SKELETAL SYSTEM - PART 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1
New cards
Functions
1. Support
2. Protect
3. Movement
4. Storage
5. Blood cell production
2. Protect
3. Movement
4. Storage
5. Blood cell production
2
New cards
Cartilage
reduce friction and model for bone formation
3
New cards
Tendons
attach bone to muscle
4
New cards
Ligaments
attach bone to bone
5
New cards
connective
Bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments are
___________ tissues
___________ tissues
6
New cards
collagen and minerals
Bone’s extracellular matrix; flexible and able to bear weight
7
New cards
collagen and proteoglycans
Cartilage’s extracellular matrix; good shock absorber
8
New cards
collagen
Tendons and ligaments’ extracellular matrix; very tough
9
New cards
Proteoglycans
- large polysaccharides attached to proteins
- part of ground substance
- store water
- part of ground substance
- store water
10
New cards
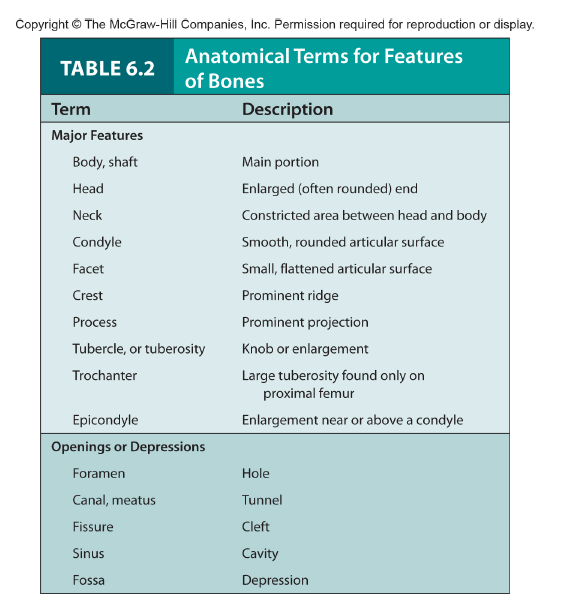
long, short, flat, irregular
Based on shape
11
New cards
compact and spongy (cancellous)
Type of bone tissue
12
New cards
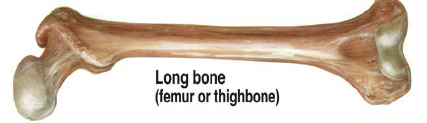
Long bones
Femur, tibia, fibula, phalanges
13
New cards
short bones
Carpals, tarsals

14
New cards
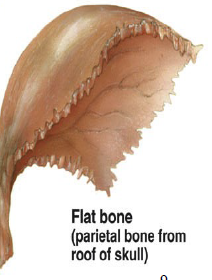
flat bones
Ribs, sternum, skull
15
New cards
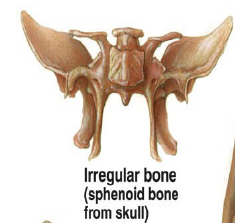
Irregular bones
Vertebrae and facial
16
New cards
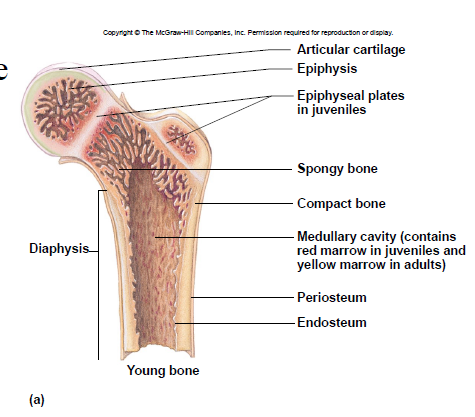
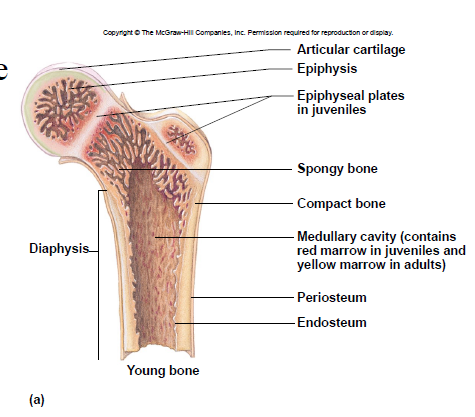
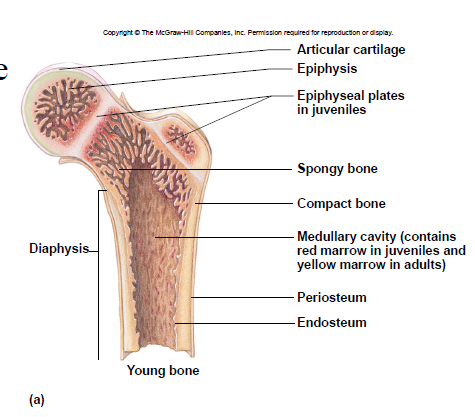
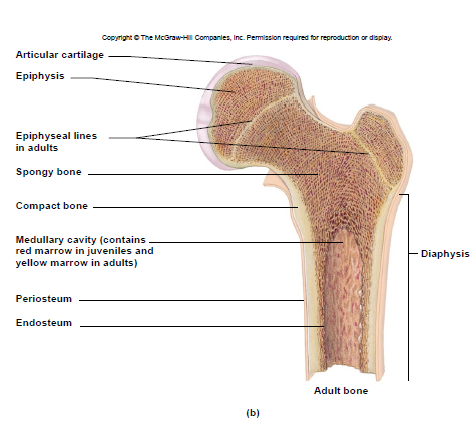
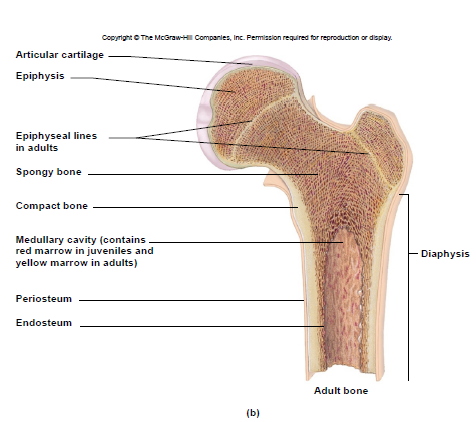
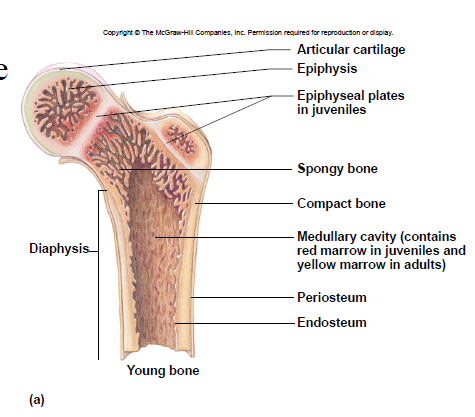
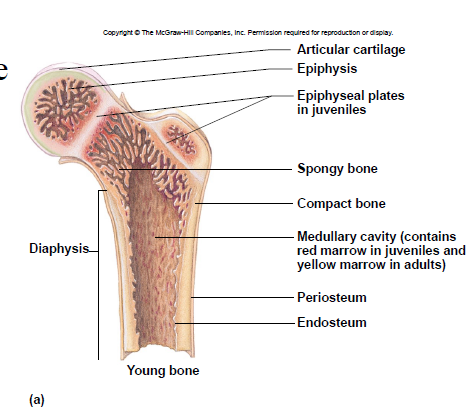
Diaphysis
– shaft
– compact bone tissue (on outside)
– compact bone tissue (on outside)
17
New cards
Epiphysis
– ends
– spongy bone tissue
– spongy bone tissue
18
New cards
Articular cartilage
- covers epiphyses
- reduces friction
- reduces friction
19
New cards
Epiphyseal plate
– site of growth
– between diaphysis and epiphysis
– between diaphysis and epiphysis
20
New cards
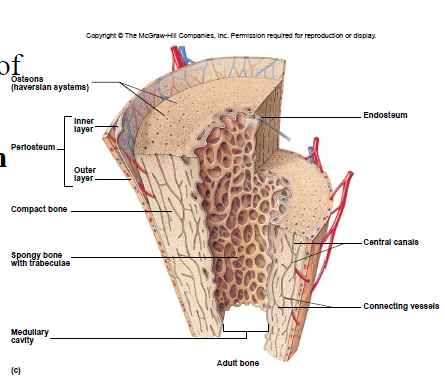
Medullary cavity
– center of diaphysis
– red or yellow marrow
– red or yellow marrow
21
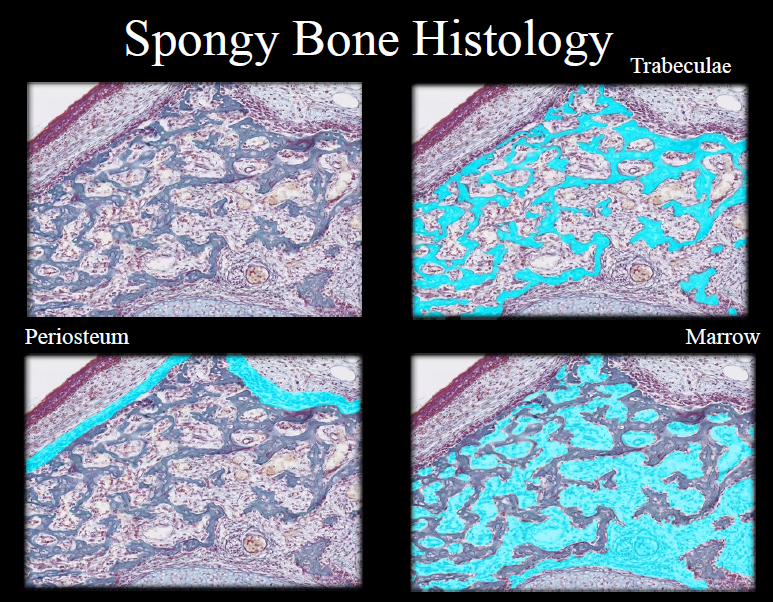
New cards
Periosteum
membrane around bone’s outer surface
22
New cards
Endosteum
membrane that lines medullary cavity
23
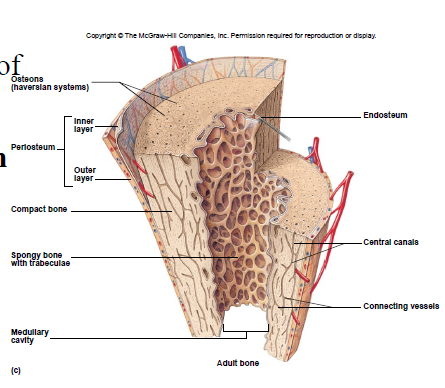
New cards
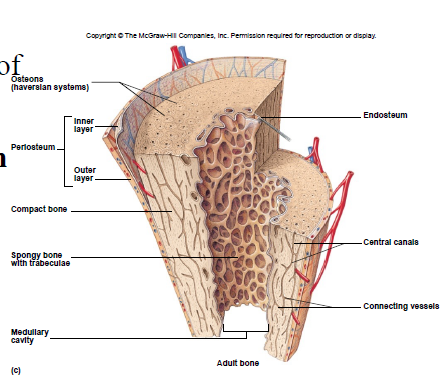
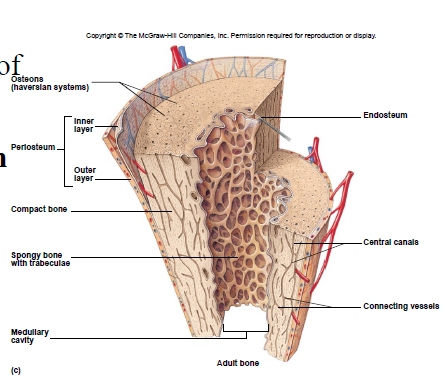
