Endocrine Glands
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 5: Thursday, September 25th:
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
the skin covers, prtects, and communicates information. for maintenance, it uses sunlight to produce _______ precursor
calciferol (vitamin D)
_______ produce and secrete chemical signals to communicate with themselves,neighboring cells, and cells at a distance
body cells
_______ produces tropic hormones that stimualte target organs/glands to release their hormones
anterior pituitary gland
true or false: thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates thyroid hormones and decreases metabolism
false. thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates thurpid hormones and increases metabolism
true or false: growth hormone (GH) increaes body growth/mass, protein synthesis, and fat metabolism; and stimulates insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I)
true
true or false: adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulates follicle growth, estrogen, and sperm
false. adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulates adrenal cortex hormones
true or false: follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stumulates follicle growth, estrogen, and sperm
true
true or false: lutenizing hormone (LH) stimulates milk and mammary glands
false. lutenizing hormine (LH) stimulates ovulation, corpus luteum, steroid hormones
true or false: prolactin (PR) stimulates milk and mammary glands
true
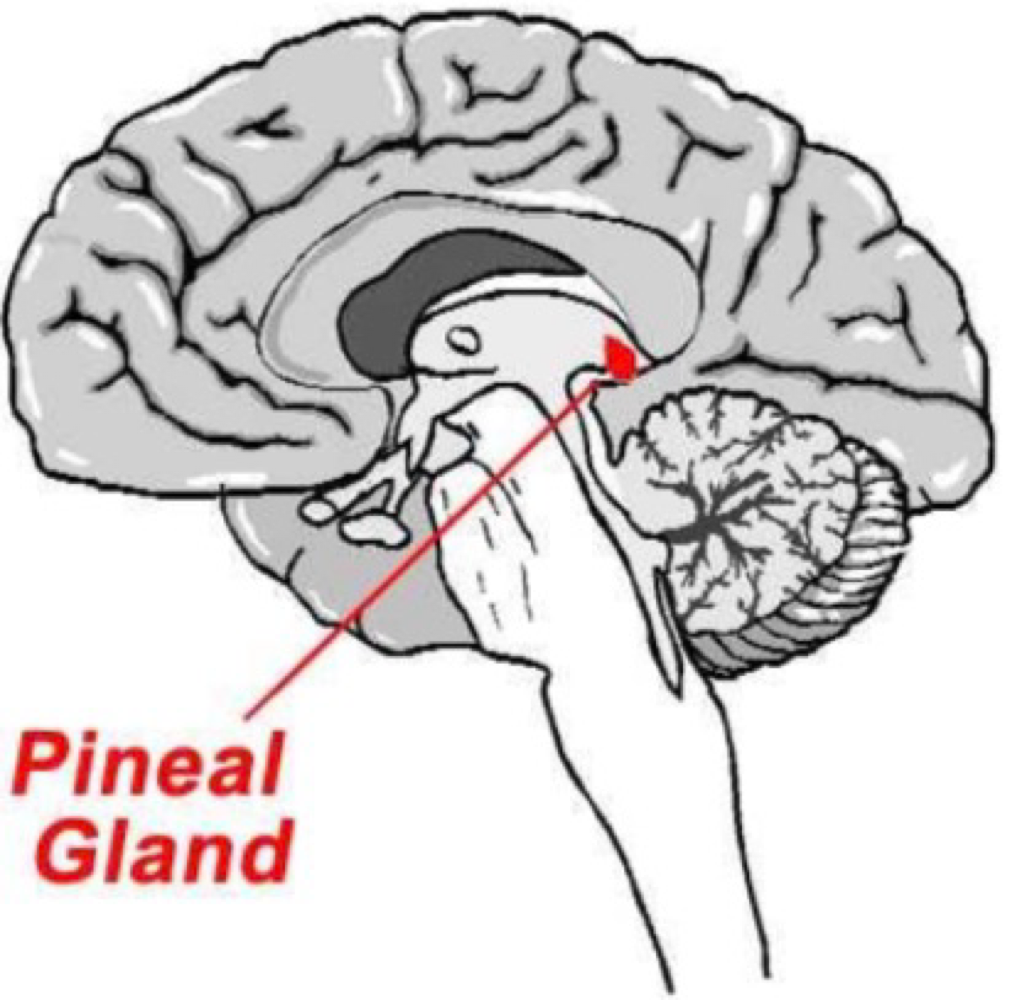
_______ is posterior to the hypothalamus and produces melatonin, which controls sleep/wake patterns
pineal gland
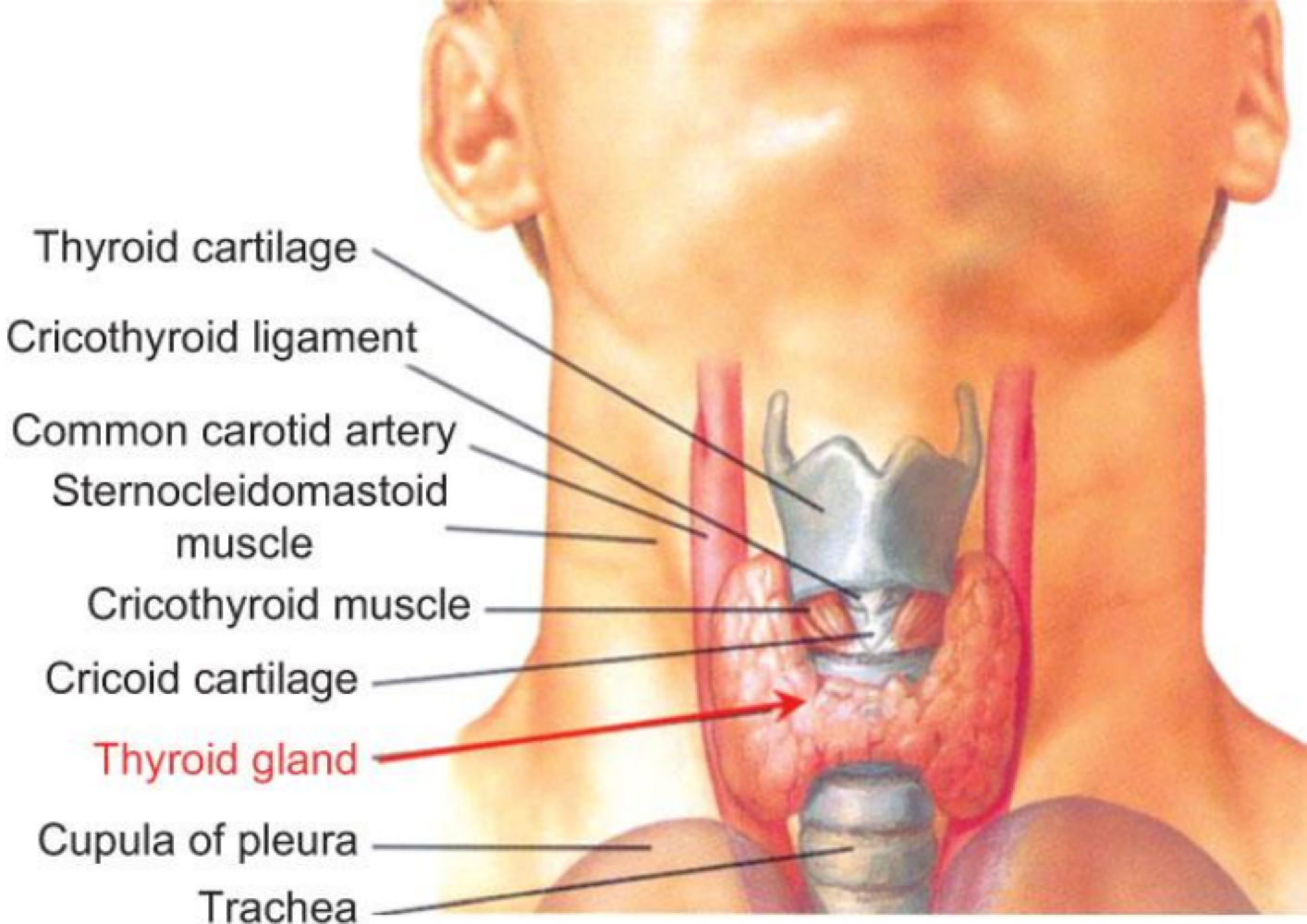
_______ releases hormones that regulate growth adn metabolism
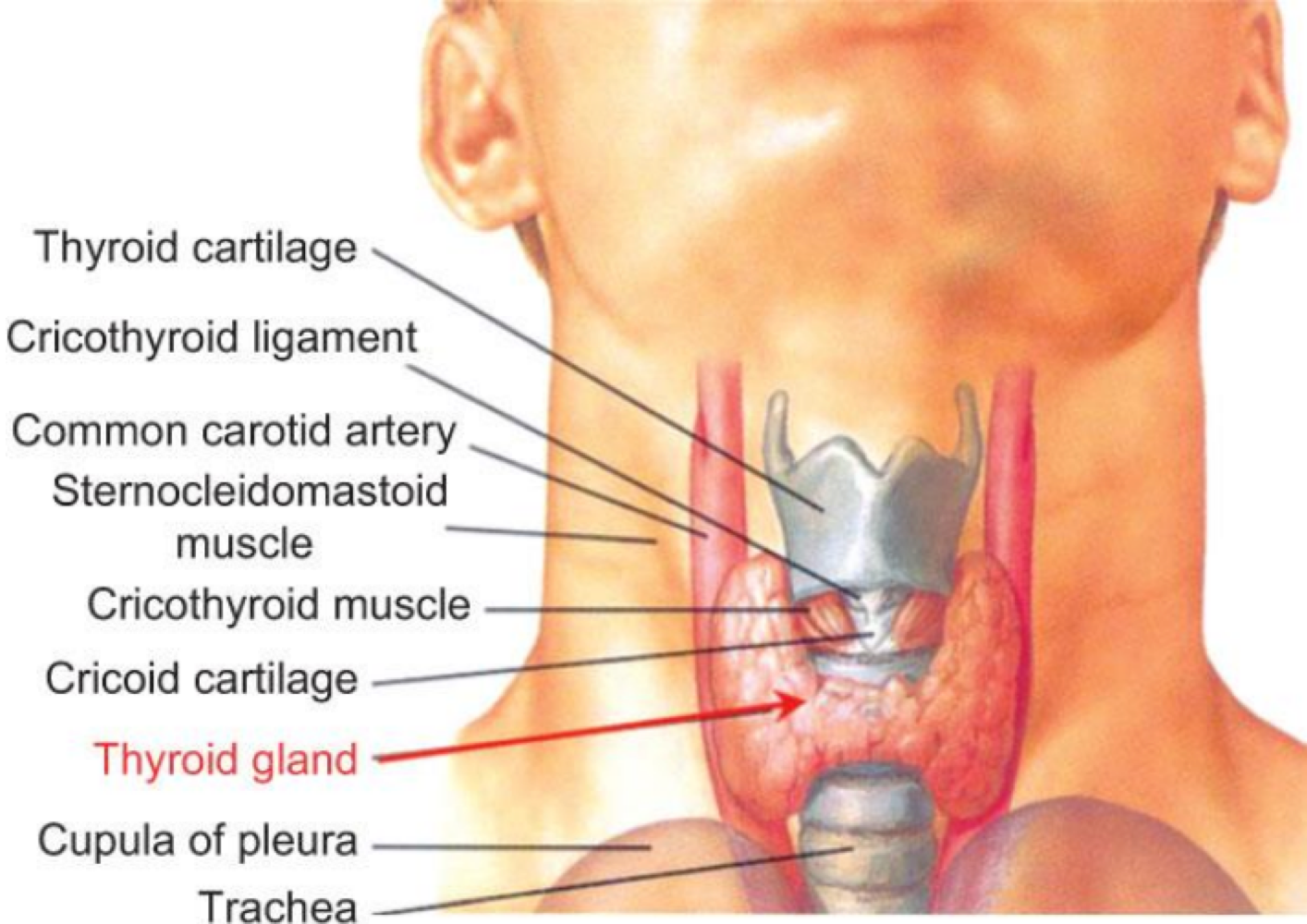
thyroid gland
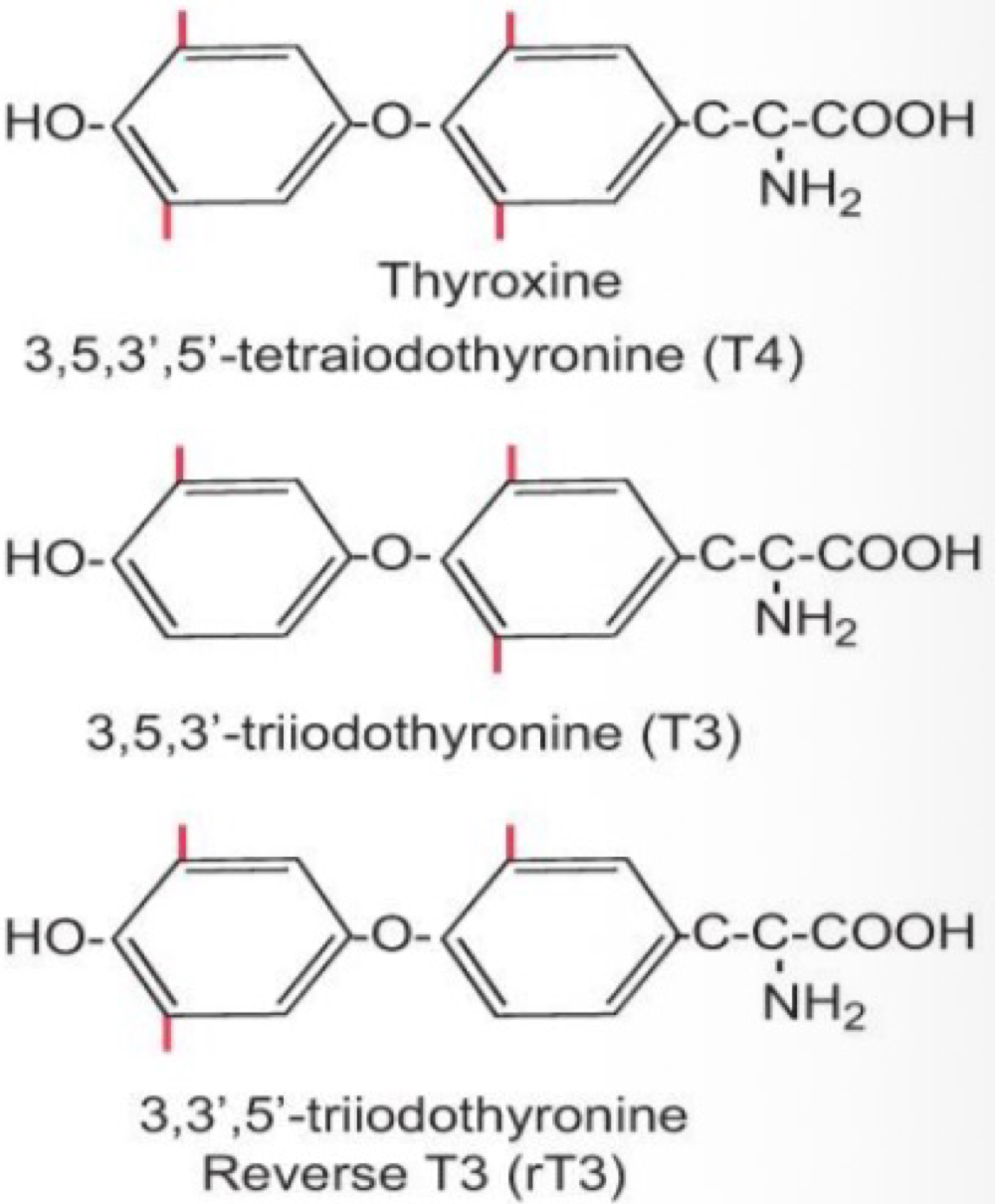
_______ is a thyroid hormone responsible for growth to adult stature, increase tissue protein availability, cartilage to bone conversion stimulation for growth and dardening, and permissive/synergistic relationship with GH and GF and GH release
triiodothyronine (T3)
