anatomy I - MIDTERM 1
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
what are the axio-appendicular muscles ?
-pectoralis major
-pectoralis minor
-serratus anterior
-subclavius
pectoral region makes up what ?
makes up the anterior chest
what is the pectoral region comprised of ?
-muscle
-fascia
-fat
what does the pectoral region provide ?
provides useful open-chain and closed-chain functions
OPEN-CHAIN: distal segment is FREE on fixed proximal segment (bench press)
CLOSED-CHAIN: distal segment is FIXED on moving proximal segment (push ups- humerus fixed, shoulder moving over it)
can the pectoral region affect posture ?
yes, if dysfunctional
abduction ROM is measured using what as a landmark ?
mid axillary line
what other line are used for descriptors for surface anatomy ?
-anterior median line (going down middle body in front)
-scapular planes
-posterior median line (going down middle of back)
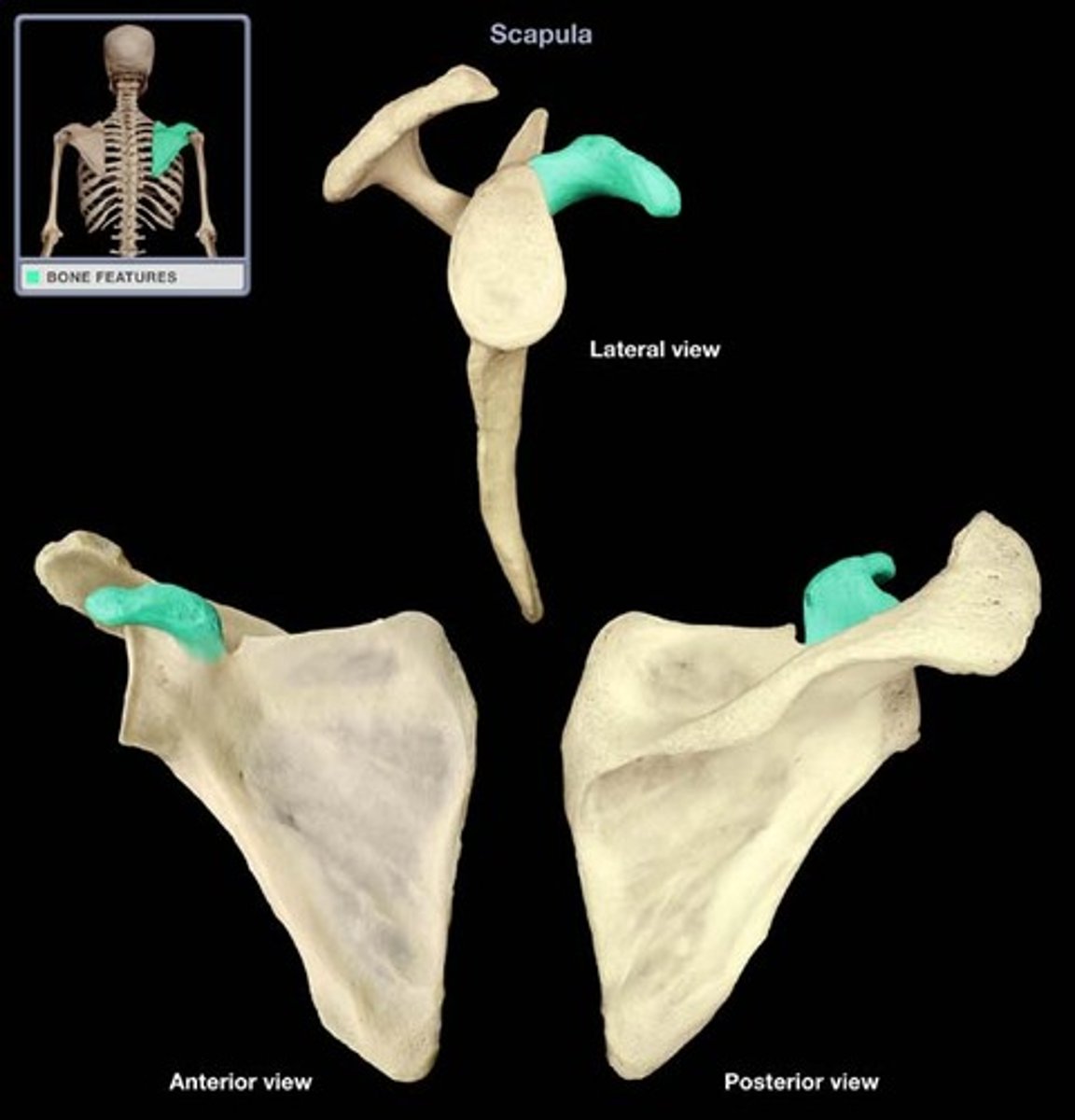
coracoid process of scapula
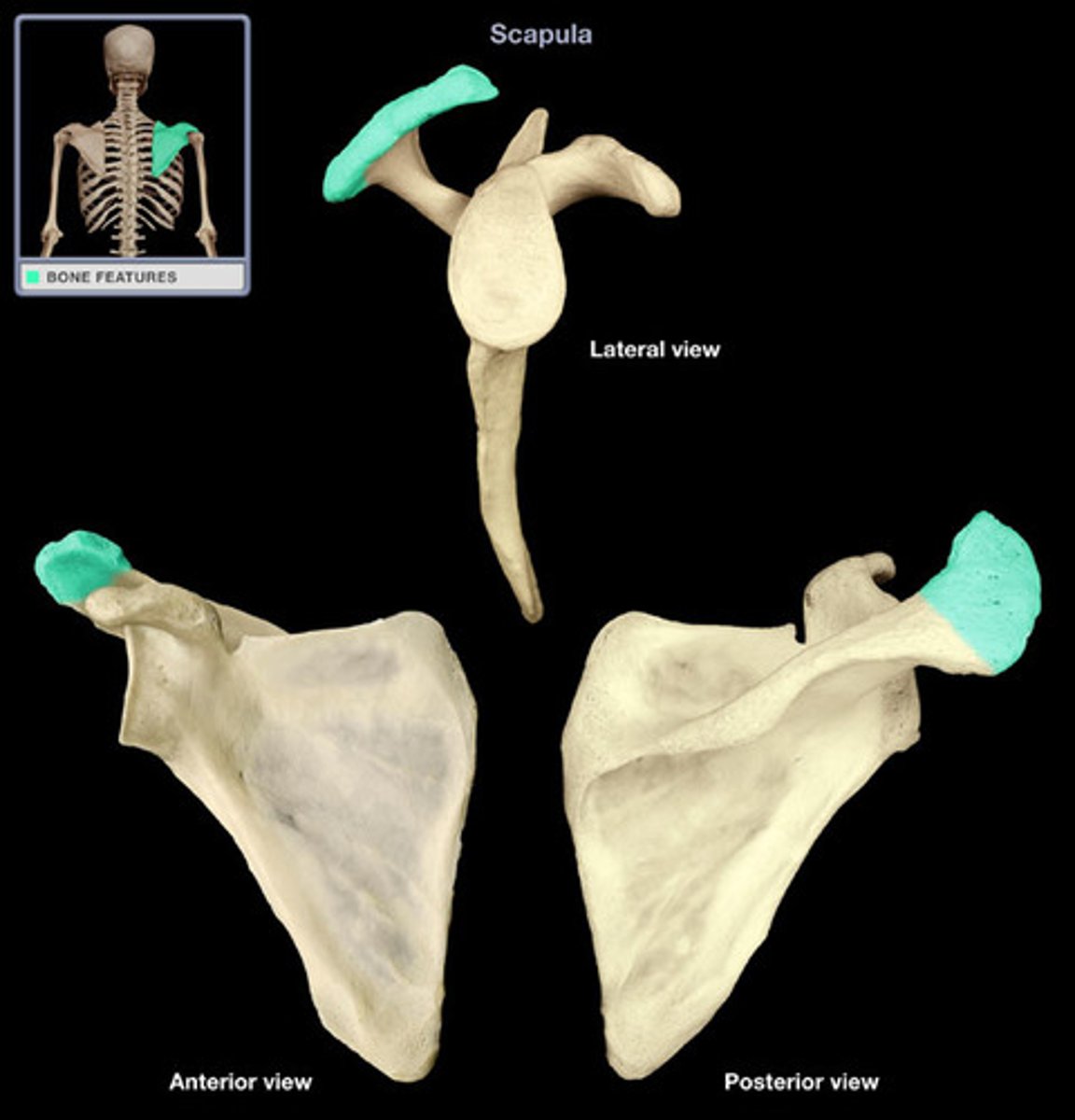
acromion process of scapula
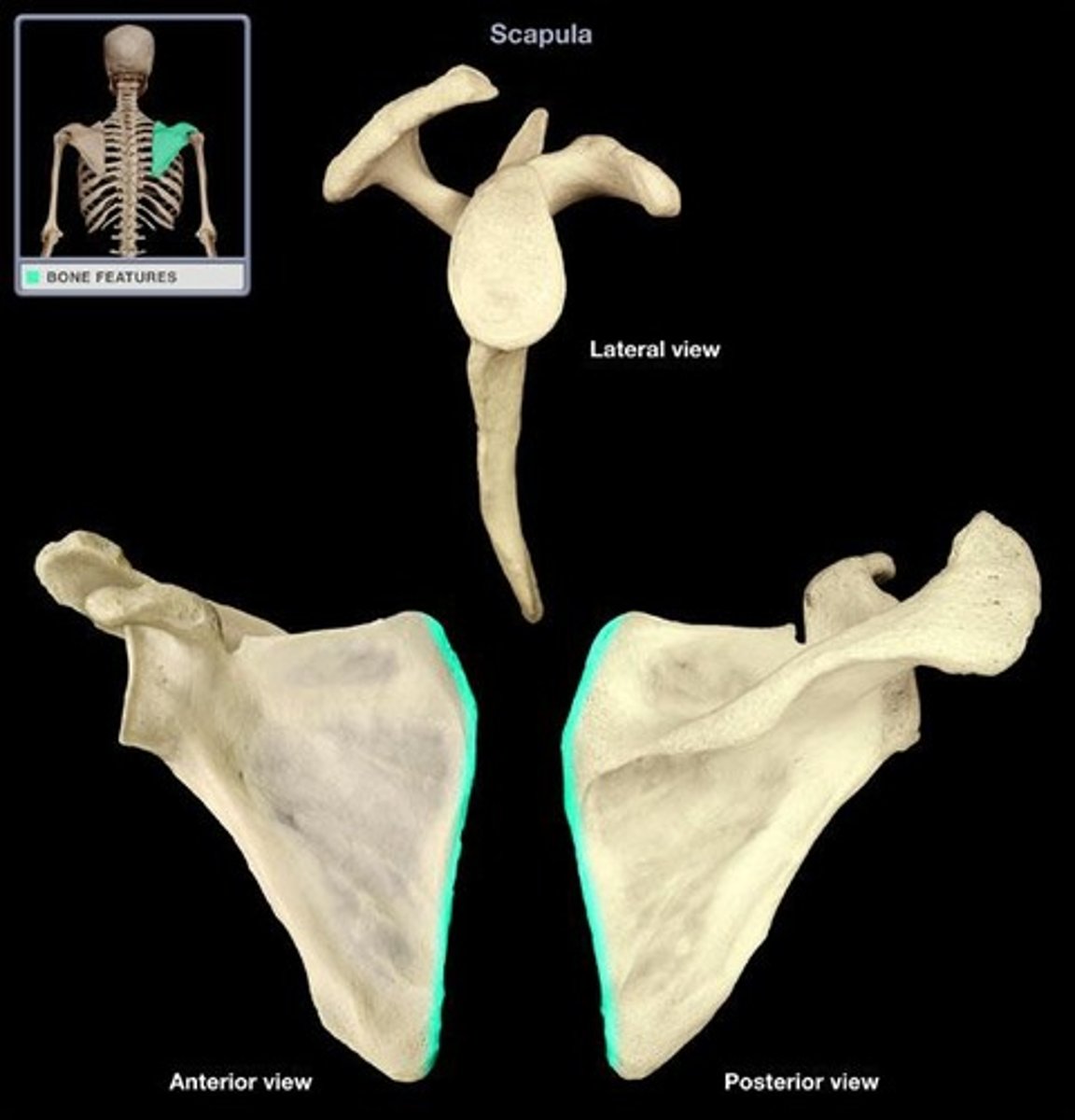
anterior surface of medial border of scapula
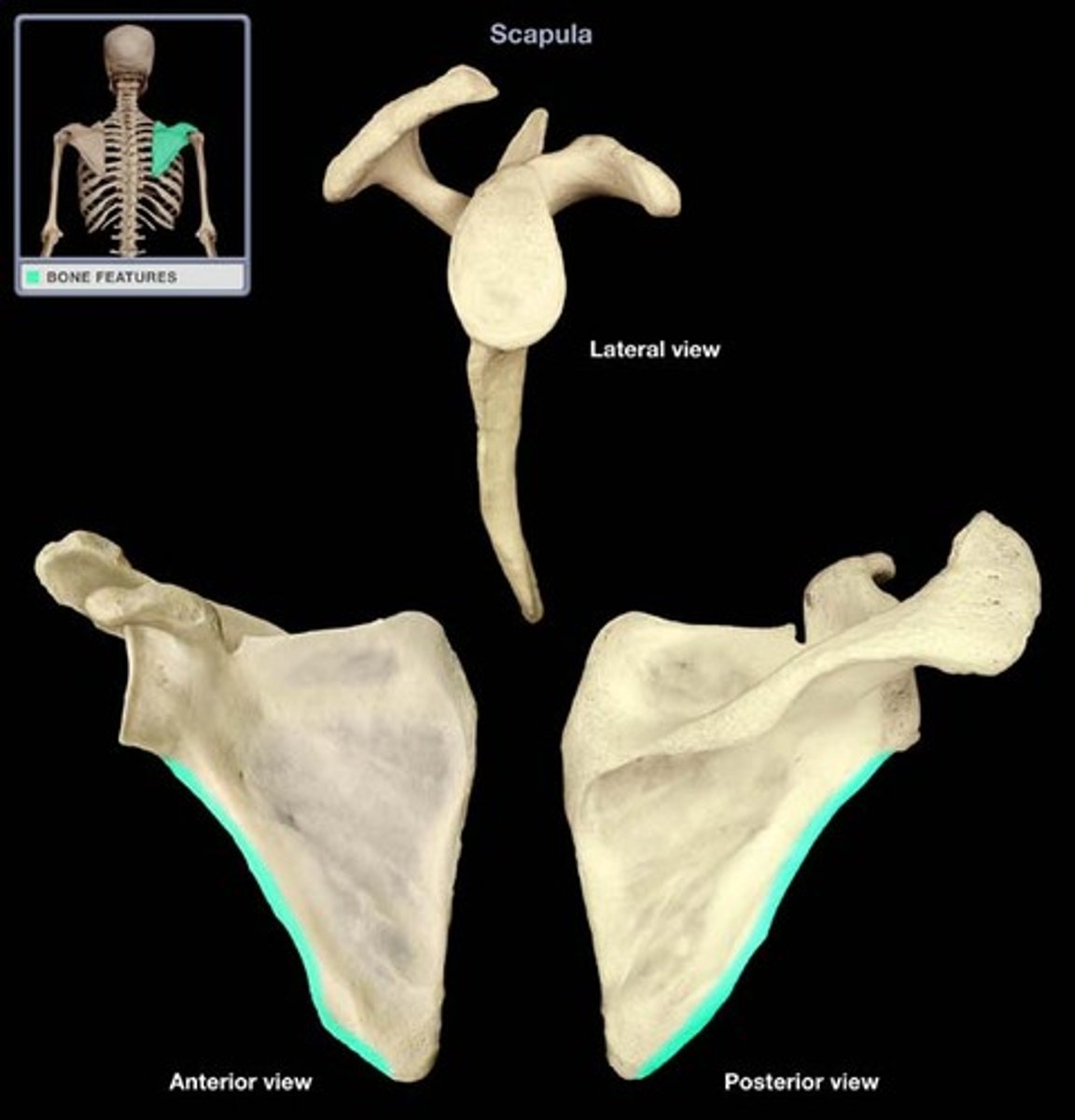
lateral border of scapula
what is the most common site for clavicle fracture ?
