Upper Limb Regional and Functional Anatomy
1/150
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 2 Wednesday, Week 3 Monday girll you do not have to know individual origins and insertions do not study those (only need to know attachment sites which are common to multiple muscles)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
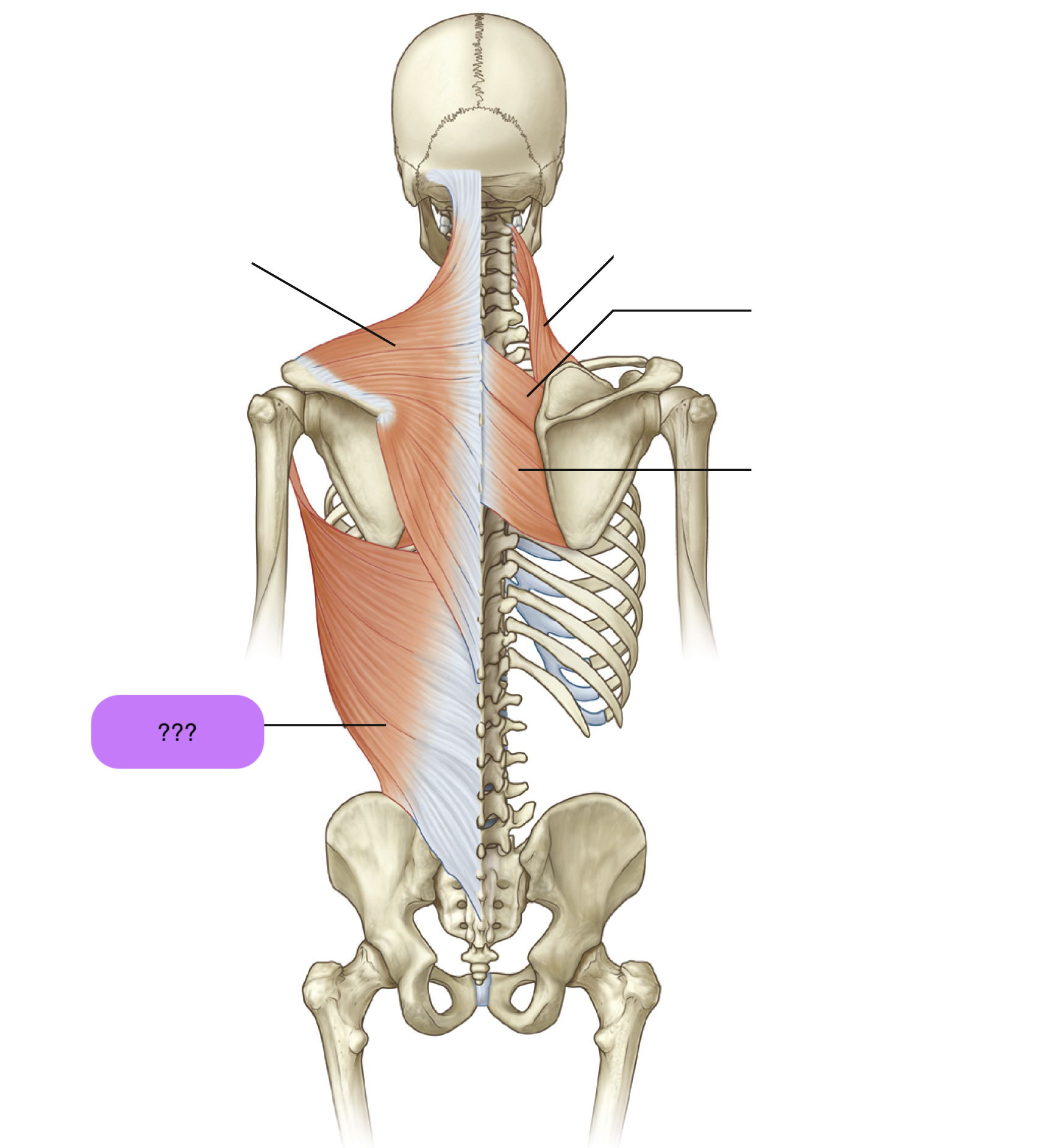
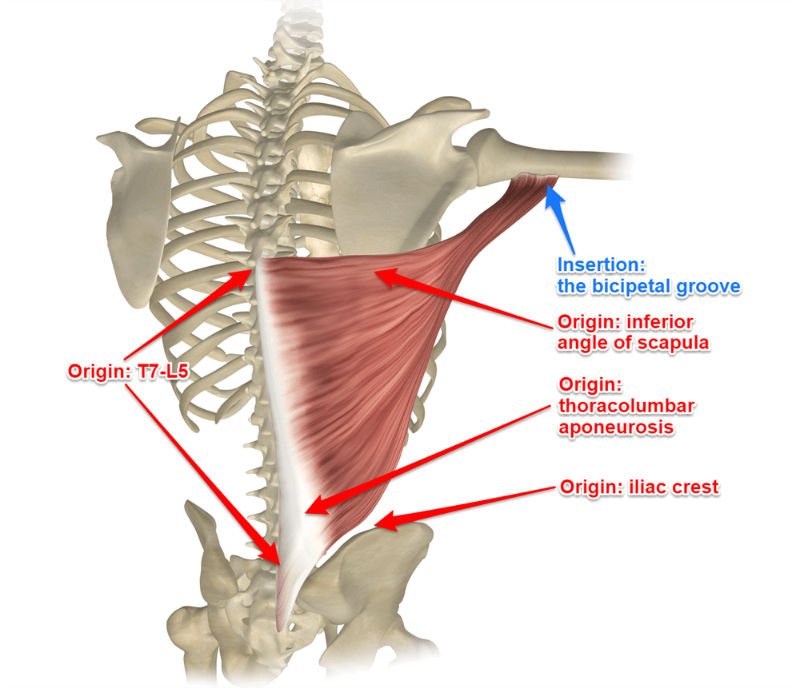
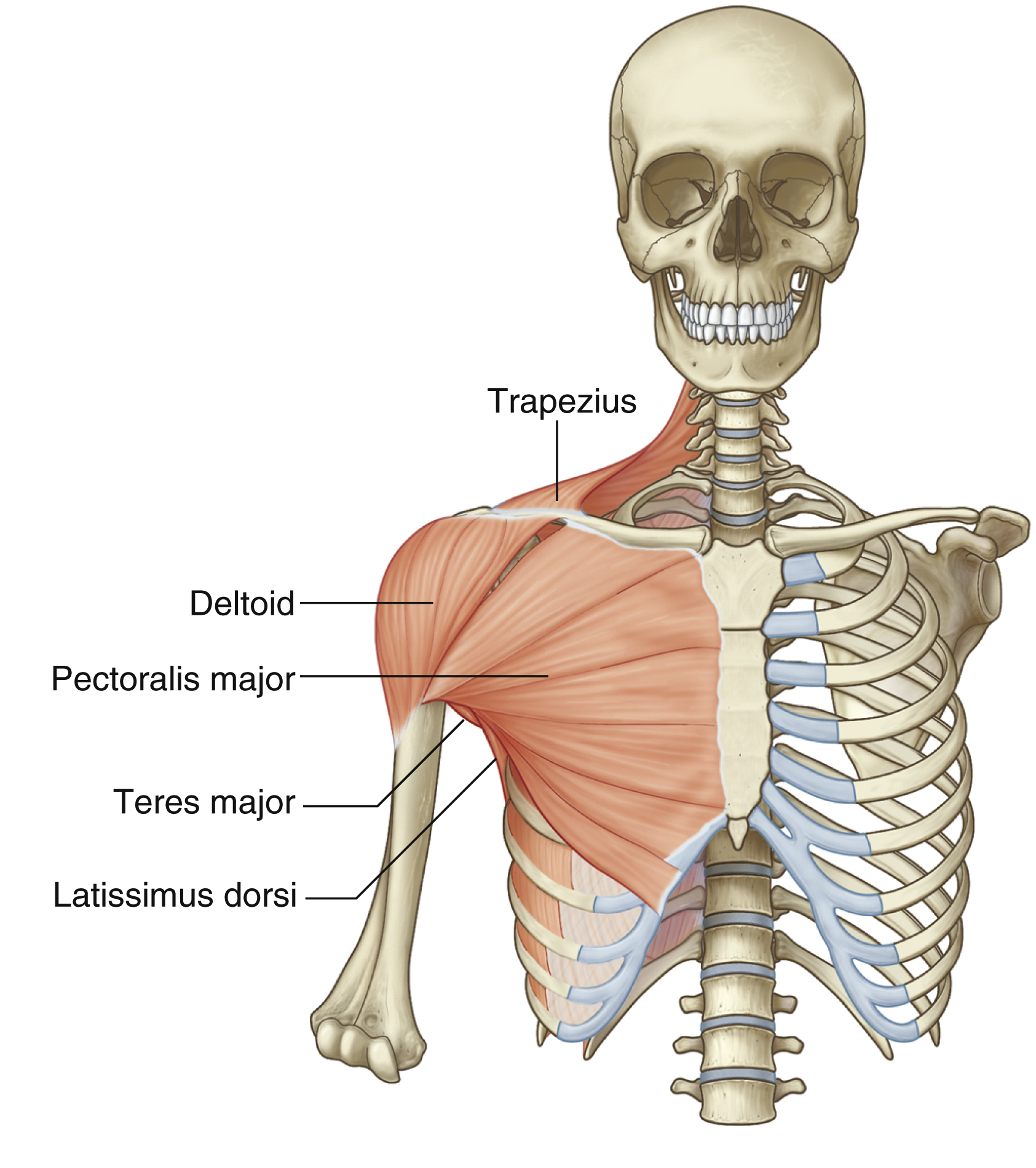
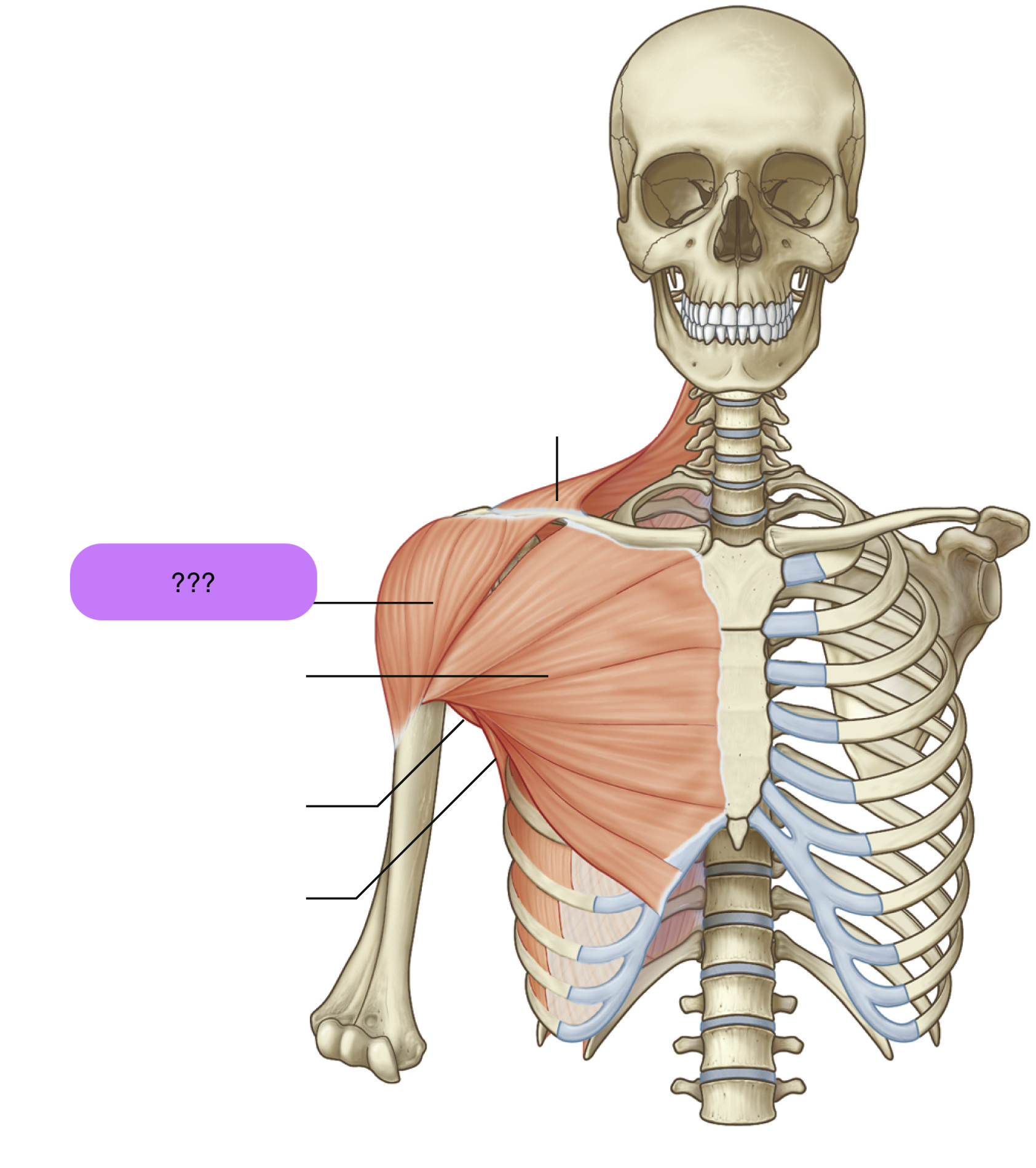
latissimus dorsi
Origins: T7 to L5 spinous processes + iliac crest to intertubercular groove of humerus
Prime Actions:
Extends
ADDucts arm
medially rotates arm
(important for swimming and climbing)
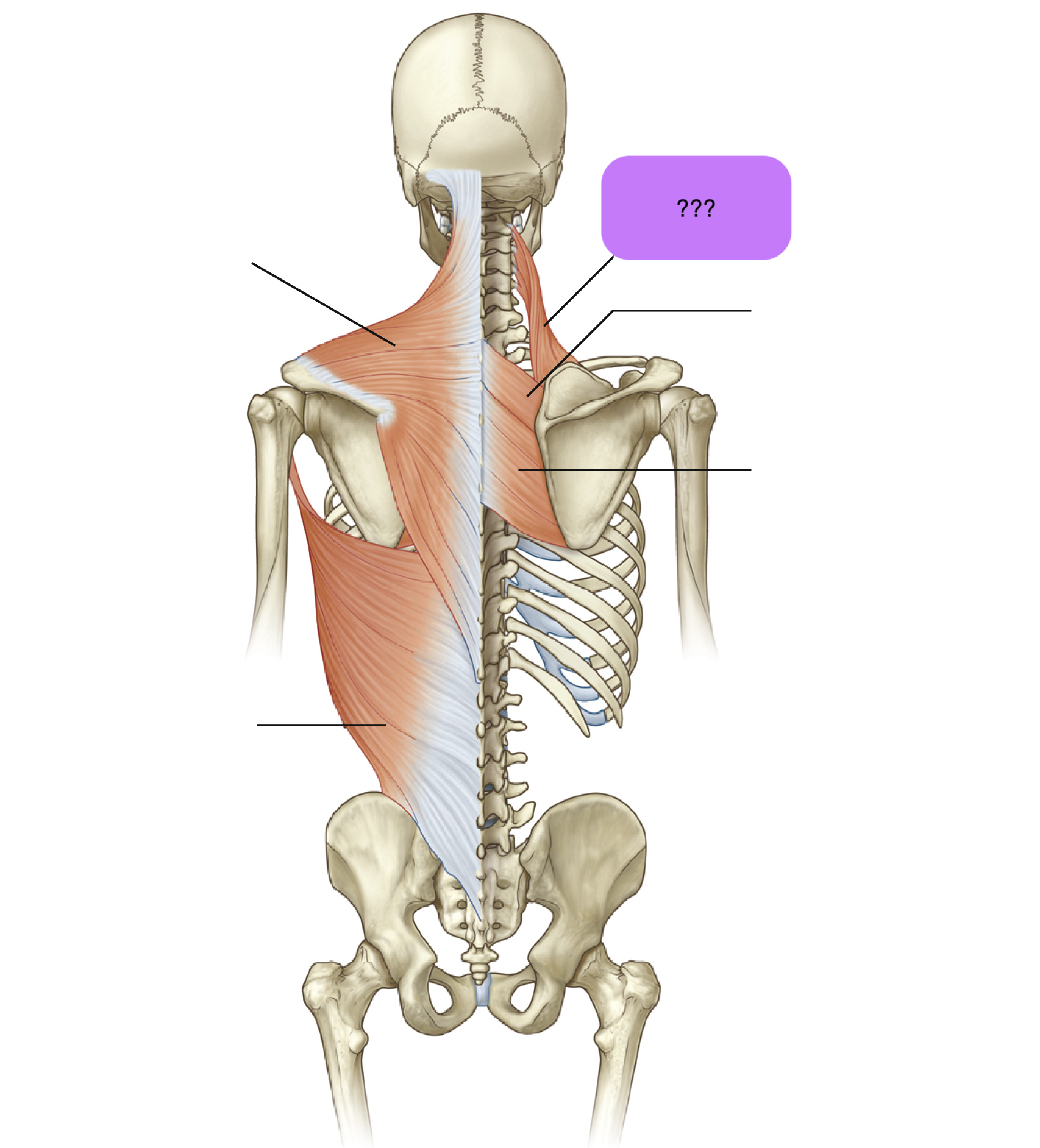
levator scapulae
Attachments: Supero-medial border of scapula to transverse processes of C1-C4 vertebrae
Prime action: Elevates scapula & downward rotation
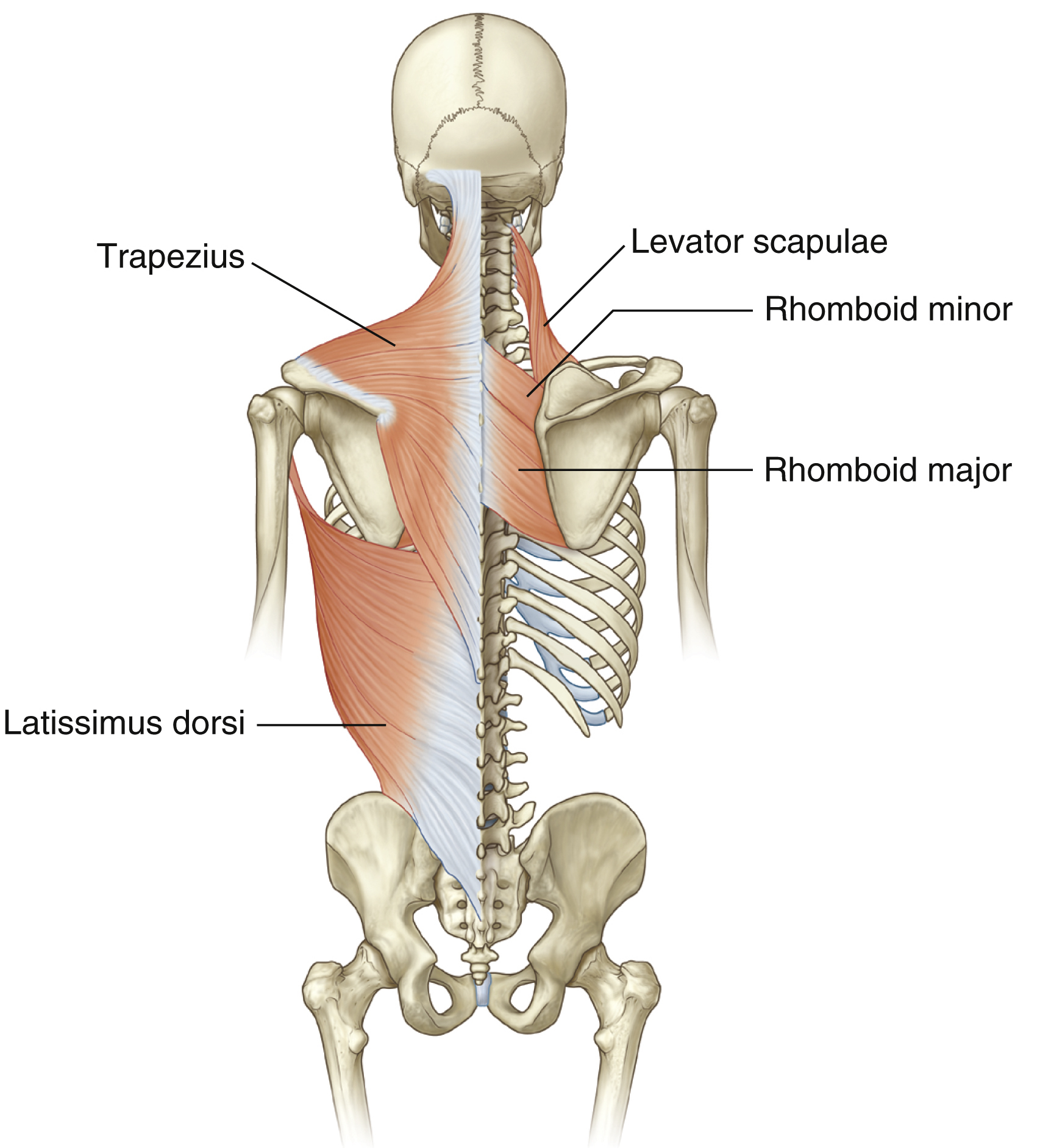
rhomboid major
Attachments: C7-T5 spinous processes of vertebrae to medial border of scapula
(same as rhomboid minor)
Prime Actions:
Retracts scapula
downward rotation
(same as rhomboid minor)
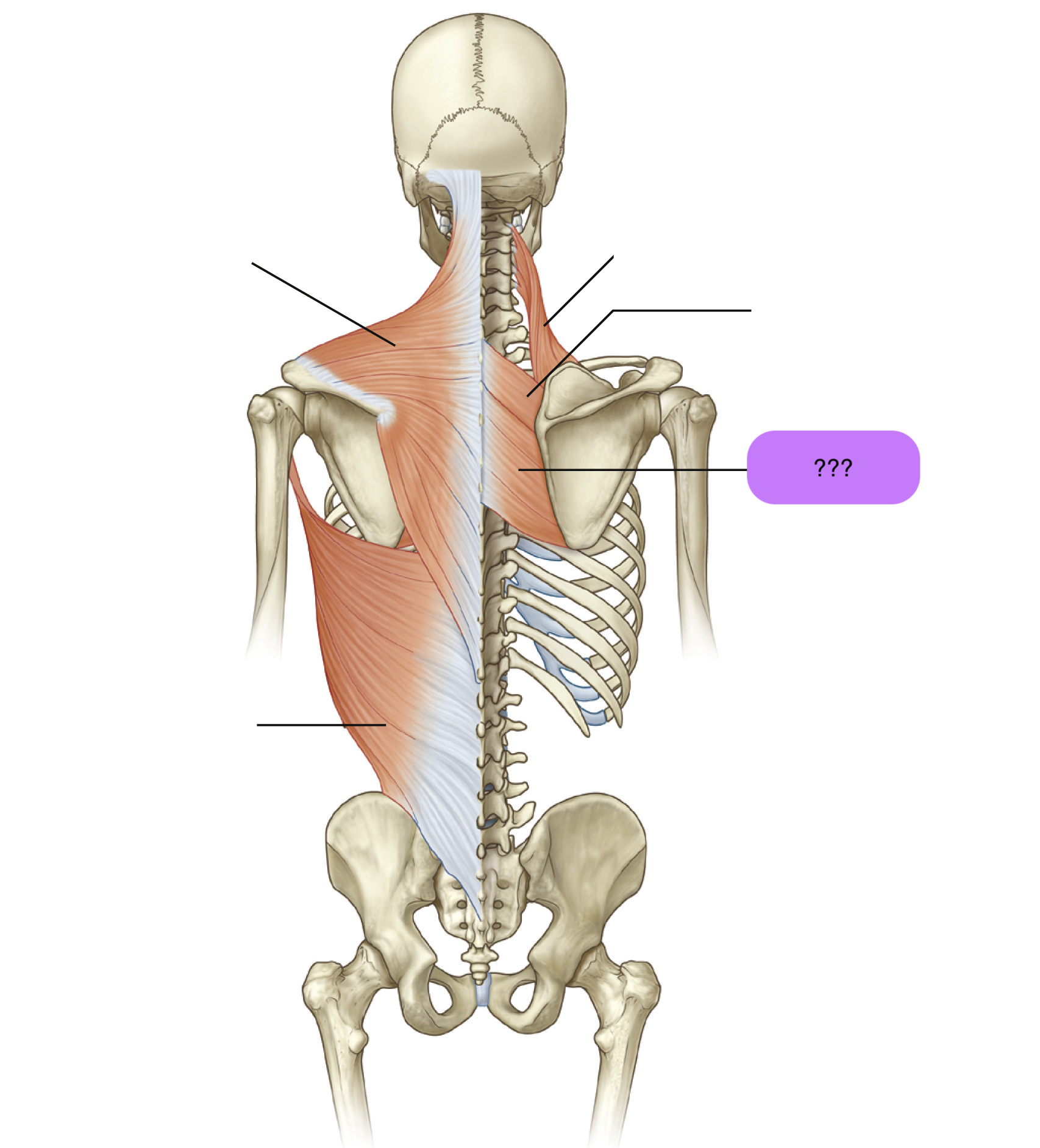
pectoralis major
Attachments: Medial clavicle and sternum to intertubercular sulcus of humerus
Prime actions:
ADDuction (+horizontal & diagonal)
Medial Rotation of humerus
Flexion to 60 degrees
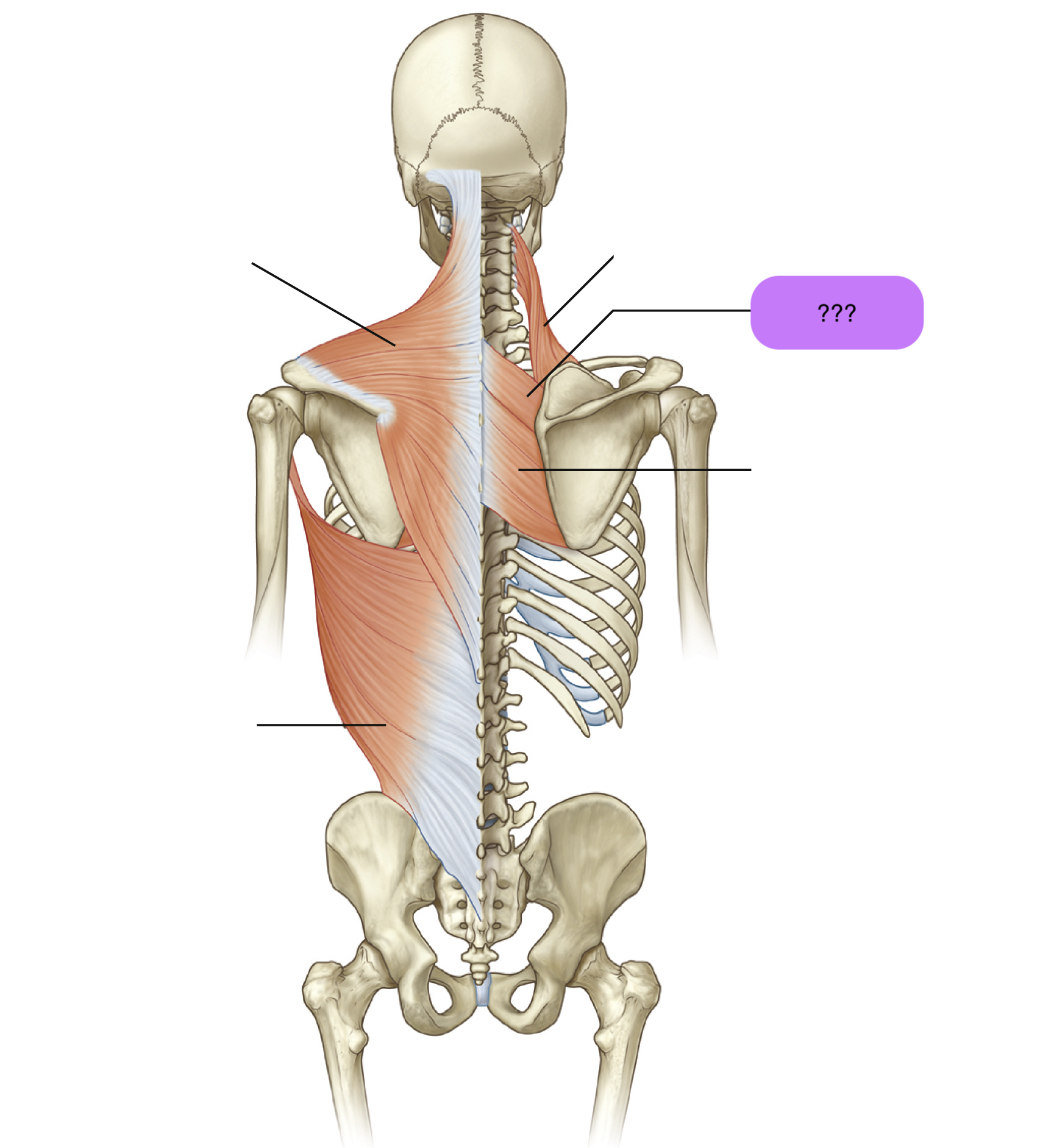
rhomboid minor
Attachments: C7-T5 spinous processes of vertebrae to medial border of scapula
(same as rhomboid major)
Prime Actions:
Retracts scapula (opposite of hugging)
downward rotation
(same as rhomboid major)
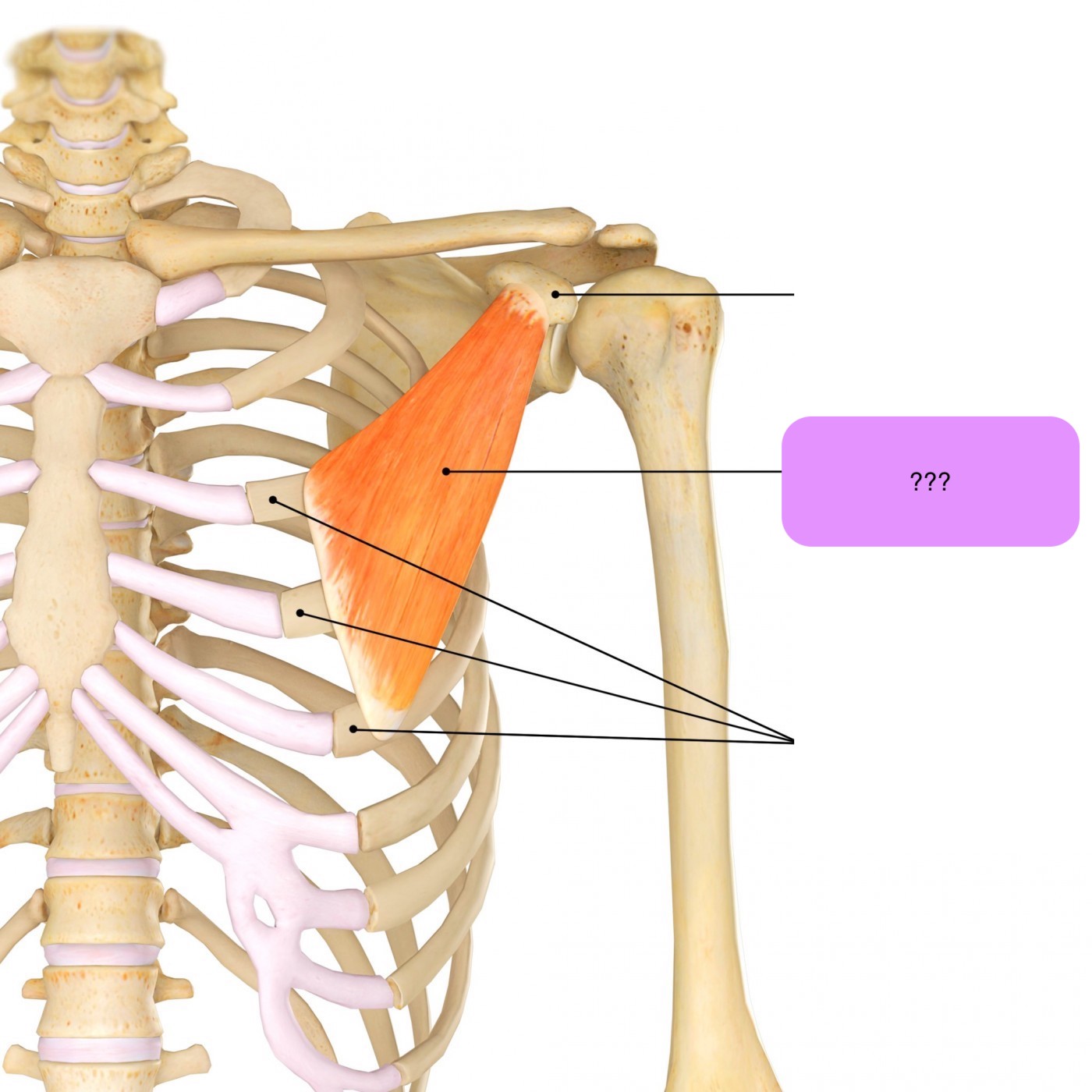
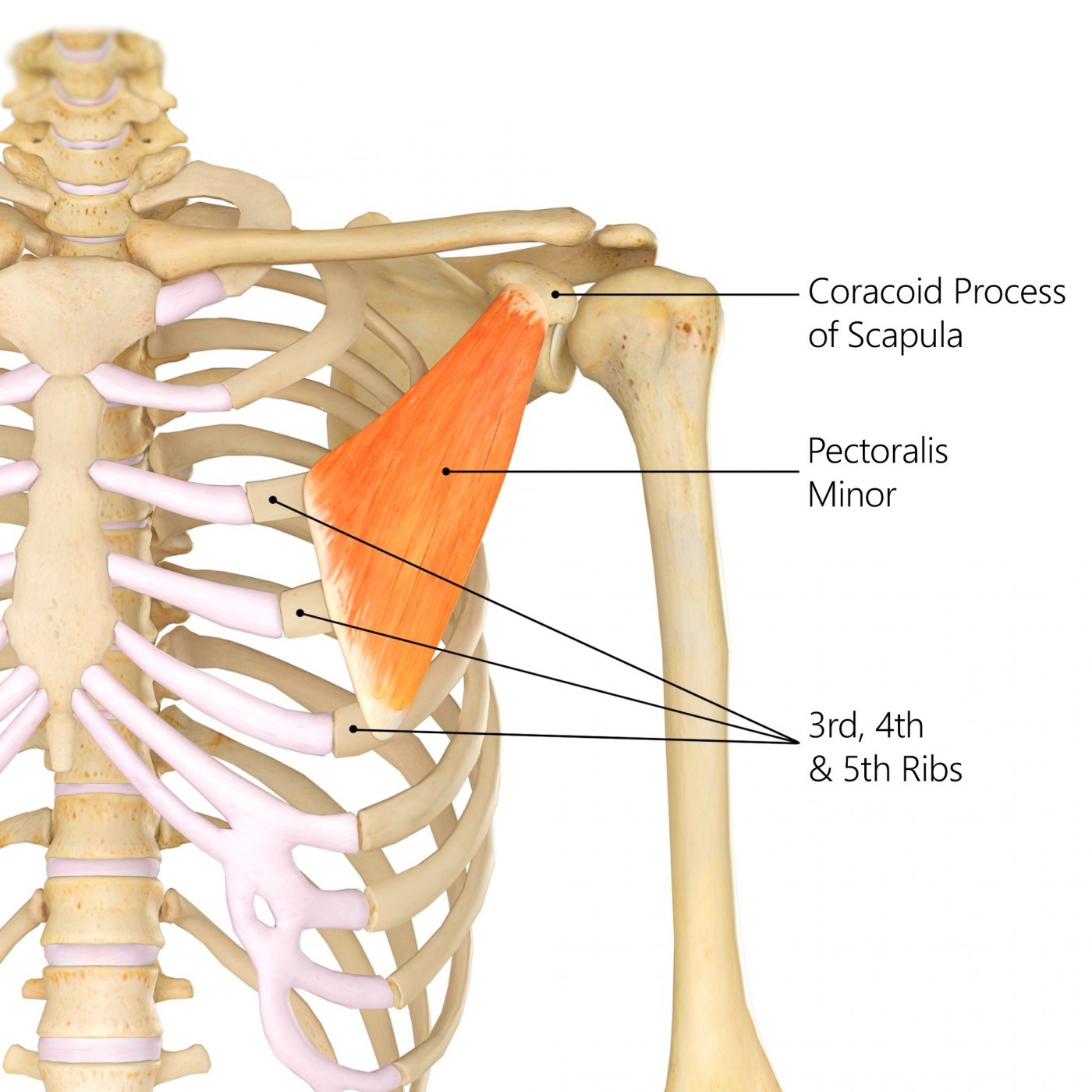
pectoralis minor
Attachments: Ribs 3-5 to Coracoid process of scapula
Prime Actions:
Stabilisation
Scapula protraction (hugging motion)
Scapula depression
Scapula downward rotation
(same as serratus anterior)
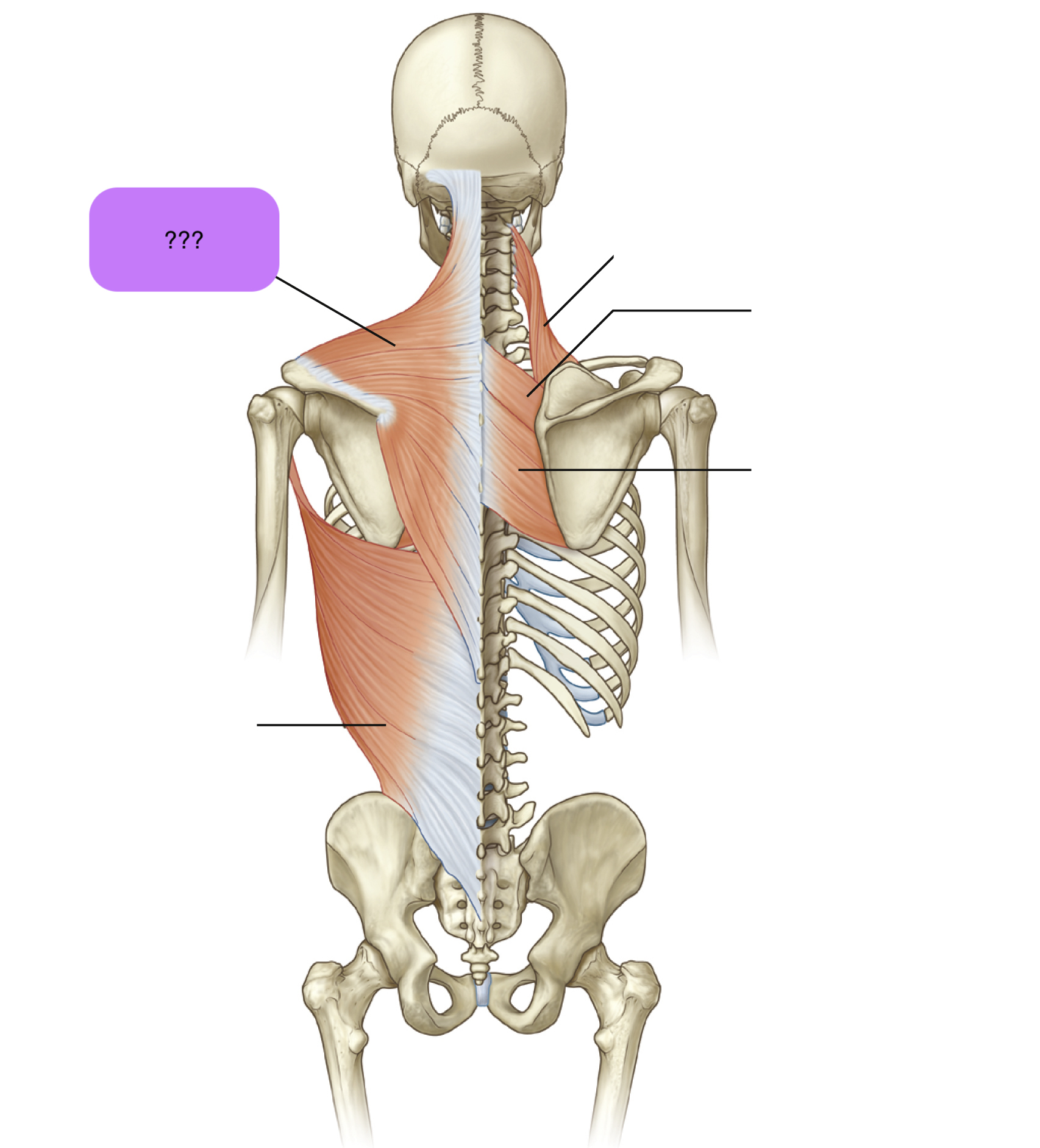
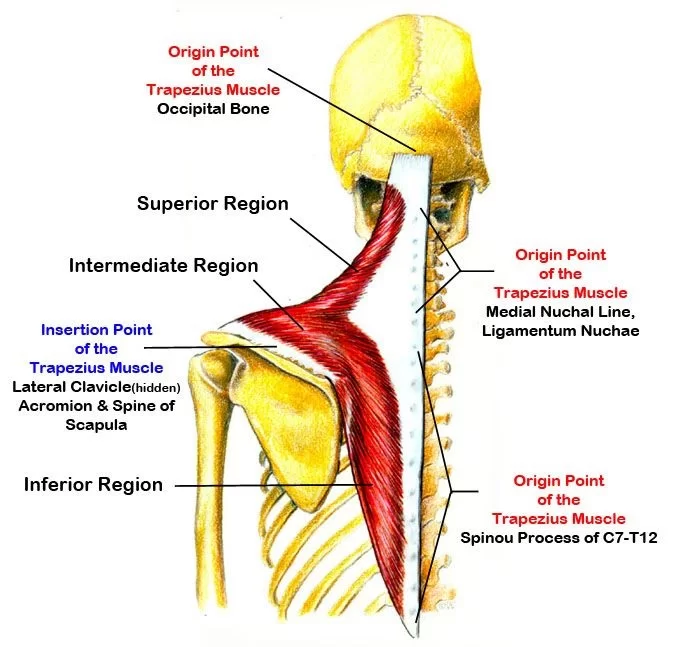
