Perception Quiz 1
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Abnormal pitch
pitch is consistently too low or too high for age and sex
Pitch breaks
pitch shows sudden and uncontrolled variation (e.g., falsetto breaks).
Monopitch
voice is characterized by monopitch or monotone. Voice lacks normal pitch variation
Monoloudness
Voice shows monotony of loudness. It lacks normal variations in loudness.
Voice tremor
voice shows fairly regular tremor, usually in 4-7 Hz range.
Excess loudness variation
Voice shows sudden, uncontrolled alternations in loudness, sometimes becoming too loud, sometimes too quiet.
Loudness decay
Progressive diminution or decay of loudness within an utterance
Alternating loudness
Alternating changes in loudness within an utterance
Loudness level (overall)
Voice is insufficiently or excessively loud
Harsh voice
Voice is harsh, rough, and raspy.
Hoarse (wet) voice
There is wet, "liquid-sounding" hoarseness.
Breathy voice, or breathiness (continuous)
Voice is continuously breathy
Breathy voice, or breathiness (transient)
breathiness is transient or intermittent
Strained (stained-strangled) voice
Voice quality sounds strained or strangled (an apparently effortful squeezing of voice through glottis)
Voice stoppages (interruptions/arrests)
There are sudden stoppages of voice, as if airflow has been impeded
Hypernasality
resonance is excessively nasal
Hyponasality
resonance is hyponasal/denasal
Increased rate in segments (accelerated rate)
Rate increases progressively within given segments of connected speech.
Increased rate overall (rapid rate)
Rate increases progressively from beginning to end of sample
Reduced stress
Speech shows reduction of proper stress or emphasis patterns.
Variable Rate
Rate varies within or across utterances.
Prolonged intervals
There is prolongation of interword or intersyllable intervals.
Inappropriate silences
There are inappropriate silent intervals.
Short rushes of speech
There are short, rapid rushes of speech separated by pauses.
Excess and equal stress
There is excess stress on usually unstressed syllables or parts of speech.
Imprecise consonants/articulation
Consonants lack precision. They show inadequate sharpness, distortions, and lack crispness.
Prolonged phonemes
Phonemes are prolonged
Repeated phonemes or syllables
There are slow or rapid repetitions of phonemes
Laryngeal (oral mech exam)
· vocal fold paralysis (breathy voice); weak cough (lacking sharpness) and coup (lacking sharpness); stridor; audible inhalation
· possible unilateral paresis or paralysis
· Stridor/audible inhalation: both features can reflect abductor vocal fold weakness
· Immobile (paralyzed vocal fold): indication of unilateral Vagus nerve lesion. Associated with flaccid dysarthria (breathy)
Facial (oral mech exam)
Asymmetry at rest and during movement; Reduced or asymmetric smile, rounding, puffing; Chin fasciculations (LMN involvement, CN VII, can be associated with flaccid dysarthria)
-Synkinesis
Upper + lower face weakness on one side + tongue normal
cranial nerve (VII paralysis (LMN) of one side (can be associated with flaccid dysarthria)
Bilateral lingual fasciculations, chin fasciculations, reduced lip retraction and rounding, vocal flutter (associated with laryngeal weakness)
LMN involvement (CN VII, X, and XII) can be associated with flaccid dysarthrias
Synkinesis
