Exam 3 - Animals
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/54
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
1
New cards
What is the significance of the Cambrian explosions?
There was an “explosion” of genetic diversity due to the increased O2 in the atmosphere.
2
New cards
When was the Cambrian explosion?
Approximately 538.8 million years ago
3
New cards
What is common in most animals?
Multicellularity, complex tissue, heterotrophy, active movement, and diversity in size.
4
New cards
How many extinctions have happened on our planet?
At least five
5
New cards
What develops first in protostomes?
Mouth
6
New cards
What is an example of a protostome?
Arthropods, octopus, and flatworms
7
New cards
What develops first in deuterostomes?
Anus
8
New cards
What is an example of a deuterostome?
Humans
9
New cards
What is cleavage?
series of mitotic cell divisions
10
New cards
What is blastula stage?
In between 6-32 cells and is hollow.
11
New cards
Gastrulation is the stage between…
blastula and gastrula
12
New cards
What is the main difference between the blastula and gastrula?
The gastrula has developed a blastopore.
13
New cards
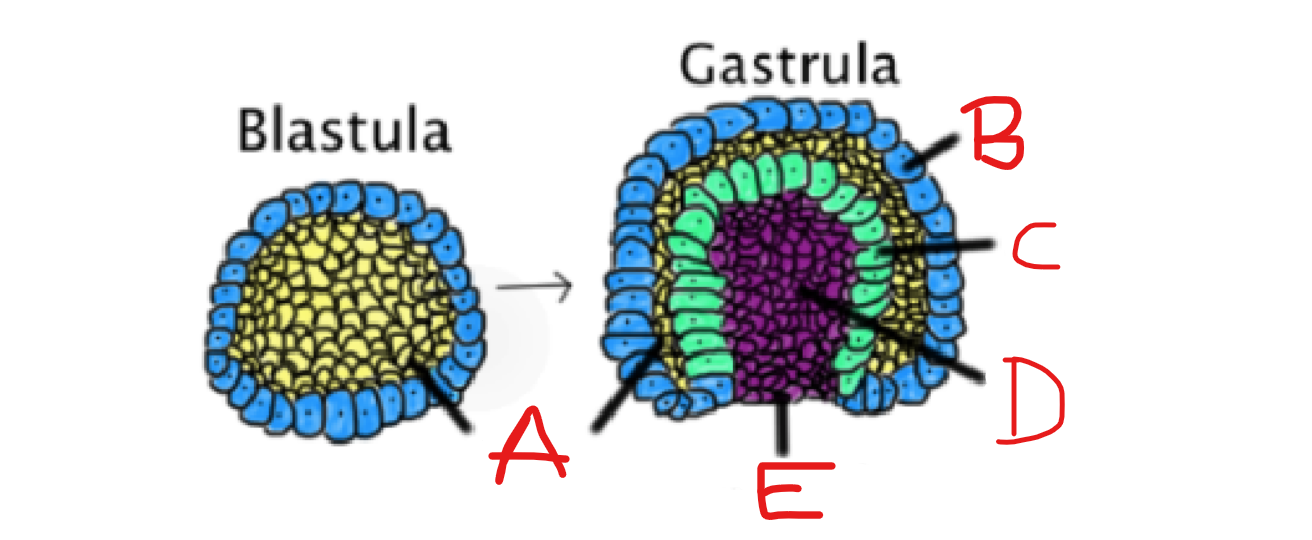
What is A?