middle 1/3 of the clavicle
what kind of action, activity, or motion causes a clavicular fracture ?
-indirect force transmitted from outstretched hand through the bones of the forearm & arm to the shoulder during a fall
-fall directly on the shoulder
when the clavicle fractures, what does the displacement look like ?
-sternocleidomastoid M. elevates the medial fragment of the bone
-trapezius M. is unable to hold the lateral fragment up, resulting in shoulder drop
**the end of the superiorly directed fragment is prominent**
what is a dermatome ?
a segment of skin innervated by a spinal segment
motions of the shoulder
-abduction/adduction
-flexion/extension
-internal rotation/external rotation
-horizontal abduction/horizontal adduction
-scaption
what is the muscle pierced by under the fascial layer ?
several cutaneous nerves
what are the boundaries of the deltopectoral triangle ?
clavicle (superior)
pectoralis major (medial)
deltoid (lateral)
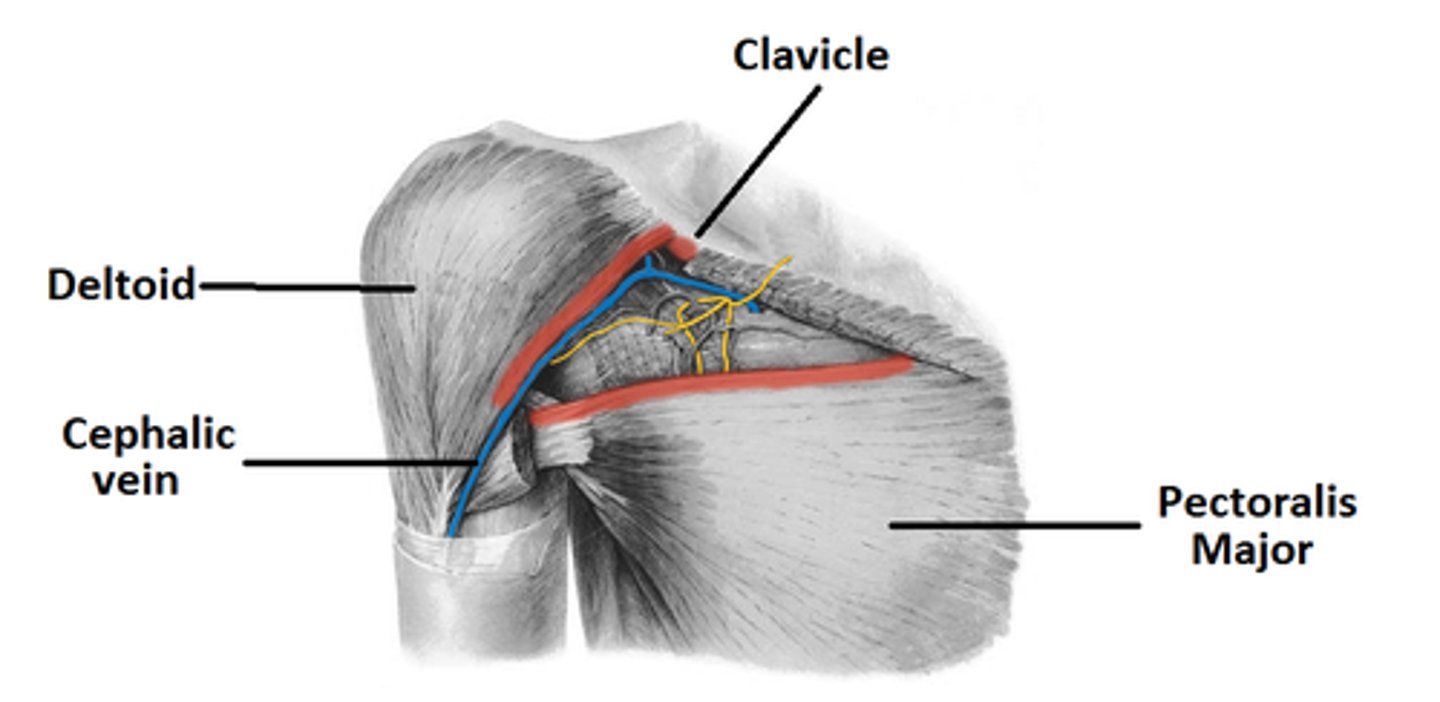
what travels through the deltopectoral triangle ?
the celphalic vein (travels w deltoid branch of thoracoacromial artery)
what opens at the deltopectoral triangle ?
clavipectoral fascia opens here
first branch of axillary artery contains what ?
superior thoracic artery
second branch of axillary artery contains what ?
-thoracoacromial artery
-lateral thoracic artery
third branch of the axillary artery contains what ?
-anterior circumflex humeral artery
-posterior circumflex humeral artery
-subscapular artery
what is the axilla ?
-main highway from head/neck/thorax/ to the upper limb
-"armpit"
what are the sides to the pyramid within the axilla ?
-anterior border= pectoralis major
-posterior border= lats, teres major, subscapularis
-medial border= serratus anterior
-lateral border= humerus
-apex= superior aspect of acromion process and under
-floor/base= axillary fascia/skin/adipose tissue
why are there not a lot of structures under the axilla ?
allows for more ROM
why is the axillary fascia highly vascularized ?
for protection, this is where all blood/nerves get through
when does the subclavian artery become the axillary artery ?
after it passes 1st rib
when does the axillary artery become the brachial artery ?
after passing the inferior border of teres major
what are the muscles of the axillary region ?
pect major
pect minor
teres major
teres minor
lat dorsi
serratus anterior
biceps brachii
coracobrachialis
subscapularis
what is the orientation of the brachial plexus ?