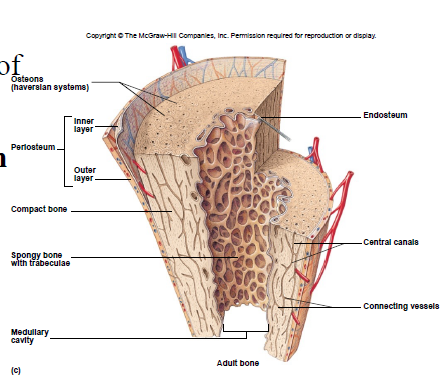
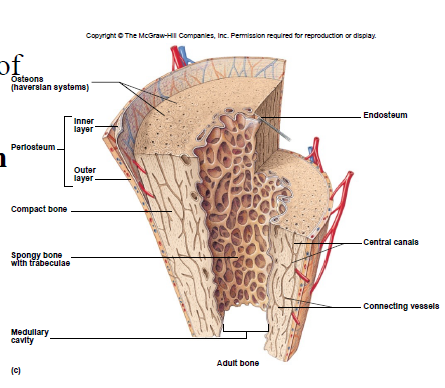
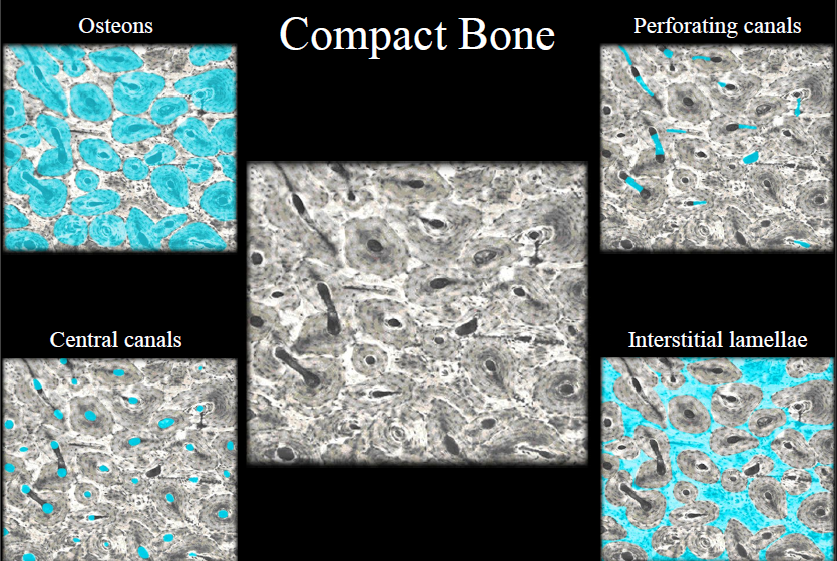
Compact Bone Tissue
Location: outer part of diaphysis (long bones) and thinner surfaces of other bones
24
New cards
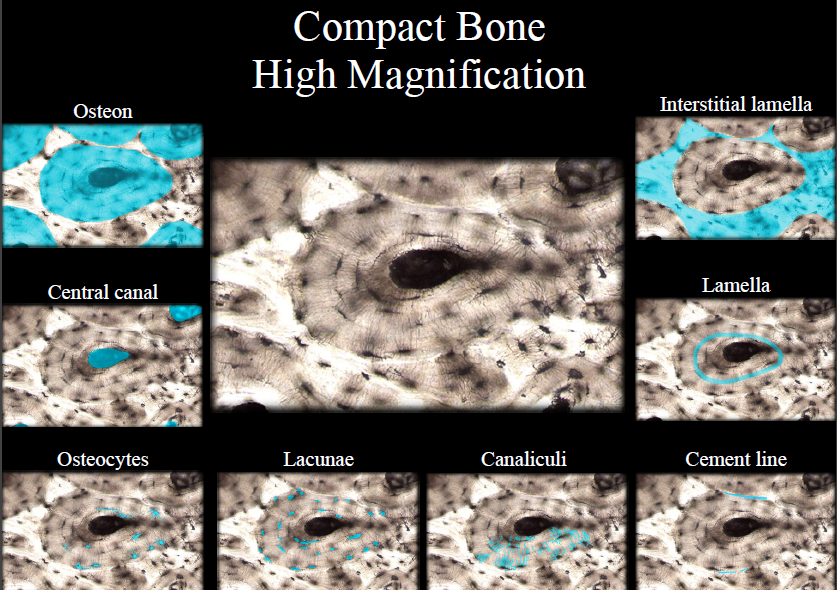
Osteon/Haversian system
- structural unit of compact bone
- includes lamella, lacunae, canaliculus, central canal, osteocytes
- includes lamella, lacunae, canaliculus, central canal, osteocytes
25
New cards
Lamella
rings of bone matrix
26
New cards
Lacunae
spaces between lamella
27
New cards
Canaliculus
- tiny canals
- transport nutrients and remove waste
- transport nutrients and remove waste
28
New cards
Central canal
- center of osteon
- contains blood vessels
- contains blood vessels
29
New cards
compact bone
30
New cards
compact bone
31
New cards
Spongy Bone Tissue
• Cancellous bone
• Location: epiphyses of long bones and center of other bones
• No osteons
• Location: epiphyses of long bones and center of other bones
• No osteons
32
New cards
Trabeculae
interconnecting rods, spaces contain marrow
33
New cards
spongy bone
34
New cards
Osteocytes
maintain bone matrix
35
New cards
Osteoblasts
build bone
36
New cards
Osteoclasts
carve bone
37
New cards
Ossification
process of bone formation (occurs in utero)
38
New cards
Osteoblast’s role
- build bone
- after an osteoblast becomes surrounded by bone matrix it becomes an osteocyte
- after an osteoblast becomes surrounded by bone matrix it becomes an osteocyte
39
New cards
Ossification center
where bone formation begins
40
New cards
Primary ossification center
- where bone 1st begins to appear
- forms diaphyses
- forms diaphyses
41
New cards
Secondary ossification center
forms epiphyses
42
New cards
Intramembranous Ossification
• Bone formation within connective tissue membranes
• Osteoblasts build bone
• Ex. Skull bones
• Osteoblasts build bone
• Ex. Skull bones
43
New cards
Endochondral Ossification
• Bone formation inside cartilage
• Cartilage models are replaced by bone
• Ex. All bones (except skull)
• Cartilage models are replaced by bone
• Ex. All bones (except skull)
44
New cards
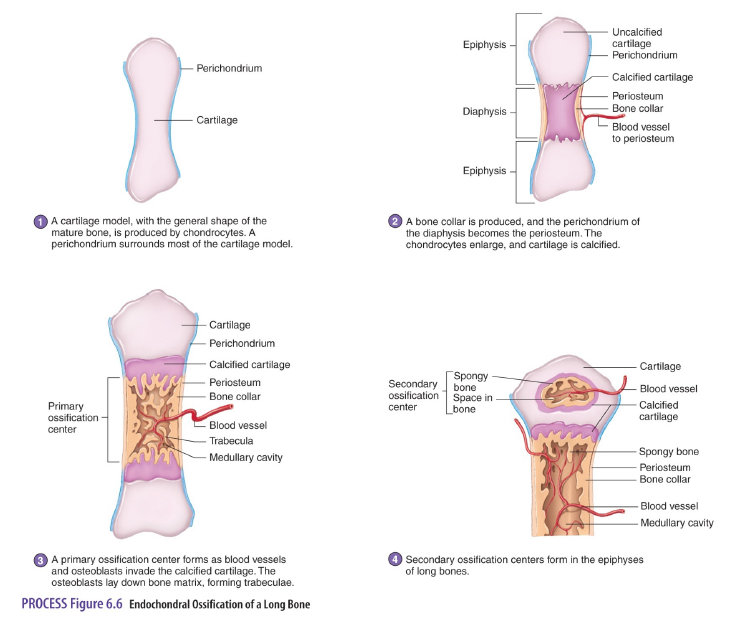
Steps in Endochondral Ossification
1. Chondroblasts build a cartilage model, the chrondroblasts become chondrocytes.
2. Cartilage model calcifies (hardens).
3. Osteoblasts invade calcified cartilage and a primary ossification center forms diaphysis.
4. Secondary ossification centers form epiphysis.
