Linking Innate and Adaptive Immunity
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to innate and adaptive immunity as presented in the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
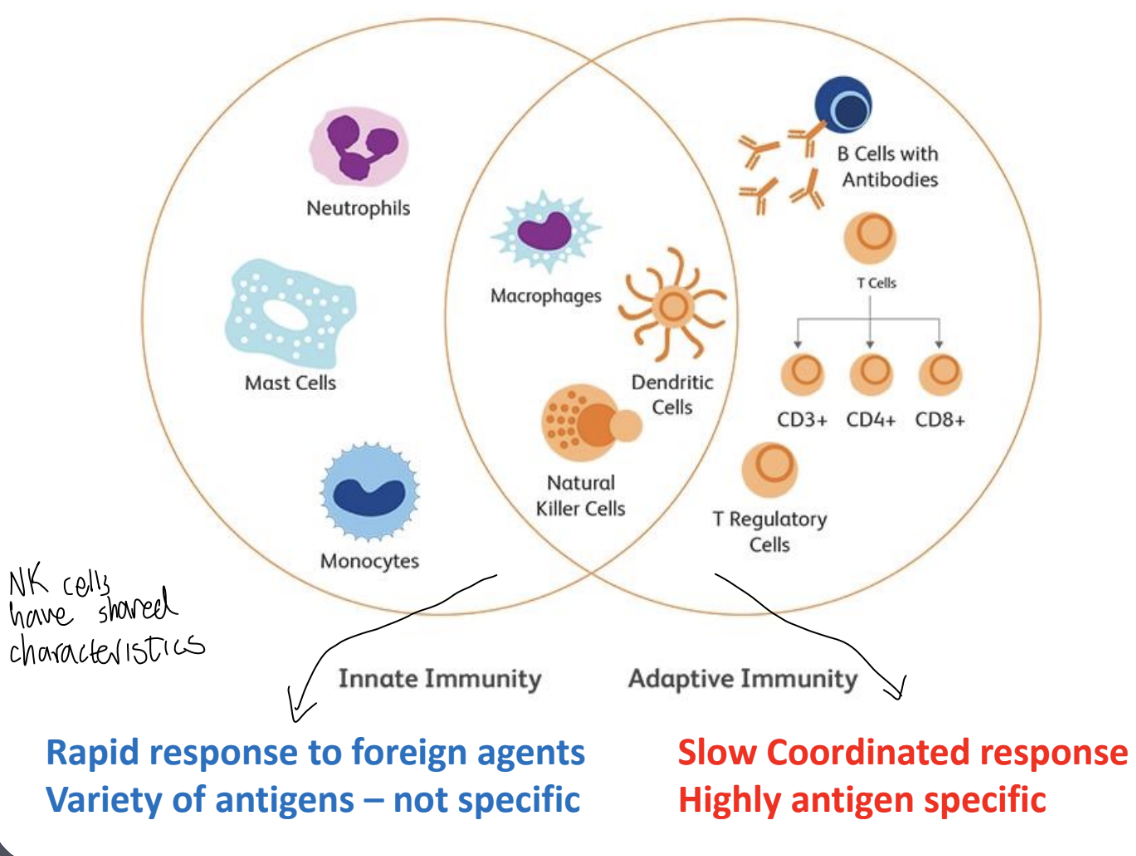
What do neutrophils, mast cells, and macrophages have in common?
They are all components of the innate immune system:
They act as the “fire alarm” , rapid 1st response (i.e. inflammation) to pathogens and injury, before the adaptive immune system “the fire brigade and then clean up team arrive”
(Review) Innate immunity involves a _________ response to foreign agents, produces a _________ that are ________
While adaptive immunity involves a _________ response and produces ______ that are _________
Rapid response to foreign agents; Variety of antigens – not specific
Slow Coordinated response; antigens that are highly specific
The lag phase for the innate system is _____ whereas in the adapative system it is ______
Absent - response is immediate upon recognition of foreign agents (non specific)
Present - response takes longer to develop and is specific to the antigen.
Specificity for the innate system is _____ whereas the adaptive has ______
Limited - same response applied to a variety of antigens
High - response is only directed towards the agent that initiated it
Diversity of receptors in the innate system is ______ whereas in the adaptive it is _______
Limited - few types of receptors;
Extensive - numerous antibodies and T cell receptors that recognize a vast array of antigens.
Memory of receptors in the innate system is ______ whereas in the adaptive it is _______
Limited - there is no memory;
Present - memory cells are formed after an initial response, allowing for quicker, amplified reactions upon re-exposure.
What happens to dendritic cells during the maturation process?
Immature DC have dendrites for phagocytosis, sweep out pathogens and uptake antigens
How do antigen presenting cells (APCs) interact with T helper cells?
APCs present antigens to T helper cells, initiating adaptive immune responses.
What role do lymph nodes play in the immune response?
Lymph nodes are sites where dendritic cells interact with B and T cells.
What is the primary function of B cells in the immune response?
B cells produce antibodies.
What receptors do T cells require in order to respond to antigens effectively?
T cells need CD4 or CD8 co-receptors to stabilize interactions with MHC molecules.
What is the difference between Th1 and Th2 cells?
Th1 cells focus on cell-mediated immunity, while Th2 cells are involved in humoral immunity.
What is an antigen?
An antigen is something that generates antibodies, also known as an immunogen.
What is the function of CD3 in T cell activation?
CD3 forms a complex with TCR that is essential for signaling and T cell activation.
What defines the specificity of T cell receptors (TCR)?
TCRs are extremely specific for one antigen, recognizing distinct pathogen epitopes.
What are the two main types of lymphocytes?
The two main types of lymphocytes are B cells and T cells.
What is the significance of MHC class I and MHC class II molecules?
MHC class I presents to CD8+ T cells, while MHC class II presents to CD4+ T cells, crucial for immune recognition.