1. passes through the axilla
2. wraps around the axillary artery
3. branches of the brachial plexus spread out throughout the neck, chest, upper thorax & arm
where does the brachial plexus emerges from ?
-spine at C5-T1
-emerges from between the anterior and middle scalene muscles in the neck
what is the brachial plexus made up of ?
anterior rami
where does the brachial plexus pass under ?
passes under the clavicle into the axilla
3 muscular men, assassinate, 5 rats, 4 mice, 3 ok uncles
musculocutaneous N= C5, C6, C7
axillary N= C5, C6
radial N= C5, C6, C7, C8, T1
median N= C6, C7, C8, T1
ulnar N= C7, C8, T1
peripheral nerve innervation
segments of skin supplied by individual peripheral branches
winged scapula
-medial border sticking out
-long thoracic nerve damage
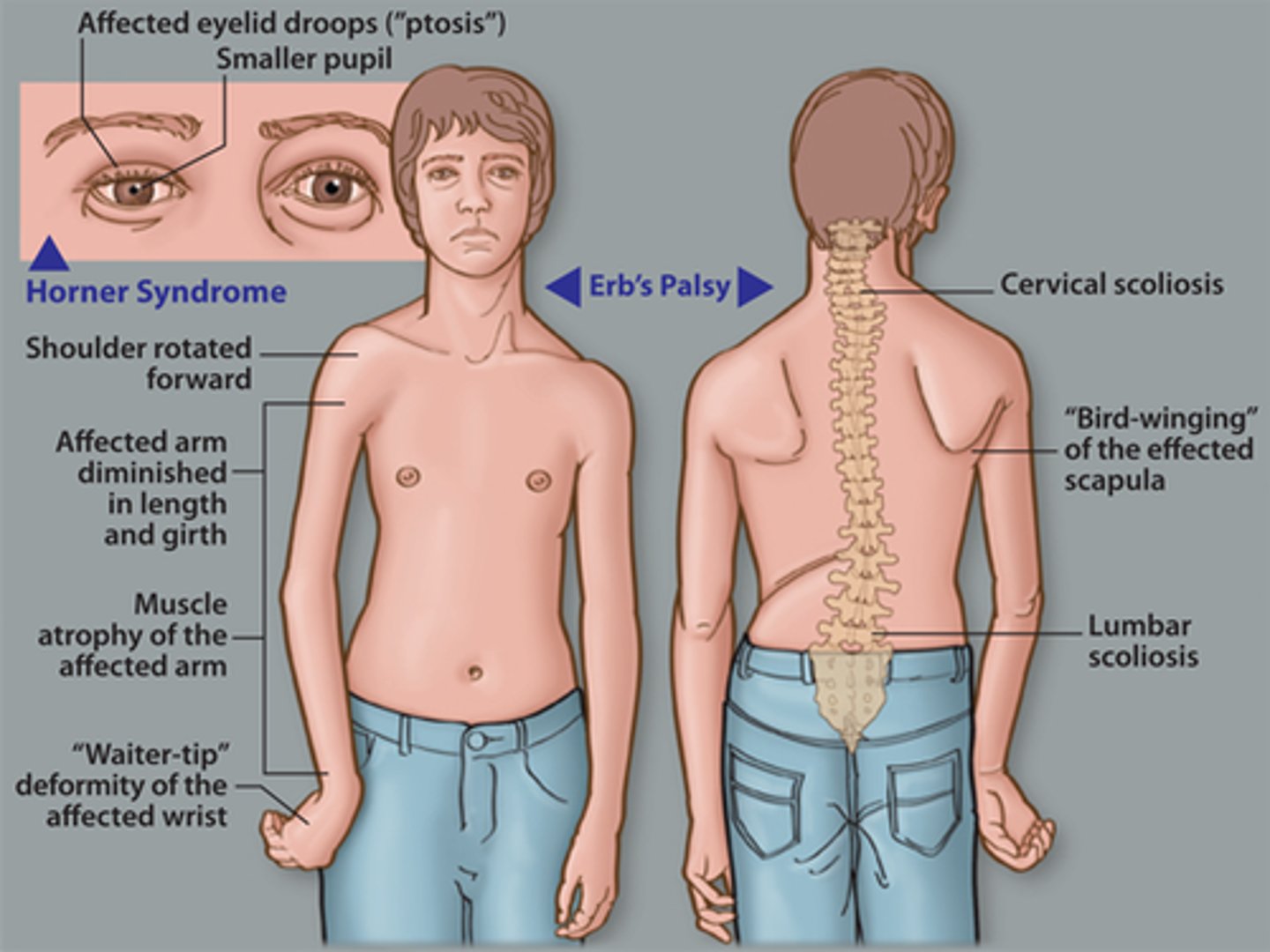
upper brachial plexus injury
"erbs palsy"
-upper brachial plexus injury (superior trunk)
-waiters tip (int. rotated and hanging at side)
-C5, C6
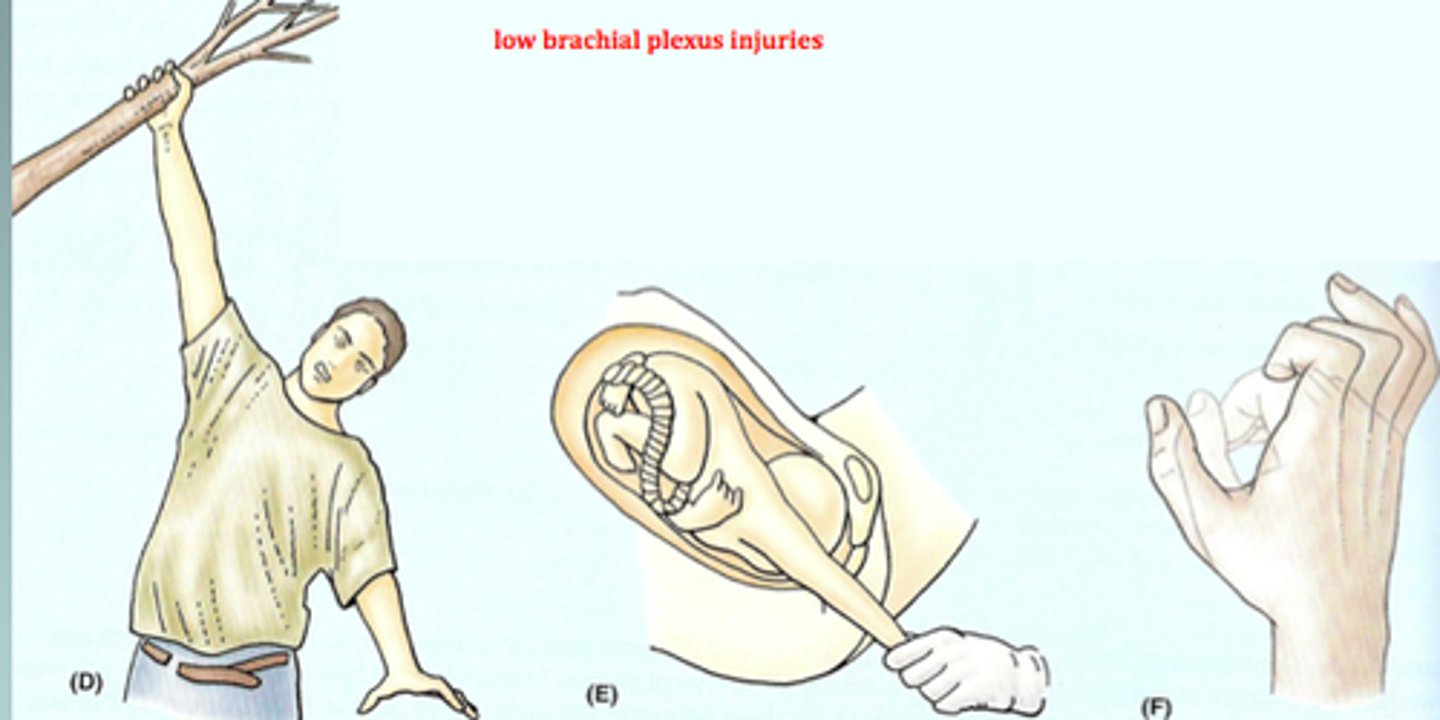
lower brachial plexus injury
"klumpke's palsy"
-lower brachial plexus injury (inferior trunk)
-claw hand
-arm raises too much over body, unable to extend
