Intro to IT Section 4: Computer Networks Starter Set
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
What is a network?
A collection of two or more connected devices that can communicate with one another
What is networking?
Sharing information and resources through linked computer systems. Networking enables users to exchange messages and share resources
What are the 3 network types in the geographic sense?
PAN, LAN, WAN
PAN
Personal area network; used for short-range communications. Ranges a couple of feet (like mouse to a PC or headphones to smartphone)
LAN
Local area network; consists of a collection of computers in a single building
WAN
Links systems over a greater distance, even on opposite sides of the world. The Internet is the greatest example of a WAN
What are the 2 network types in the internal workings sense?
Open network and closed network
Open Network
Designs that are in the public domain
Freely circulated and are more popular than closed network
EX) the internet
Closed Network
Designs owned or controlled by third parties
Designs are restricted by license fees and contracts
TCP/IP protocol
An open collection of standards that governs communication over the internet
What are the 4 common network types based on topology?
Bus, star, ring, and mesh
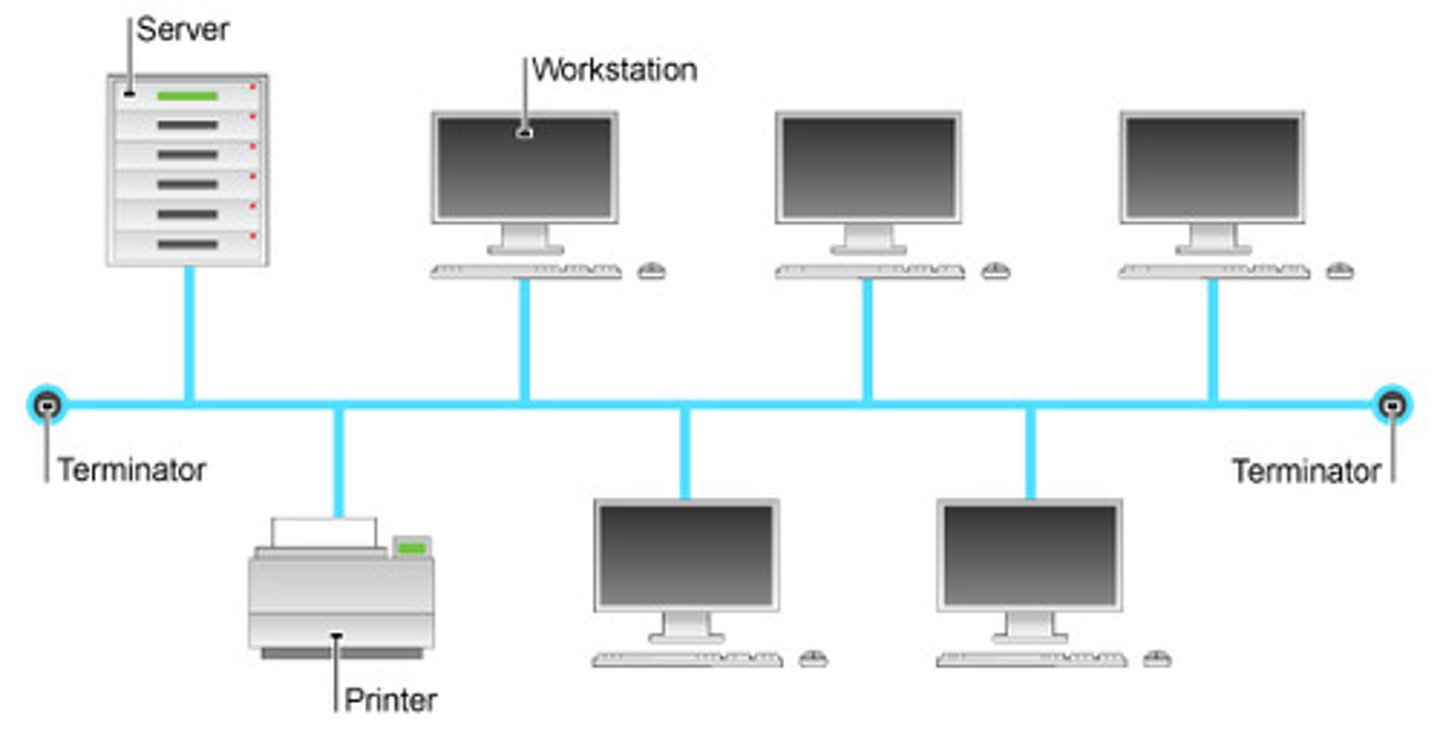
Bus network
the machines are connected to a common communication line called a bus
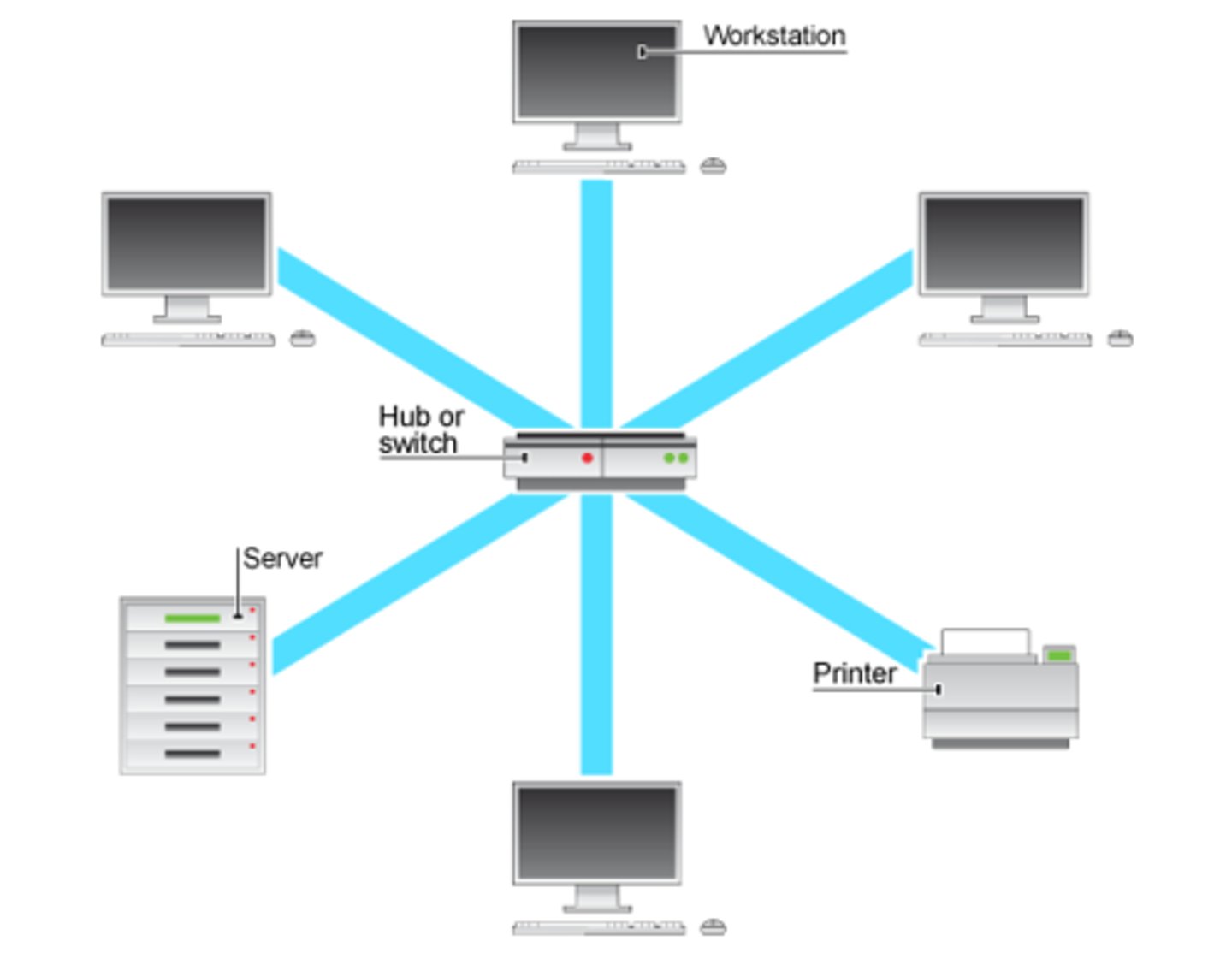
Star network
A singular machine serves as a central point to which all others are connected.
