Physiology: Renal system
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Kidney functions
Maintains H2O balanced in body
Regulate the volume of extracellur fluid
Regulate concentration of extracellurlar fluid
Regulate concentration of ECF ions (Na+, Cl-, HCO3-)
Maintains plasma volume +osmolarity
Excretion of waste products
Secreting hormones (erythropoietin and renin)
The nephron
Primarily maintain plasma homeostasis and excrete
Done via
- filtration
- reabsorption
- secretion
Vascular component vs tubular
Vascular Compartment - Afferent/Efferent arteriole + glomerulus
Afferent arteriole (“in”) carries blood to the glomerulus
Glomerulus - a ball like tuft of capillaries that filters blood plasma into the tubular component
Efferent arteriole (“out”) carries blood from the glomerulus and divides into peritubular capillaries
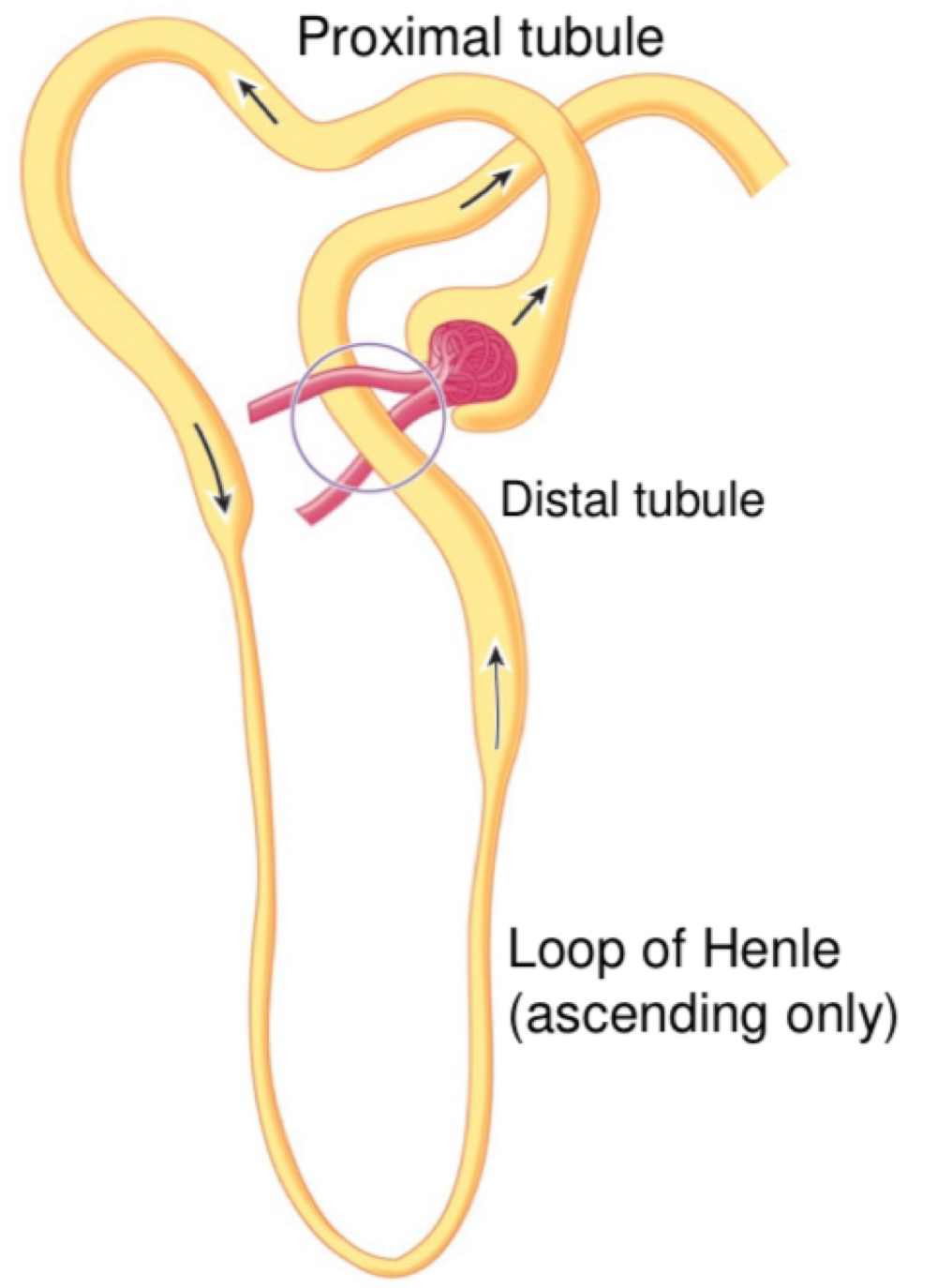
The Tubular Compartment: Bowman’s capsule, proximal tubule, lope of Henle, distal tubule and collecting duct.
