Ch. 9 - Embalming vessel sites and selections
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
One Point Injection
an artery and a vein at one location are used for injection and drainage.
Split injection
The injection is made in an artery at one location and the drainage occurs from a vein at another location.
Restricted cervical injection
Both right and left common carotid arteries are raised; tubes are placed into each of the arteries and directed toward the head. A tub ein inserted toward the trunk of the body, either in the right or left arter. The inferior portion of the other artery is tied off. Drainage is generally taken from the right internal jugular vein.
Multipoint injection
is vascular injection from two or more arteries.
Six point injection (Sectional embalming)
In the unatopsied body, six arteries are raised that will separately inject the head and the limbs.
Most commonly used arteries in unautopsied body is;
The common carotid, femoral and axillary arteries. Because of the value of using an accompanying vein for drainage, the femoral and common carotid vessels are preferred to the axillary artery.
4 step method of embalming analysis
observation
evaluation
implementation
results
selection of injection site and vascular injectio procedure involve two criteria:
1. factors concerning the vessels and
2. general body conditions.
Situations in which it may be necessary to locate severed or cut portions of arteries to inject arterial solution include:
1. bodies where extensive autopsies have been performed.
2. bodies where partial autopsies have been performed,
3. bodies from which one or more organs and or tissues for transplantation have been removed, and
4. bodies with traumatic injuries.
Nerves
have silvery appearance ,show striations along their surface. When cut, they have no lumen their cut edges take on a frayed appearance to that of a frayed rope.
Veins
Thinner than arteries, contain valves, which arteries do not, bluish in color when cut they have alumen. when their sides are cut, ceins collapse creating a funnel effect.
Arteries
have very thick walls compared to veins. Creamy white in appearance have vasa vasorum (small vessels) over artery surface. when cut the lumen remains open and very pronounced.
Sizes of arteries
common carotid aretery is the largest, because it is nearest to the heart.. The femoral (external iliac) is second in size and axillary artery is the smallest in diametery.
factors used in selection of an artery
