eye movements
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
oculomotor musculature
six muscles that are attached to each eye, arranged in three pairs
superior and inferior rectus
control vertical orientation of the eye
lateral and medial rectus
control horizontal orientation of he eye
superior and inferior obliques
control torsion of the eye
lateral intraparietal aera (lip)
in the parietal cortex
frontal eye fields (fef)
in the frontal cortex
superior colliculus (sc)
in the midbrain
involuntary eye movements
fixational eye movements, optokinetic nystagmus (okn), vestibulo-ocular reflex (vor)
voluntary eye movements
vergence, smooth pursuit, saccades
fixational eye movements
tremor, drift, microsaccades
tremor
noisy oscillating movement with frequency of about 90 Hz an amplitude about the diameter of a cone
drift
slow motions of the eye that occur between microsaccades; seem to be important for reducing information redundancy in retinal image
microsaccades
fast, jerky eye movements tat carry the retinal image over a range of many (dozens to hundreds of) photoreceptor widths; critical for forestalling troxler fading
optokinetic nystagmus
movement triggered by tracking of a moving field (i.e., as opposed to tracking a single target)
nystagmus
a jerky-looking oscillatory movement of the eyes
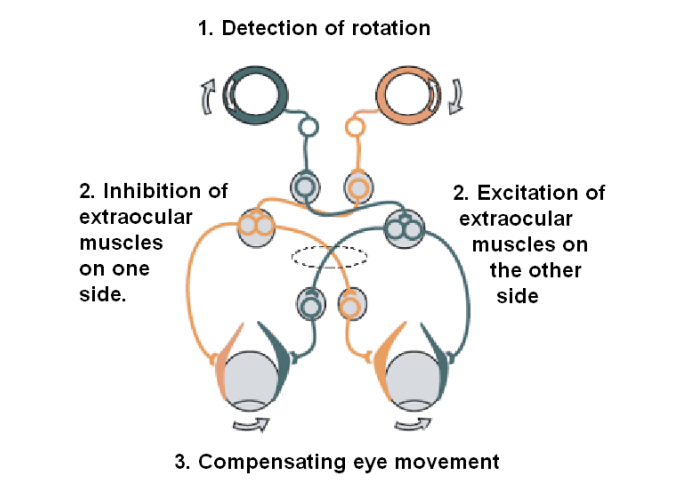
vestibulo-ocular reflex
maintain vergence and line of sight when head is moved during fixation or smooth pursuit; works as a reflex that depends, in part, on input from the vestibular system, necessary for stabilizing vision during body movements s
vergence
eye movements meant to bring a common point into fixation (‘focus’) in both eyes
convergent
eye movements turn the eyes inward
divergent
eye movements turn the eyes outward
smooth pursuit
movements are voluntary eye movement in which the eyes move smoothy to follow a moving object; useful for tracking objects and for discriminating or identifying physical details of moving objects
saccades
type of eye movement that can be made voluntarily or elicited involuntarily, in which the eyes rapidly change fixation from one object or location to another
efference copy
or corollary discharge signal; when an eye movement is issued, the motor command is copied and sent to other areas of the sensory cortices
afferent
signals sent from peripheral nervous system (pns) and/or sensory receptors to central nervous system (cns)
efferent
signals sent from cns (usually but not always, to pns)
comparator
an area of the visual system that receives one copy of the order issued by the motor system when the eyes move (the other copy goes to the eye muscles) can compensate for the image changes caused by the eye movement
saccadic suppression
the reduction of visual sensitivity that occurs when we make saccadic eye movements; eliminates smear from retinal image motion during eye movement
dynamic remapping of receptive fields
a saccade is planned but not yet executed, some neurons in lip remap their receptive fields relative to the upcoming fixation location- saccade is executed, receptive fields are already processing info from new location before eye lands there