Bowman’s capsule “cups” the glomerulus and collects glomerular filtrate.
Proximal tubule: reabsorption and secretion of selected substances
Lope of Henle: establishes establishes an osmotic gradient and reabsorption ions
Distal tubule: selectively absorbed and secretes ions to maintain pH and electrolyte
Collecting duct: collects fluid from distal tumbles, reabsrobes water/solutes
Juxtamedullary nephron
20% of total glomeruli in inner cortex
Loop of Henle descends further into medulla
Osmotic gradient
Cortical Nephron
80% of total glomeruli in outer cortex
Loop of Henle dips slightly into medulla
Involved in basic filtration and reabsorption
Renal processes to form Urine
Glomerular filtration: non-selective filtration of protein-free plasma
Tubular reabsorption: valued substances reabsorbed from Tubular lumen and transferred back to blood
Tubular secretion: waste substances removed from blood to the tubular lumen via tubular cells
Plasma constituents not reabsorbed pass into the renal pelvis → urine
Glomerular filtration
Blood enters glomerular capillaries via Afferent arteriole
Fluid then passes through three layers of the glomerular capillary
Three layers layers of the glomerular capillary wall are:
endothelium; large pore allow passage of solute/fluid but not blood cells
Basement membrane: mix of collagen (structure) and glycoproteins (repel proteins)
Podocytes: epithelial cells which have slits between them.
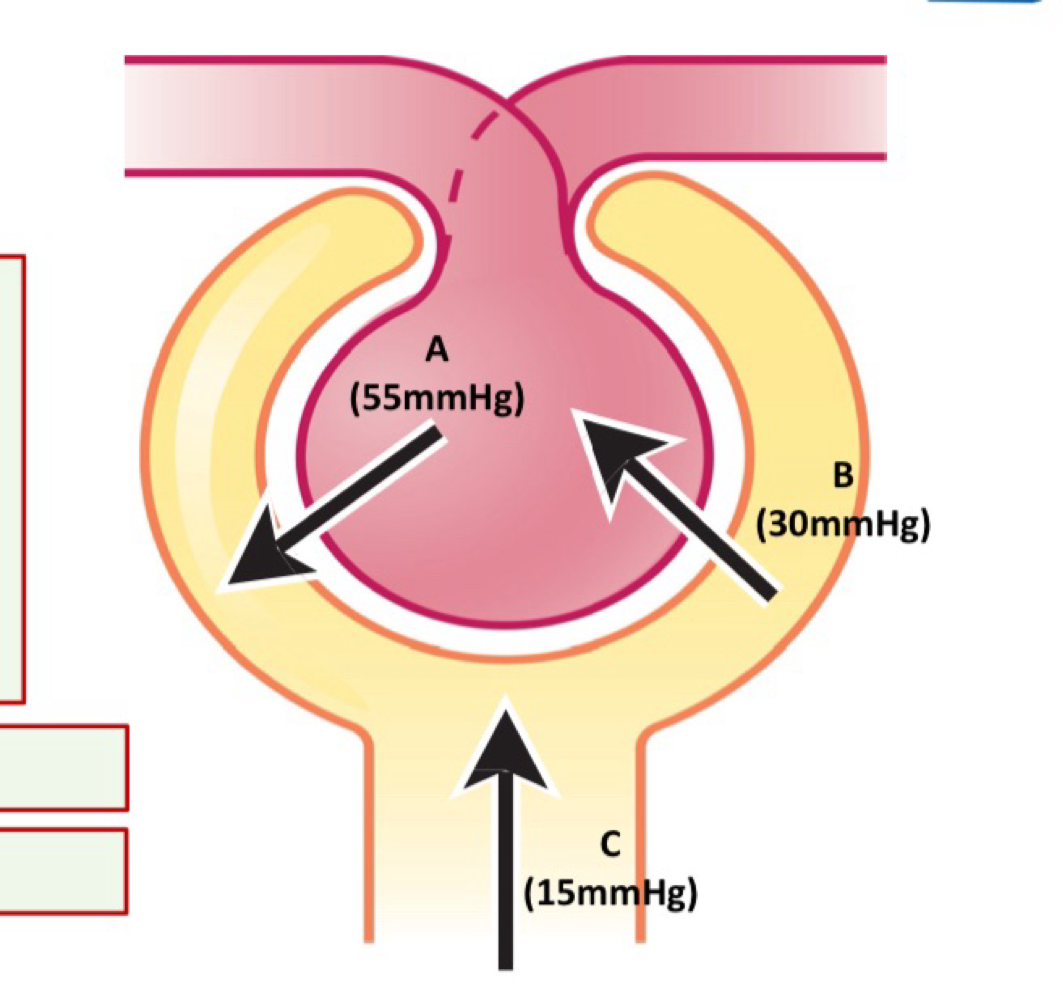
Affecting glomerular Filtrtion - glomerular capillary blood pressure (A)
Can be impacted by:
arterial blood pressure
Afferent arteriole Fluid diameter
Efferent arteriole diameter
Increases if:
arterial blood pressure increases
