Topic 4: Water and Aquatic Food Production Systems and Societies
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
how much of the earths water is fresh?
2.5%
hydrological cycle
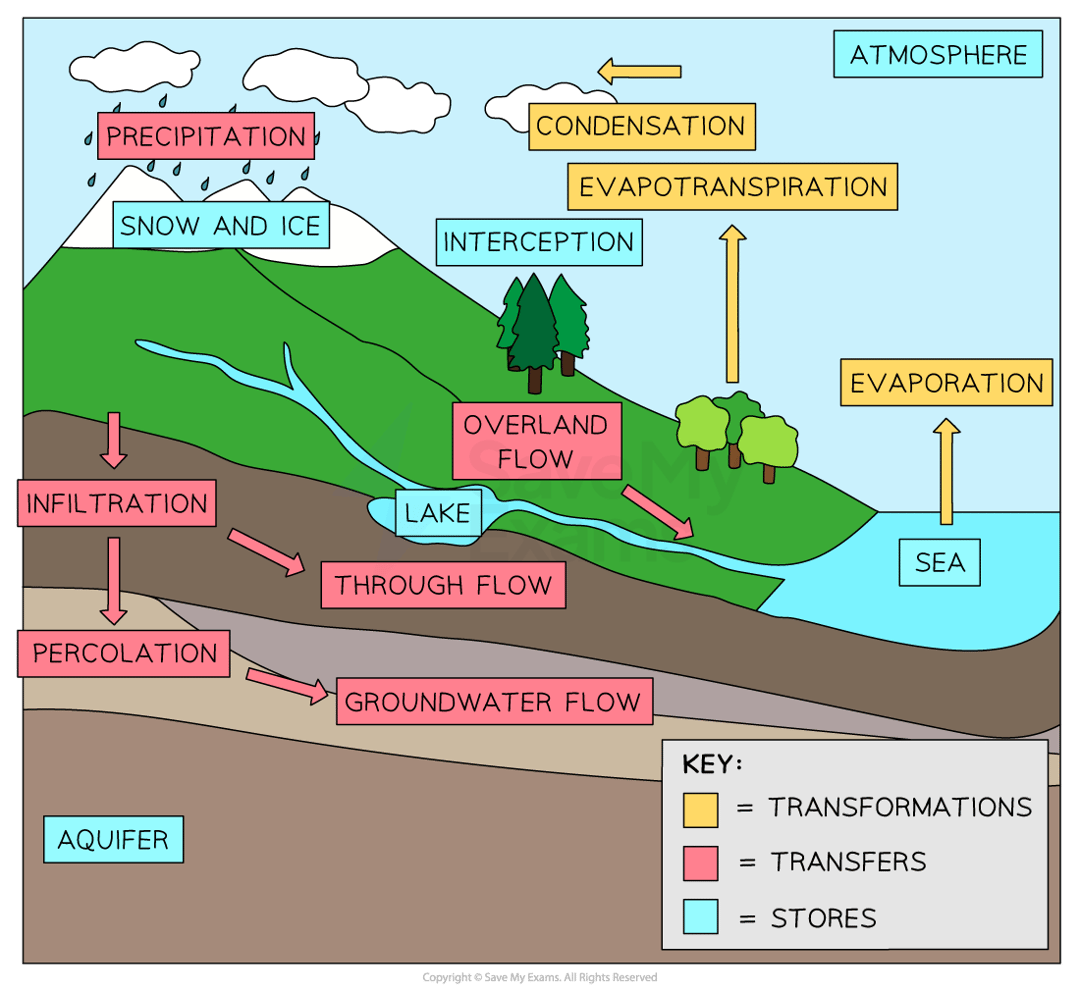
aquifer
a body of permeable rock that can hold water underneath
evapotranspiration
combination of evaporation and transpiration that requires heat from sunlight and biological action of plants
convection
water carried by hot, moist rising air higher up in the atmosphere
advection
wind-driven movement of water horizontally through the atmosphere
sublimation
snow and ice moving directly to atmospheric storage from solid to gas
percolation
movemenet of water through porous rock and sediment
groundwater
storage of water in rocks underground
what is the process of ocean circulation?
