chapter 15
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
A mutation is defined as
heritable change in the genetic material (any permanent change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA)
although RNA and protein molecules can be altered
they are not heritable and not technically considered mutations
Not al mutations cause a
chanage or significant effect on a protein
ultimate effect on RNA/protein may be a gain or loss of
functions, altered function, or no change in function
beneficial mutations
evolution form chimp to human
detrimental mutations
genetic disorders and extinction
Point mutation
a mutation that alters a single nucleotide (base) within the DNA
can change the base sequence within the DNA
base substitution: can be silent, missense, or nonsense
Can add or delete bases of the DNA sequence:
Addition (insertion) or deletion (loss) of a base: can result in a frameshift mutation
change the arrangement/ sequence of the codon
base substitution is when
one base is wrongly paired with another base during DNA replication
Some base pair substitiutions have little or no impact on protein function
some alterations of nucleotides still indicate the same amino acids because of redundancy in the genetic code
other changes lead to switches from one amino acid to another with similar properties
still other mutations may occur in a region where the exact amino acid sequence is not essential for function
Some base pair substitutions may have a drastic effect
ex: sickle cell disease
Normal hemoglobin DNA : CTT
mRNA Normal hemoglobin : GAA
Mutant hemoglobin DNA: CAT
mRNA sickle cell hemoglobin : GUA
a base substitution mutation within a gene can result in three types of mutation to the codons of the mRNA
silent mutation, missense mutation , nonsense mutation
can change and effect the codon becoming a start or stop and effect mRNA and effect the protein
a frameshift mutation results from
the addition (insertion) and or deletion (loss) of nucleotides in a gene
cystic fibrosis
CFTR
sickle cell disease
HBB
marfan syndrome
FBN1
progeria
LMNA
tay sachs disease
HexA
several human genetic diseases are due to alterations to