Afferent arteriole diameter increases (increase flow)
Efferent arteriole diameter decreases
Osmolarity
the concentration of the total number of solute particles per litre.
Unit: osmolarity per L (osm/L)
Eg: 200mmoles of glucose and 300mmoles of fructose in a litre of water= 500mosm/L
Eg: 300mM of salt dissociates into 300mH Na+ and 300mM Cl- = osmolarity of 600mOsmol/L
Affecting glomerular filtration - plasma colloid osmotic pressure - B
retention of blood proteins in the glomerulus increases the osmolarity of glomerular blood, compared with Bowman’s Capsule
This draws H2O back into the glomerulus.
Hypo-osmotic
a solution with lower osmolarity than inside a cell or another solution
Hyper-osmotic
a solution with higher osmolarity than inside a cell or another solution
Affecting Glomerular Filtration - Bowman’s Capsule Hydrostatic pressure (C)
Fluid already in Bowman’s capsule exerts a pressure which resists the influx of more fluid from the glomerulus - reducing filtration.
Glomerular Filtration rate calculation
flow rate of filtration from the glomerulus into Bowman’s Capsule, (ml/min or L/min)
Net filtration pressure = A-B-C
Filteration coefficient (kf) = 12.5ml/min
GFR = NFP x kf
Glomerular Filtration rate - stats
High rate allows for rapid removal f waste and foreign chemicals.
Normal rate is 125ml/min (180L/day) at normal mean arterial pressure (100mmHg)
Autoregulation - Renal system
Autonomic regulation of renal blood flow occurring in response to blood pressure controlled at the local level.
Increased MAP → autoregulation induces vasoconstriction of the Afferent arteriole
Decreased Map → autoregulation induces vasodilation of he Afferent arteriole.