5. Original cartilage model is almost completely ossified and remaining cartilage is articular cartilage.
2. Cartilage model calcifies (hardens).
3. Osteoblasts invade calcified cartilage and a primary ossification center forms diaphysis.
4. Secondary ossification centers form epiphysis.
5. Original cartilage model is almost completely ossified and remaining cartilage is articular cartilage.
45
New cards
Third month of embryonic development
Ossification in long bones beginning
46
New cards
Fourth month
Most primary ossification centers have appeared in the diaphyses of bone.
47
New cards
Birth to 5 years
Secondary ossification centers appear in the epiphyses
48
New cards
5 years to 12 years in females, 5 to 14 years in males
Ossification is spreading rapidly from the ossification centers and various bones are becoming ossified
49
New cards
17 to 20 years
Bone of upper limbs and scapulae becoming completely ossified
50
New cards
18 to 23 years
Bone of the lower limbs and os coxas become completely ossified
51
New cards
23 to 25 years
Bone of the sternum, clavicles, and vertebrae become completely ossified
52
New cards
By 25 years
Nearly all bones are completely ossified
53
New cards
Infancy and youth
- long bones lengthen at epiphyseal plate
- long bones widen by adding more lamella
- long bones widen by adding more lamella
54
New cards
Appositional growth
increase in bone width and diameter
55
New cards
End of bone growth (in length)
epiphyseal plate is replaced by an epiphyseal line
56
New cards
Bone Remodeling
- removal of existing bone by osteoclasts and deposition of new bone by osteoblasts
- occurs in all bones
- responsible for changes in bone shape, bone repair, adjustment of bone to stress, and calcium ion regulation
- occurs in all bones
- responsible for changes in bone shape, bone repair, adjustment of bone to stress, and calcium ion regulation
57
New cards
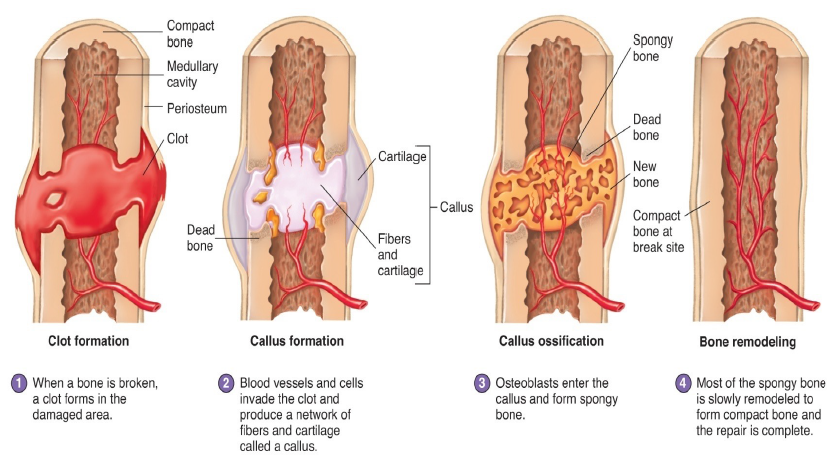
Bone Repair
1. Broken bone causes bleeding and a blood clot forms.
2. Callus forms which is a fibrous network between 2 fragments.
3. Cartilage model forms first then, osteoblasts enter the callus and form cancellous bone this continues for 4-6 weeks after injury.
4. Cancellous bone is slowly remodeled to form compact and cancellous bone.
2. Callus forms which is a fibrous network between 2 fragments.
3. Cartilage model forms first then, osteoblasts enter the callus and form cancellous bone this continues for 4-6 weeks after injury.