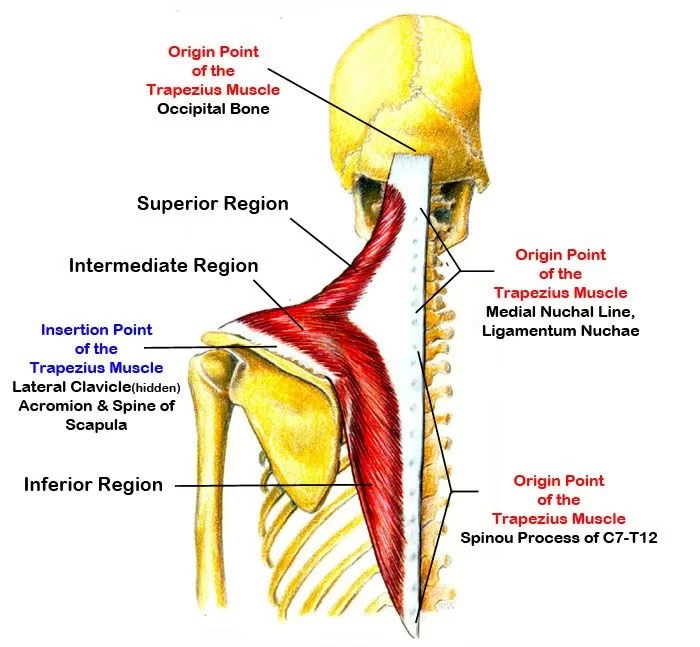
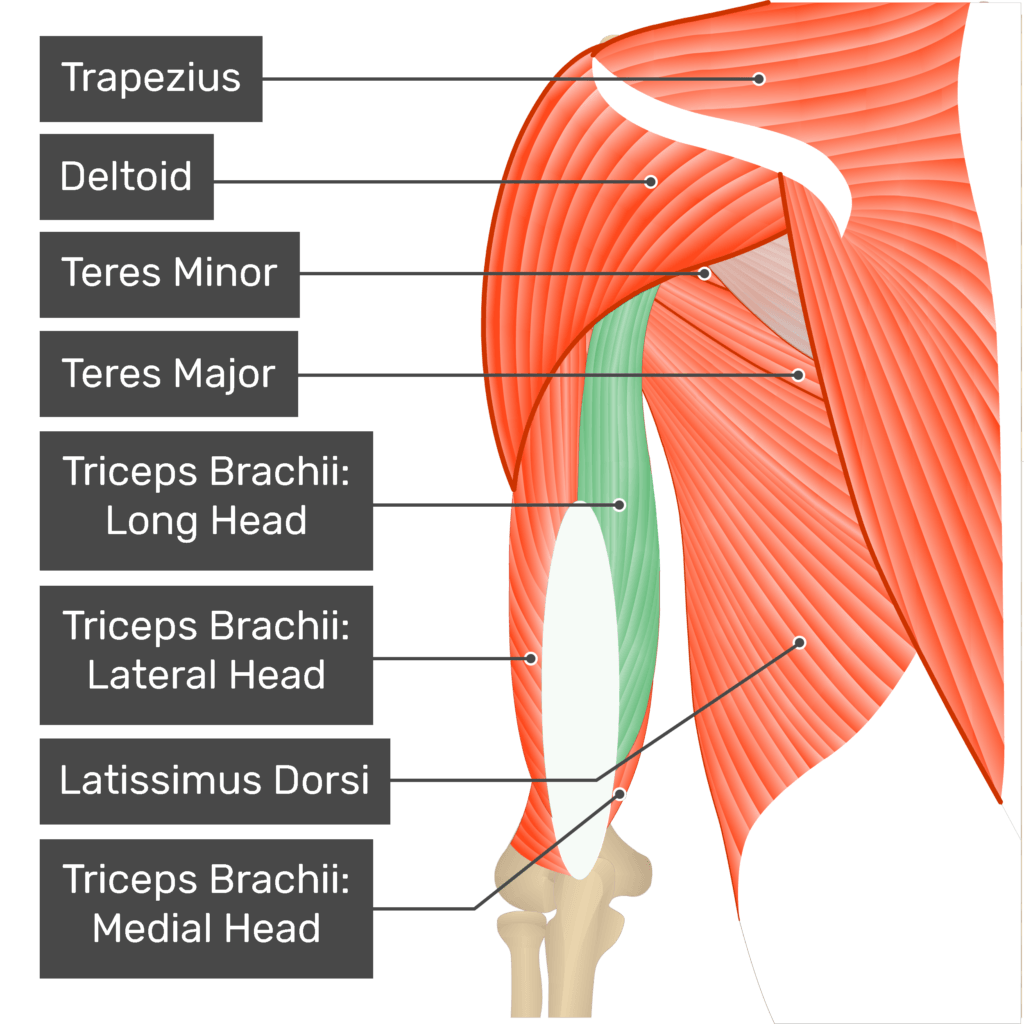
trapezius
Origin:
Nuchal line (skull)
External occipital protuberance (skull)
C7-T12 spinous processes
Insertion: spine of scapula + lateral third of clavicle + acromion
Prime Actions:
Elevates & depress scapula
retracts
upward rotation of scapula
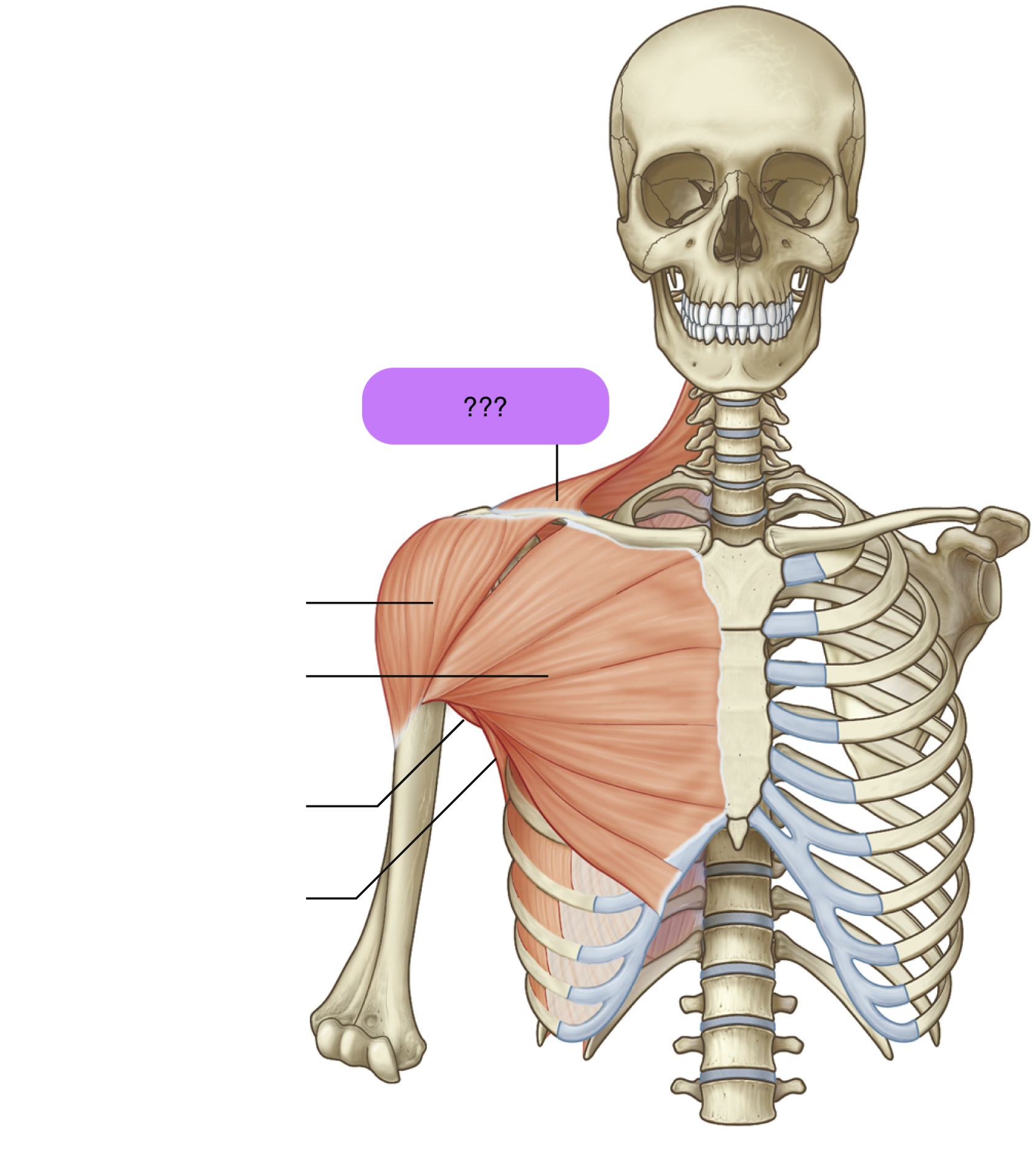
Origin:
Nuchal line (skull)
External occipital protuberance (skull)
C7-T12 spinous processes
Insertion: spine of scapula + lateral third of clavicle + acromion
Prime Actions:
Elevates & depress scapula
retracts
upward rotation of scapula
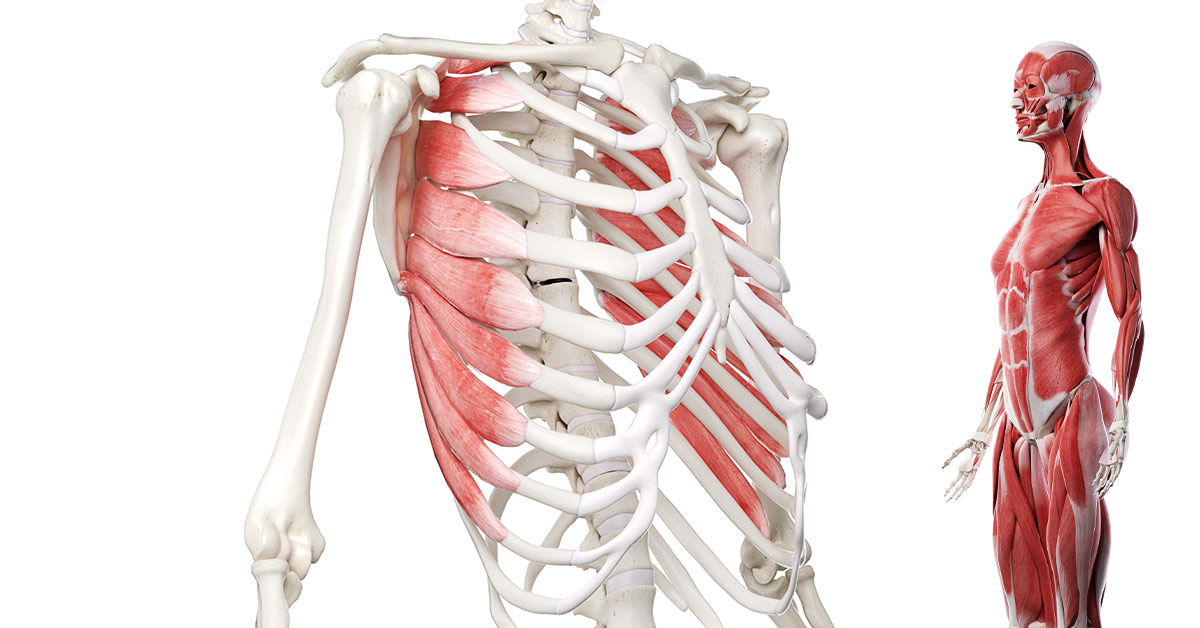
serratus anterior
Attachments: Ribs 1-8 to medial border of scapula
Prime Actions:
scapula protraction (hugging motion)
scapula depression
scapula upward rotation
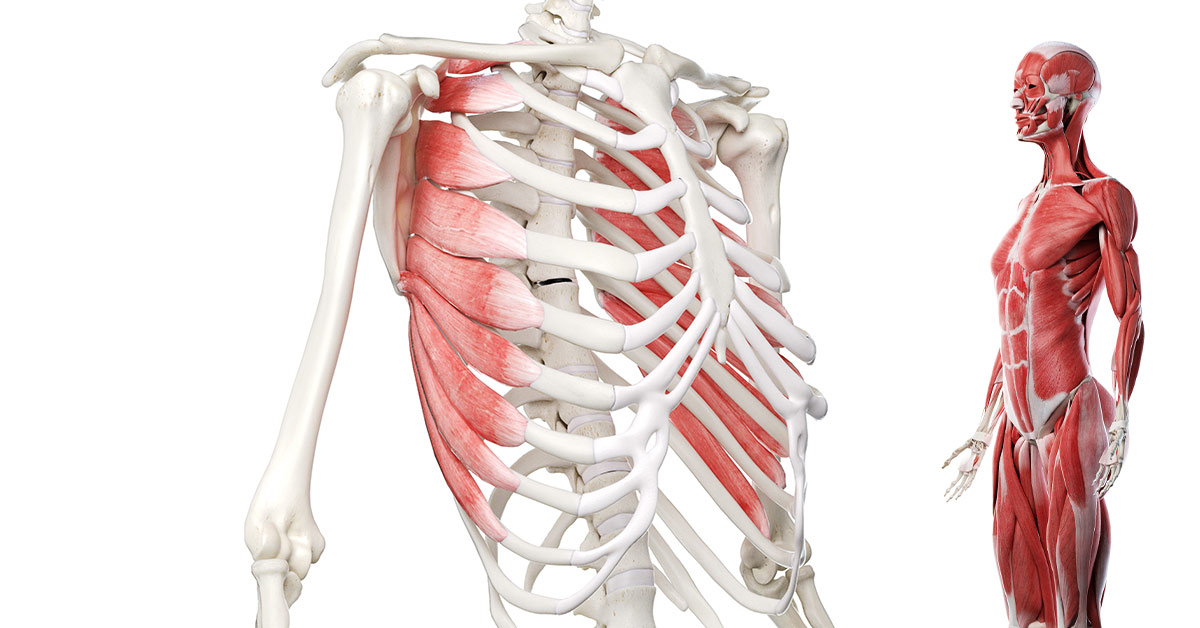
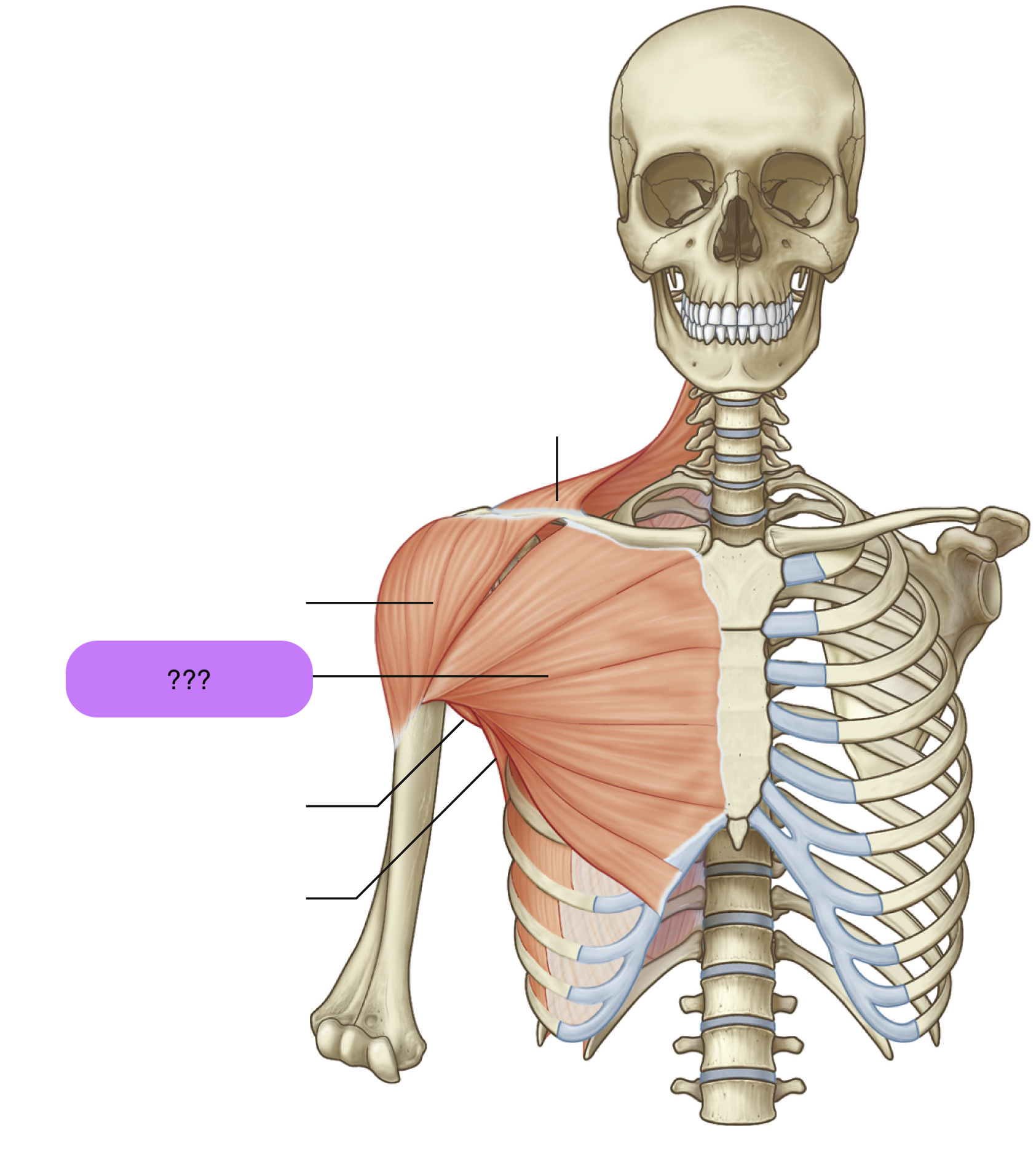
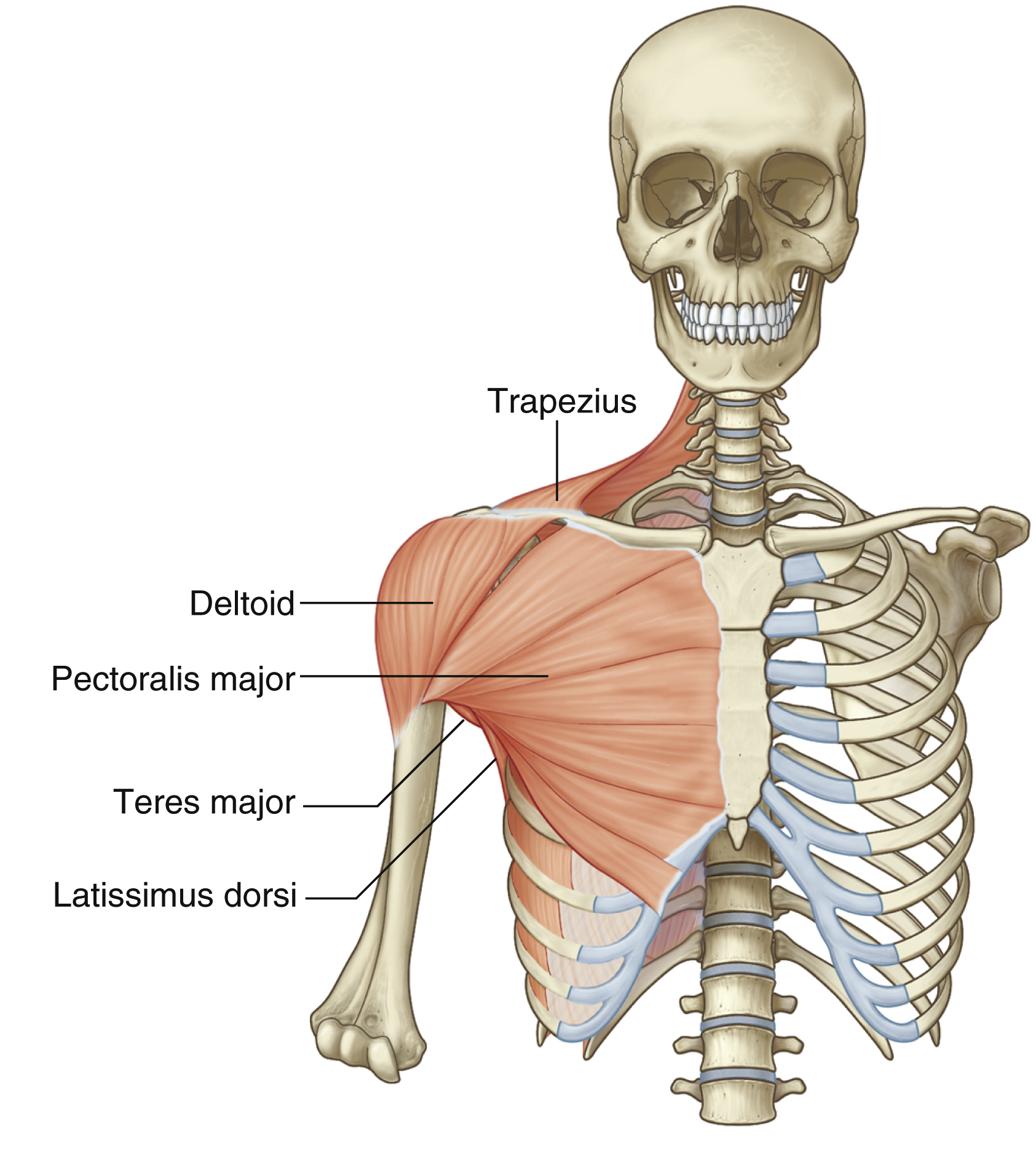
deltoid
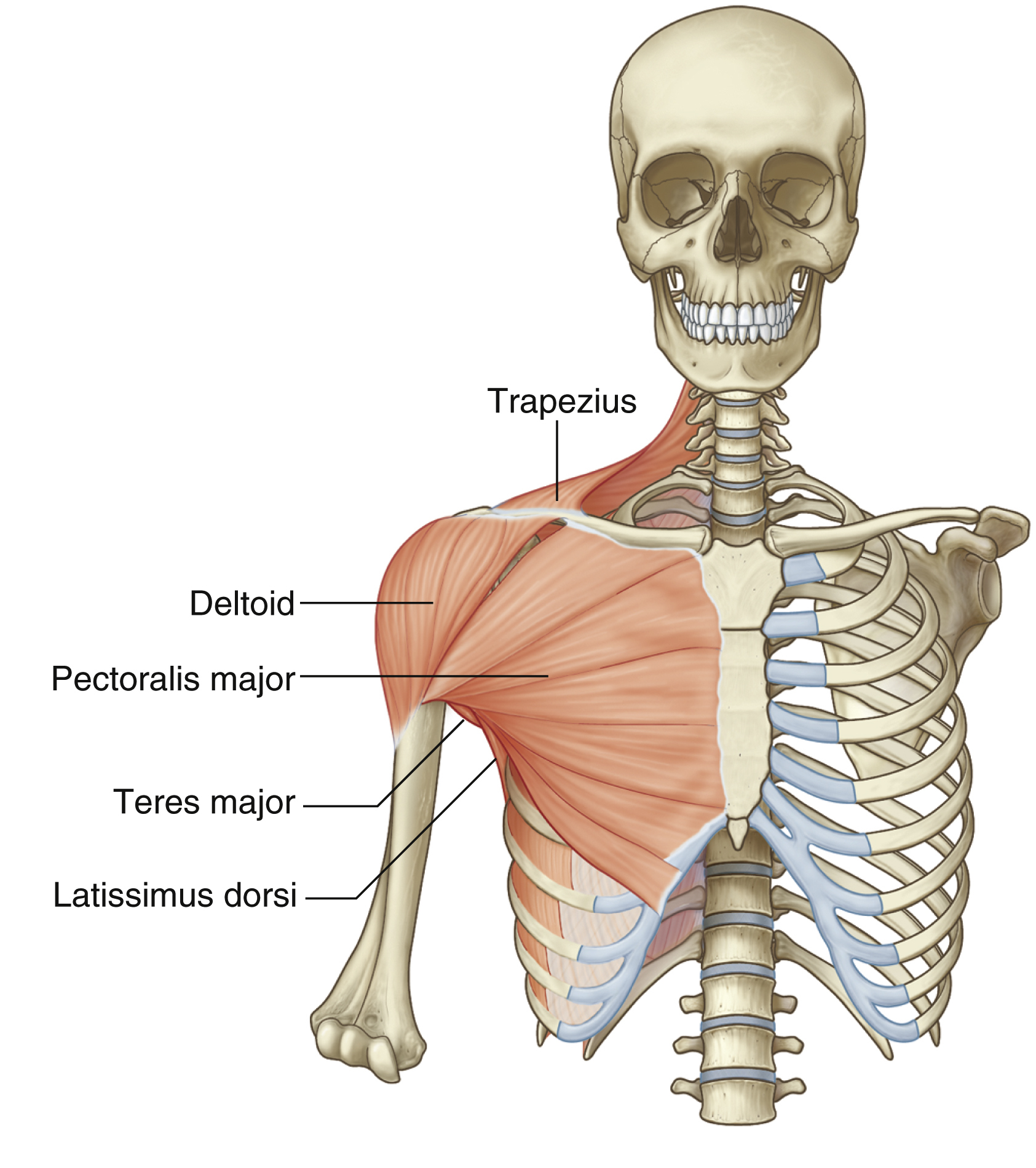
teres major
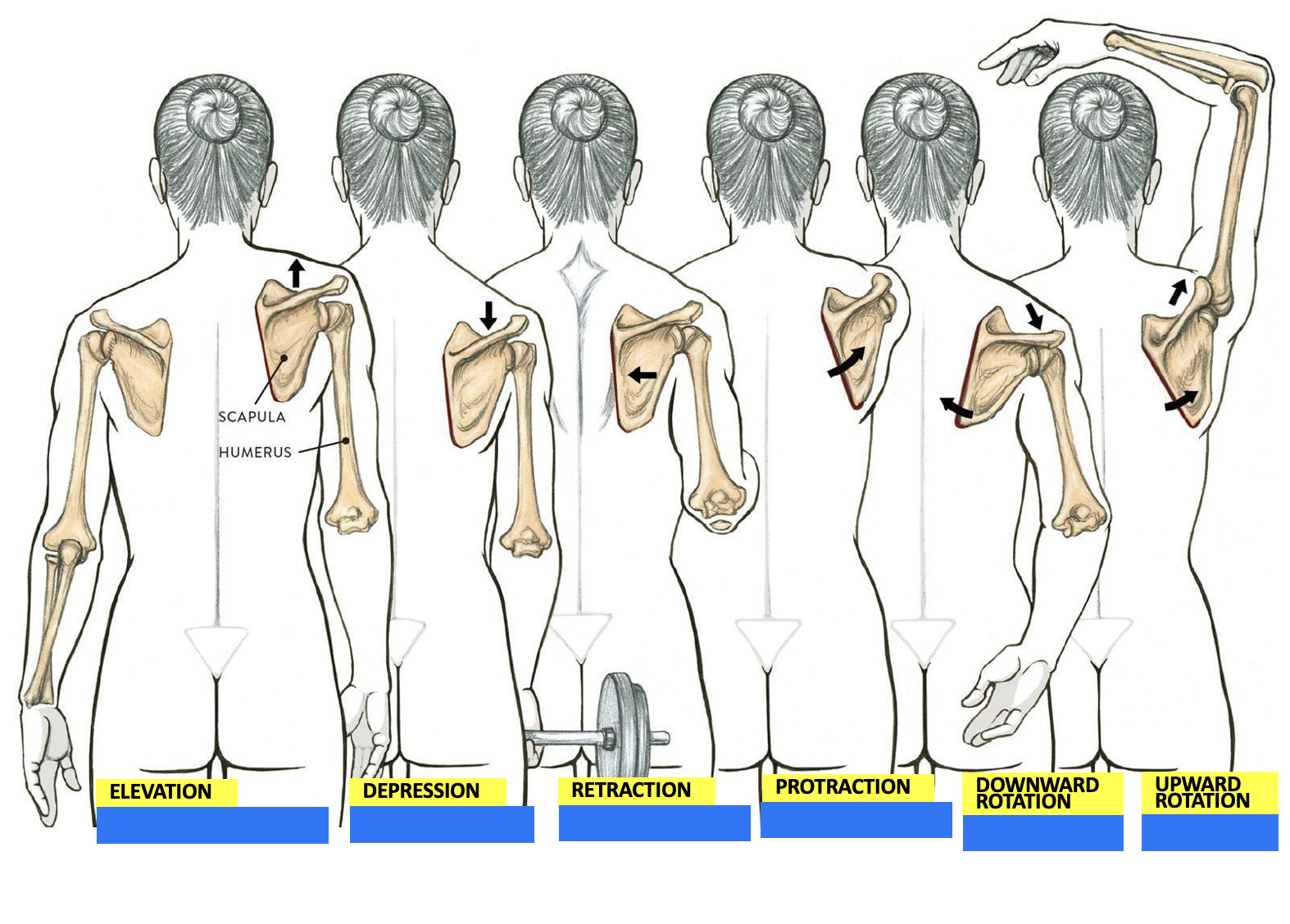
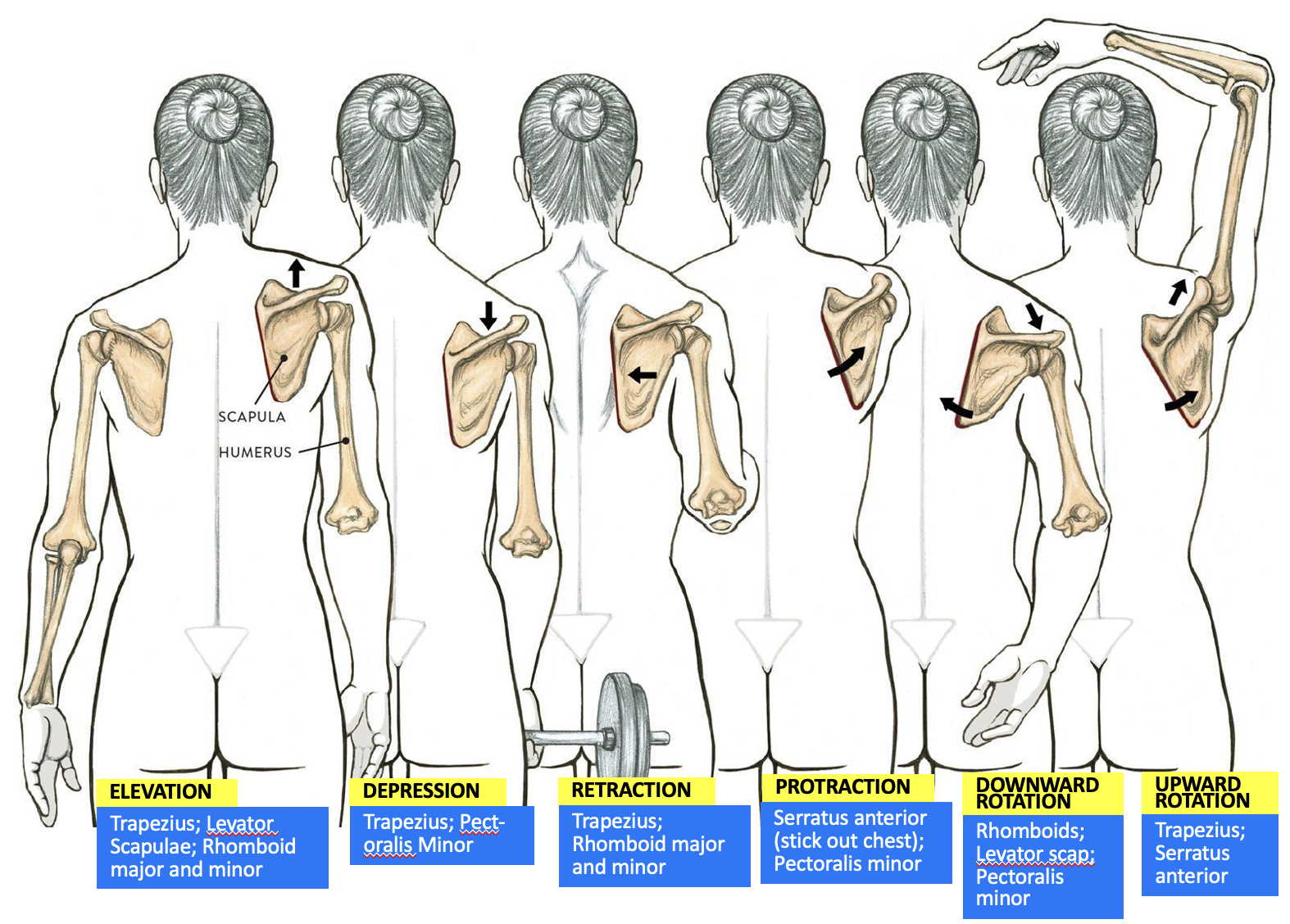
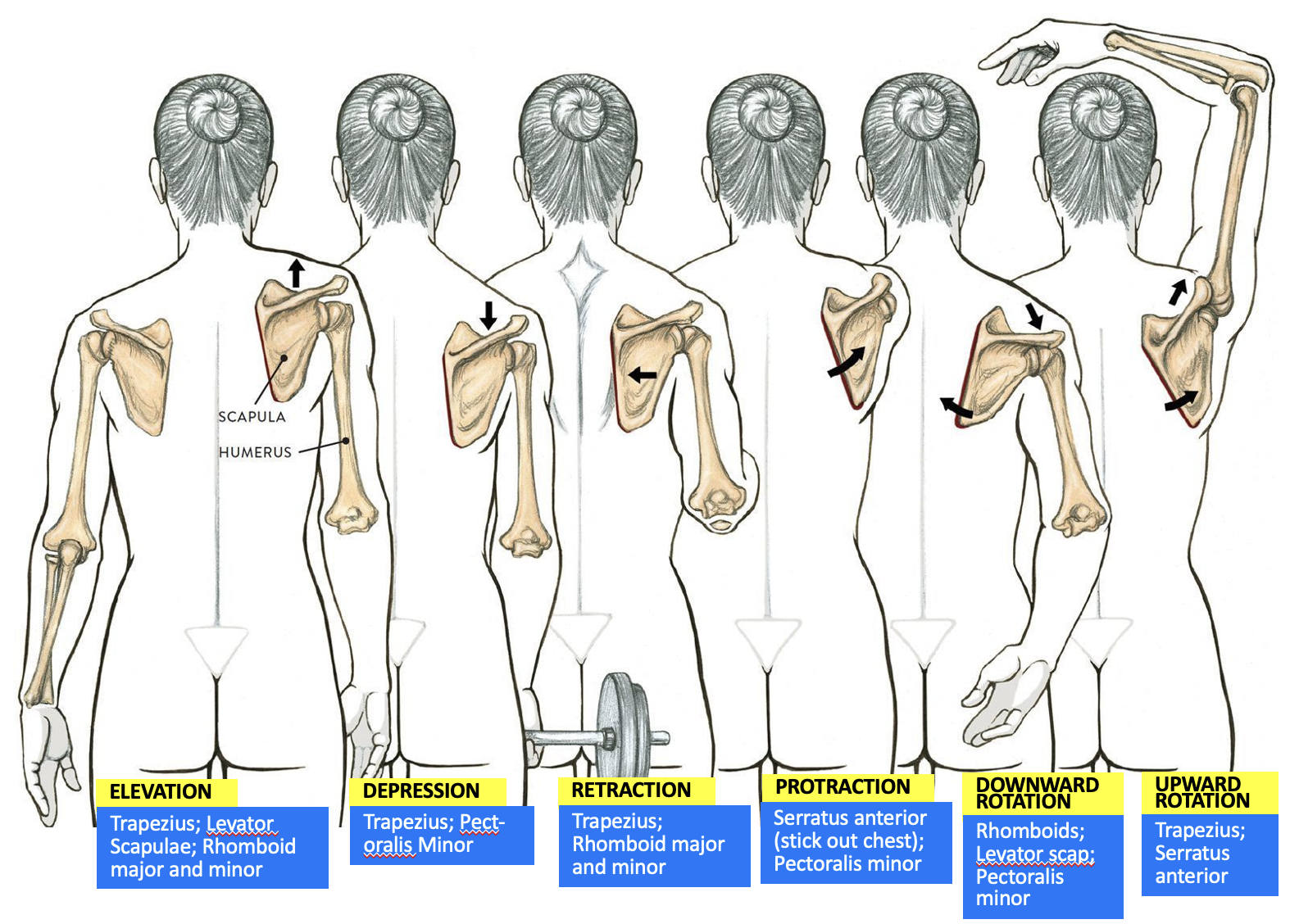
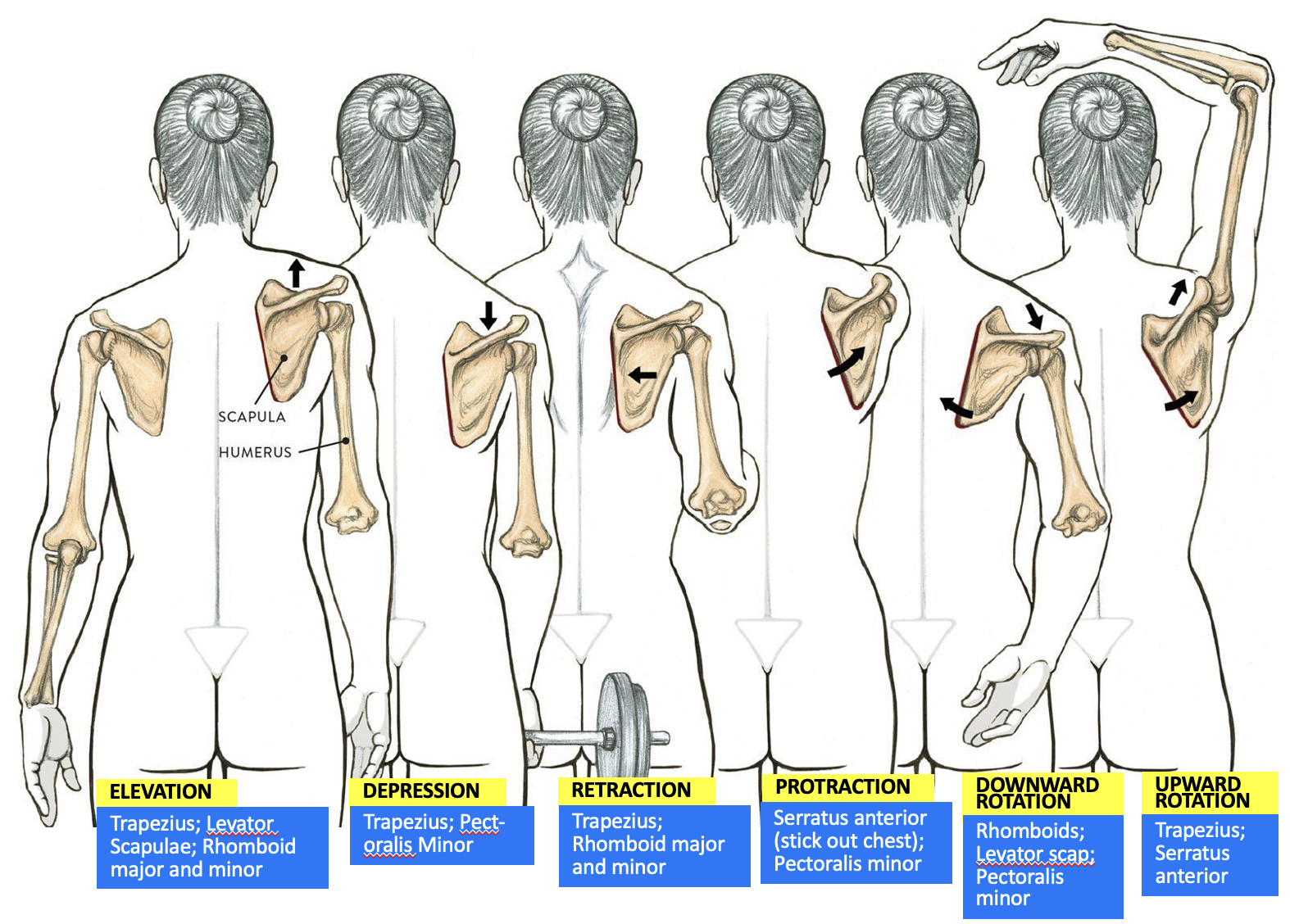
muscles responsible for scapula elevation
Trapezius
Levator Scapulae
Rhomboid major and minor
muscles responsible for scapula depression
Trapezius
Pectoralis minor
muscles responsible for scapula retraction
Trapezius
Rhomboid major and minor
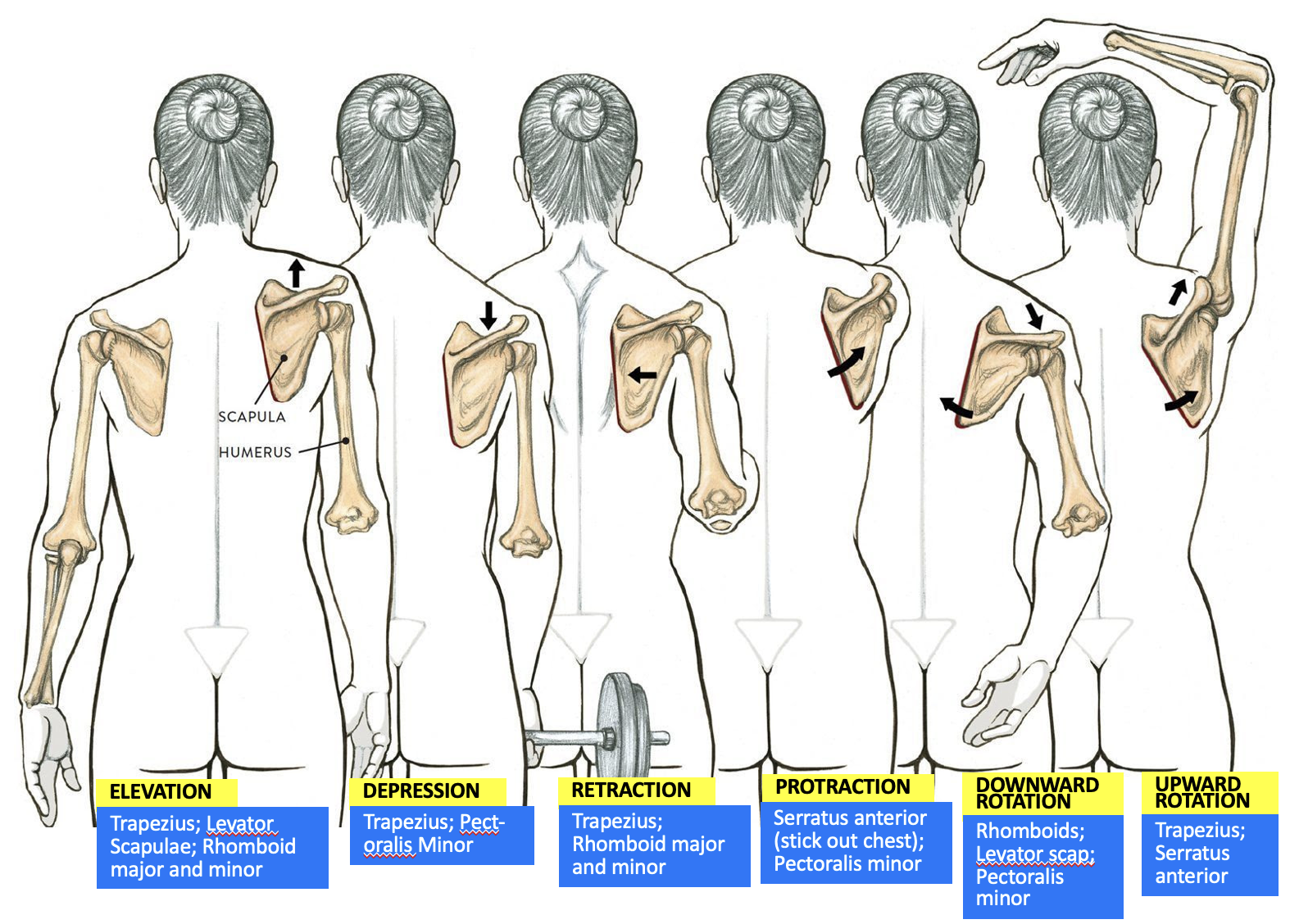
muscles responsible for scapula protraction
Serratus anterior
Pectoralis minor
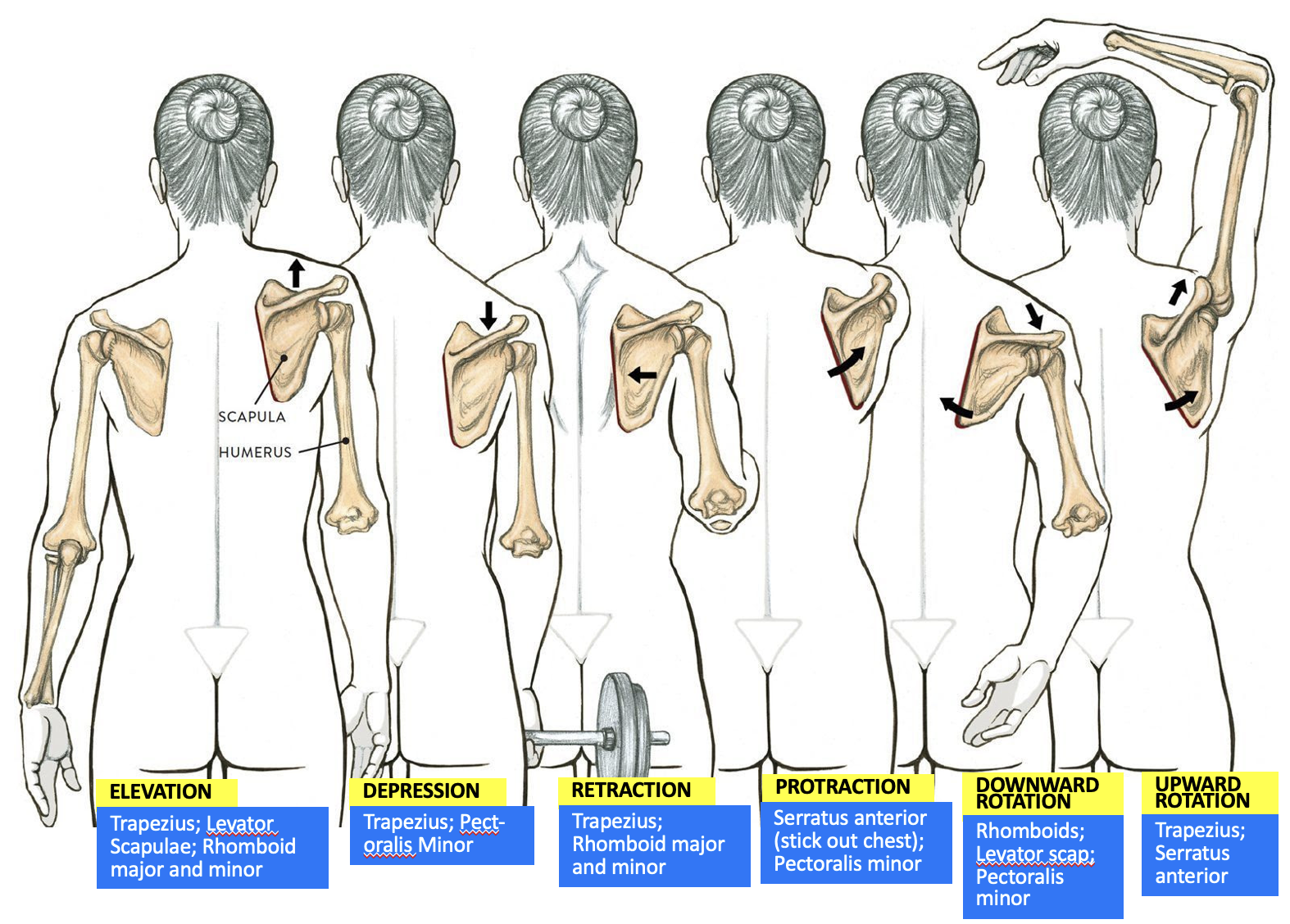
muscles responsible for scapula downward rotation
Rhomboid major and minor
Levator scapulae
Pectoralis minor
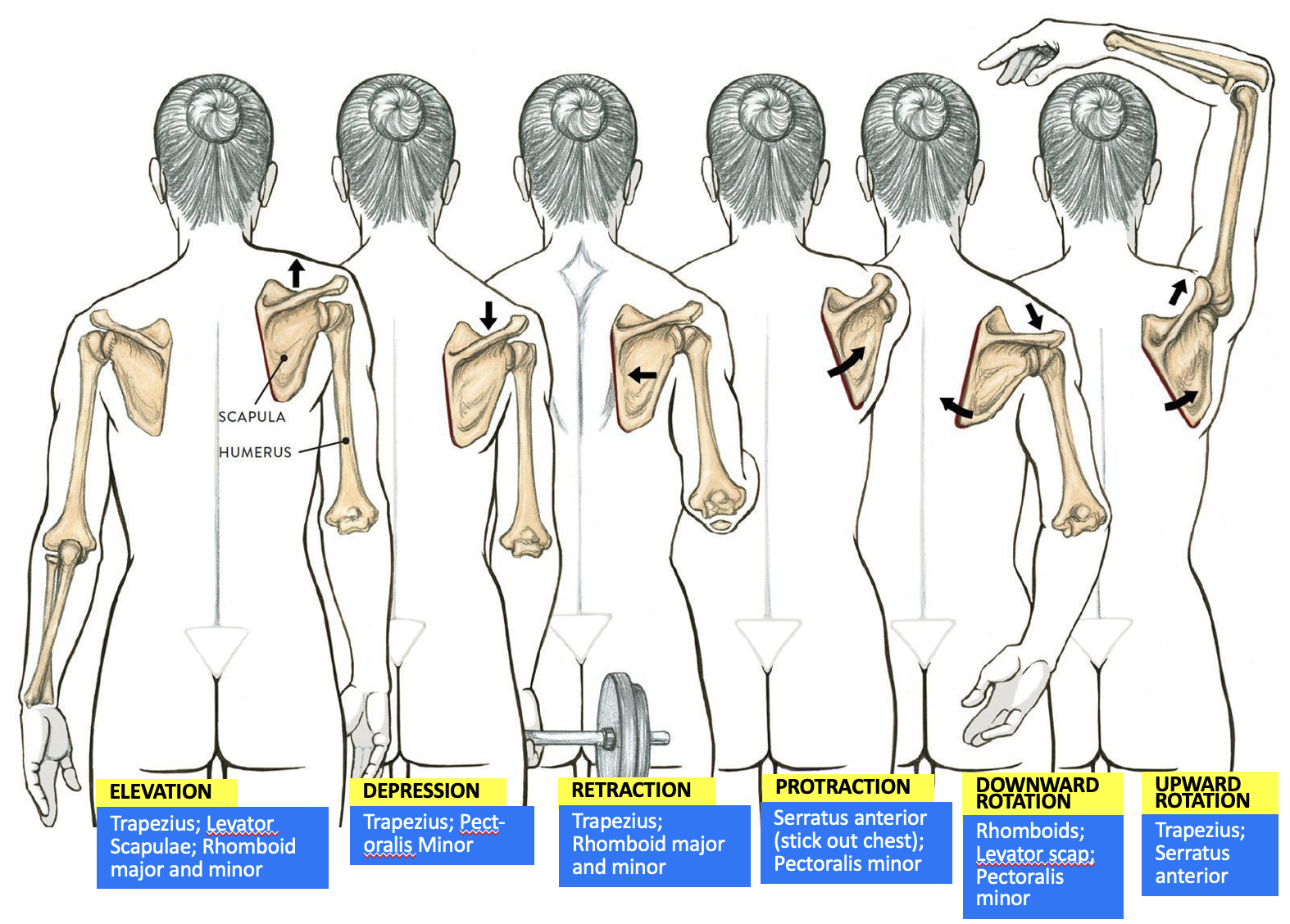
muscles responsible for scapula upward rotation
Trapezius
Serratus anterior
deltoid origin and insertion
Origins:
lateral 1/3 clavicle
acromion
scapular spine
insertion:
deltoid tuberosity
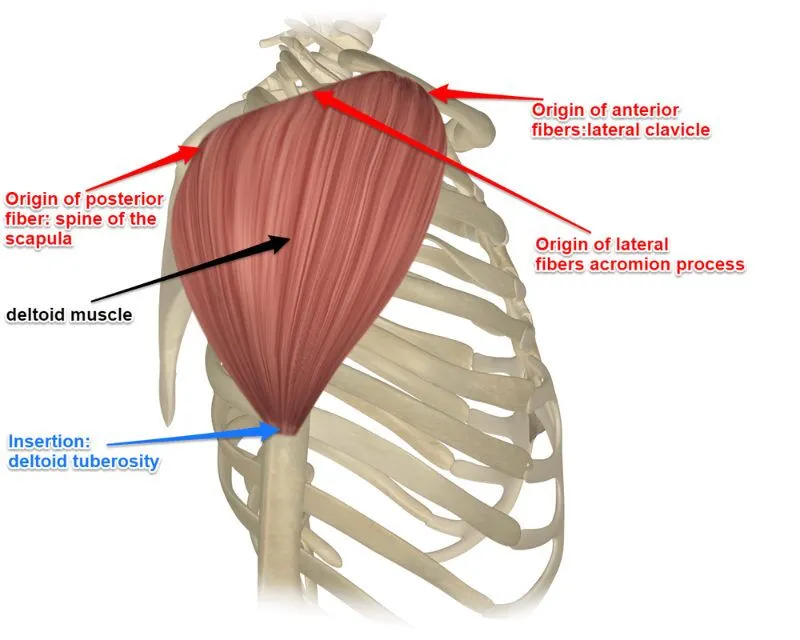
deltoid actions
shoulder abduction (flexion & extension)