-C8, T1
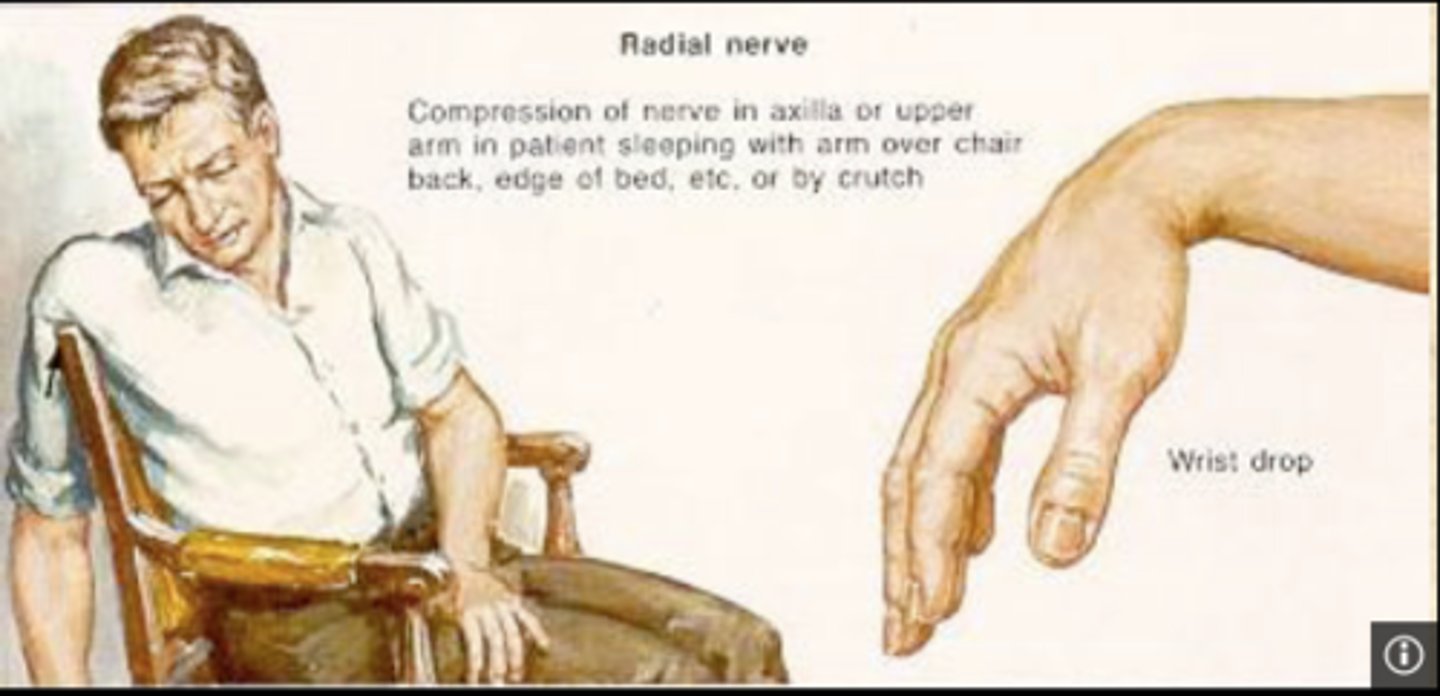
radial nerve injury
"saturday night palsy"
-hyperabduction
-fall asleep w arm up
supraspinous ligament
travels along tip of spinous processes
-resists flexion/over spreading of spinous process
-C7 and below is the supraspinous ligament
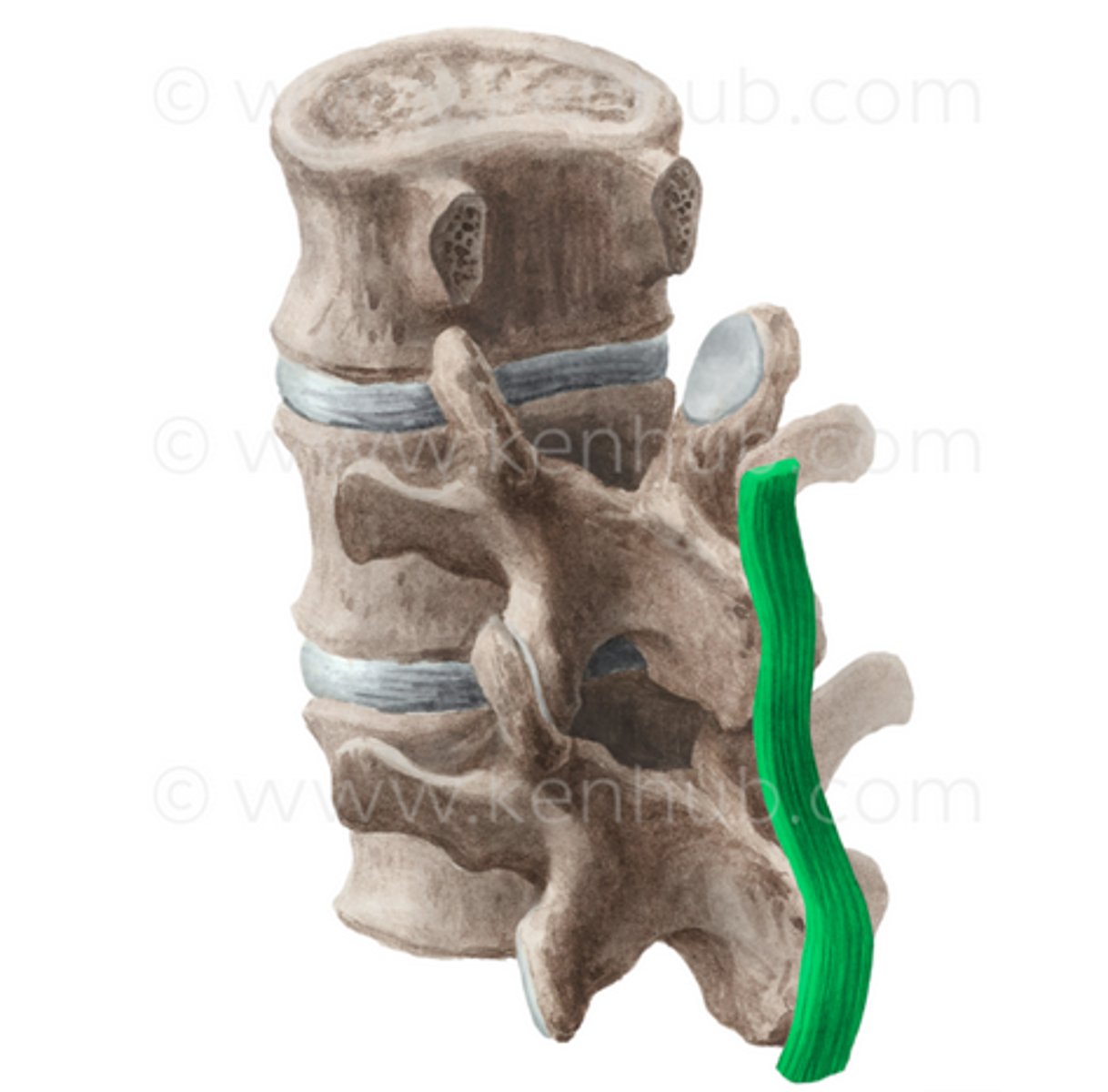
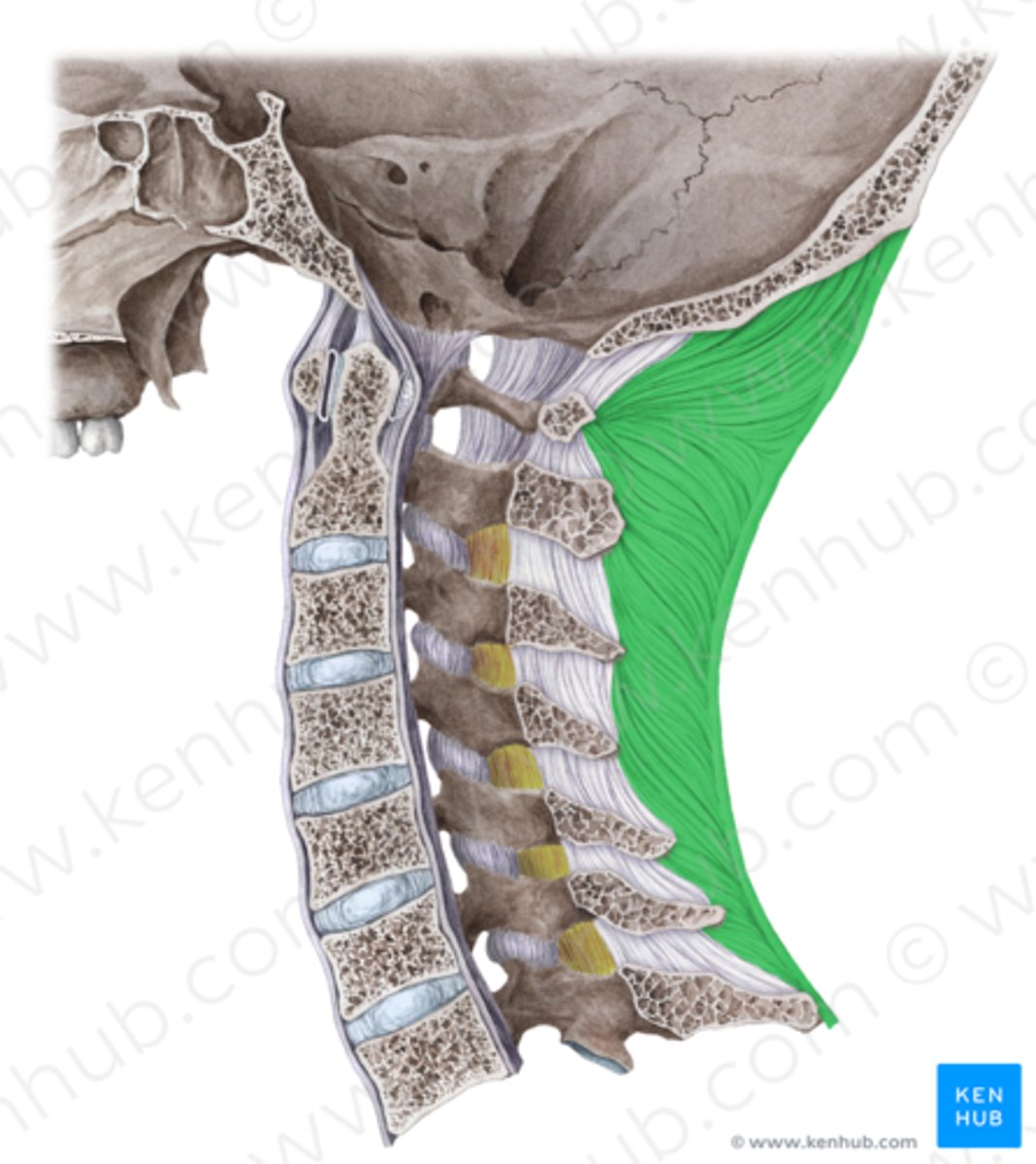
nuchal ligament
-broad dense ligament spanning from spinous processes to skin
-C7 and above is the nuchal ligament
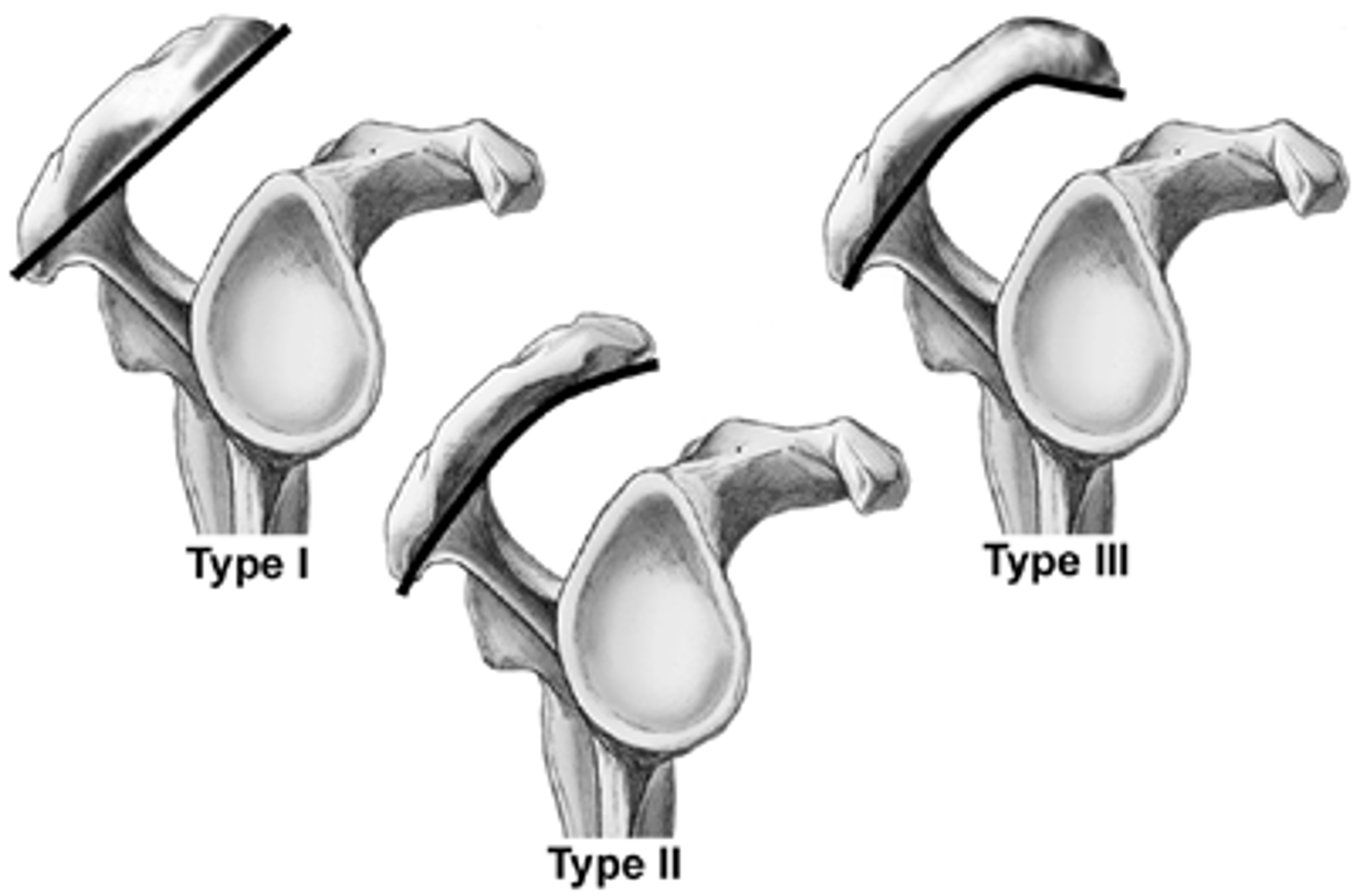
types of acromion
