9-Trilobites and Echinoderms
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is a trilobite?
An extinct marine arthropod with a segmented body and a calcite exoskeleton.

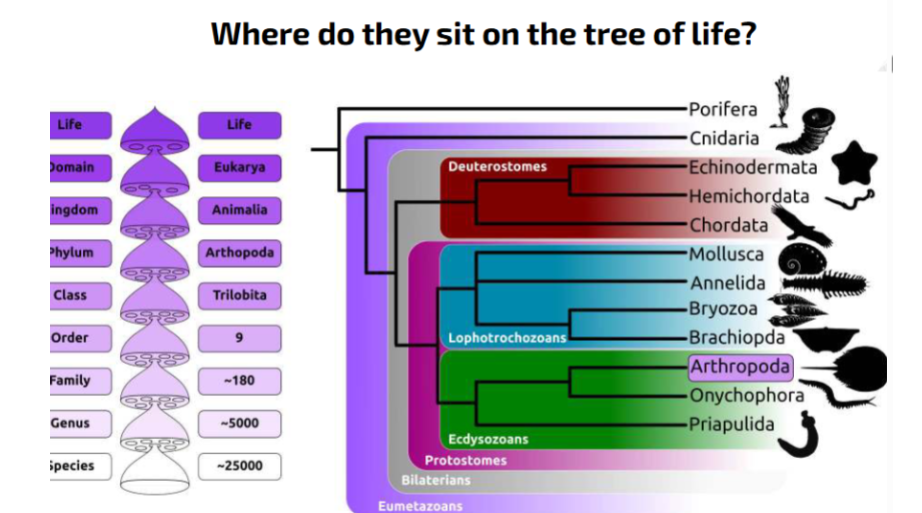
Which group do trilobites belong to?
Arthropoda
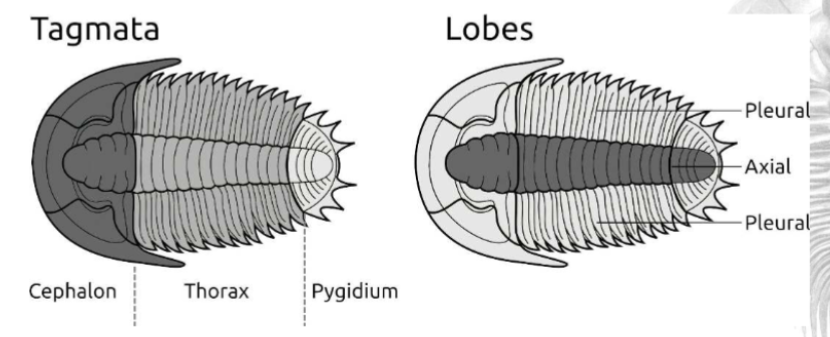
What are the body regions (tagmata) of a trilobite?
Cephalon (head), thorax (middle), pygidium (tail)
How many lobes does the trilobite have?
Three lobes: axial (middle) and two pleural (sides)
What is the glabella?
Raised central part of the cephalon that housed the stomach.
When did trilobites live?
Cambrian to Permian; extinct at end-Permian mass extinction
Why are trilobites important fossils?
