Axial and Appendicular Skeleton
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Axial Skeleton
80 bones
includes ribs, sternum, skull, vertebrae, and hyoid bones
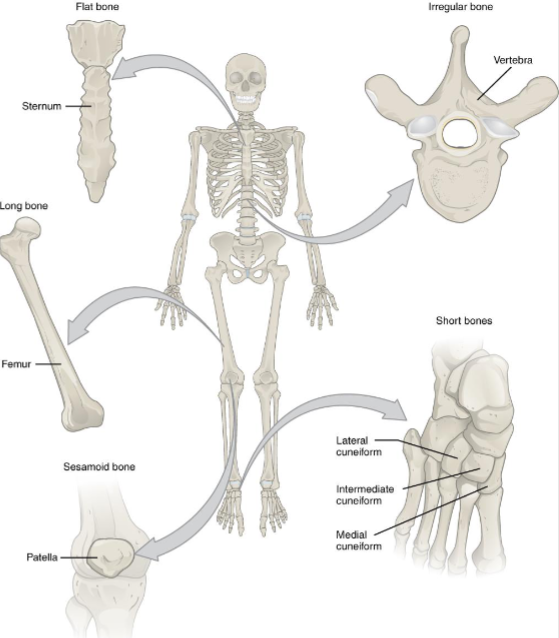
Bone Classification
short- cube shaped
wrist and ankle
flat- thin with sides parallel
frontal, parietal skull
long (discussed in ch 6)
femur, humerus
Sesamoid- no bone-bone attachment;
develop in tendons, patella
Irregular- odd shapes that don’t fit other categories;
vertebrae, pelvic
LOOK AT BONE MARKINGS IN ADDITIONAL TERMS
Axial Skeleton Structures: Head
calvarium/skullcap- roof of skull
fontanels- uncalcified portions of the calvarium in a fetal skull.
the fibrous membranes are not replaced until 2 years old
slightly flexible
skull can change shape during birth process
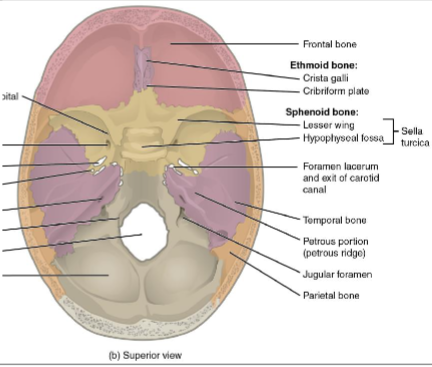
Parietal Bone
Frontal Bone
Occipital Bone
Sella Turcica- on sphenoid bone.
site where pituitary gland/hypophysis rests.
ENDOCRINE GLAND
Cribriform plate- on ethmoid bone. tiny perforations
olfactory nerves pass through these holes from nasal epithelium to brain
Ethmoid bone
Sphenoid bone
Axial skeleton structures: face
orbit- eye sockets
para nasal sinuses- several bones on face contain this
sinuses make bones lighter
resonance chambers to affect voice
sinus problems- voice differs
zygomatic arch- cheek bone
formed by zygomatic bone and a process of the temporal bone
Petrous portion- on temporal bone.
densest bone of the body
surrounds inner ear
Wormian/sutural bones- small bones often found along sutures
“extra bones of skull”
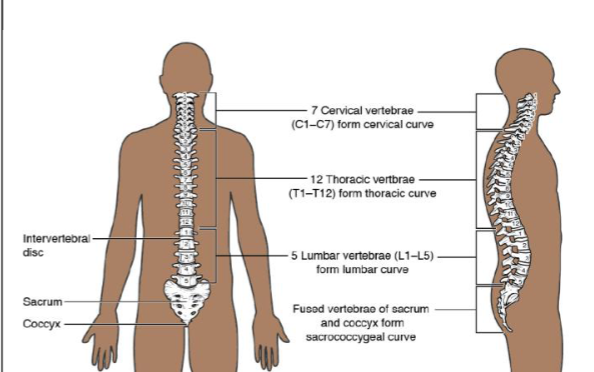
Vertebrae
7 cervical vertebrae (neck)
12 thoracic vertebrae (articulate with 12 pair of ribs)
5 lumbar vertebrae
1 sacrum (5 fused vertebrae
1 coccyx (4 fused vertebrae)
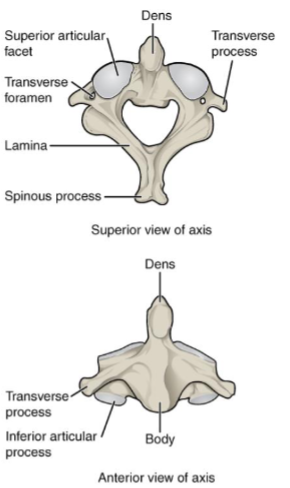
atlas- most superior/first cervical vertebra
holds up skull like mythology
Axis- second cervical vertebra.
