pharm 2: GI rx
1/242
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
243 Terms
What is an important aspect of patient education in GI medications?
Develop comprehensive patient education and counseling for drugs used for the gastrointestinal system/nutrition; renal system; EENT; and musculoskeletal system.
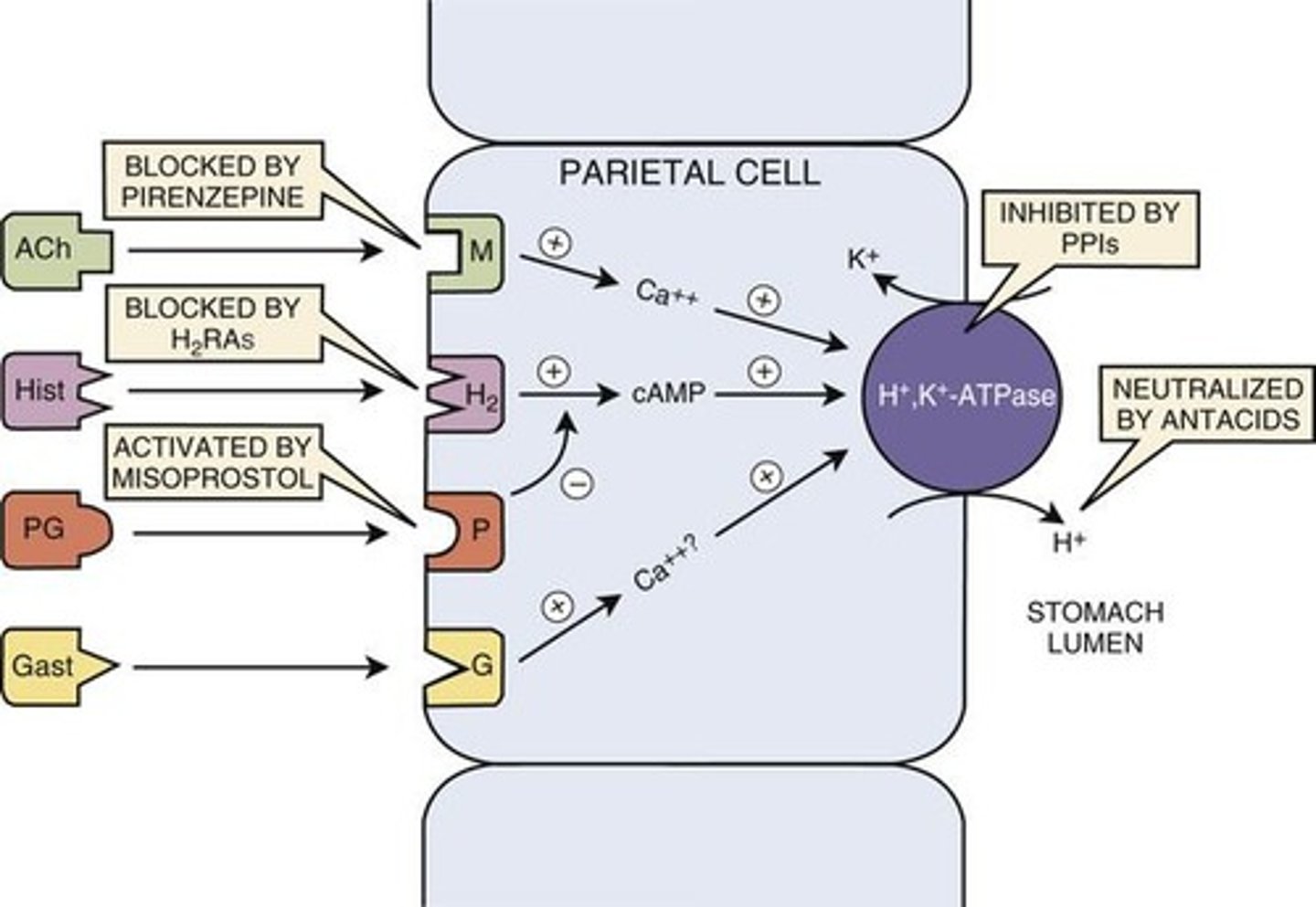
What is the MOA for antacids used in GERD/PUD?
React with gastric acid -> neutralizing acid
What is the indication for using antacids?
ACUTE relief of acid reflux (GERD).
What are the adverse effects of aluminum hydroxide?
Constipation.
What are the adverse effects of magnesium hydroxide?
Diarrhea.
What is a potential issue to consider when using antacids?
Drug interactions.
what are the medications used for GERD/Peptic Ulcer Disease
- Aluminum hydroxide
- Ca Carbonate
- Mg Hydroxide
What are the 3 main Histamine 2 Receptor Antagonists (OTC)?
