Ib 104 Unit 2
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
what does true breeding mean?
when plants are self-pollinated, this causes offspring to be the same variety as the parent.
what is the genetic basis of a true breeding parent?
two alleles that are the same
what is the genetic basis of the F1 generation hybrids?
two different alleles
what is a phenotype?
an observable trait
what is a genotype?
genes responsible for traits
Prezygotic Barriers
habitat isolation, temporal isolation, behavioral isolation, mechanical isolation, gametic isolation- no successful mating or fertilization
postzygotic barriers
reduced hybrid viability, reduced hybrid fertility, hybrid breakdown- individuals or their offspring are not fertile
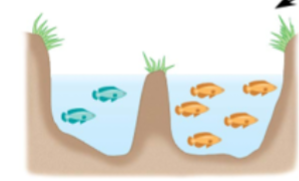
allopatric speciation
populations are geographically isolated, gene flow is interrupted from habitat change or colonization.
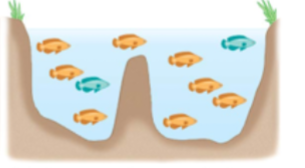
sympatric speciation
speciation occurs in populations that live in the same geographic area
a species
a group of populations whose members have the potential to interbreed in nature, produce viable fertile offspring, and do not produce viable offspring with members of other such groups
Phylogeny
the evolutionary history of a species or group of related species
systematics
a discipline focused on classifying organisms and determining their evolutionary relationships
Branch point
point that represents the divergence of two evolutionary lineages from a common ancestor
evolutionary lineage
a sequence of ancestral organisms leading to a particular descendant taxon
sister taxa
groups that share a common ancestor that is not shared by any other group
shared ancestral character
character that originated in an ancestor of the taxon
shared derived character
evolutionary novelty unique to a particular clade but may still have a shared ancestral character
Radial Symmetry
animals are sessile or planktonic, body parts arranged around a single central axis, drift or swim weakly
Bilateral Symmetry
body parts are arranges around two axes of orientation, the head-tail and the dorsal- ventral.
what are the three layers of tissues from outside in?
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
coelom
body cavity surrounded by tissues derived from mesoderm
protosome
blastopore develops into mouth
deuterostome
blastopore develops into anus
sponges
do not belong to eumetoazoa, they do not have tissues
porifera
asymmetrical, no body cavity (pores), no segmentation, spicules for support- ex: sea sponge
cnidaria
radial, 1 mouth, no segmentation, stinging cells- ex: jellyfish, coral, sea anemone
platyhelmintha
bilateral, 1 mouth, flattened body shape to increase SA volume- ex: tapeworms and planaria
annelida
bilateral, 1 mouth 1 anus, ringed segments with specialization of segments- ex: earthworms and leeches
mollusca
bilateral, 1 mouth 1 anus, body composed of visceral mass, muscular foot and a mantle, sometimes a shell- ex: snails, clams, octopi, clams
arthropoda
bilateral, 1 mouth 1 aunus, jointed body appendages, chitin exoskeleton- ex: insects, crustaceans, spiders, scorpions
chordata
bilateral, 1 mouth 1 anus, notochord and hollow dorsal nerve tube- ex: mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish,
medusozoans
cnidarians that produce a medusa (jellies)
anthozoans
occur only as polyps, include sea anemones and corals
echinodermata
radial, 1 mouth. start bilateral and then become radial- ex: starfish, sea urchins, and sea cucmbers
what are the five clades of echinoderms
asteroidea (sea stars), ophiuroidea (brittle stars), echinoidea (sea urchins and sand dollars), crinoidea (sea lillies) holothuroidea (sea cucumbers)
what are examples of jawless vertebrates
hagfish and lampreys
chondrichthyans
have a skeleton composed primarily of cartilage (shark, ray, chimera/ratfish)
osteichthyes
bony fish, largest class of vertebrates, instead of cartilage they have bones, and have a swim bladder for buoyancy.
what is the function of the dorsal fin?
stabilizers so fish don’t roll
oviparous
eggs hatch outside the mothers body
ovoviviparous
eggs are retained within the oviduct, young are born after hatching in the uterus.
viviparous
young develop in the uterus and are nourished by a yolk sac placenta, absorption of fluid or by eating other eggs.
