Cell and Mitosis: Location, Function, and Cell Cycle Key Concepts
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Plasma membrane
Selectively permeable barrier with proteins for transport, signaling, and recognition.
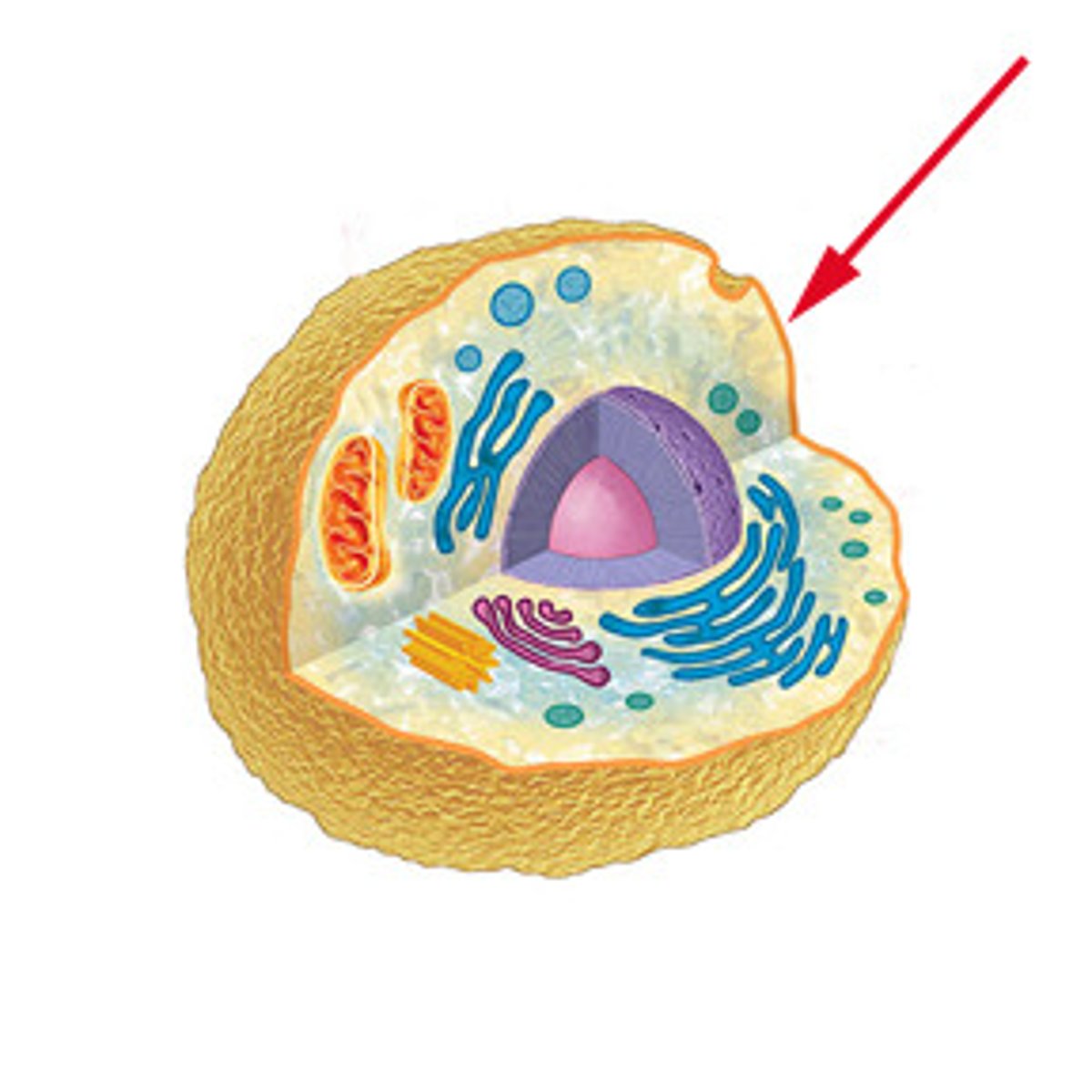
Cytoplasm
Located between the plasma membrane and the nucleus; houses organelles, site for chemical reactions, stores materials.
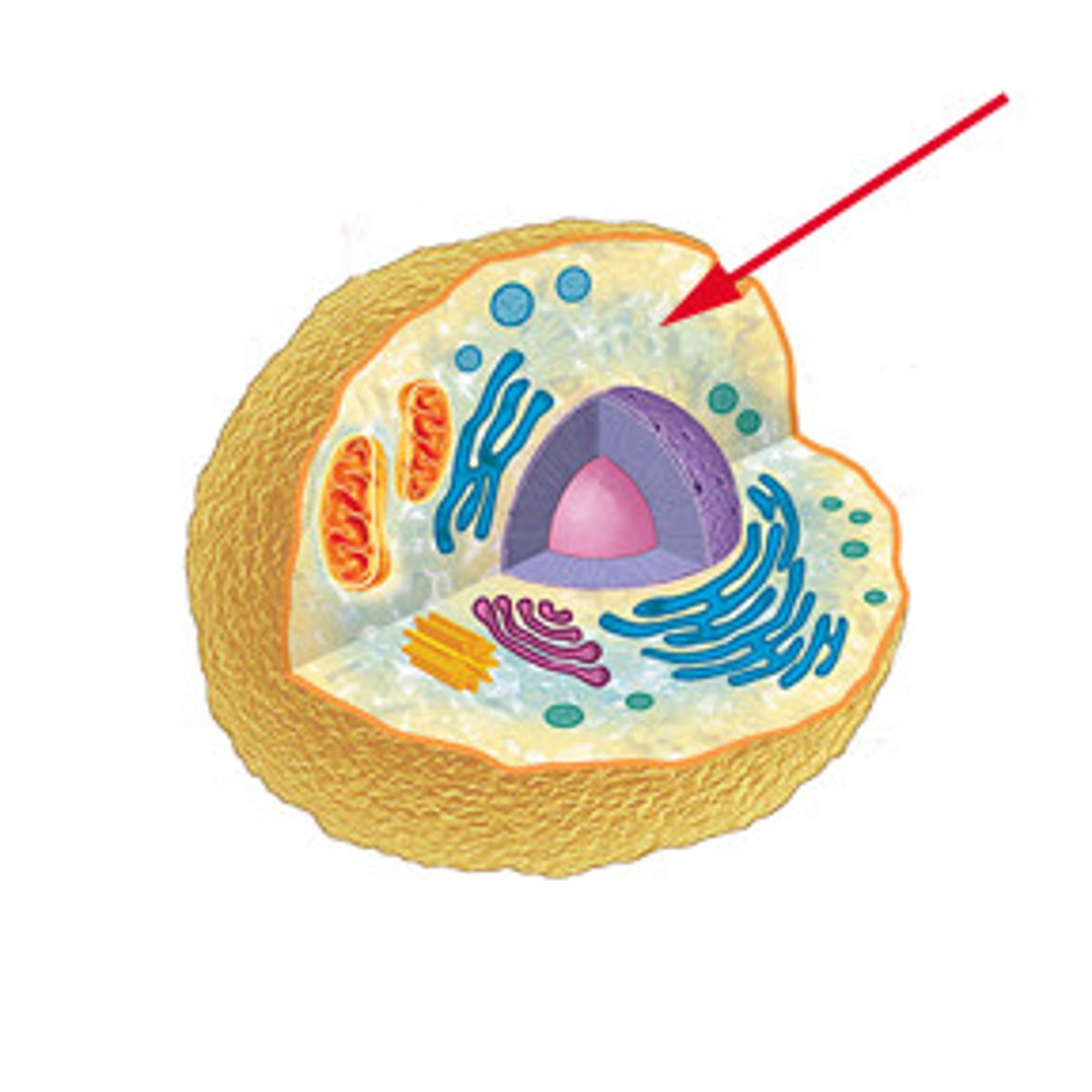
Cytoskeleton
Network of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules for support and movement.