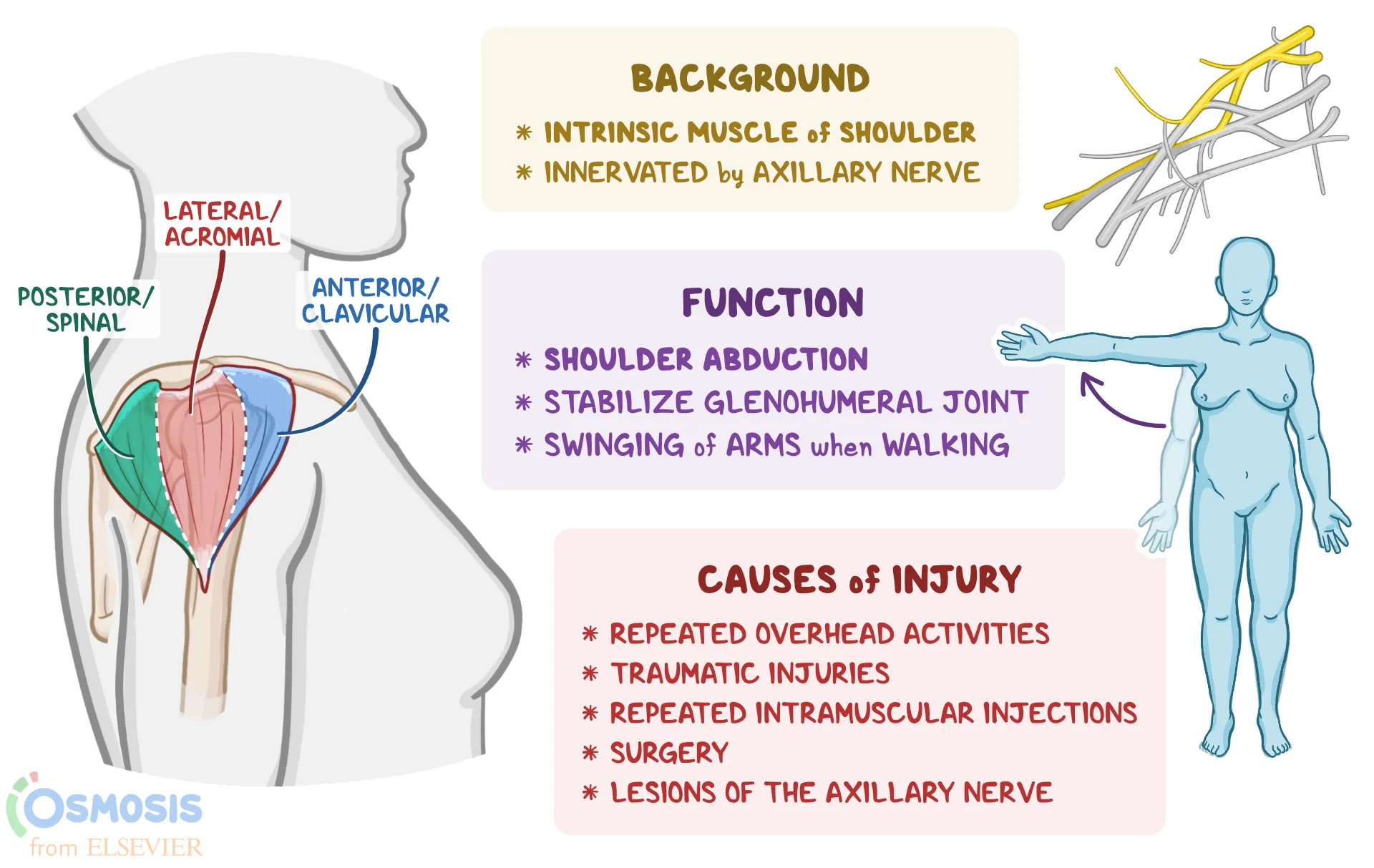
deltoid nerve supply
axillary nerve (C5)
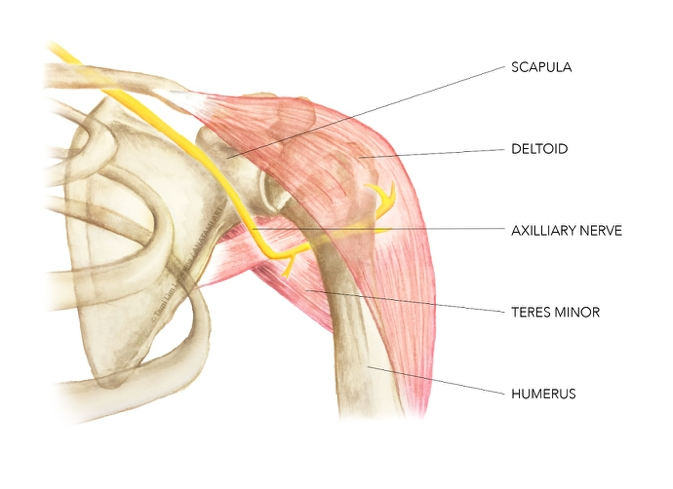
dynamic ligaments
required to stabilise the shoulder (restrain it to prevent a shoulder joint subluxing when deltoid muscle contracts)
muscles of the rotator cuff perform this role
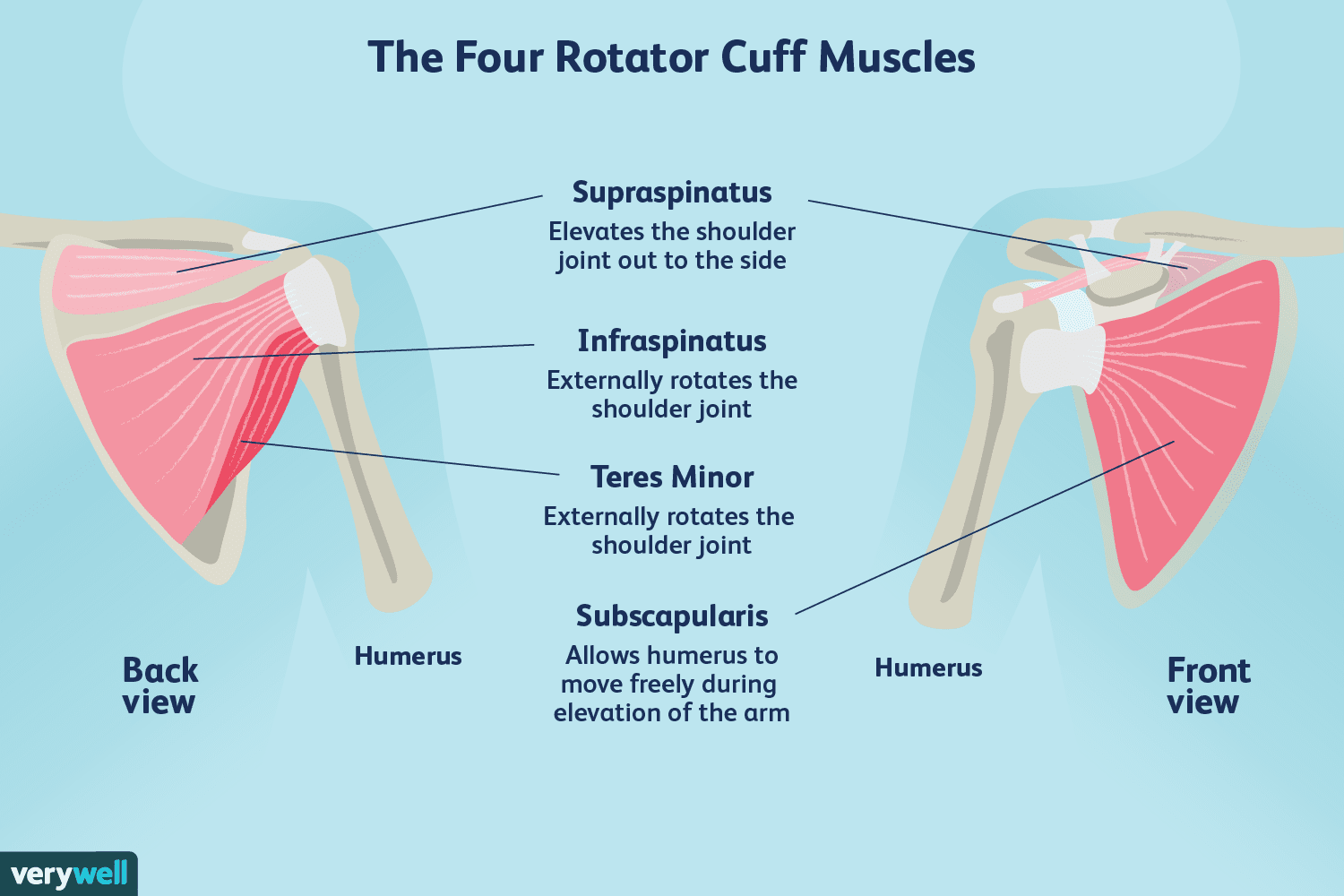
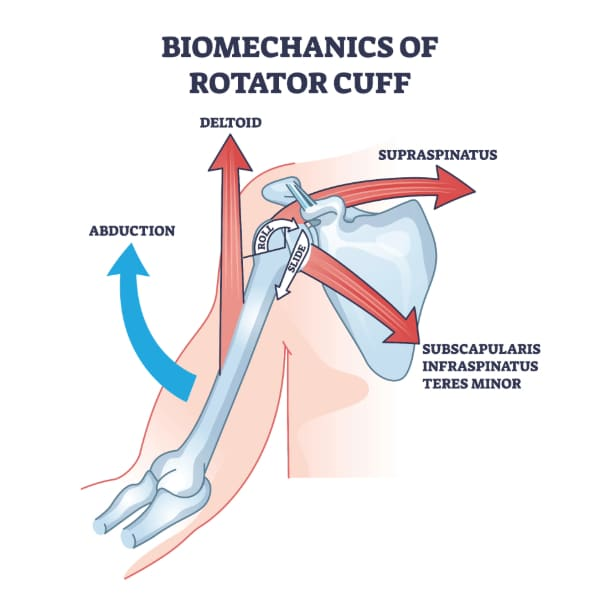
supraspinatus
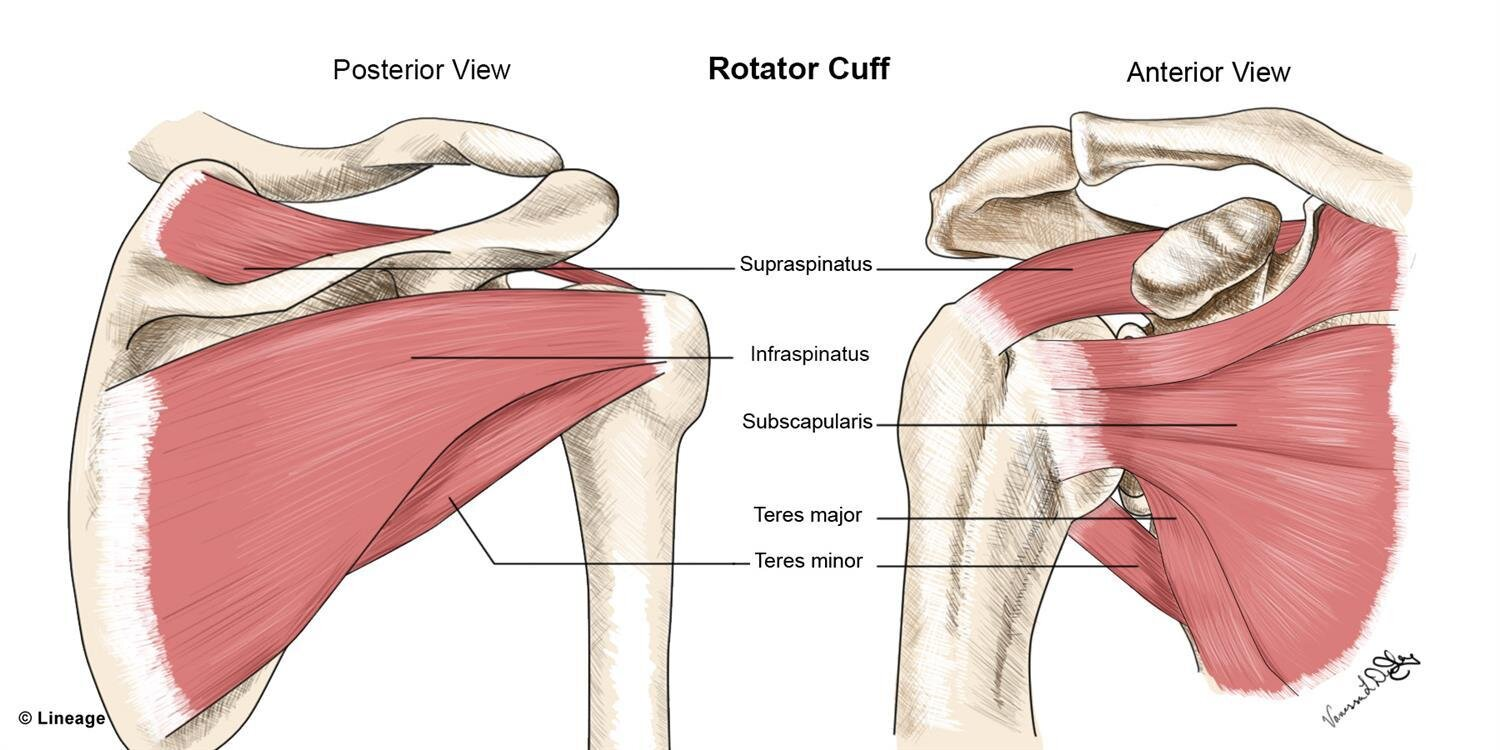
supraspinatus origins and insertions
origin:
medial ¾ supraspinous fossa and spine
insertion:
smooth facet on upper part of GT
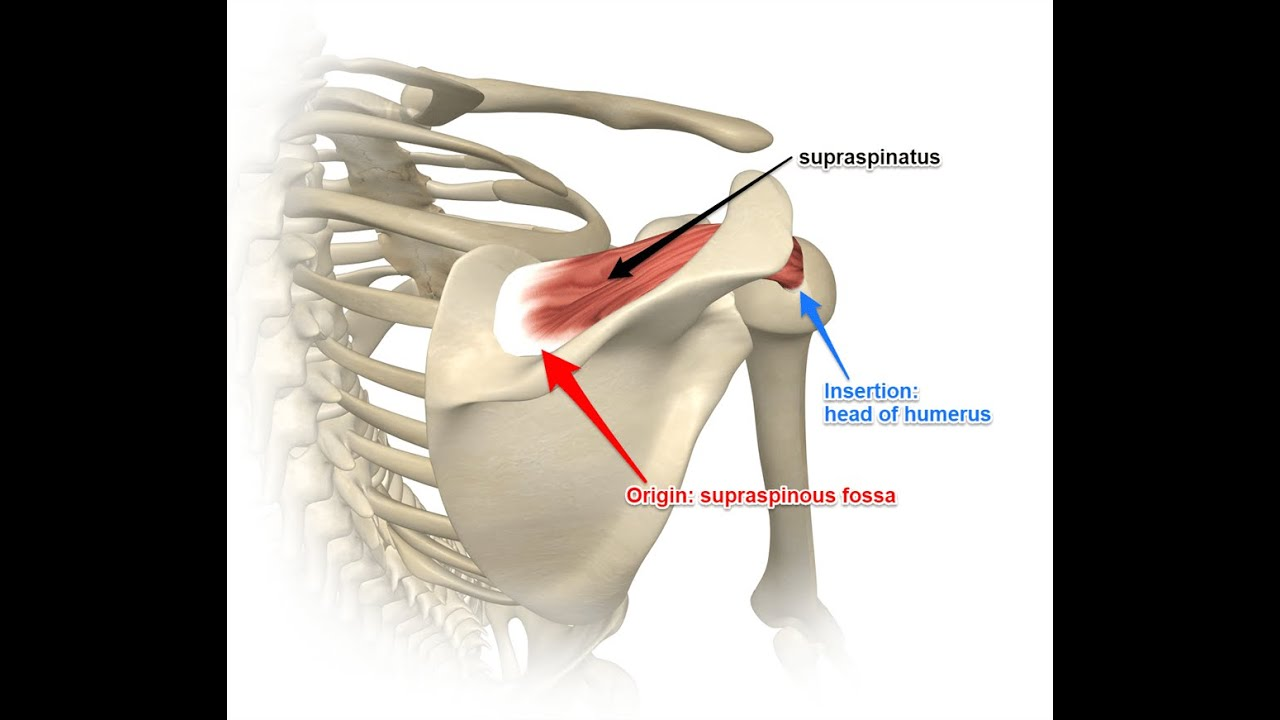
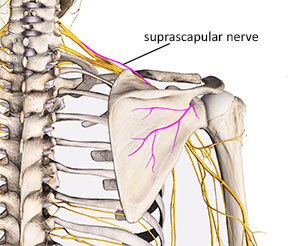
supraspinatus nerve supply
suprascapular nerve (C5)
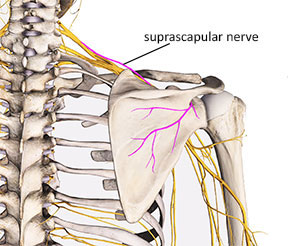
supraspinatus actions
stabilises head of humerus
initiates abduction
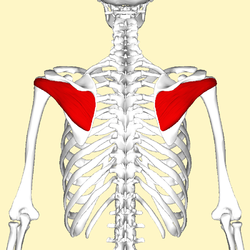
infraspinatus (posterior)
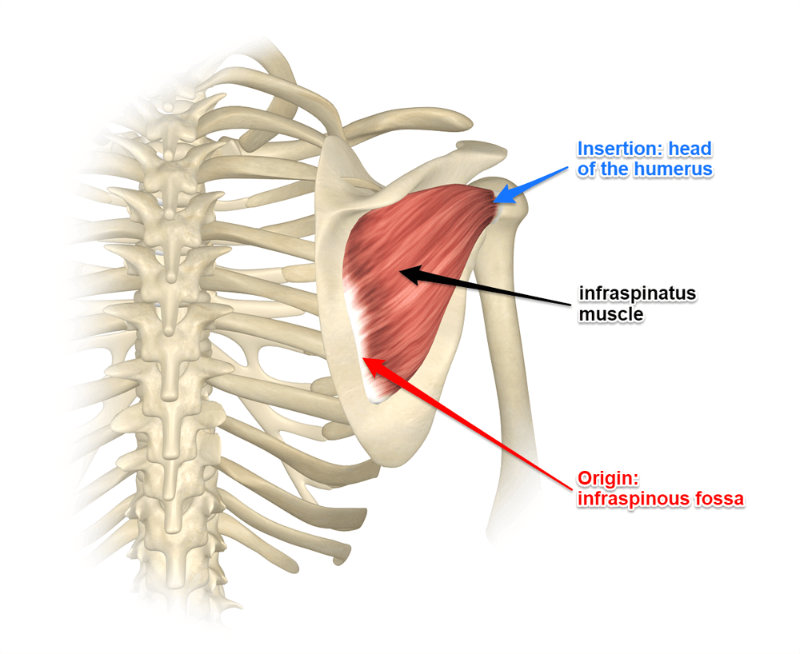
infraspinatus origin and insertion
origin: infraspinous fossa
insertion: greater tuberosity (central facet)
infraspinatus nerve supply
suprascapular nerve (C5)
infraspinatus action
stabilises head of humerus
GH external rotation
teres minor
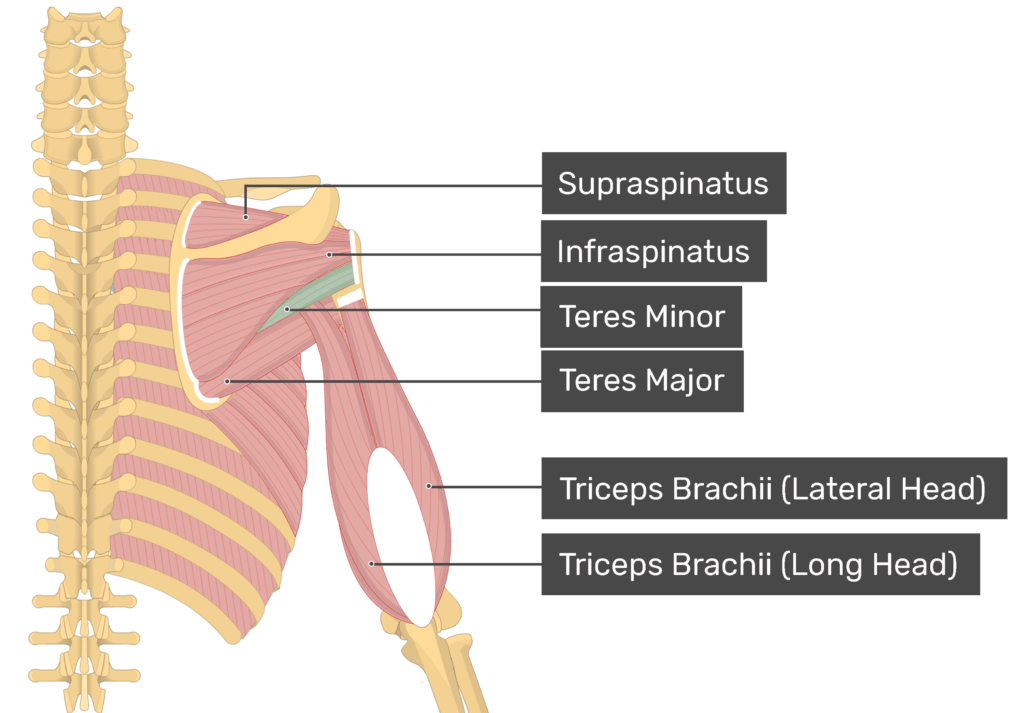
teres minor origin and insertion
origin: lateral scapular border
insertion: greater tuberosity (lowest facet)
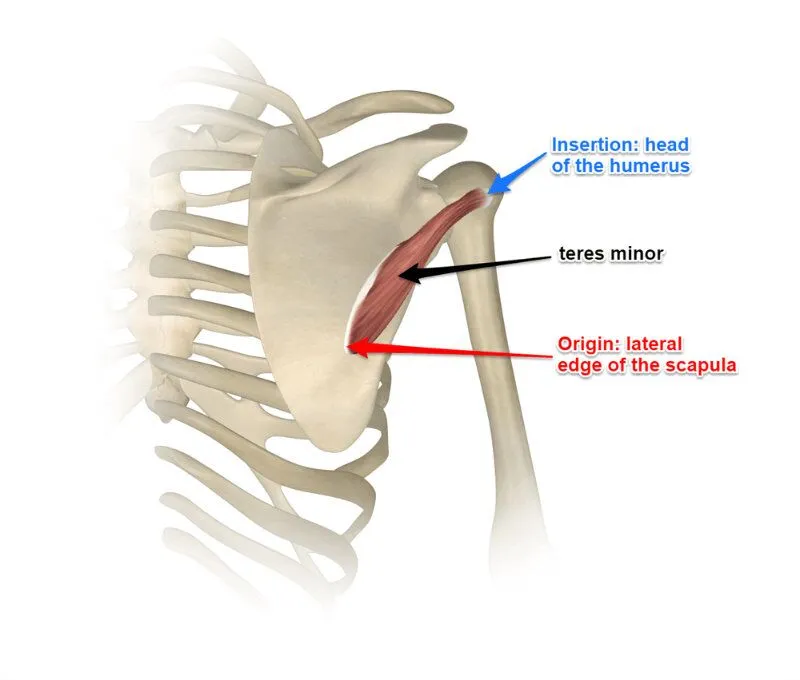
teres minor nerve supply
axillary nerve (C5)
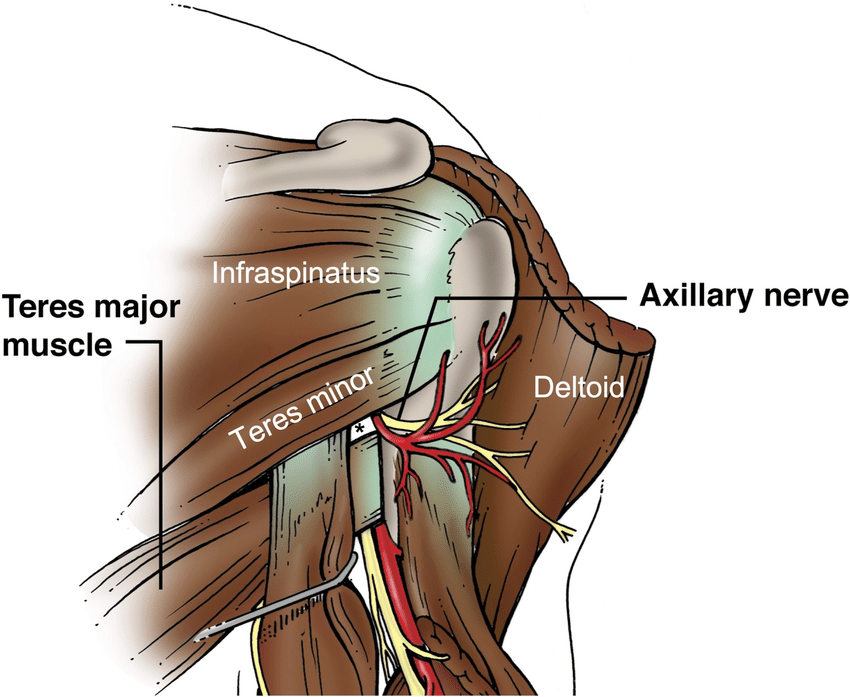
teres minor action
stabilises head of humerus
external/lateral rotation
(weak adduction)
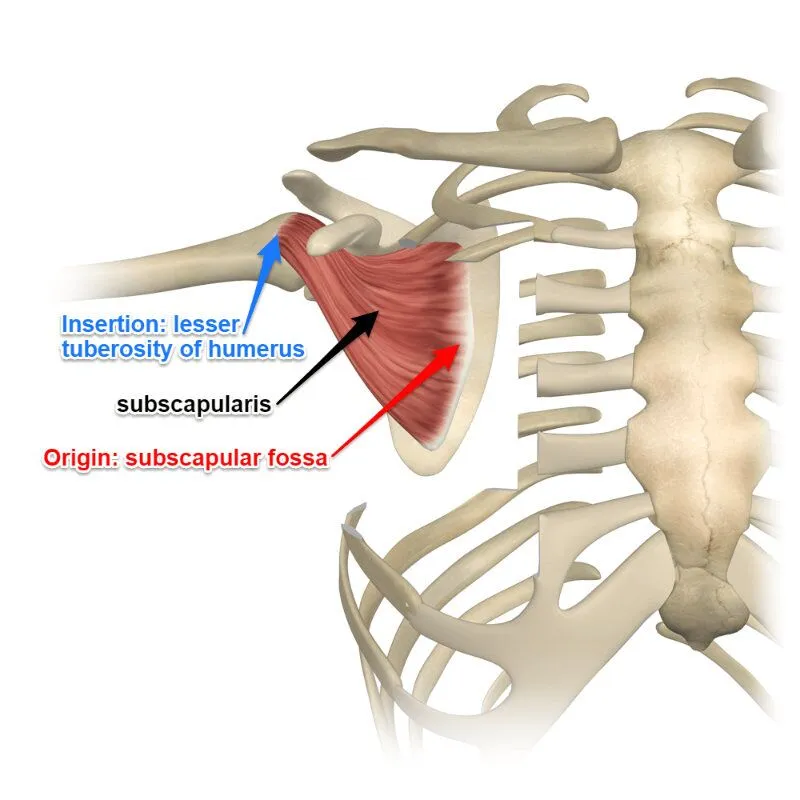
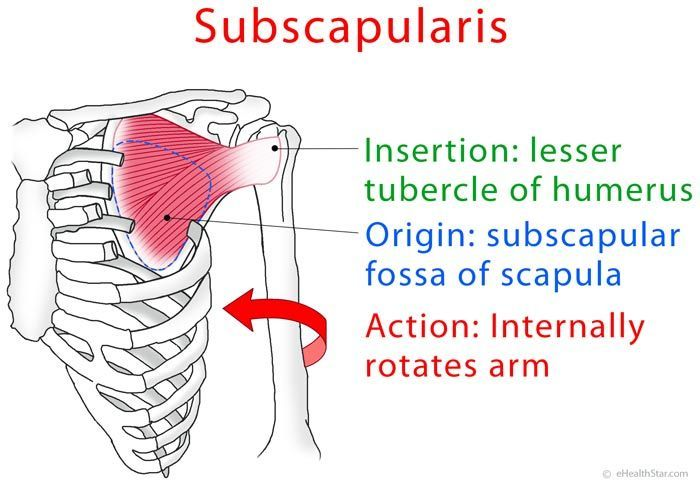
subscapularis (anterior)
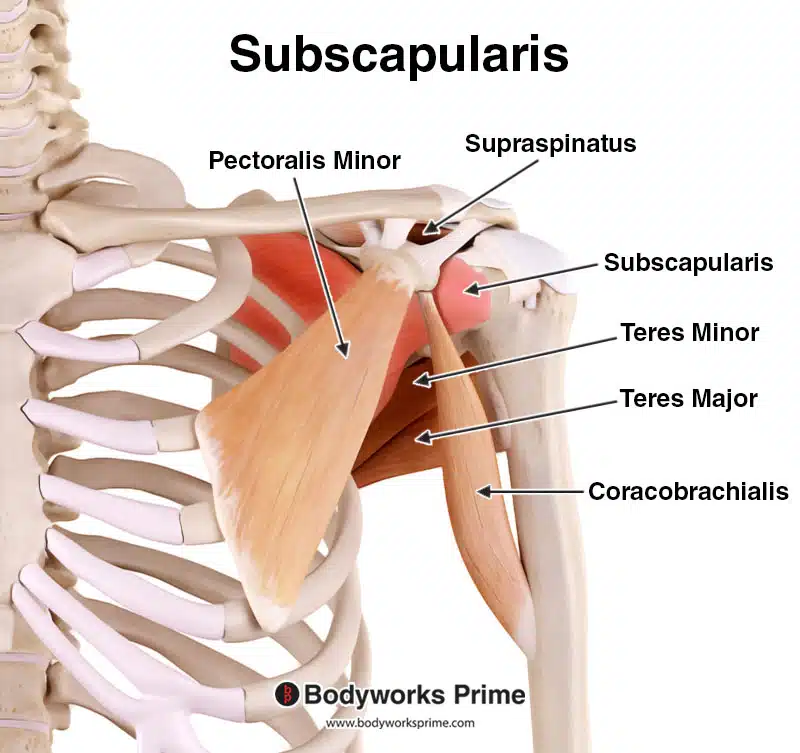
subscapularis origin and insertion
origin: scapula costal surface
insertion: lesser tuberosity
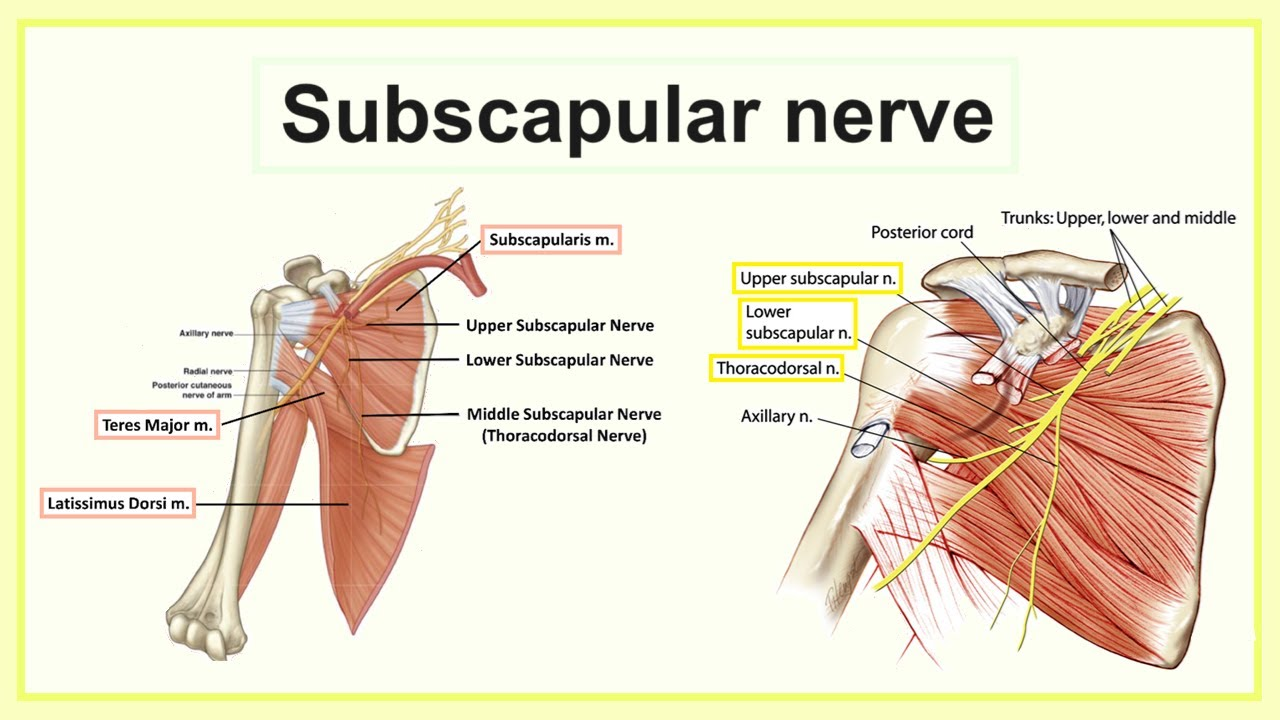
subscapularis nerve supply
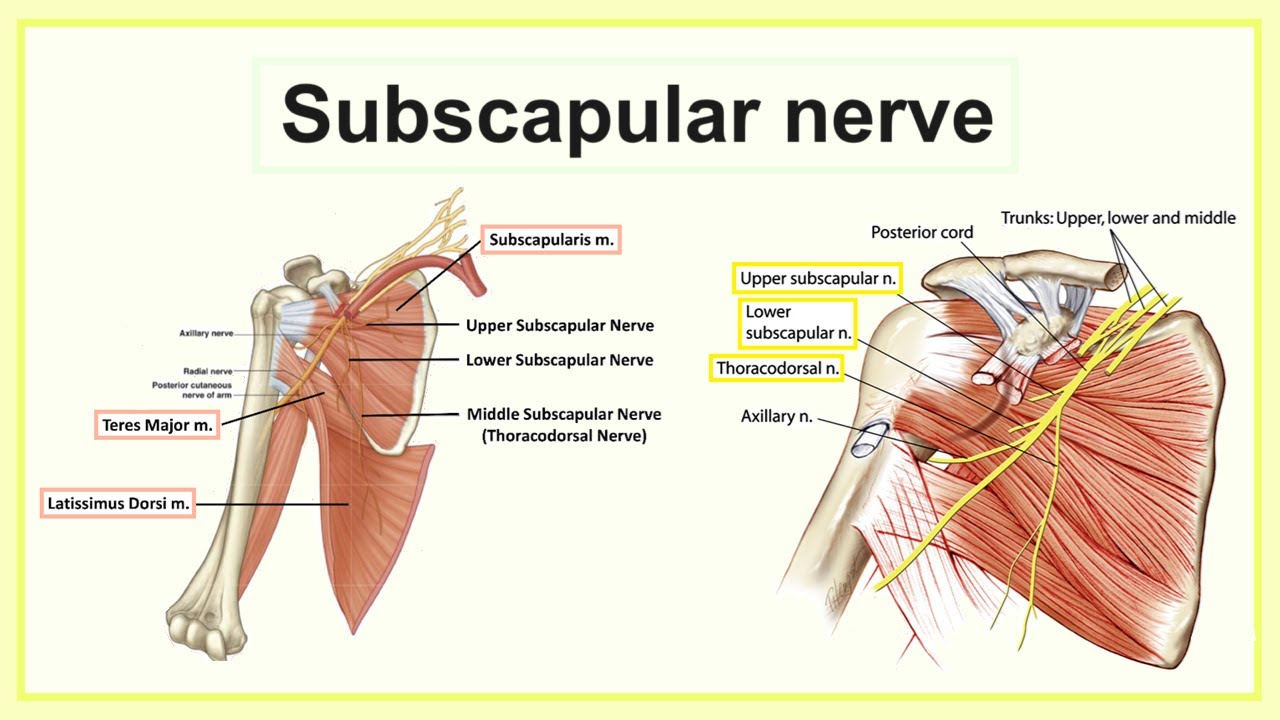
upper and lower subscapular nerves (C6, C7)
subscapularis action
stabilises head of humerus
internal/medial rotation