4. Cancellous bone is slowly remodeled to form compact and cancellous bone.
58
New cards
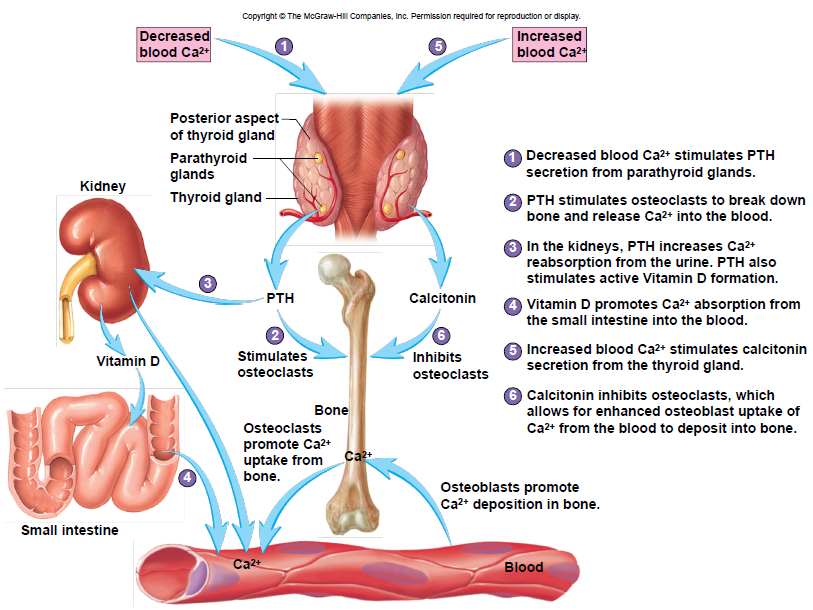
Bone and Calcium Homeostasis
• Bone is a major storage site for calcium
• Movement of calcium in and out of bone helps determine blood levels of calcium
• Calcium moves into bone as osteoblasts build new bone
• Calcium move out of bone as osteoclasts break down bone
• Calcium homeostasis is maintained by parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitonin
• Movement of calcium in and out of bone helps determine blood levels of calcium
• Calcium moves into bone as osteoblasts build new bone
• Calcium move out of bone as osteoclasts break down bone
• Calcium homeostasis is maintained by parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitonin
59
New cards
Hematopoietic Tissue
tissue that makes blood cells
60
New cards
Red marrow
location of blood forming cells
61
New cards
Yellow marrow
bone marrow that is yellow with fat; found at the ends of long bones in adults
