genuinely why is this still relevant
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
foldable bs
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
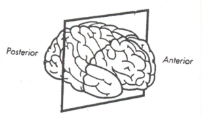
what plane is this?
frontal
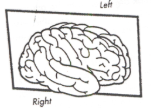
what plane is this?
sagittal
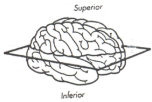
what plane is this?
transverse
levels of organization
chemical —> cellular —> tissue —> organ —> system —> organismal
chemical
atoms combined to form molecules; e.g. macromolecules (carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids)
cellular
molecules combine to form cells
tissue
similar cells working together to form tissues
organ
different tissues working together for a common purpose to form organs
system
different organs that work closely together for a common purpose
organismal
made up of the organ systems to accomplish life functions
needs for life
heat
pressure
food
oxygen
water
pressure
FORCE that creates a pressing action.
Atmospheric - oxygen —> lungs —> blood
Hydrostatic (blood, body fluids, into and out of cells, intracellular fluids between cells)
heat
Reactions occur at optimal temperatures (98.6’F)
Heat can increase or decrease reaction rates.
food
Chemicals used for:
Burning (energy requirements)
Building (new cells and molecules)
water
Environment for reactions to take place.
Involved IN reactions
Transports material
Regulated body temperature.
oxygen
Required for the release of ENERGY from FOOD to generate ATP’s.
reproduction
MITOSIS- cell division for repair, growth and replacement
MEIOSIS- production of cells for sexual reproduction
movement
External - to find food, water, survival
Internal- transport of food, water, oxygen.
