Microeconomics (Year 1)
1/323
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
324 Terms
What is the basic economic problem
unlimited wants vs. limited resources (so resources have to be allocated between competing uses)
why is choice central to the basic economic problem
all economic decisions incur and opportunity cost
economics is the study of
how society allocates its scarce resources in order to maximise welfare
Central purpose of economic activity
Production of goods and services to satisfy the needs and wants of society
what are economic resources
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
definition of labour
human resources which contribute to output
What does a PPF show
They allow economists to analyse trade offs by showing the maximum combination of two goods or services that can be produced when a fixed number of resources are efficiently used, at a given level of technology
Why is the PPF bowed out?
increasing opportunity costs and specialization
would a fall in unemployment shift a PPF?
no, it would move closer to the line. (we are not producing at productive capacity)
economic good
a product which requires resources to produce it and therefore has an opportunity cost
what are intermediate goods
goods used in the production of other goods
why are experiments in econ hard to conduct?
economists can rarely conduct experiments and partly because it is often hard to isolate the effects of any particular event.
science experiments have controlled conditions but economic experiments are often uncontrolled
what are final goods
finished goods and services produced for the ultimate user
What are the 3 basic economic questions?
1. What to produce?
2. How to produce?
3. For whom to produce?
3 economic agents
1. Consumers
2. Producers
3. Government
Buffer stock scheme
A scheme intended to stabilise the price of a commodity by purchasing excess supply in periods when supply is high, and selling commodity reserves when supply is low.
Ceteris Paribus
all other things held constant. When variables that are not mentioned remain constant
why do economists build models?
Impossibility of undertaking a lab experiment. It summarises the relationships among economic variables. Models are useful because they abstract from the many details in the economy and allow one to focus on the most important economic connections.
To "think like an economist," decisions should include:
which variables will and will not be studied
Why is supply inelastic in the short run?
at least one factor of production is fixed
factors effecting demand
- consumer income
- consumer tastes
- substitute, - complements, - expectations, - population and demographic changes
factors effecting supply
- production costs
- technological advancements
- government policies
- natural disasters/weather conditions
- changes in expectations
- government intervention
- natural resource availability
how could worker productivity be improved?
- more training
- better technology
- specialisation
- more experience
what is the public sector
government
what is the private sector
part of the economy involving the private ownership of businesses
opportunity cost
the loss of the next best alternative forgone
positive statement
can be proven or disproven by data
normative statement
cannot be tested or validated and may contain a value judgement
are decisions made by the government normative or positive
normative, they make decisions based on their value judgements
value neutrality
the characteristic of being free of personal beliefs and opinions that would influence the course of research
economist focus on positive analysis
An economist might present data on the economic impact of a carbon tax without advocating for or against it.
Free goods
Goods that are unlimited in supply and which therefore have no opportunity cost
example of a free good
air
economic goods
Goods that are scarce because their use has an opportunity cost. They are created from scarce resources and therefore command a price
When price increases it causes...
a contraction along the demand curve
This contraction is explained by which two effects?
substitution effect: prices rise -> consumers retract their demand and find other, cheaper goods
income effect: as prices rise, consumers experience a fall in their real incomes so they demand less
When demand increases
extension along the price curve
demand definition
amount of goods or services that consumers are willing and able to buy at various prices
draw the demand curve
Why is the demand curve downward-sloping
- The law of diminishing marginal utility
- As prices rise consumers are less willing to spend
Real balance effect
increase in the price level reduces the purchasing power of households
Substitution effect
when consumers react to an increase in a good's price by consuming less of that good and more of other goods
why does inequality occur in the free market?