62
New cards
Location of hematopoietic tissue in newborns
most bones (red marrow)
63
New cards
Location of hematopoietic tissue in adults
- red is replaced with yellow marrow
- red marrow is mainly in epiphyses of femur and humerus
- red marrow is mainly in epiphyses of femur and humerus
64
New cards
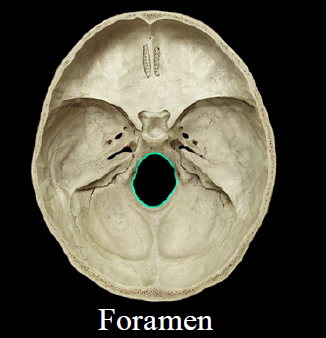
Foramen
- hole
- Ex. Foramen magnum
- Ex. Foramen magnum
65
New cards
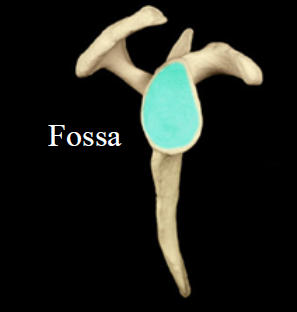
Fossa
- depression
- Ex. Glenoid fossa
- Ex. Glenoid fossa
66
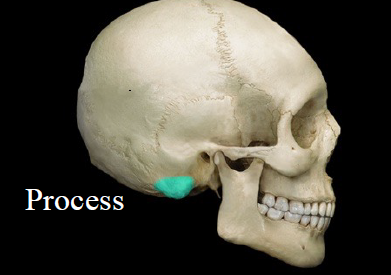
New cards
Process
- projection
- Ex. Mastoid process
- Ex. Mastoid process
67
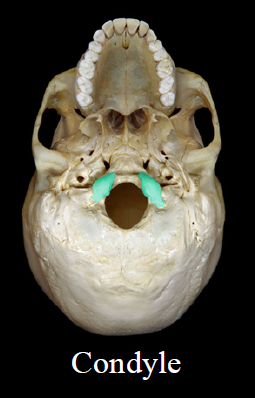
New cards
Condyle
- smooth, rounded end
- Ex. Occipital condyle
- Ex. Occipital condyle
68
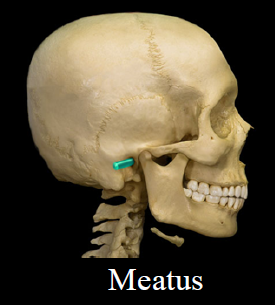
New cards
Meatus
- canal-like passageway
- Ex. External auditory meatus
- Ex. External auditory meatus
69
New cards
Tubercle
- lump of bone