used today in wireless networks where communication is carried out via radio broadcast to a central machine called the access point (AP)
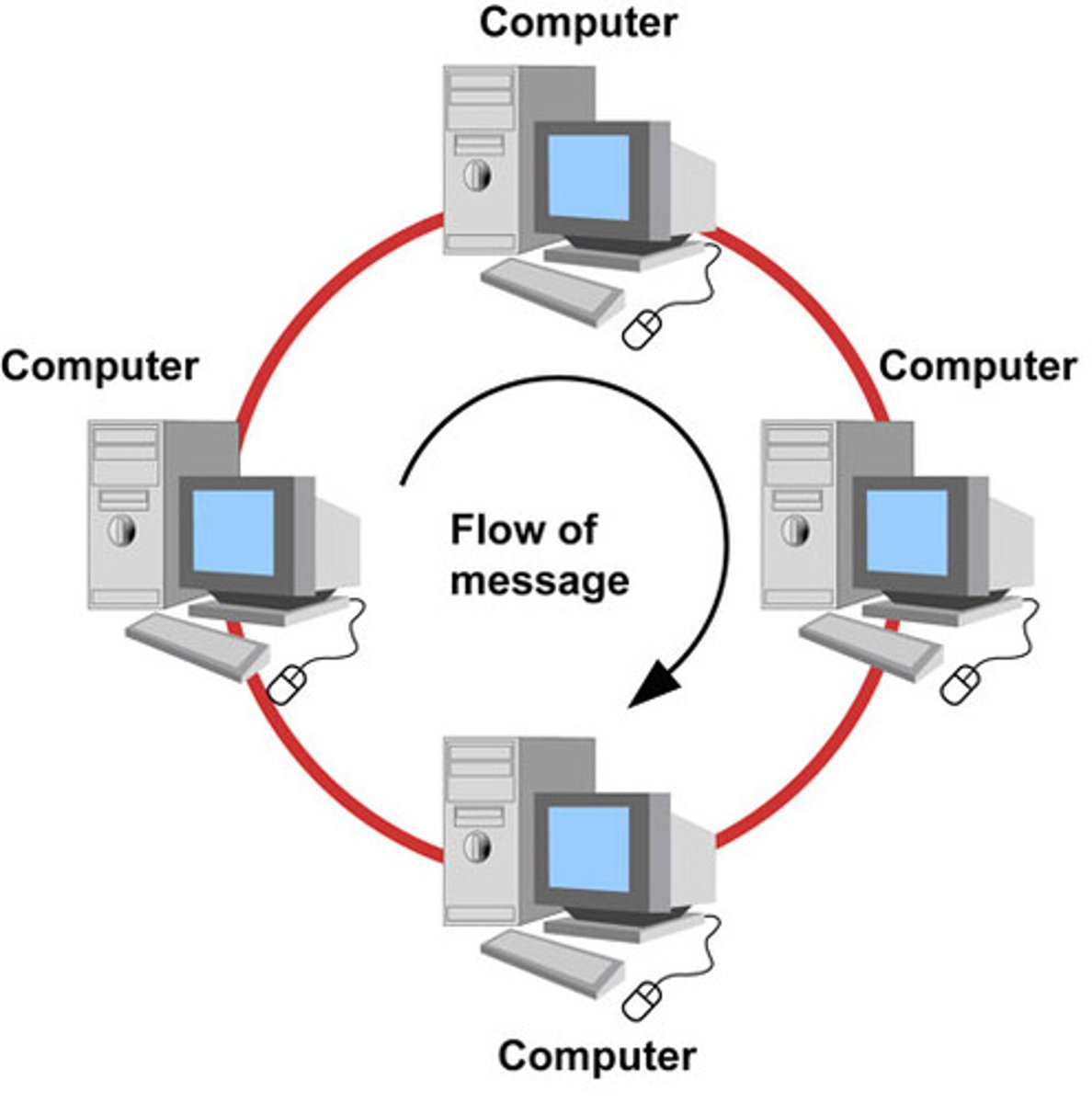
Ring network
All devices are directly connected to each other as a peer
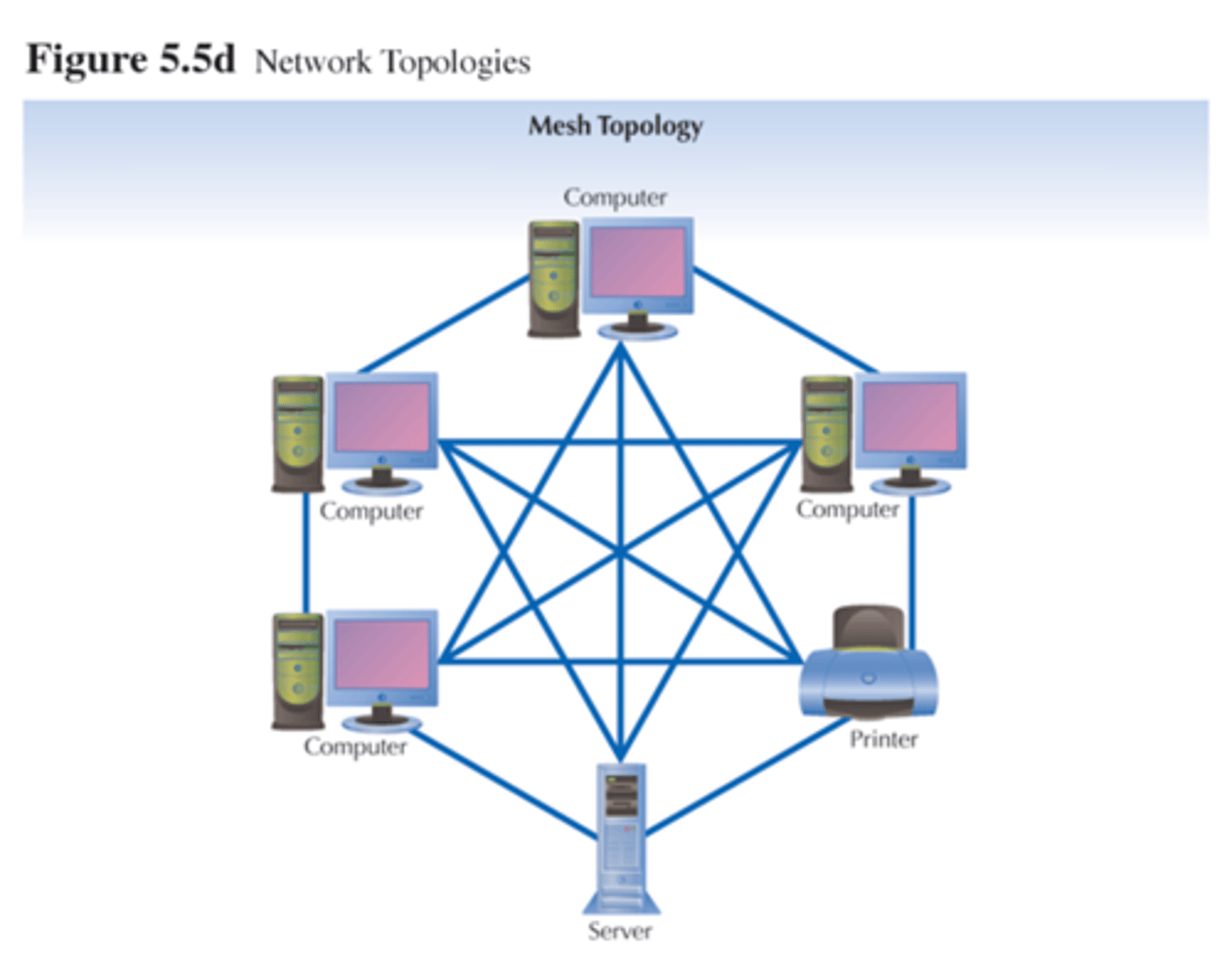
Mesh network
Every device is connected to every other device. This type enables redundancy while also introducing more network traffic
What is interprocess communication?
It allows the activities or processes on different computers within a network to coordinate actions and complete tasks.
Client/Server Model
The basic roles are either a client making requests or a server satisfying client request
EX) Computers requesting a printer to print
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Model
Processers both request and provide service to each other.
EX) Instant messaging and interactive games played by users on multiple machines
What do distributed systems do?
They execute software as processes on more than one computer. It includes cluster computer, grid computing, and cloud computing
Cluster computing
Uses many independent computers to provide computation or services comparable to those of a larger machine.
High availability in case a computer becomes unavailable, can balance loads by shifting requests among cluster members
Grid computing
Typically includes specialized software to make it easier to distribute the workload and data among the machines in the grid.
Cloud computing
Provides large pools of shared computers that can be allocated to clients as needed. It provides reasonable guarantees for reliability and scalability while raising concerns about security and privacy.
What is the transmission medium?
