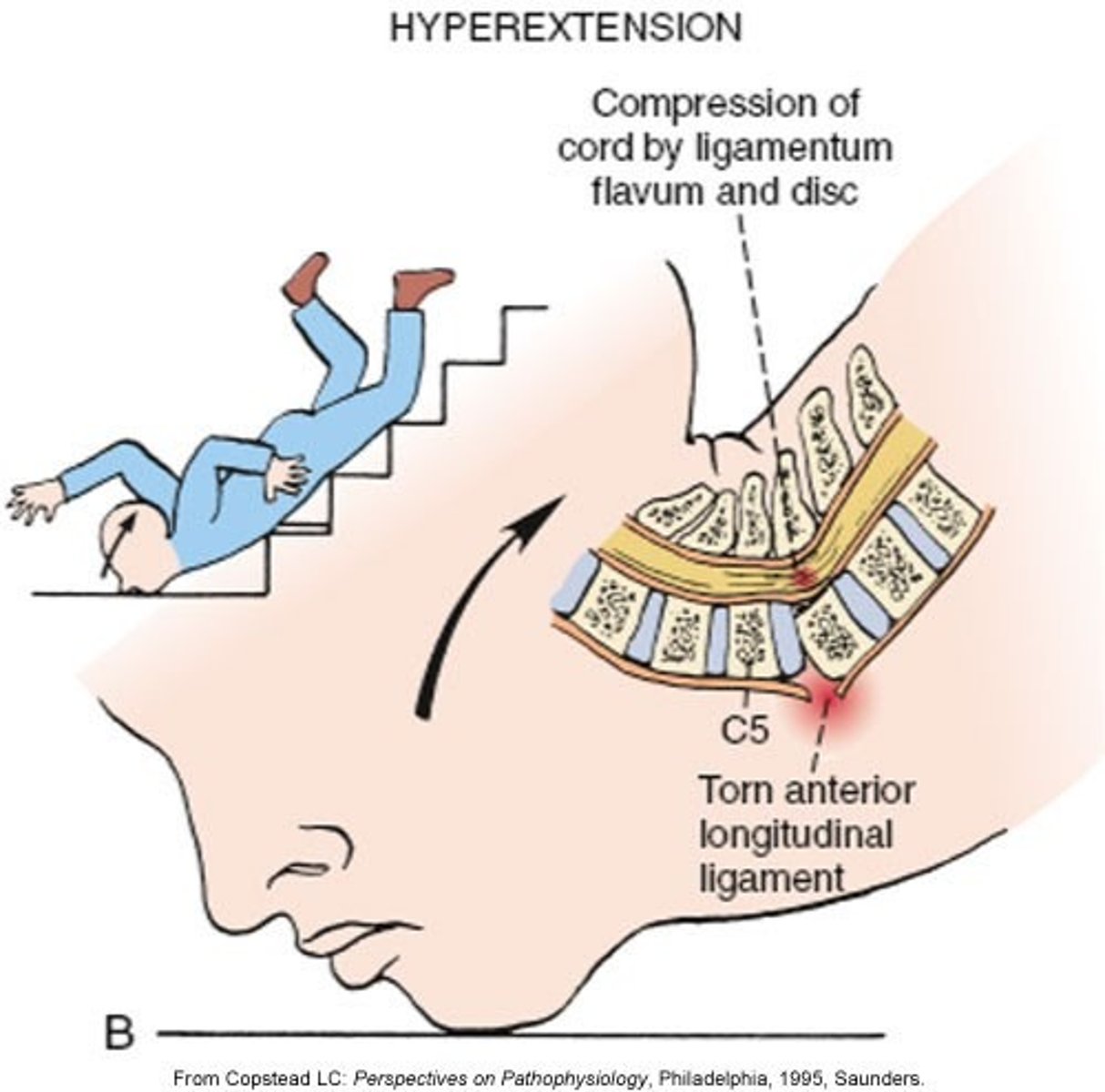
anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL)
Which ligament is typically affected in a hyperextension injury?
hyperflexion injuries
MVA hit from the front
*results in ligament strains/muscle sprains
MUSCLES INVOLVED:
1. trap
2. levator scap
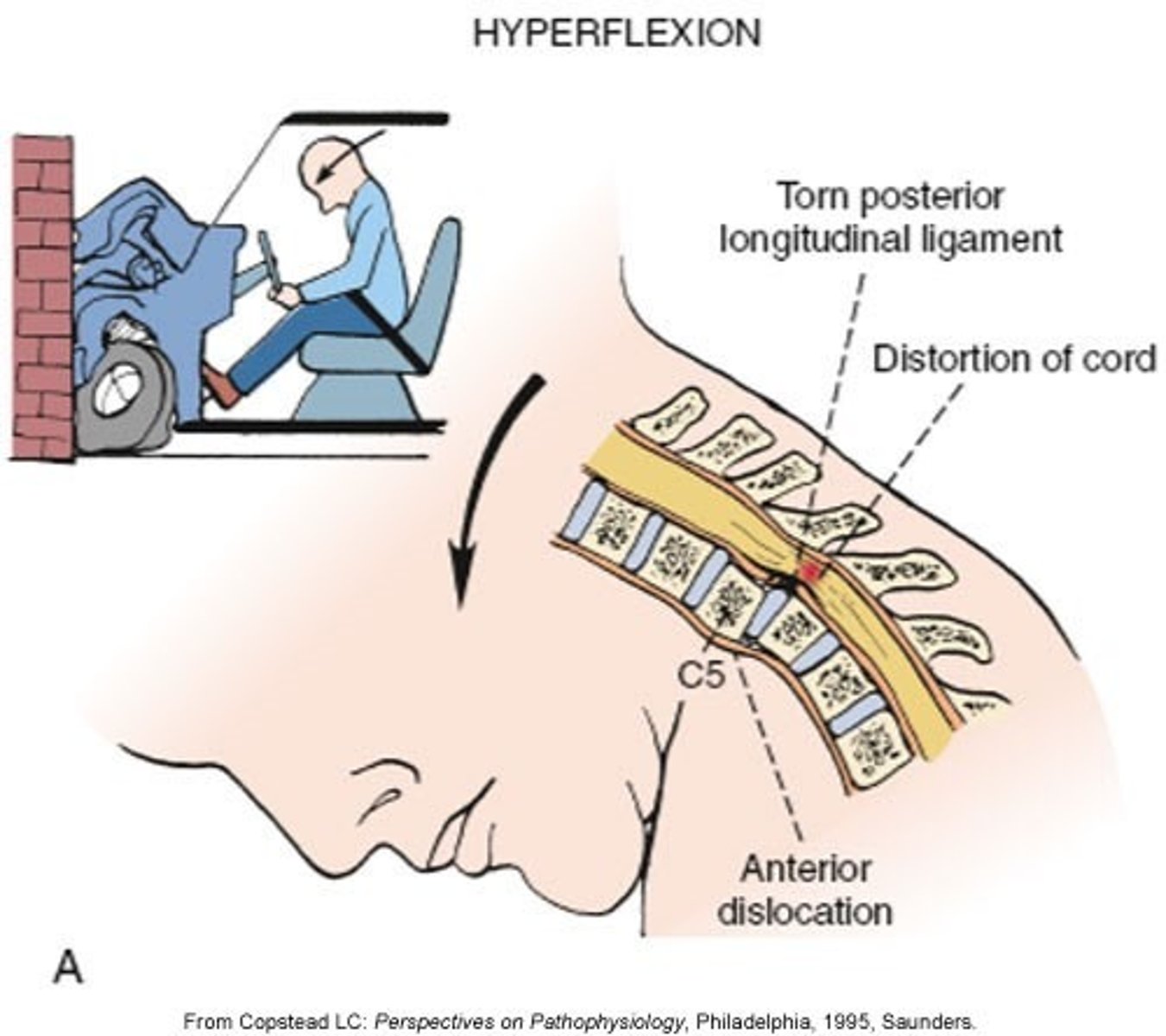
interspinous, supraspinous, ligamentum flavum, PLL
Which 4 ligaments are commonly sprained during a hyperflexion injury?
facet joint dysfunction
postural or traumatic
*limited in capsular pattern
**may have nerve root irritation
***review FRS and ERS lesions
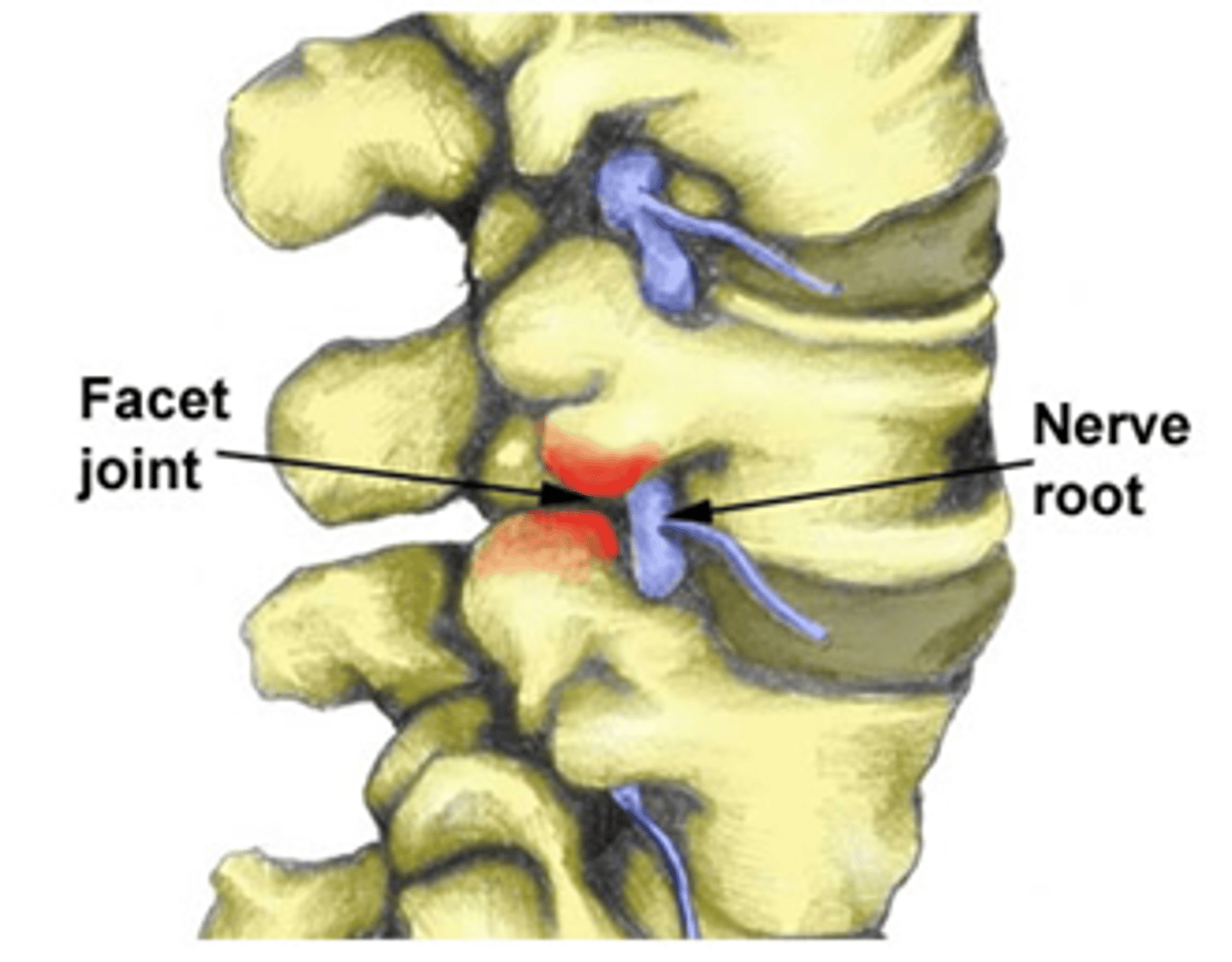
cervical disc dysfunction
disc impinges on nerve root
determined based upon neurologic exam:
1. myotomes
2. dermatomes
3. reflex testing
myotomes, dermatomes, reflex testing
What are the 3 components of a neurologic exam?