responsiveness
irritability; e.g. loud sounds, hot stove, bright lights, thirst
assimilation
changing absorbed materials into new forms/molecules
digestion
food breaks down into usable forms
absorption
transport of foods or fluids across membranes and into cells for use
respiration
generates energy; internal, external, and ventilation
circulation
movement of materials through water or fluid
growth
development and maturation of cells and their functions
excretion
waste removal; exocytosis, exhalation, urination
metabolism
sum of all the chemical reactions and processes in the body

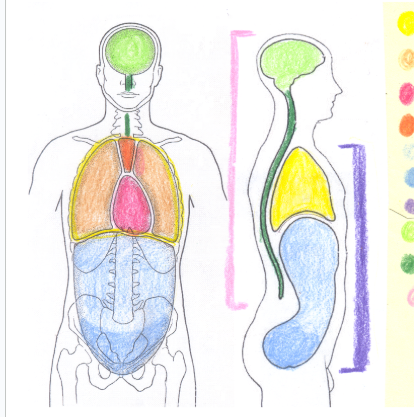
yellow
thoracic cavity
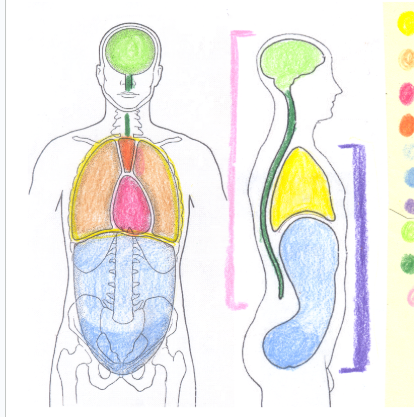
light orange
pleural cavity
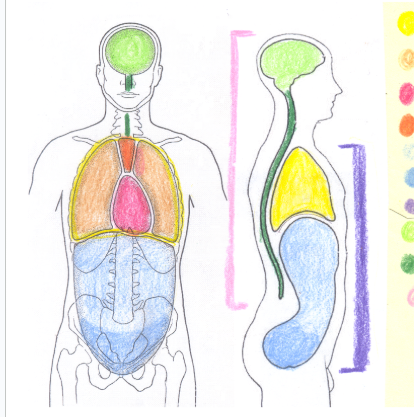
dark pink
pericardial cavity
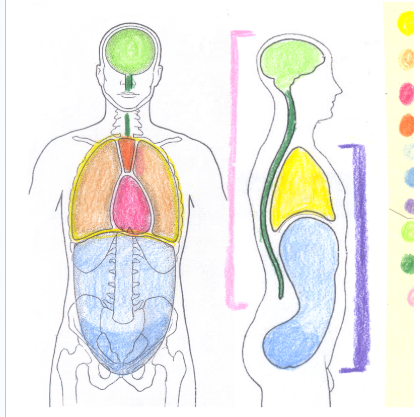
dark orange
mediastinum
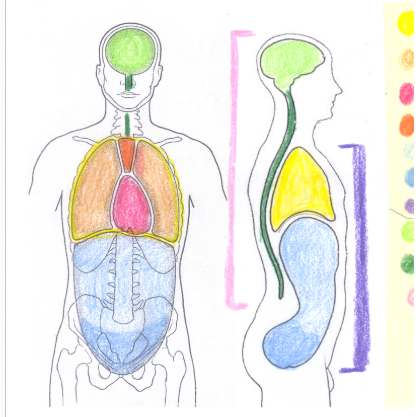
light blue
abdominal cavity
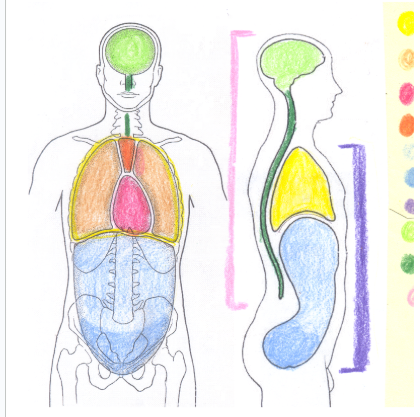
dark blue
pelvic portion of the abdominopelvic cavity
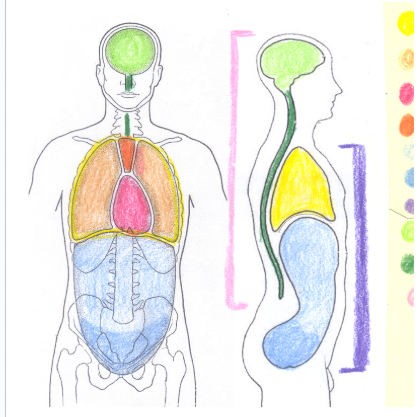
light green
cranial cavity
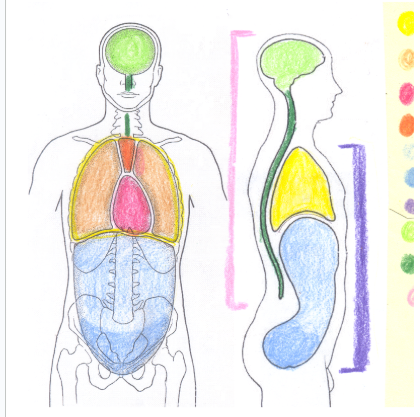
dark green
spinal cavity
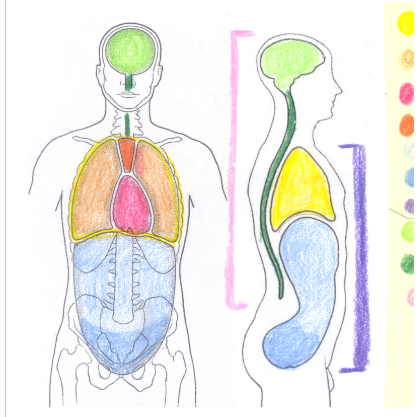
light pink
dorsal cavity
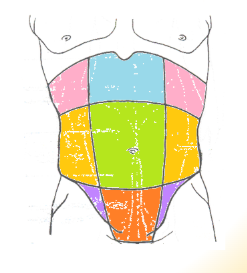
abdominal regions: green
umbilical
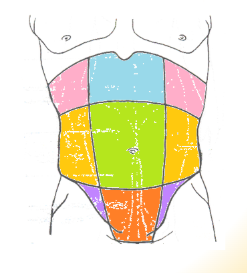
abdominal regions: blue
epigastric
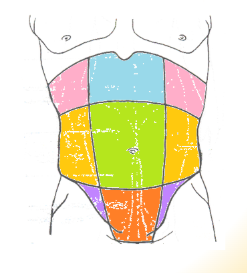
abdominal regions: red
hypogastric
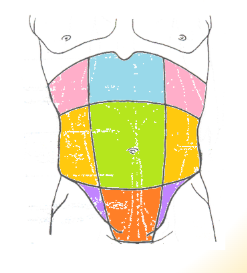
abdominal regions: pink
hypochondriac
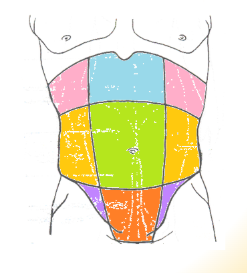
abdominal regions: orange
lumbar
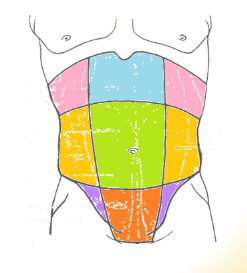
abdominal regions: purple
iliac