Chromatography
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
What is chromatography?
Separation of a mixture into all its constituents
There are two key components:
Stationary phase
Mobile phase
Stationary phase
This is the chromatography paper or the think layer chromatography plate (TLC)
The TLC is a thin sheet of paper with a thin layer of silica gel or aluminium hydroxide
There are free OH- groups pointing outwards in contact with the mobile phase
Mobile phase
This is the solvent for the biological molecules
Water can be used to polar molecules
Ethanol for non polar molecules
Mobile phase flows through and across the stationary phase carrying the biological molecules with it
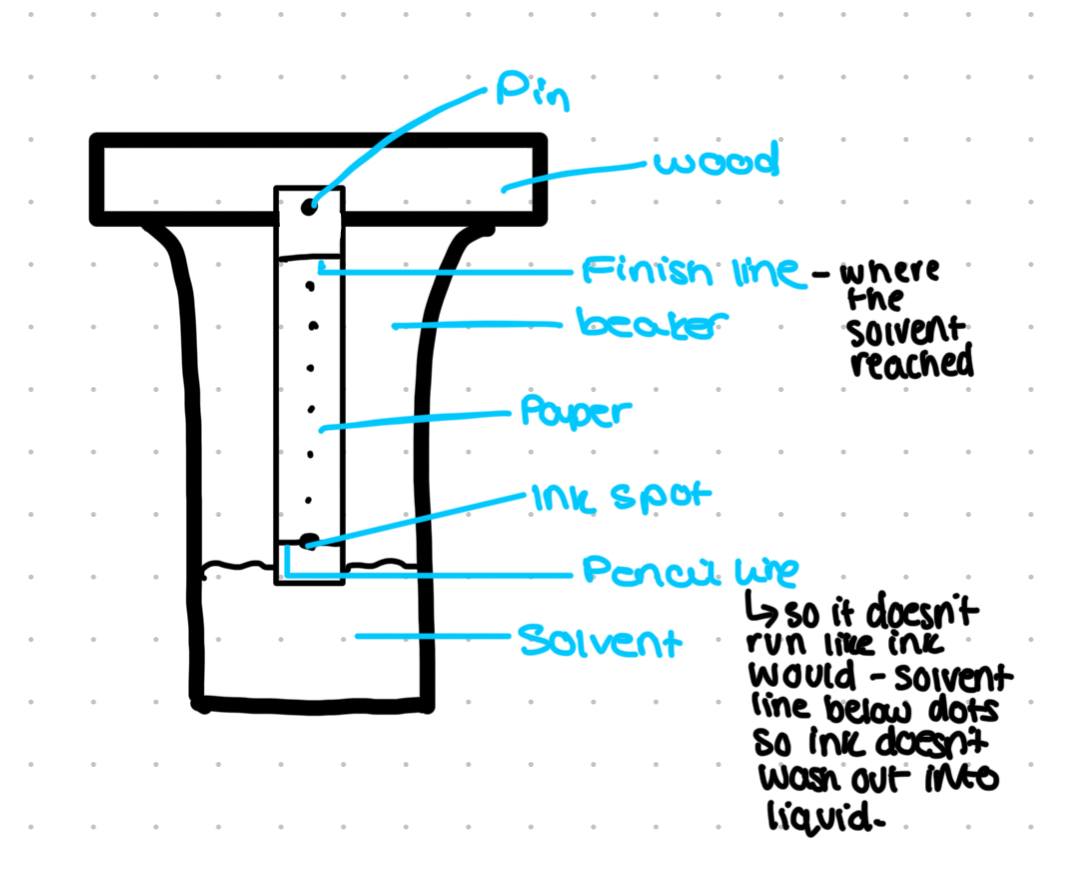
How does this occur?
Solvent travels up the paper or plate with components of the solution mixture with it
Different components travel at different speeds dependent on their solubility in the mobile phase; this is also dependent on the polarity of the molecule as well
Exposed OH- groups make the surface of the plate or paper very polar, it forms hydrogen bonds with the molecules
A highly polar solute will stick to the surface and move more slowly
A non polar solute will travel quickly
How to identify pigments
Measure distance from the pencil line to the centre spot of the pigment and the distance from the pencil line to solvent front
Rf value= spot distance/ front distance
If the experiment is repeated under the same conditions each pigment will always have the same Rf value
If you know the Rf values of particular pigments it allows you to identify them
Chromatography with colourless molecules
Using TLC there are ways to see colourless molecules:
Ultraviolet light
Under the UV light the plate will glow and the spots ink travelled will not
Ninhydrin
To see amino acids
Allow plate to dry and spray with ninhydrin
Binds to amino acids to make visible brown/ purple spots
Iodine
Allow plate to dry and place in a container with iodine crystals
Iodine forms a gas, which binds to the molecules of each spot
How is chromatography used?
Monitor progress of reactions
Urine testing athletes for drugs
Analysing drugs for purity
Analysis of food for contaminants