cervical myotomes
C1, C2: neck flexors
C3: lateral neck flexors
C4: shoulder shrugs
C5: shoulder abduction
C6: elbow flexion, wrist extension
C7: elbow extension, wrist flexion
C8: thumb extension
T1: finger abduction
neck flexors
What is the C1-C2 myotome?
lateral neck flexors
What is the C3 myotome?
shoulder shrugs
What is the C4 myotome?
shoulder abductors
What is the C5 myotome?
elbow flexors, wrist extensors
What is the C6 myotome?
elbow extensors, wrist flexors
What is the C7 myotome?
thumb extensor
What is the C8 myotome?
finger abductors
What is the T1 myotome?
8, 7
There are ___ cervical nerve roots and ___ vertebrae.
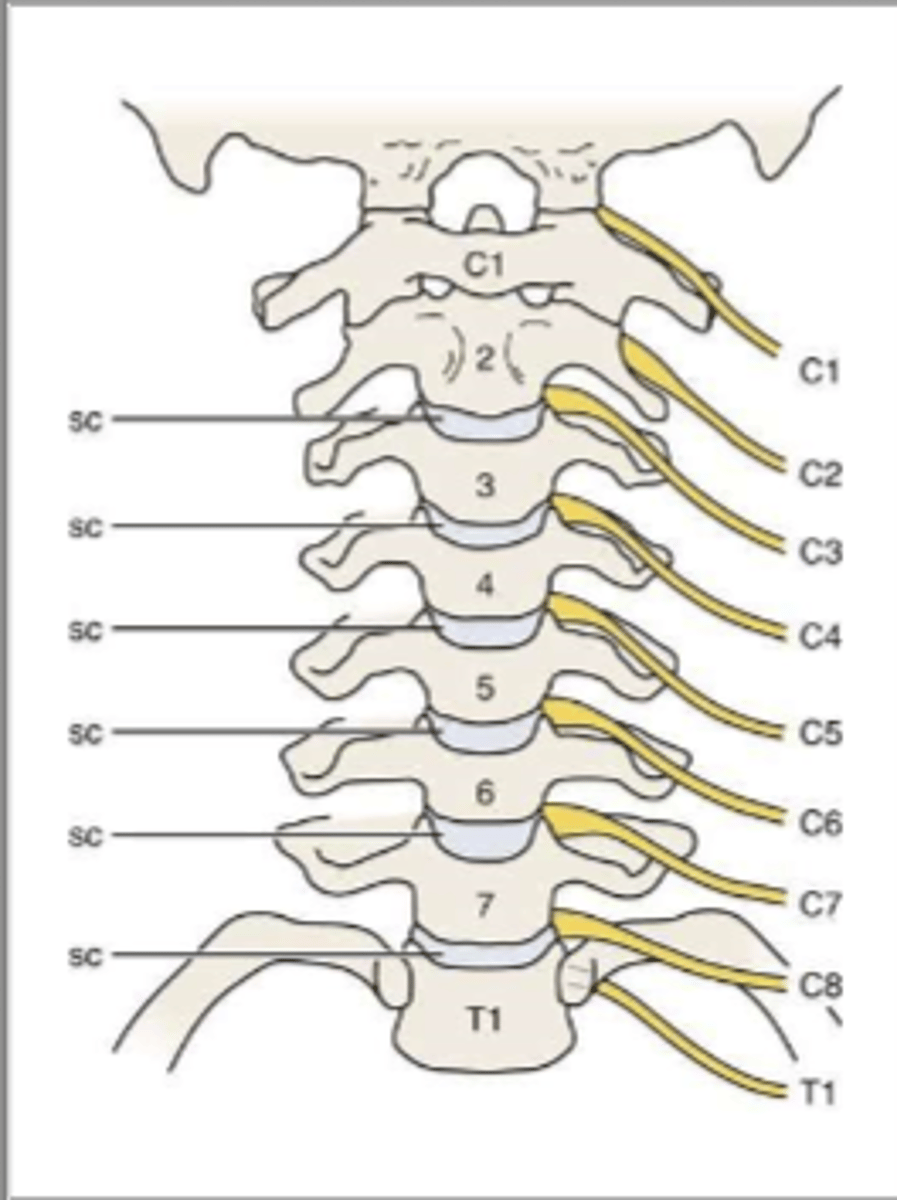
above
In the cervical spine, do the nerve roots come out above or below the vertebrae?
lower
In the cervical spine, the disc always impinges on the _____________ vertebrae's nerve root.
ex. C2-C3 disc impinges on the C3 vertebrae
C6
The C5-C6 disc will impinge what nerve?