A component that carries data from one network device to another. There are two types of transmission media: wired and wireless.
Wired transmission mediums
Twisted pair cables, coaxial cable, and optical fiber cables are common network media used in wired networks
Wireless transmission mediums
wireless networks use radio waves, microwaves, and infrared waves.
What's the most commonely used type of transmission media?
Twisted pair cables.
What are the 2 common types of twisted pair cables?
Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP)
STP vs UTP
Shielded Twisted-Pair
-Better protection from EMI
-More expensive than UTP
Unshielded Twisted-Pair
-Most common for ethernet cable
*Distance limitation = 100 meters; after 28 ft needs repeater
Coaxial cables (coax)
have an outer plastic that is used in computer networks and to deliver cable TV services. Used for both baseband and broadband data communication services. The bandwidth of coaxial cables is about 80 times the bandwidth of twisted wires.
Cable modems and televisions typically use coaxial cables.
Baseband vs broadband
Baseband is a signal at a very narrow frequency range on which data or information is superimposed and then transmitted. Examples include Ethernet LANs and serial cables.
Broadband is considered high-capacity transmission technologies that are used to transmit data, voice, and video across long distances and at high speeds. Examples include coaxial cable, fiber optic cable, and radio waves.
Fiber optic cable
uses the concept of reflection of light through a core made up of glass or plastic
Their bandwidth can provide up to 26,000 times the bandwidth of the twisted pair wires, at the time of this writing.
Wireless Transmission
Electromagnetic waves of different frequencies can be used to transmit data within a network with the use of Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or even near field communication
SOMETIMES more convenient and practical than installing cables
Wi-Fi Adapters vs Bluetooth
Wi-Fi adapters enable devices to connect to each other or to the internet.
Bluetooth supports distances shorter than 30 feet, while Wi-Fi devices can be accessed up to 300 feet away.
What are the 4 common devices used to connect networks?
Repeaters, Bridges, Switches, and Routers
Repeaters
They extend the range of cabling types so connections can be made by increasing the strength of the network signal.
Bridges
They are used to connect to different types of network and provide management of the message. It analyzes the network message and will only bridge the network if a message is addressed to a device on the other side.
Switches
They are used to reduce network traffic by management of network messages.
Routers
They are the device that make the internet possible. It connects to your LAN and acts as a gateway to the internet.
They manage network traffic by having a routing table of known devices. If a destination address is unknown to the Router, it will forward the message to another router. This analyze and forward process continues until the message reaches the correct address.
What does ISP stand for and what do they do?
Internet Service Provider; these construct and maintain the individual networks comprising the internet
Tier 1 ISP
The least common type of ISP and serves as the backbone of the internet
high speed, high-capacity, international WANs that are usually operated by large communication companies
Tier 2 ISP
More common and regional in scope. Tier 1 and Tier 2 ISPs are essentially networks of routers that collectively provide the internet's communication infrastructure.
Tier 3 ISP (AKA, access ISPs)
typically are independent internets (AKA, intranets) operated by a single organization that supplies internet access to homes and businesses.
What are end systems/ hosts
These are the devices used to connect to the access ISPs
EX) common internet devices like PCs, laptops, and smartphones, but also devices like cameras, automobiles, and home appliances.
What's the point of internet addressing systems?
To assign a unique identifier to each computer in the network.
What kind of bit address do we use now?
128-bit addresses (IPv6) in addition to 32-bit (IPv4)
IPv4 addresses
traditionally written in dotted decimal notation, with the bytes of the address separated by periods
EX) 192.207.177.103
IPv6 addresses:
Written in hexadecimal EX) 2001:DB8:12:34::1111
Computer Domains are:
a section of the internt operated by a single authority, such as a university or business.
EX) the domain name of WGU is "wgu.edu"
What's a TLD and give some examples?
a top-level domain
"edu" denotes an education institution
"com" is for commercial institutions
"gov" is for governmetn agencies
"org" is for nonprofit organizations
"tv" is for television stations
TLD's include two-letter country codes like "au" for Australia and "kr" for Korea
DNS
Domain Name System
a hierarchical and decentralized system that translates human-readable domain names into numerical IP which computers use to identify one another on a network.
Domain Names
the familiar, easy-to-read names that are used to navigate the internet, such as "www.google.com." These names are easier for humans to remember than IP addresses.
Hierachy
The DNS is organized hierarchically with the root DNS servers at the top, which direct requests to the appropriate TLD servers.