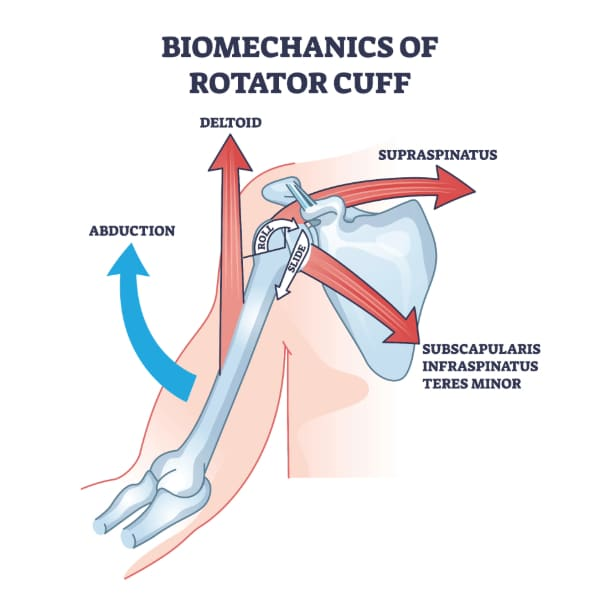
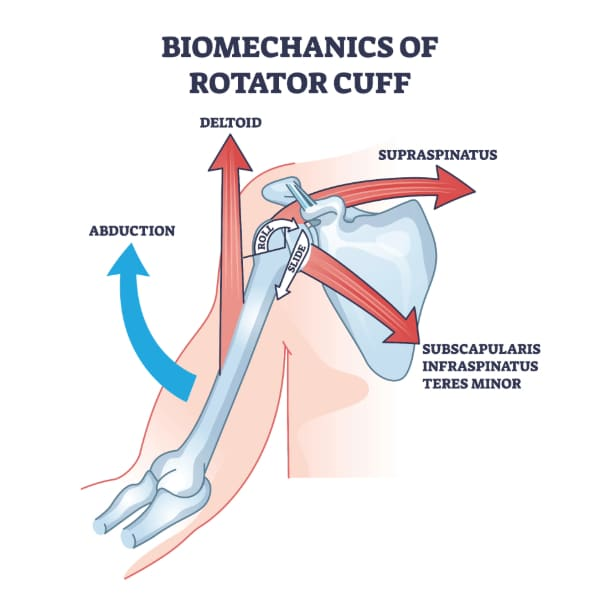
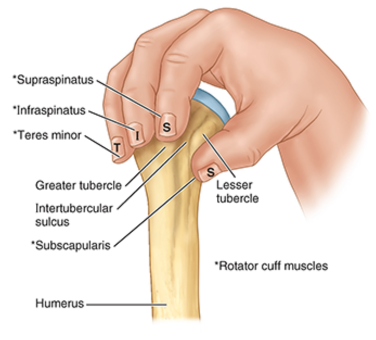
four muscles (rotator cuff muscles) sitting on the head of the humerus and function
function: stability and motility of the should (GH) joint during abduction and rotation
muscles:
S: Supraspinatus
I: Infraspinatus
T: Teres Minor
S: Subscapularis
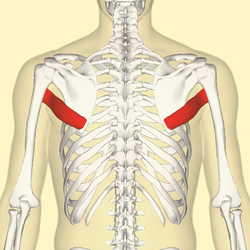
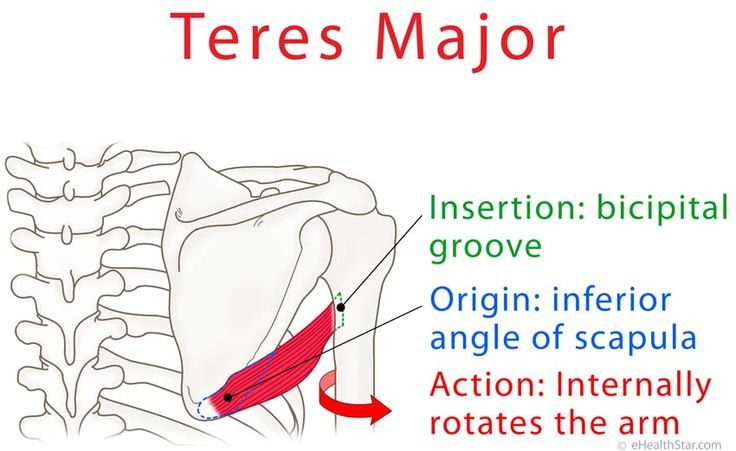
teres major
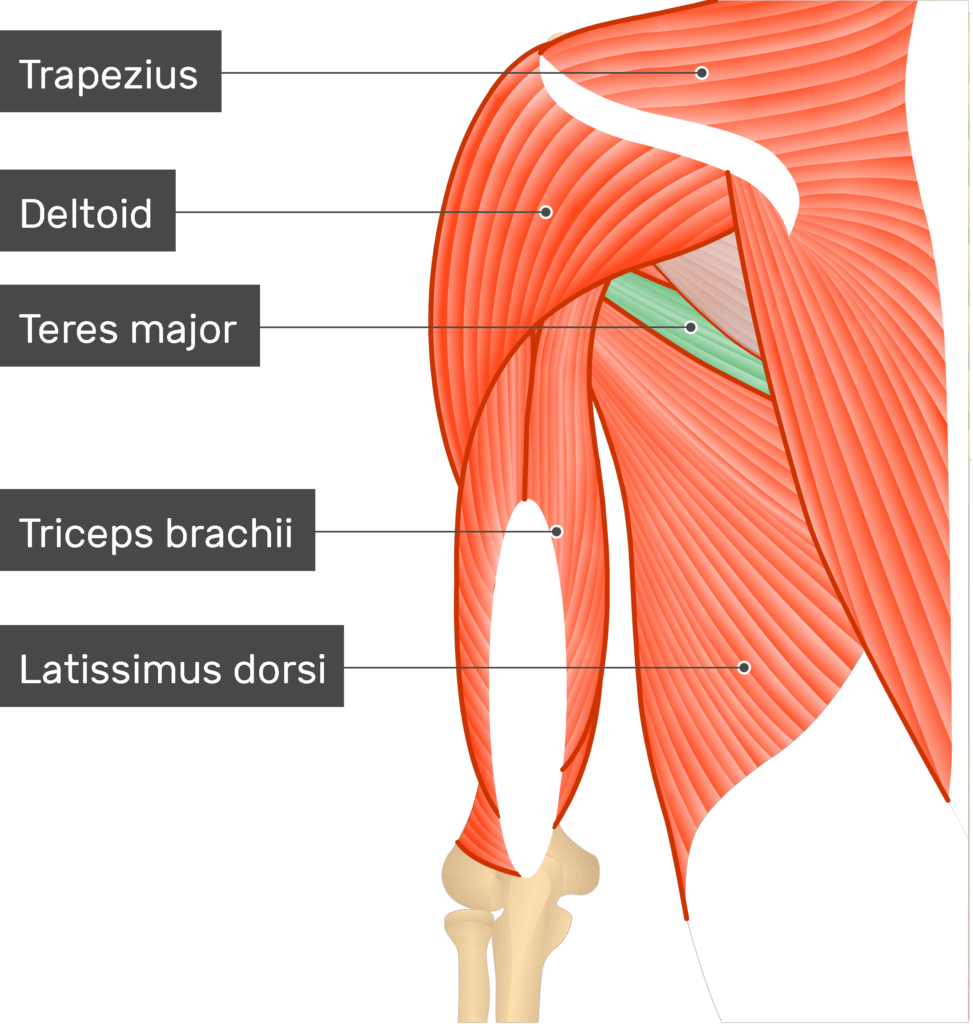
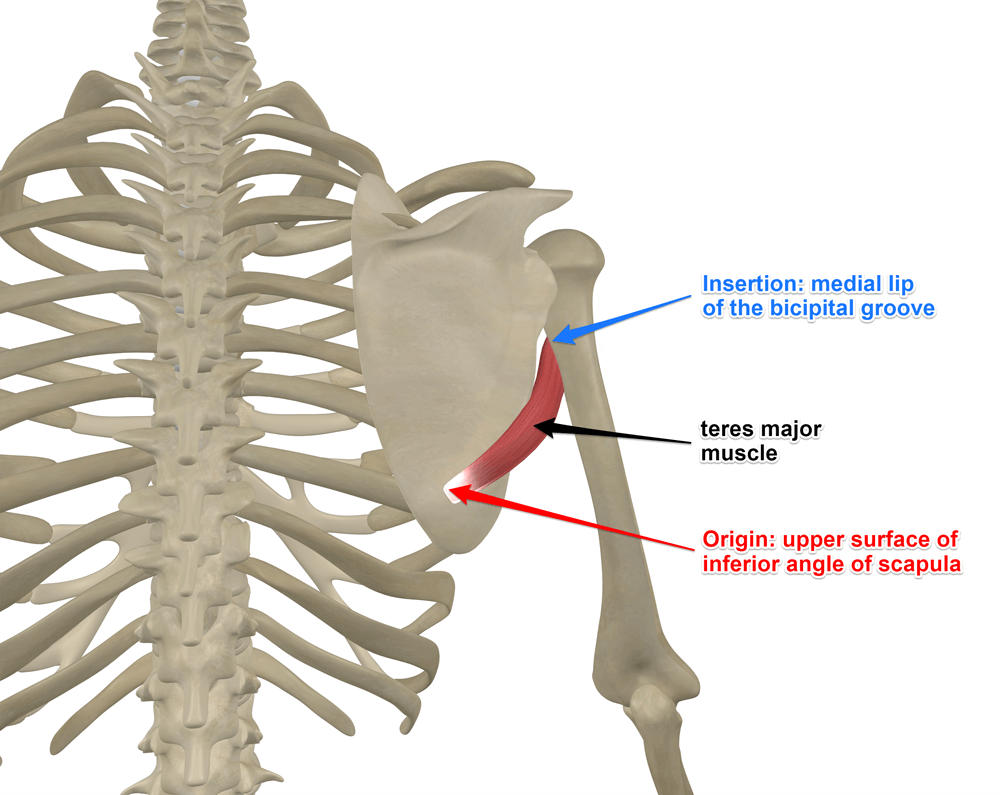
teres major origin and insertion
origin: lateral, inferior scapular angle
insertion: medial bicipital groove (below subscapularis)
teres major nerve supply
lower subscapular nerve
teres major action
stabilises upper humerus (against action of deltoid)
adductor
medial humerus rotation
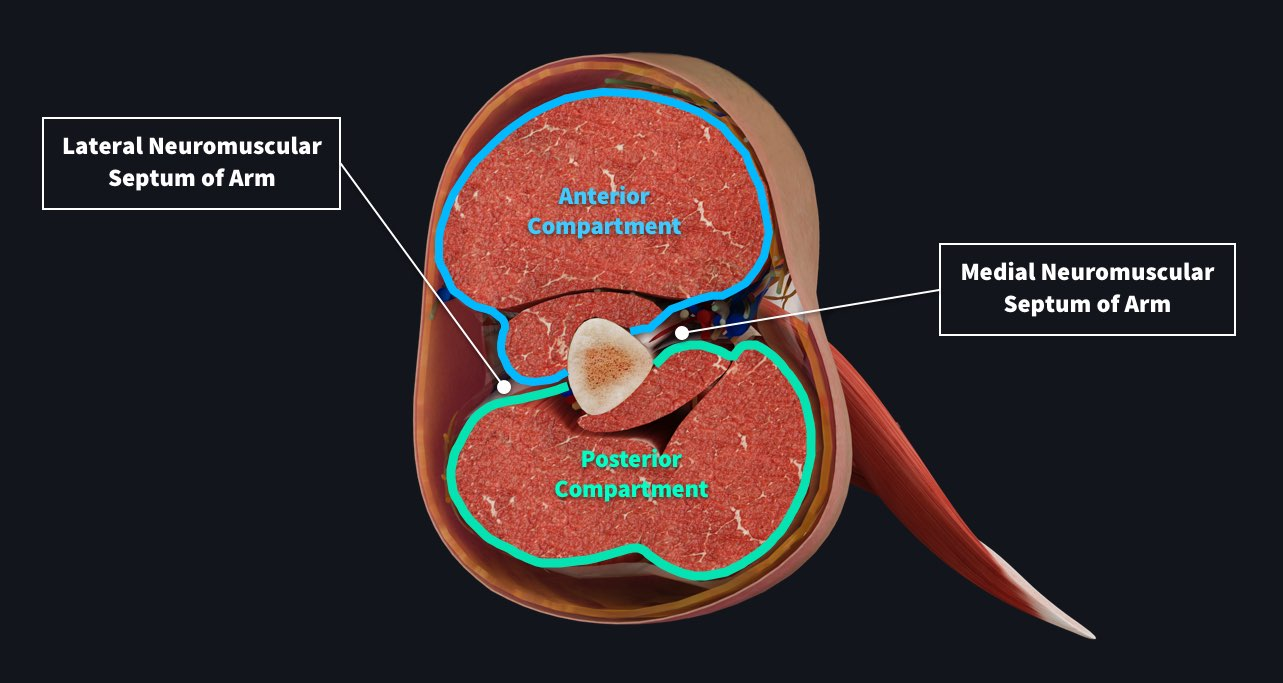
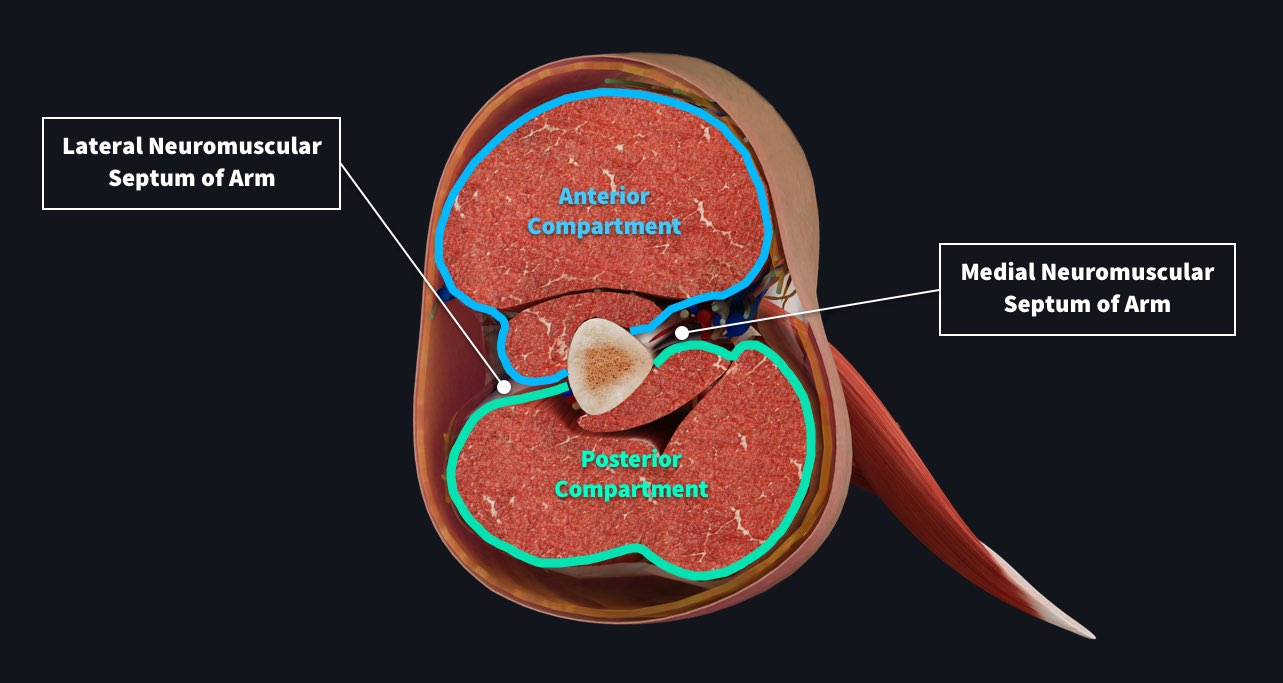
humerus posterior compartment
triceps brachii
anconeus
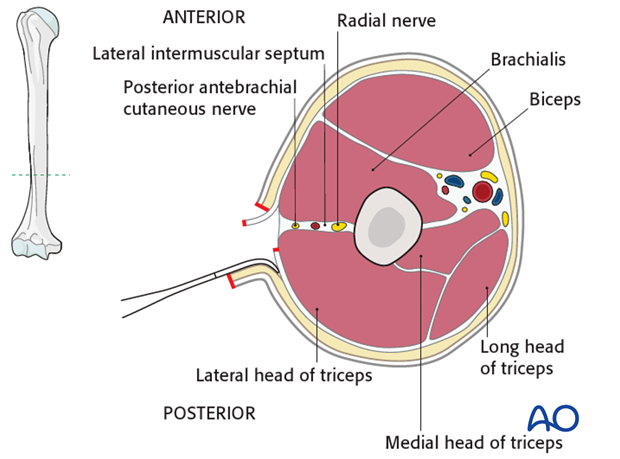
humerus anterior compartment
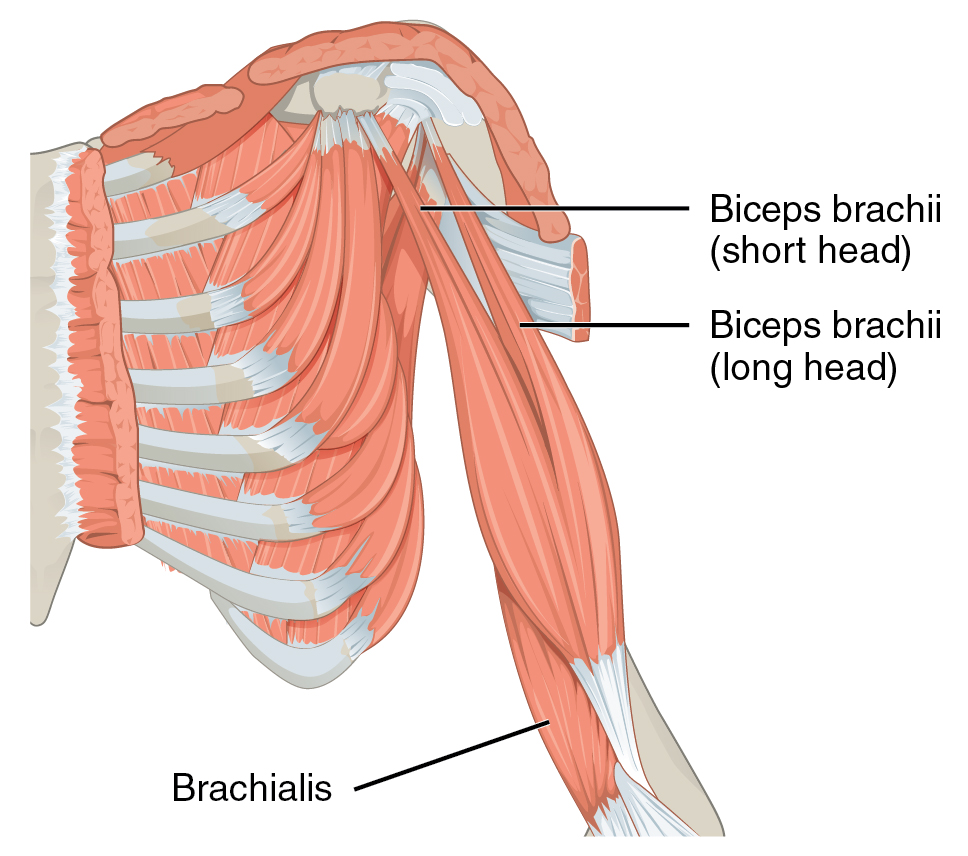
biceps brachii
coracobrachialis
brachialis
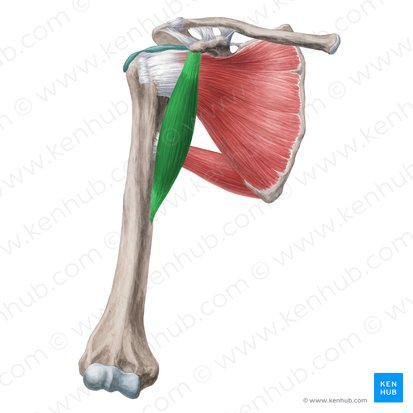
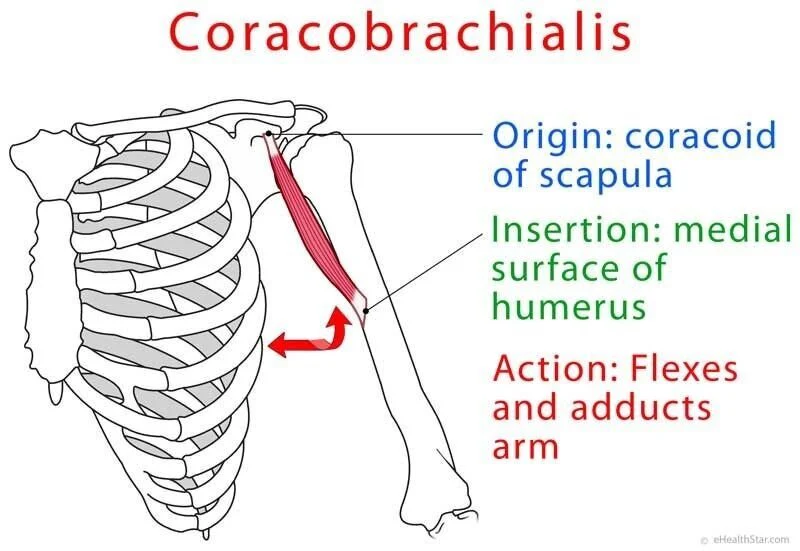
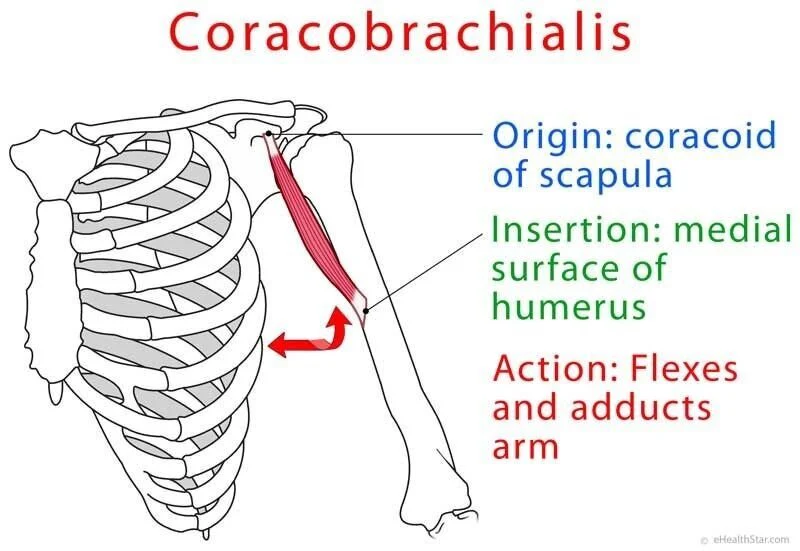
coracobrachialis
coracobrachialis action
shoulder flexion
shoulder adduction
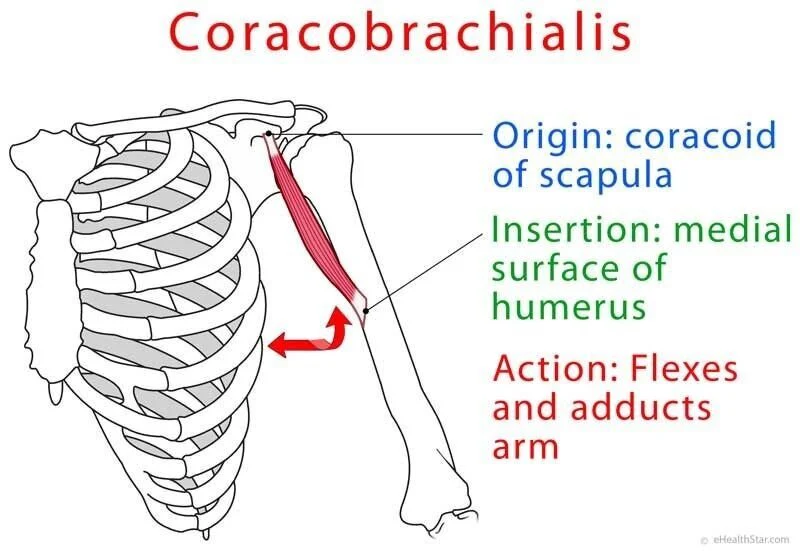
coracobrachialis origin and insertion
origin:
humerus (anterior shaft)
insertion:
coracoid process
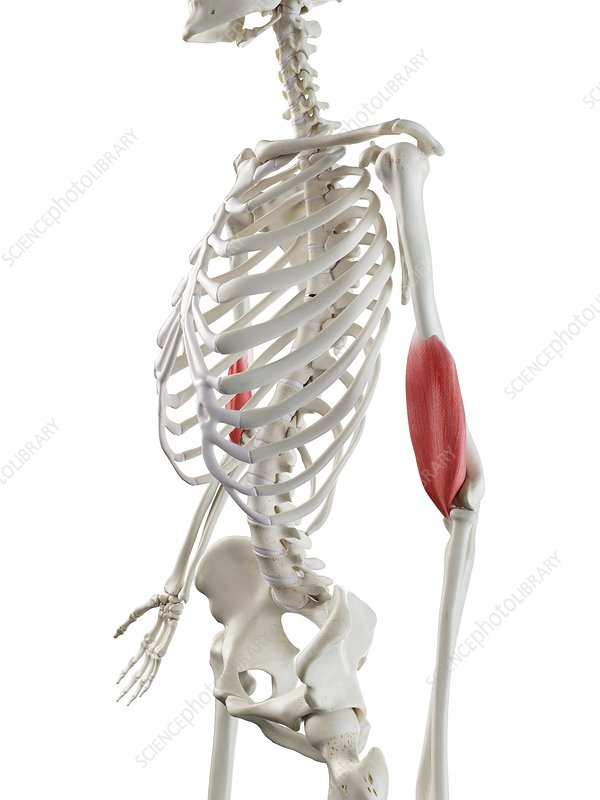
brachialis
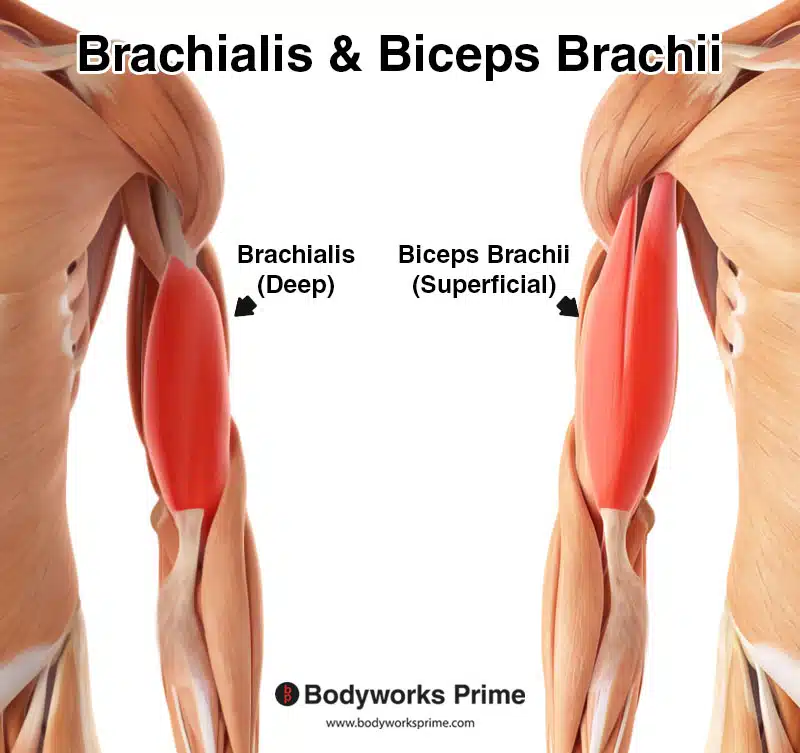
brachialis origin and insertion
origin:
humerus (anterior shaft)
insertions:
coronoid process
ulna tuberosity
brachialis action
elbow flexion
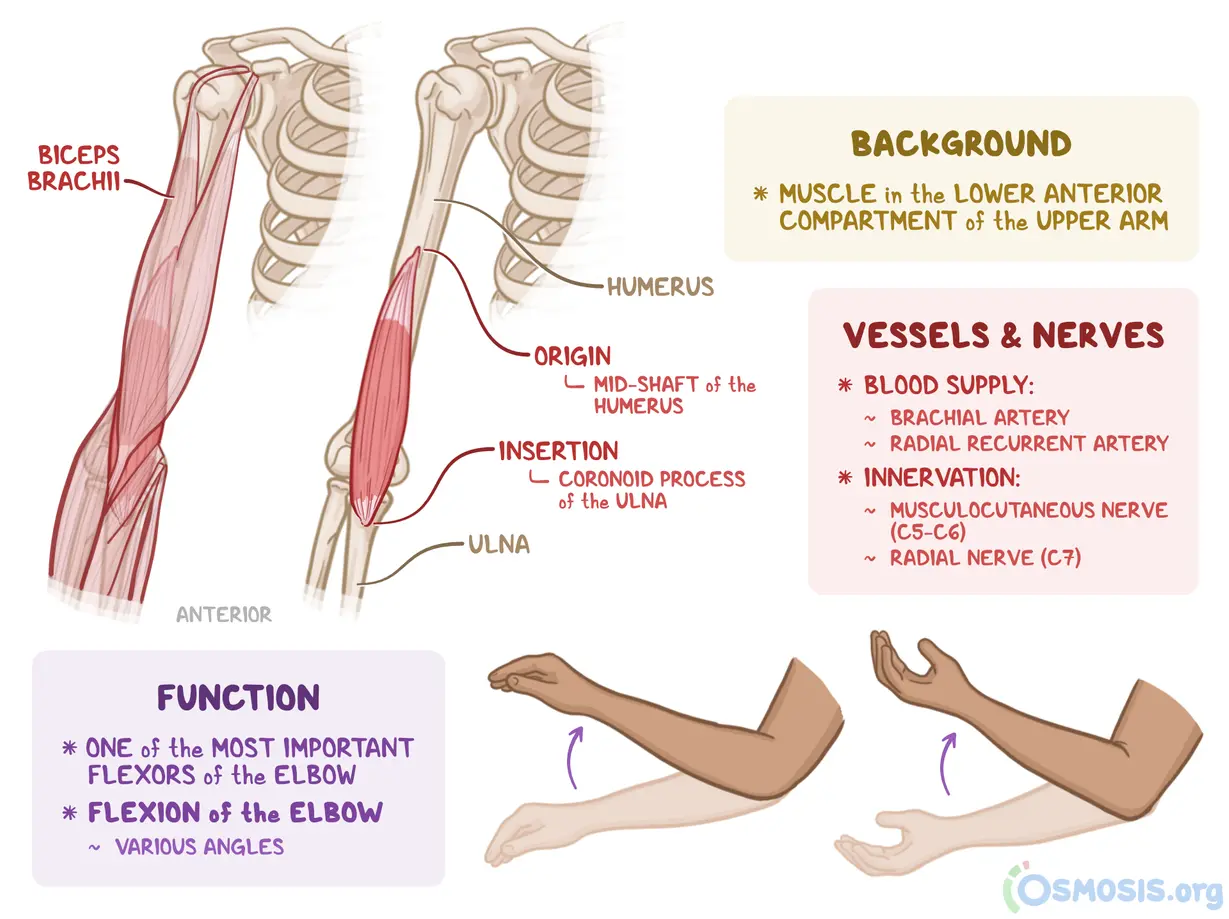
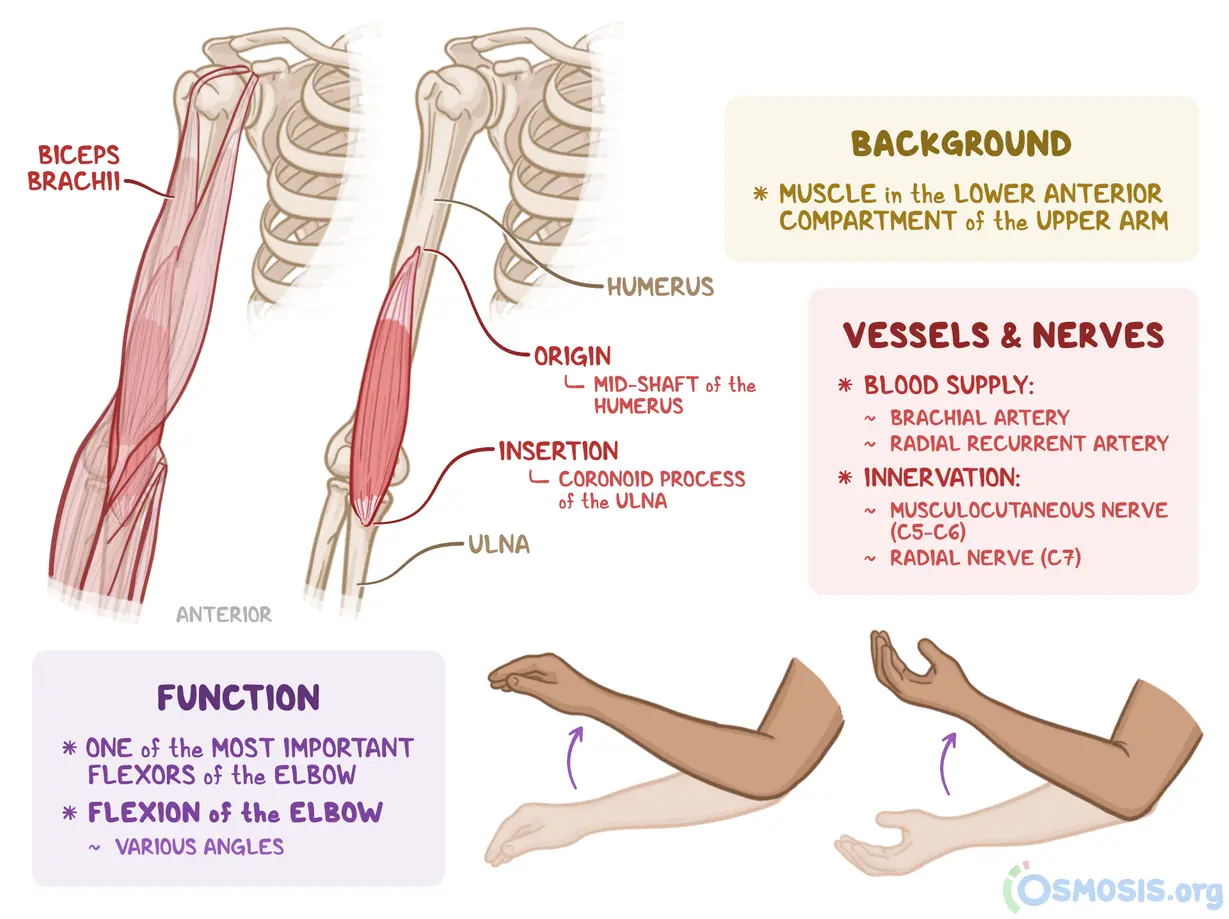
biceps brachii
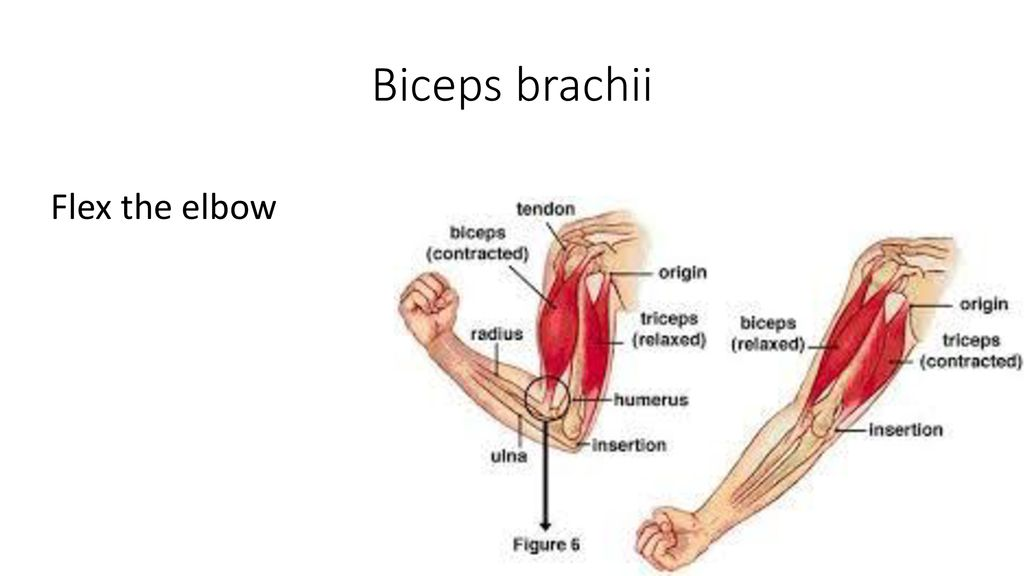
biceps brachii action
elbow flexion
elbow supination
GH flexion (weak)
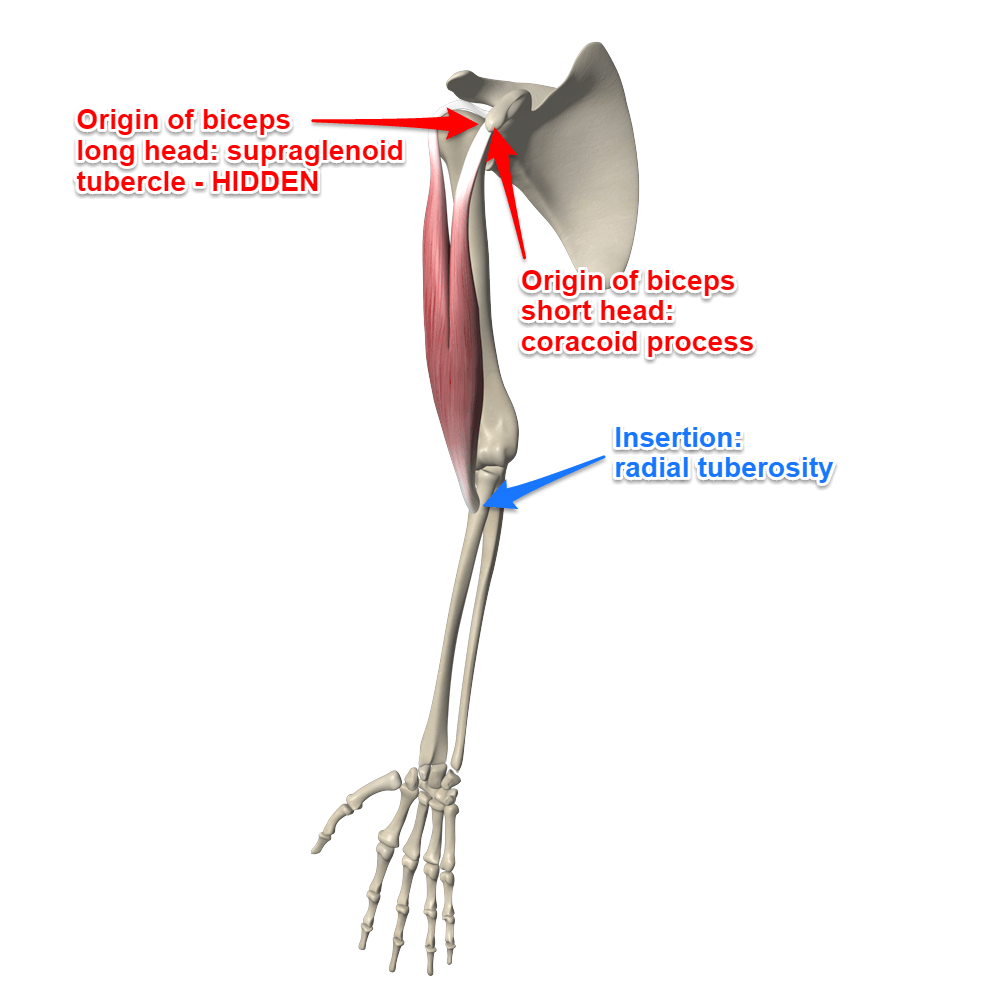
biceps brachii origin and insertion
origin:
short: coracoid process