posterior, posterior-lateral, anterior
What are the 3 types of disc displacement?
fissure/bulge/protrusion/contained
disc bulge, but NO rupture of annulus fibrosis
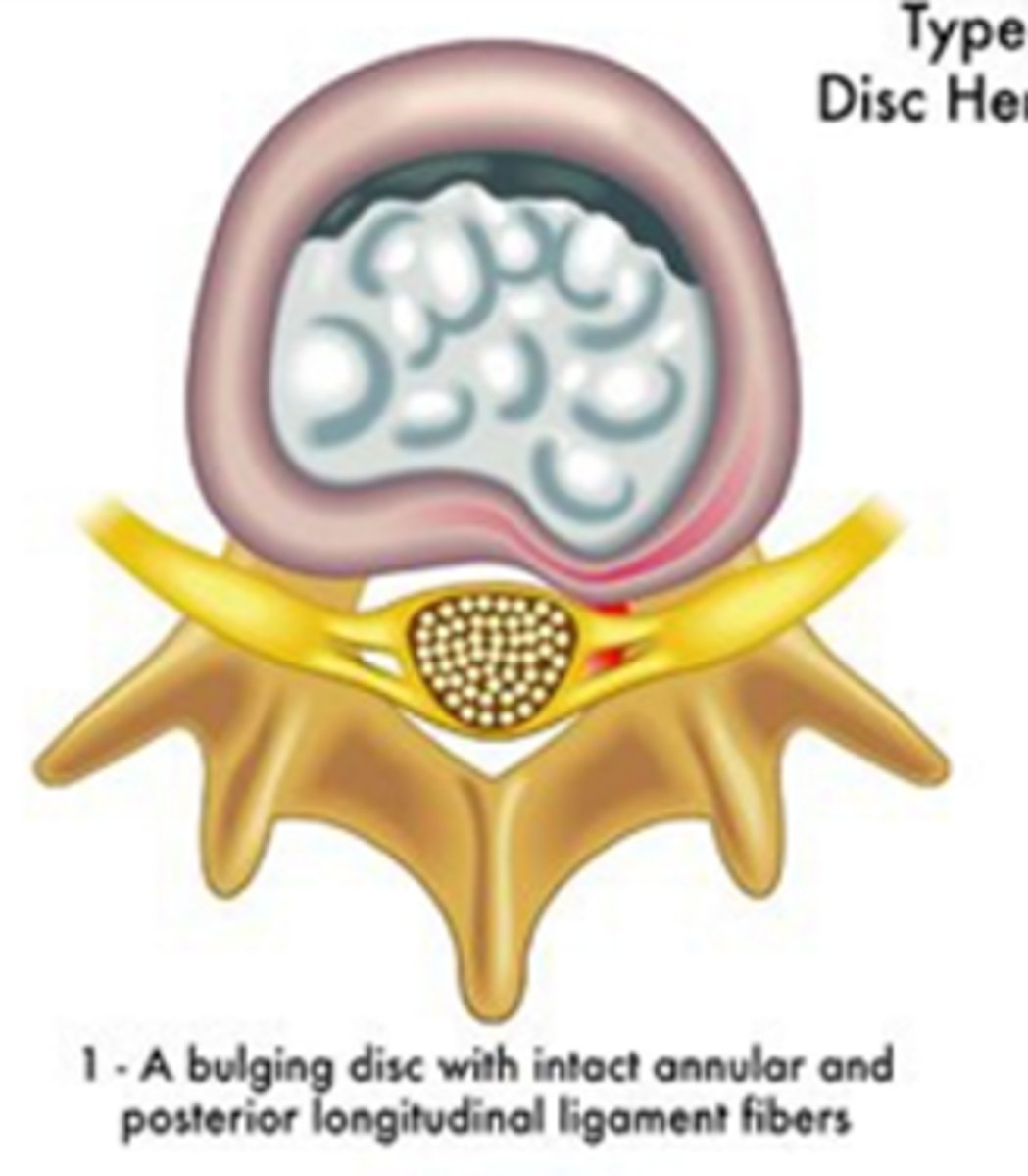
prolapse/sub-ligamentous extrusion
outermost fibers contain nuclear material, but none has escaped

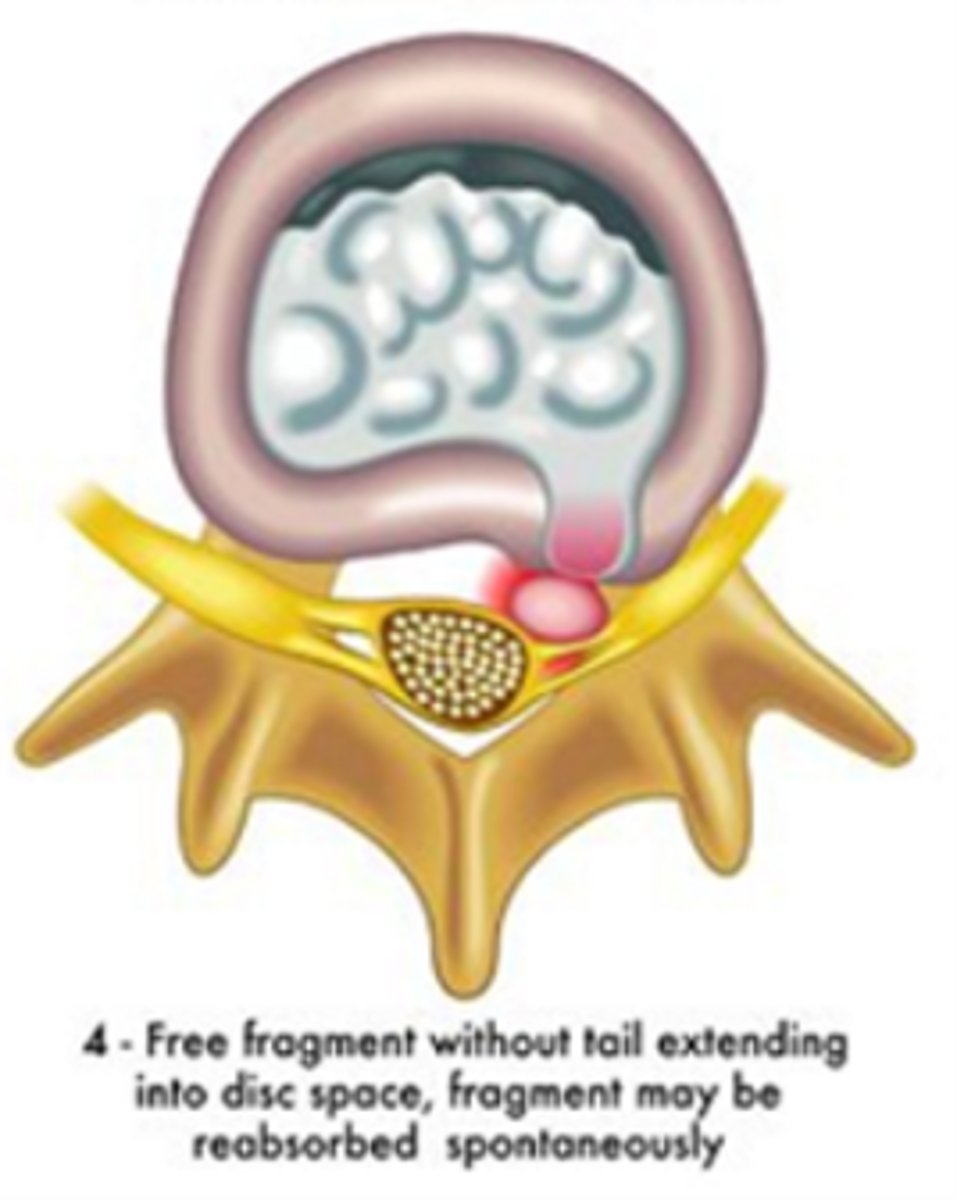
herniation/extrusion/trans-ligamentous extrusion
nuclear material has perforated the annulus fibrosis
*leaked into epidural space
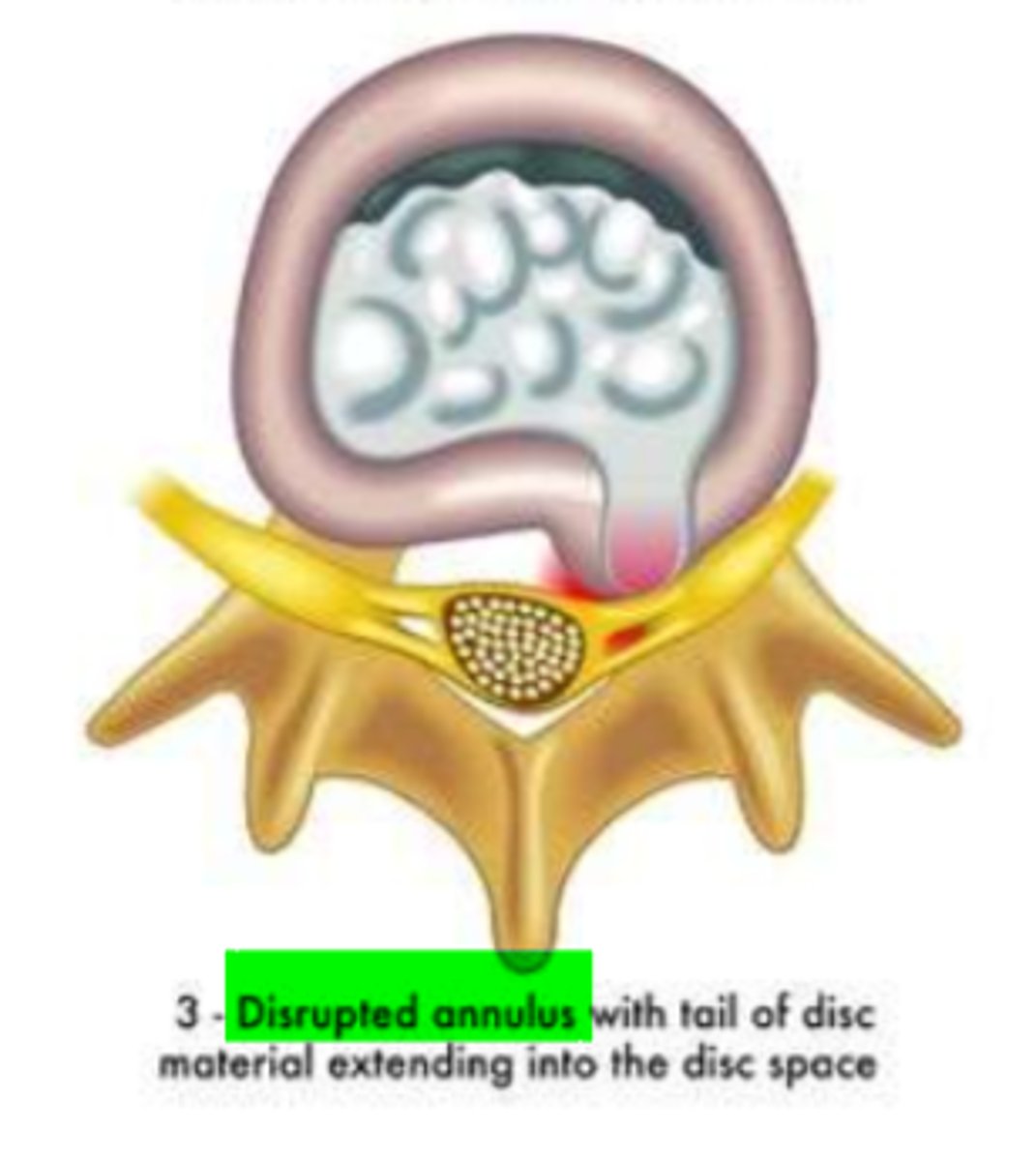
ruptured/fragmented/sequestered
discal fragment broken off
cervical spinal stenosis
narrowing of the cervical spinal canal
*usually age-related changes (most common in people older than age 50)
COMPLAINTS:
- stiffness, pain, numbness, or weakness in the neck, shoulders, arms, hands, or legs
- balance coordination problems
- loss of bowel or bladder control (incontinence)
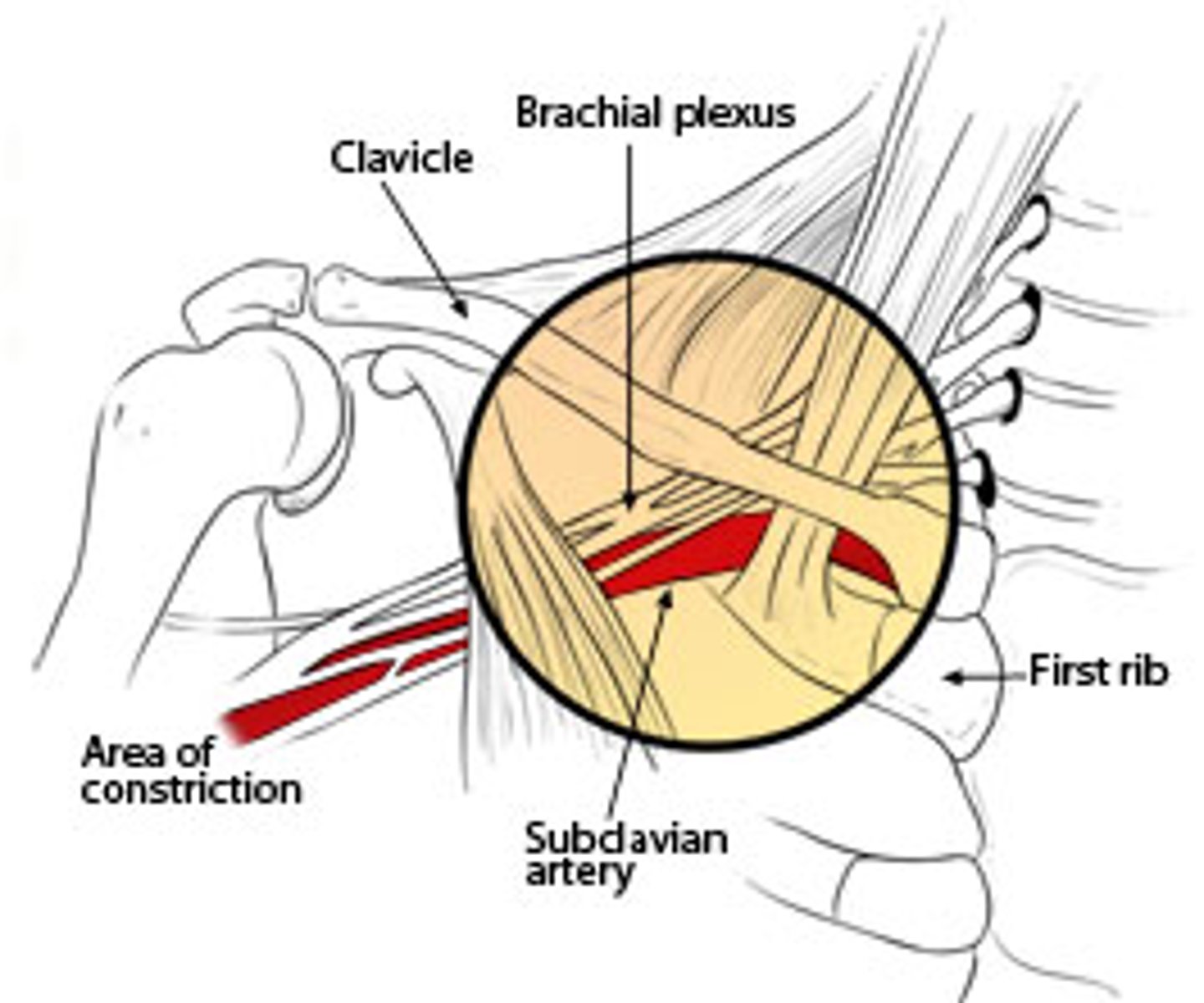
thoracic outlet syndrome
compression of the neurovascular bundle