- Famotidine (Pepcid)
- Ranitidine (Zantac)
- Cimetidine (Tagamet)
What is the MOA of Histamine-2 Receptor Antagonists?
block H2 receptors to reduce the acid secretion in stomach
What are the indications for using Histamine 2 Receptor Antagonists?
PUD and acute/preventative GERD.
How long does it typically take to heal duodenal and gastric ulcers with Histamine 2 Receptor Antagonists?
- 4-6 weeks for duodenal ulcers
- 8-12 weeks for gastric ulcers.
side effects of Histamine 2 Receptor Antagonists?
- Headache
- dizziness
- constipation
What significant drug interactions are associated with Cimetidine?
- inhibit CYP enzymes
- increase levels of warfarin (bleeding) , lidocaine, and theophylline
how does GERD cause pneumonia?
bacteria can flourish and travel up to lungs and cause pneumonia
What are the four main Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) ?
- Omeprazole (Prilosec)
- Esomeprazole (Nexium)
- Pantoprazole (Protonix)
- Dexlansoprazole (Dexilant)
What is the MOA of PPIs?
They irreversibly inhibit the H/K ATPase pump, reducing acid secretion
when do you take PPIs for acid reflux
30 min before a meal
What are the indications for PPI?
Peptic ulcer disease and acute/preventative GERD.
How do PPI compare to Histamine 2 Receptor Antagonists in terms of acid secretion reduction?
PPIs reduce acid secretion more than H2RAs.
What are the common side effects of PPI?
- Pneumonia
- Fractures (long term)
- Decreased magnesium and B12
- diarrhea (C. diff)
- AKI/CKD
- potential dementia
What is a notable statistic about patients taking PPI?
About 2/3 of patients who take PPIs don't actually need them.
What should PCP do regarding patients on PPIs?
They should review the ongoing need for a PPI
What condition should not lead to the discontinuation of PPIs?
Barrett's esophagus
What advice should be given to patients who d/c PPIs?
can develop transient upper GI symptoms due to rebound acid hypersecretion.
discontinuation of PPI should be based on...
lack of indication, NOT adverse effects
What is the MOA of Sucralfate (Carafate)?
creates a sticky gel that adheres to the ulcer and forms a barrier to hydrogen ions.
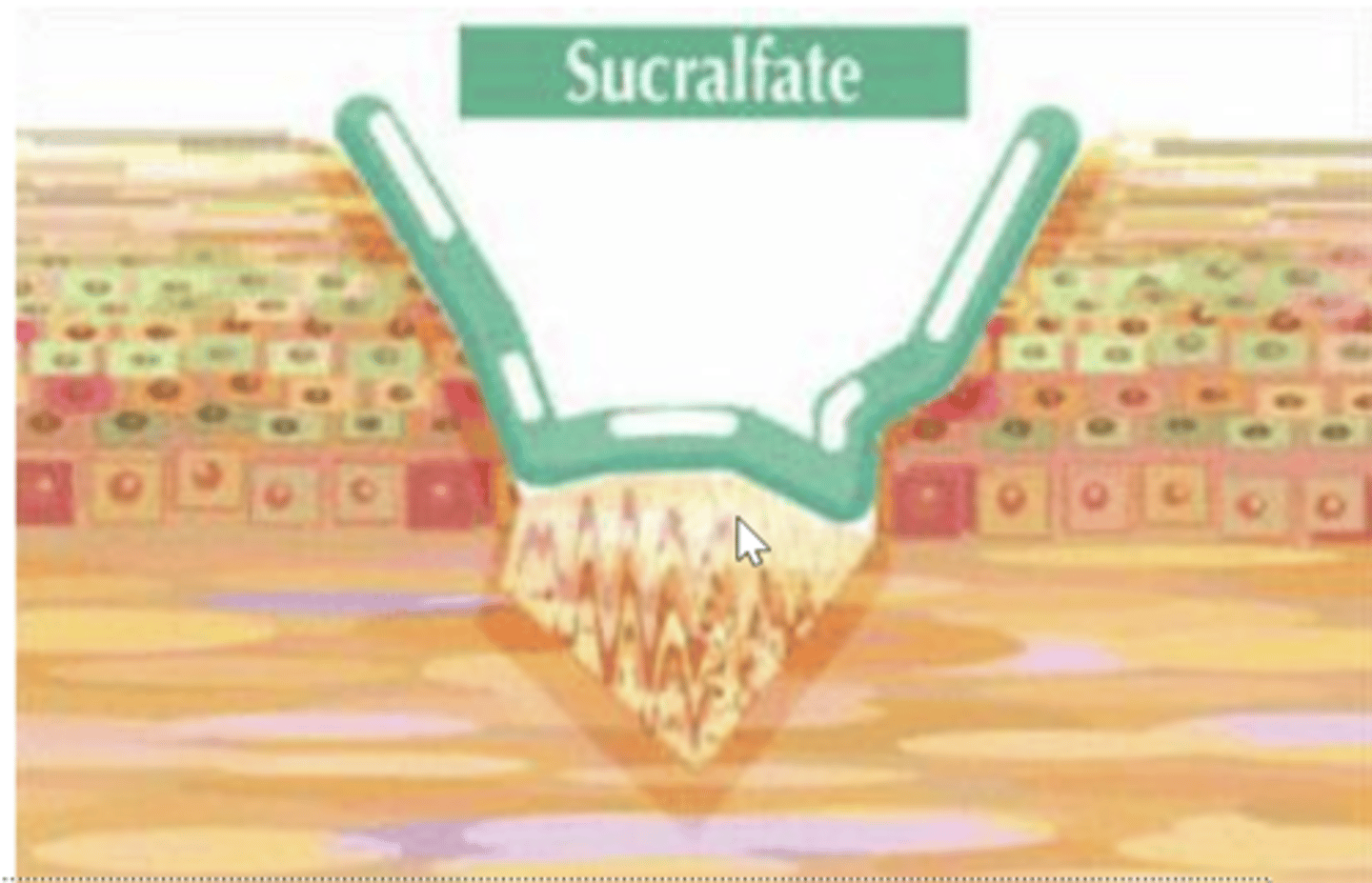
What is the indication for Sucralfate?