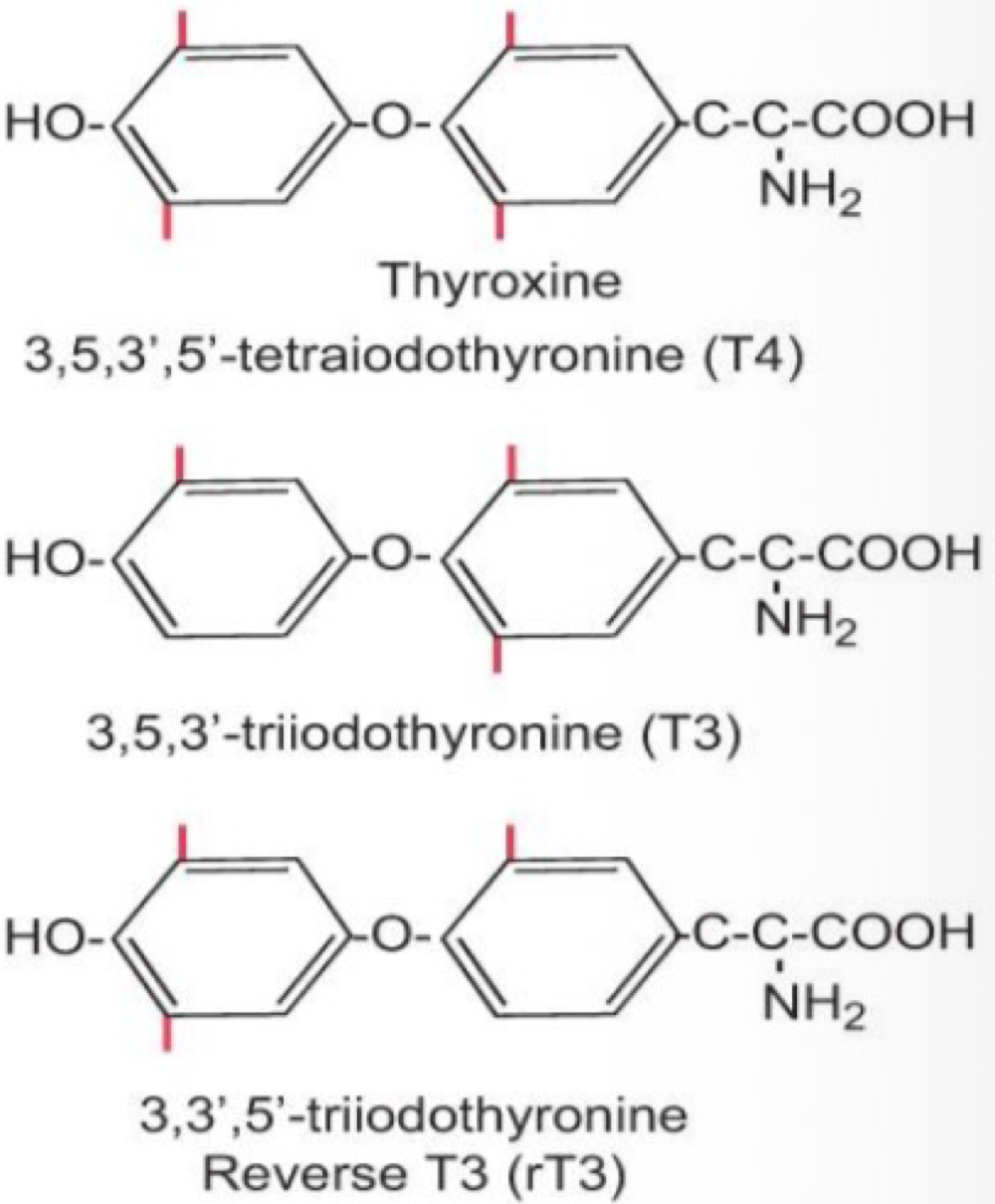
_______ works with T3 to promote neural development before adn after birth, and maintains their function in adulthood
tetraiodothyronine (T4)
_______ is a thyroid gland disorder involving low thyroid hormone levels that causes retardation and children, lack of energy, speech and memory problems, psychosis, and decreased sensory capacity
Hypothyroidism
_______ is a symptom of hypothyroidism involving short stature and bone malformation
Cretinism
_______ is a thyroid gland disorder involving high thyroid hormone levels that causes hyperexcitability, irritability, exaggerated sensory responses, and restlessness
Hyperthyroidism
_______ is a symptom of hypothyroidism that involves long stature and bone malformation
Gigantism
For maintenance, the thyroid gland releases _______ to decrease calcium level levels by acting on bone and kidneys
Calcitonin
As a stress response, the thyroid gland increases _______ use for energy
Glucose
