Microbiology Chapter 2: Biochemistry Basics
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Define acid
Substance that contribute hydrogen ions (H+) to a solution
Define amphipathic
A molecule that has both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region.
Define atom
The smallest chemical unit of matter
Define atomic mass
the number of protons and neutrons in an atom
Define atomic number
the number of protons in an atom
Define base
Substances that contribute hydroxide ions (OH-) to a solution
Define chemical bond
The force that holds atoms together
Define functional group
part of a molecule that typically participates in a chemical reaction and that gives the molecule some of its chemical property
Define hydrophilic
water-loving substances that easily dissolve in water
Define hydrophobic
water-fearing substances that do not dissolve easily in water
Define ion
Charged atom formed when an atom loses or gains an electron
Define molecule
two or more atoms joined chemically
Define solution
Mixture of 2 or more substances in which one substance is dissolved within another
Define covalent bond
sharing of electrons
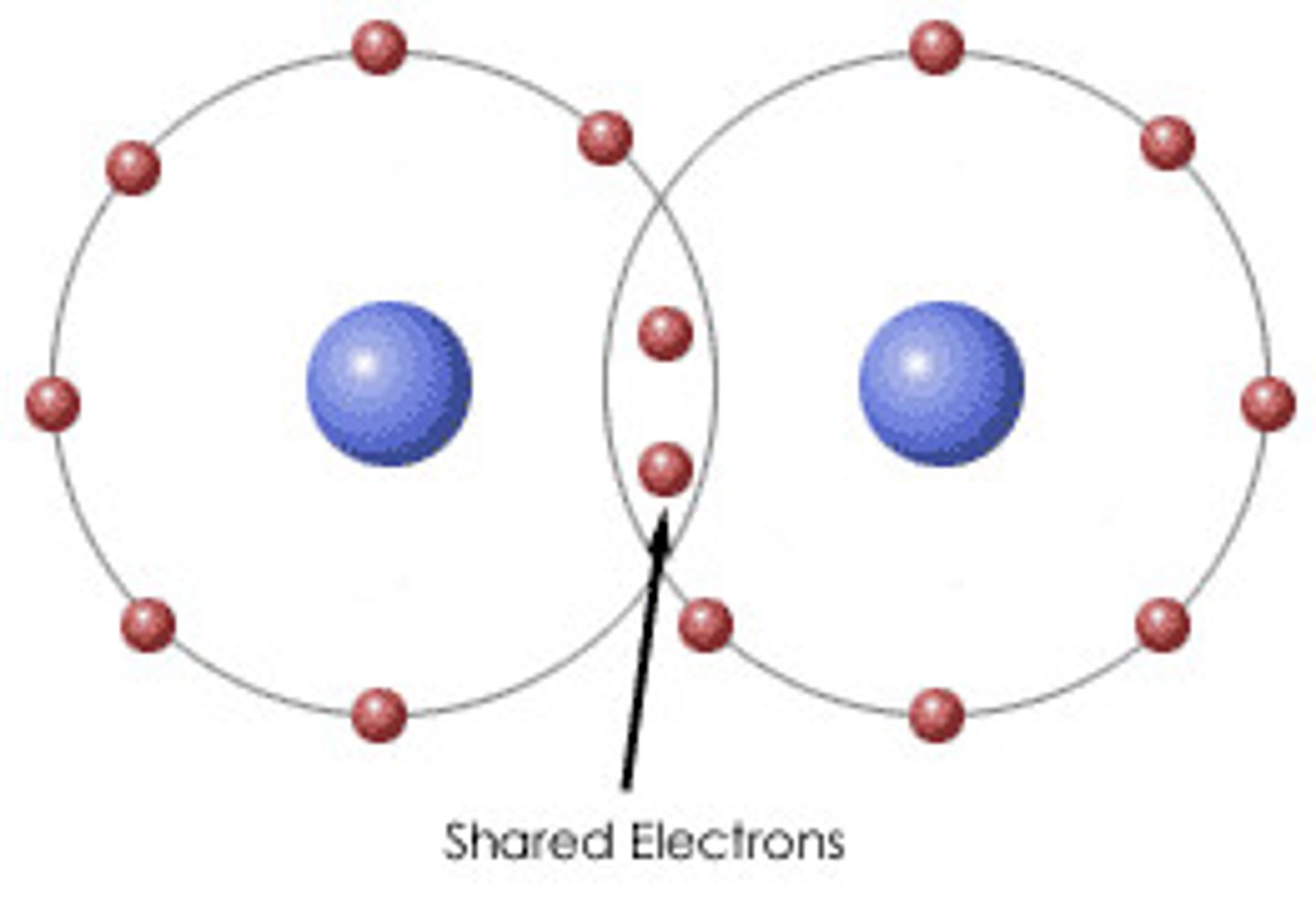
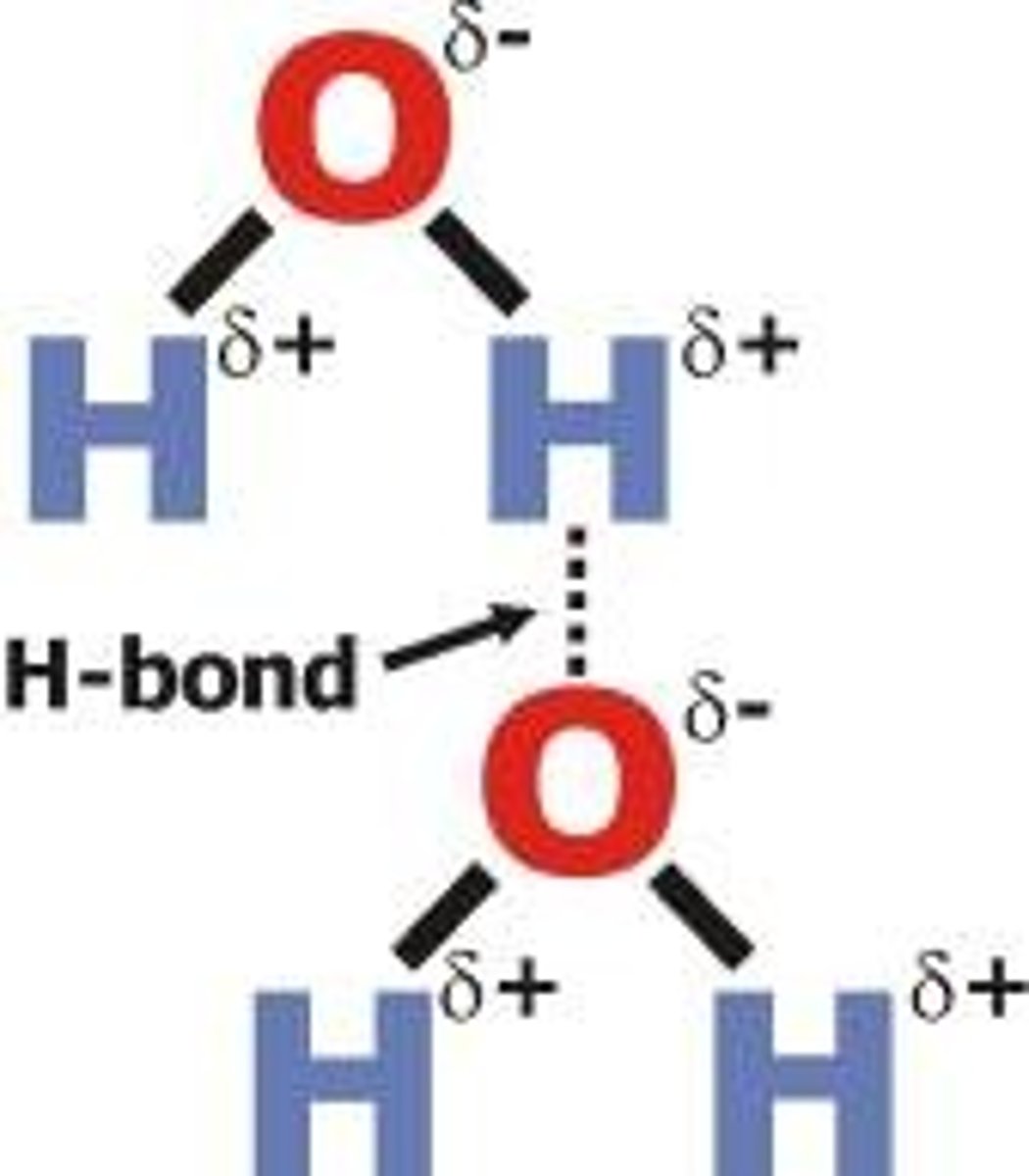
Define hydrogen bond
does not bond atoms into molecules; noncovalent electrostatic attraction between two or more molecules
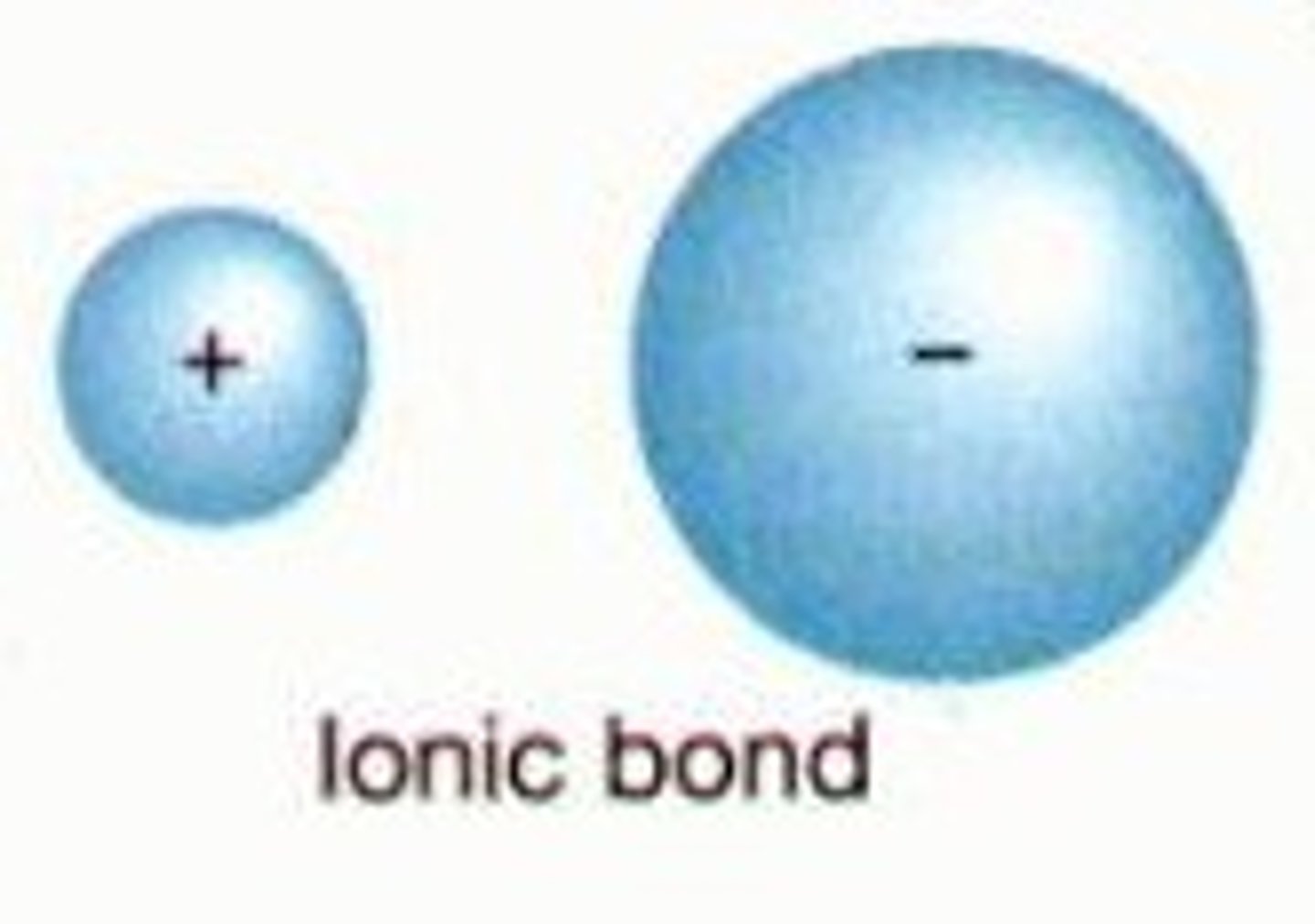
Define ionic bond
the strong attractive force between ions of opposite charge (between cation and anion)
The ____ is the medium in which substances are dissolved
solution
The substance that is being dissolved is called the ____
Solubility
The most common solvent in living cells is ____
water
The pH scale ranges from __ to __
0 (most acidic) to 14 (most basic)
Neutral level on pH scale
7
Example of a substance with pH of 1
Hydrochloric acid
Example of a substance with pH of 7
pure water
Example of a substance with pH of 14
Sodium Hydroxide
Describe synthesis reactions
builds substances by combining two or more reactants
Describe decomposition reactions
breaks a substance down into simpler components (AB --> A+B)
What can be used for decomposition reaction breakdowns
Water
Define endergonic reaction
require an energy investment to make products that have a higher final energy than the reactants