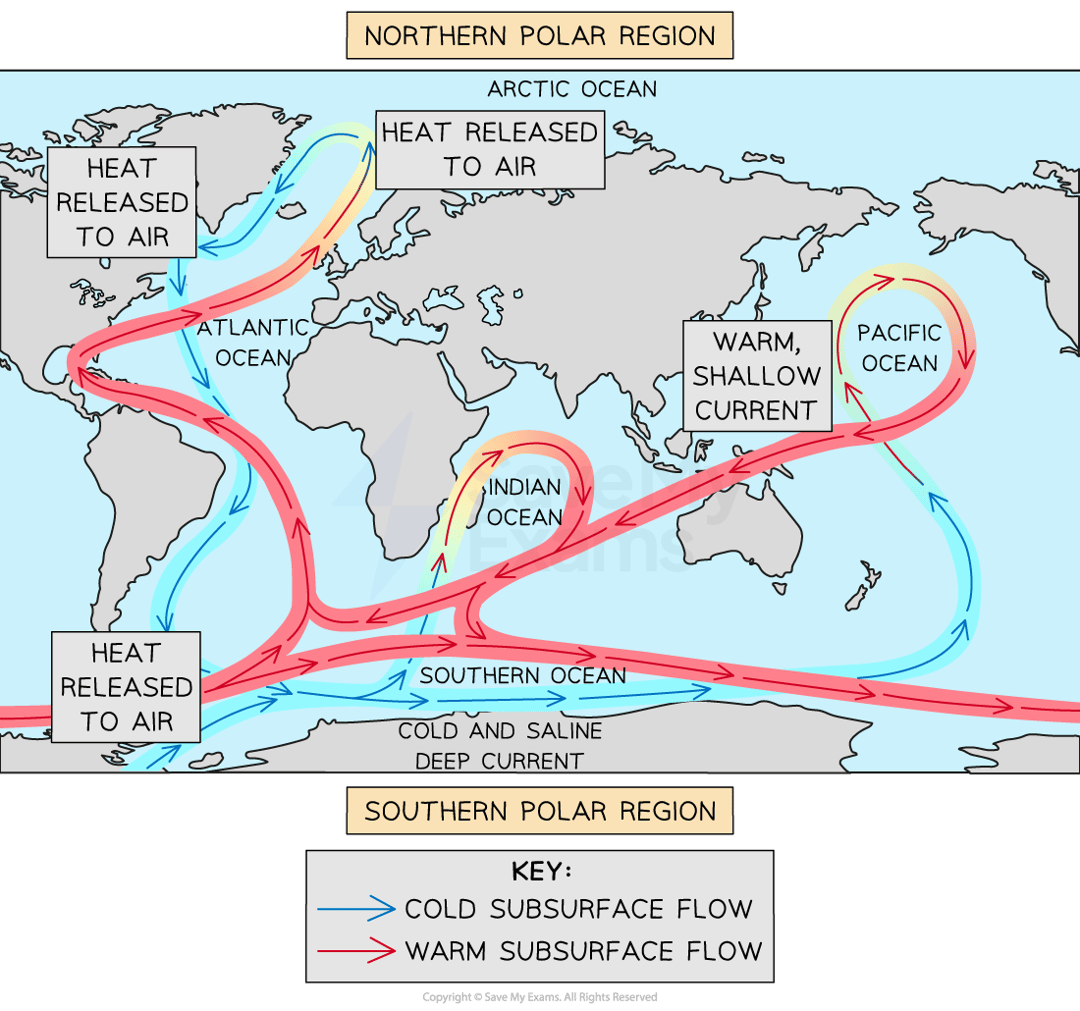
convection currents are lead by:
cold water is denser than warm, so cooler currents run deeper in the ocean
freshwater is less dense than salty so it stays close to the surface
surface currents are triggered by prevailing winds
reservoirs
a large natural or artificial lake that stores water
desalination
dissolved mineral salts are removed from water
grey water
household waste water
water budget
measure of ohow much s available in a system per year
advection
microbes are carried in groundwater flow
irrigation
large scale agriucltura watering systems
el nino southern oscillation
chnags in surface temperature of water in central and easter tropical pacific ocean wat
water scarcity
the level of accesability to water to sustain life
phytoplankton
microscopic marine algae
continental shelf
the seabed and subsoil of submarine areas that extend beyond its coastal state
upwelling
deep,cold water rises toward the surface
biorights
compensating poorer people who depend on areas that need protecting as they depend on it for income
maximum sustainable yeild
the maximum amount we can harvest or collect that doesn’t prevent future generatiosn from using it
rights of indigenous people
indigenous people have the right to live on their land and use it’s resources within carrying capacity
aquaculture
commercial farming of sea produce uch as fish
tragedy of the commons
acting in self interest when consuming resources at the extent of others
limiting factors
an abiotic or biotic factos that limits a population size
organic pollutant
toxic chemicals that are harmful to humans and wildlife that has carbon in its structure
inorganic pollutant
pollutants without carbon in its strucutre
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
amount of oxygen needed to remove waste from water from aerobic bacteria breaking it down
indicator species
species that tell us how polluted an area (usually a body of water) is
biotic index
measure of the level of pollution based on population sizes in certain habitats
eutrophication
when algae grow excessively due to excess nutrients (usually fertiliser run-off) in a body of wtaer
dead zones
area in bodies of water where oxygen is low
what are the problems with aquaculture?
habitat loss - usually requires the conversion of natural habitats, clearing it or modifications cause disruptions to communities
pollution - eutrophication the dead zones, additives in feeds can be harmful, use of antifouling agents to prevents barnacles growths leak in to the surrounding natural habitats and harm to members there, leaking antibiotics
spread of diseases - close quarters and low genetic diversity increases risk of diseases spreading, if individuals escape then they can give those diseases to wild individuals
escaped species - spread of foreign diseases, genetically modified fish breeding with natural species may cause issues
ethical issues and biorights - intensive farming usually have low animal welfare and stress on individuals, intrinsic rights debate
rights of indigenous cultures - introduction of industrial aquaculture and non-native species may disrupt the native traditions and fishing communities, could push them out of work
international conservation agreements - there are agreements to conserve genetic diversity (CBD)
what are the benefits of aquaculture?
helps to meet rising demand - instead of over fishing in the oceans, controlled populations for consumption allows for wild numbers to be sustained
technological advancements - rising technology help to increase this method’s sustainability
natural species can be genetically modified to contain more nutrients
governments can address food security
from irreversible ecosystem damage, some populations can continue to be farmed using aquaculture
winkler test
to measure the amount of dissolved oxygen in a sample, chemicals are added ass soon as possible to a sealed bottled sample then titrating a reagent into it until it turns to the ‘endpoint colour’ (dark blue). the amount of reagent used is the equivalent to the concentration of dissolved oxygen in the mixture
what can excessive biodegradation of organic materials cause?
depleted oxygen levels cause anoxic conditions
anaerobic decomposition takes place thern methane, hydrogen sulfide and ammonia are produced
methane is a strong greenhouse gas
hydrogen sulfide is toxic to marine animals
ammonia is also toxic and contributes to nutrient pollution increasing eutrophication