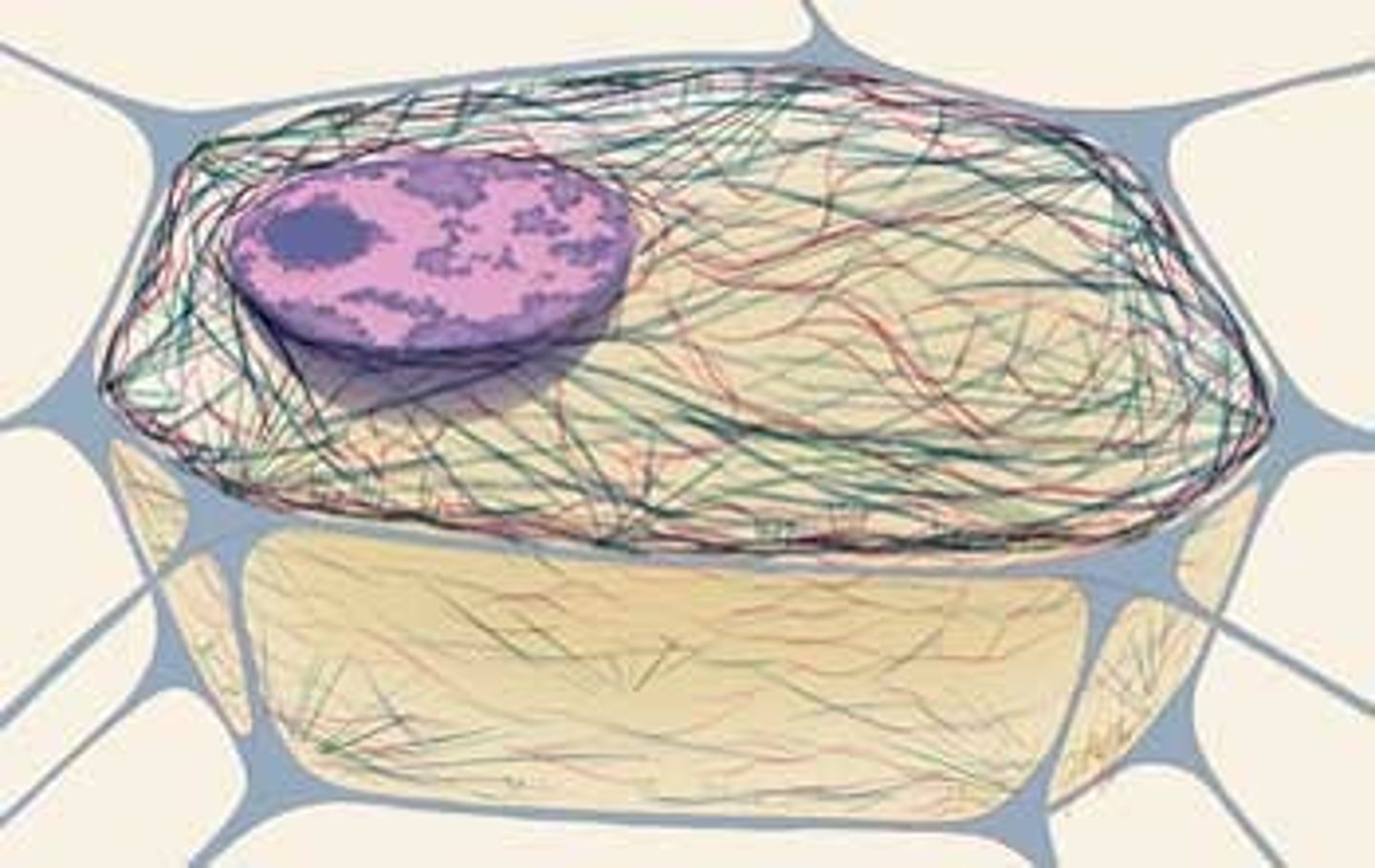
Centrosome with centrioles
Near the nucleus, helps form spindle fibers for cell division.
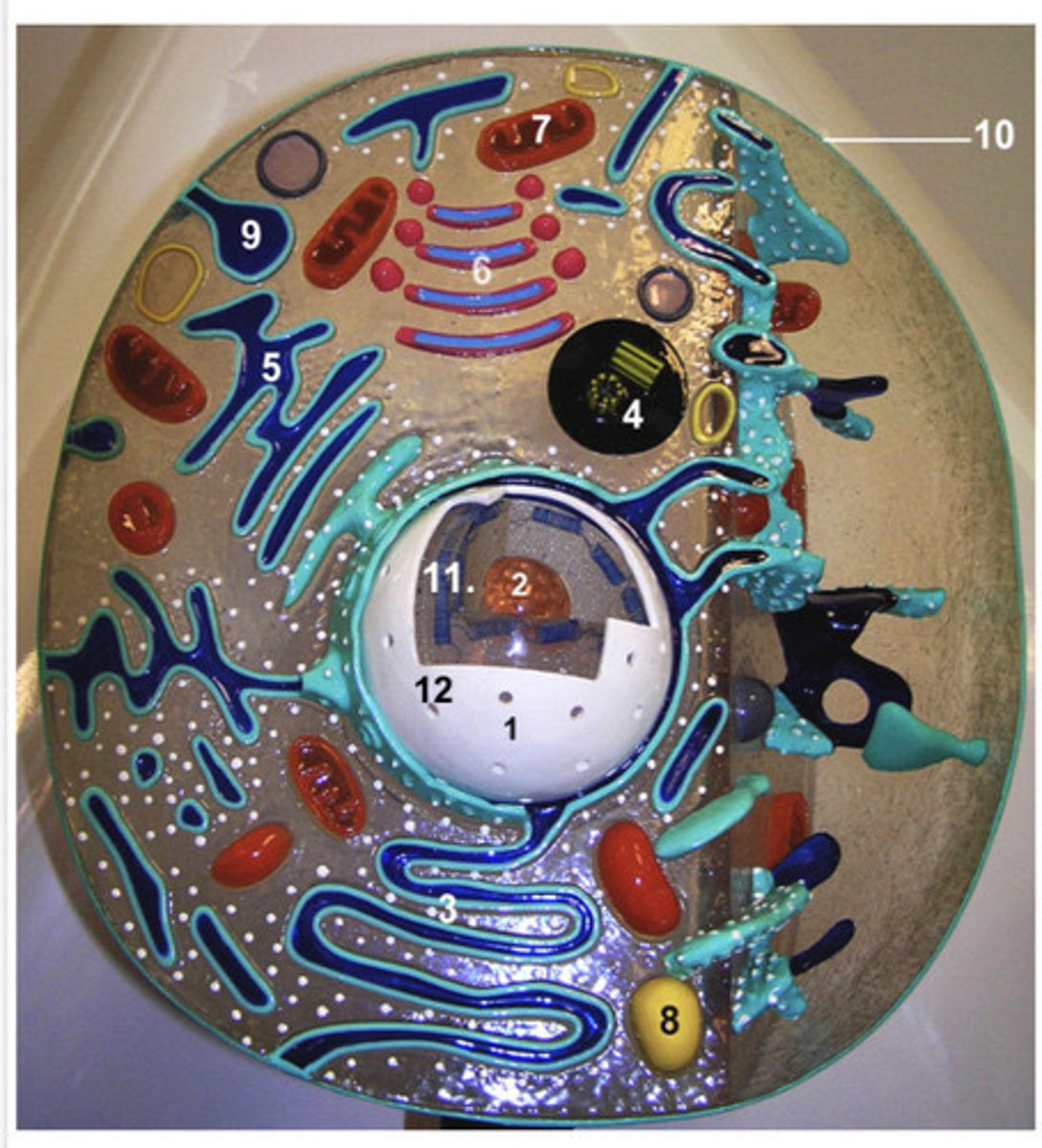
Cilia and flagella
Cilia move mucus and particles; flagella propel whole cells.