long: supraglenoid tub
insertion:
radial tuberosity
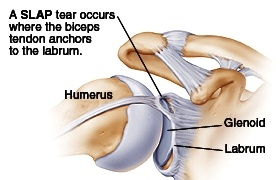
slap lesion
Muscle involved: long head of the biceps tendon (primarily)
Mechanism: A tear in the labrum cartilage at the point where the biceps tendon attaches.
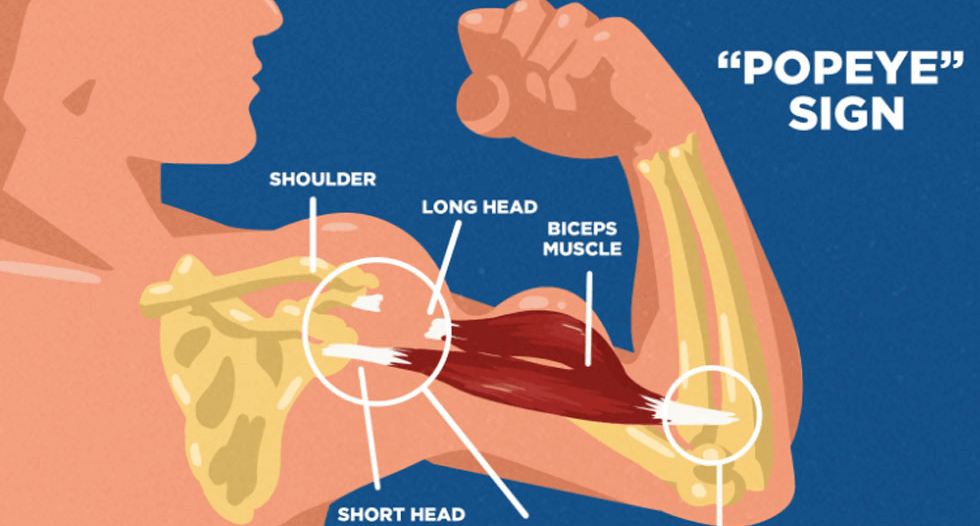
popeye’s sign
a bulge in the upper arm that occurs when the biceps tendon ruptures
triceps brachii
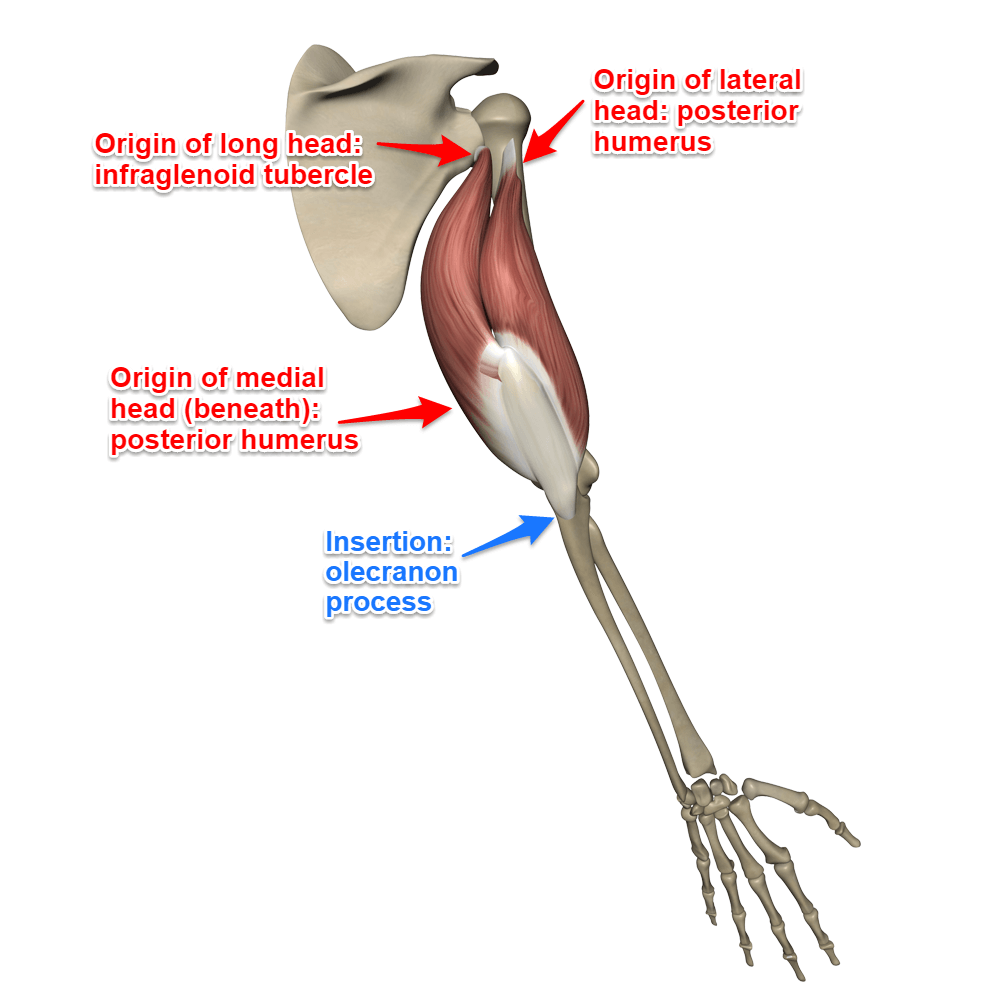
triceps brachii origin and insertion
origin:
long: infraglenoid tubercle
lateral: humerus (posterior shaft)
medial: posterior humerus (inferior to radial groove)
insertion:
olecranon of ulna
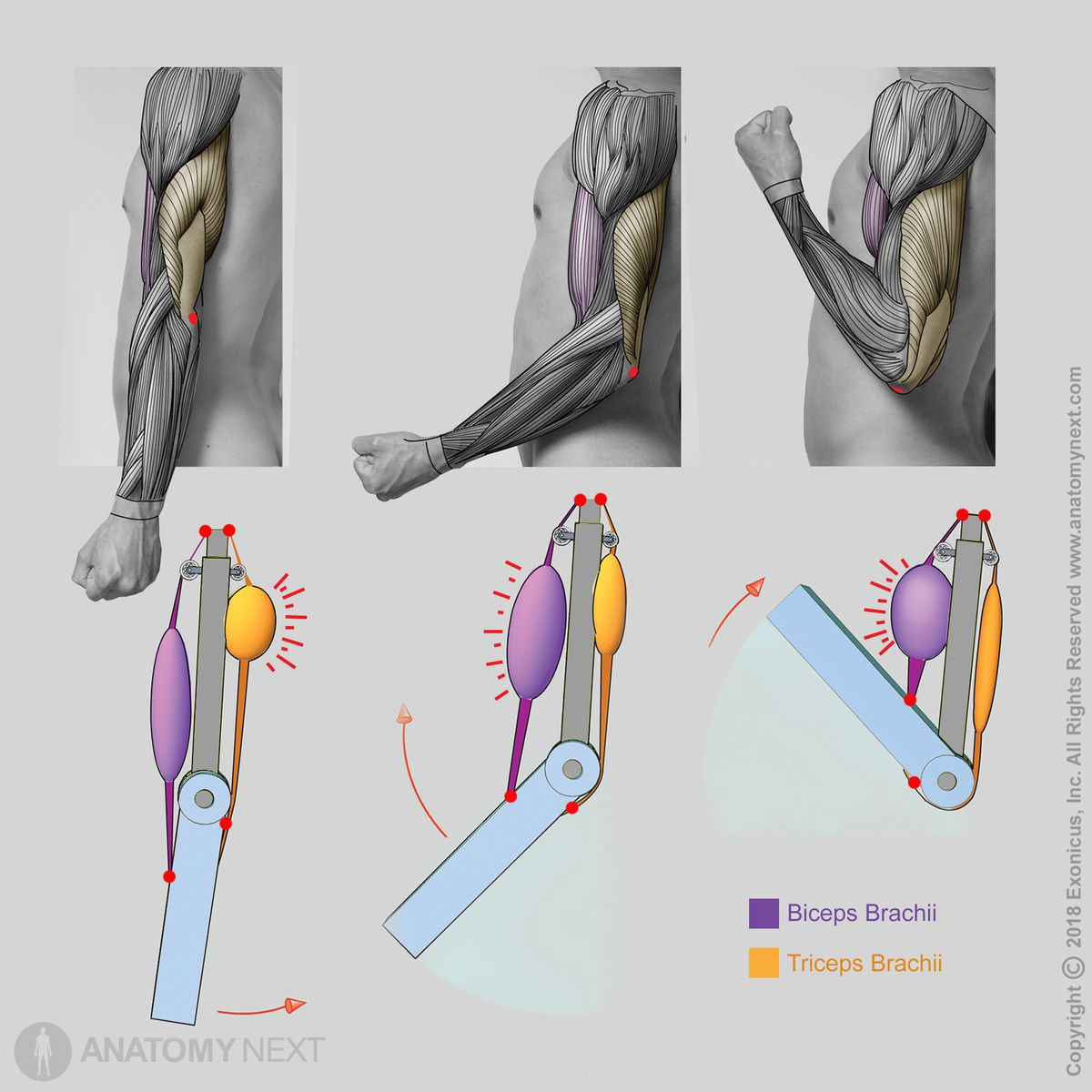
triceps brachii action
chief extensor of elbow
GH extension (long head)
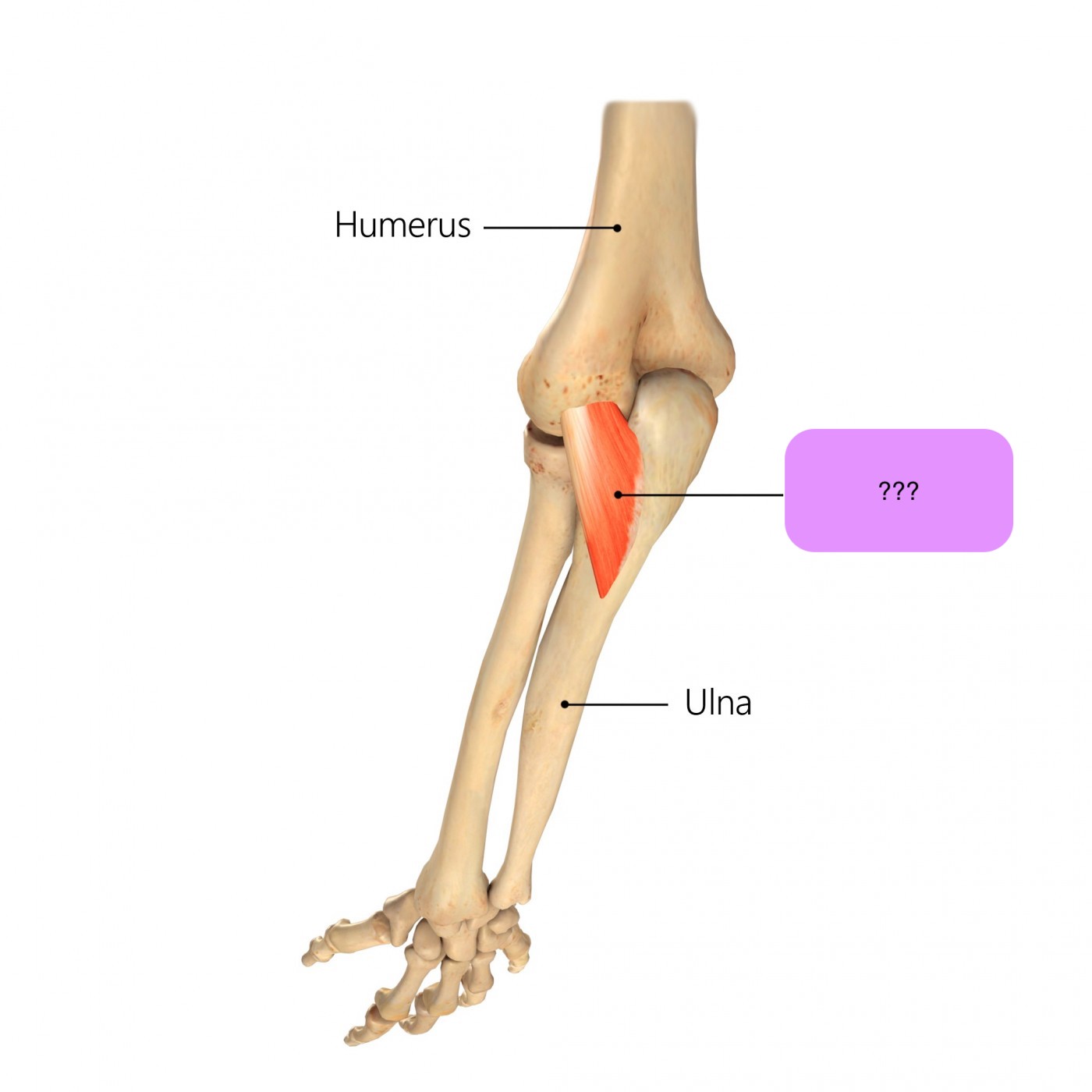
anconeus
(posterior humerus + posterior superficial antebrachium)
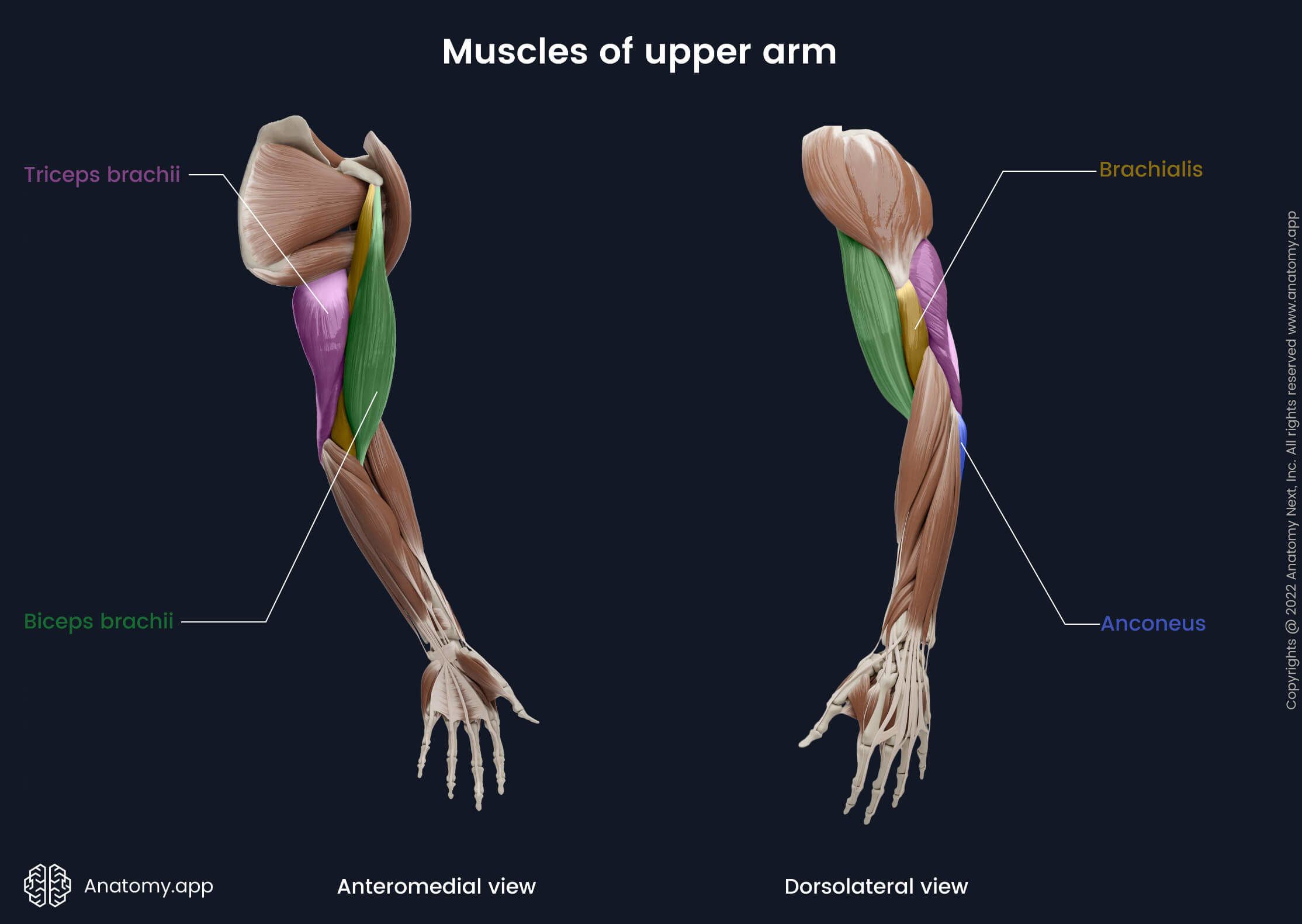
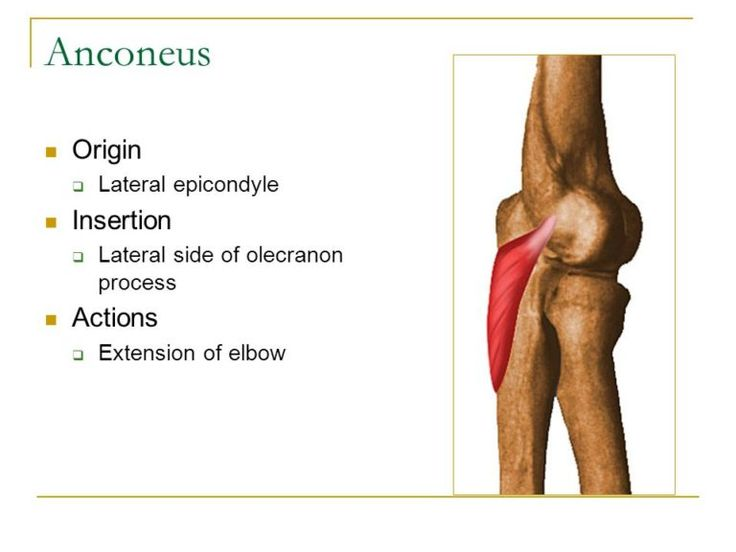
anconeus origin and insertion
origin:
lateral epicondyle of humerus
insertion:
lateral olecranon
posterior ulna shaft
anconeus action
assists triceps in elbow extension
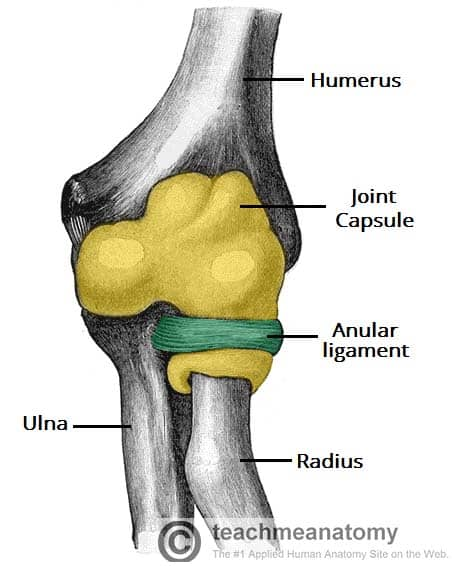
annular ligament
stabiliser of the proximal radioulnar joint
allows for smooth and unrestricted rotation of the forearm during pronation and supination
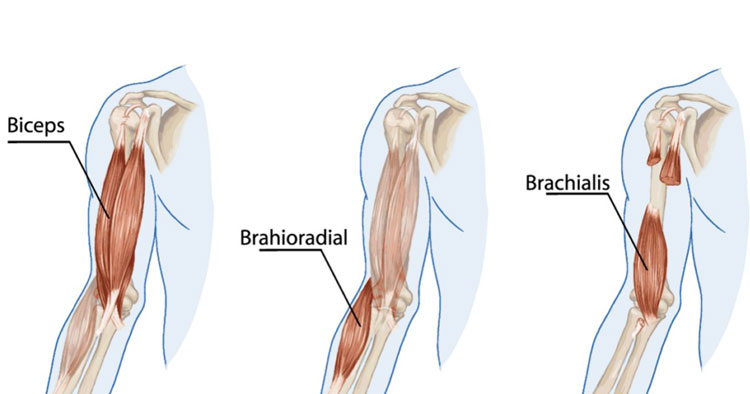
elbow flexion muscles
brachialis (slow)
biceps brachii (slow)
brachioradialis (fast)
elbow extension muscles
triceps brachii
anconeus (minor assistance)
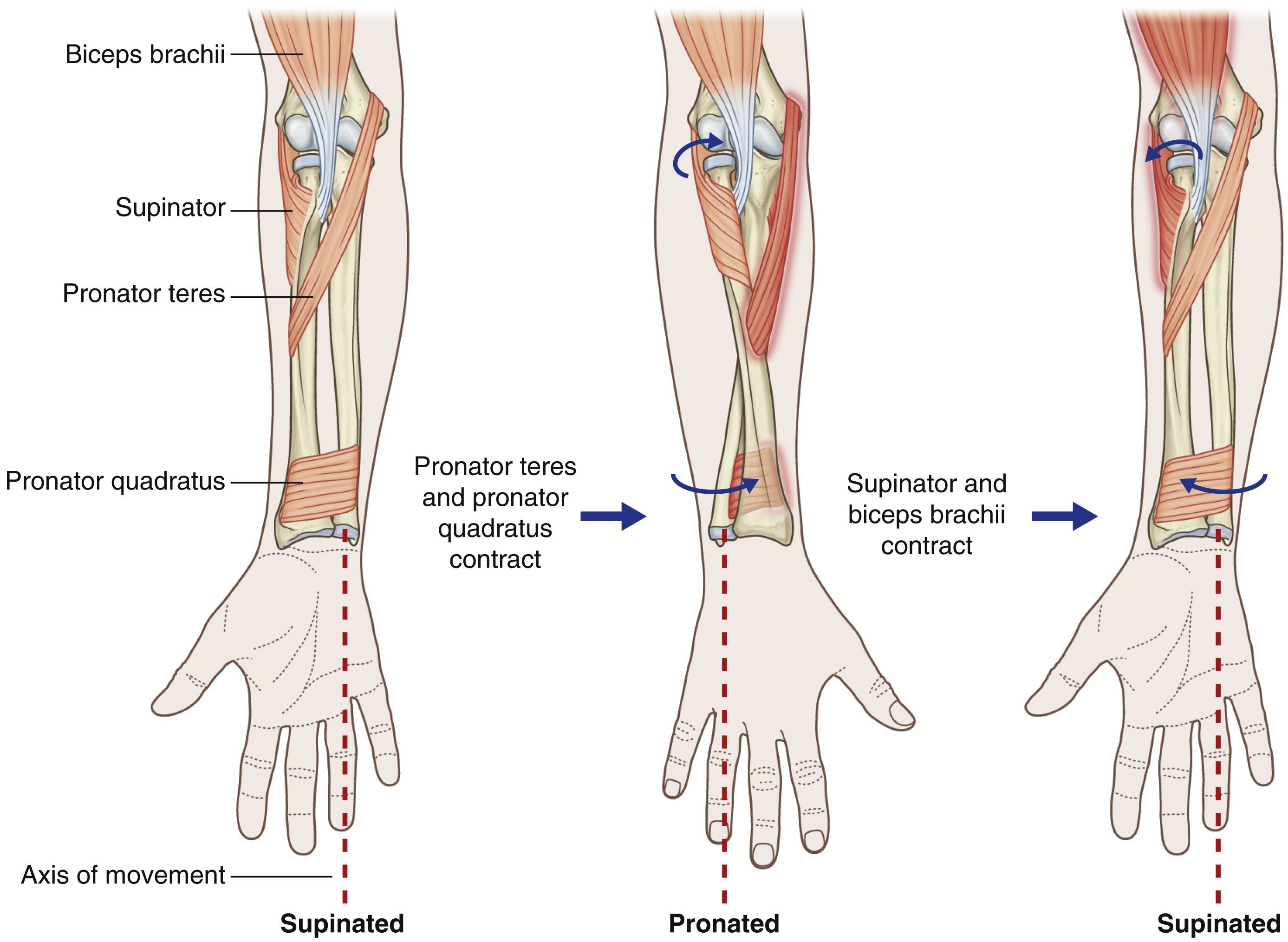
arm supination muscles
supinator
biceps brachii (assists only when movements are fast/forceful)
(sup high five)
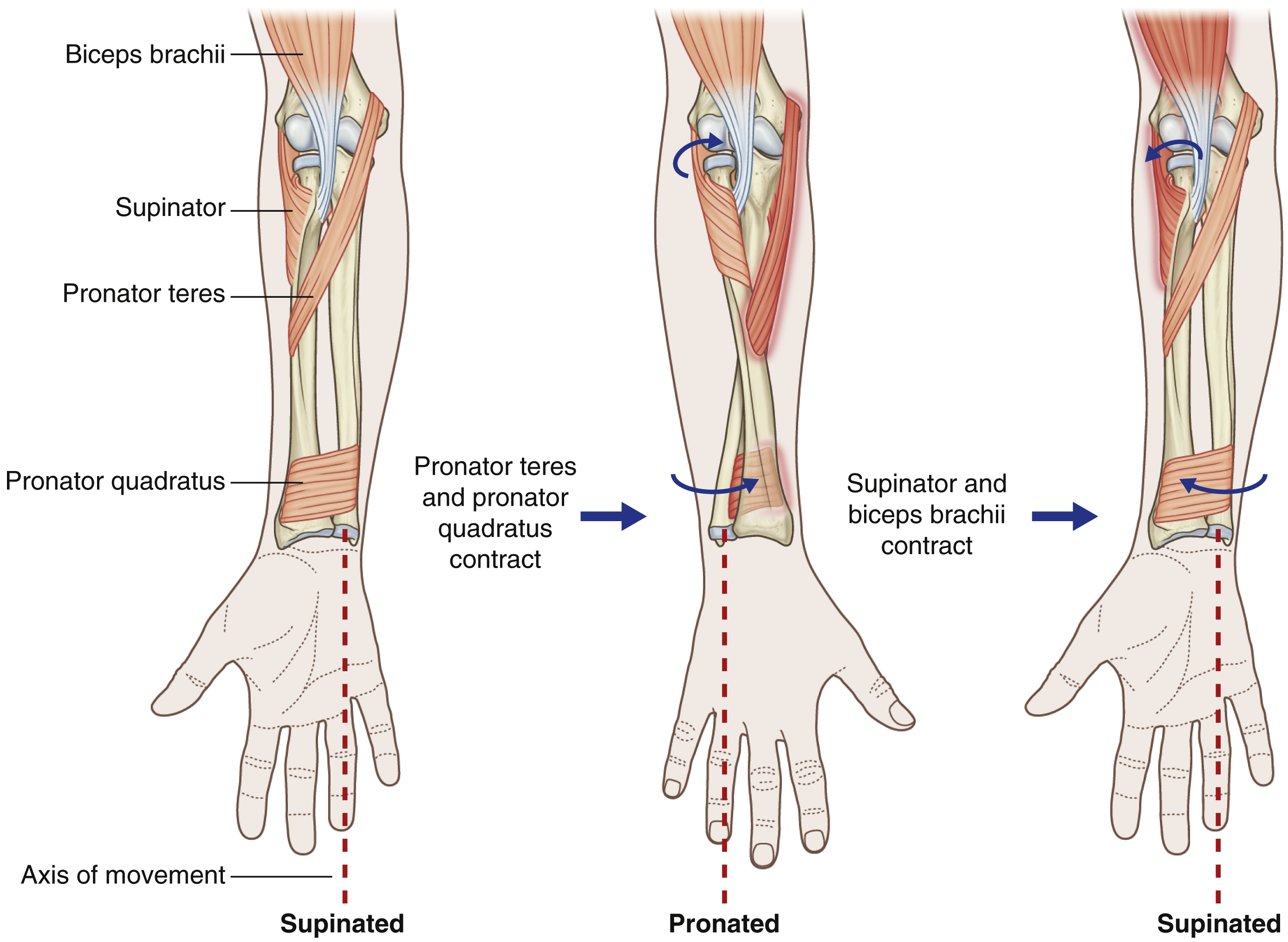
arm pronation muscles
pronator quadratus
pronator teres

(i’m kind of a pro)
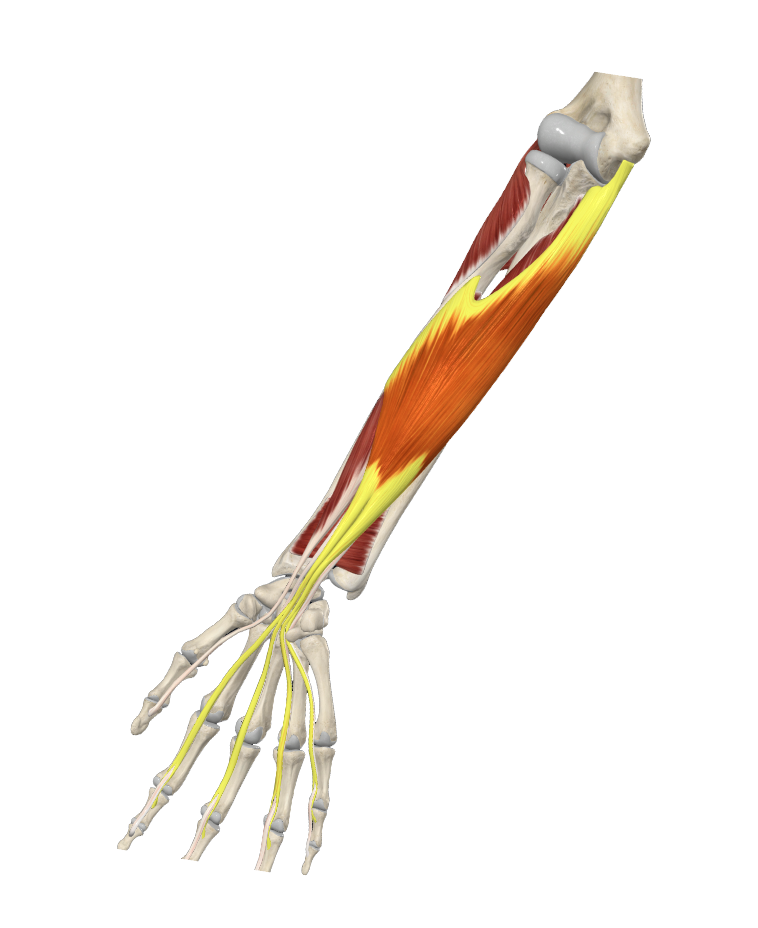
anterior forearm/antebrachium muscles
flexors of the wrist and hand
three layers (deep, middle, superficial)
superficial: common attachment to medial epicondyle
anterior antebrachium signs of weakness