Define exergonic reactions
Make products with a lower final energy than the reactants
4 major classes of macromolecules
1. Carbohydrates
2. Lipids
3. Proteins
4. Nucleic Acids
What are the building blocks macromolecules
monomers
Single units build large polymers through a process called ____
Polymerization
Define monosaccharide
smallest unit of a carbohydrate and also known as "one sugar"
What is an example of a monosaccharide
glucose, fructose, galactose
Define disaccharide
consists of two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic linkage "two sugars"
What is an example of disaccharide
sucrose, lactose, maltose
Define polysaccharide
consists of many monosaccharides linked together "many sugars"
What is an example of polysaccharide
starch, glycogen, cellulose
What is a triglyceride composed of?
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids
What is a phospholipid composed of?
a glycerol backbone, two fatty acid chains, and a phosphate group
The basic building block of a protein is what?
amino acid
How are proteins bonded?
peptide bonds
What is an amino acid composed of?
carboxyl group, amino group, variable side chain (R group)
Define primary structure
Linear sequence of amino acids in a protein.
Define secondary structure
The twisting of a polypeptide into either an alpha helix or beta-pleated sheets
Define tertiary structure
The folding of a polypeptide into a three-dimensional structure
Define quaternary structure
The fourth level of protein structure; the shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits.
3 functions of proteins
structural scaffolds, enzymes, cellular transporters
components of a nucleotide
phosphate group, 5 carbon sugar, nitrogenous base
Sugars in DNA
deoxyribose
Sugars in RNA
ribose
Bases of DNA
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
The bases of RNA are...
adenine, cytosine, guanine, uracil
What is the "strandedness" of DNA
double stranded helical
What is the "strandedness" of RNA
single stranded
What type of bonds are carbohydrates built with?
Glycosidic bond
What type of bonds are Lipids built with?
Ester bond
What type of bonds are Nucleic Acids built with?
Phosphodiester bond
What type of bonds are proteins built with?
Peptide Bond