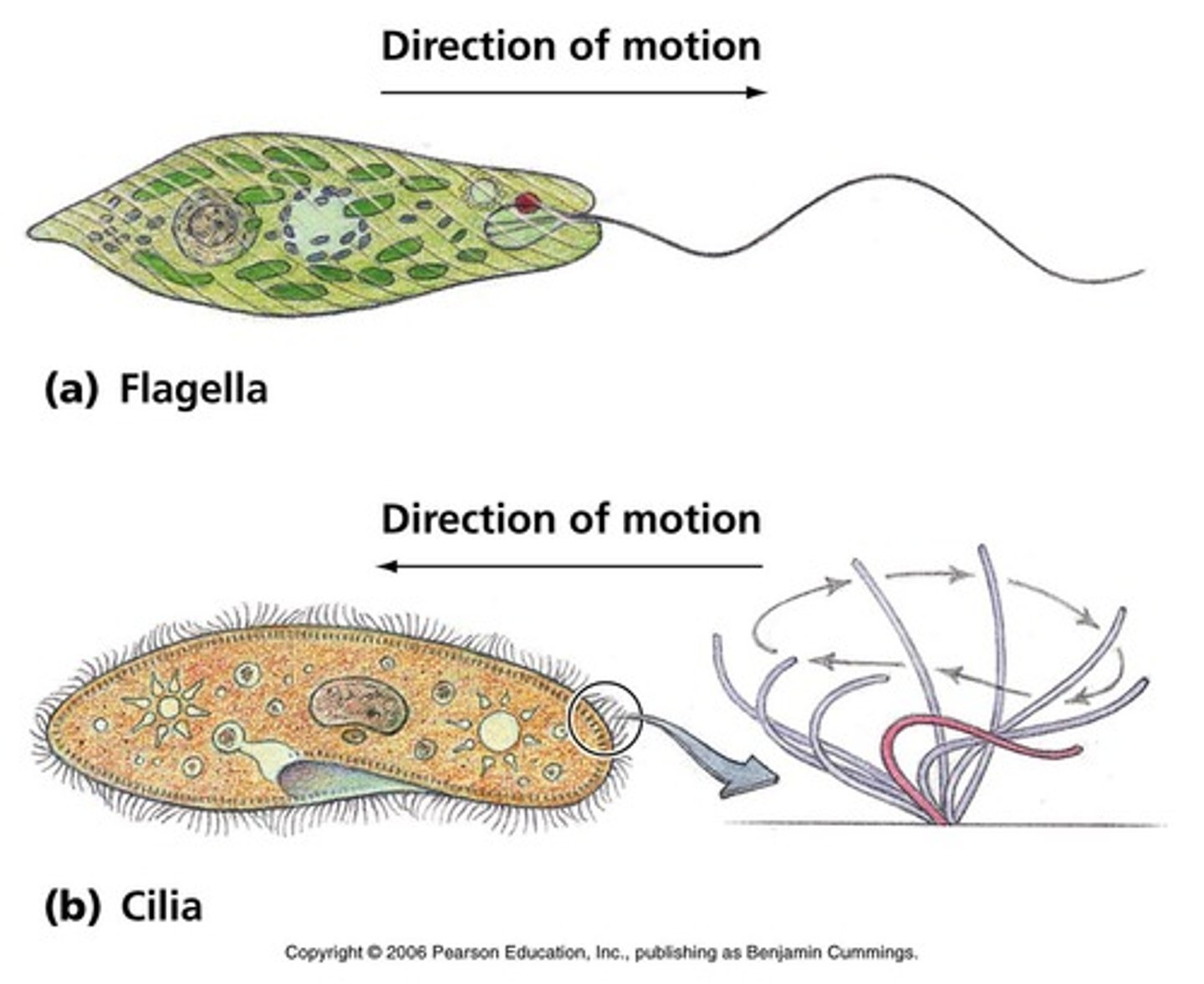
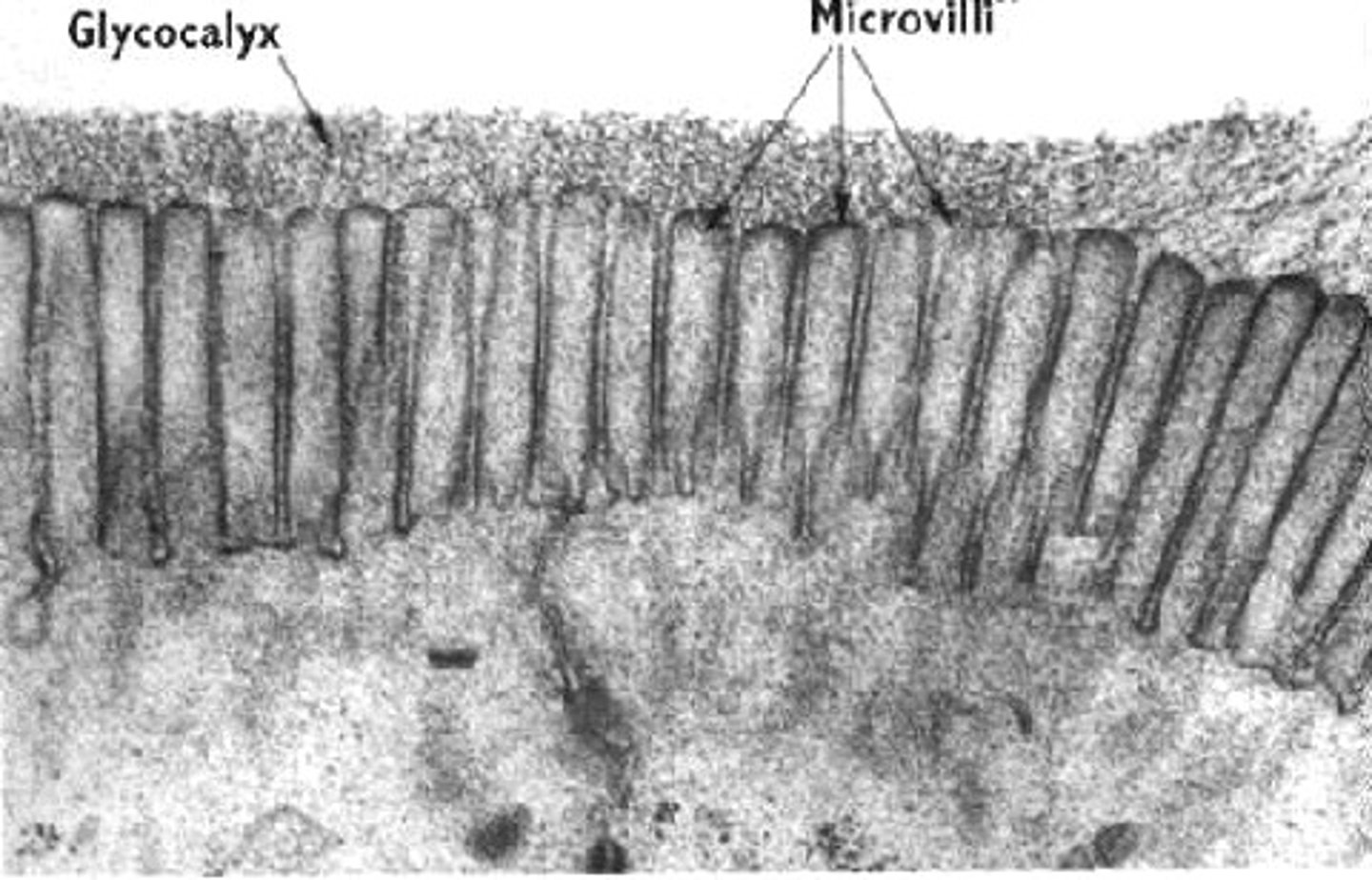
Microvilli
Small projections on cell surfaces that increase surface area for absorption.
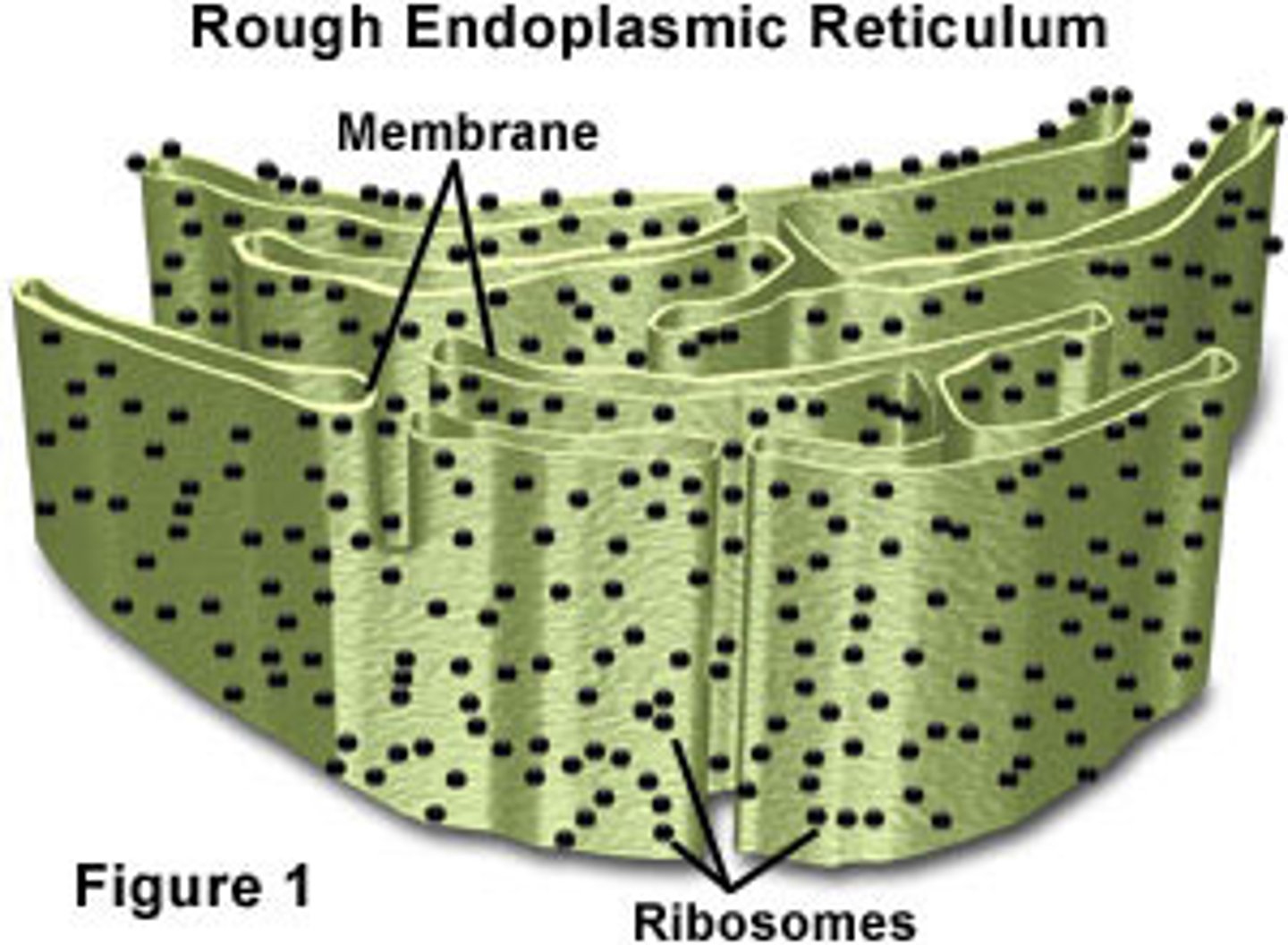
Rough ER
Extends from nuclear envelope, studded with ribosomes, modifies and transports proteins.