Duodenal/peptic ulcers.
How is Sucralfate administered and what are its side effects?
- orally 4x/day
- no known serious side effects.
What drug interactions are associated with Sucralfate?
It may impede absorption of theophylline, warfarin, digoxin, H2RAs, and PPIs (should be taken 2 hours apart from these drugs).
What is the MOA of Misoprostol?
analog of prostaglandin E1 that suppresses gastric acid secretion & promotes bicarbonate secretion
What are the indications for Misoprostol?
Prevention of peptic ulcers caused by long-term NSAID therapy
- pregnancy termination
- inducing labor
- missed miscarriage.
What are the side effects and contraindications of Misoprostol?
- diarrhea
- abdominal pain
- spotting
- dysmenorrhea in female
- contraindicated in pregnancy
What are the four Serotonin (5-HT3) Receptor Antagonists mentioned?
- Ondansetron
- Granisetron
- Dolasetron
- Palonosetron
- Think Megatron= bad guy = antagonist
What is the mechanism of action of Serotonin (5-HT3) Receptor Antagonists?
block type 3 serotonin receptors that cause nausea
What are the indications for Serotonin (5-HT3) Receptor Antagonists?
- Nausea and vomiting with chemotherapy
- radiation
- pregnancy.
What are the common side effects of Serotonin (5-HT3) Receptor Antagonists?
- Fatigue/dizziness
- Headache
- consTipation
- <3 QT prolongation.
What are the two glucocorticoids for nausea/vomitng?
- Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol)
- Dexamethasone (Decadron)
- through inh. of prostaglandin synthesis.
What is the indication for glucocorticoids in this context?
Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV).
PK for glucocorticoids
PO or IV long acting
ADE for glucocorticoids
- agitation
- insomnia
- hunger
- hyperglycemia
- intermittent use leads to low SE
- take with food to avoid ulcerations
What are common side effects associated with the use of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists?
Fatigue and mild elevation of liver function tests (LFTs).
What is the mechanism of action of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists?
blockage of neurokinin-1-type receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ).
What are the indications for neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists?
Prevention of post-operative N/V and CINV
What is the PK of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists?
- PO or IV
- long acting
- metabolism via CYP3A4.
What are the drug interactions associated with neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists?
- inhibitor and inducer of CYP3A4
- inc levels of glucocorticoids
- dec warfarin (clots)
- dec ethinyl estradiol
examples of NK-1 receptor antagonists
- aprepitant
- netupitant
- fosaprepitant
- think french NK UK
What are the main drugs classified as phenothiazines?
Prochlorperazine and Promethazine
What is the mechanism of action of phenothiazines?
Blocks dopamine-2 receptors in the CTZ.
What are the indications for phenothiazines?
- N/V associated with surgery and cancer
what are the indications for metaclopramide
gastroparesis and diarrhea
What are the side effects of phenothiazines?
- Extrapyramidal symptoms: tremors
- hypotension
- sedation
- anticholinergic effects
- QT prolongation.
What is a black box warning associated with promethazine?
- sedation and severe respiratory depression
- contraindicated in children < 2 yo
What are the main drugs classified as butyrophenones?
- Haloperidol (haldol)
- Droperidol
What is the mechanism of action of butyrophenones?
Blocks dopamine-2 receptors in the CTZ, similar to phenothiazines.
What are the indications for butyrophenones?
Post-op N/V and CINV
What are the side effects of butyrophenones?