Key index fossils for Cambrian-Ordovician biostratigraphy
What is palaeobiogeography?
Study of fossil distribution through space and time
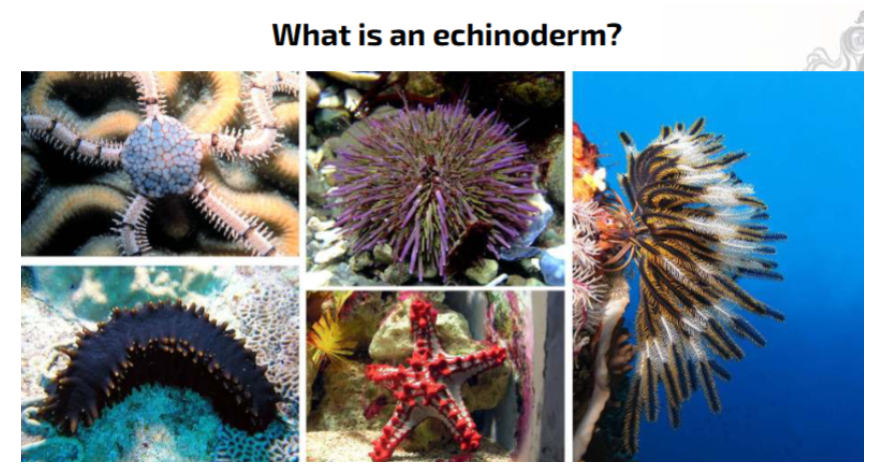
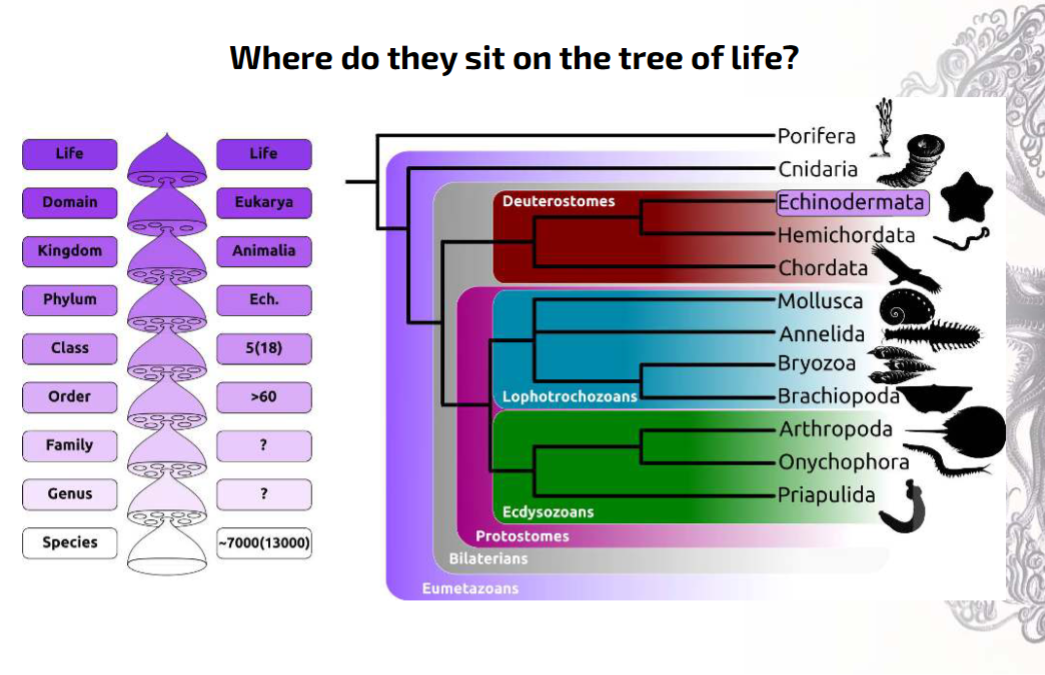
Echinoderms: What defines echinoderms?
Marine animals with five-fold symmetry and a hydraulic water-vascular system

What is stereom?
Skeleton made of magnesium rich calcite mesh
What is sister group to echinoderms?
Hemichordata
Why are echinoderm fossils rare?
Skeleton disarticulates quickly after death.
Main echinoderm groups in fossils?
Crinoids, echinoids, asterozoans
What are crinoids?
Stalked or free living sea lilies with arms for filter feeding
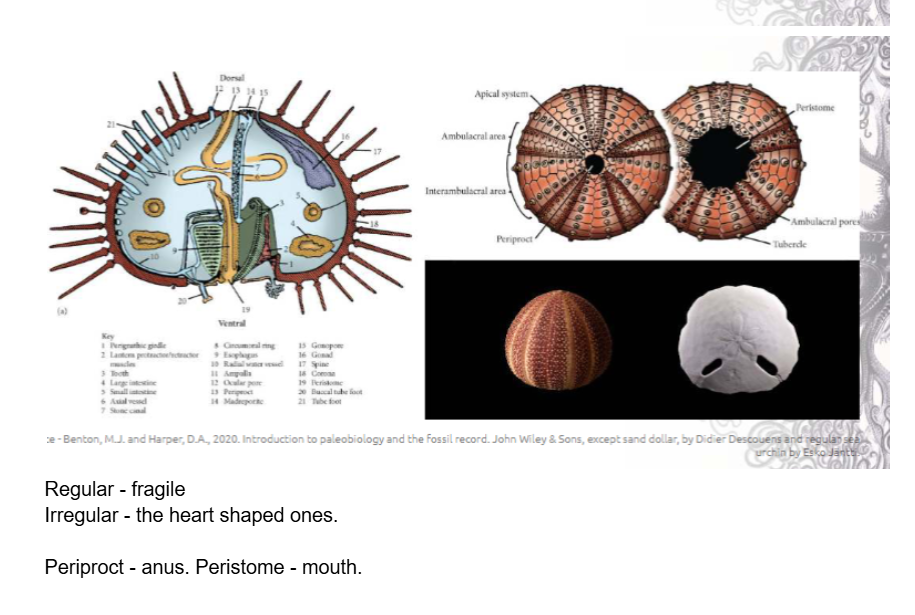
What are echinoids?
