Populations and sustainability
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Draw and describe the population growth curve
Phase 1: At first there is a slow development: birth rate > death rate.
Phase 2: Then there is a period of rapid growth of the population size, due to few limiting factors on the population growth resulting in increasing numbers of organisms living and surviving.
Phase 3: The stable phase. Further population growth is limited due to external constraints leading to fluctuations in population growth. This is where carrying capacty is met.
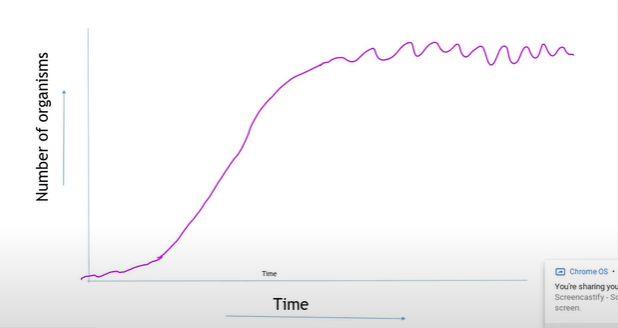
What is carrying capacity?
Where the population has reached its maximum size that the environment can support - the carrying capacity is not subject to any more succession
What are the factors that can limit population growth?
Abiotic factors:
nutrients, oxygen, pH etc.
Biotic factors:
Intra/inter-specific competition
Finding a mate, predator prey relationships etc.
Define immigration and emigration
Immigration - the movement of organisms into an area
Emigration - the movement of organisms out of an area
What is interspecific competition?
Competition between different species
What is intraspecific competition?
Competition within the same species
Describe predation as a biotic factor
Predation is a biotic factor that can influence population size. Many predators have evolved ways to catch their prey e.g. speed and stealth. Likewise, prey has evolved ways to avoid capture e.g. camouflage, stings and mimicry.
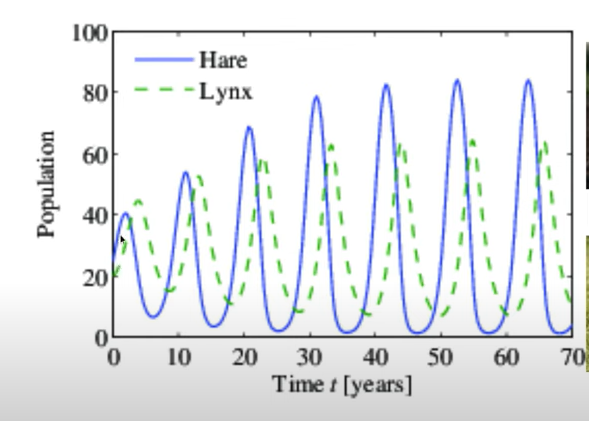
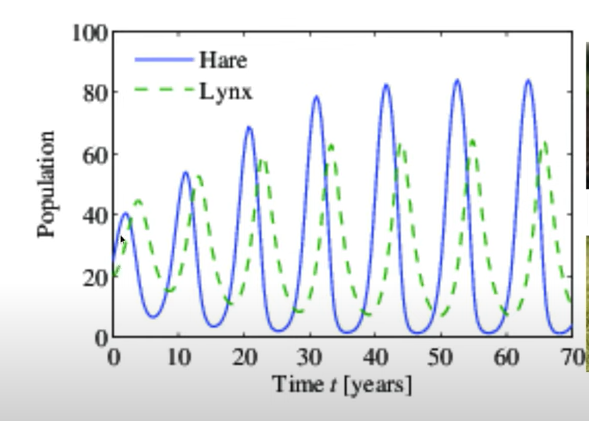
Explain what a predator-prey graph shows
As the prey population increases in size (birth rate > death rate), there is more food for the predator, and thus the predator population will increase.
However, as the predator population begins to increase (birth rate > death rate), the prey population will begin to decrease (death rate > birth rate) due to increased predation.
Due to a decrease in the prey population (death rate > birth rate), the predator has less food and the population of predator will decrease (death rate > birth rate).