Smooth ER
No ribosomes, involved in lipid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, and detoxification.
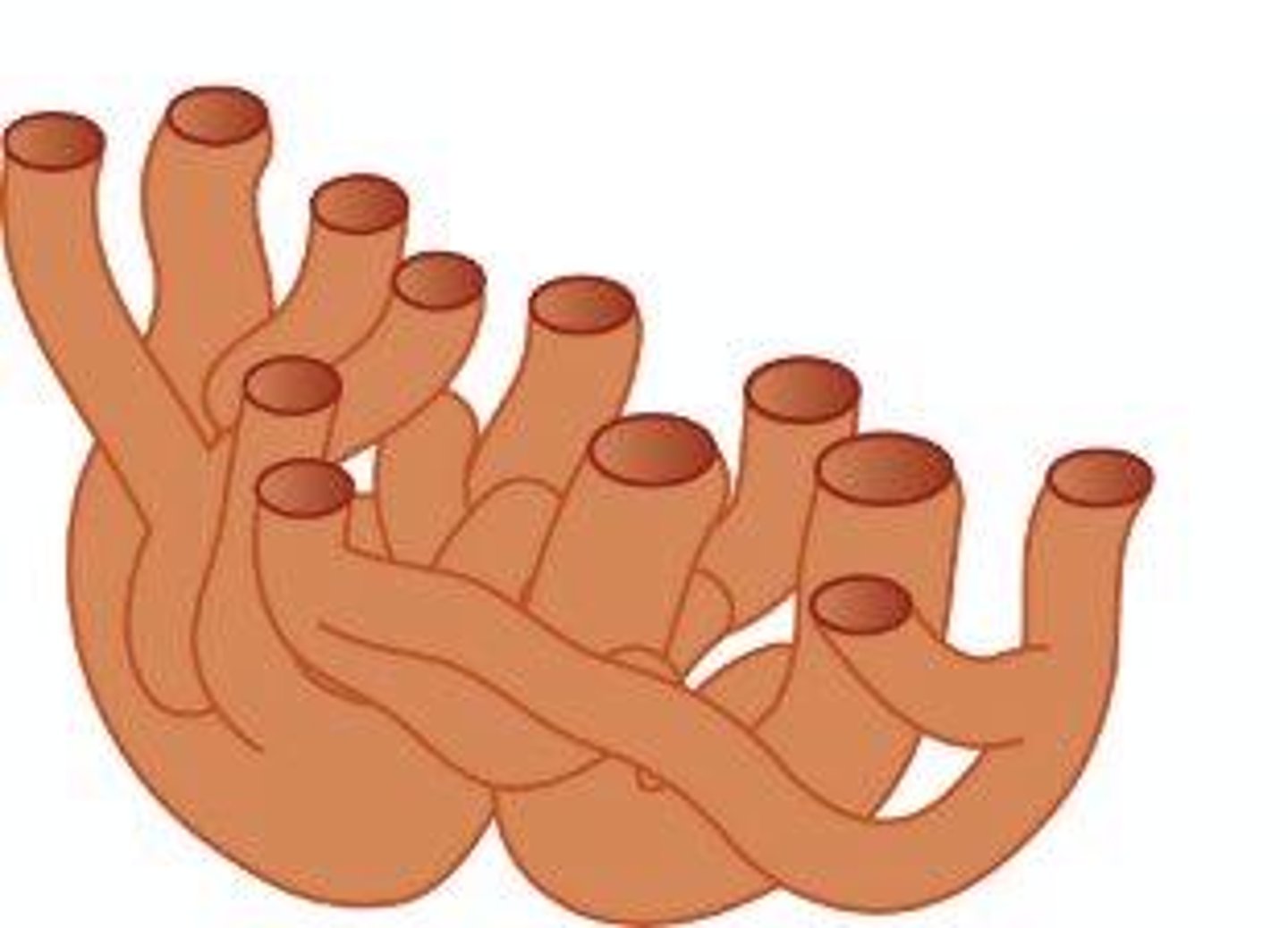
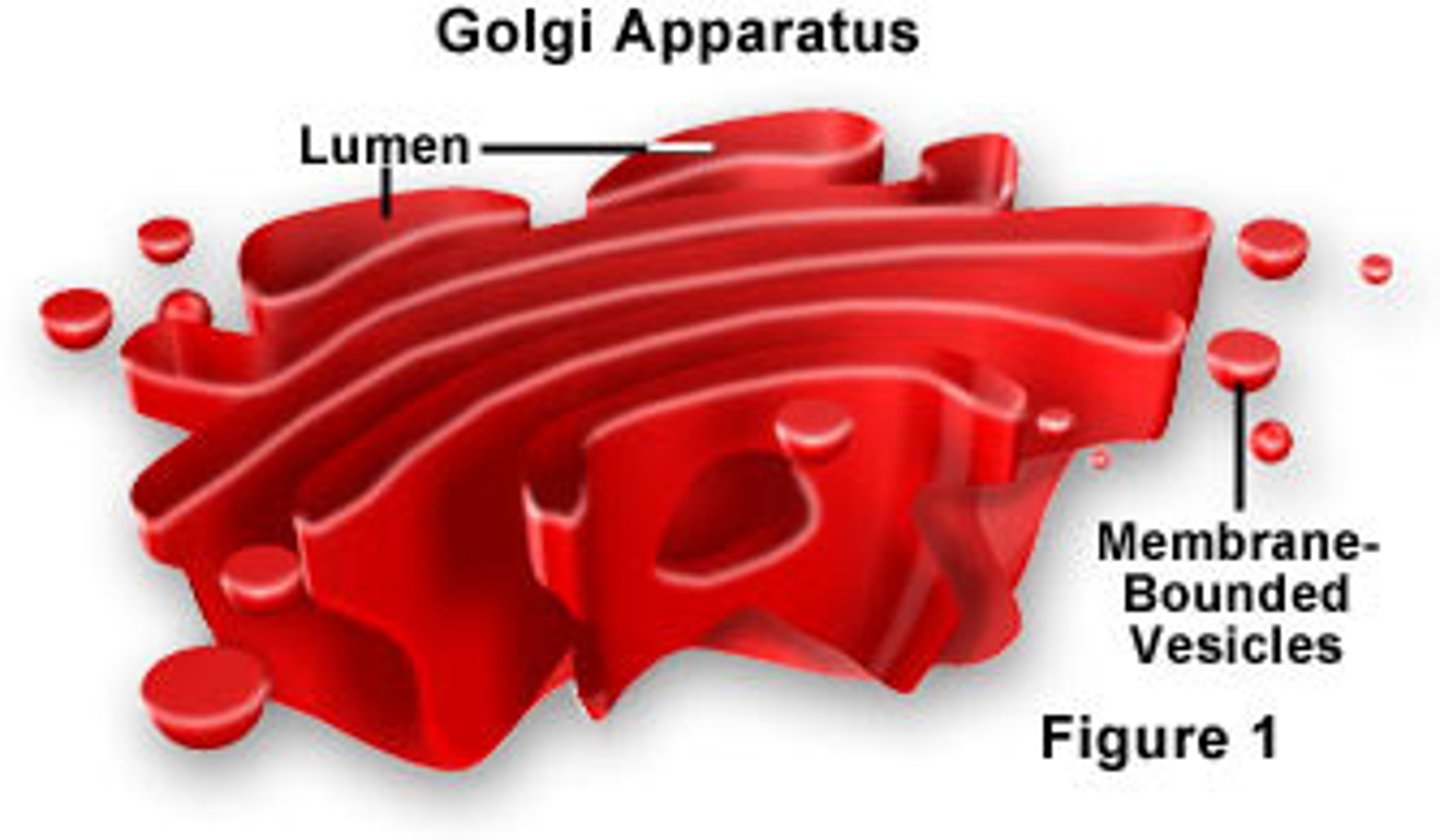
Golgi apparatus
Processes, sorts, and ships proteins; located near ER and nucleus.