Blastocoel
14
New cards
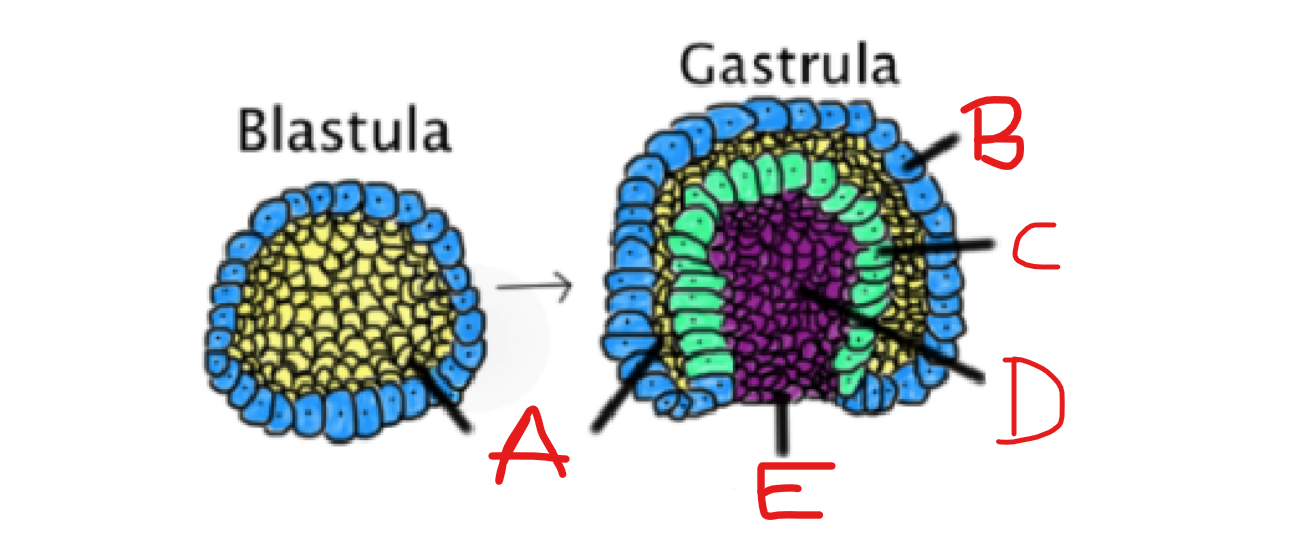
What is B?
Ectoderm
15
New cards
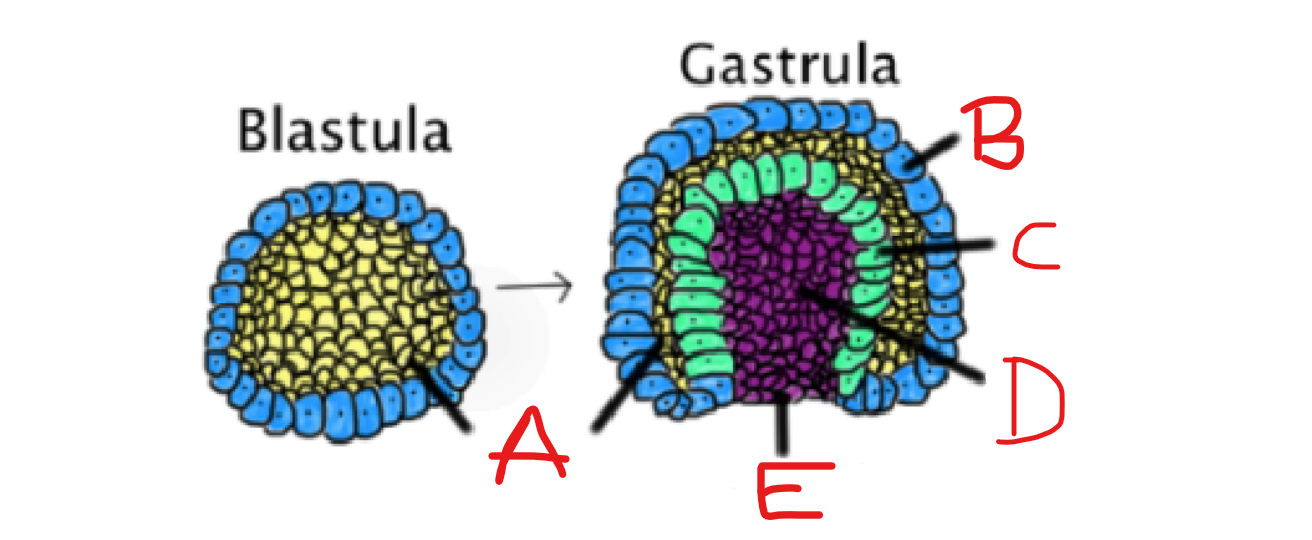
What is C?