*brachial plexus
CAUSES:
- pec minor tightness
- cervical rib
- compression over shoulder (ex. heavy bags, tight bra)
- overhead activities
- sitting with poor posture
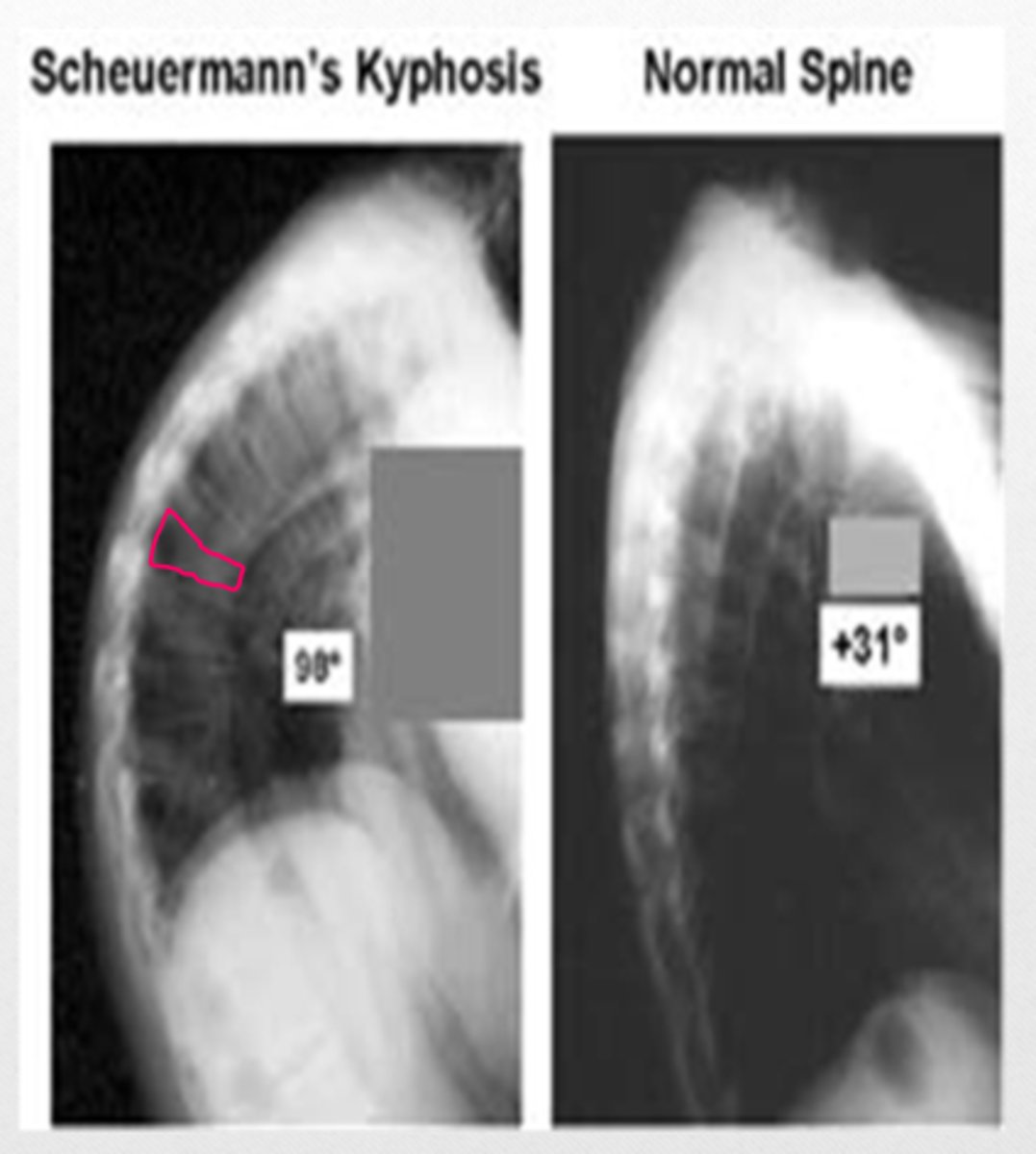
Scheuermann's disease
osteochondritis of the thoracic spine that results in wedge-shaped vertebrae
*growth disturbance of the epiphyseal plates
**accentuated thoracic kyphosis
***Schmorl's nodes
Schmorl's nodes
herniation of the nucleus pulposus through the vertebral endplate into the vertebral body
*occurs Scheuermann's disease
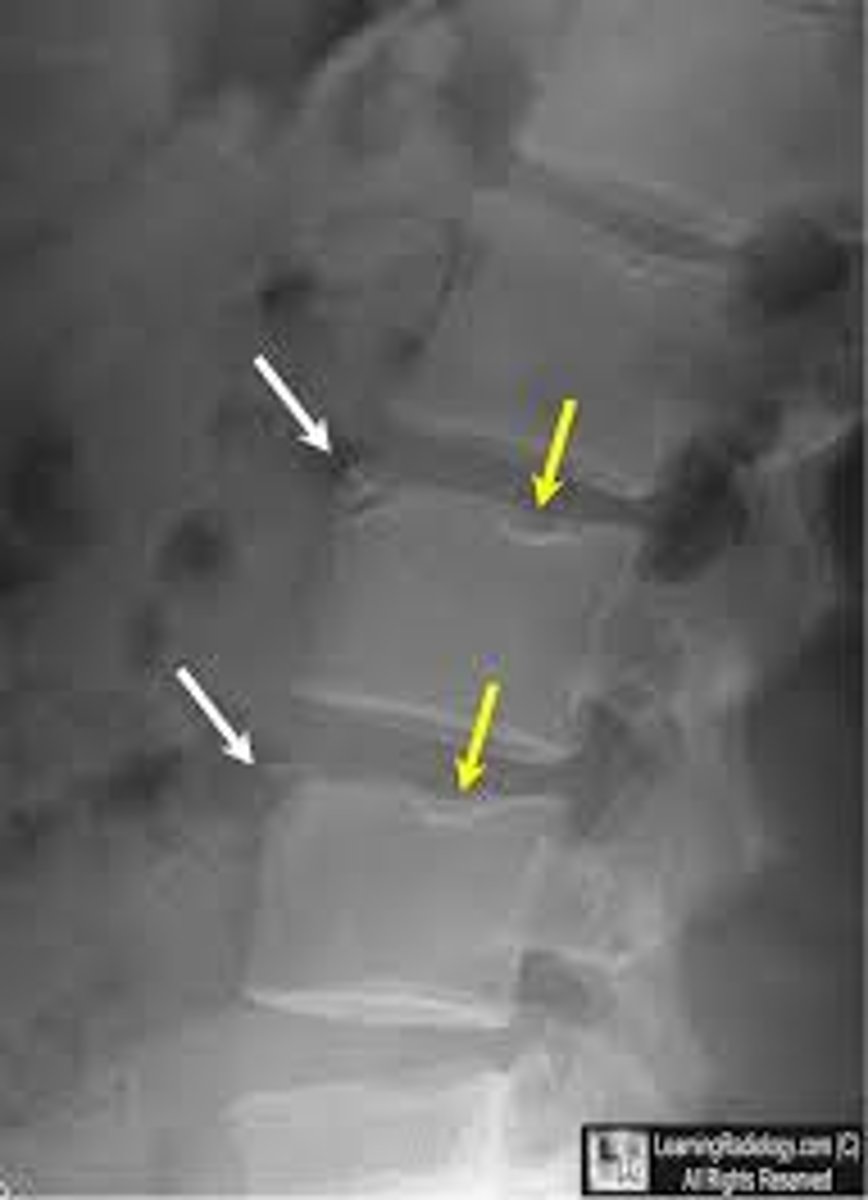
osteoporosis
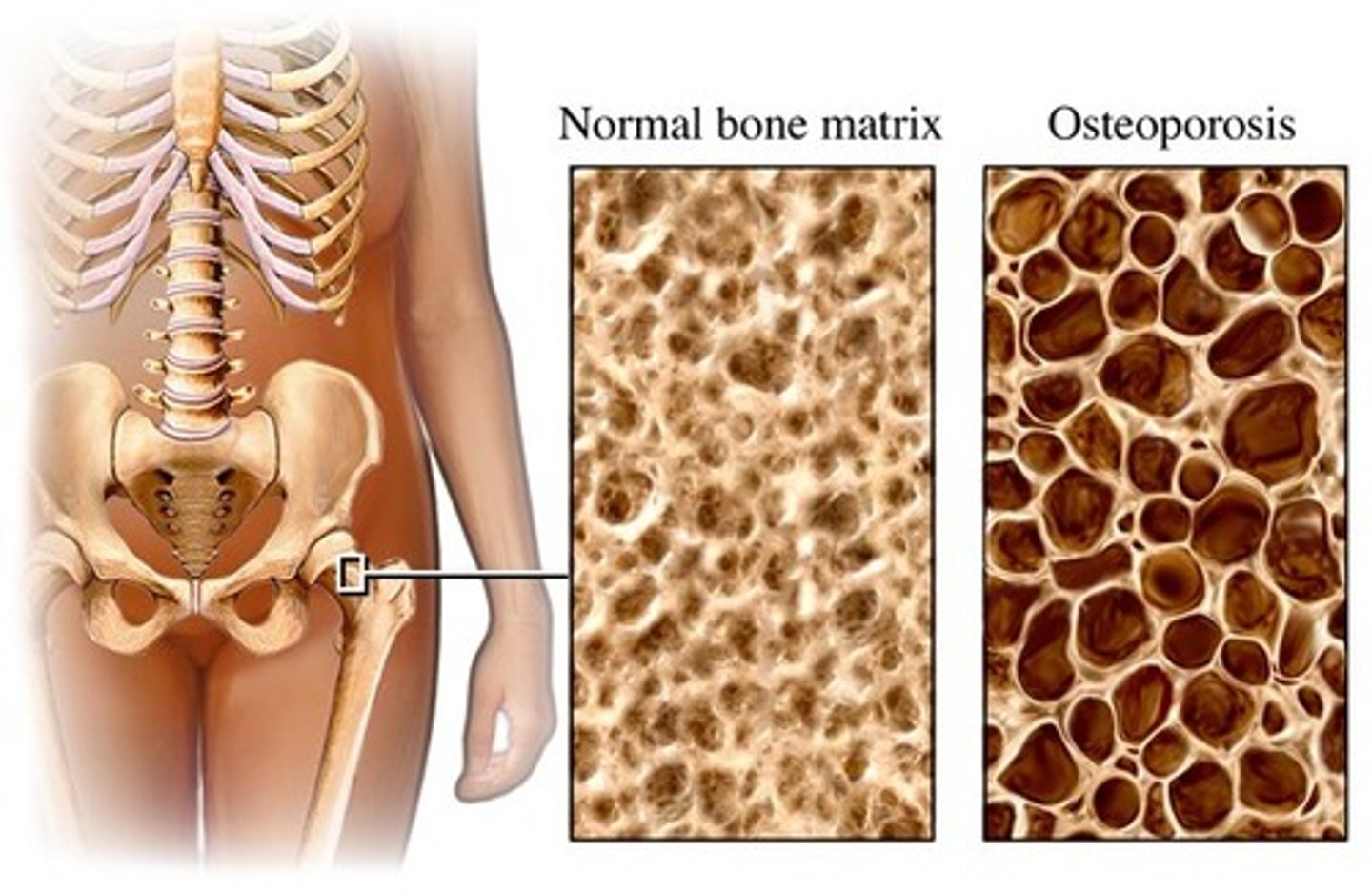
decreased mass of normally mineralized bone
TYPES:
1. post-menopausal
2. age-related
*increased change of compression fracture in thoracic and lumbar vertebrae
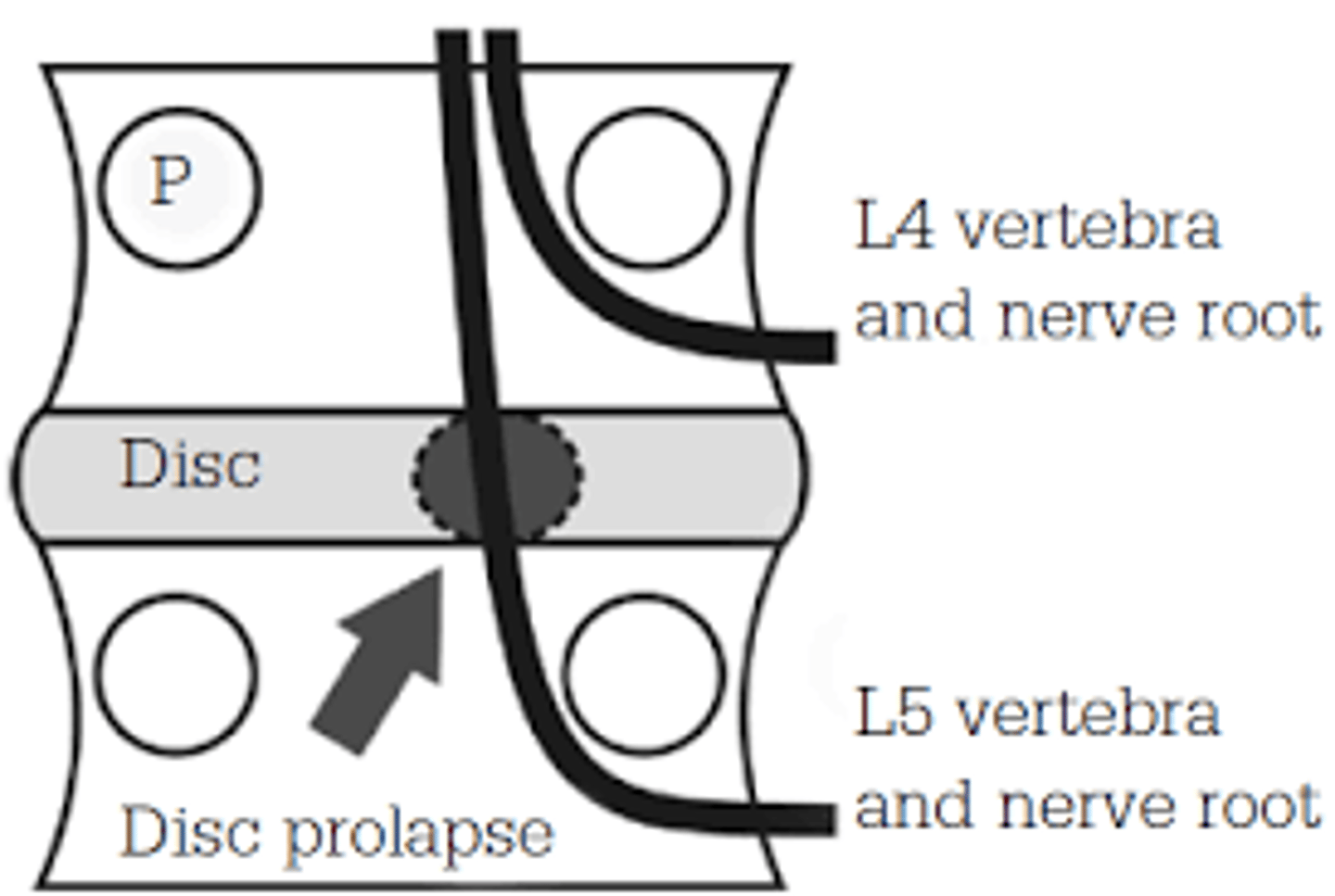
lumbar disc dysfunction
nerves exit below the vertebrae
ex. L3-L4 disc impinges on L4 nerve root

traversing root
In the lumbar spine, is the exiting root or the traversing root more likely to be impacted?
lumbar myotomes
L1, L2: hip flexors
L3: knee extensors
L4: ankle dorsiflexors
L5: great toe extension
S1: plantarflexors, ankle evertors
S2: knee flexors
hip flexors
What is the L1-L2 myotome?
knee extensors
What is the L3 myotome?
ankle dorsiflexors
What is the L4 myotome?
great toe extensors
What is the L5 myotome?
plantar flexors, evertors
What is the S1 myotome?
knee flexors
What is the S2 myotome?
L4 (ankle dorsiflexors)
Having a patient walk on their heels tests what myotome?
S1
Having a patient walk on their toes tests what myotome?
lateral shift
shifting of the trunk either toward or away from the painful side
*depends where bulging lumbar disc is

away
If the lumbar disc is bulging laterally, the patient will lean __________ from the painful side.

toward
If the lumbar disc is bulging medially, the patient will lean _____________ the painful side.