-abnormal contraction of muscle adjacent to normally contraction muscle
-Such as when eye blinking causes simultaneous movement of lower facial muscles
-It reflects aberrant branching of regenerating axons or abnormal activity of residual motor units
-Commonly seen after recovery from Bell's (VIIth nerve) palsy
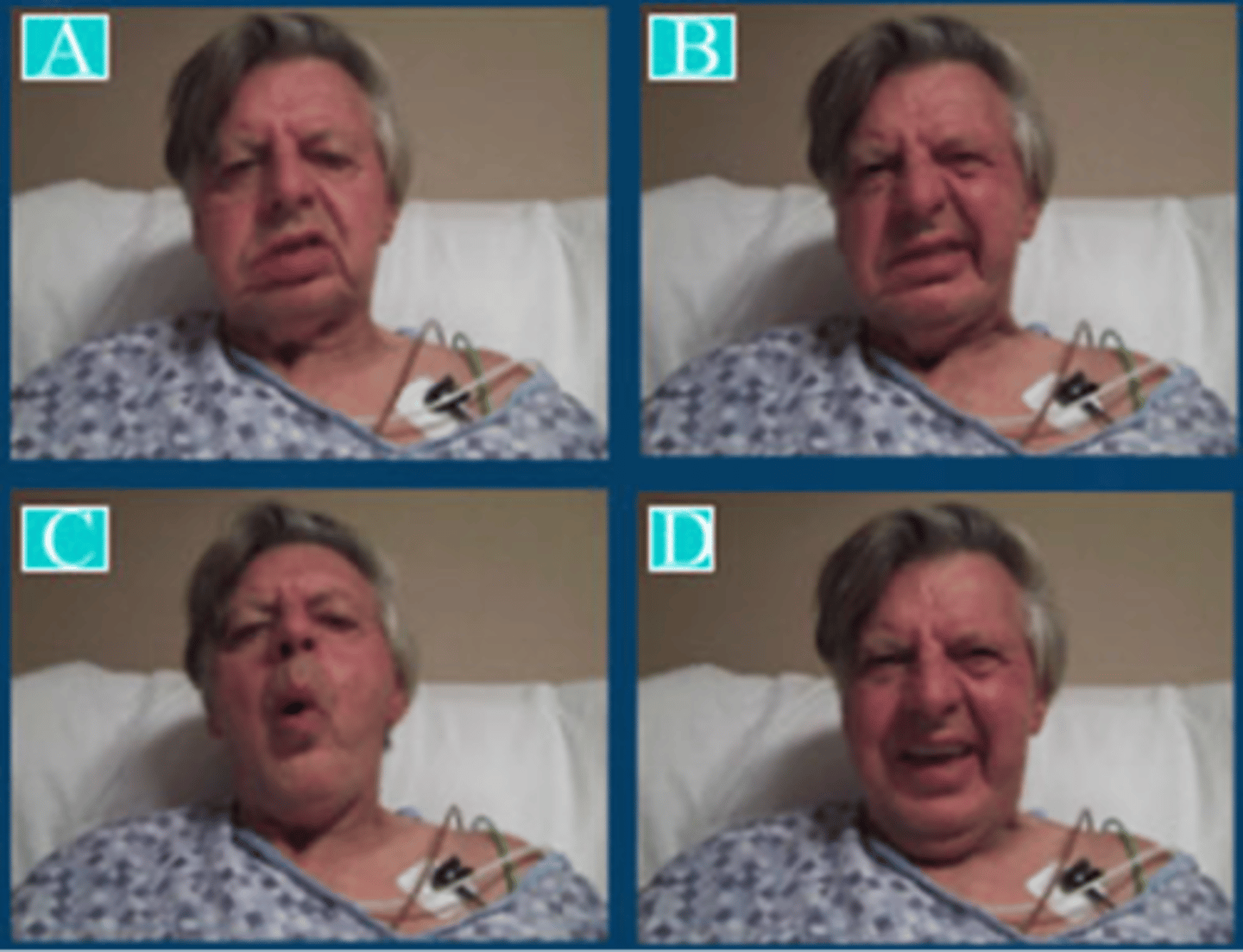
Characteristics: right face (lower): droop at corner of mouth with flat nasolabial fold, reduced right face retraction on smiling, retraction rounding, upper lip arch reduced on right on mouth opening (no drop of eyelid or forehead, tongue grossly normal)
neurological meaning: right CNS face weakness indicative of left UMN lesion
Right CNS face weakness; indicative of left UMN lesion
Observe: Right face (lower)
o Right face droop and flat nasolabial fold at rest (A)
o Reduced right face retraction on volitional lip retraction (B)
o Reduced volitional lip rounding on right (C)
o Relatively symmetric emotional smile (D)
Lingual (oral mech exam)
· Deviation on protrusion (same side as sight of lesion. EX: right deviation = right lingual weakness); Fasciculations; Weak or reduced lingual movements
· Fasciculations and atrophy are indicators of weather weakness is UMN or LMN
· Elevation of soft palate to one side during phonation indicative of palatal weakness
Elevation of soft palate to one side during phonation indicative of palatal weakness
-elevation of soft palate to the right = left palatal weakness
-elevation of soft palate to the left = right palatal weakness
Velopharyngeal (asymmetry)
Pathologic oral reflexes
· Sucking reflex
· Snout reflex
· Palmomental reflex: contraction of right and left mentalis or lower lip (In response to brisk stroking of right and left palms)
· when response is prominent and easily elicited, suggestive of CNS pathology
· present more often in spastic than in other dysarthria types
Pseudobulbar affect
· Poorly inhibited, fairly stereotypic laughter reflecting pseudobulbar affect (Smiling, crying, and verge-of-tears facial expression are other manifestations of this form of labile affect)
· Neurologic meaning: usually occurs with bilateral UMN involvement, not unlike pathologic reflexes
· not uncommon in people with spastic dysarthria
Involuntary movements
· Essential tremor
· Tongue and chin tremor
· Chorea
· Palatal-pharyngeal tremor
Essential tremor
o head tremor
o markedly severe voice tremor with voice interruptions
o probably involving cerebellar control circuit
Tongue and chin tremor
Relatively rhythmic chin and tongue tremor, most evident during static postures (mouth opening and tongue protrusion) and movement
Chorea
o Relatively quick, unsustained movements of shoulders, head, and lips; difficulty sustaining steady posture
o reflecting basal ganglia control circuit pathology
o Ex: Huntington's disease

Palatal-pharyngeal tremor
o Laryngeal tremor is reflected in fluctuations during vowel prolongation
o Right face weakness is present but is a problem distinct from the beating tremor
o lesion in Guillain-Mollaret triangle (dentate nucleus, inferior olive, red nucleus)
Nonverbal oral apraxia
· Groping, off-target efforts to achieve postures and movements
· Vocalization or verbalization as part of, or in place of, target
· Neurologic meaning: left (dominant) hemisphere localization
o Often but not always associated with AOS and aphasia
o Rare in dysarthria without AOS or aphasia