Introduction to Chemistry and Matter Classification
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Chemistry
The study of the physical material of the universe and the changes it may undergo.
Matter
The physical material ("stuff") that makes up the universe, defined as any substance that has mass and occupies space.
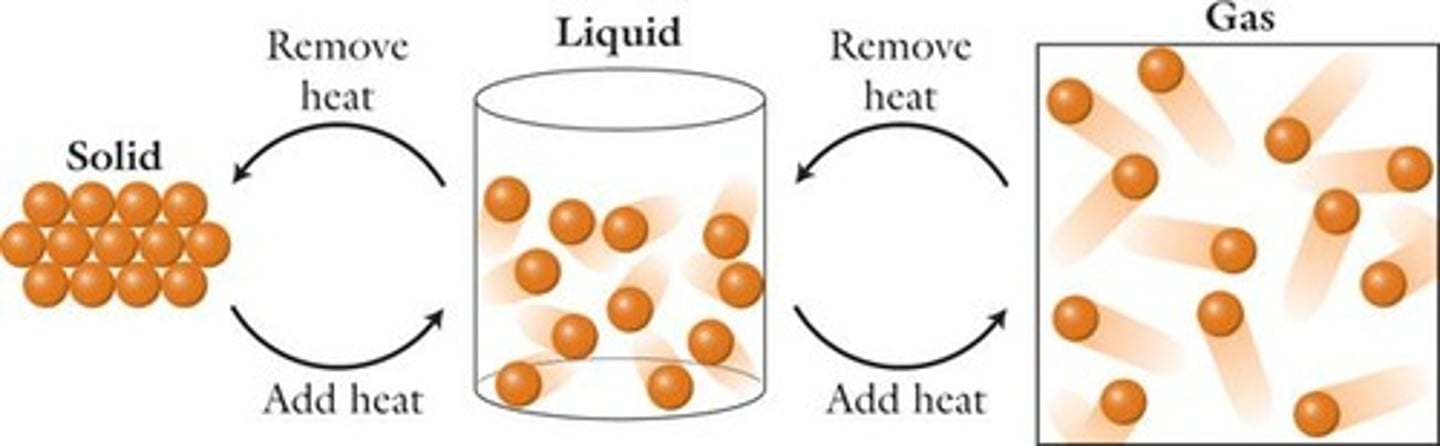
States of Matter
Three forms of matter: solid, liquid, and gas.

Solid
A state of matter where particles are closely packed, held in fixed positions, with a fixed volume and shape.
Liquid
A state of matter where particles are farther apart than in a solid, can flow, and takes the shape of the container.
Gas
A state of matter with large distances between molecules, where molecules move at high speeds and take the volume and shape of the container.
Pure Substance
Any form of matter that has a uniform composition and cannot be separated by physical methods.
Element
The simplest form of a pure substance that cannot be decomposed and has unique atoms.
Atom
The smallest unit of an element that retains all of the properties of the element.
Compound
A substance made up of atoms from two or more elements chemically bonded together.
Molecular Compound
A compound where the simplest unit is a molecule.
Ionic Compound
A compound where the simplest unit is a formula unit.
Mixture
A combination of two or more pure substances that are physically mixed together but not chemically bonded.
Homogeneous Mixture
A mixture where the substances are evenly distributed and consist of visibly indistinguishable parts.
Heterogeneous Mixture
A mixture where the composition varies from one region to another and has different properties in different regions.
Phase Changes
Changes between states of matter.
Examples of Solids
Ice cube, diamond, iron bar.
Examples of Liquids
Gasoline, water, alcohol, blood.
Examples of Gases
Helium, air, oxygen.
Examples of Pure Substances
Aluminum (Al), Sodium (Na), Oxygen (O2), Iron (Fe).