There is freedom to own resources. Those who own resources are likely to earn more income than those who do not own resources
factors that may cause a shift in the demand curve
Advertising, income, fashion and tastes, price of substitute goods, price of complementary goods, demographic changes
define direct tax
a tax that must be paid directly to the government by the person on whom it is imposed (ex. property tax)
define 'indirect tax'
A tax on consumer expenditure
when will the government receive more tax revenue?
when demand is inelastic
what type of goods should the government tax during a boom?
income elastic goods (normal/luxury)
factors effecting PES?
spare capacity, state of economy, availability of FoPs stockpiles and perishability, whether the raw materials are scarce,
length of the production process
if you can't stockpile a good is it elastic or inelastic?
inelastic
subsidies diagram? top, bottom,
top rectange is benefit of subsidy to producer
bottom is benefit of subsidy to consumer
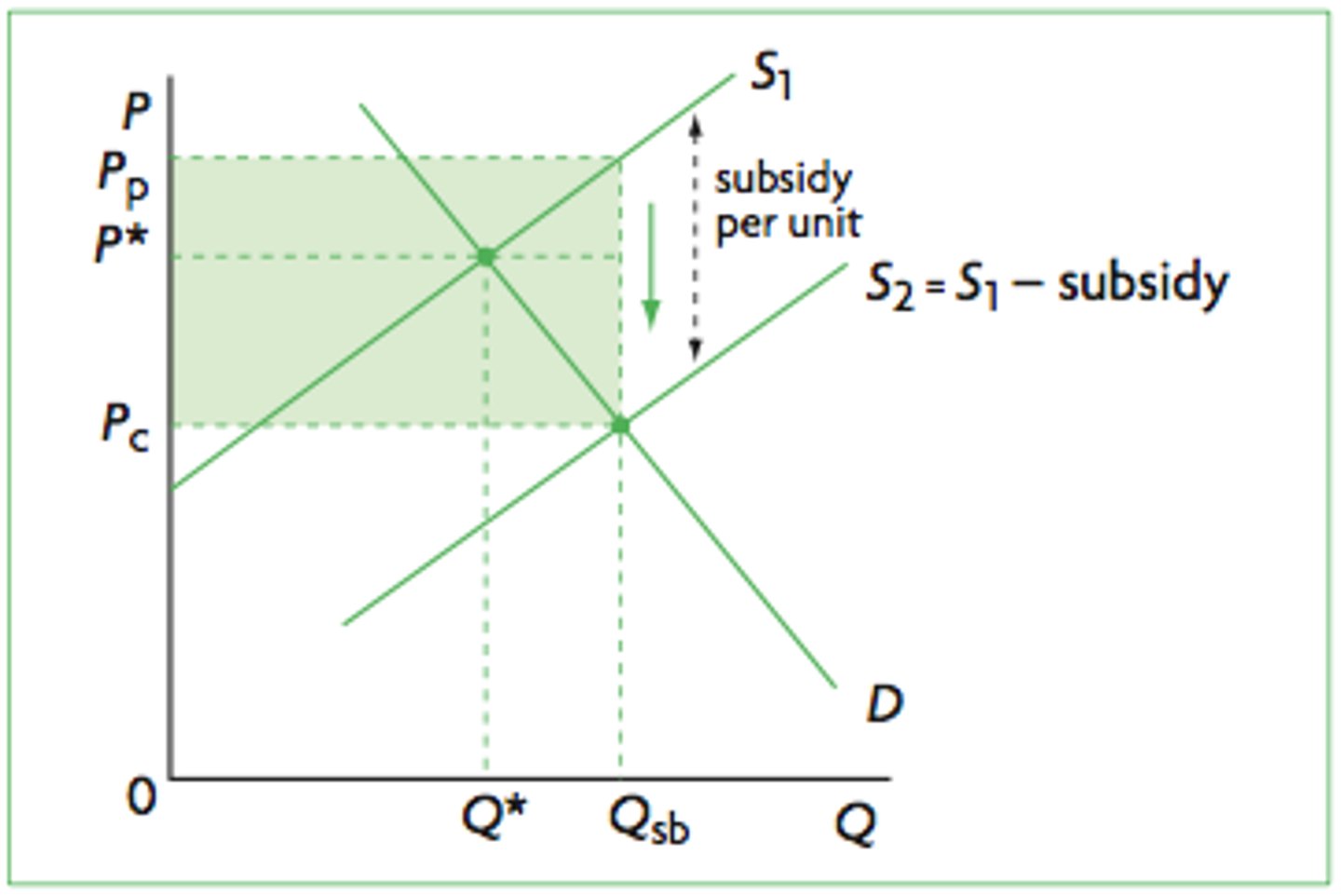
what is ad valorem tax?