ray-finned fishes
over 27,000 species, modifications in body form and fin structure affect maneuvering, defense, and other.
lobe fin lineages
coelacanths, lungfishes, tetrapods
what is unusual about the lungfish’s circulatory system?
they live in environments with low oxygen levels so they utilize gills to diffuse oxygen and lungs to gulp water and take in oxygen
amphibians three clades
salamanders (Urodela, tailed ones), frogs (Anura, tail-less ones), caecilians Apoda, legless ones)
Salamanders (urodela)
550 species, some are aquatic but most live on land as adults, paedomorphosis
frogs ( Aunura)
5,420 species, lack tails and have powerful hind legs, frogs with leathery skin are toads.
caecilians (apoda)
170 species, legless and nearly blind, resemble earthworms, legs lost as a secondary adaptation
what does the term amphibian mean
both ways of life- many species live first in water and then on land.
amniotic egg
egg that contains four membranes that protect the embryo, key adaptation for life on land, reduced dependence on water for reproduction
reptiles characteristics
scales containing keratin to protect, shelled eggs on land, fertilization occurs internally, ectothermic- absorbing external heat
Diapsids
earliest reptiles that resembled lizards about 310 million years ago, pair of holes on either side of skull where muscles attach to jaw
diapsids three main lineages
turtles, lepidosaurs ( tuataras, lizards, snakes), archosaurs (crocodilians)
tuatara
Lepidosaur- lizard like species, live in 30 islands off the coast of New Zealand, threatened by rats.
turtles
351 known species, most closely related to crocodilians and birds, lost the holes in the skull.
Lizards and Snakes
lepidosaur- squamates. around 10,425 species.
snakes
move by producing waves of lateral bending from head to toe, can use belly scales to grip the ground
crocodilians
24 species, restricted to warm regions of the globe, descendants of quadrupeds.
characteristics of birds
no urinary bladder, one ovary, small gonads, toothless mouths, air-filled bones with honeycombed internal structure
ratites
order of flightless birds ostrich, rhea, kiwi, cassowary, and emu
what was the earliest known bird?
archaeopteryx
mammal characteristics
mammary glands, hair and a fat layer, kidneys, endothermy a high metabolic rate, respiratory and circulatory systems, extensive parental care, teeth modified for shearing, crushing, or grinding.
when were the first true mammals alive?
during the jurassic period?
three major lineages of mammals
monotremes, marsupials, eutherians
monotremes
egg laying mammals, found in Australia and New Guinea, females lack nipples and secrete milk from glands, echidna and platypus
marsupials
higher metabolic rates, nipples, birth of live young, placenta, , live in australia snd the americas, kangaroos, wolverine, woodchucl
eutherians
placental mammals, complete emdyonic development within a uterus, elephants, dolphins
primates
hands and feet, digits, fingers and fingerprints, forward looking eyes, parental care, lemurs, tarsiers, monkeys and apes
three main groups of living primates
lemurs, tarsiers, anthropoids
four genera of great apes
pongo, gorrilla, pan, homo
earliest trace of humans
homo sapiens fossils found from ethiopia that are 195,000 and 160,000 years old
Heterozygous gene
Xx
Natural Selection
genetic variation due to differences in alleles, to help an animal survive (color or neck length) allows them to survive and reproduce.
genetic drift
two main types: bottleneck effect and founder effect. changes allele frequencies and reduces genetic diversity. not adaptive
bottleneck effect
drastic reduction in population size due to a sudden change in environment or random event
founder effect
colonization’s of a new habitat by a few individuals
gene flow
movement of alleles among populations through the movement of fertile individuals or gametes, reduces genetic differences between populations over time
directional selection
favors individuals at one extreme end- giraffes
stabilizing selection
favors intermediate variants- different colored mice
disruptive selection
favors induviduals at both extremes- both light and dark colored moths
how can we define a biological species?
a group of populations whos members have the potential to reproduce viable, fertile offspring and do not produce viable offspring with members of other such groups
pre-zygotic barrier
mechanical isolation - physical incompatibility ie- snails that have shells coiled in opposite directions, physically prevents their genitalia from aligning properly
postzygotic barrier
reduced hybrid fertility- hybrid offspring are infertile, like a mule, and offspring cannot reproduce
taxonomic groups in order
domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species