age of body, weight of body, drainage, disease conditions, clotting, facial tissue distention, facial discolorations, volume and strenth of arterial soltions and medicolegal requirements.
transverse incisions
from the edge of vessel to the center or just beyond the center.
Common Carotid Artery
largest vesselt he embalmer can raise. Incision in inferior portion of neck. Closely situated near arch of aorta.
Common Carotid Artery regions supplied
If injected superiorly, the head and face are embalmed. If injected inferiorly, the opposite side of face, and head are embalmed in addition to the trunk and appendages.
Common Carotid Artery Considerations
large in diameter, no branced except terminal brances, very elastic, rarely found to be sclerotic, supplies fluid directly to the head, situated close to the arch of aorta, is accompanied by a very large vein for drainage, arterial coagula are pushed away from the head.
Precautions for using the common carotid arteries
head may be over injected, leakage may be seen, some types of instruments may mark the face or jaw line, incisions may be visible with some types of clothing,
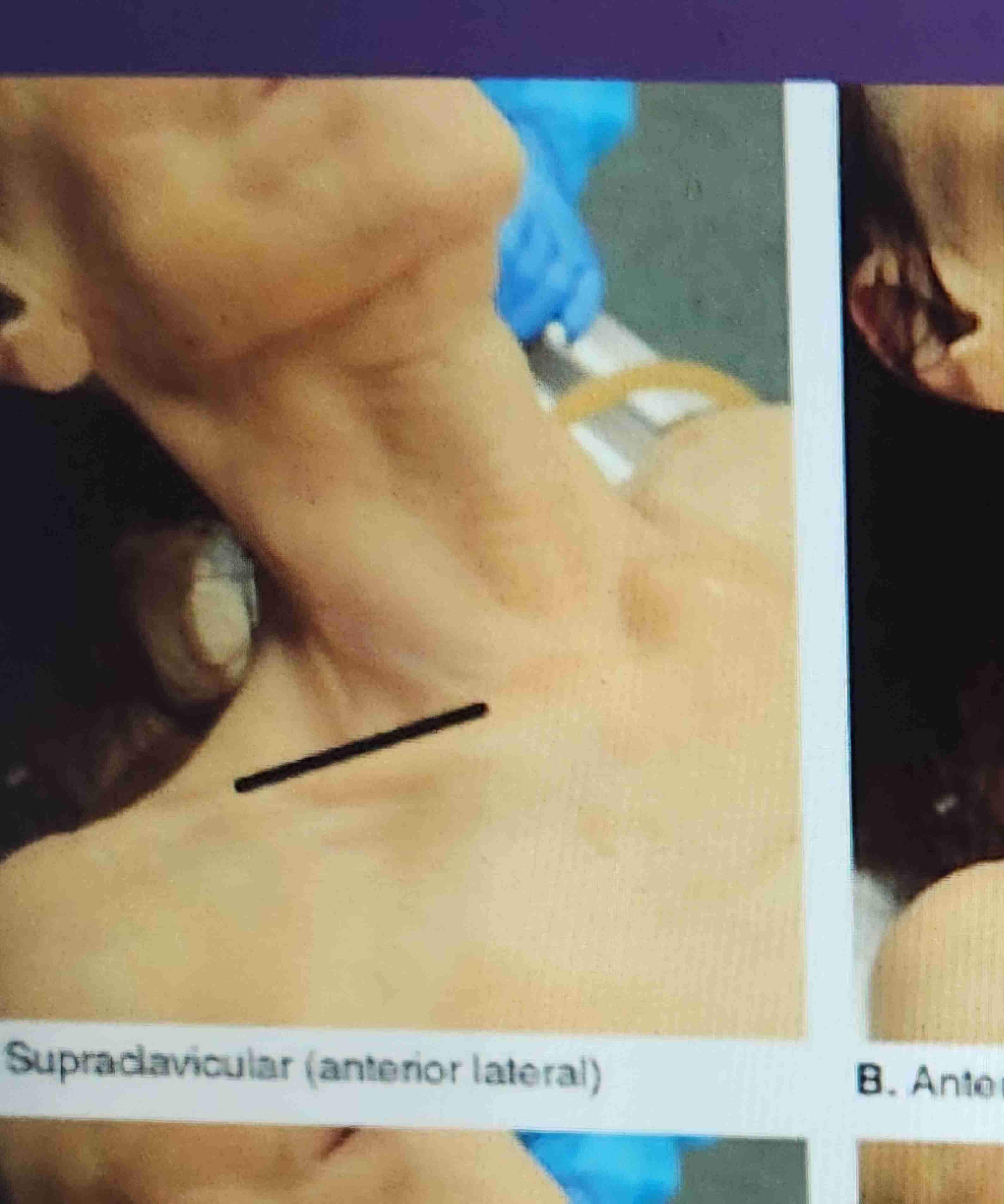
supraclavicular incisions
The incision is made on the clavicle from a point near the sternoclavicular articulation and is directed laterally