_______ releases parathyroid hormone (PTH) which increases calcium levels, and decreases calcium levels in body fluids by acting on bone kidneys and intestine for maintenance
Parathyroid gland
_______ is the outer layer of the adrenal gland; responsible for maintenance
Adrenal gland cortex
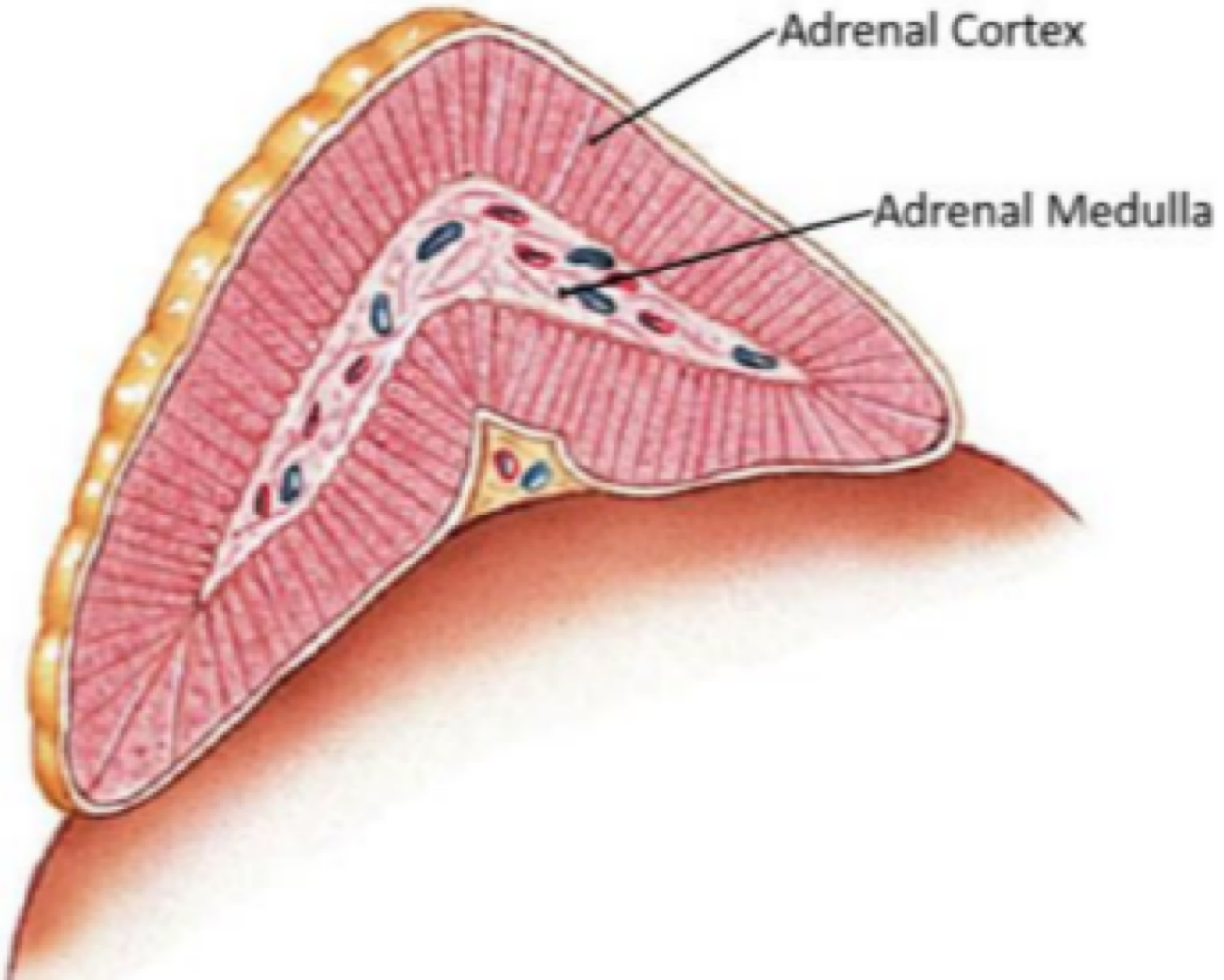
_______ is released by the adrenal gland cortex, and controlled sodium, potassium, hydrogen, and water levels in body fluids
Mineralcorticoids (aldosterone)
_______ is released by the adrenal gland cortex, and maintain nutrient reserves, makes nutrients available for energy when needed, controlled water levels, decreases response, and reduces inflammation
Glucocorticoids (cortisol)
_______ is released by the adrenal gland cortex, and maintains reproductive functions
Steroids (androgens)
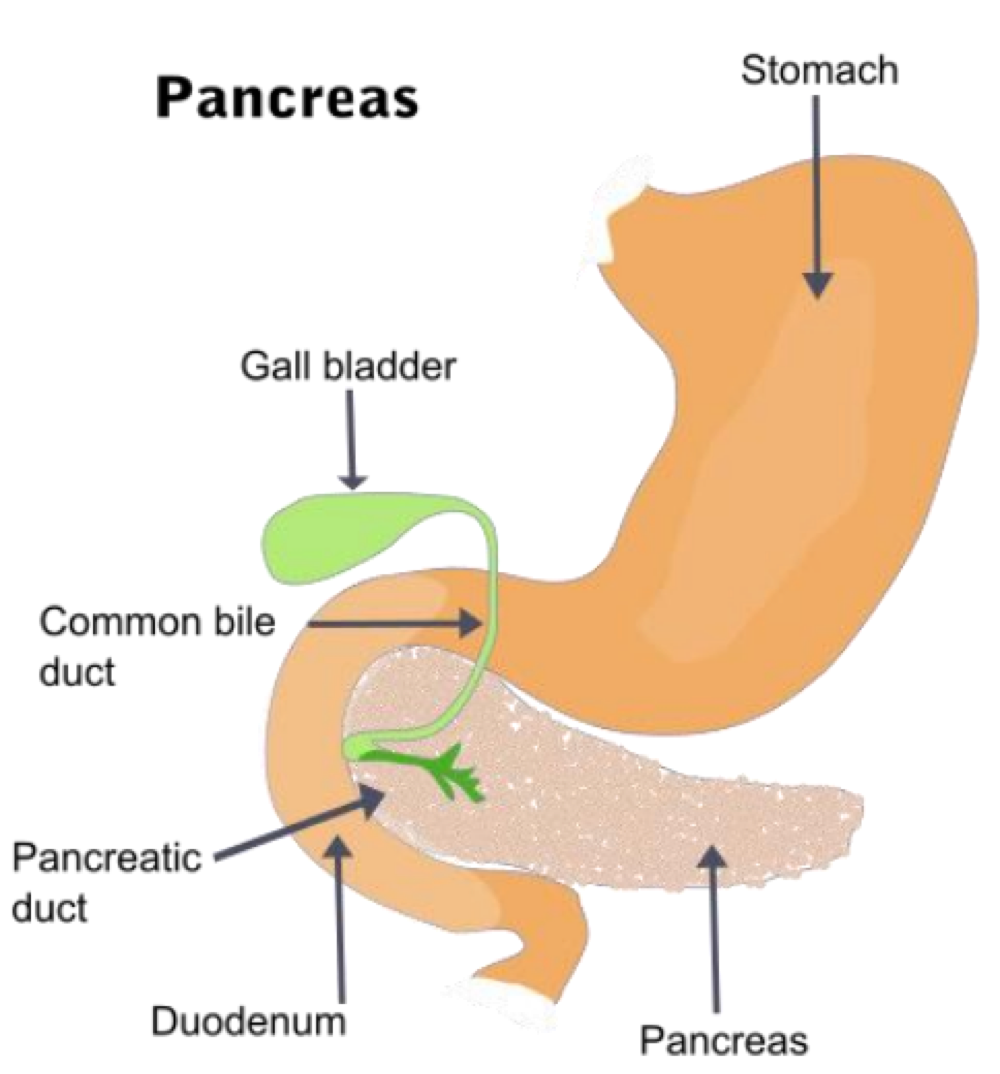
_______ is the region of the pancreas that releases endocrine cells
Pancreas (islets of Langerhans)
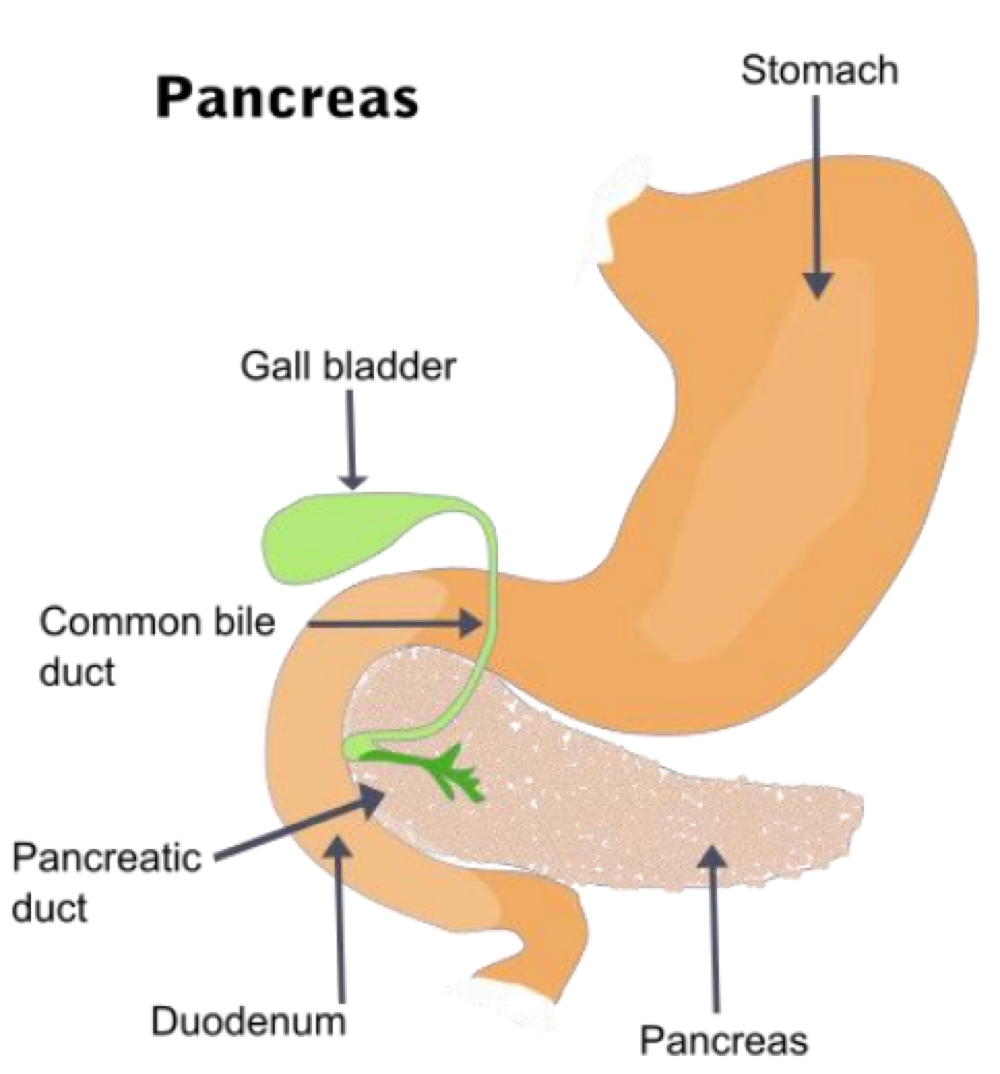
the Pancreas (islets of Langerhans) releases _______ for glucose and ________for fat and protein used for metabolism
Insulin, glucagon
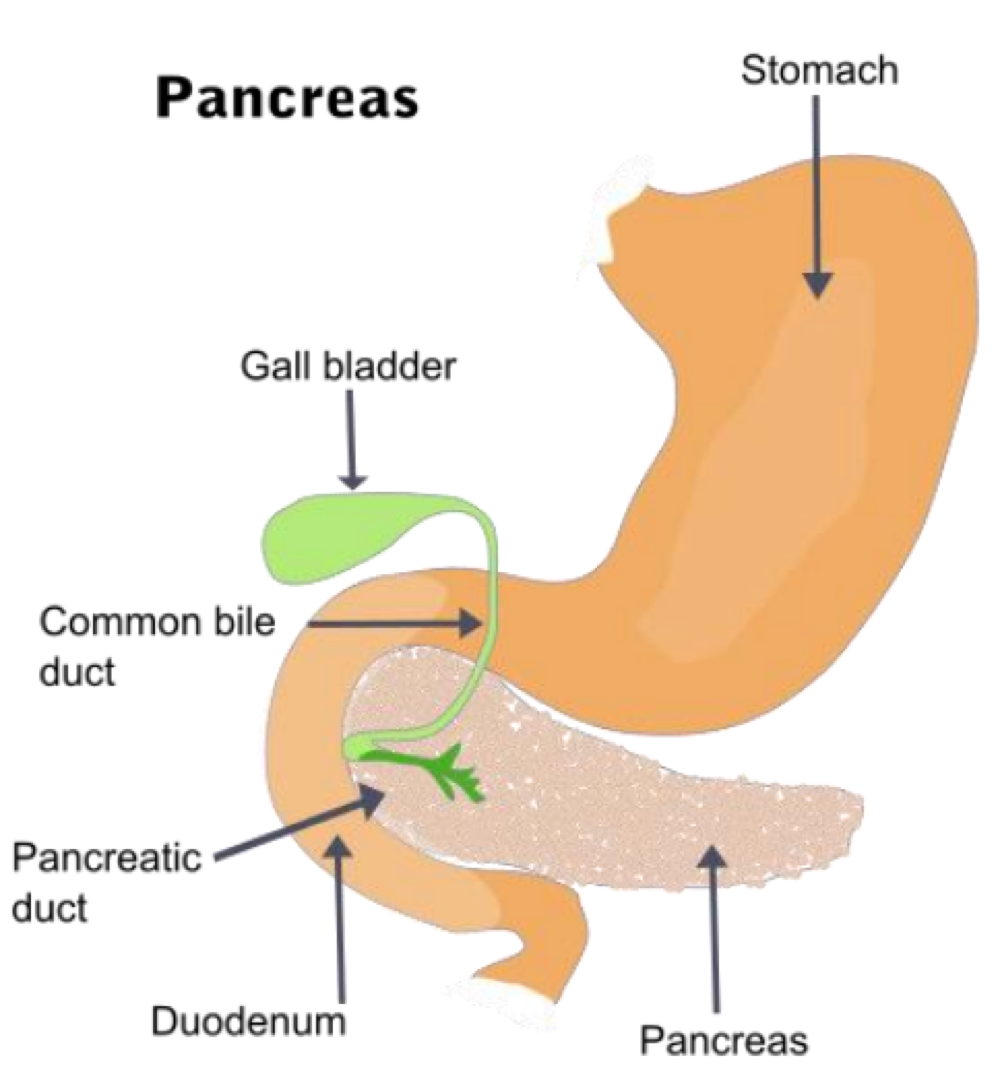