rotates around a prominence called DENS/Odontoid process
looks like a tooth
Spinal Curves
no naturally occurring lateral curves
cervical curve- anterior
thoracic curve- posterior
lumbar curve- anterior
sacral curve- posterior
Scoliosis- lateral abnormal curve
kyphosis- excessive thoracic abnormal curvature
lordosis- excessive lumbar abnormal curvature
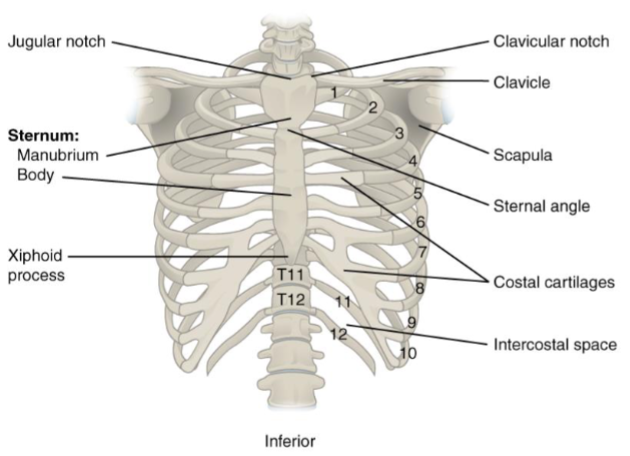
Ribs
12 pairs of ribs that articulate with a thoracic vertebrae
vertebrosternal/true ribs- most superior 7 pairs have direct hyaline cartilage connection to sternum
vertebrochondrial ribs- 3 pairs of ribs that have common cartilage connection to cartilage of the 7th true rib. FALSE RIBS
vertebral/floating- most inferior 2 pairs of ribs have no anterior articulation. FALSE RIBS
manubrium- superior to sternum
body/gladiolus- middle part of sternum
xiphoid process- inferior part of the sternum
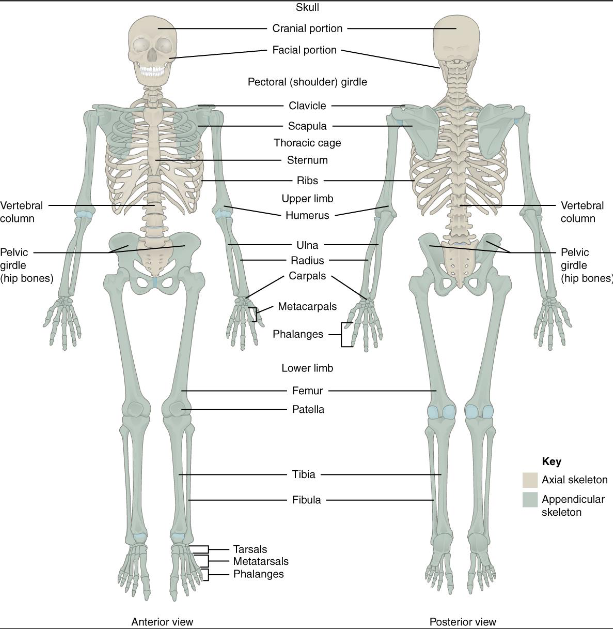
Appendicular skeleton
126 bones
fomrs the limbs and the bones that support the extremities, pelvic girlde and pectoral girdle
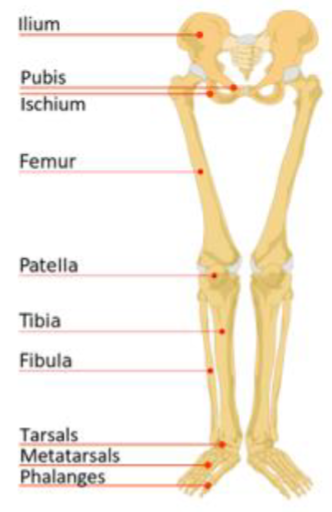
pectoral girdle- bones that support the upper extremity; the scapula and clavicle
pelvic girdle- supports lower limbs; os coxae or coxal bones
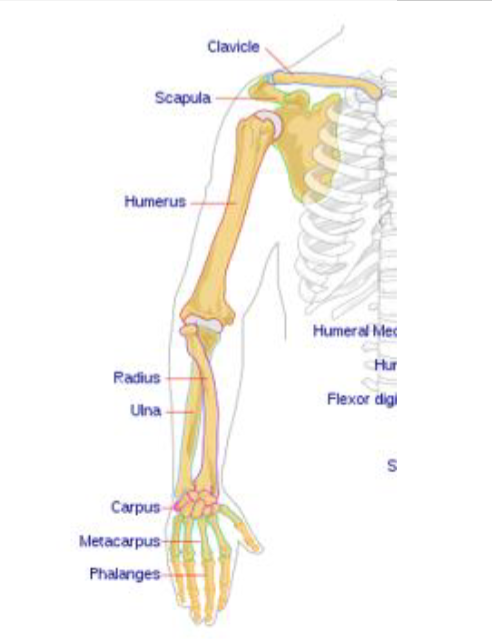
Bones of Upper Extremity
arms (brachium)- humerus
forearm (antebrachium)- radius on thumb, ulna on pinky
wrist- carpals
refers to the group of bones in the writs
palm- metacarpal bones
fingers- phalanges
Bones of the Lower Extremity
thigh- femur
patella- knee cap
leg- tibia
large bone- shin
fibula- small lateral
ankle- tarsals refer to group of bones in the ankle
calcaneous- heel bone, one of the tarsal
metatarsal bones
toes-phalanges