- Ex. Greater tubercle
- Ex. Greater tubercle
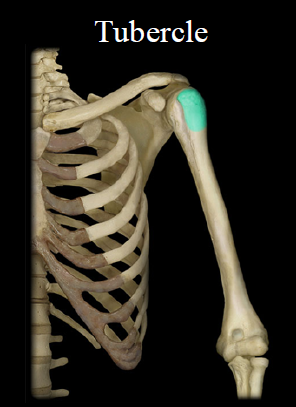
70
New cards
anatomical terms for features of bones
71
New cards
axial skeleton
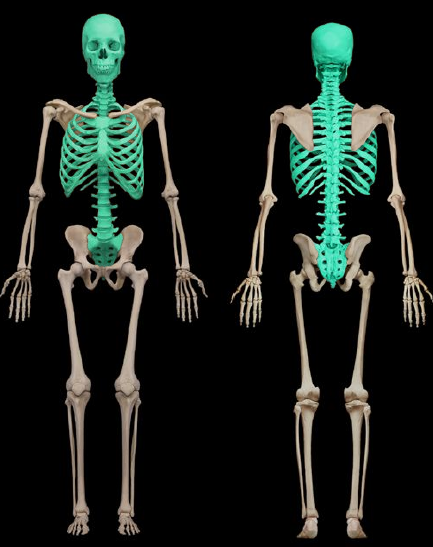
72
New cards
Mastoid process
attached to neck muscles
73
New cards
External auditory meatus
ear canal
74
New cards
Nasolacrimal canal
- canal between nasal cavity and eye
- conducts tears
- conducts tears
75
New cards
coronal suture
the suture between the parietal and frontal bones of the skull
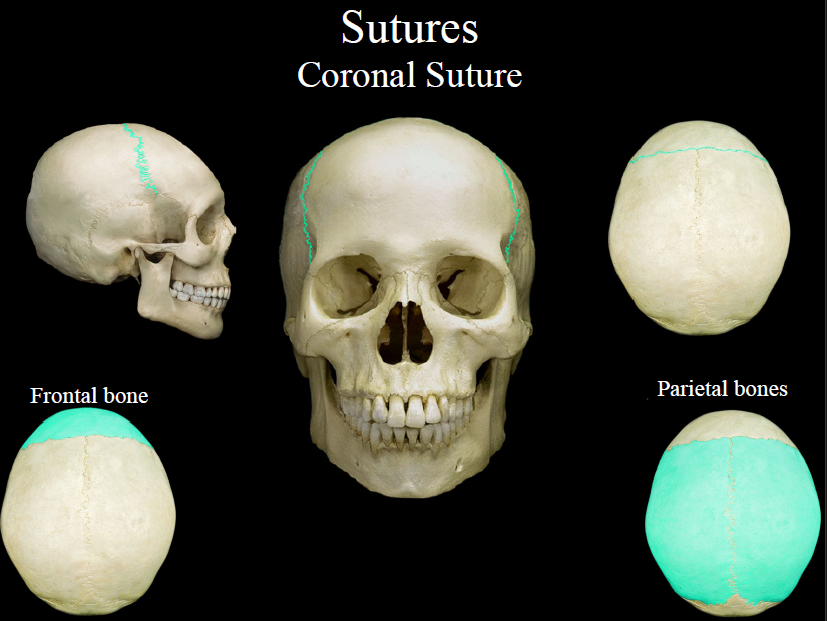
76
New cards
lambdoid suture
suture between the parietal and occipital bones
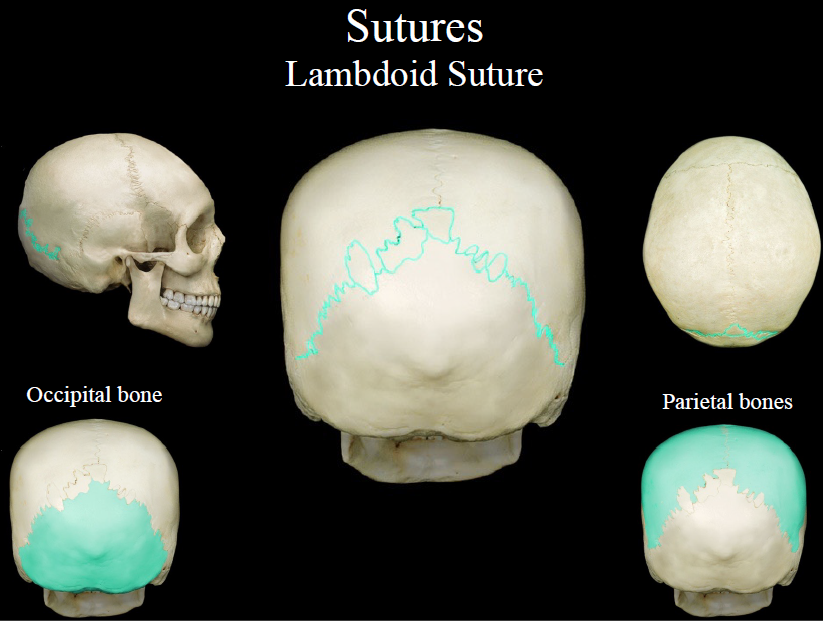
77
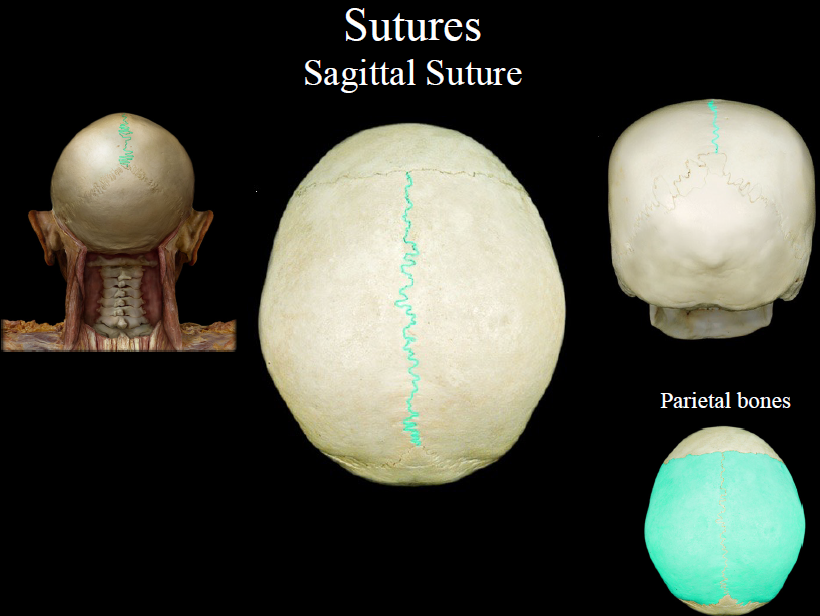
New cards
sagittal suture
the suture uniting the two parietal bones
78
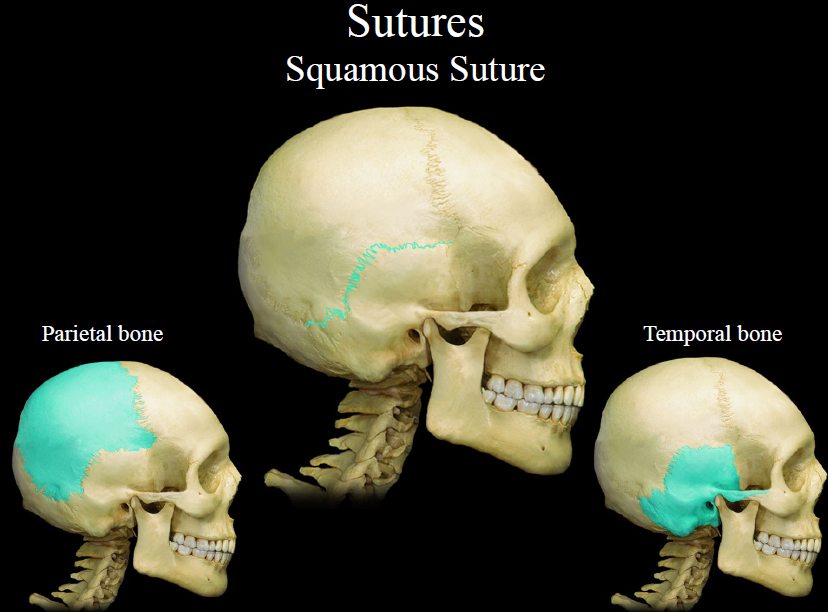
New cards
squamous suture
suture between the parietal and temporal bones
79
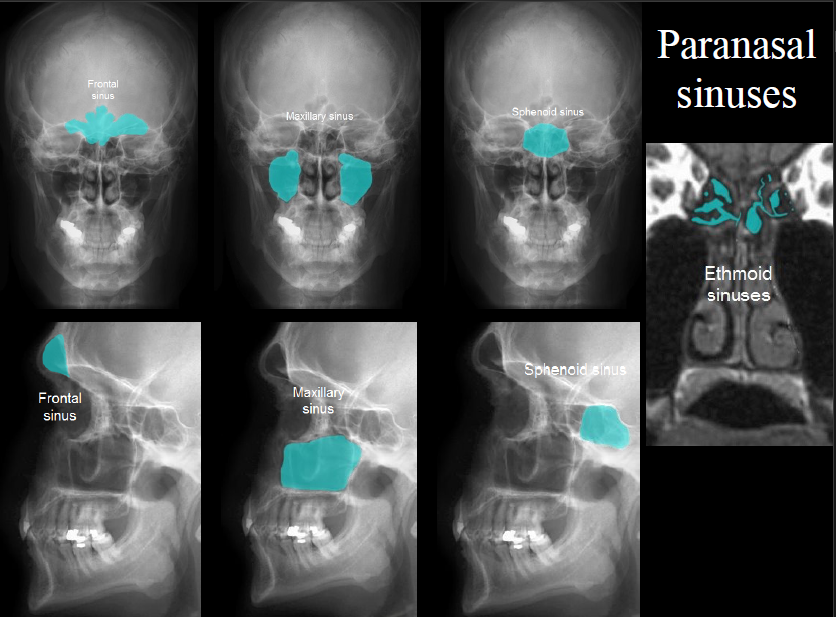
New cards
paranasal sinus