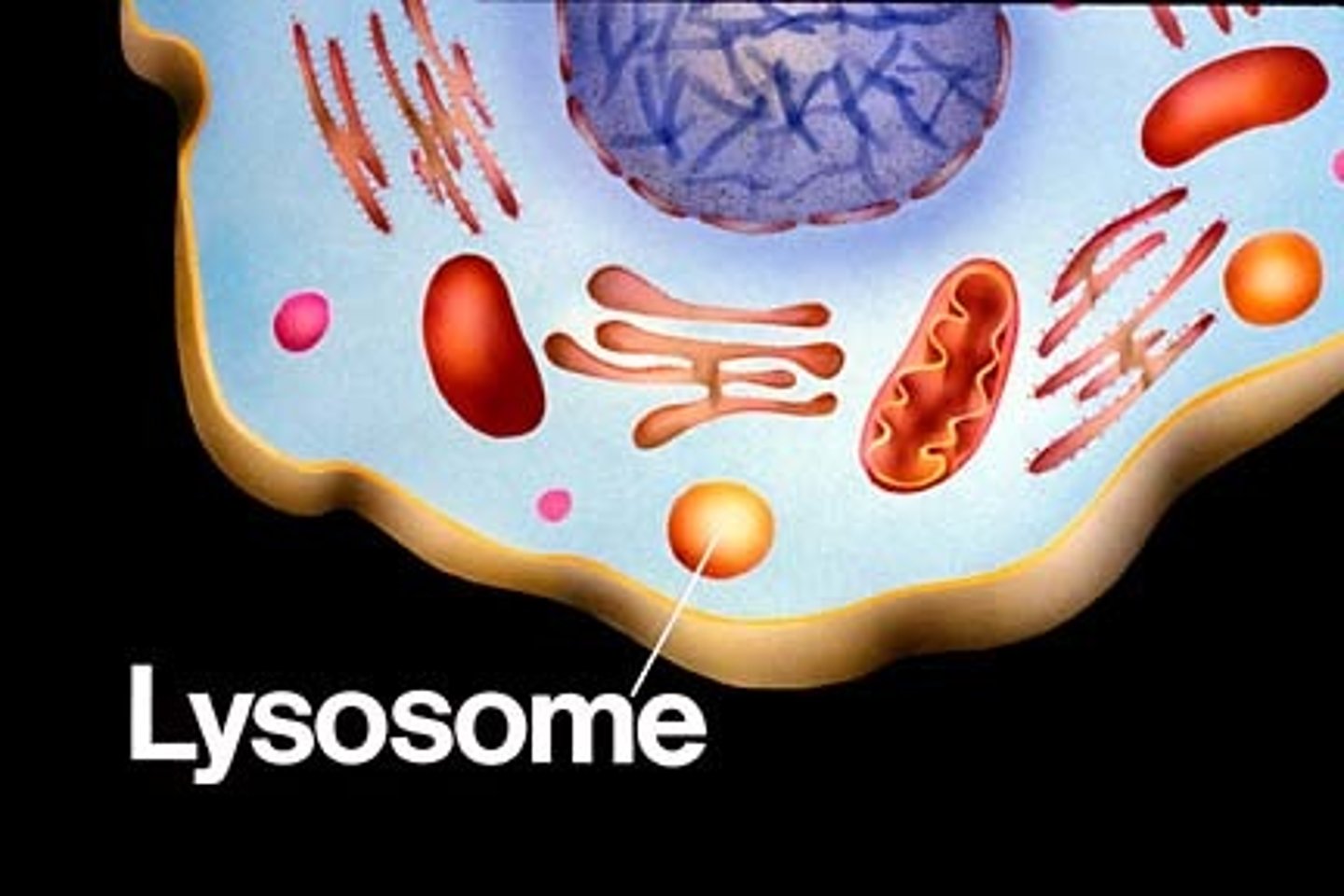
Lysosomes
Contain enzymes for breakdown and recycling of waste and old organelles.
Peroxisomes
Especially in liver cells, detoxify harmful substances and break down fatty acids and toxins.
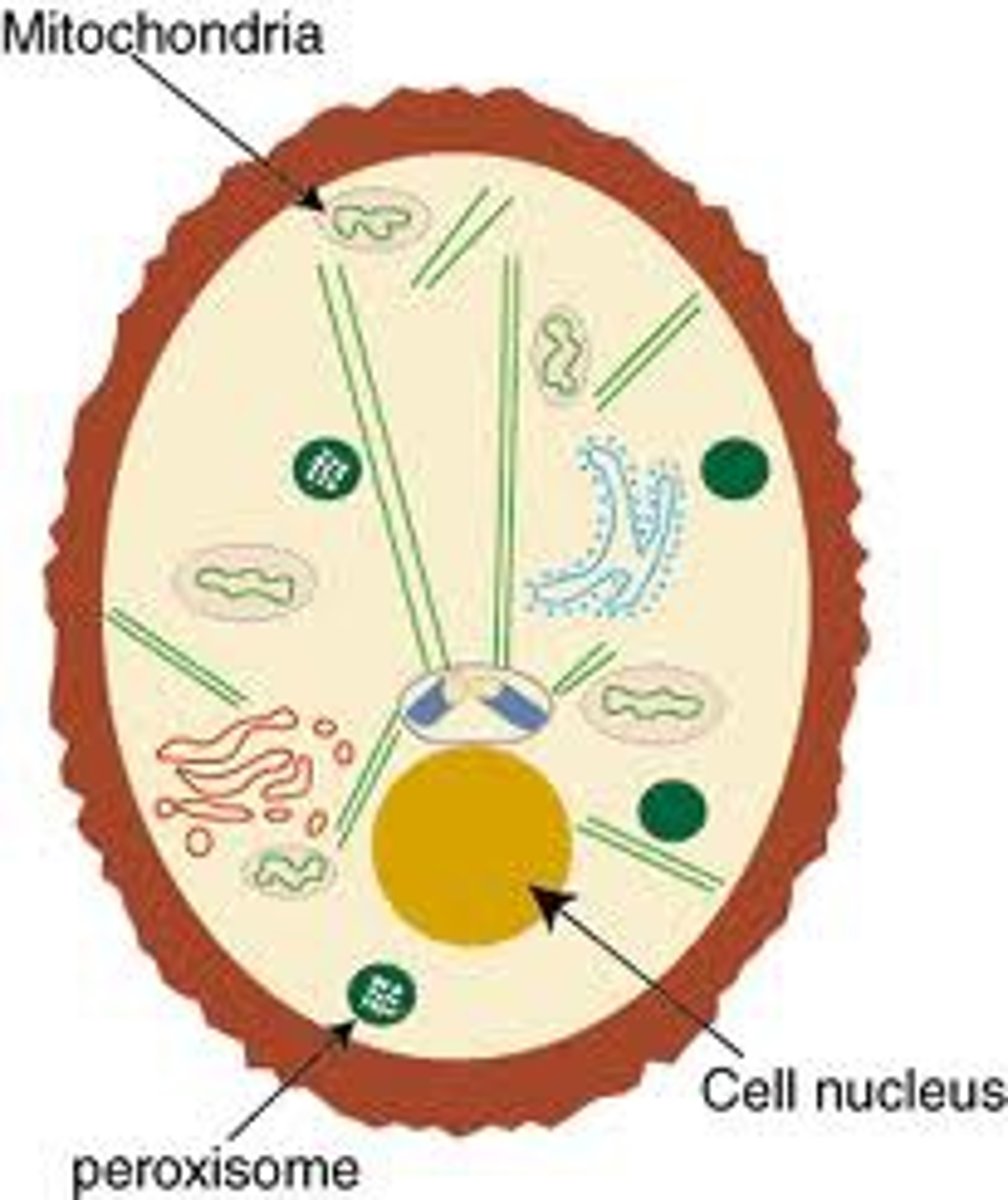
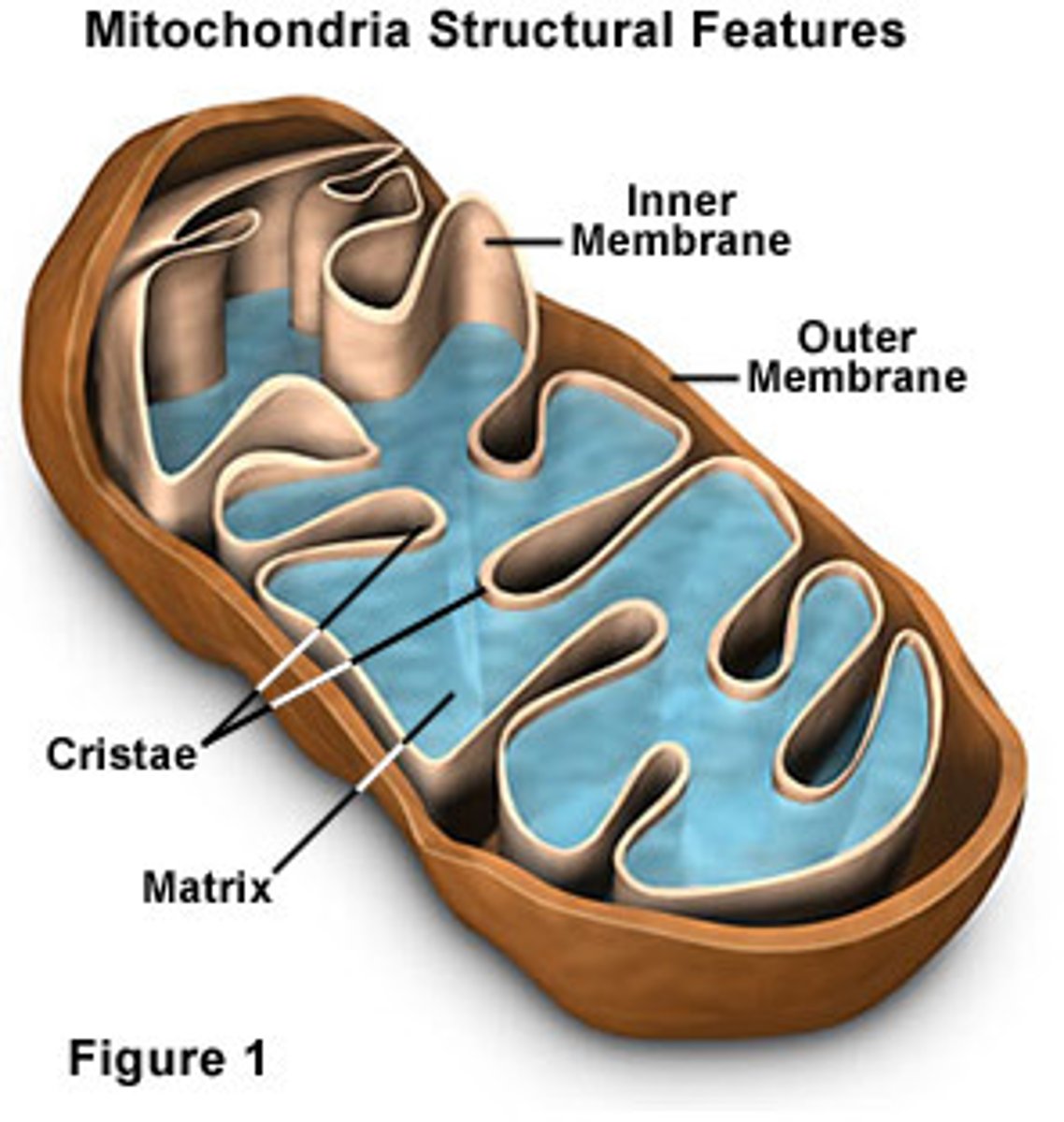
Mitochondria
Power plant of the cell that makes ATP and can replicate itself.