Mechanism of GFR Autoregulation
Myogenic
Tubuloglomerular feedback
Autoregulation - Myogenic Mechanism
The process by which arteries/ arteriole react to changes in blood pressure to maintain constant blood flow
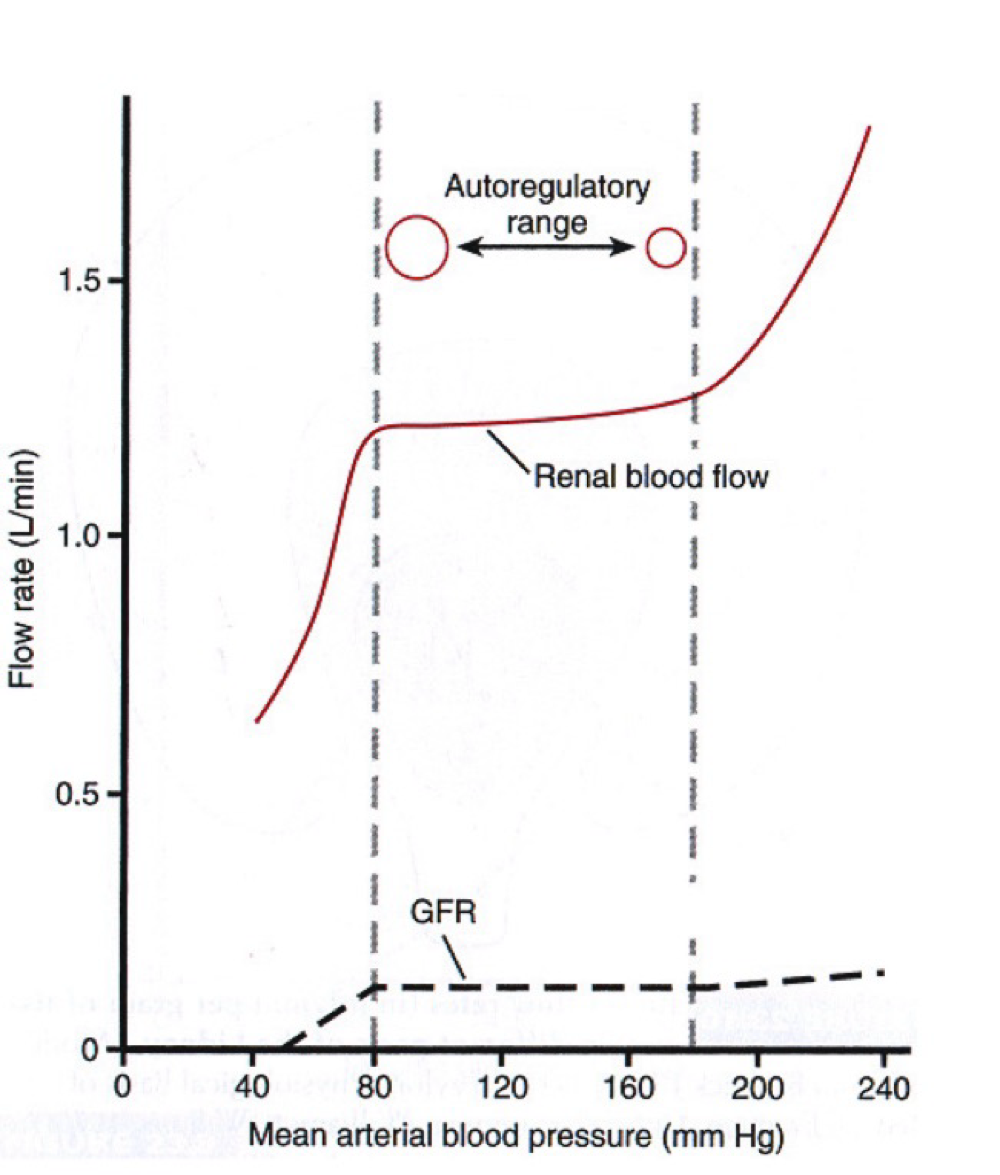
Autoregulation - Tuboglomerular feedback
Macula dense cells since tubular flow/NaCl levels in ascending tubule (these increase with BP)
Release ATP (converted to adenosine) in repsonse
Granular Cells respond to adenosine by contracting and reducing Afferent arteriole blood flow