the Pancreas (islets of Langerhans) releases _______ to control insulin and glue gun activity and digestion, and inhibit GH
Somatostatin
true or false: the ovaries produce and release human chorionic gonadotripin (hCG) and human placental lactogen (hPL)
false. the ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone
in the ovaries, _______ is responsble for female sexual behavior, typical features, and increases protein synthesis
estrogen
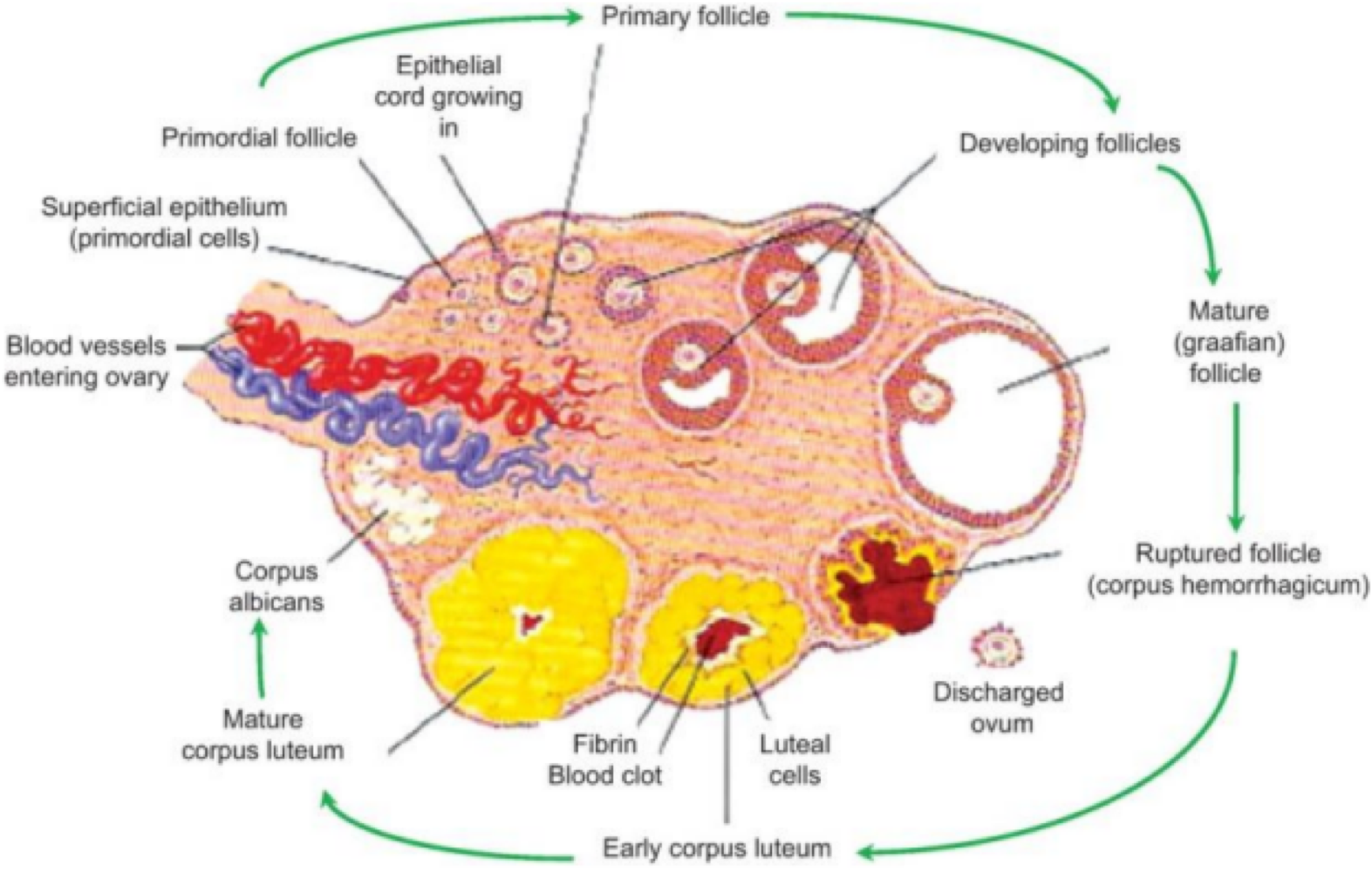
in the ovaries, _______ is responsble for preparing the uterus for pregnancy and breasts for milk
progesterone
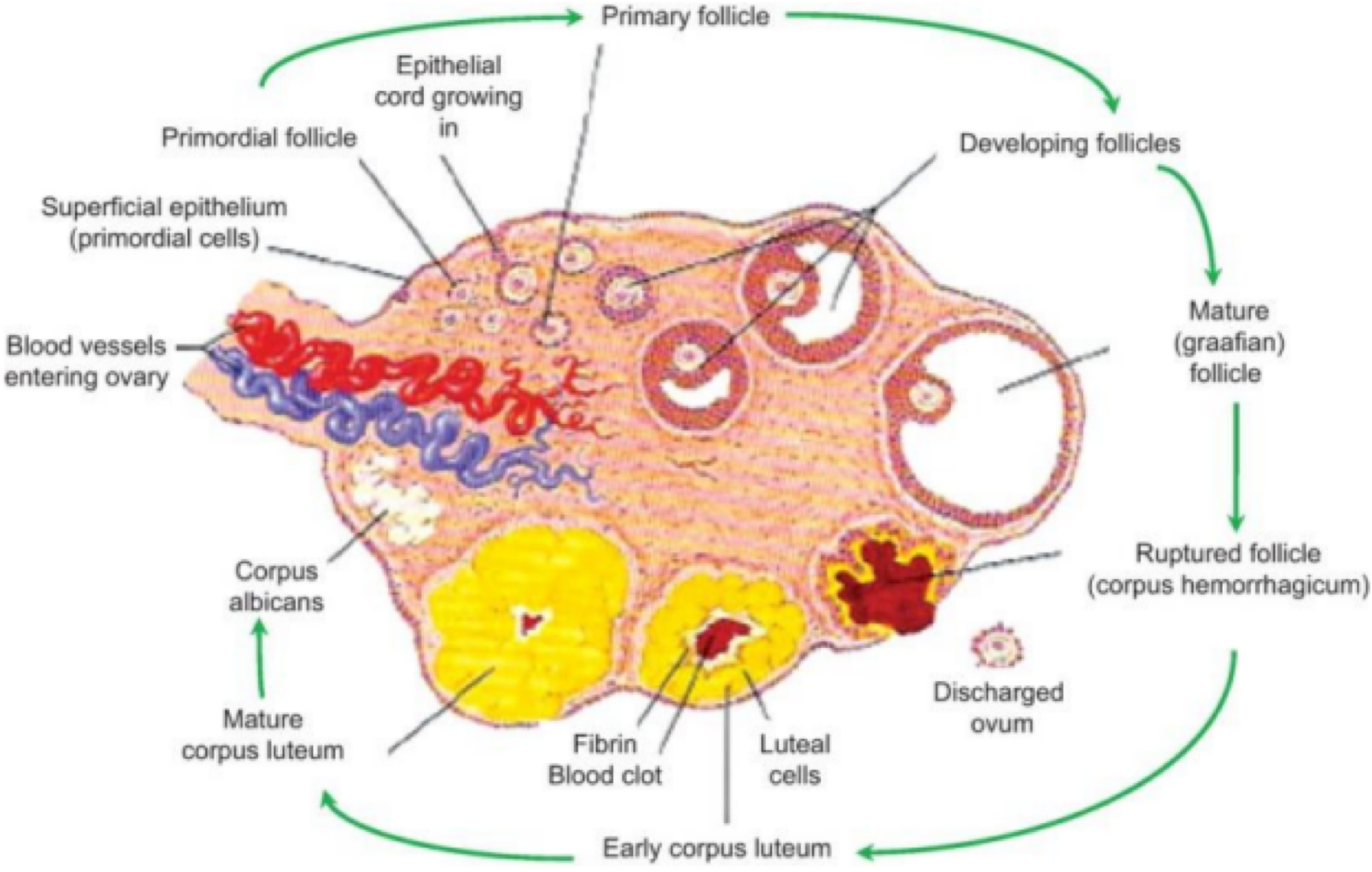
in the placenta, the embryo produces _______, which maintains corpus lutem and reduces mother’s immune response
human chorionic gonadotripin (hCG)
the placenta produces _______, which is responsible for mammary gland development, regulating bother’s blood glucose, fat, and protein for fetus development
human placental lactogen (hPL)