type I= forms straight angle (best for tendon to run under)
type II= small curve
type III= hook (can damage tendon)
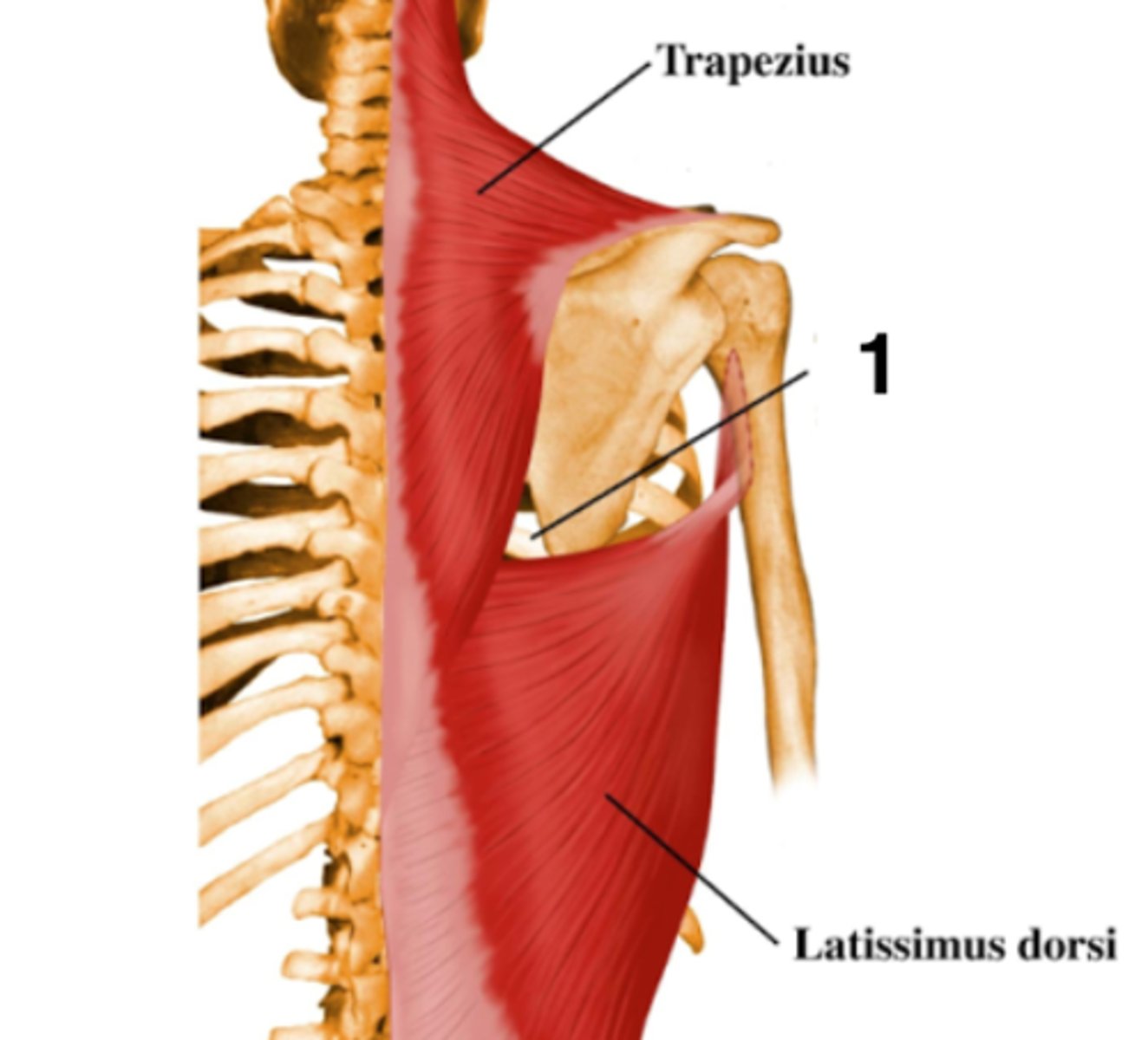
what is the triangle of auscultation good for ?
to listen for breath/lung sounds bc just the ribs there
what is the triangle of auscultation made of ?
trapezius
lat dorsi
medial border of scapula
force couple (ex: scapula)
the scapula can rotate upward and downward due to multiple muscles working together
what does the rotator cuff act as ?
acts as a stabilizer for the GH joint during movement
what is the most common rotator cuff muscle tear ?