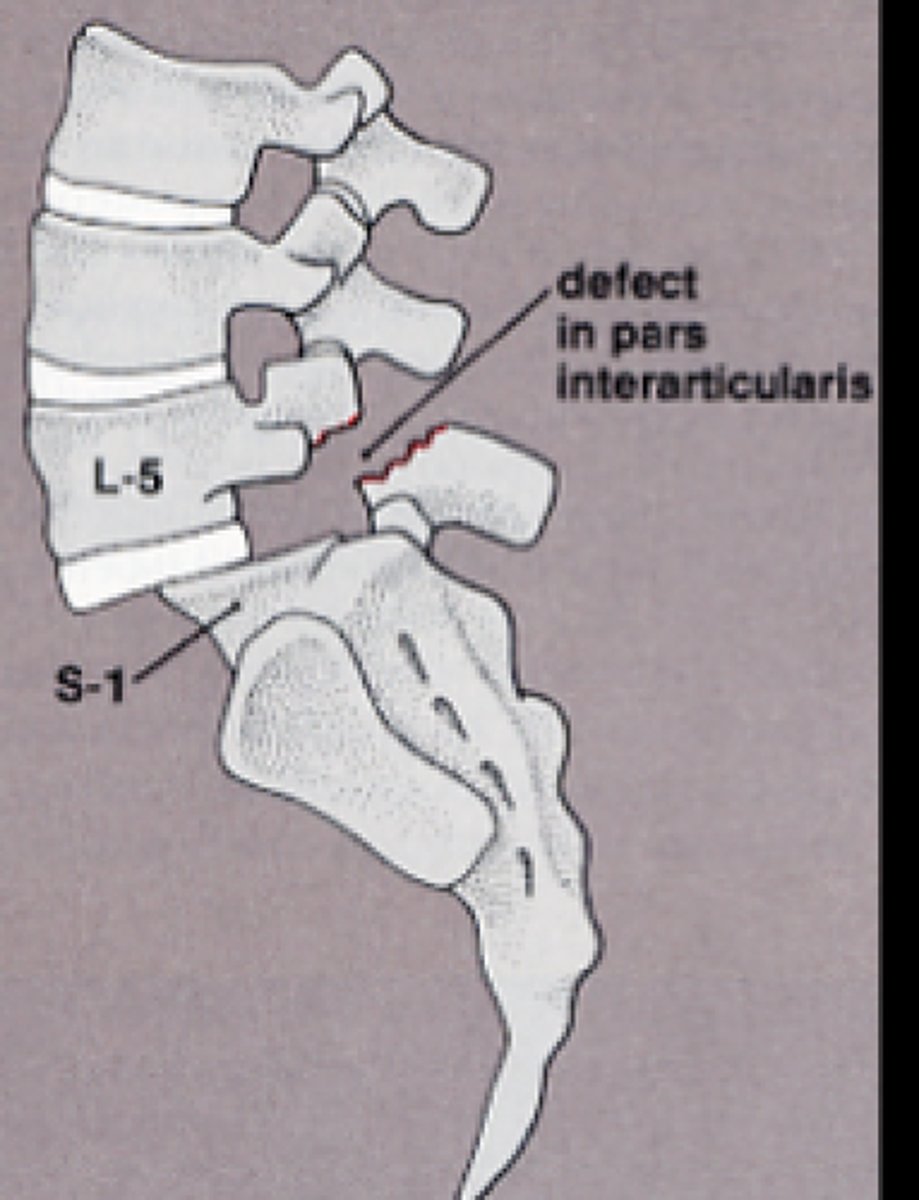
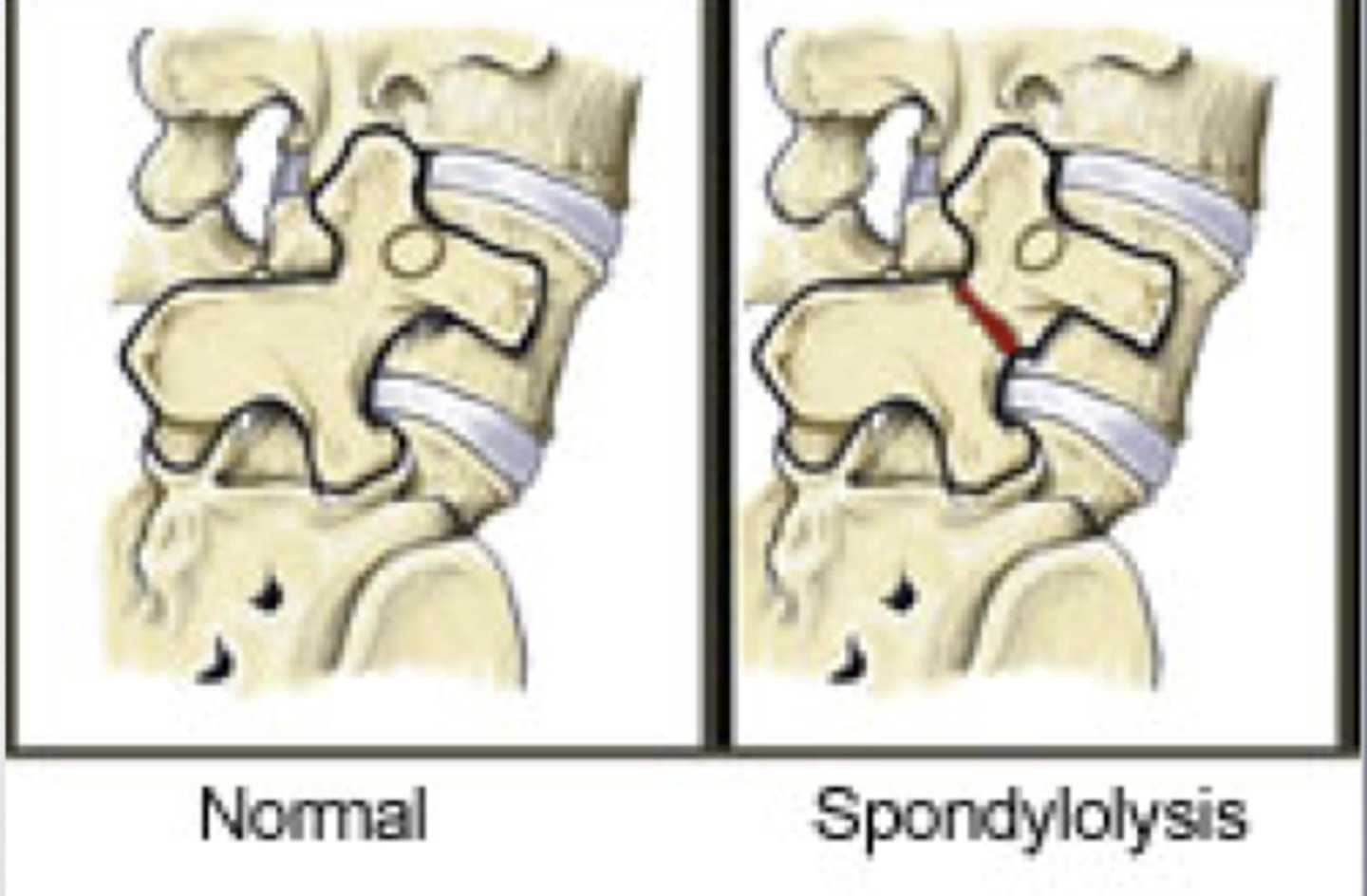
spondylolysis
fracture of pars interarticularis
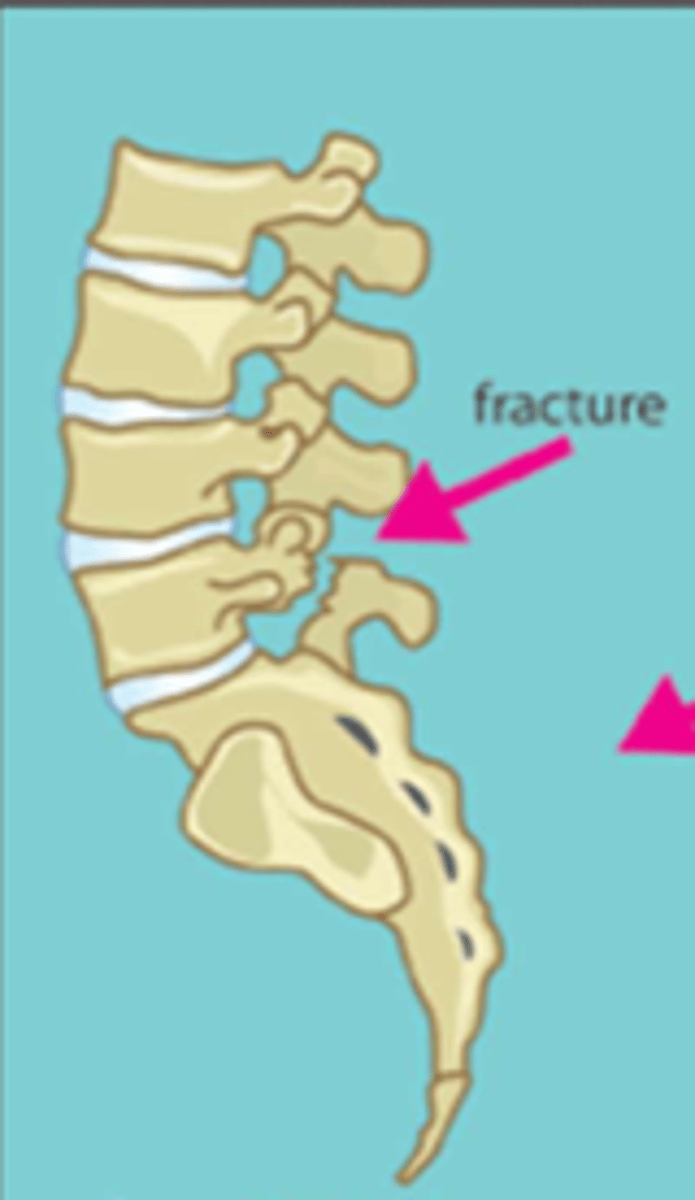
spondylolisthesis
the forward slipping movement of the body of one of the lower lumbar vertebrae on the vertebra or sacrum below it
TYPES:
1. congenital
2. isthmic
3. degenerative
__________________
less common:
4. traumatic
5. pathological
6. post-surgical
degenerative
What is the most common type of spondylolisthesis?