in the placenta, _______ is responsible for uterine growth and breast development, and _______ is responsible foruterin eline maintenance during pregnancy
estrogen, progesterone
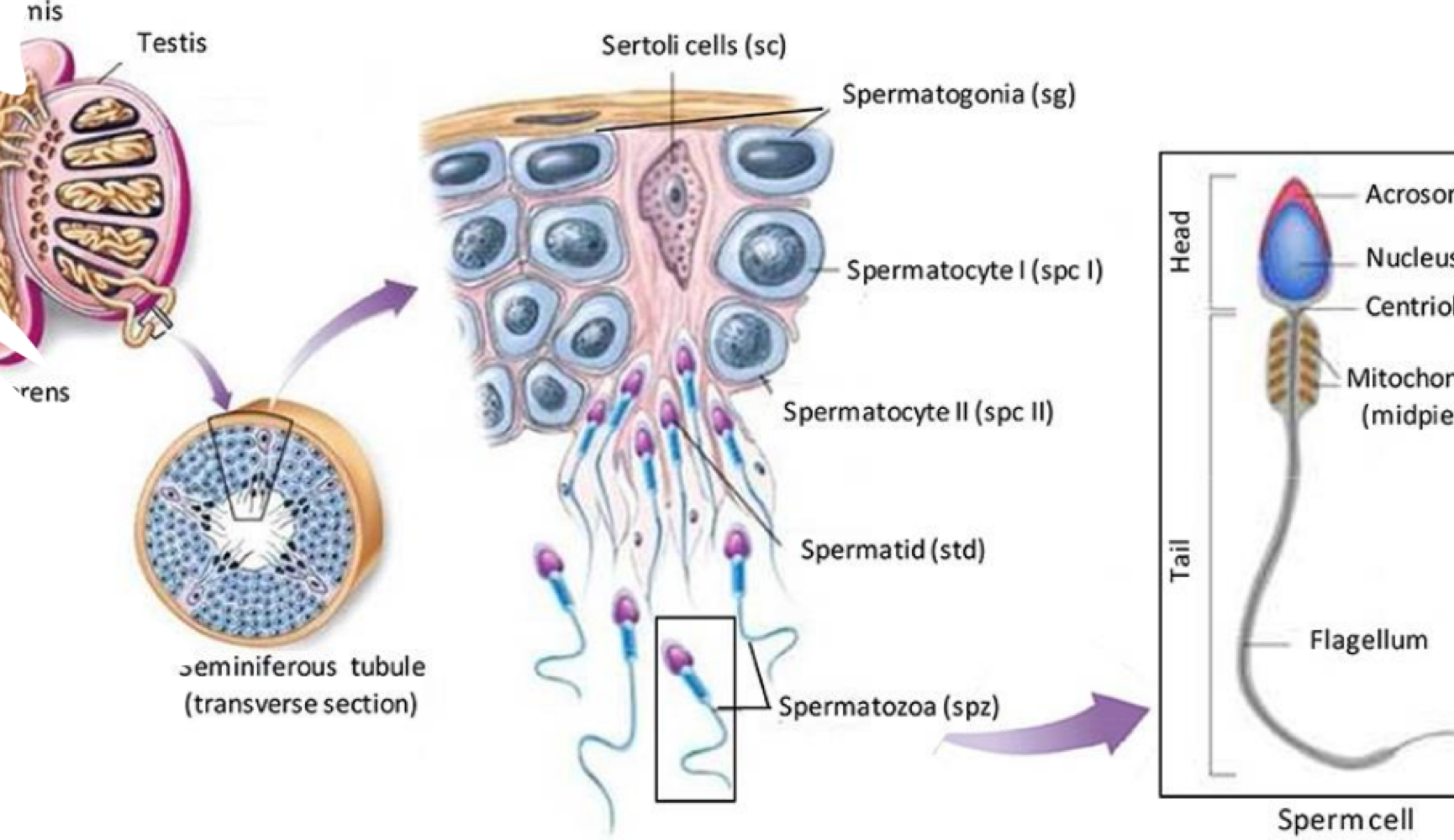
the testes produce _______, which is responsible for sexual behavior, pattern of development before birth, and typical features after birth
testosterone
the _______ produces releasing hormones that stimulates secreting hormones from the adenohypopsis
hypothalamus
corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH), arginine vasopressin (AVP), oxytocin (OXT), and thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) are released from the _______ of the hypothalamus
paraventricular nucleus
gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) is released from the _______ of the hypothalamus
arcuate nucleus
growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH), somatostatin (STT), and dopamine adn prolactin inhibiitng factor (PIF) are released from _______ of the hypothalamus
another nucleus
_______, which is produced and stored in the posterior pituitary gland, increases blood pressure, controls reproductive behavior, and increases water retension by acting on kidneys
vasopressin (AVP/ADH)