Tax levied as a percentage of the value of the good
Why are taxes ineffective when trying to counter inelastic demand
Because the consumers will continue to consume the goods even if the consumer burden is as large as it can be.
what does the whole rectangle represent on a subsidy diagram?
the cost of a subsidy
Utility Maximization
The proposal that people make decisions by selecting the option that has the greatest utility.
what is total utility?
The overall benefit gained from consuming a good
Specific tax: top rectangle, bottom rectangle and total square
top: incidence of tax on consumer
bottom: producer burden
total: tax revenue
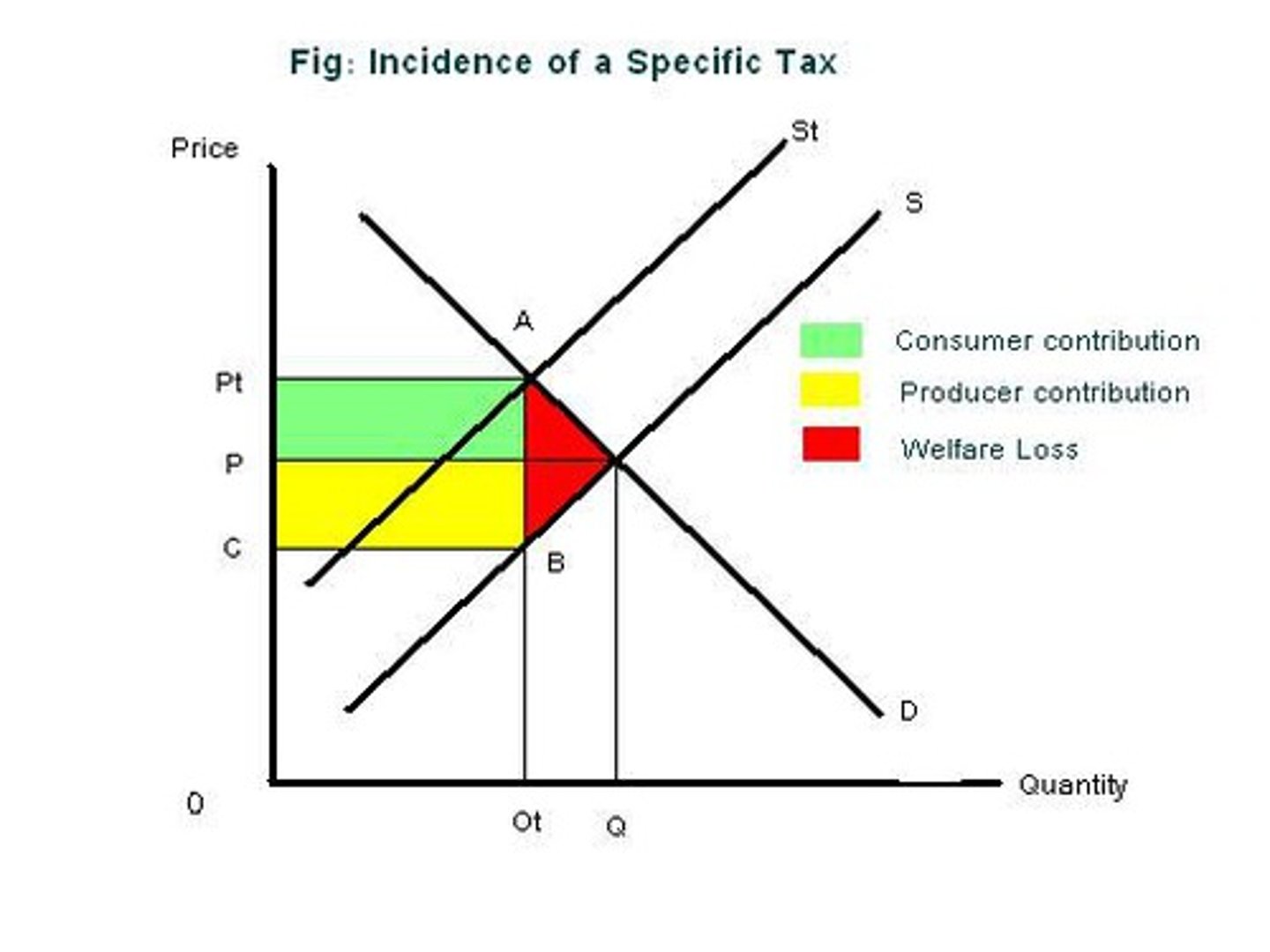
On a graph showing the effects of an ad valorem tax, where do we find the price received by producers?