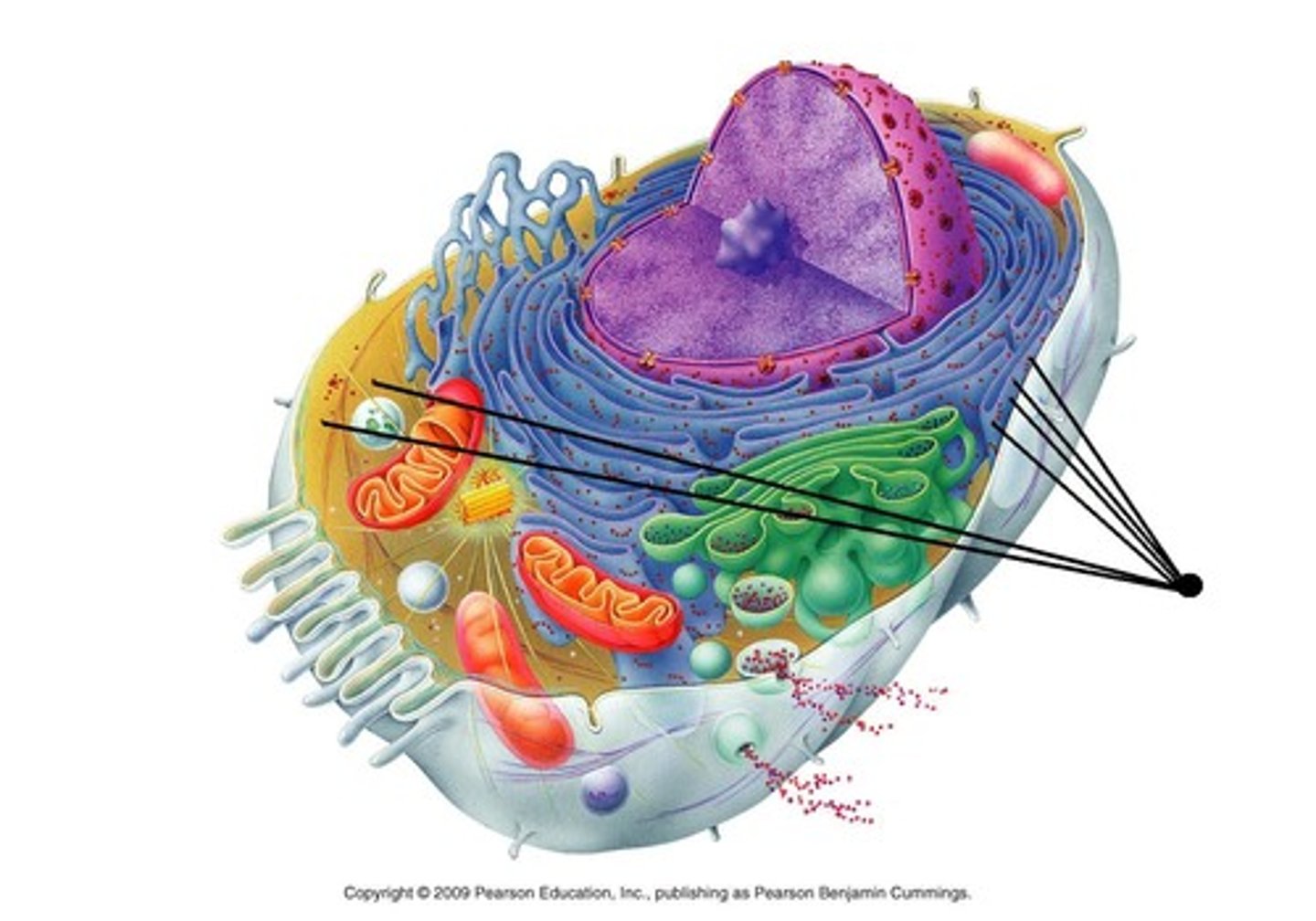
Ribosomes
Free in cytosol for internal proteins or bound to ER for export/membrane proteins.
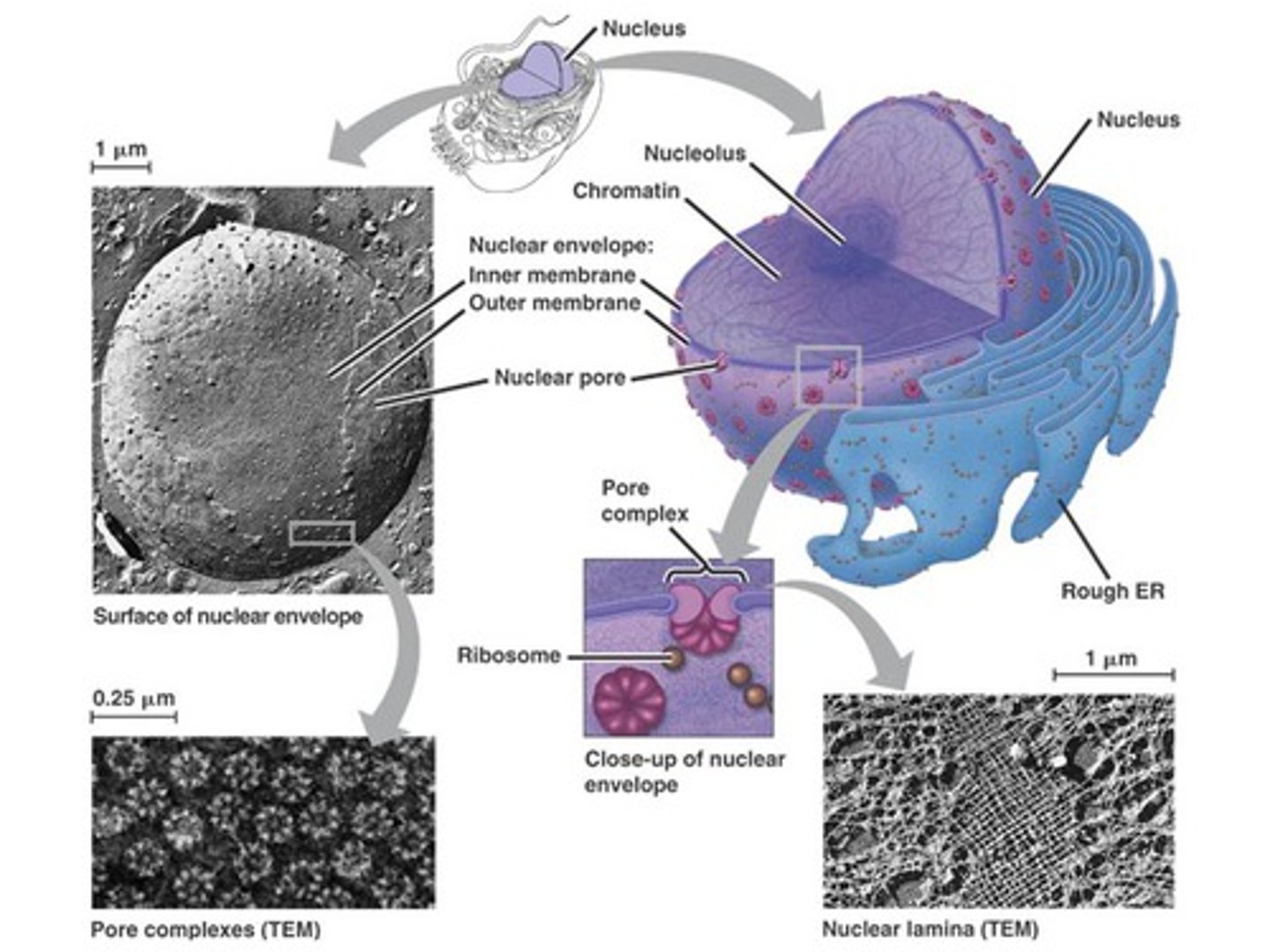
Nuclear envelope
Surrounds the nucleus with pores, protecting DNA and controlling access to it.