when lifting heavy objects, patient is not able to sufficiently stabilize wrist with supinated forearm; tilting dorsally
deep anterior antebrachium signs of weakness
When lifting heavy objects, the affected patient is not able to sufficiently stabilize the wrist with supinated forearm; thus wrist tilts in a dorsal direction
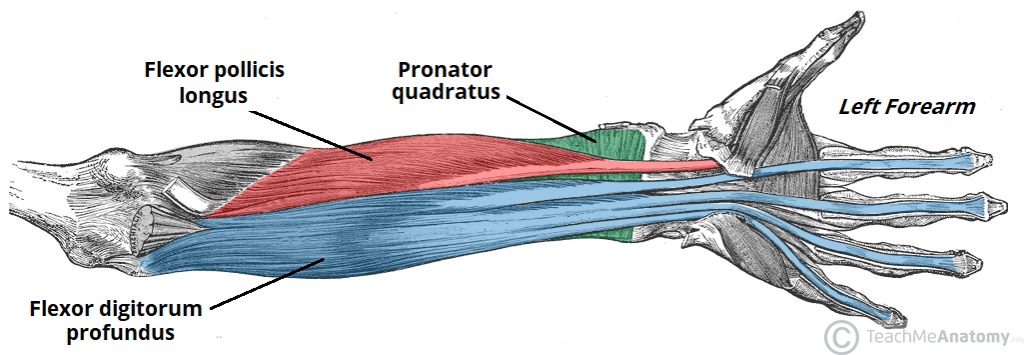
supinator
flexor digitorum profundus
flexor pollicis longus
pronator quadratus
(sffp - median nerve)
golfer’s elbow
epicondylitis medialis
inflammation of tendons attached to muscles of the anterior antebrachium
posterior forearm muscles
extensors of the wrist and hand
two layers (deep and superficial)
superficial: common attachment to lateral epicondyle
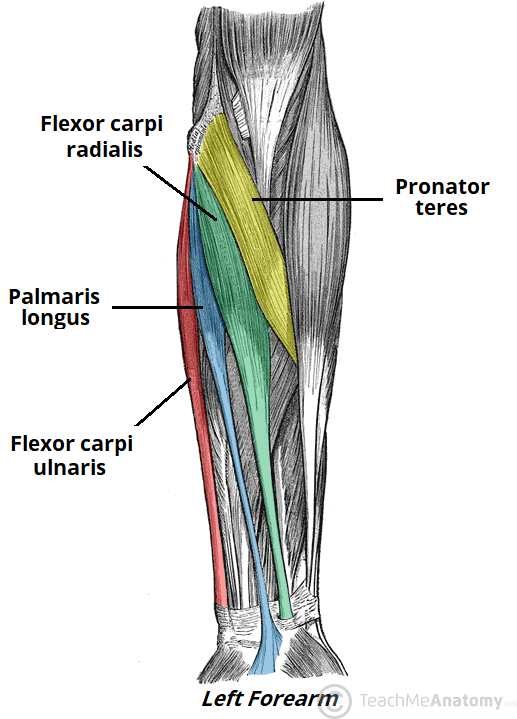
flexor carpi radialis (anterior superficial antebrachium)
→pointer finger
flexes and abducts wrist
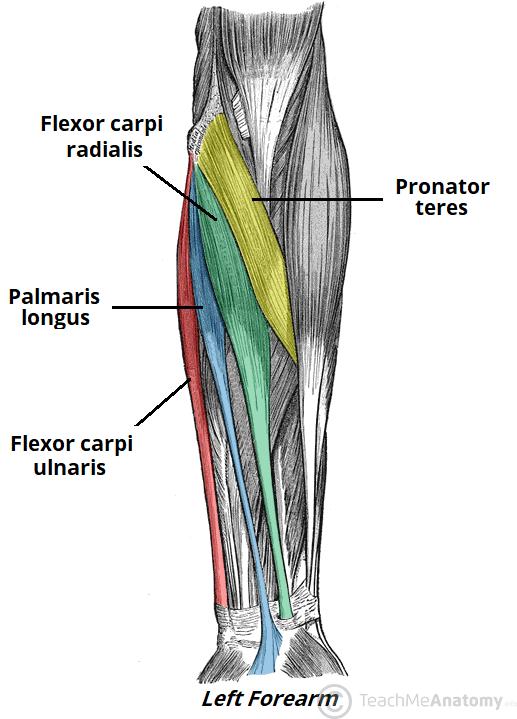
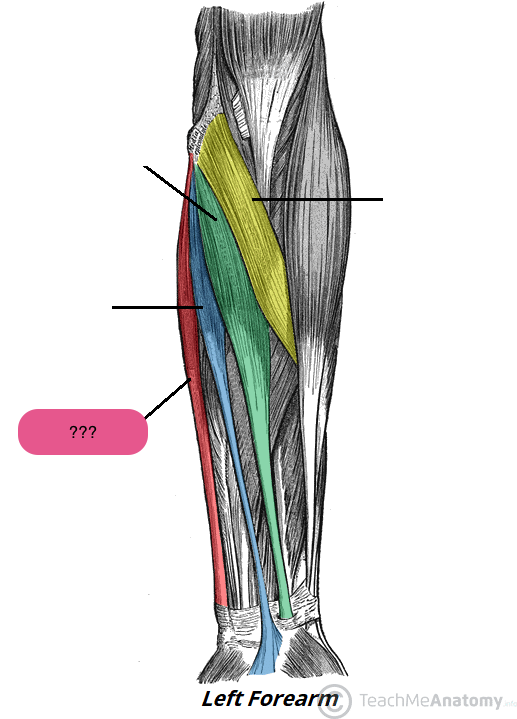
flexor carpi ulnaris (anterior superficial antebrachium)
→ring finger (professional frogs partake (in) fun)
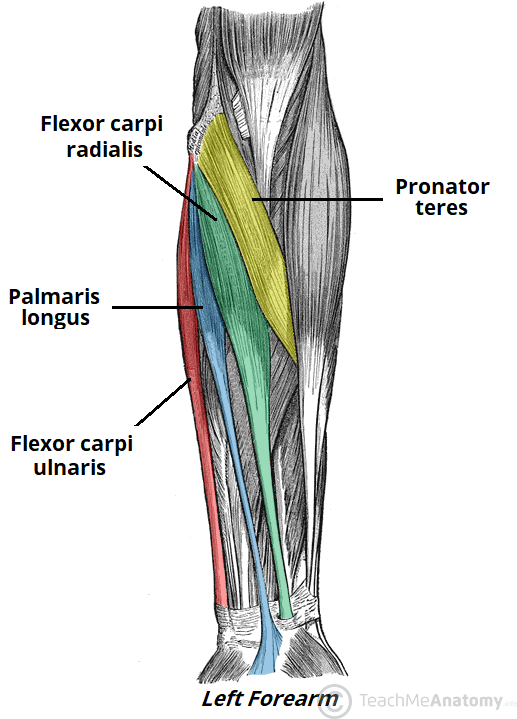
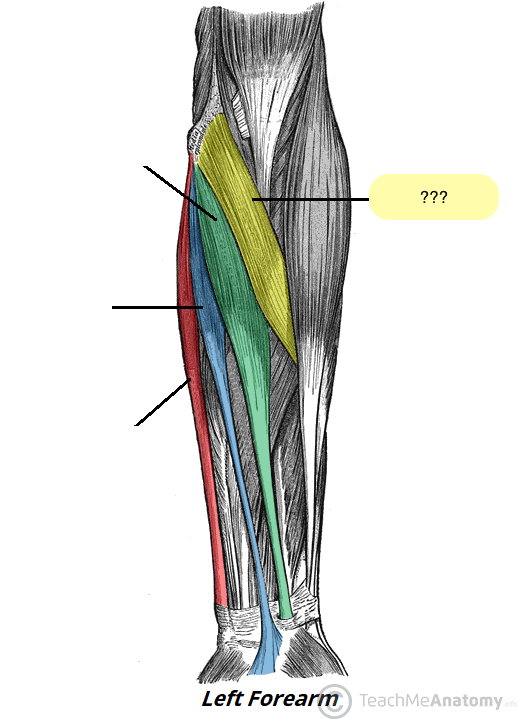
pronator teres (anterior superficial antebrachium)
→thumb (professional frogs partake (in) fun)
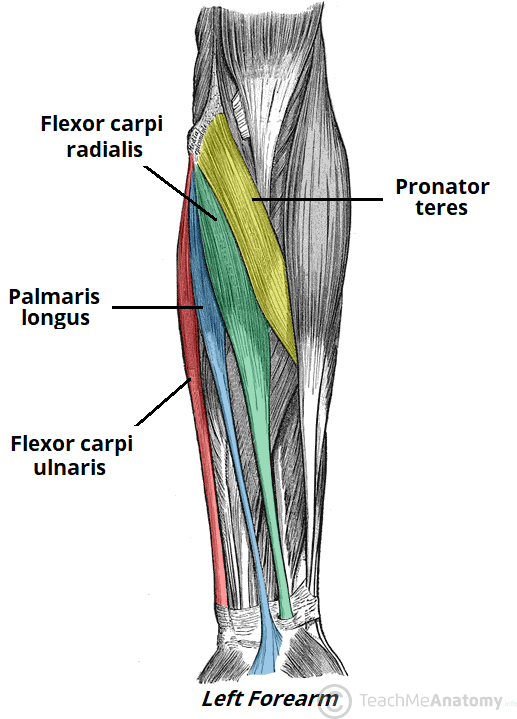
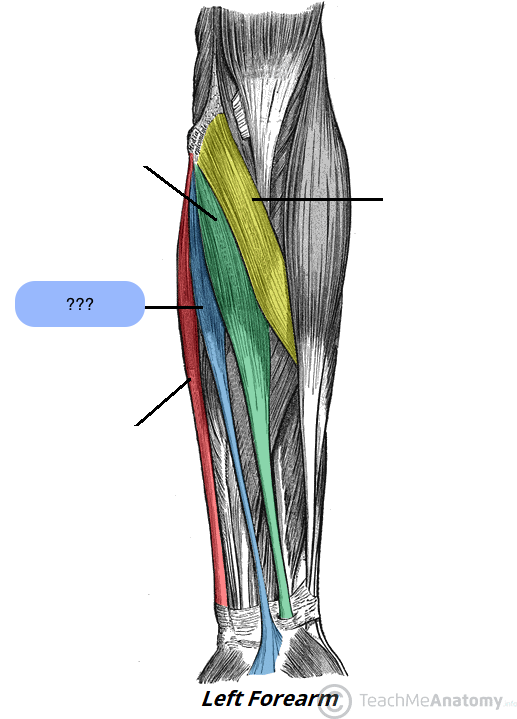
palmaris longus (anterior superficial antebrachium)
→middle finger (professional frogs partake (in) fun)
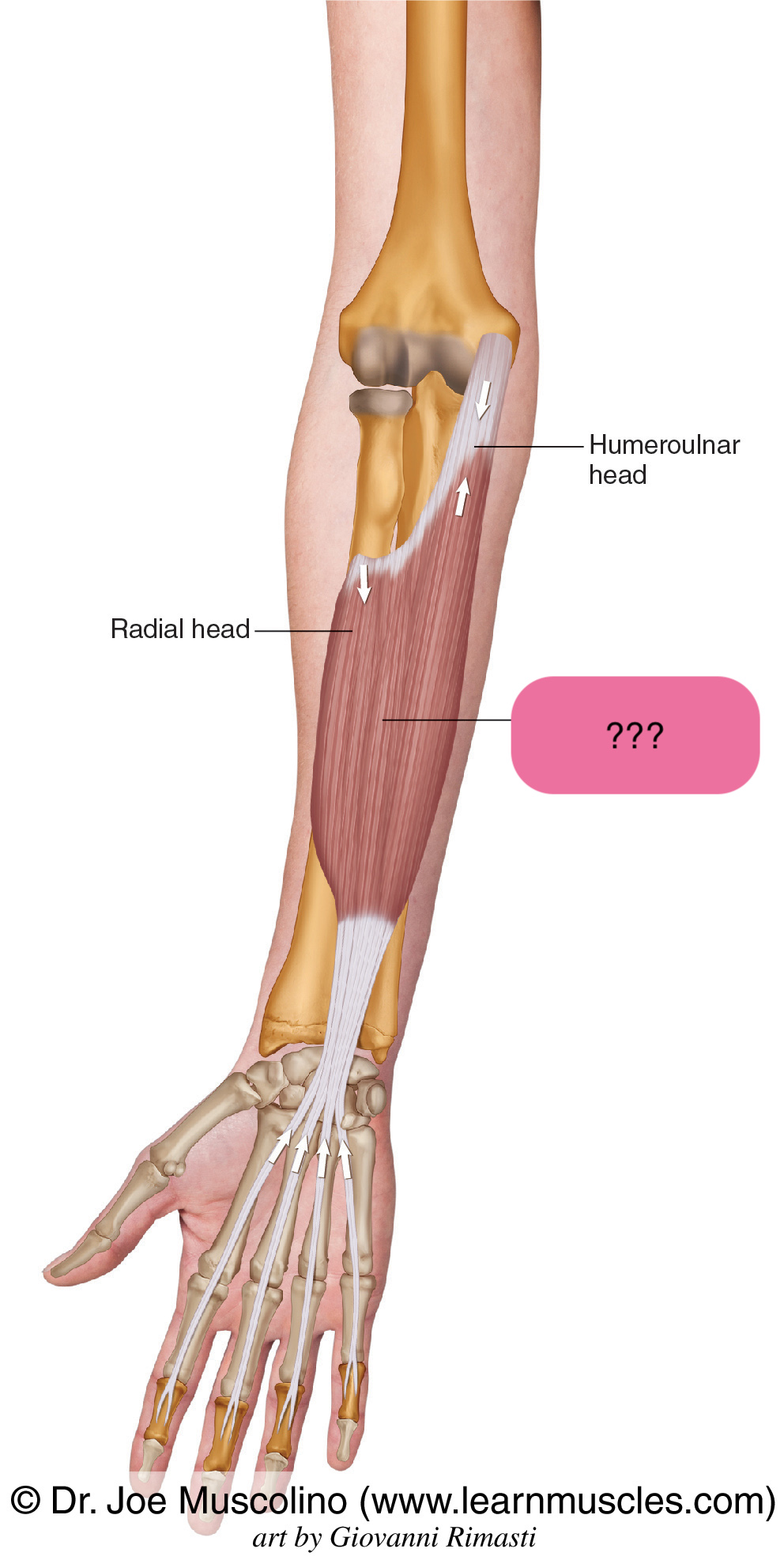
flexor digitorum superficialis (anterior intermediate antebrachium)
insertion on the middle phalanges
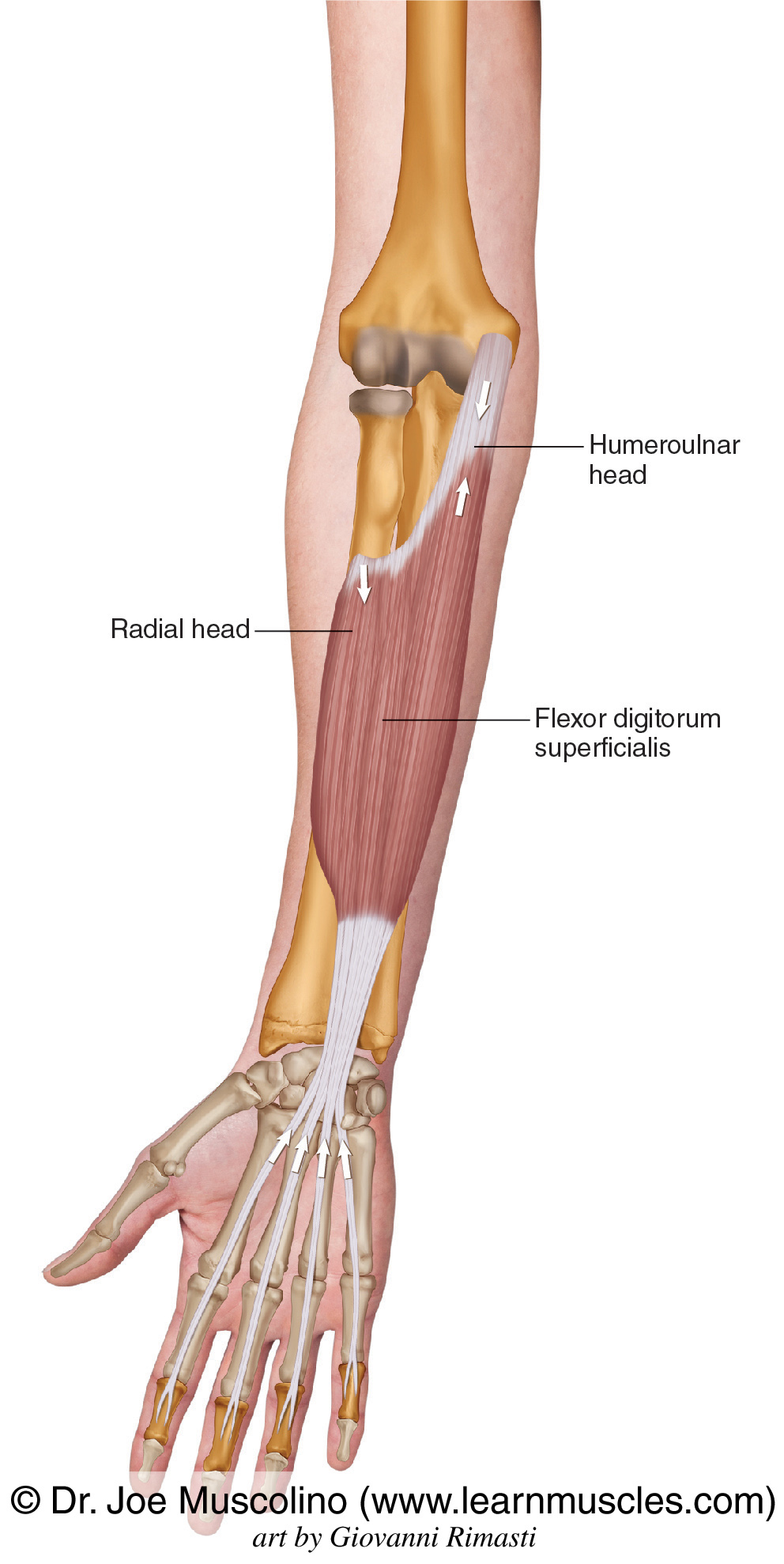
flexor digitorum superficialis actions
primary flexor of PIPJ (proximal interphalangeal joints) and secondary flexor of MCPJ (metacarpophalangeal joints)
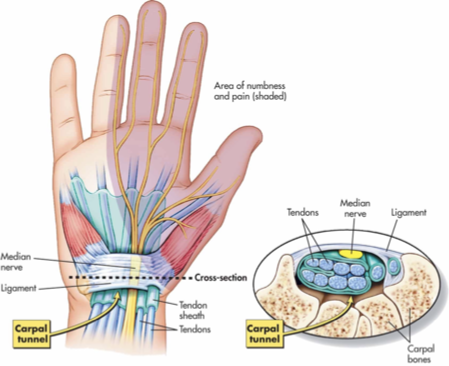
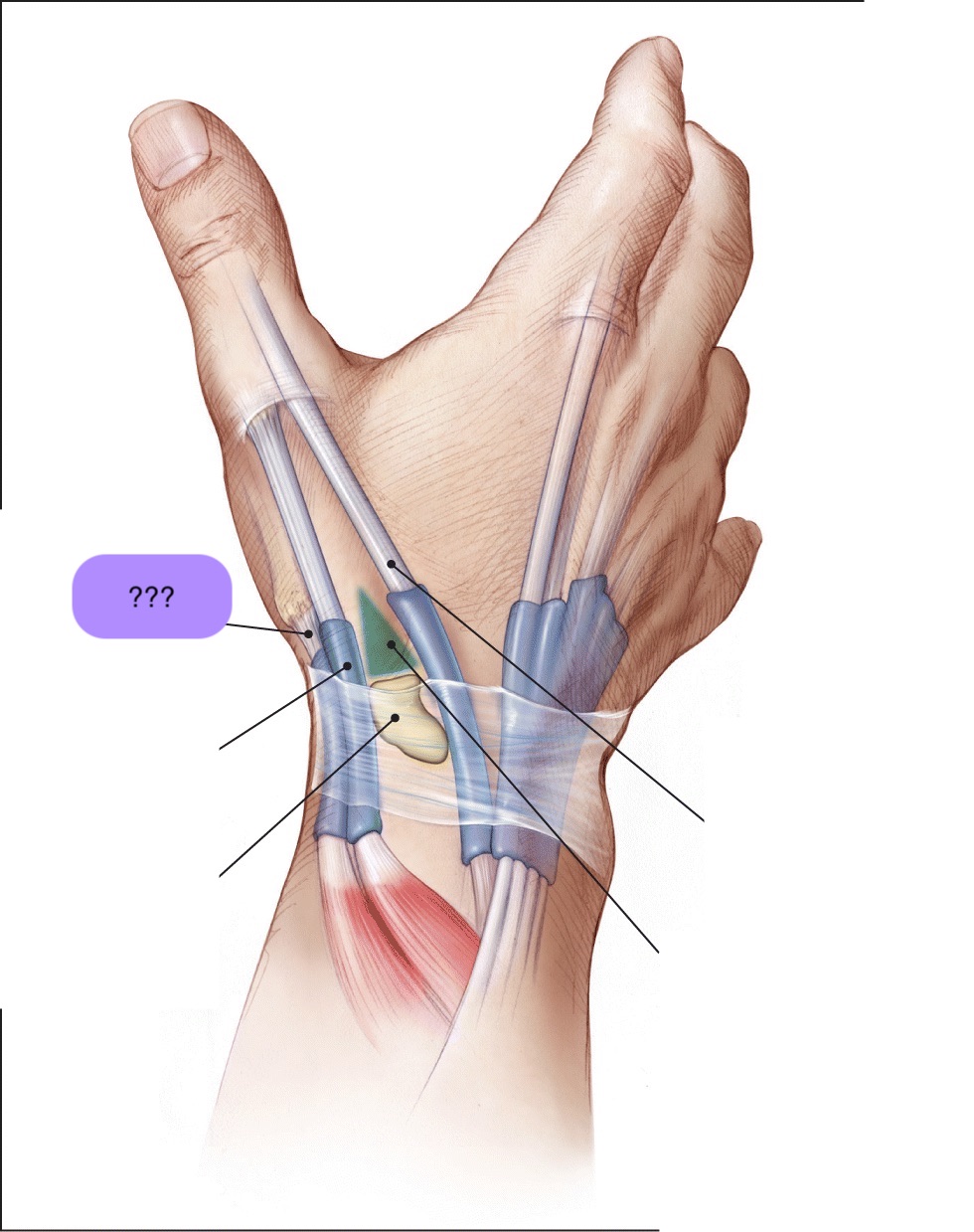
carpal tunnel
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway in the wrist that's made up of the carpal bones and the transverse carpal ligament.