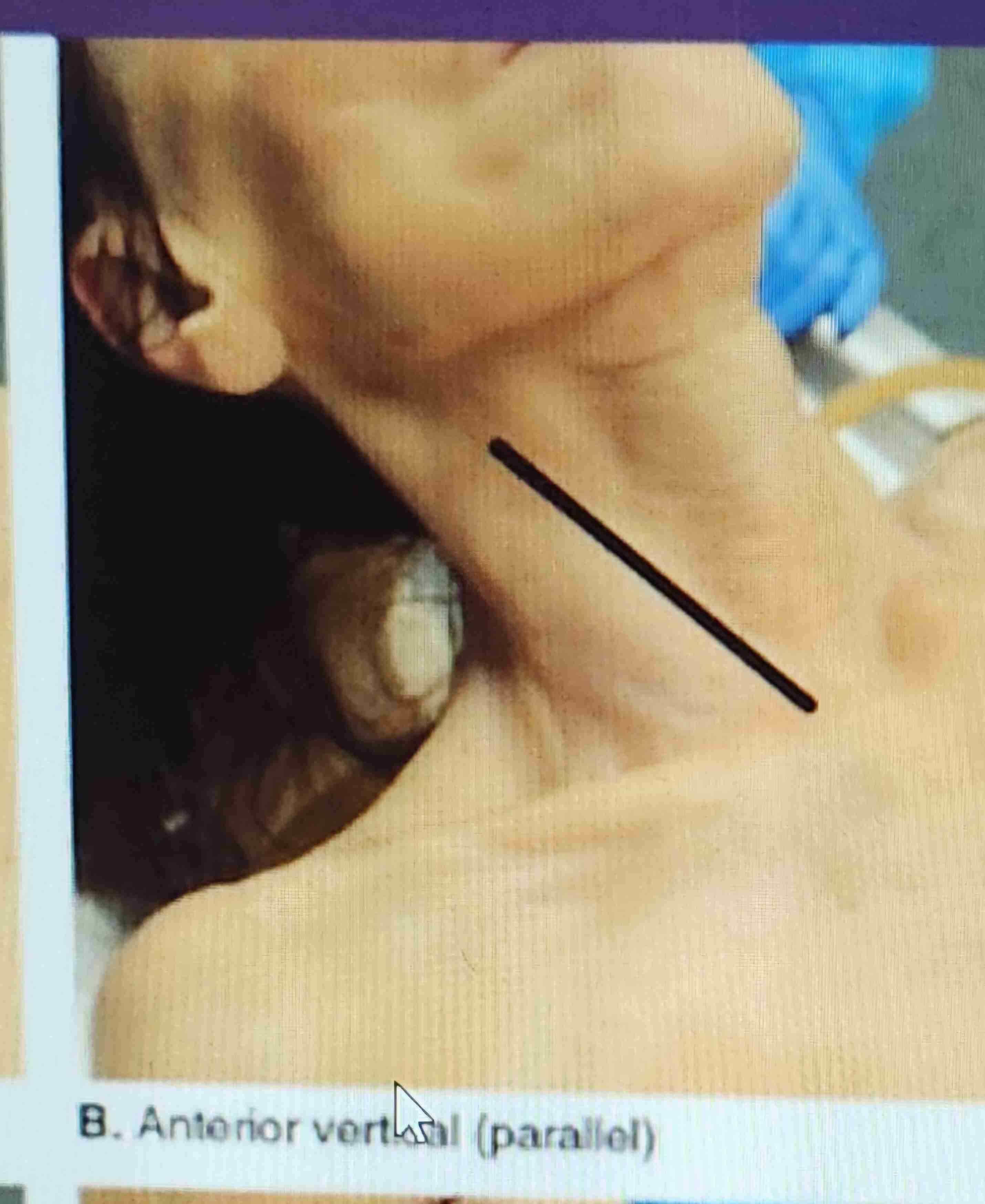
Anterior verticle (parallel)
The incision is made from a point near the sternoclavicular articulation and is directed upward on the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
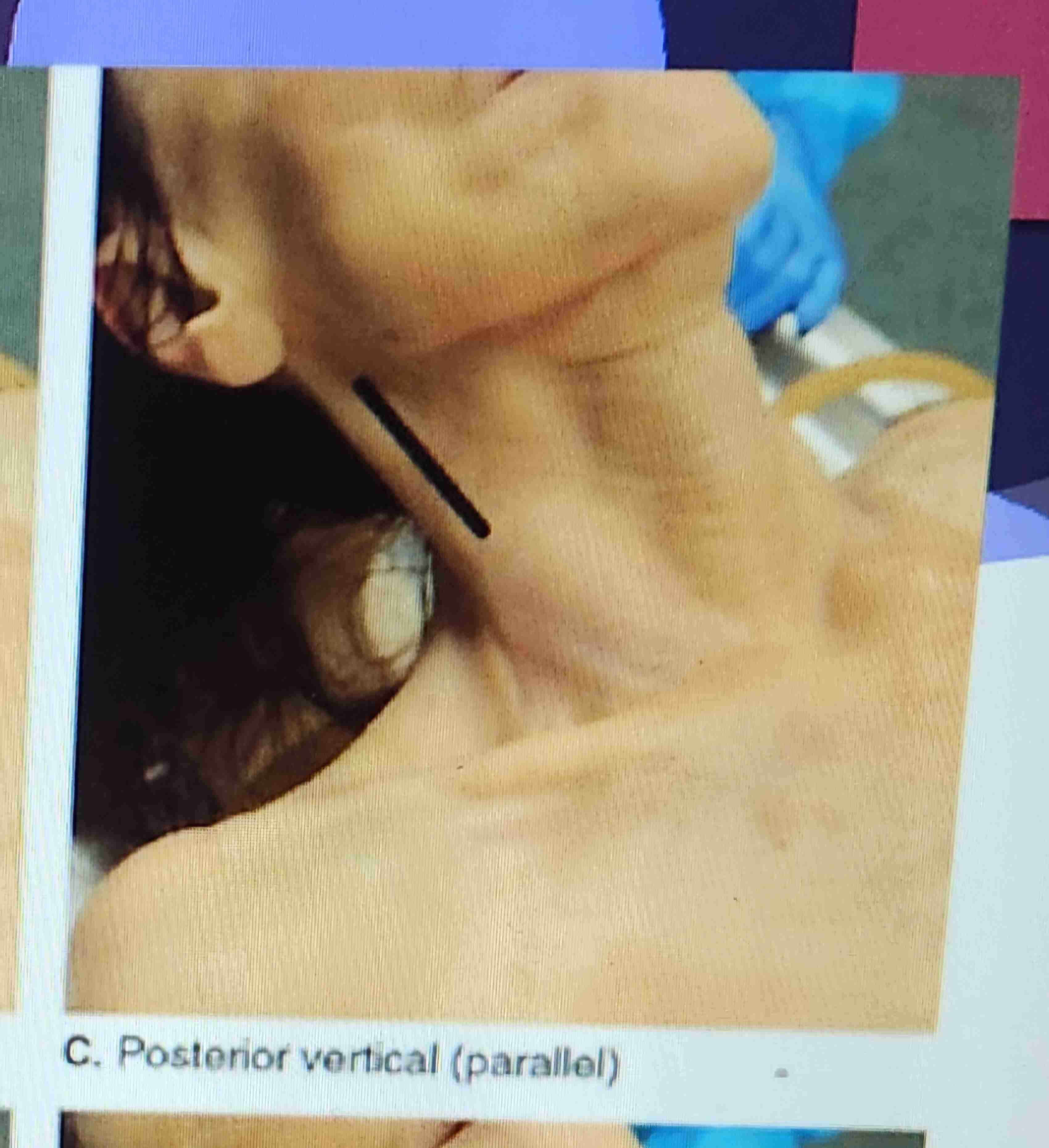
Posterior Verticle (Parallel)
The incision is made posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle 2 inches below the lobe of the ear and is directed downward toward the base of the neck
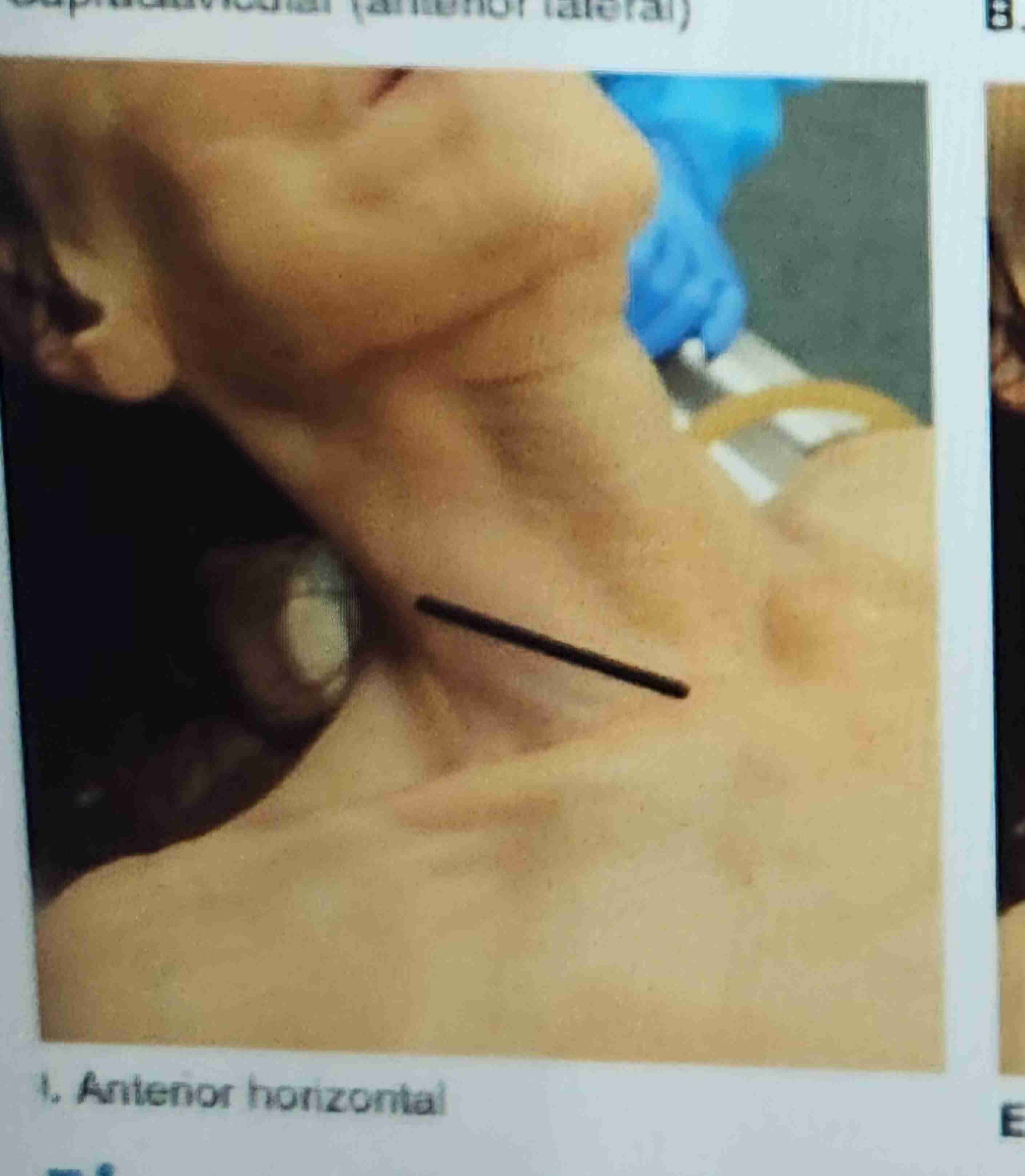
Anterior Horizontal
The incision is made at the base of the neck from a point on the sternocleidomastoid muscle and is directed posteriorly.
Flap incision (semilunar)
This incision is used by the operator when it is necessary to raise the vessels on both the right and left sides for infection or drainage. The incision extends from a point lateral and slightly superor to the seternoclavicular articulation and is directed downwarrd on the upper checst wall, across and upward to a simple location on the opposit side, the pattern may be either a U or an inverted C in shape.
Strap line
The incision is adaptable to the embalming of females, the incision is made approximately 2 inches lateral to the base of the neck on the line where the strap of undergarments crosses.
Sectional vascular embalming
Can be used for an autopsied and unautopsied body. It is used to separately inject a particular body region
Internal jugular vein considerations
IJV
Large in diameter, vessel provides direct drainage from the face and head
Accompanied by the common carotid artery
Close to atrium allowing easy removal of blood clots
Facial artery
One of the eight branches of the external carotid artery
When is the facial artery used
Autopsies.
Carotid arteries or portion of them are removed
Severe clotting of sclerosis or Carotid
Closing facial artery
Aaron alpha (super glue) interdermal suture
Axillary considerations
Arterial solution flows directly into arm and hand
Close to the face, superficial vessel, artery is close to the center of arterial solution distribution (arch of aorta)
Precautions of axillary
Arm must be extended (abducted)
Artery is small to use for injection of body
Accompanying vein is small
Facial tissue could be over injected if injection is directed to head
Brachial supplies
Arm and hand
Radial artery
Supplies thumb side of hand
Ulnar artery supplies
Medial side of hand
Femoral artery supplies
Leg and foot
Or when directed to head, supplies the body