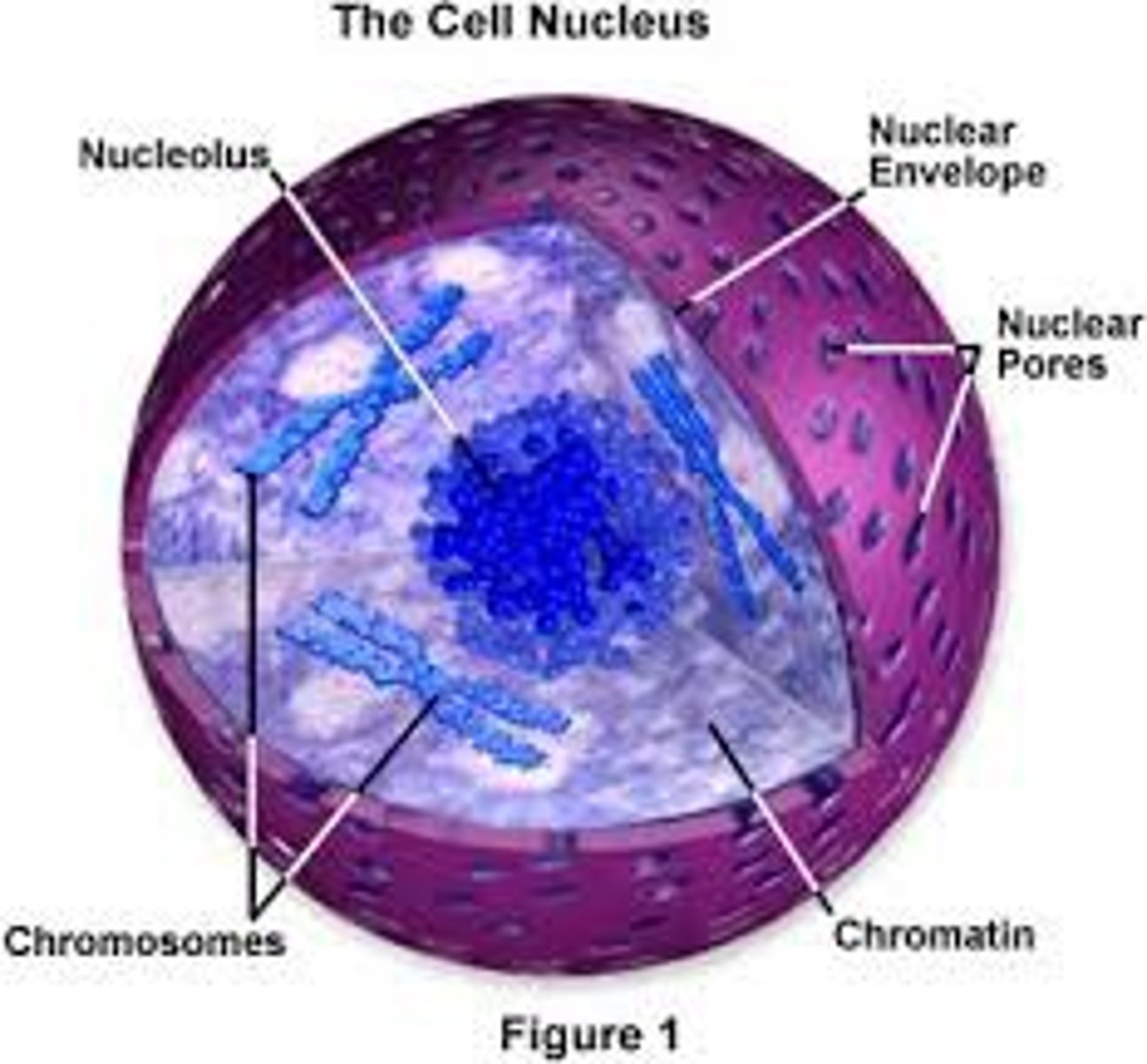
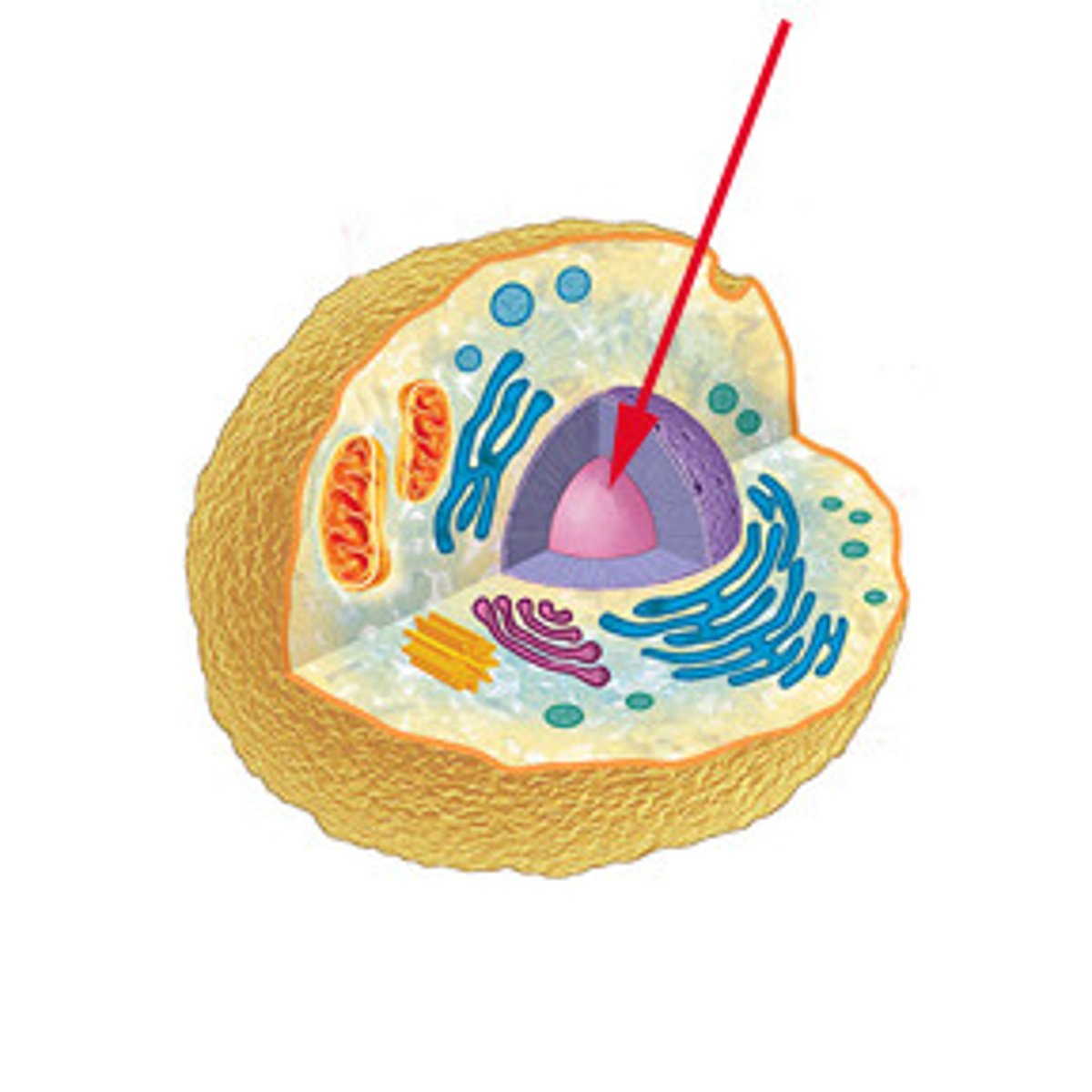
Nucleolus
Located inside the nucleus, produces ribosomal parts.
Chromatin/DNA
Stored inside the nucleus; contains instructions for proteins.