The median nerve and nine tendons run through the carpal tunnel
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a condition that occurs when the median nerve in the wrist is compressed → shooting pain
chronic = thenar atrophy (muscles in the base of the thumb to waste away)
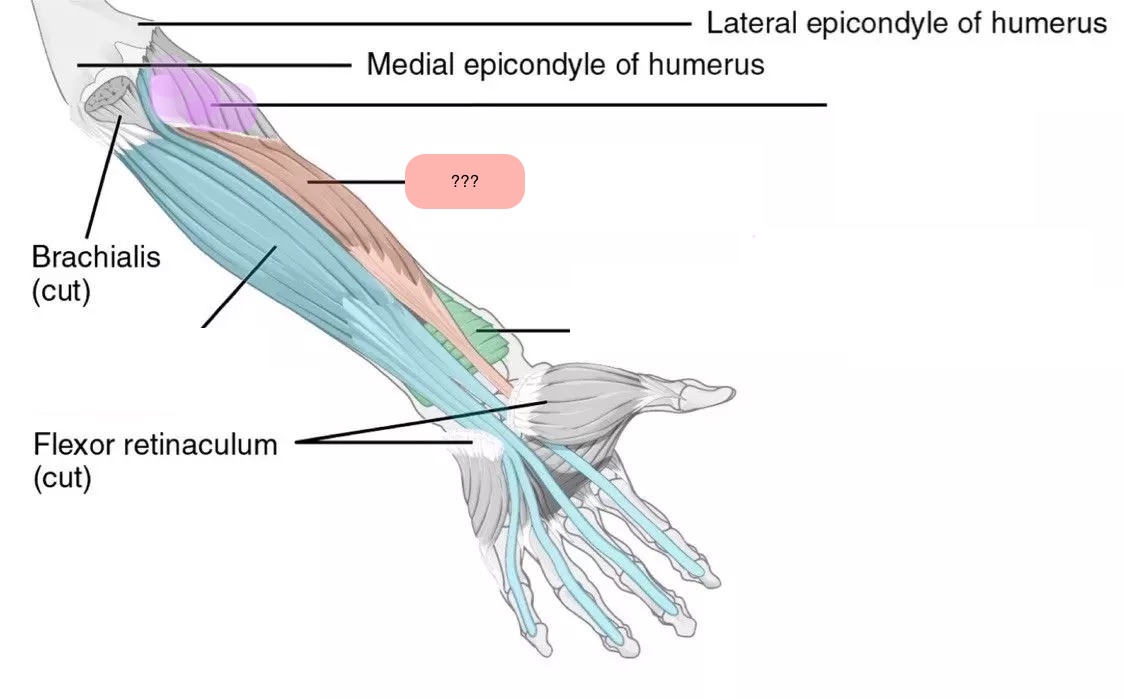
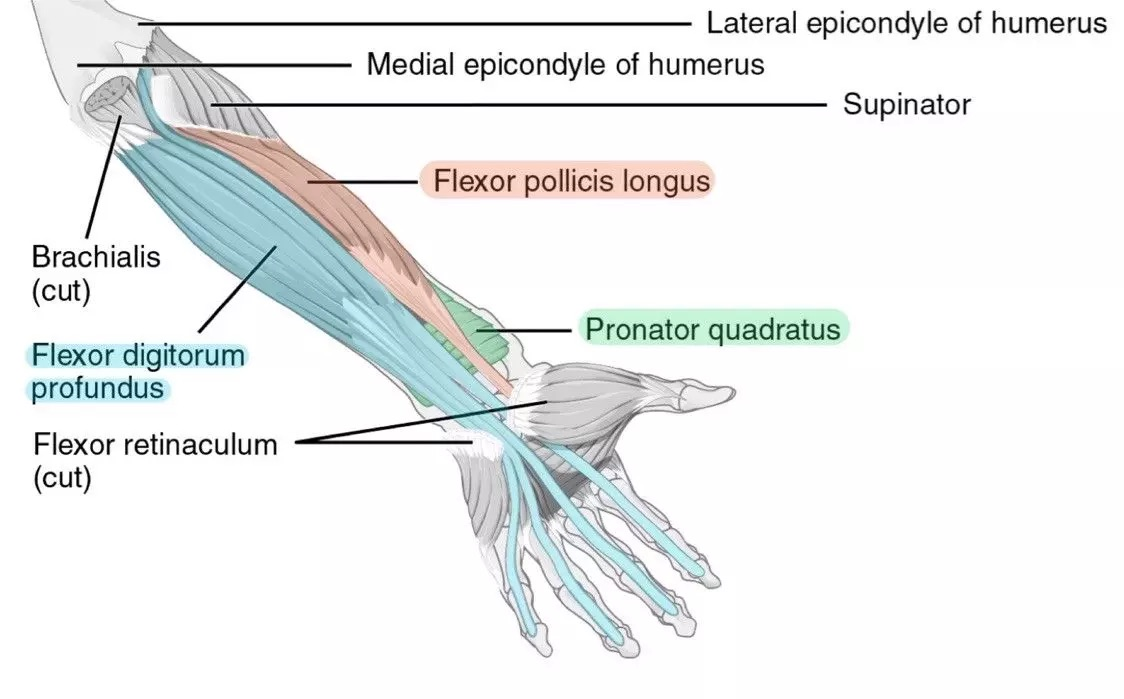
flexor pollicis longus (anterior deep antebrachium)
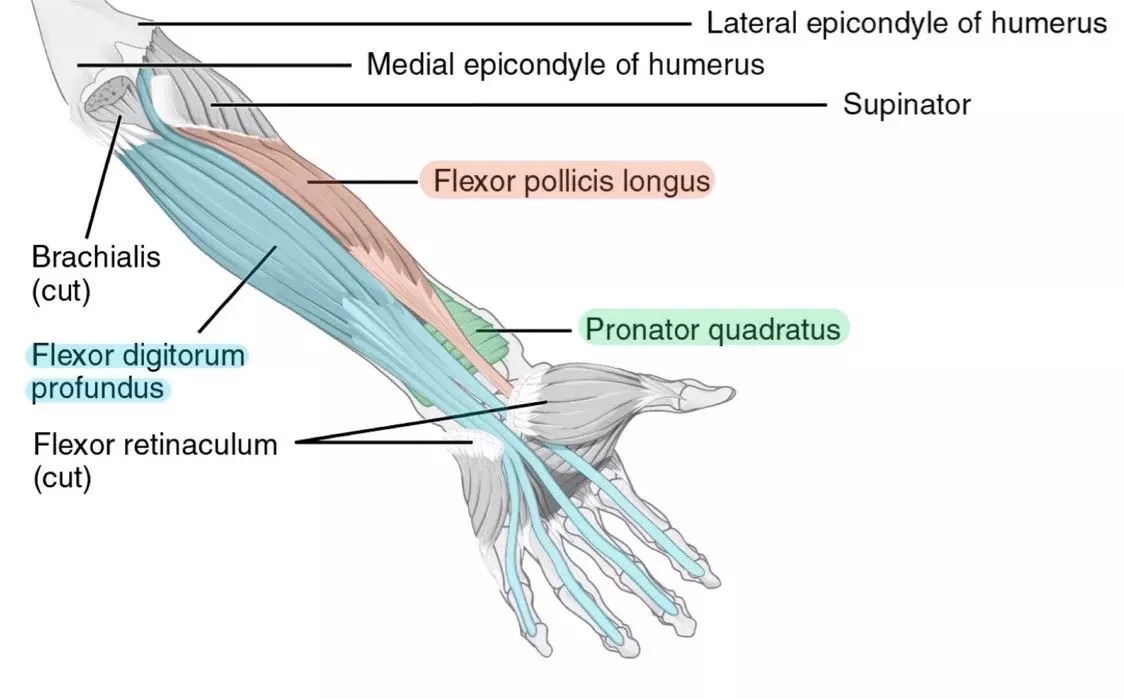
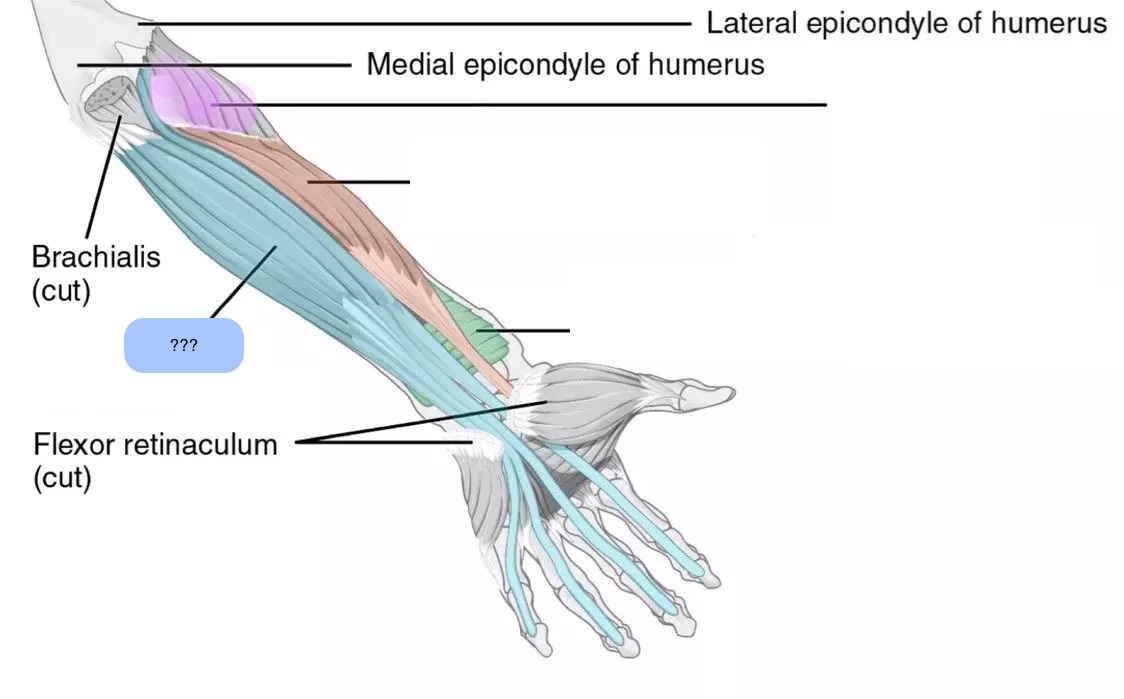
flexor digitorum profundus (anterior deep antebrachium (sffp))
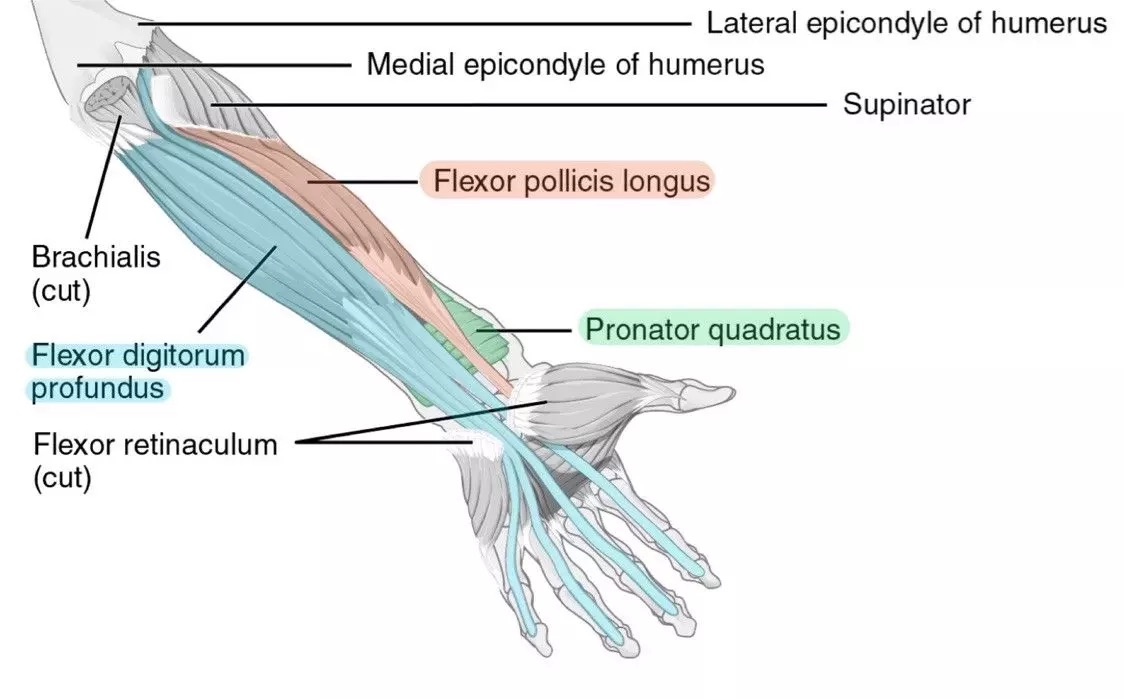
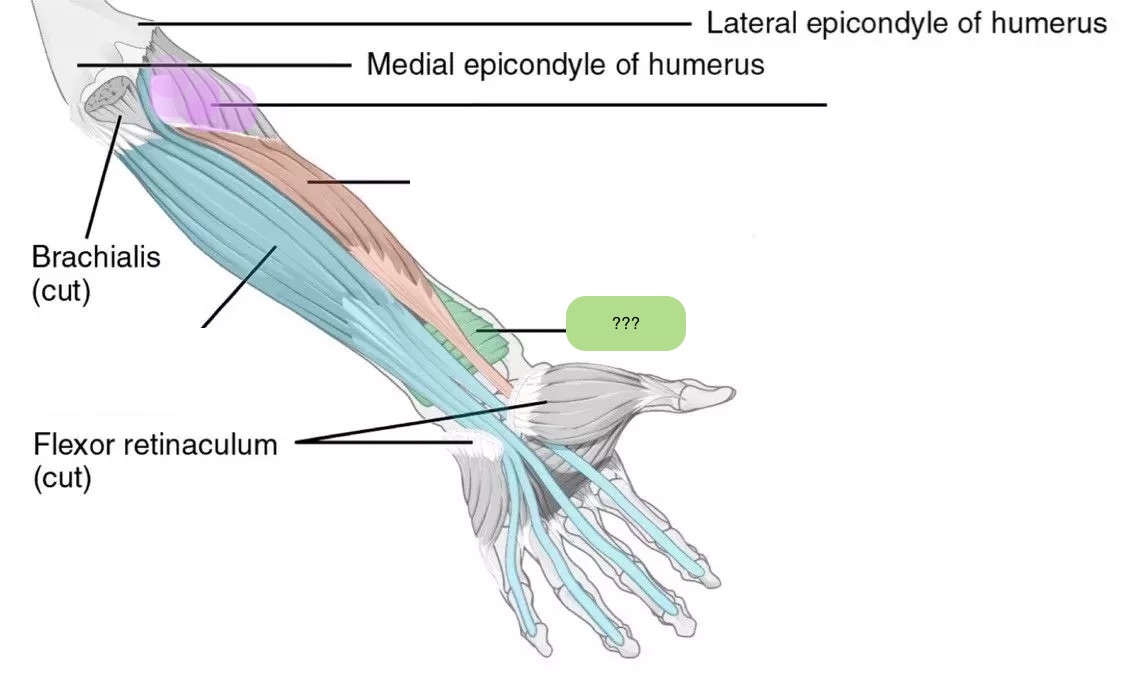
pronator quadratus (anterior deep antebrachium)
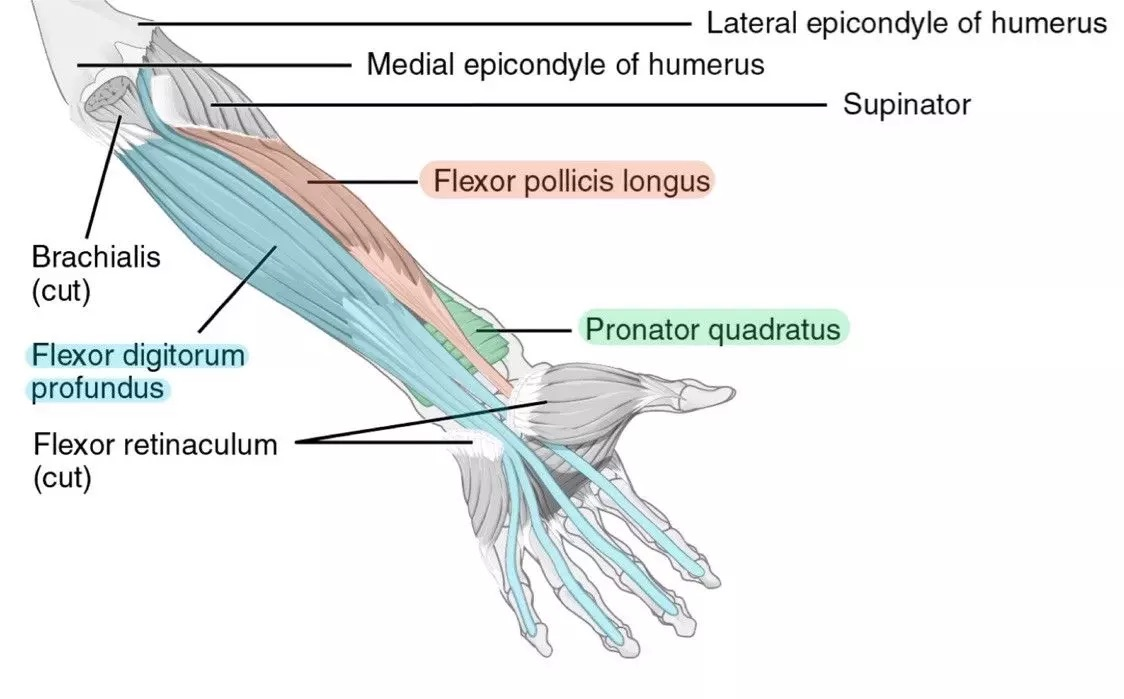
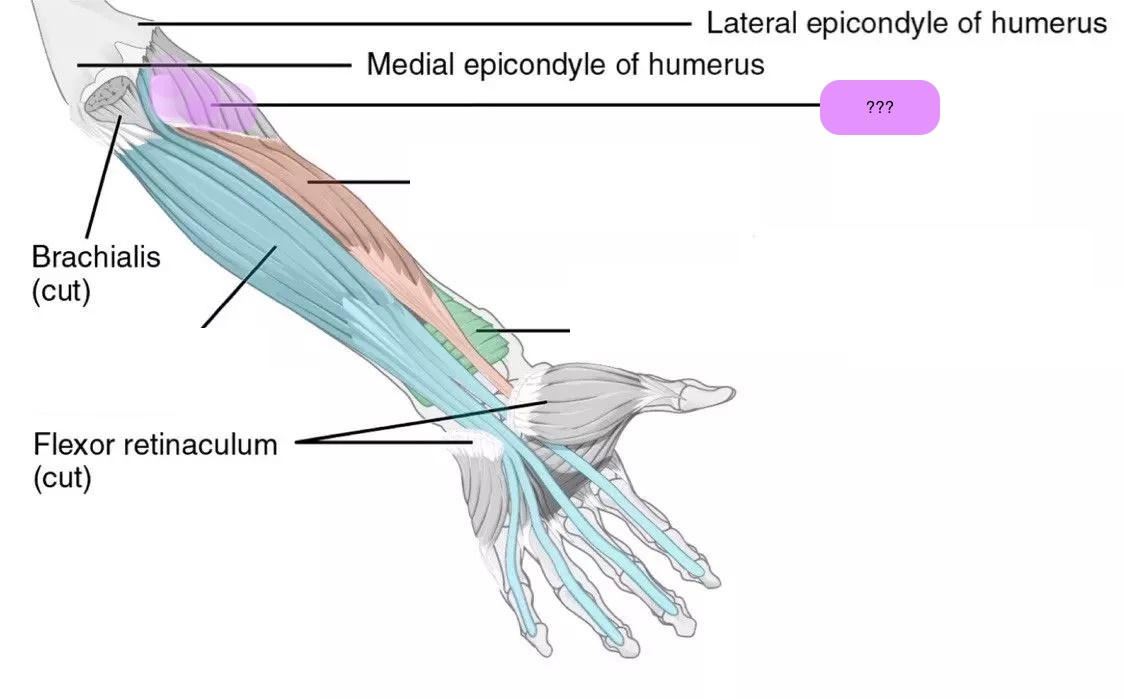
supinator (anterior deep antebrachium)
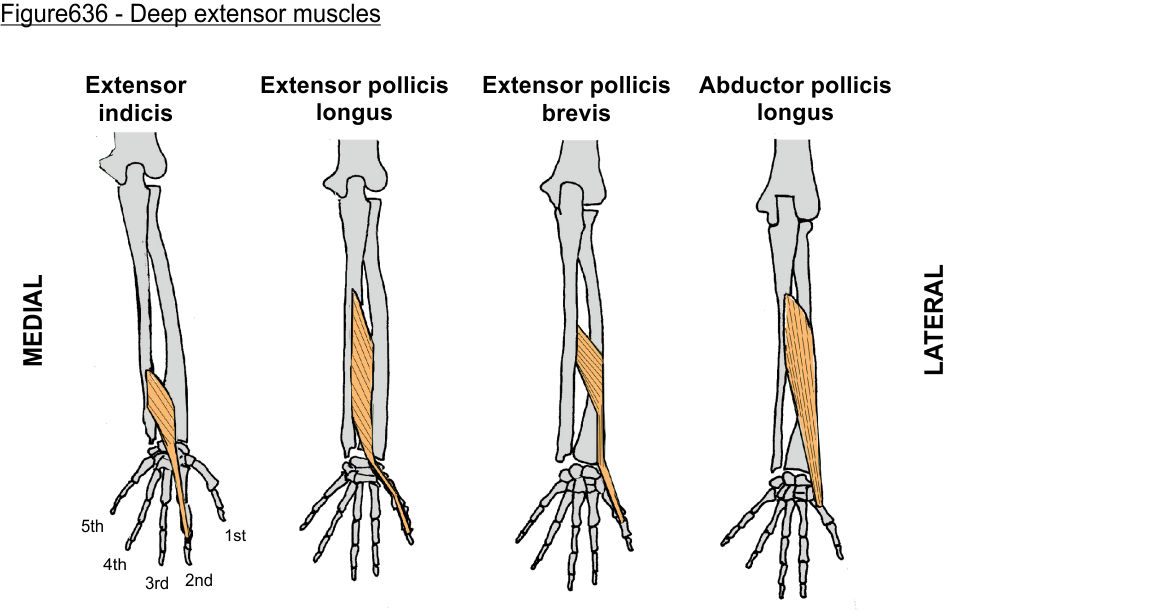
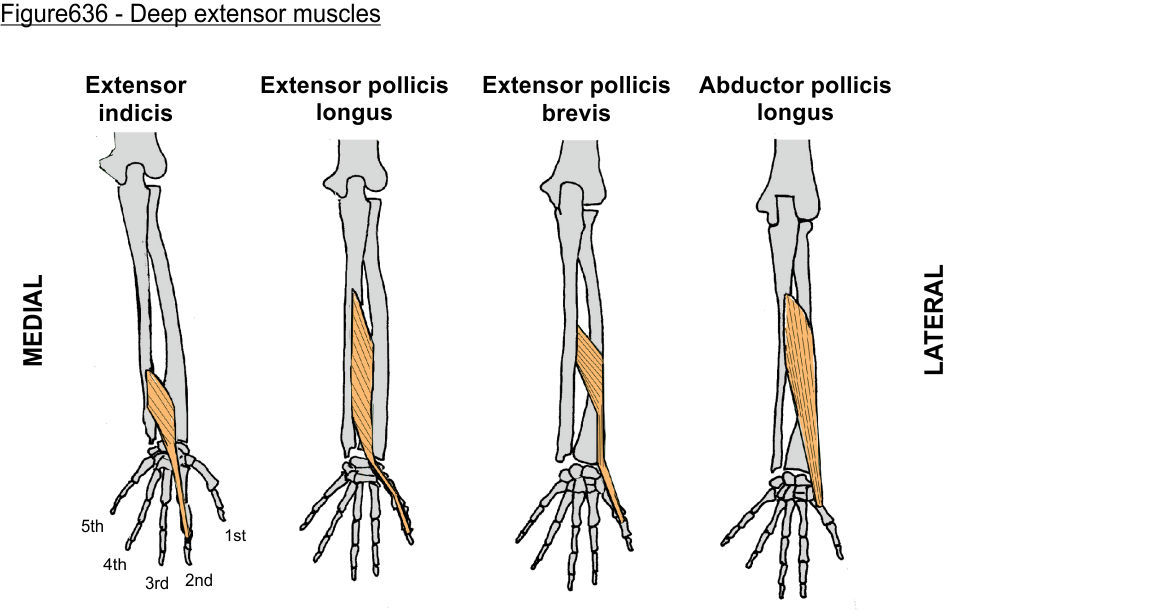
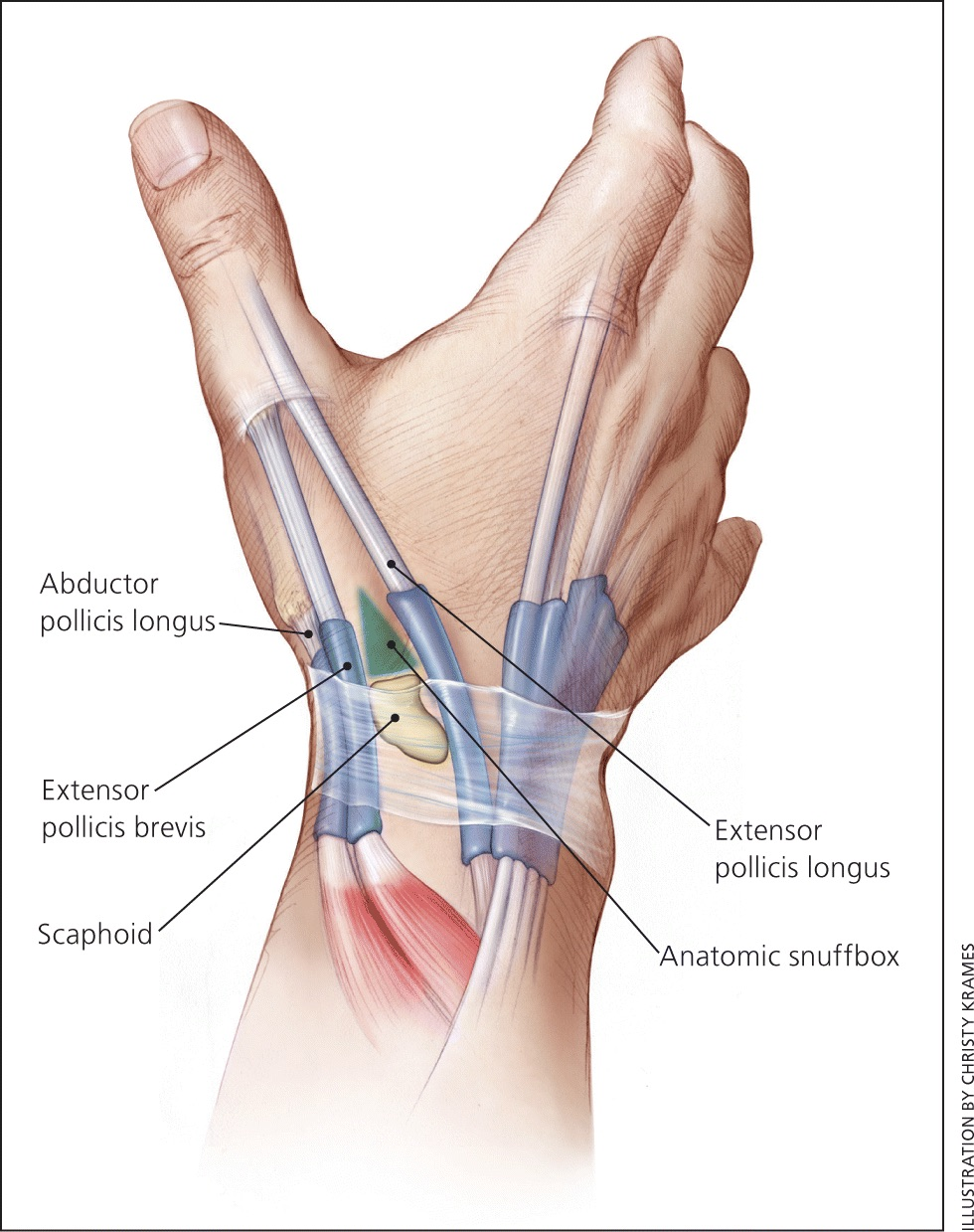
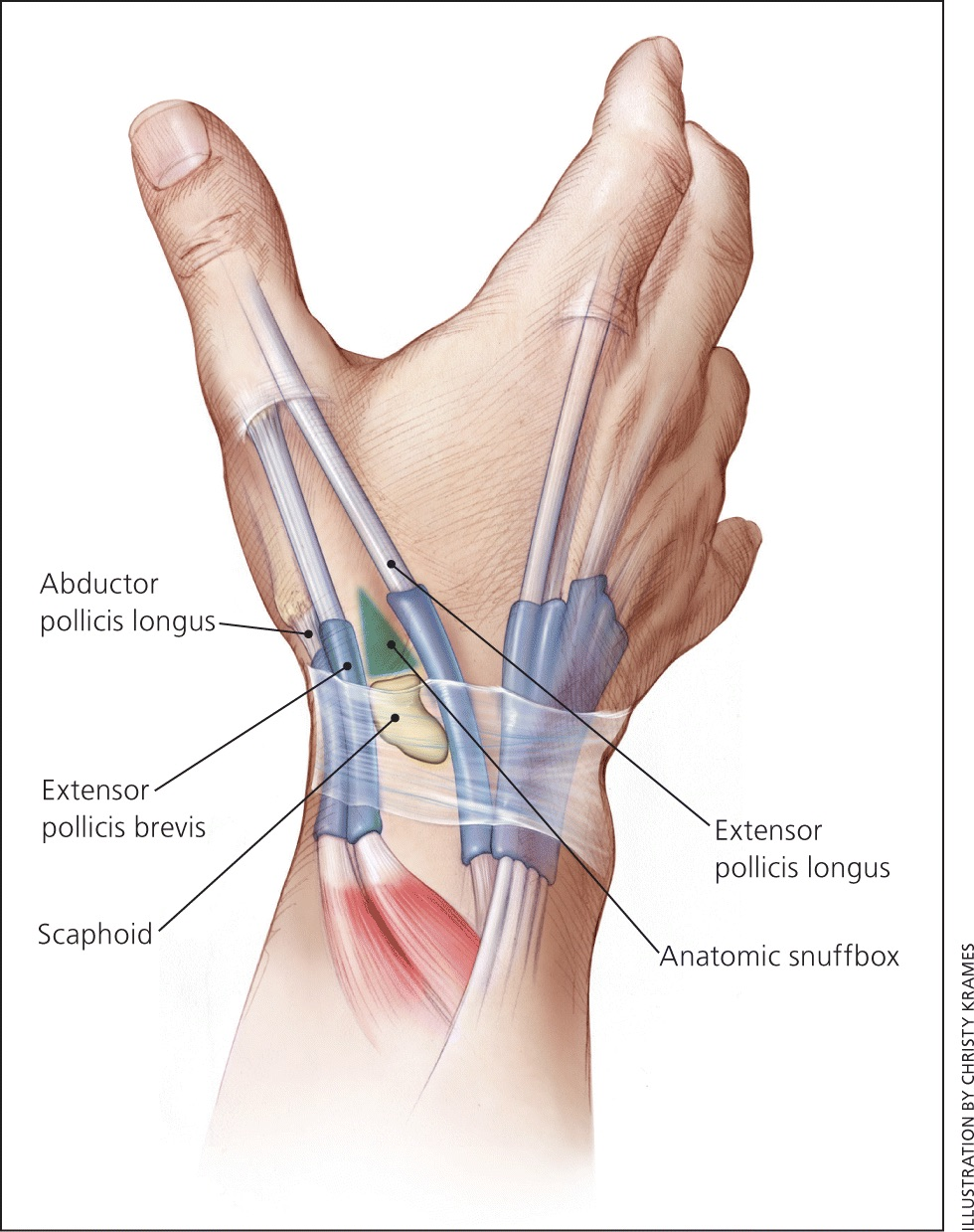
‘outcropping muscles’/muscles making up the ‘anatomical snuffbox’
think ‘brevis sandwich’:
abductor pollicis longus
extensor pollicis brevis
extensor pollicis longus
extensor indicis (sometimes excluded)
(posterior deep antebrachium)
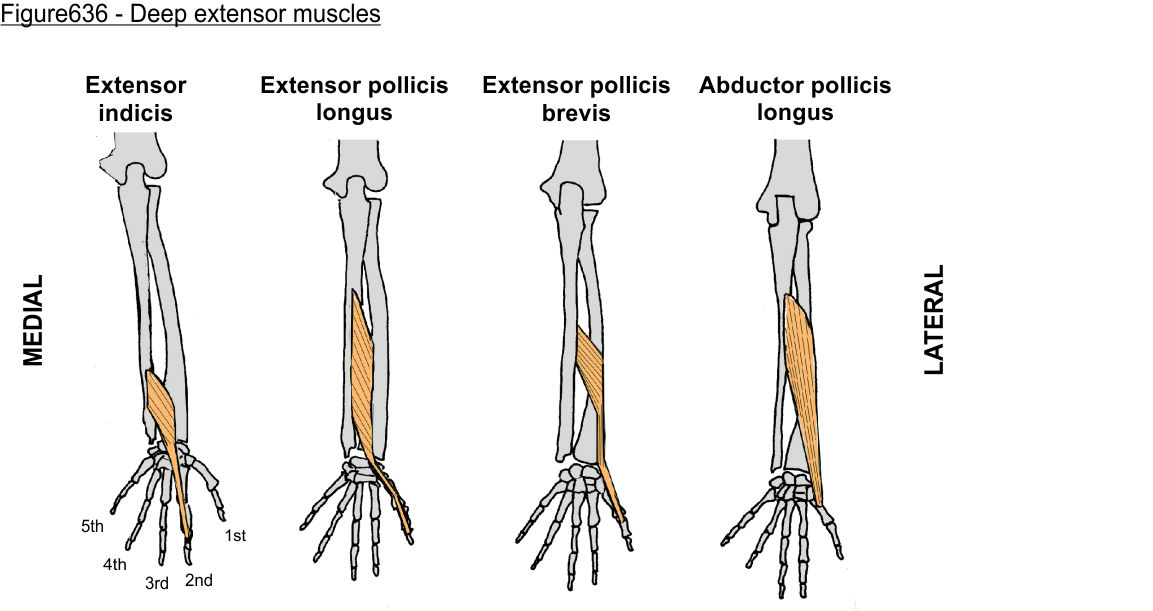
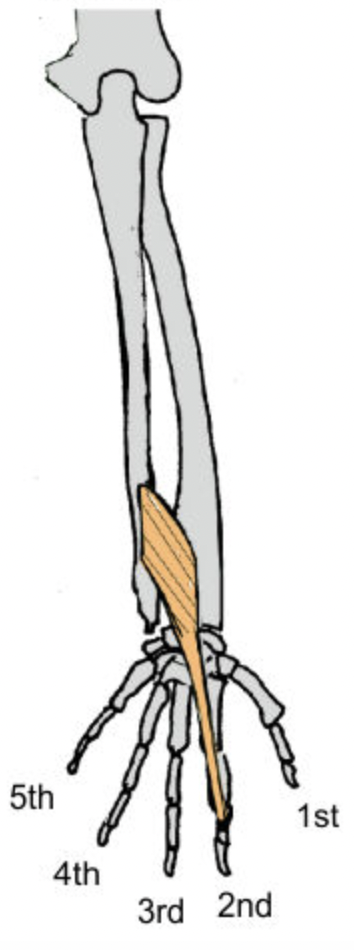
extensor indicis (posterior deep antebrachium)
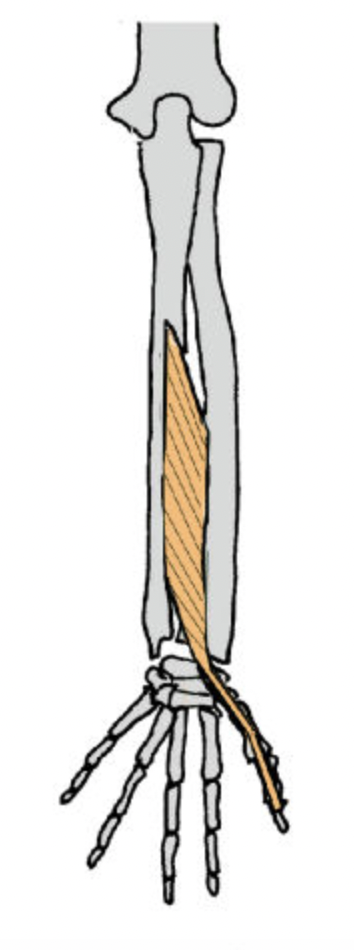
extensor pollicis longus (posterior deep antebrachium)
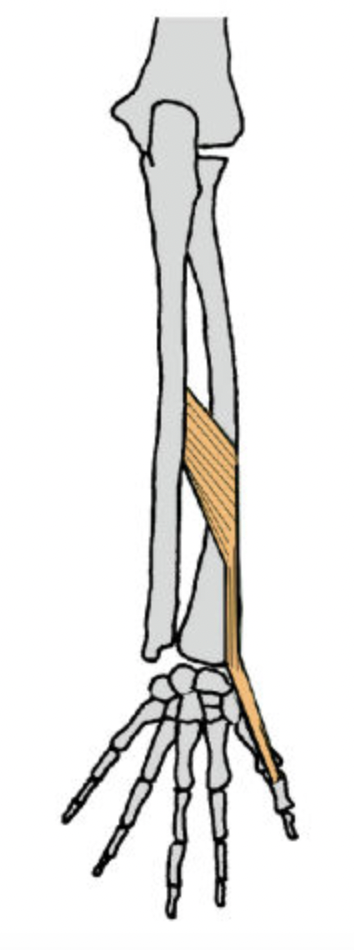
extensor pollicis brevis (posterior deep antebrachium)
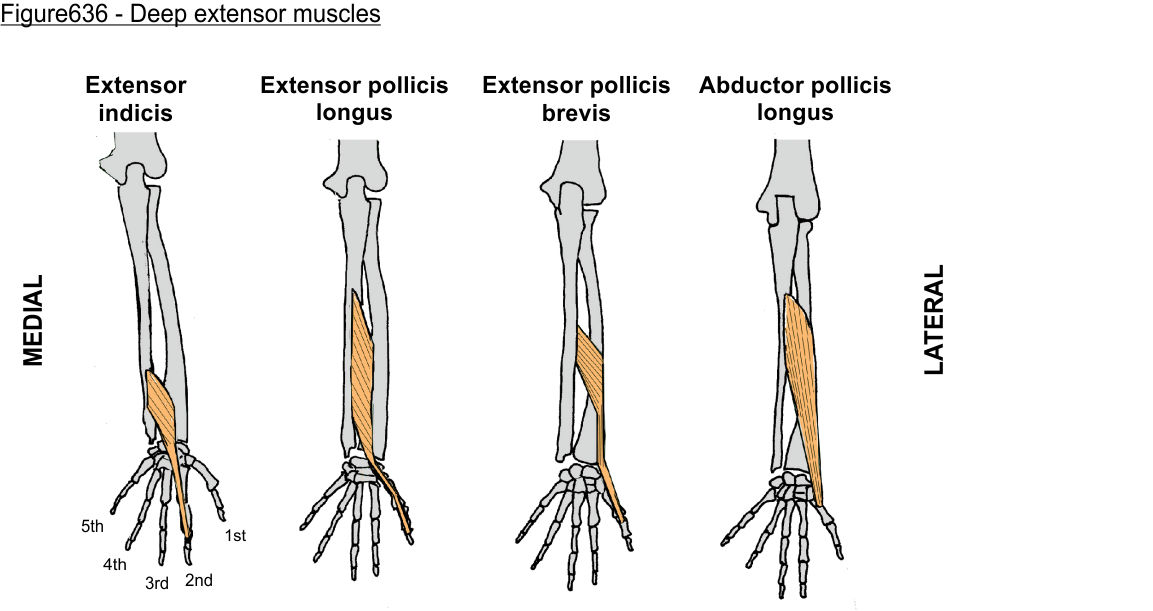
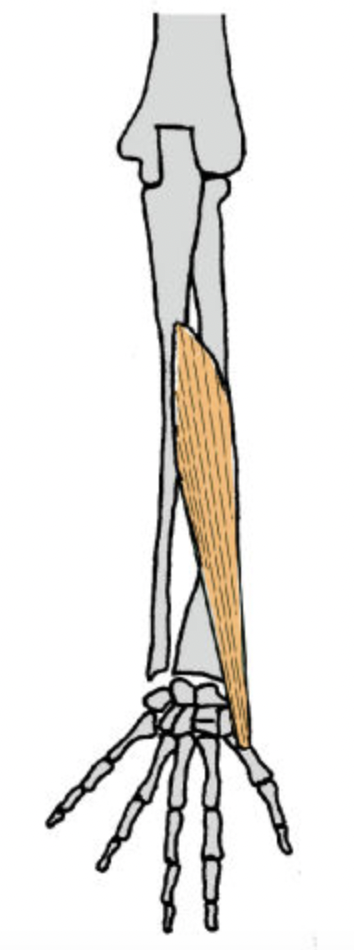
abductor pollicis longus (posterior deep antebrachium)
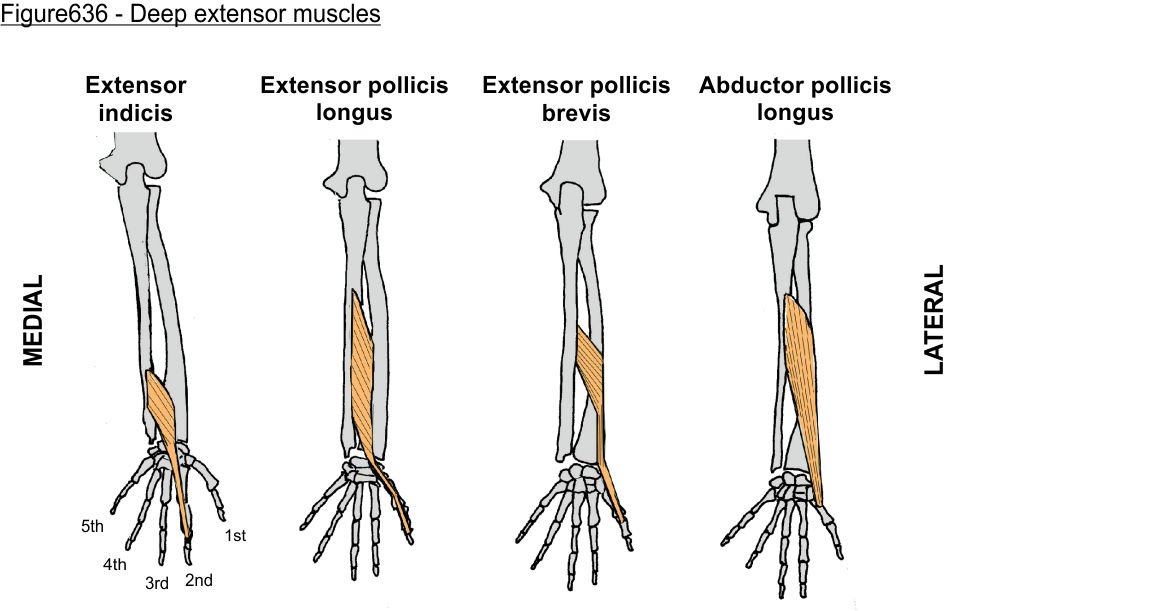
abductor pollicis longus (posterior deep antebrachium) (bottom of the thumb)
(part of anatomical snuffbox)
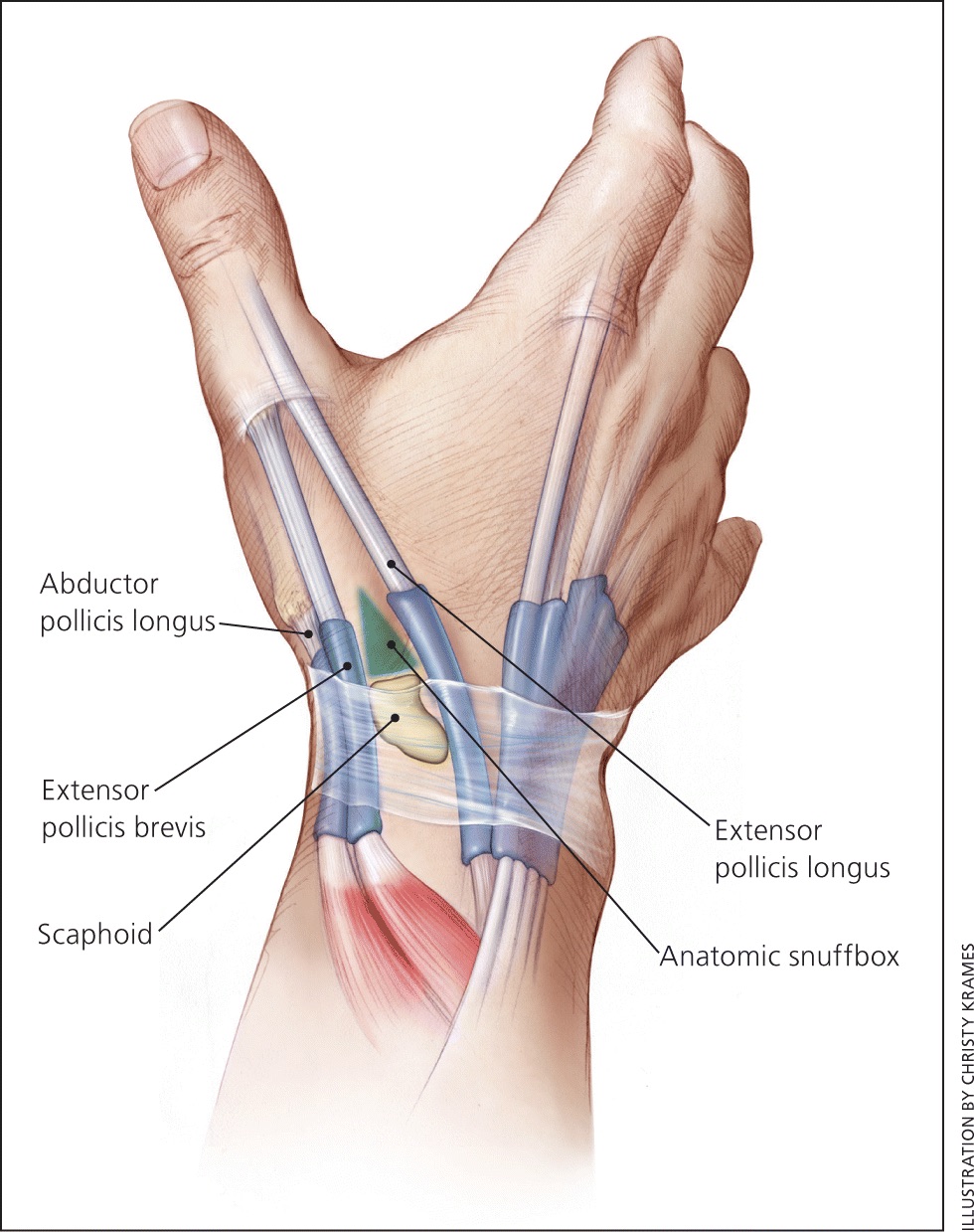
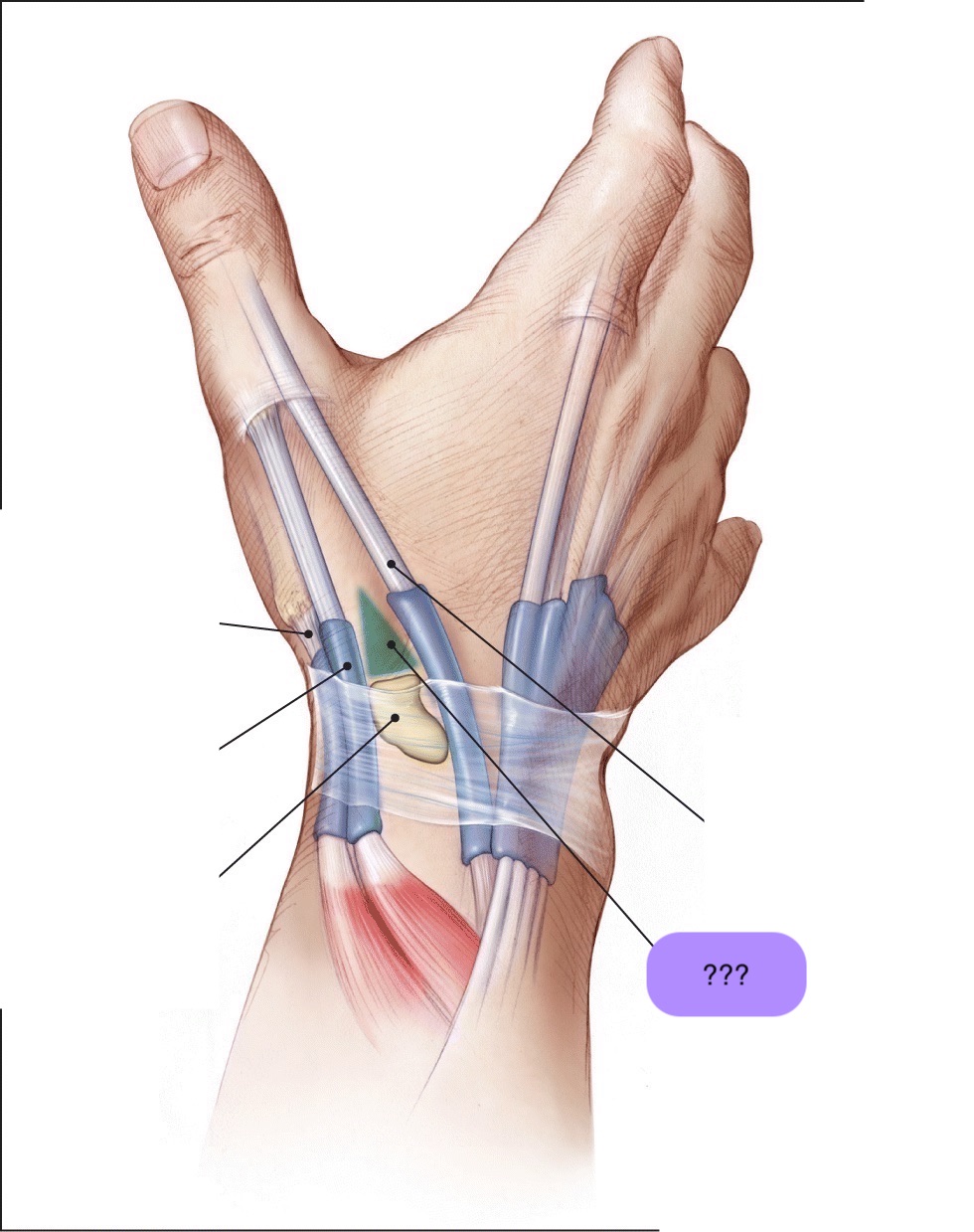
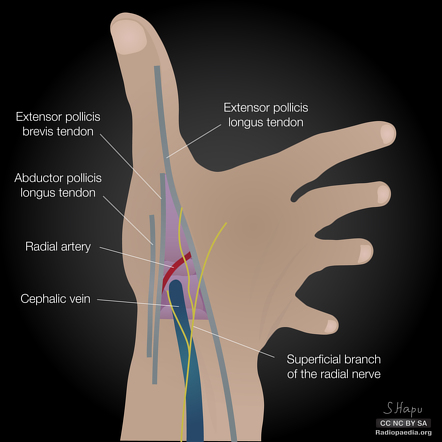
anatomical snuffbox