Examples of Compounds
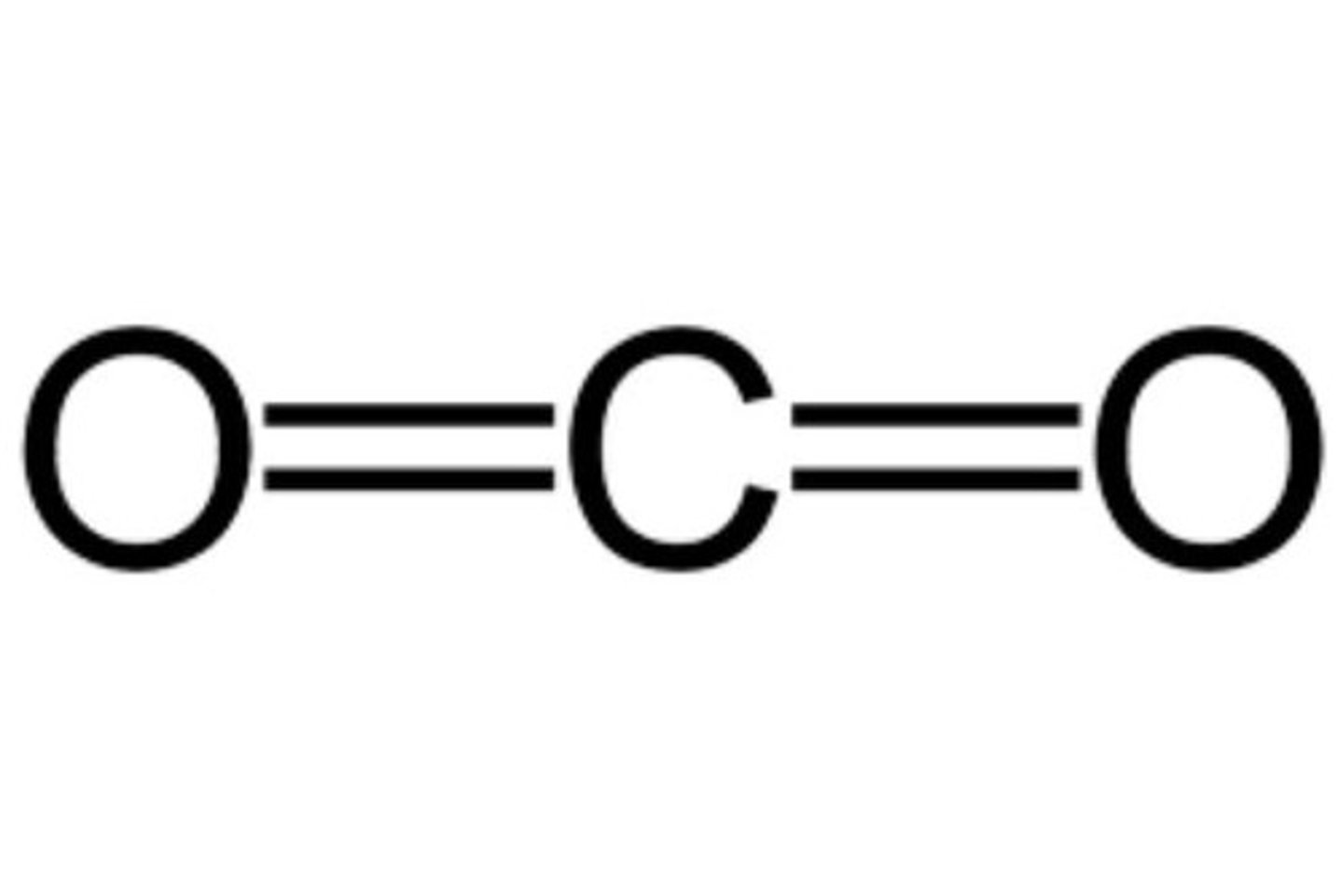
Water (H2O), Carbon dioxide (CO2), Ethanol.
Examples of Homogeneous Mixtures
Salt water, wine, distilled water, air around you, brass.

Examples of Heterogeneous Mixtures
Chocolate chip cookie, gravel, tap water, oil and vinegar dressing, sand stirred into water.