Endoderm
16
New cards
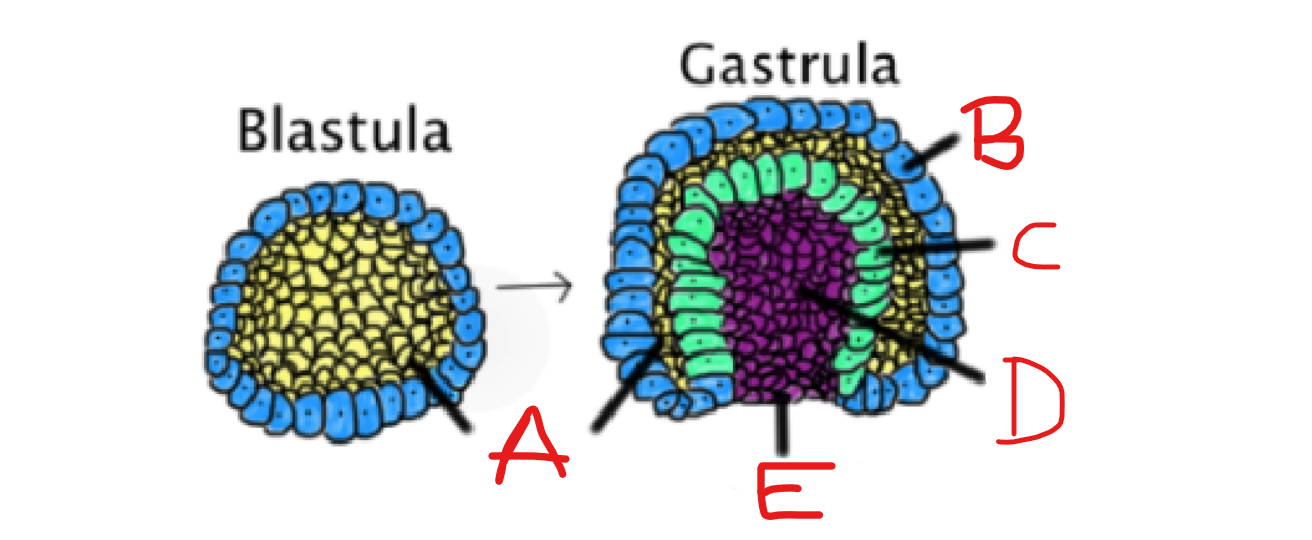
What is D?
Archenteron
17
New cards
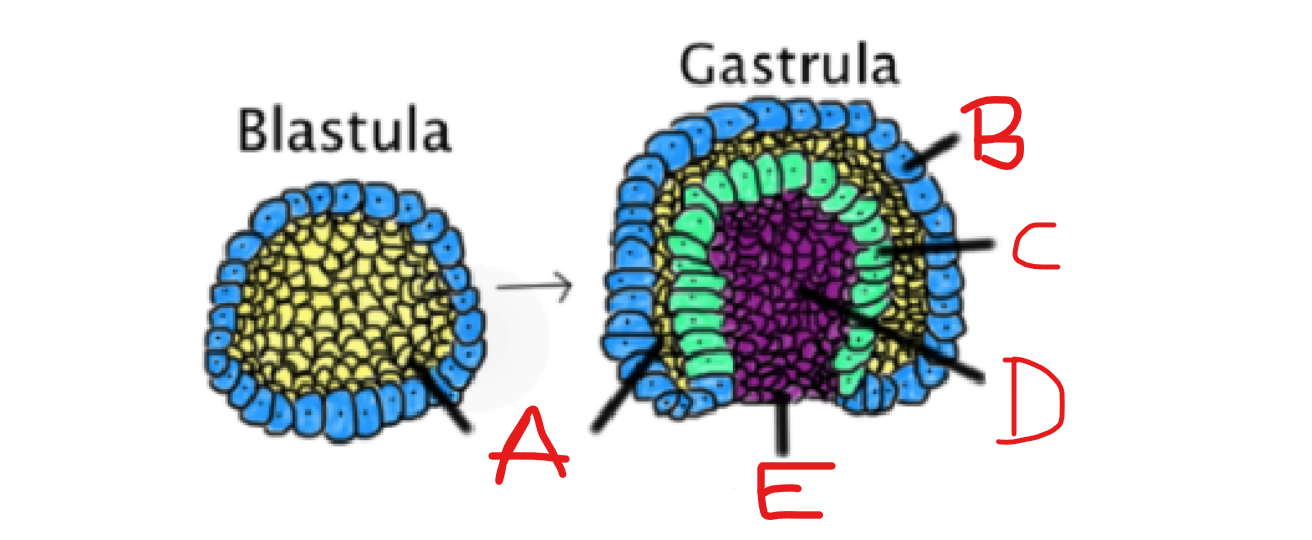
What is E?