supraspinatus
-hypovascular zone
-runs under acromion process= narrow space
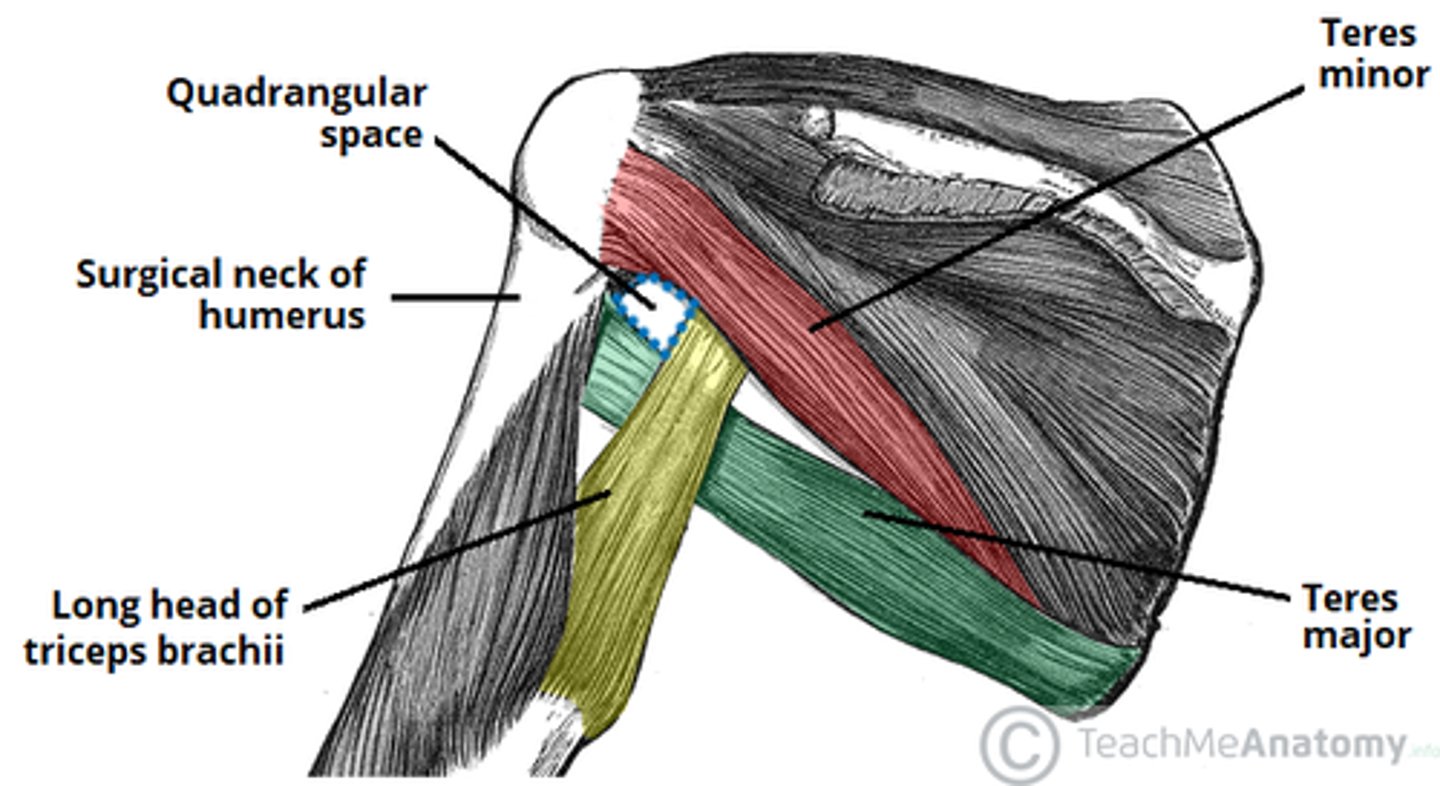
the quadrangular space
long head triceps
teres minor
humerus
the triangular space
teres minor
teres major
long head triceps
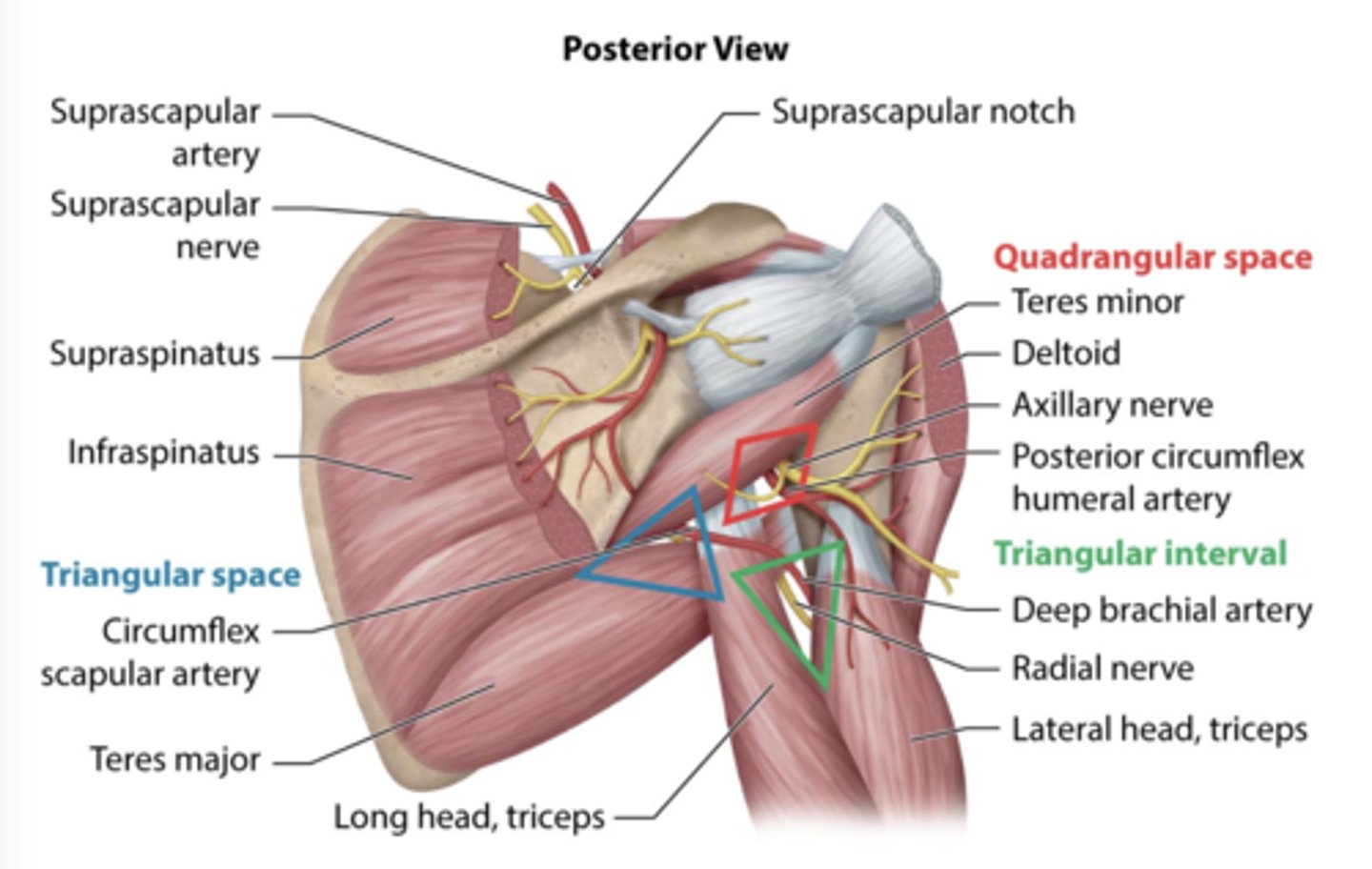
what travels through the triangular space ?
circumflex scapular artery
what travels through the quadrangular space ?
axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery
fascia and septa
-fascia surrounds regions under skin
-fascia separates compartments
-compartments are functional units
what muscle is working when doing a chin up ?
biceps brachii
what muscle is working when doing a pull up ?
brachialis
is musculocutaneous nerve motor, sensory or both ?
-motor (flexing)
-sensory (lateral forearm) - turns into lateral cutaneous N