branch of the radial nerve + radial comes through this region
scaphoid fractures (common) can lead to laceration of artery and damage to nerve
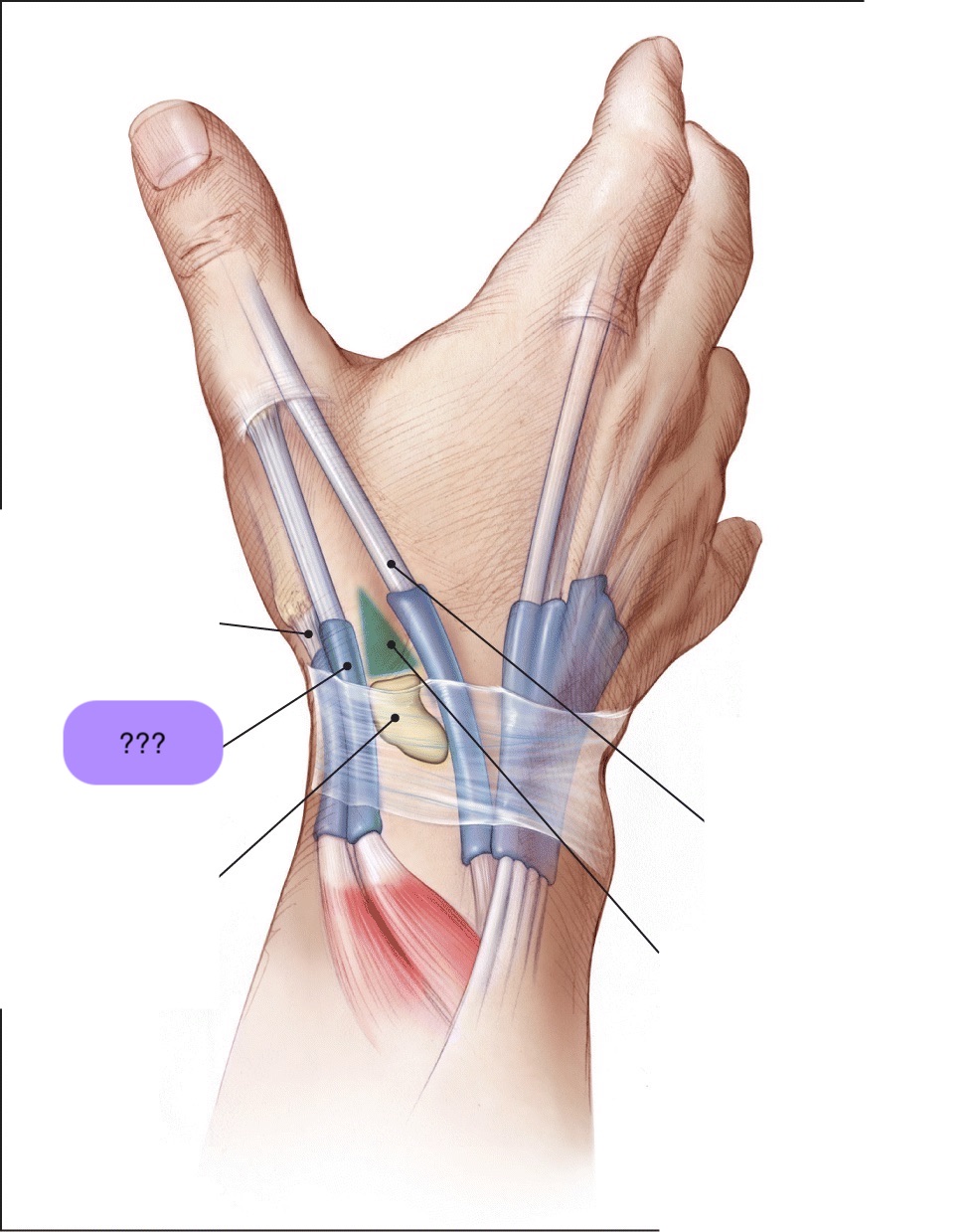
extensor pollicis brevis (posterior deep antebrachium) (attaches to the thumb, shorter than longus)
(part of anatomical snuffbox)
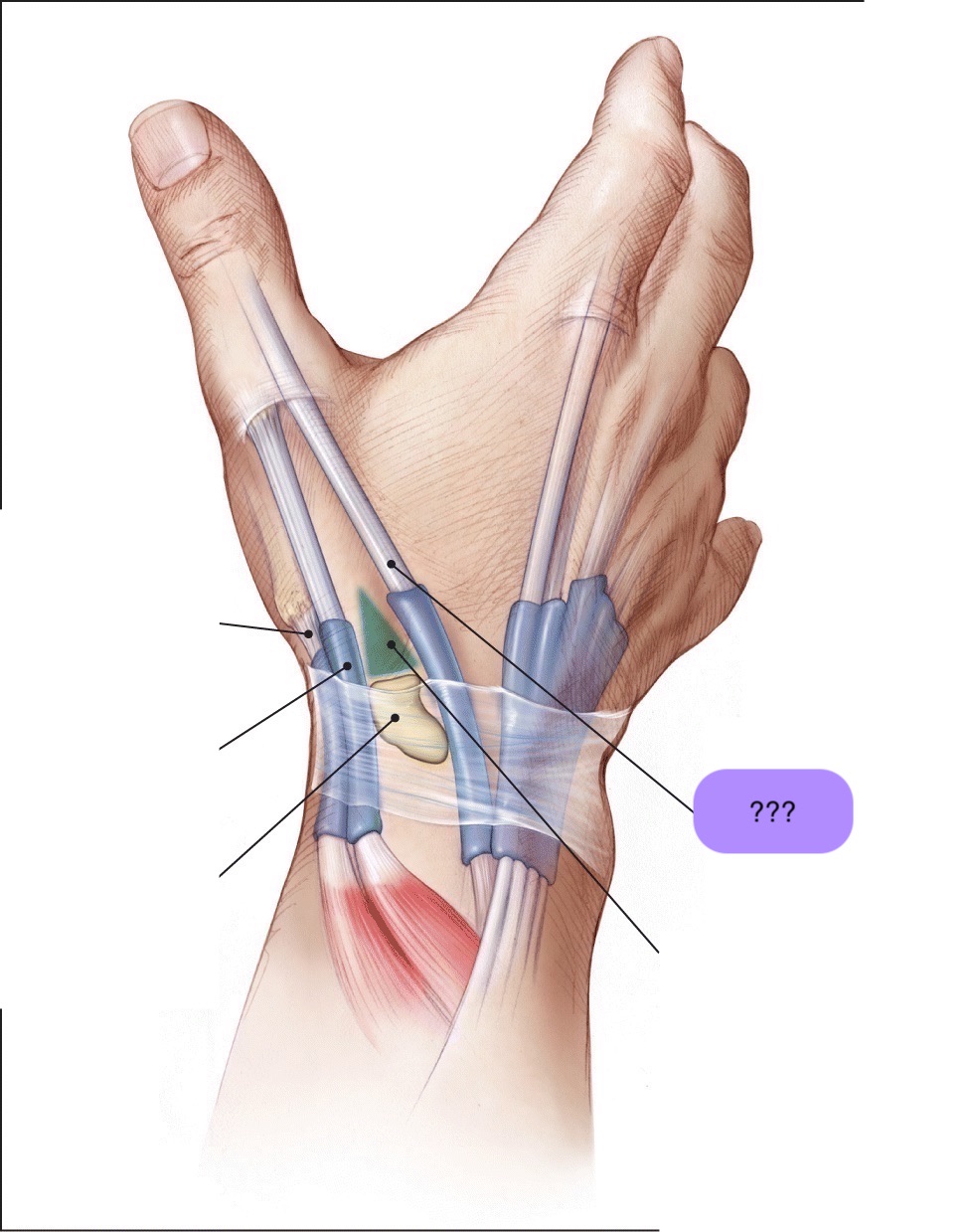
extensor pollicis longus (posterior deep antebrachium)

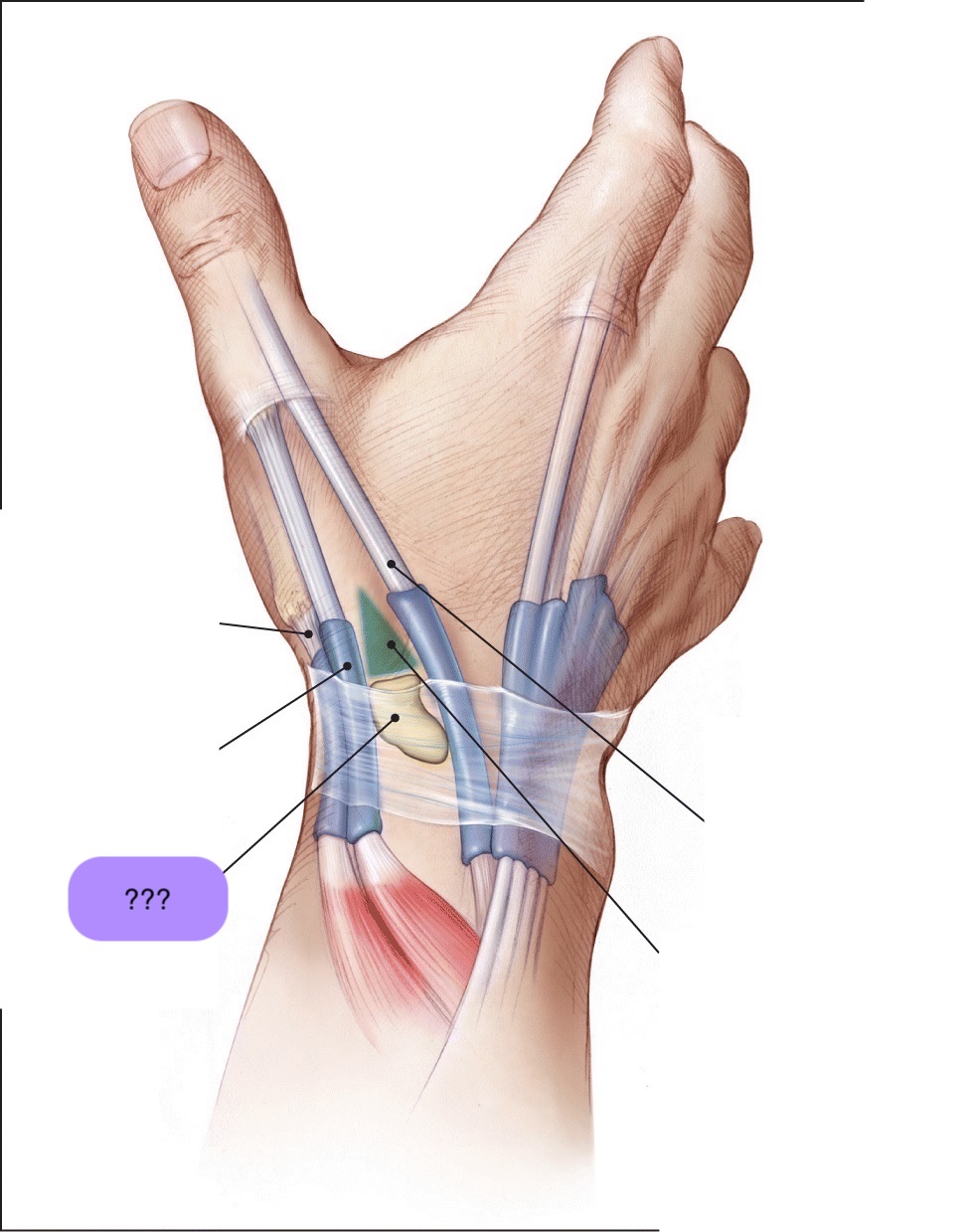
scaphoid
posterior superficial antebrachium muscles
anconeus
extensor carpi ulnaris
extensor digiti minimi
extensor digitorum
arise from the lateral humeral epicondyle, via the common extensor tendon
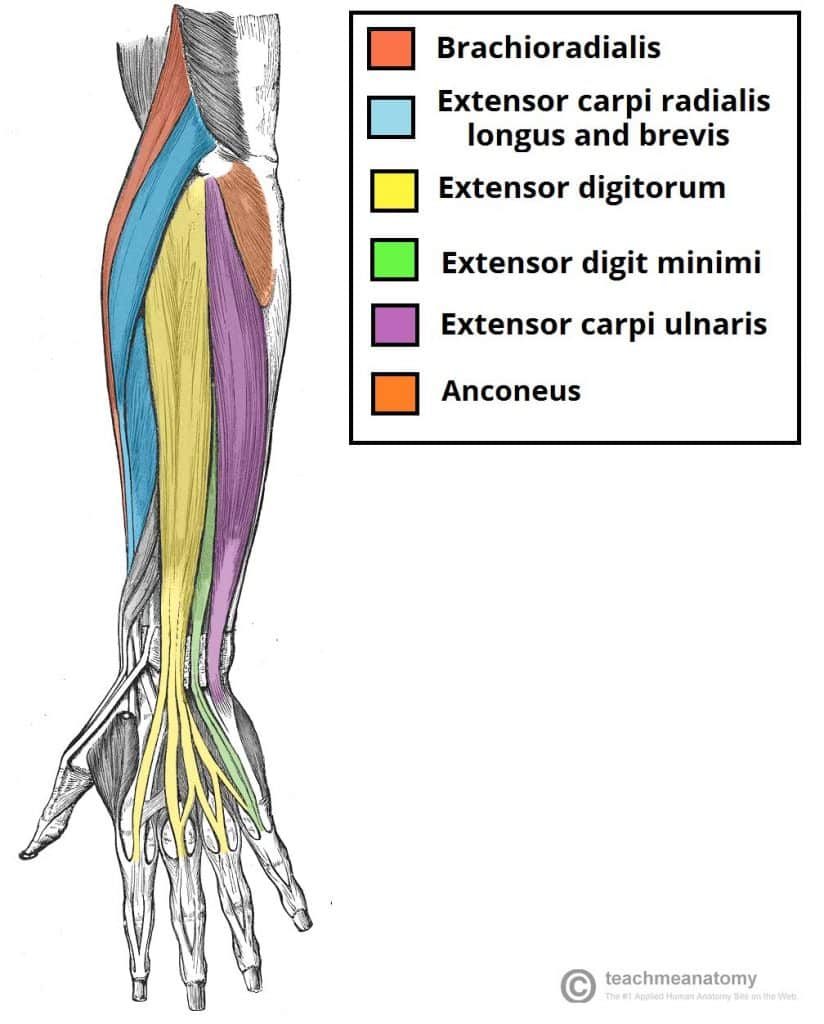
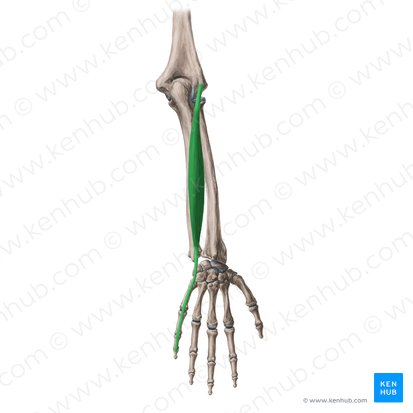
extensor digiti minimi (insertion: 5th digit) (posterior superficial antebrachium)

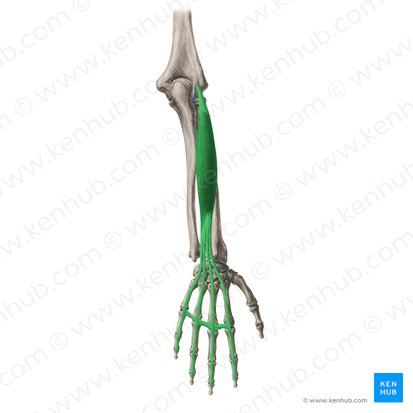
extensor digitorum (insertion: medial four digits) (posterior superficial antebrachium)

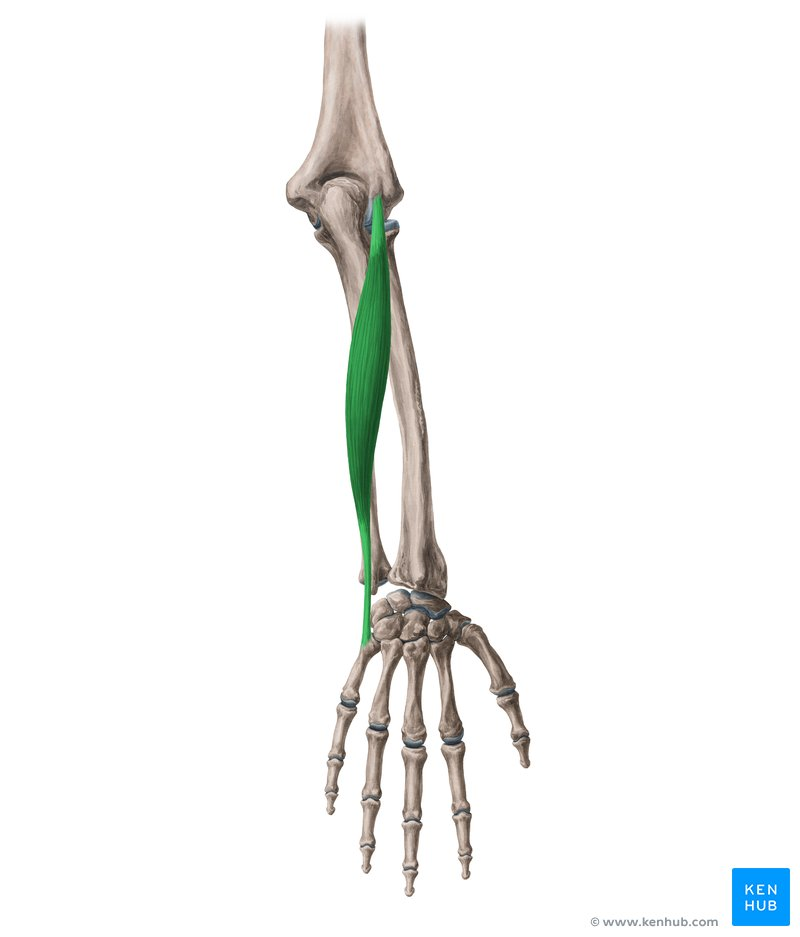
extensor carpi ulnaris (insertion: base of 5th metacarpal) (posterior superficial antebrachium)

tennis elbow
epicondylitis lateralis: inflammation of lateral epicondyle
attachment point for the four posterior superficial antebrachial muscles (extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi, extensor carpi ulnaris, and anconeus)
+ extensor carpi radialis brevis
pain on extension of the wrist
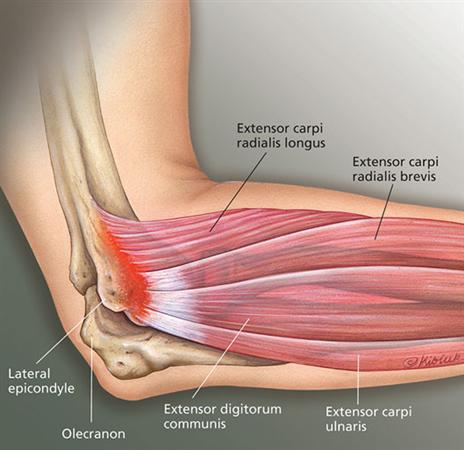
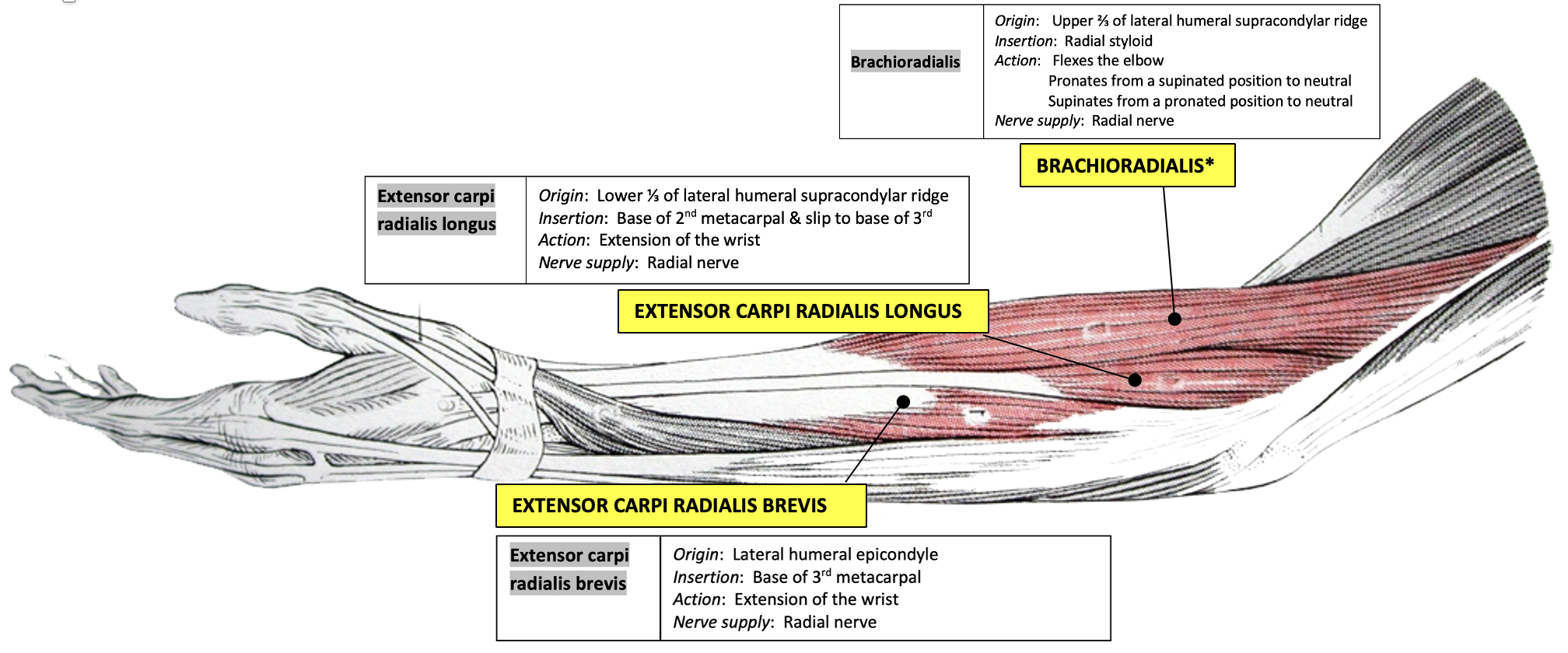
mobile wad of three
three muscles forming the lateral bulge at the elbow:
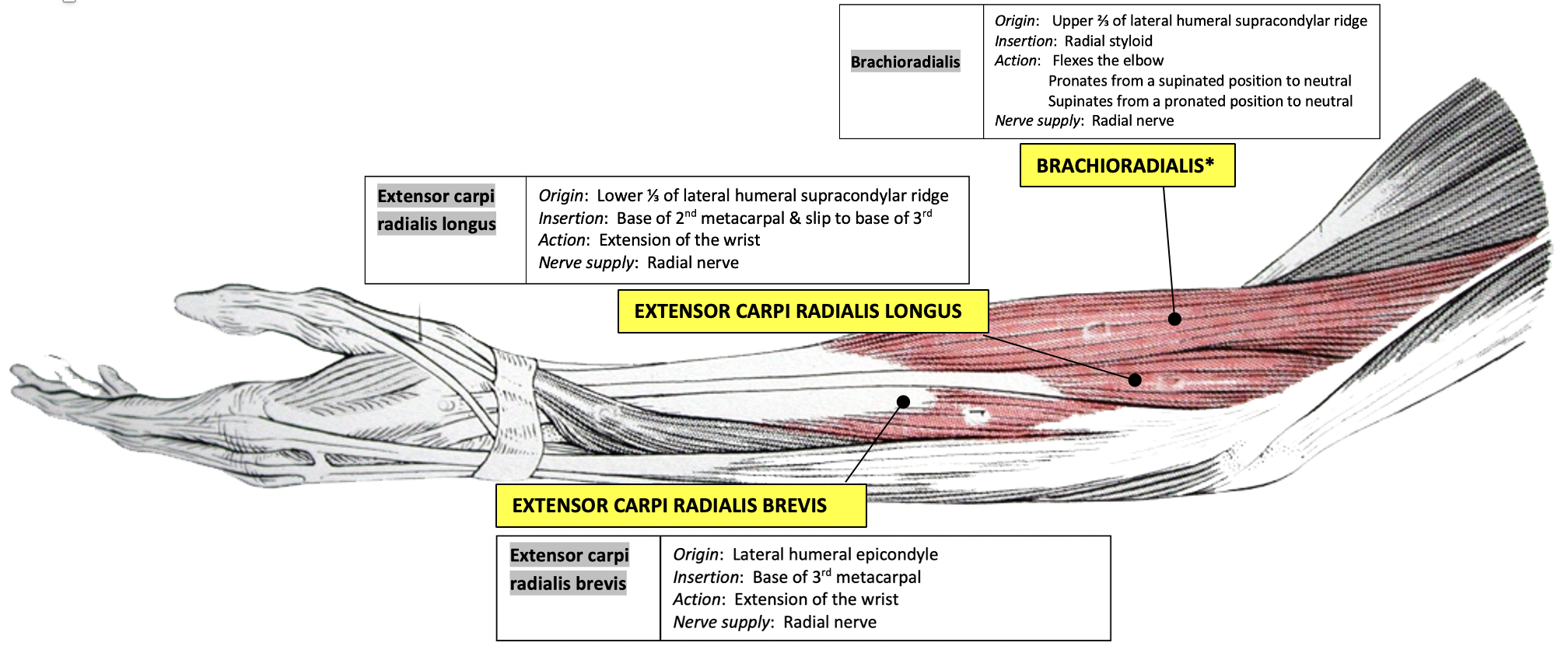
brachioradialis
(flexes elbow)
extensor carpi radialis longus
(base 3rd metacarpal)
extensor carpi radialis brevis
(base 2nd metacarpal)
nerve supply: radial nerve
posterior antebrachium
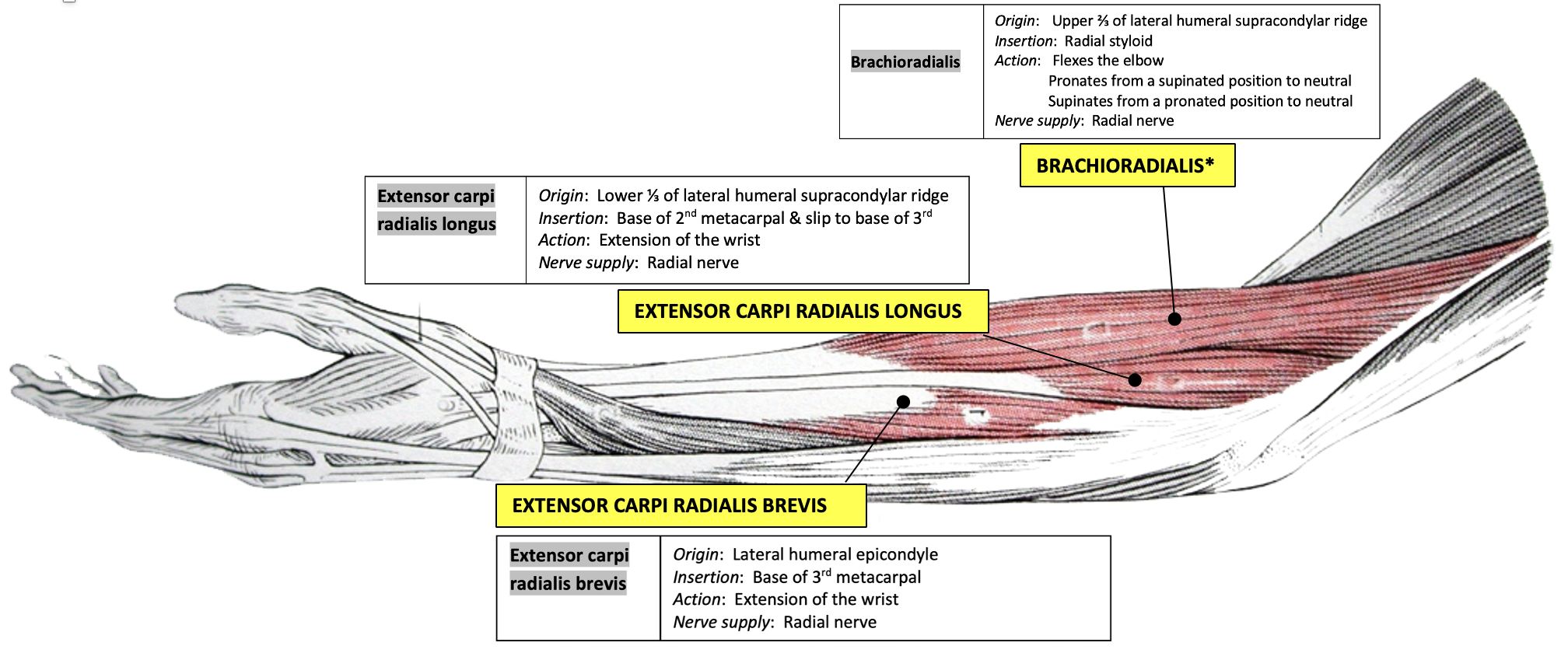
brachioradialis (“beer drinking muscle”)
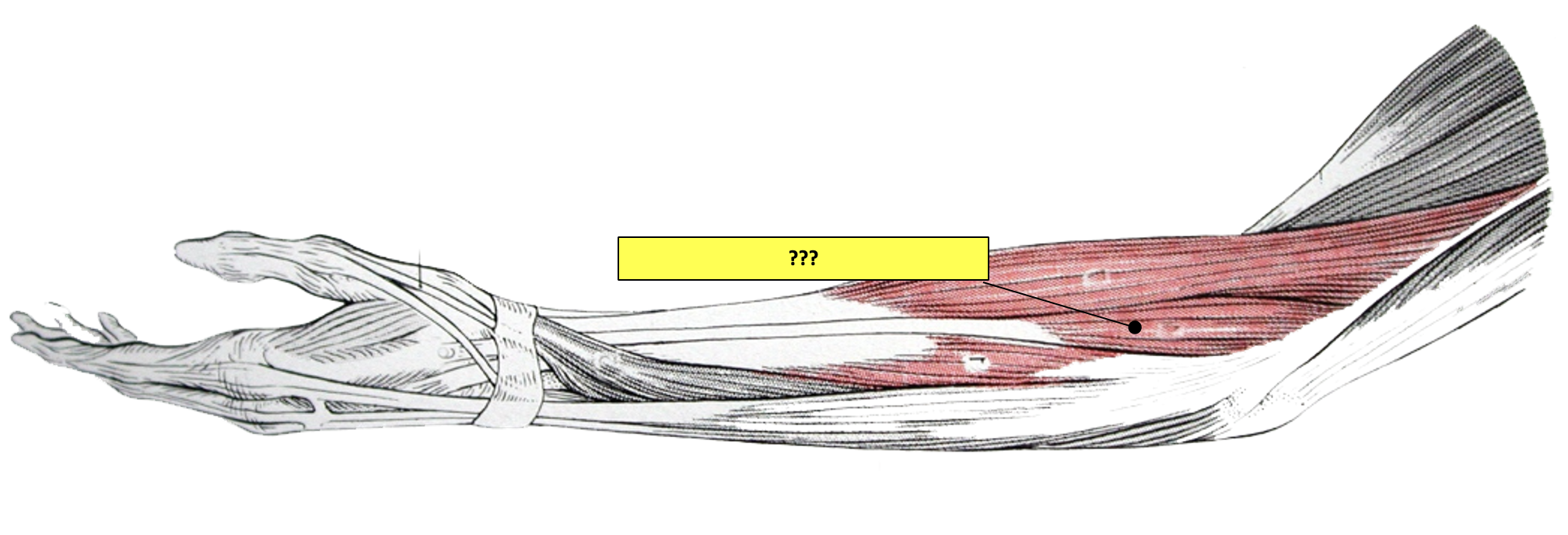
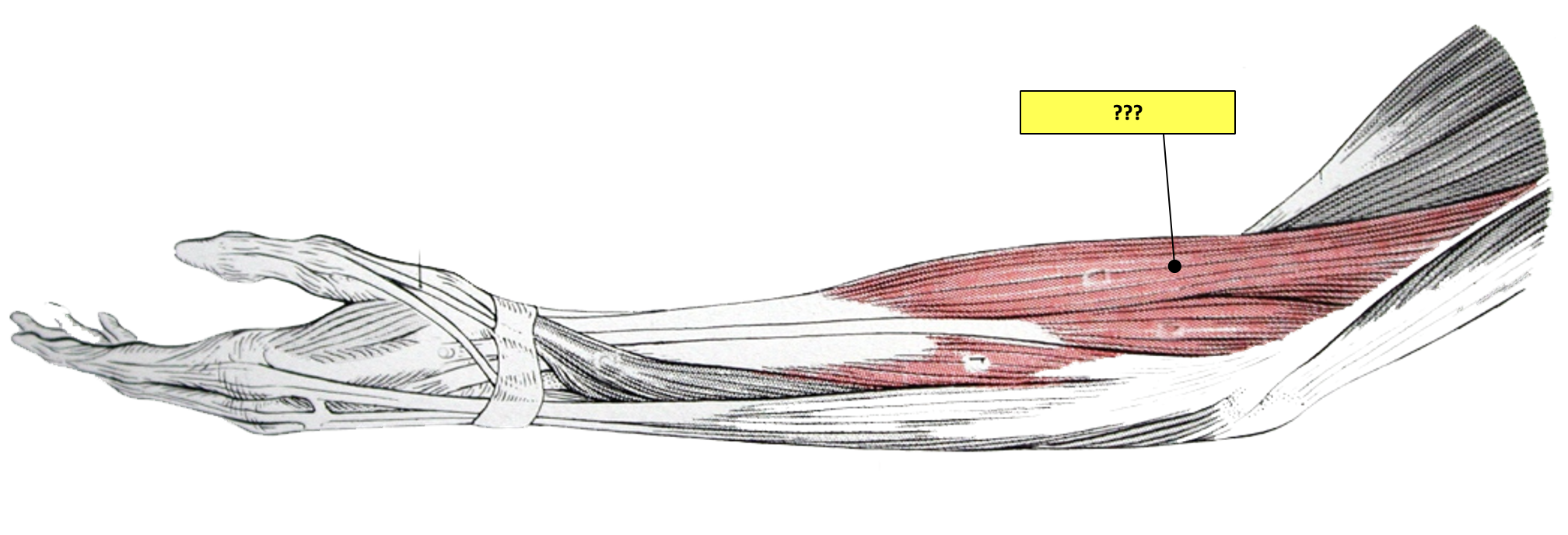
extensor carpi radialis longus