HINT: aging
scottie dog sign
normal appearance of the lumbar spine in an oblique radiograph
*fracture occurs at the "collar"
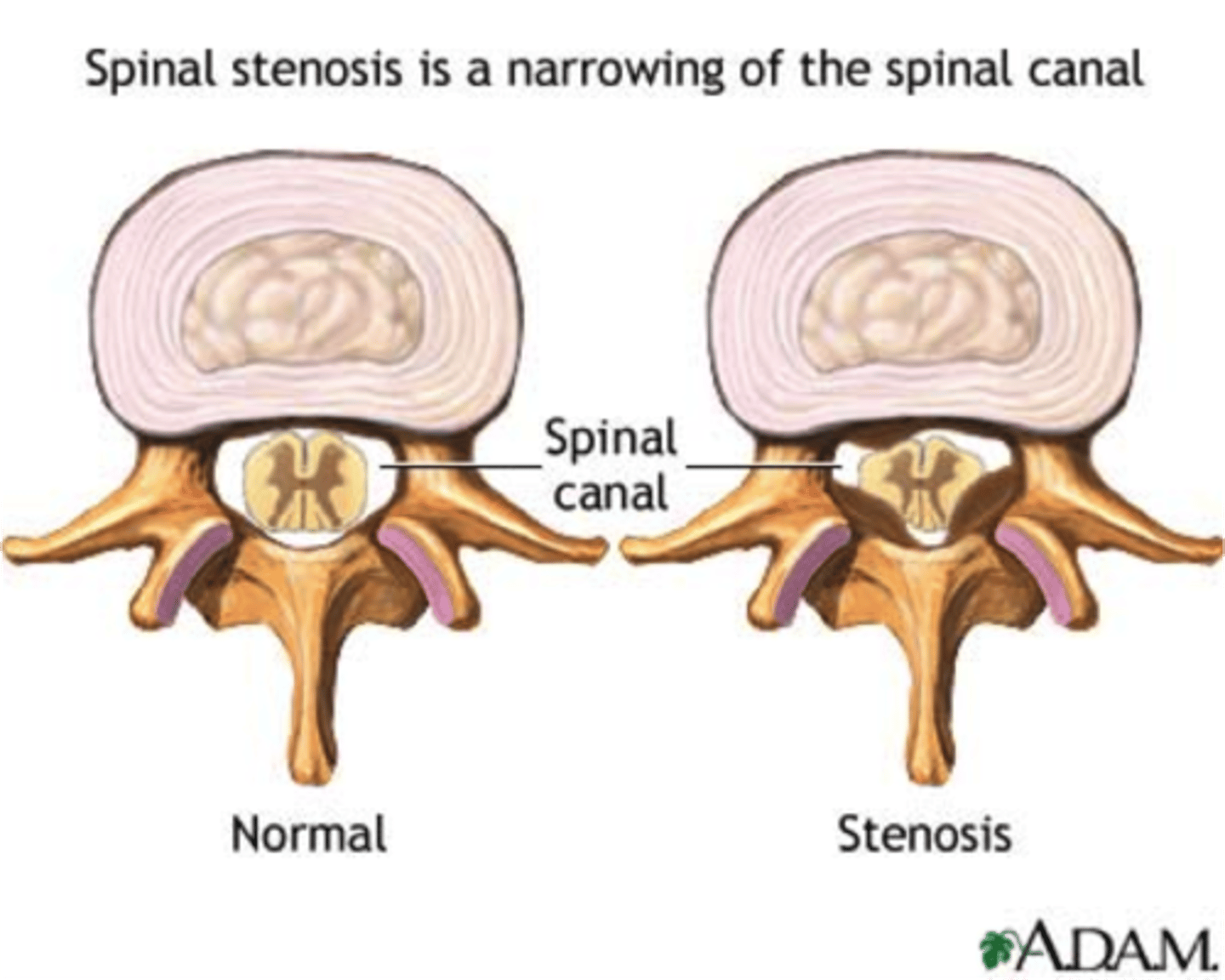
lumbar spinal stenosis
narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal
*common in elderly (degenerative)
STRUCTURES INVOLVED:
- bone hypertrophy
- ligamentum flavum buckles
- enlargement of inferior facets
- osteophytes
*BILATERAL SYMPTOMS*
ankylosing spondylitis
form of spinal arthritis
*ages 25-45 years of age
CHARACTERISTICS:
1. bamboo spine
- starts to fuse
2. decreases lordosis, decreases flexibility
3. restricted chest expansion
4. increased thoracic kyphosis
muscle strains (ligament sprains)
MOI or repetitive activity
- resisted testing (isometric contraction) of muscle is painful
- active movement is painful due to muscle contraction
- passive stretch in the opposite direction is painful
- palpation of muscle reproduces pain
*tends to be accompanied by ligament sprains
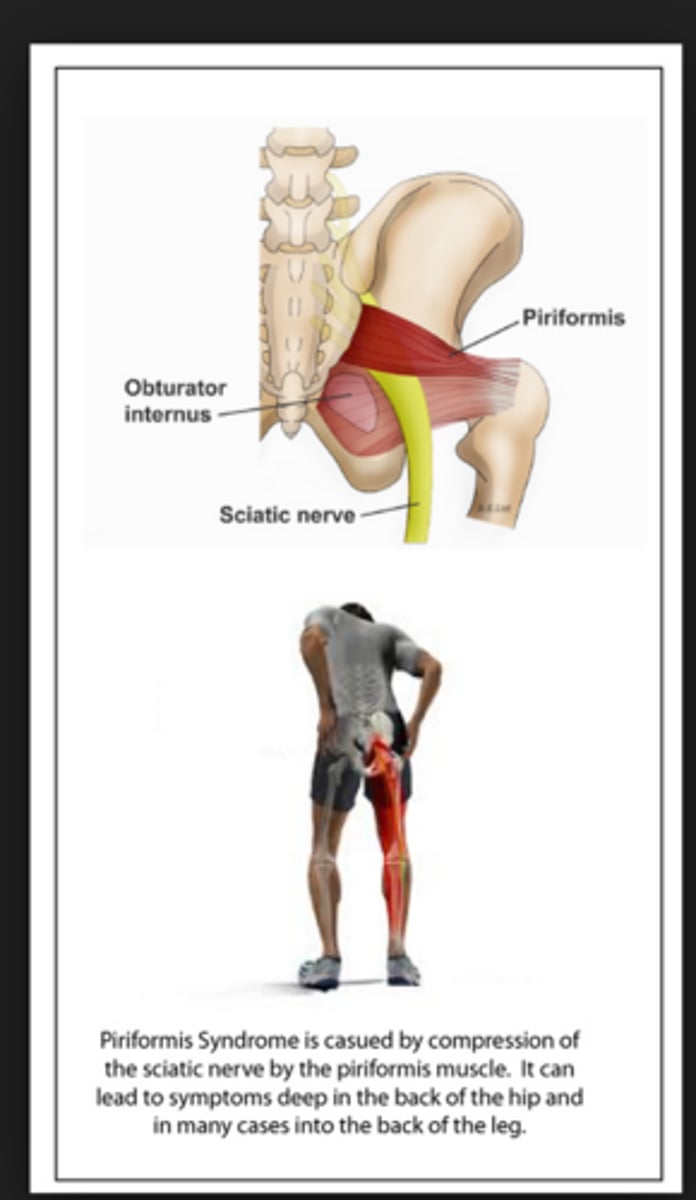
piriformis syndrome
compression of the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle
*sciatica
**lumbosacral dysfunction
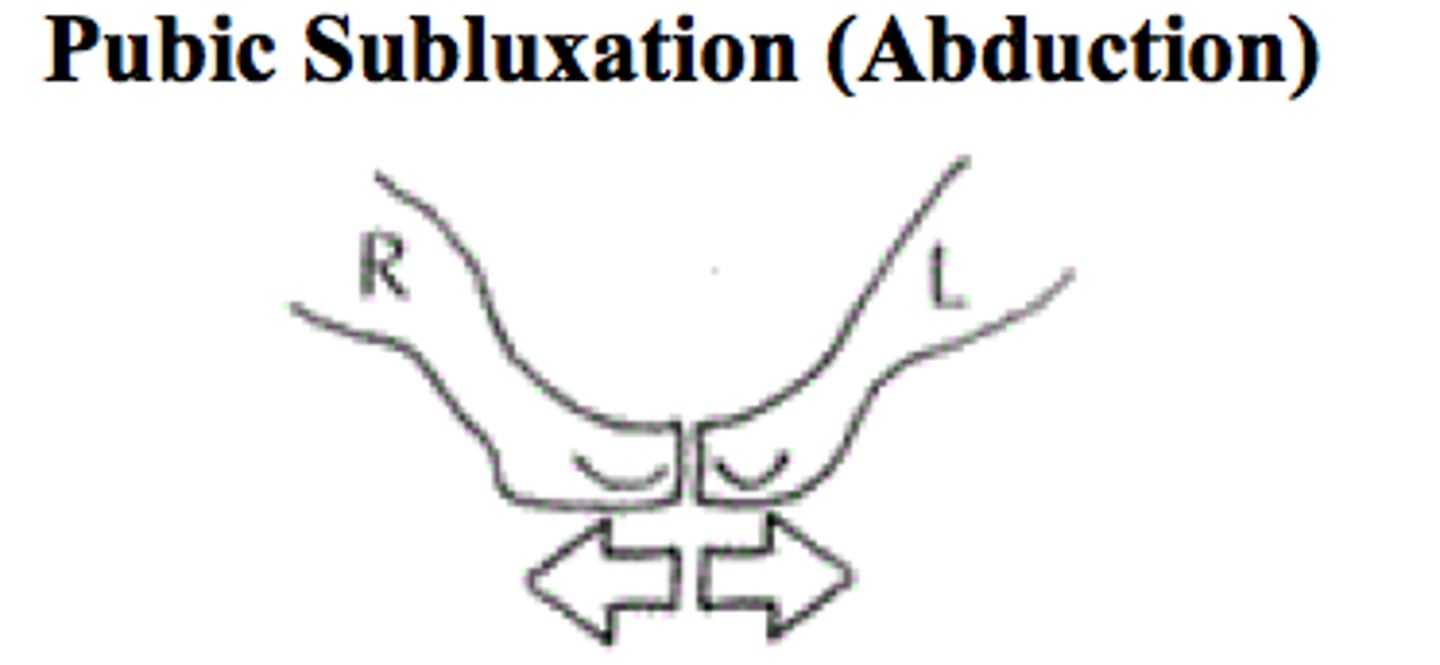
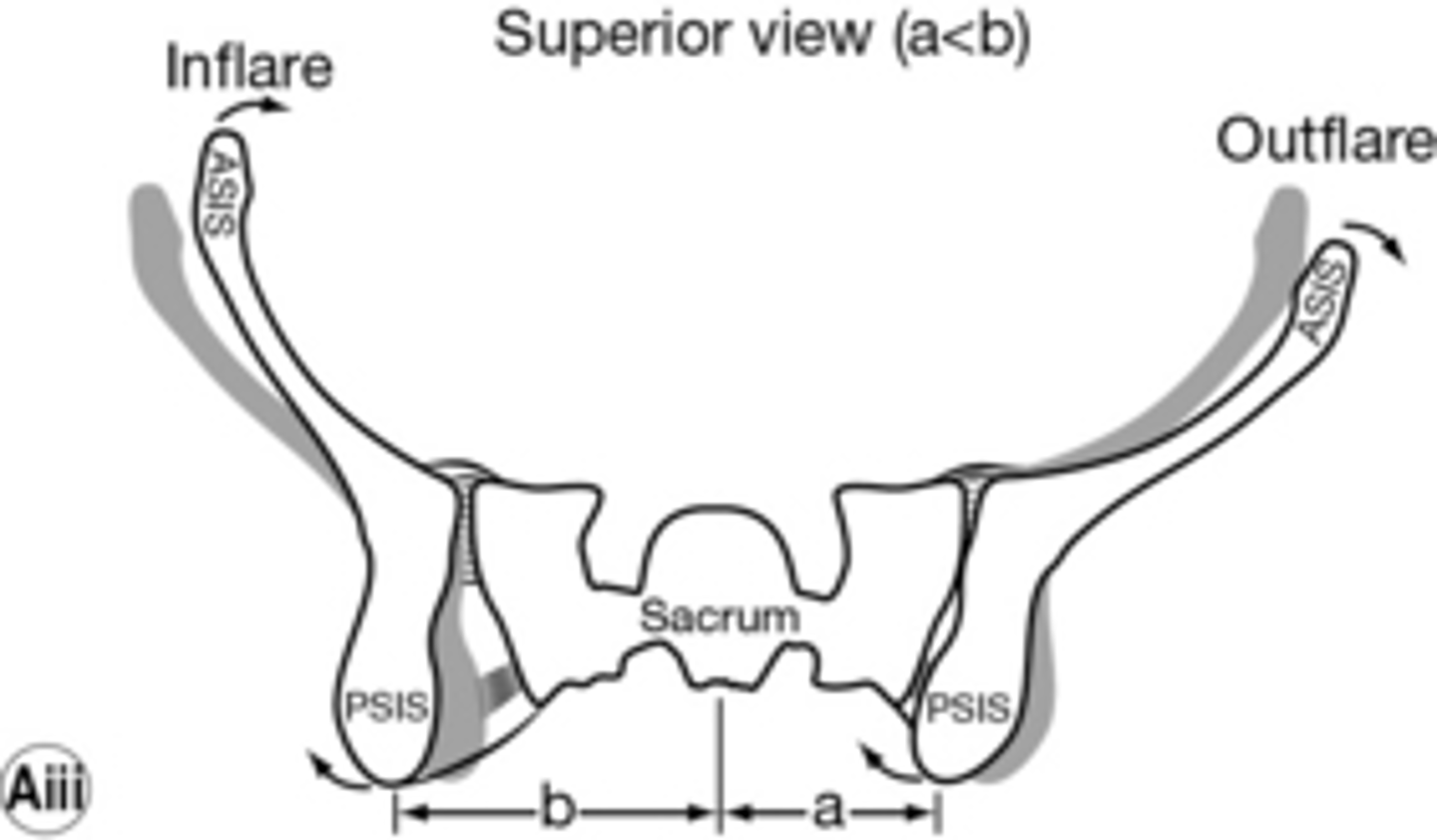
pubic subluxation, upslide/downslip, inflare/outflare, anterior/posterior tilt
What are the 4 iliosacral/innominate dysfunctions?