Tubular reabsorption
99% of water is reabsorbed
100% of sugars
99.5% of salts
Sodium reabsorption locations
80% of energy in the kidney is for Na+ reabsorption
Proximal tubule (67%) - obligatory
Loop of Henle (25%) - obligatory
Distal tubule (8%) - hormonal
Obligatory = regardless of body needs, hormonal = in response to Na+ levels
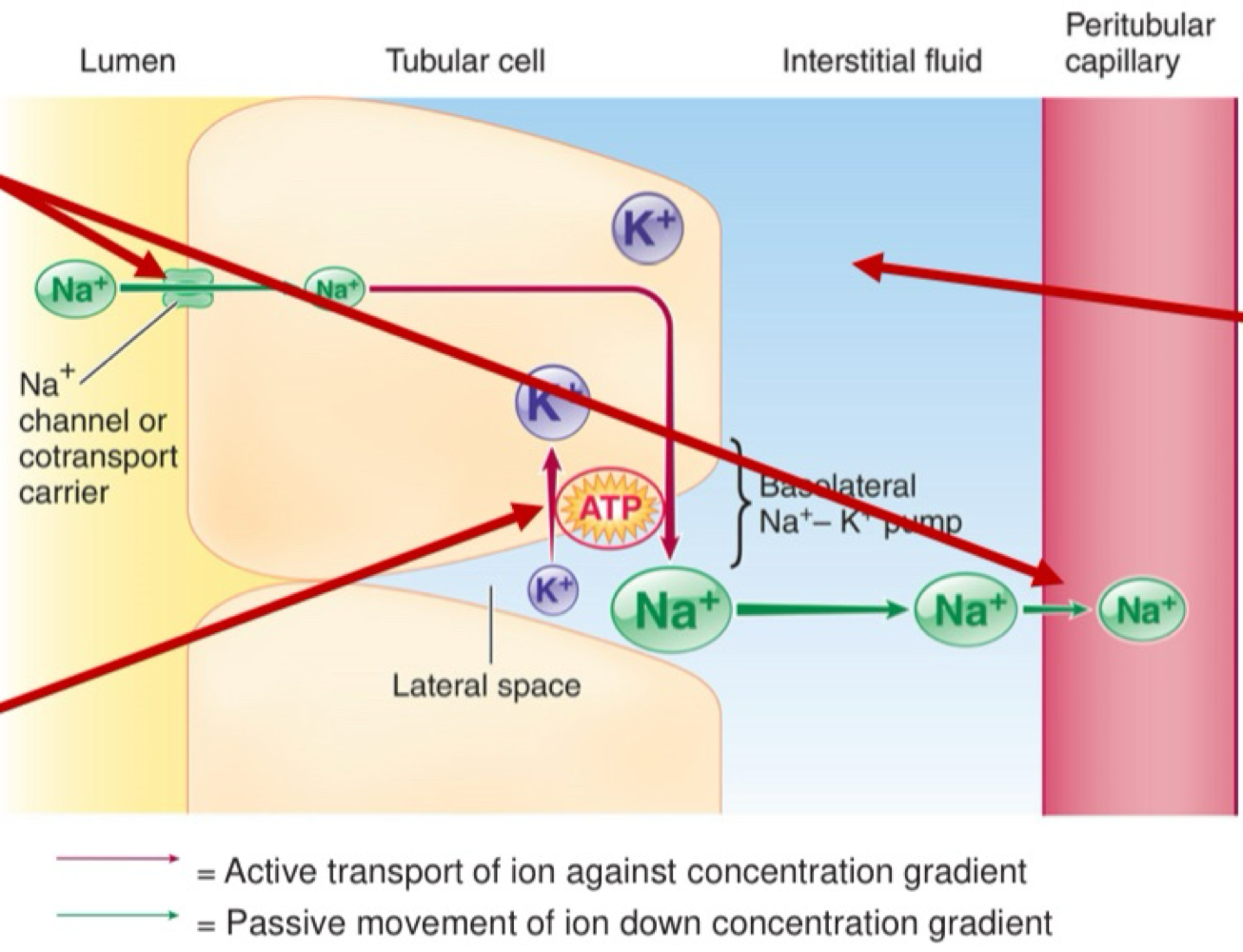
Tubular reabsorption - All barriers
Luminal cel membrane
Cytosol
Basolateral cell membrane
Interstitial fluid
Capillary wall.