Blastopore
18
New cards
How many germ layers do diploblastic organisms have?
Two
19
New cards
What is an example of a diploblast?
Jelly fish
20
New cards
How many germ layers do triploblastic organisms have?
Three
21
New cards
What is an example of a triploblast?
A human
22
New cards
What are Hox genes responsible?
They are responsible for putting the right number of appendages in the right place.
23
New cards
If the Hox genes fail what is likely to happen?
Too few/many appendages
24
New cards
What are the four traits used to differentiate animals?
1. Symmetry
2. Number of germ layers
3. Origin of the mouth and anus
4. Body plan and cavities
25
New cards
A sponge is ----, because ----.
Asymmetrical / they lack symmetry
26
New cards
An anemone has ---, because ----.
Radial symmetry / they have symmetry around a central axis
27
New cards
A goat has ---, because ----.
Bilateral symmetry / because there right and left sides.
28
New cards
Endoderm
Inner lining of most digestive tract organs
29
New cards
Mesoderm
all muscle, bone, cartilage, blood, most other visceral organs
30
New cards
Ectoderm
outer epithelium of body surface, central nervous system
31
New cards
Coelom
Body cavity
32
New cards
Acoelomates
Lack of a coelom
33
New cards
Pseudocoelomates
False coelom
34
New cards
coelomates (eucoelomates)
Has a coelom
35
New cards
What is the cleavage pattern of a protostomes?
determinate spiral cleavage
36
New cards
What is the cleavage pattern of a deuterostomes?
indeterminate radial cleavage
37
New cards
sagittal plane
divides the body into right and left portions
38
New cards
midsagittal plane
Divides the body exactly in the middle, making two equal right and left halves
39
New cards
frontal plane
separates the front from the back
40
New cards
transverse plane
divides the animal into upper and lower portions.
41
New cards
What two cavities make up the dorsal cavity?
cranial and vertebral (or spinal)
42
New cards
What two cavities make up the ventral cavity?
thoracic or abdominopelvic cavity
43
New cards
what are the two limitations on size and shape?
Gravity and drag
44
New cards
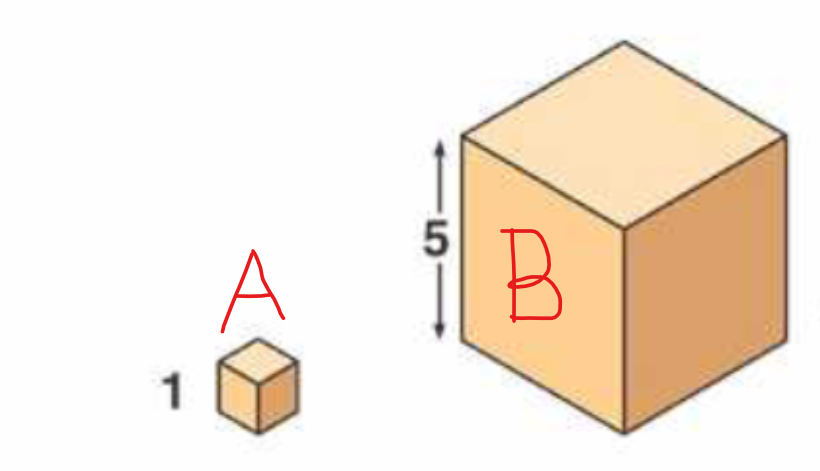
What has the largest surface area to Volume ratio?
A
45
New cards
Endotherms
Warm blooded animals
46
New cards
Ectotherms
cold blooded animals
47
New cards
Which animals spend more energy on heating themselves?
Endotherms
48
New cards
What are the two different types of epithilial tissue?
Stratified and simple
49
New cards
Were can you find epithelial tissue?
Line cavities, open spaces, and surfaces
50
New cards
Where can you find connective tissue
Connect tissues together, provide support
51
New cards
What is the purpose of muscular tissue?
Movement
52
New cards
What are the three types of muscular tissue?
Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth
53
New cards
What is the purpose of neurons?
Generate and send electrical signals
54
New cards
Negative Feedback Loop --- the direction of change.
reverses
55
New cards
Positive Feedback Loop --- the direction of change.
strengthens