any of the paired sinuses in the bones of the face adjacent to the nasal cavity that are lined with mucous membrane that is continuous with the lining of the nasal cavities
80
New cards
paranasal sinuses
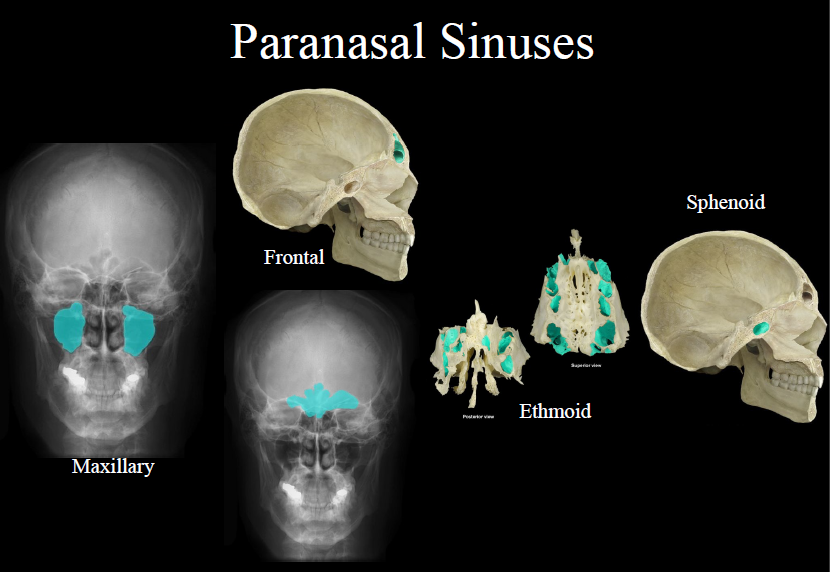
81
New cards
frontal bone
the large cranial bone forming the front part of the cranium: includes the upper part of the orbits
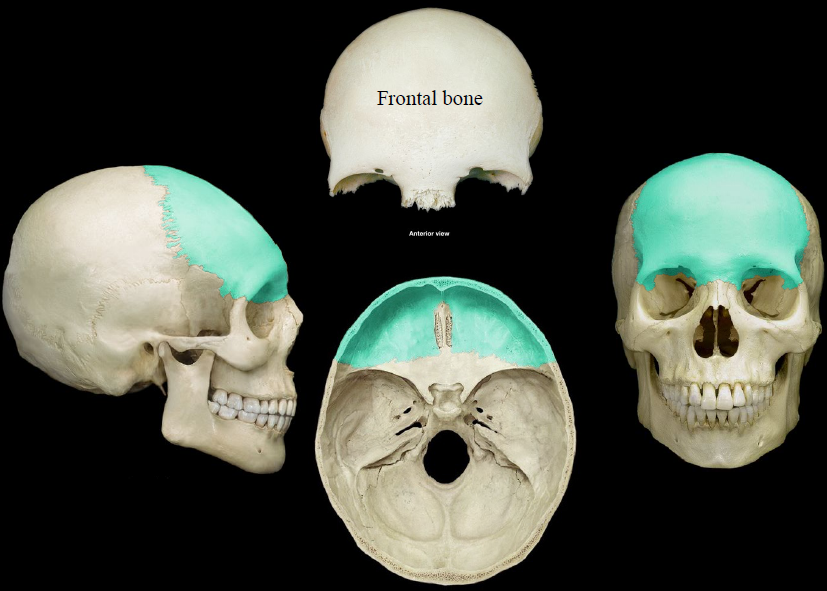
82
New cards
parietal bone
either of two skull bones between the frontal and occipital bones and forming the top and sides of the cranium
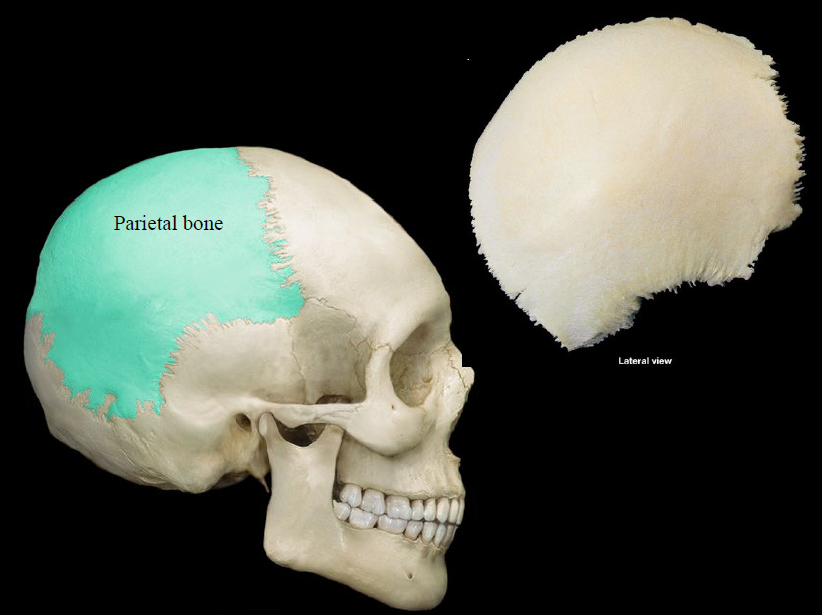
83
New cards
occipital bone
a saucer-shaped membrane bone that forms the back of the skull
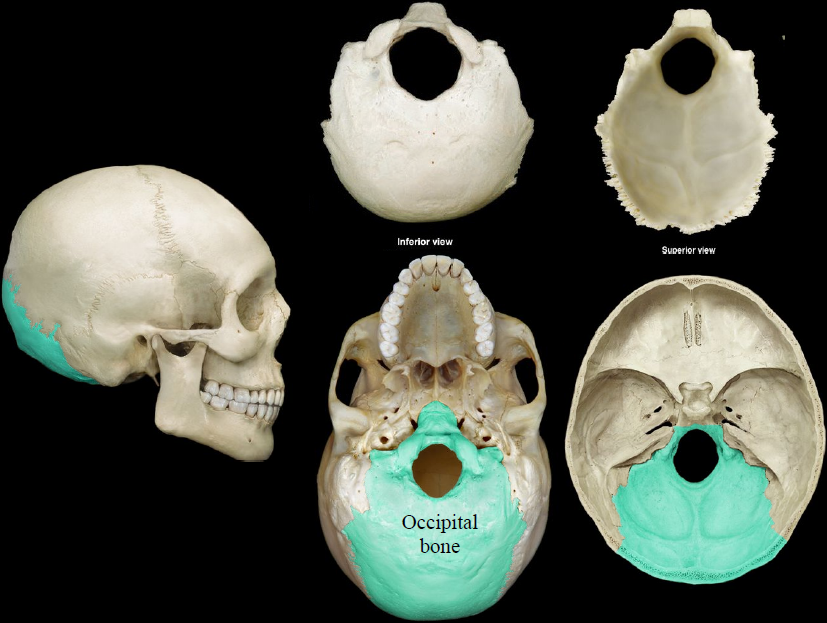
84
New cards
temporal bone
a thick bone forming the side of the human cranium and encasing the inner ear
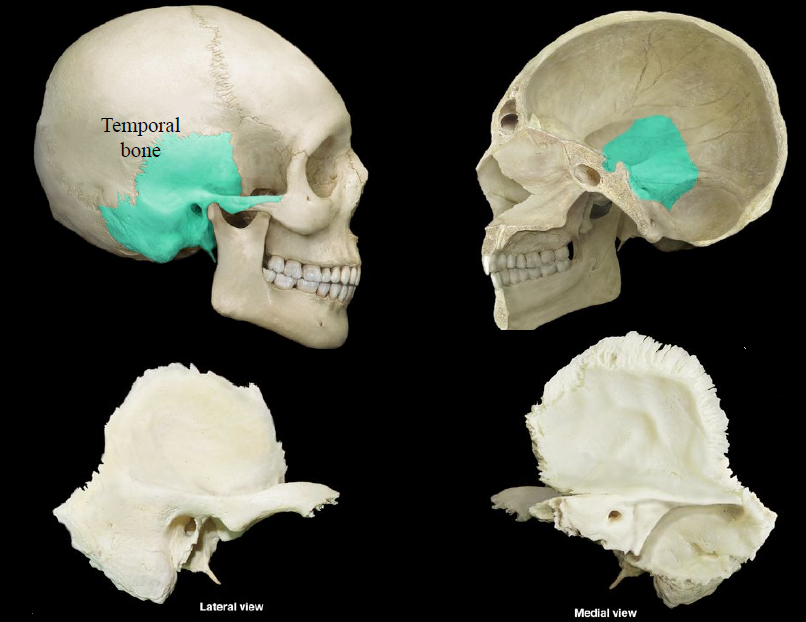
85
New cards
Styloid process
attachment site for tongue
86
New cards
Mandibular fossa
depression where lower jaw and skull meet
87
New cards