_______, which is produced and stored in the posterior pituitary gland, is responsible for uterine contractions, milk ejection, and controls reproductive behavior
oxytocin (OXT)
the _______ is the inner layer of the adrenal gland
adrenal gland medulla
the adrenal gland medulla is stimulated by _______ to release _______ and _______, which controls fight or flight response
sympathetic nerves, epinephrine, norepinephrine
_______ are exocrine gland cells that synthesize, store, adn secrete digestive enzymes: proteases, lipasees, and amylases
pancreas (acinar cells)
the _______ releases insulin-like growth factor (IGF), which works with GH to maintain growth, and moblizines nutrients for energry as a stress response
liver
the stomach releases _______, which promotes acid secretion for protein digestion
gastrin
the small intestine releases _______, and _______, which are responsible for gastric mobility and emptying
motilin, ghrelin
the small intestine releases _______, which ascts on the pancreas and gall bladder to increase protein, fat, and carbohydrate digestion in the small intestine
choecystokinin (CCK)
the small intestine releases _______, which acts on the pancreas and gall bladder to increase small intestine pH
secretin
the small intestine releases _______ and _______, which decreases digestive activity in the stomach and small intestine
neurotensin, polypeptide YY (PYY)
the small intestine releases _______, which inhibits gastric activity and increases insulin secretion
gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP)
for energy balance post digestion, the small intestine releases _______, which controls nutrient delivery adn blood nutrient levels after a meal
glucagon-like peptides (GLP)
the _______ are inferior to the adrenal gland; responsible for maintenance
kidneys
for maintenance, _______ acts on the intestine and bones to increase blood calcium, which occurs in the kidneys
calcitrol (vitamin D)
for maintenance, _______ increases red blood cells, which occurs in the kidneys
erythropoietin