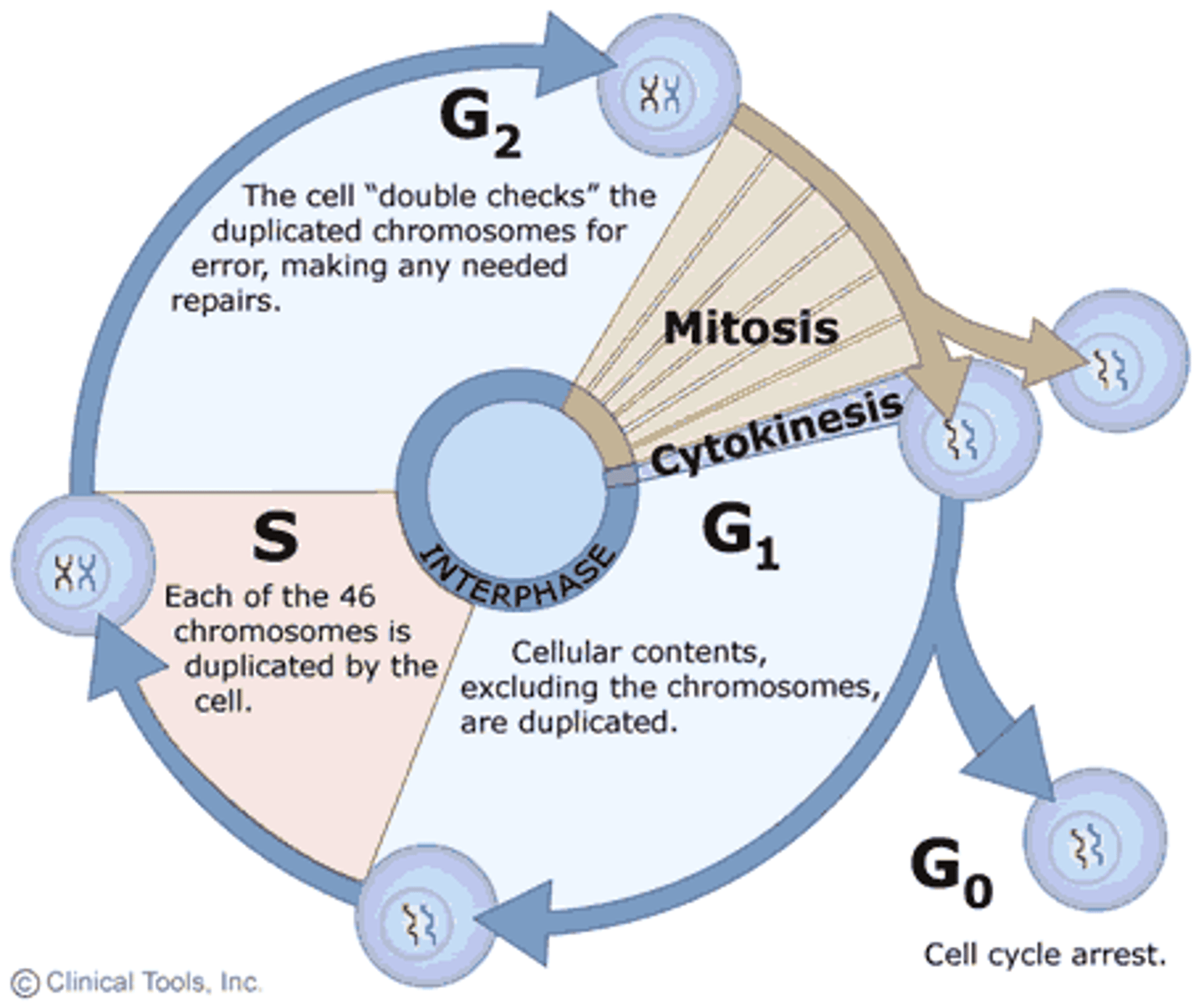
Interphase
Main steps include G1 (growth), S (DNA replication), G2 (prepare for division).
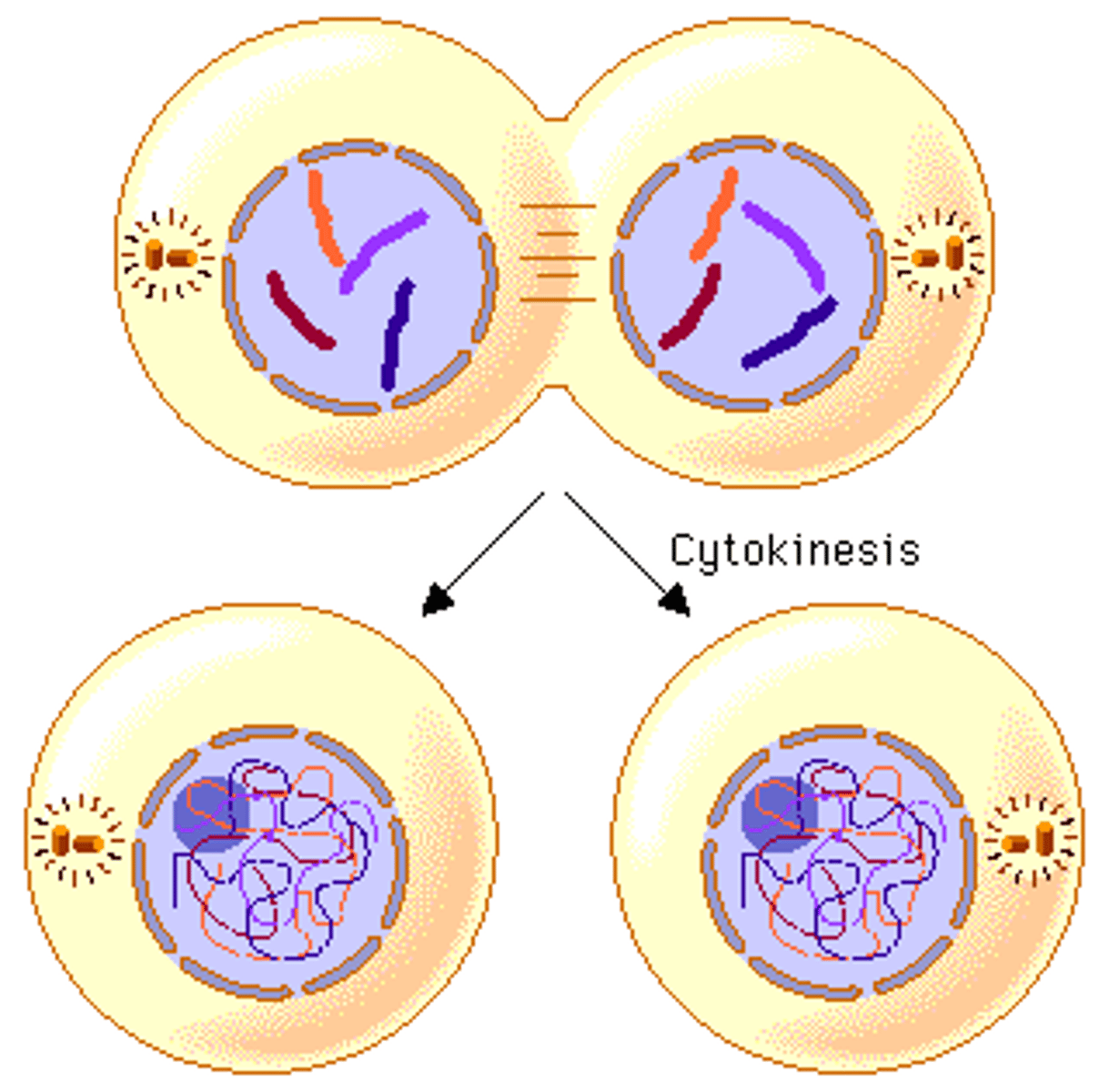
Mitosis
Includes Prophase (chromosomes condense), Metaphase (align), Anaphase (separate), Telophase (nuclear envelope reforms).
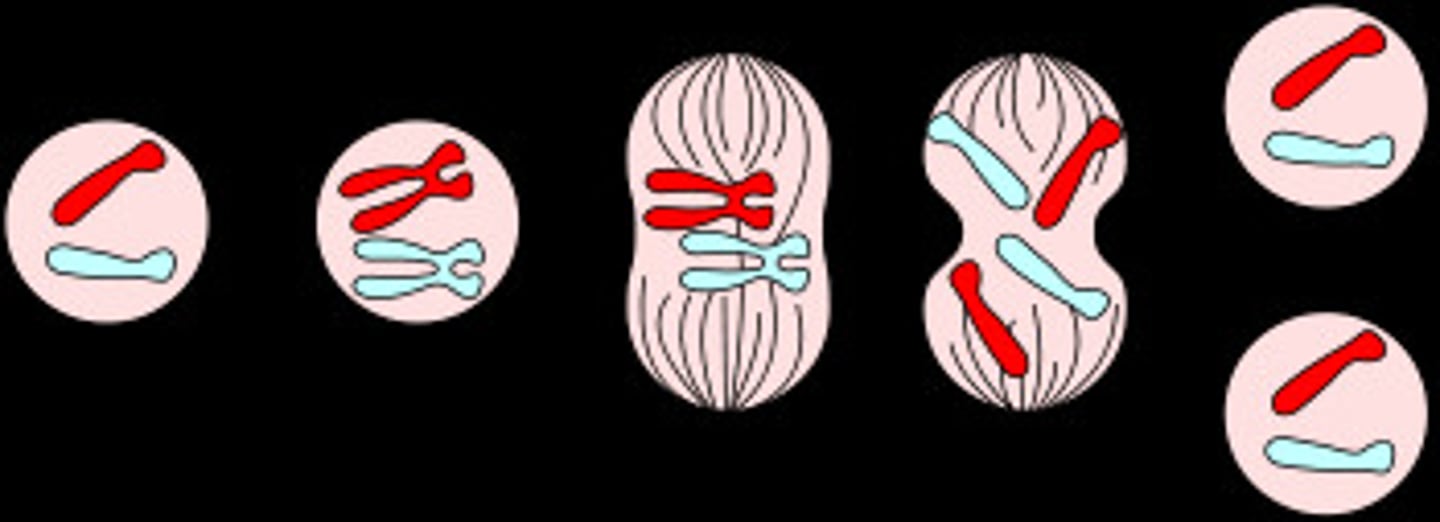
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm, forming two daughter cells.