ecology & the environment - feeding relationships
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
trophic level | definition/what it eats |
|---|---|
producers | |
primary consumers | |
secondary consumers | |
tertiary consumers |
producers - Organisms that produce their own organic nutrients (e.g Plants produce Glucose via Photosynthesis)
PRIMARY CONSUMERS - Herbivores that feed on Plants (Producers)
SECONDARY CONSUMERS - Predators that feed on primary consumers
TERTIARY CONSUMERS - Predators that feed on secondary consumers

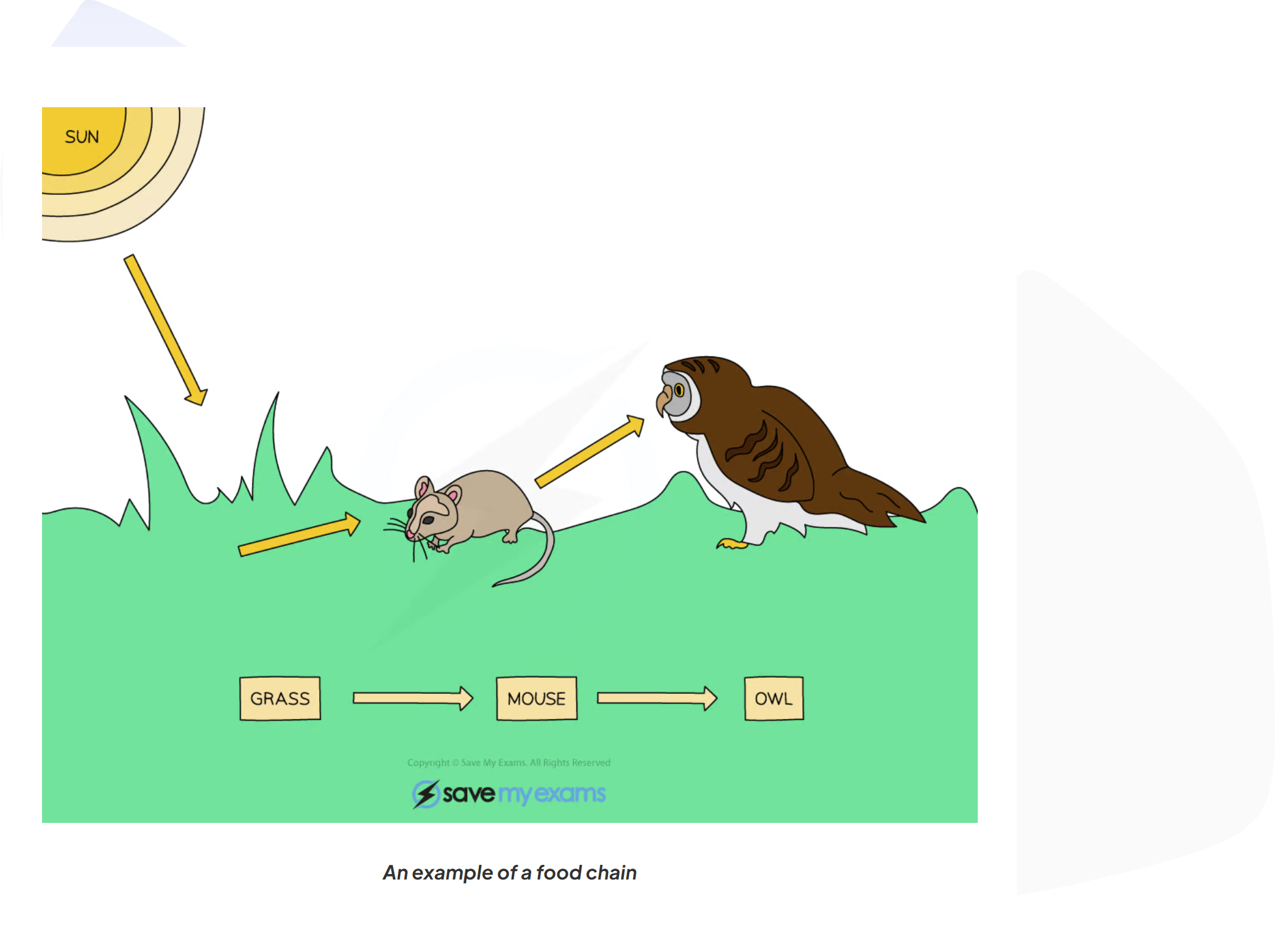
what does the arrow represent
energy transferred
name for animal at the top of the food chain
apex predator
what is a detritivore + example
organisms that INTERNALLY digest dead organic matter
e.g. worm, crab
what is a decomposer + example
Organisms that release digestive enzymes on dead organisms or non-living organic matter and absorb the externally digested nutrients.
e.g. bacteria and fungi
define a food web
why are they more realistic than food chains
A network of food chains that show how energy flows through an entire ecosystem. shows the interdependence of organisms. network of interconnected food chains
as animals rarely exist on just one type of food source
how can humans (negatively) affect food webs (2)
overharvesting of food species
introduction of foreign species to a habitat
| Pyramids of Numbers | Pyramids of Biomass | Pyramids of Energy |
What do they represent? |
| Pyramids of Numbers | Pyramids of Biomass | Pyramids of Energy |
What do they represent? | The relative number of organisms at each tropic level. | The total mass of living material at each tropic level. | The energy available at each tropic level. |
pyramids of _____ and _______ are ________ pyramid-shaped
pyramids of energy always have a _____ base
pyramids of energy and biomass are always pyramid-shaped
always have a wide base (due to the large amount of energy contained within the biomass of producers)
how much energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next
only ~10% of energy is passed on from one trophic level to the next.
percentage efficiency transfer formula
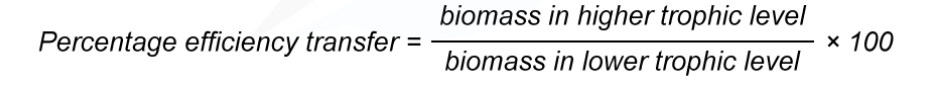
why do food chains normally not have more than 4/5 trophic levels
because the total amount of energy available eventually becomes too small to support another trophic level
e.g. 1000J to 100J to 10J to 1J and 0.1 is very small
how is only 10% transferred, where is it lost
energy lost via respiration (heat)/used in life processes
not all organism is eaten
not all organism is absorbed - some is egested/not DIGESTED
die/decomposes??? idk what this means tho