Glenoid fossa
where humerus meets scapula
88
New cards
temporal bone
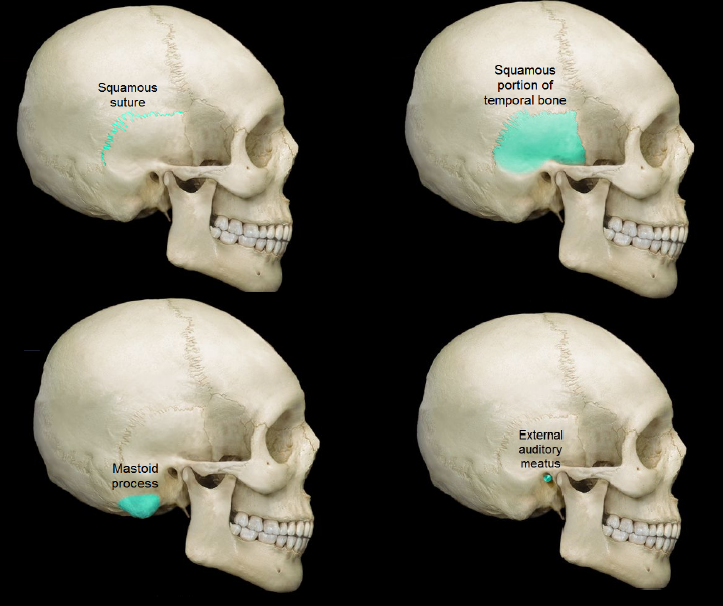
89
New cards
temporomandibular joint
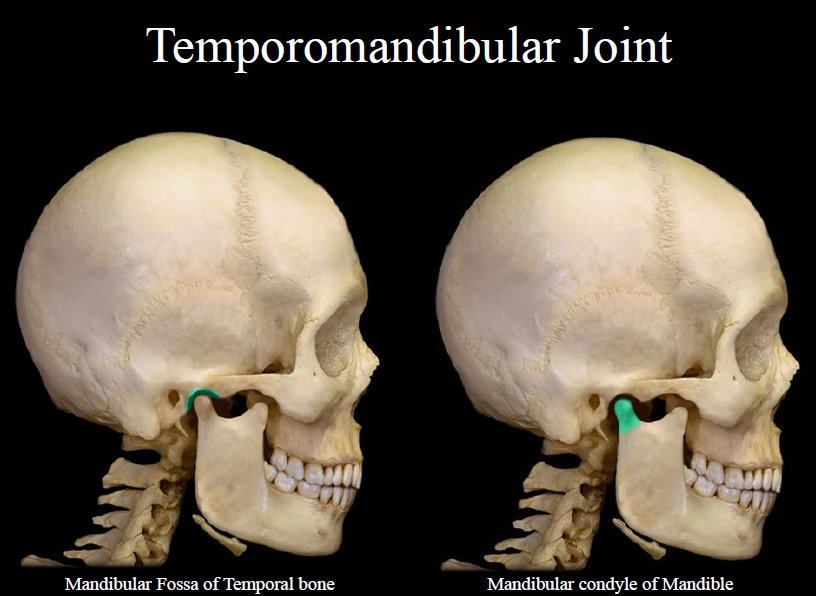
90
New cards
sphenoid bone
butterfly-shaped bone at the base of the skull
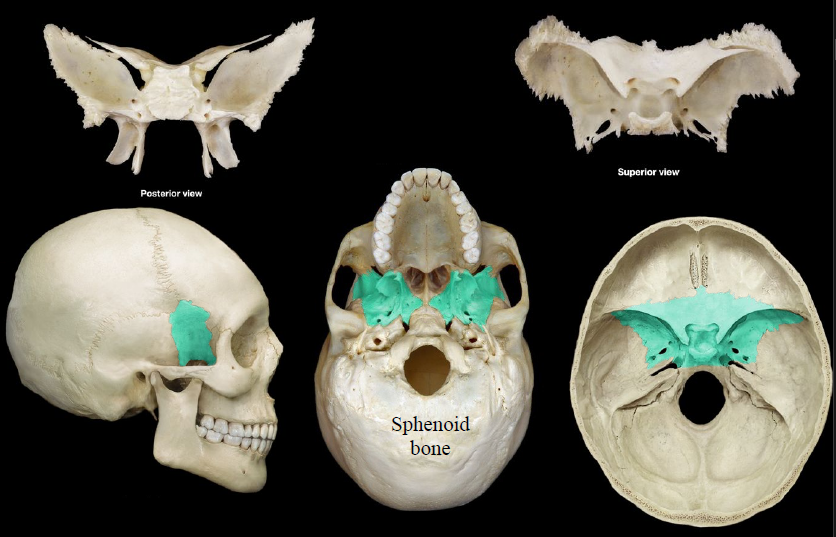
91
New cards
sphenoid foramina
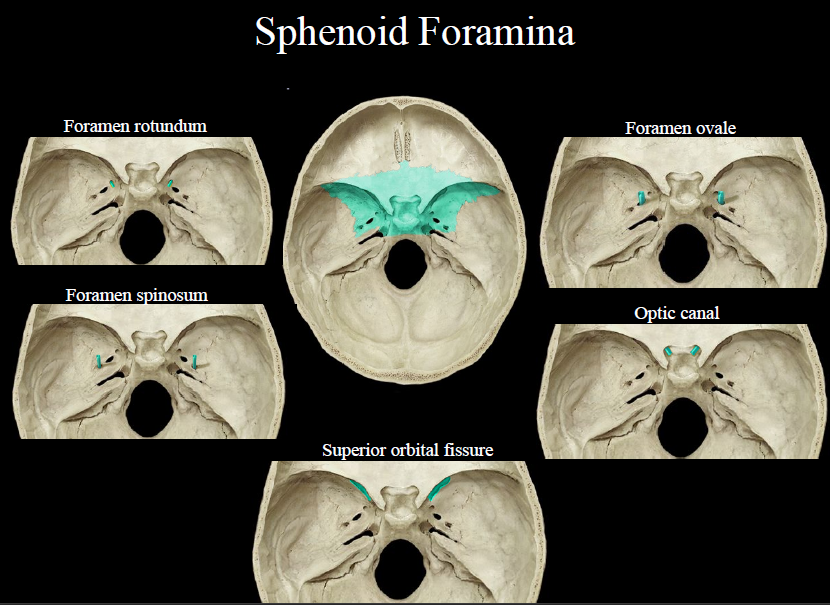
92
New cards
ethmoid bone
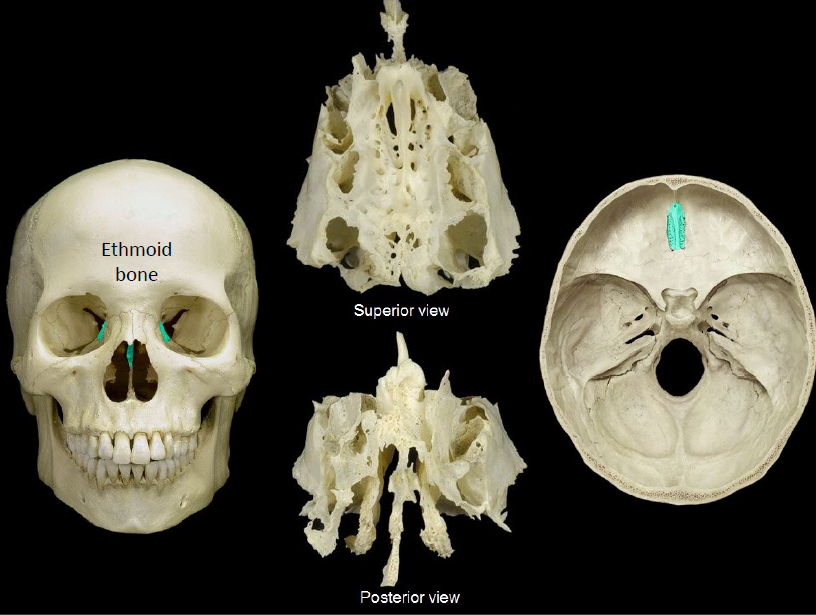
93
New cards
ethmoid bone
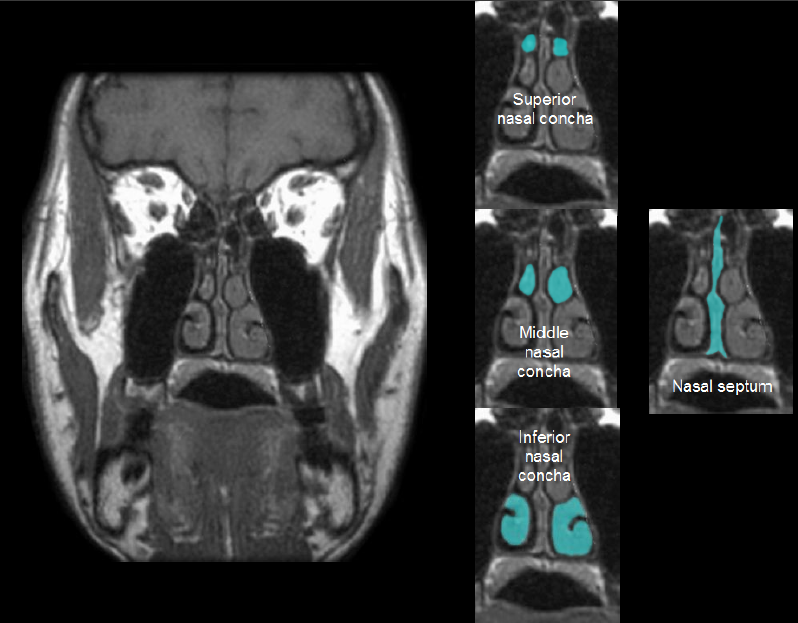
94
New cards
sphenoid bone
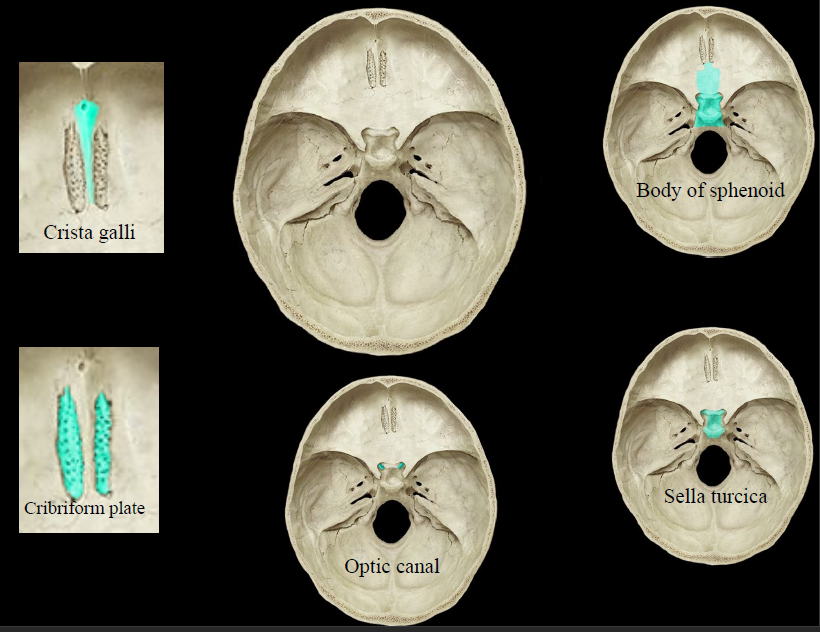
95
New cards
maxillae
of or relating to the upper jaw
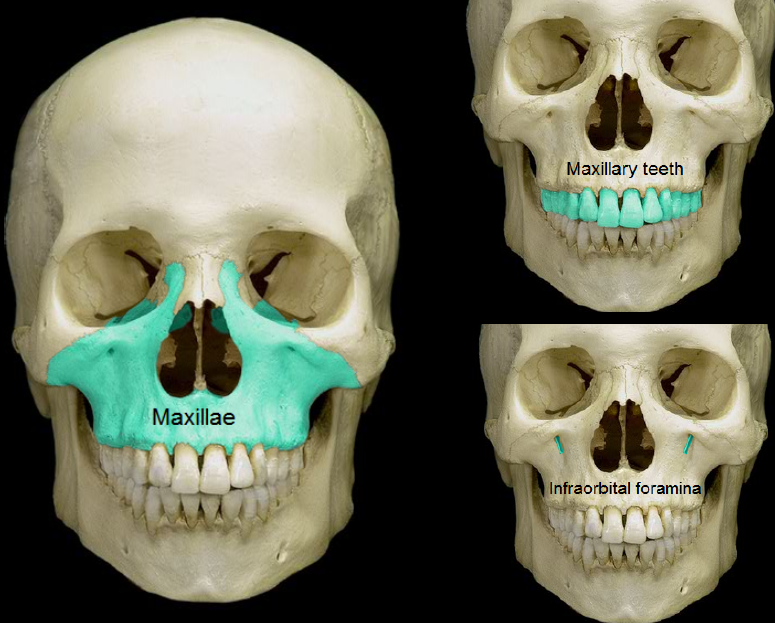
96
New cards
maxillae
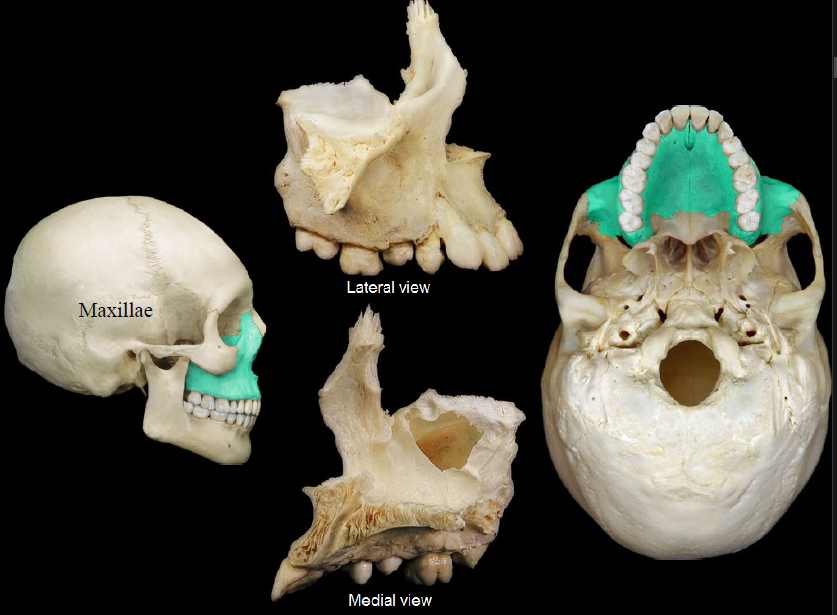
97
New cards
Hard palate
roof of mouth
98
New cards
Foramen magnum
hole where spinal cord joins brainstem
99
New cards
palatine bones
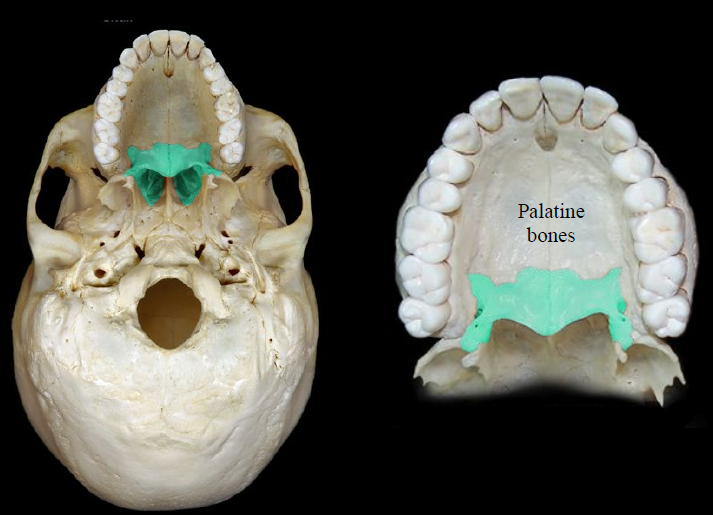
100
New cards
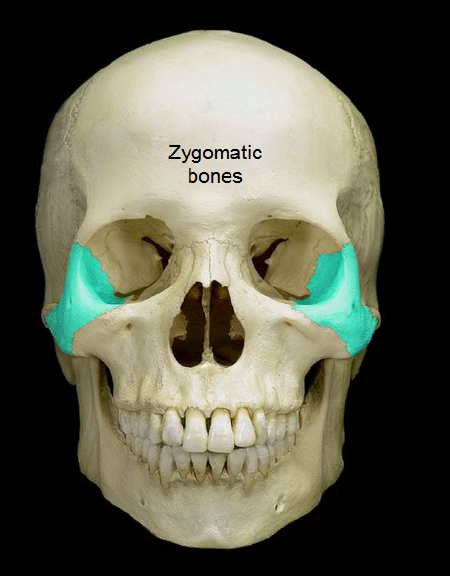
zygomatic bones