Sea urchins, heart urchins, sand dollars.
Hard, rounded or heart-shaped shell.
Have spines for movement and protection.
often free-living.
Mouth on bottom (oral surface), and anus on top (aboral surface)
Difference between regular and irregular echinoids?
Regular = round urchins.
Irregular = heart urchins adapted for burrowing
What are asterozoans?
star-shaped body
5 or more arms around central disc
What roles do starfish play?
Control algae on reefs and act as scavengers.
Biostratigraphy. What is an index fossil?
Abundant, widespread, short-lived, easy to identify species.
FAD vs LAD?
FAD - first appearance datum
LAD - last appearance datum.
Can plot borehole 1 on x axis, borehole 2 on y axis.
(FAD 1, FAD 2 ) as O
(LAD1, LAD 2) as X
What is a biozone?
Rock interval defined by presence of specific fossils?
What does a 45* LOC mean in correlation graphs?
Same sedimentation rate in both sections.
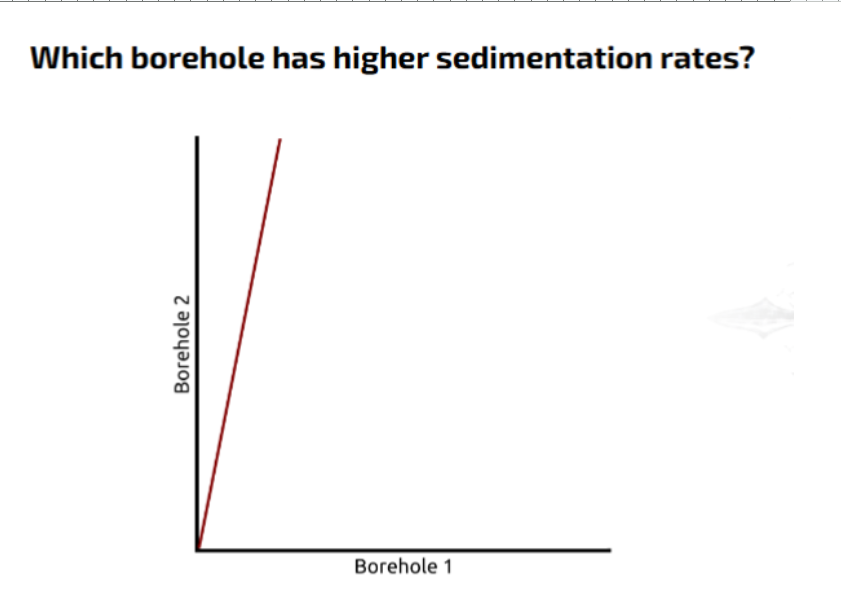
Borehole 2 has a greater rate of sedimentation
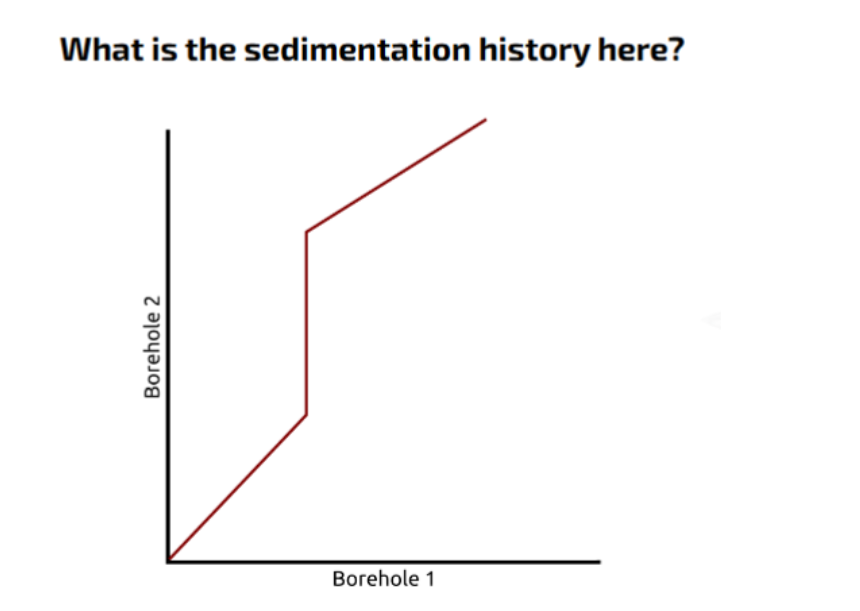
Straight line, Borehole 2 kept getting sedimentation, whilst borehole 1 didn't. Unconformity.