large segments of DNA and chromosome structure
these can be caused by external sources or problems in the cell cycle
four categories of structural changes
deletion
duplication
inversion
translocation (simple and reciprocal)
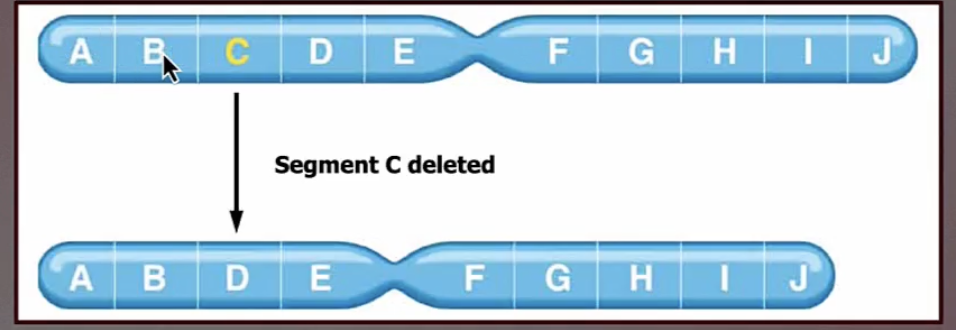
deletion chromosomal mutation
a segment of chromosomal material is removed
most cause serious disorders or are lethal
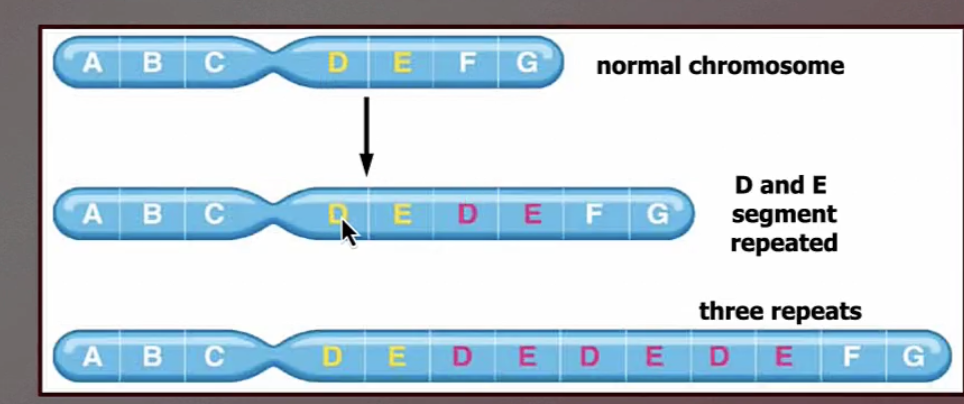
Duplication chromosomal mutation
a section of chromosome occurs two or more times
genes sequences can be repeated two or more times in a row and can occur in normal and abnormal chromosomes
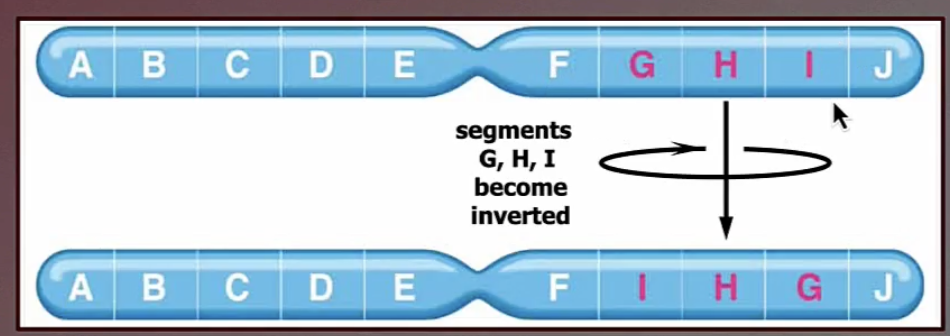
inversion chromosomal mutation
an inversion is a chromosomal rearrangement that results in a change of direction of the DNA within a single chromosome
occurs when a segment of a chromosome is broken in two places changes direction (reversed) and put back together
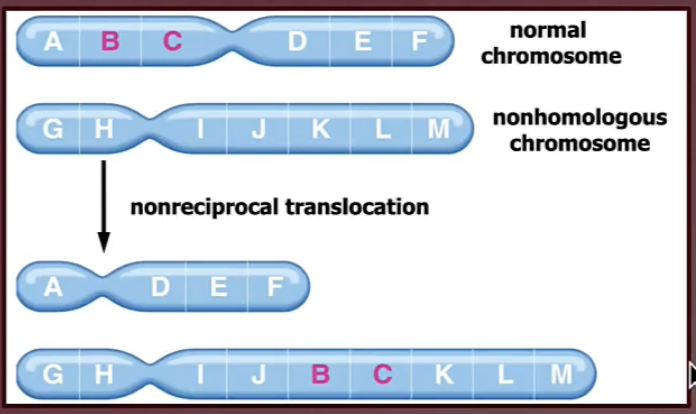
translocation chromosomal mutation
a segment of one chromosome is broken off and becomes attached to another chromosome
can be simple (or nonreciprocal) or reciprocal
Spontaneous mutations
occurs as a result of mistakes in natural biological processes
ex: DNA polymerase making an error during DNA replication that does not get corrected
Ex: normal metabolic reactions within the cell may produce toxic by products that can alter DNA sequence
there is no outside of cell influence or cause
induced mutations
occur as a result of exposure to environmental agents that can enter the cell and alter the structure of DNA
mutagen, a chemical or physical agents that interacts with the DNA to cause mutations
examples of mutagen
chemical agents (nicotine and benzo (a) pyrene)
physical agents (x-rays and UV light)
some viruses (papilloma viruses and hepatitis B virus)
spontaneous mutaiton examples
errors in dna replication
toxic metabolic products
changes in nucleotides structure
transposons
Induced mutation examples
chemical agents
physical agents
chemical mutagen agent
nitrous acid
5-bromouracil
2-aminopurine
nitrogen mustard
ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS)
Benzo[a] pyrene
Physical mutagen agent
x-rays
UV lights