HINT: ilium on sacral
pubic subluxation
ILIOSACRAL DYSFUNCTION
subluxation where the pubic bones connect
*usually superior/inferior, but can also be anterior/posterior
**common postpartum
upslip/downslip
ILIOSACRAL DYSFUNCTION
one ilium higher relative to other
*may occur with fall onto one side
PALPATIONS:
1. ASIS
2. PSIS
3. iliac crests
4. ischial tuberosities

inflare/outflare
ILIOSACRAL DYSFUNCTION
look at the distance from umbilicus to ASIS
out = greater
in = less
anterior/posterior tilt
ILIOSACRAL DYSFUNCTION
one side of pelvis is more tilted than the other
**palpate ASIS/PSIS to assess
superior, inferior
A patient with an anterior tilt of the left innominate will present with the PSIS more _____________ and ASIS more ______________.
sacroiliac dysfunction
sacral rotation
1. forward
2. backward
piriformis, multifidus
Forward sacral rotation may indicate a ________________ muscle problem, while backward sacral rotation may indicate _______________ muscle problem.
normal, decreased
Forward sacral rotation indicates ______________ lumbar mobility, while backward sacral rotation indicates _______________ lumbar mobility.
same
For a forward sacral rotation, the rotation and axis direction are the ___________.
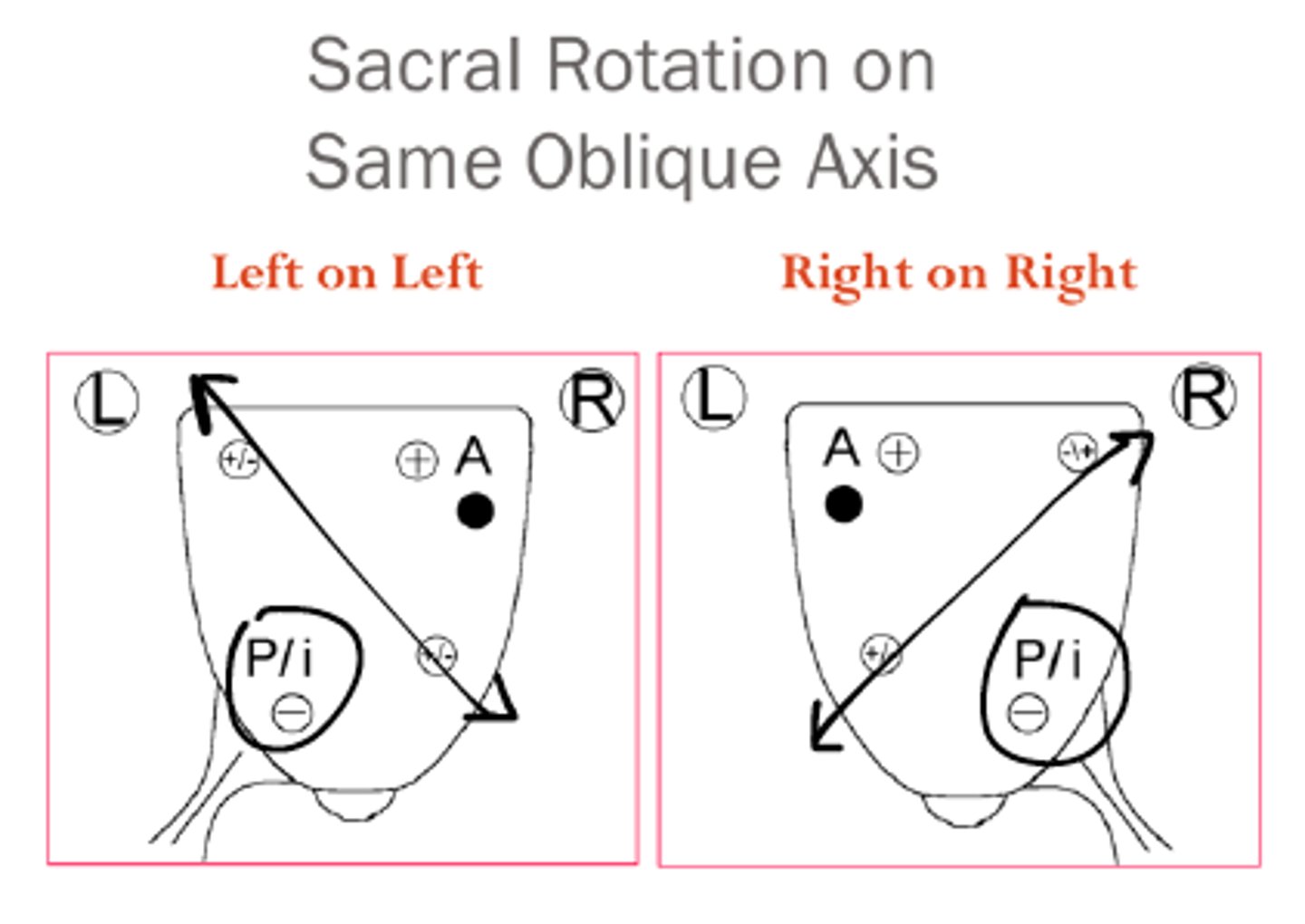
opposite
For a backward sacral rotation, the rotation and axis direction are the ________________.
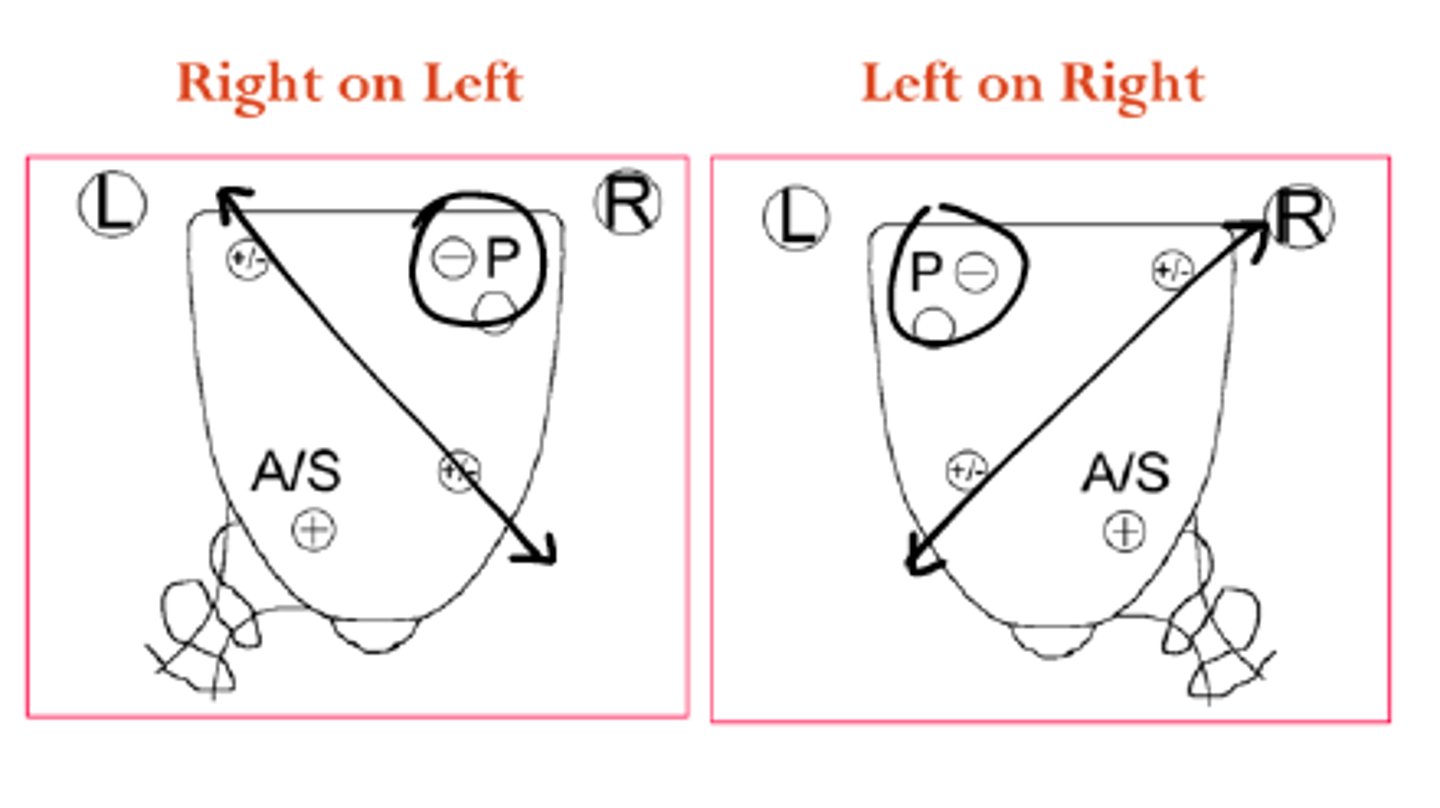
sacral sulcus, inferior-lateral angle
Which 2 structures are palpated to assess sacral rotation?
left
Forward sacral rotation to the RIGHT makes the __________ sacral sulcus and ILA deeper.
right
Forward sacral rotation to the LEFT makes the __________ sacral sulcus and ILA deeper.
left
Backward sacral rotation to the RIGHT makes the __________ sacral sulcus and ILA deeper.
right
Backward sacral rotation to the LEFT makes the __________ sacral sulcus and ILA deeper.