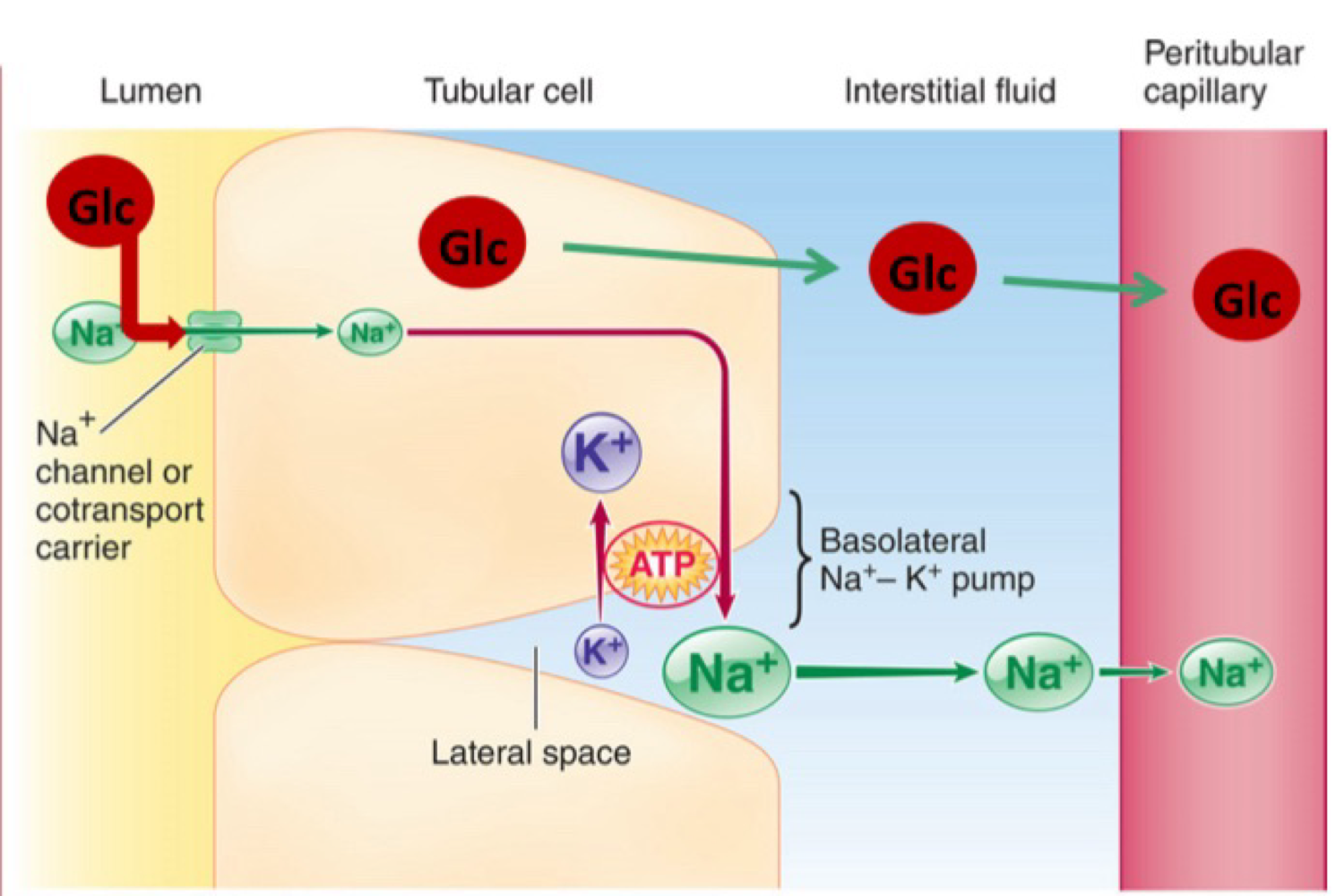
Tubular reabsorption of Na+: Step 1
Na+ - K+ ATPase pump moves Na+ from tubular epithelia cell to interstitial fluid (and K+ the other way, 1 for 1)
Tubular reabsorption of Na+: Step 2
The created concentration gradient allows the passive movement of Na+ from lumen to tubular epithelial cells and from interstitial fluid to capillaries
Tubular reabsorption of Na+: Step 3
K+ passively leaks from tubular epithelia cells back into interstitial fluid.
Reabsorption of glucose and nutrients
specialised transport proteins (support carrier) move both Na+ and glucose/nutrients in the same direction.
Glucose/nutrients then passively diffuse into the peritubular capillaries
Transport maximum (Tm) of glucose
normal plasma glucose concentration: 100-125mg/dL (100ml)
If plasma glucose increases above 300mg/100ml (e.g. in diabetes) active reabsorption mechanism max out (-375mg of glucose/min)