- Extrapyramidal symptoms
- hypotension
- sedation
what is the BB warning for butyrophenones
risk for fatal dysrhythmias due to QT prolongation
What is the mechanism of action of cannabinoids?
likely through activation of cannabinoid receptors
Examples of cannabinoids
- dronabinol
- nabilone
What are the indications for cannabinoids?
Second-line for CINV
What are the side effects of cannabinoids?
- Dissociation
- dysphoria
- tachycardia
- hypotension
- drowsiness
- appetite stimulation
cannabinoids should be avoided with...
alcohol, sedatives and SNS depressants
- CVD and Psych disorders
What is the MOA of scopolamine?
Anticholinergic agent that inhibits muscarinic actions of acetylcholine
What are the indications for scopolamine?
Prevention and treatment of motion sickness.
PK of scopolamine
- patch behind ear
- place before expected event
What are the common side effects of scopolamine?
- Dry mouth
- Blurry vision
- Drowsiness
- Dilated pupils
- Think seal with big eyes
What is the leading cause of chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma?
Hepatitis B
what is the dosing schedule for hep B
Birth, 2 months, 6 months
What is the best strategy against Hepatitis B virus (HBV)?
Prevention through vaccination for all children before entering school.
what is different from hep b and hep C treatment?
not all hep B patients get treated, only high risk
What are the first-line nucleoside analogs for treating Hepatitis B (PO)?
- Entecavir
- Tenofovir
what are the alfa interferons for hep B tx (SQ)?
- interferon alfa-2b
- peginterferon alfa-2a
What is the MOA of nucleoside analogs used for Hepatitis B?
- Incorporation into the growing DNA chain causing premature chain termination.
- think fake taylor swift tickets
What are the side effects of nucleoside analogs?
- Minimal SE (aches, F/C)
- lactic acidosis
- pancreatitis
- hepatomegaly.
what patients do you caustion for nucleoside analogs
HIV patients, or autoimmune disorders
MOA of alfa interferons
blocks viral entry into cells
What are the indications for alfa interferons in Hepatitis B treatment?
- pt who want finite duration of therapy with favorable baseline predictors
- can tolerate SE
PK for alfa interferon: interferon alfa-2b
- Conventional
- short half-life
- 3x/ week
- long-acting
PK for alfa interferon: peginterferon alfa-2a
- long half-life
- 1/week
ADE for alfa interferons
- flu like syndrome
- neuropsych. effects
- thyroid dysfunction
- BM suppression
BBW for alfa interferons
worsen AI disorders, infections, and ischemic conditions
What is the black box warning (BBW) for Hepatitis C treatments?
May cause or worsen life-threatening disorders, including autoimmune, infectious, and ischemic conditions.
How many different genotypes of Hepatitis C are there, and which is most prevalent in the US?
- 6 genotypes
- majority is genotype 1
What is the primary treatment goal for Hepatitis C?
- Cure it!
- SVR at 12 weeks
What are the general classes of treatments for Hepatitis C?
- Direct-acting antivirals (DAAs)
- interferon alfa
- Ribavirin.
what are the DAAs
- NS 3/4a protease inh
- NS5A inh
- NS5B inh
what is the most important part of hep c treatment
patient adherence
examples of ns 3/4a protease inh.
- glevaprevir
- grazoprevir
- voxilaprevir
- paritaprevir
What is the mechanism of action for NS 3/4a protease inhibitors?
Inhibits NS3 and 4a protease, halting viral replication.

What is the importance of adherence to therapy in Hepatitis C treatment?
- Adherence is crucial for achieving high cure rates
- >95% when drugs are used in combination with NS5a/b inh
What are the common ADE of NS 3/4a protease inhibitors?
- Hepatic injury
- photosensitivity
What should be tested in all patients before starting treatment with NS 3/4a protease inhibitors?
All patients should be tested for current or prior HBV infection
drug interactions with NS 3/4a protease inh
- CYP3A4
- inducers lower the PI levels
What are the contraindications for NS 3/4a protease inhibitors?
Not recommended in patients with severe liver impairment, such as decompensated cirrhosis.
What is the mechanism of action for NS5A inhibitors?
Targets NS5A, which is necessary for HCV RNA replication and assembly.
NS5A inh examples
- Elbasvir
- Ledipasvir
- Ombitasvir
- Pibrentasvir
- Velpatasvir
- Daclatasvir
- think of the 5A making SAvir
What are the common adverse effects of NS5A inhibitors?
they are generally well tolerated.
drug interactions of NS5A inh
- cyp3a4
- elevates statin and dig levels
- amiodarone= bradycardia
What is the mechanism of action for NS5B inhibitors, Sofosbuvir?
Inhibition of the NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, essential for viral replication.
What are the ADE of Sofosbuvir?
Headache, insomnia, fatigue, and pruritus.