Predator prey graphs fluctuate due to the availability of food to the predator, through the population of prey and over predation by the predator.
What is the ‘competitive exclusion principle’?
When two sifferent speces that occupy similar niches, compete with each other leading to one species population to supplant the other species - both species cannot coexist
Define conservation
The maintenance or management of nature by human intervention to protect species or habitats
Define preservation
Leaving the environment alone by restricting human access to keep the ecosystem untouched
What are the reasons for Conservation?
Economic - ecotourism / a potential source for medicines
Social - aesthetic / use for excersize and enrichment
Ethical - preserve biodiversity and stop extinction / support the ingigenous population
What are the aims of sustainability?
Preserve the environment
Ensure resources are available for future generations
Allow humans in all socities to live comfortably
Enable less economically developed countries to develop through exploiting their natural resources
Create a more even balance in the consumption of these resources in more economically developed countries and less economically developed countries
Describe the process of copicing
The trunk cut close to ground level, several new shoots will grow from cut surface, process is repeated after a certain time, you need to protect young shoots from grazers, can be repeated indefinitely
What are the advantages of coppicing?
New stems grow more rapidly than saplings
Lifespan of tree is extended
Provides a variety of light levels
Fewer large trees means tehre is more light for smaller plants
Provides a variety of habitats - maintains biodiversity
Maintains soil quality
Prevents succession
Large machinery is not needed so there is less disturbance
What is selective felling?
The cutting down of mature trees in a forest. This allows other trees to grow to maturity and also leaves enough for habitats for animals.
What is rotational felling?
This consists of planting a site and then felling the trees when they have reached maturity. Depending on tree species this usually takes between 8 and 20 years.
What is strip felling?
The cutting down of selected trees in a forest in a strip. This allows other trees to grow to maturity and also leaves enough habitat for animals.
What are the methods for sustainable fishing?
Introduce quotas - limits the number of certain species of fish that can be caught.
Certain hole size in the nets to allow smaller fish to escape and reach maturity and therefore breeding age.
Fishing is only allowed at certain times of the year allowing the population to reach a sustainable level.
Describe the conflict between conservation and human needs in the Masai Mara region in Kenya
Poaching has lowered animal population numbers
Park rangers have been employed and provided with the necessary equipment
Elephants trample on crops therefore farm land is fenced off
Legal hunting of overpopulated species is allowed at certain times
Describe the conflict between conservation and human needs in the Terai region of Nepal
Forests are being cleared to make products
There has been an increase in the retail price of forestry products leading to greater economic input into the region
More sustainable wood fuel sources
Promotion of fruits / vegetables from other areas
Improved irrigation from cops
Use more nitrogen fixing plants
Describe the conflict between conservation and human needs in peat bogs
Used for fertilisers
Takes thousands of years to form
It supports rare species of plants
No large trees are planted nearby (they will remove the water)
No grazing of sheep or cattle
Describe the effects of human activies on the animal and plant populations and how these are controlled in the Galapagos Islands
Habitat/ecosystem destruction - for buildings and roads
Deforestation of land - used for farming, overgrazing by introduced species
Increase in boats
More pollution - sewage in the sea and oil spills
Overfishing or over-hunting
Competition from introduced species
Introduction of new pathogens and diseases
Describe the methods to control the human impact in the Galapagous Islands
Introduction of park rangers
Limiting human access to particular islands
Stricter control on migration and introduction of animals
Describe the effects of human activies on the animal and plant populations and how these are controlled in the Galapagos Islands
Whale and fish populayions have been impacted through overfishing and whaling. There are now bans on whaling and restrictions on fishing.
Waste must be taken with you when you leave.
Boats can’t dump their ‘waste’ into the sea.
Describe the effects of human activies on the animal and plant populations and how these are controlled in Snowdonia National Park and the Lake District
Visitors encouraged to use paths to protect native species
Litter is encouraged to be placed in bins / taken home with you
Speed limits on the boats