At the point on S below the point where S+tax intersects D.
What is allocative efficiency?
point on the PPF that maximises social welfare
What are demerit goods?
Goods that are considered to be undesirable for consumers and are over-provided by the market, maybe due to the good having negative externalities.
What is Asymmetric information
Where consumers and producers have unequal access to information about a good or service in the market.
e.g the over-consumption of tobacco or under-consumption of education
why is indirect tax seen as regressive?
because even when people have a high income they pay the same tax as those who have a low income
Definition of information failure?
information failure occurs when consumers do not have sufficient information to take decisions that will maximise their welfare
what is a stockpile?
stock of goods held in reserve
how short is the short run and how long is the long run?
short run: at least one FOP is fixed, long run they are all variable
Formula for Savings ratio?
Total Savings/Disposable Income x 100
What is the social optimum?
the price and quantity combination that would exist if there were no externalities
where is the social optimum?
where MSB = MSC
Why are merit goods underprovided?
they have a higher private cost than social cost so these externalities are ignored and the good is underproduced
internalise the externality
an attempt to deal with an externality by bringing an external cost or benefit into the price system through tax
Why does the government impose specific taxes?
- increases revenue
- can internalise the externality
In order to internalise the externality, the tax imposed must be equal to ....
the external cost at the socially efficient quantity
what is market failure
when the market fails to allocate society's resources efficiently, instead of producing and consuming goods at the socially optimal level of output.
how is the unequal distribution of wealth considered as market failure?
some economists argue that wealth should be redistributed to benefit society
advantages and disadvantages of subsidies on goods with positive externalities
- internalises the benefit of the good
- could change consumer preferences
but
- difficult to put a monetary value on the externalities
- opportunity cost
How does market failure come about?
the price mechanism has not taken into account all the costs and/or benefits in the production/consumption of the g/s
What is the social benefit?
private benefit + external benefit
(e.g a child goes through education - private benefit of a job that pays a reasonable income
- social benefit that she becomes a doctor, treating people so that they can return to work)
What is the private benefit?
the benefit received by the consumer of a good or service
what are remittances?
a transfer of money by a foreign worker to an individual in their home country
consumer surplus
the amount a buyer is willing to pay for a good minus the amount the buyer actually pays for it
factors affecting consumer surplus
The gradient of the demand curve (more inelastic, more surplus)
Changes in the condition of demand (e.g increase demand will increase the surplus)
producer surplus
the difference between the lowest price a firm would be willing to accept for a good or service and the price it actually receives
different word for producer surplus
profit
factors affecting producer surplus
The gradient of the supply curve (more inelastic, more surplus)
Changes in the conditions of supply
effect of a subsidy on consumer surplus
increases size
Effect of tax on surplus
both decrease
Where is consumer surplus on a graph?