DNS resolution
This is the process of translating a domain name into an IP address.
What are network protocols?
Rules, procedures, and formats that govern the communication of multiple devices over a network. This ensures timely, secure, and managed network communication
What is HTTP?
Hypertext transfer protocol; As web servers and browsers became more sophisticated, traditional networks became handled by web pages using this
What is email transmission supported by?
basic network protocols like Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3), or Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
What is VoIP?
Voice over Internet Protocol; used for voice communication over the Internet
It operates by establishing a connection between two devices and then performing real-time, two-way transmission of audio data
What are softphones?
Softphones allow two or more computers to share a call without any additional hardware
What are analog telephone adaptors?
They allow users to connect their physical phones to a port that digitizes and then transmits real-time audio data.
What is streaming?
Transporting audio and video data across the Internet in near real-time
What is on-demand streaming?
Where the end user expects to view or listen to media at an arbitrary time of their choosing
What is broadcasting?
Where a server transmits content to several users simultaneously like traditional radio and TV stations.
What are CDNs?
Content delivery networks; groups of servers distributed strategically over the internet that stream copies of content to nearby end users
What is anycast?
A networking technology that enables an end user to connect to the closest server automatically.
What is the WWW?
World Wide Web It is composed of: (1) a hypertext document format for embedding hyperlinks to other documents (2) a protocol for transferring hypertext over the network (3) a server process that supplies hypertext pages upon request
also supports images, audio, and video.
What are browsers or web servers?
Software packages that allow users to access hypertext
What is a browser?
A program that resides on the user's machine to obtain the requested materials and present them in to the end user in an organized way
What is a web server?
This resides on the computer containing the hypertext documents
What is a URL?
Each hypertext document available through the World Wide Web is given a unique address called a uniform resource locator
What does the URL include?
It includes the protocol, domain, all subdomains, the resource path ID, and the name of the document.
What is HTML?
HyperText Markup Language is a way of encoding a document. Special symbols called tags describe how the document should appear on a display screen, what multimedia resources should accompany the document, and which elements within the document are linked to other documents.
What is XML?
Extensible Markup Language; A generalized language provides a standardized style for designing notational systems for representing data as text files.
XML vs HTML
XML emphasizes semantics, while HTML focuses on appearance.
What is malware (malicious software)?
Any software intentionally designed to cause damage to a computer, server, client, or computer network.
EX) computer viruses, worms, spyware, and phishing, etc
What is a software bug?
Software that causes unintentional harm due to some deficiency
What is a virus?
a software program that infects a computer by inserting itself into programs that already reside in the machine. When the host program is executed, the virius is executed too
What is a worm?
an autonomous program that forwards copies of itself to other machines in a network and could result in detriment of individual machines or the operations of the network.
What is spyware?
Spyware resides on a computer, collecting information about the computer's activities and reporting back to the spyware's instigator. Passwords or credit card numbers can be exposed via spyware.
What is phishing?
A technique used to obtain private information by simply asking for it. The perpetrator sends emails posing as a legitimate business asking for information.
What is a DoS attack?
A denial-of-service attack is the process of overloading a computer with messages and results in suffocating the network resources
What is packet sniffing (man-in-the middle)(MITM)?
Where the attacker intercepts the data as it is traveling to or from the victim's device, including authentication credentials. MITM is just one way an attacker can get unauthorized access to resources and systems
What is brute force attack?
This is where the attacker uses all possible combinations of characters to learn a user's password. There are multiple variations of the brute force attack, such as rainbow table attack and dictionary attack.
What is a dictionary attack?
Performed by the attacker by using an application and a large dictionary text file with just words.
When the attacker runs the application, it tries identifying the password by trying hundreds or thousands of words per minute from that dictionary file.
What is a rainbow table attack?
An attack that tries to identify the hash value of the password, then convert it back to plain text.
What is a firewall?
A "filter program"
Firewalls block outgoing messages with certain destination addresses or block incoming messages from untrustworthy sources
What is a proxy server?
A software that acts as an intermediary between a client and a server to shield the client from adverse actions of the server.
What is network auditing software?
Software that monitors network behaviors such as the origin and volume of traffic, looking for anomalies to proactively or reactively mitigate unwanted occurrences.
What is antivirus software?
Software that detects and removes known viruses from the network
What is the point of encryption?
Encryption encodes information to keep it confidential even if the data is stolen.