below the demand curve and above the price (the top one)
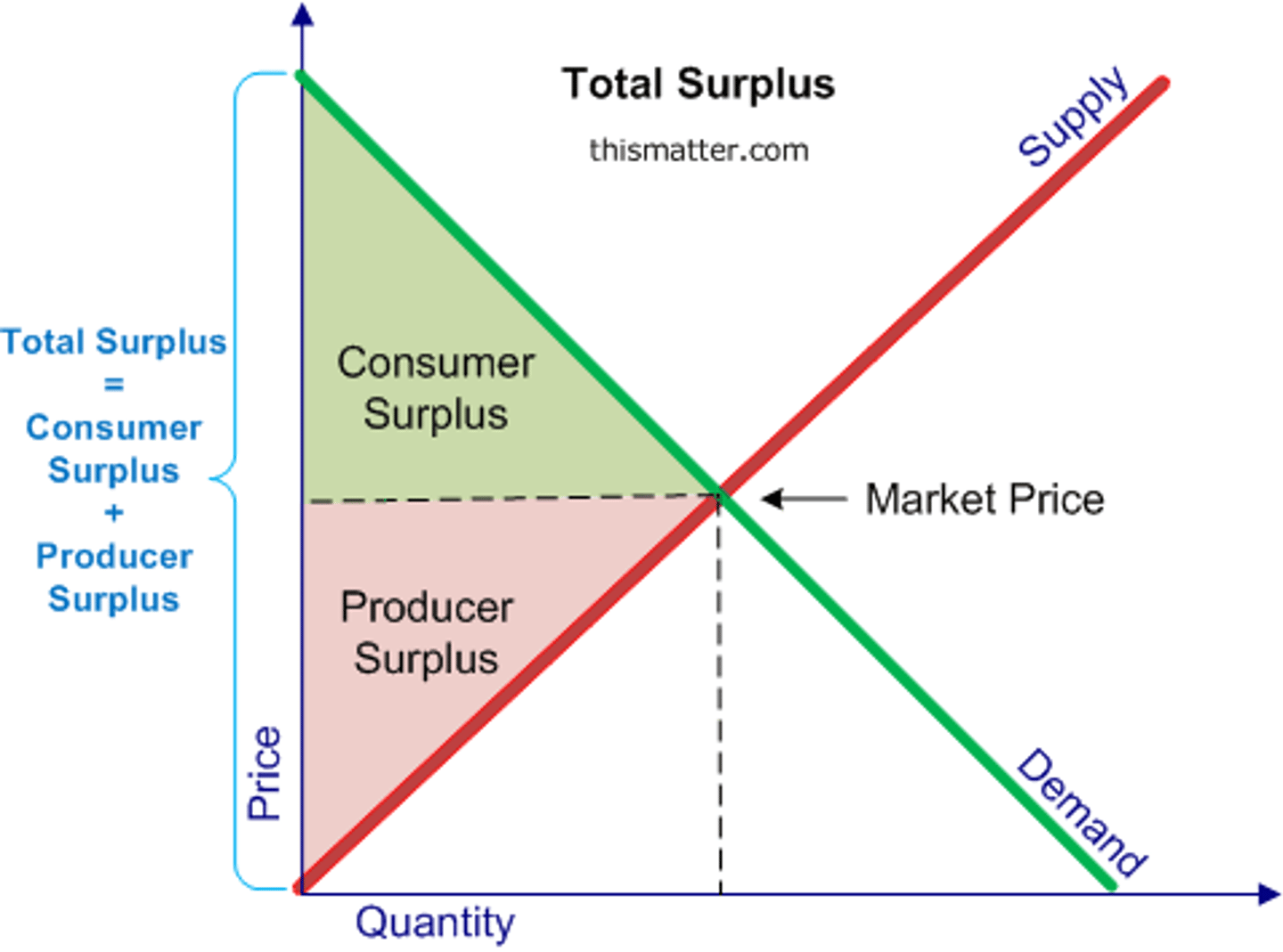
Where is producer surplus on a graph?
The area below the price and above the supply curve (the bottom one)

What is oligopolistic competition?
occurs when only a few firms dominate a market so they have to watch the other firm's actions
3 parts of price mechanism
rationing - makes sure supply = demand
incentivising - suppliers can determine whether there is profit to be made
signalling - it highlights to producers whether they need to increase or decrease their levels of supply
Disadvantages of the price mechanism? (3)
- Some goods objectively shouldn't be produced through the price mechanism (organs)
- There will be missing markets for some goods
- The price mechanism usually has no moral overlay or beliefs before a government intervenes.
what did Smith call the price mechanism?
the invisible hand
Y axis on macroeconomics PPF
X axis on macroeconomics PPF
y - consumer
x - capital
effect of emigration on ppf
inward shift
What is meant by Enterprise/Entrepreneurship?
An entrepreneur combines and organises land, labour and capital to produce a good
what could cause demand for houses to increase?
- Limited supply, would be difficult to increase the supply of houses due to time lags
- buying of second homes by the wealthy
- migrants buying homes
formula for accelerator effect?
It=A(Yt-Yt-1)
Why do goods become more elastic over time?
because people find more alternatives
what is a public good?
a good that is both non-rivalrous and non-excludable
What 2 characteristics do public goods have?
- non-excludable, people cannot be prevented from consuming the good
- non-rival, consuming does not reduce the quantity available for the next person
What are quasi-public goods?
Public goods which take on some of the characteristics of private goods