Pulmonary - Sinonasal Pathology
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Sun exposed skin of the face, lip, ears, scalp,neck, arms, etc are at an increased risk of developing...
solar (actinic) keratosis
what pathology may remain stable, may regress, may progress to SCC?
solar actinic keratosis
scaly plaques are a presentation of what pathology?
solar (actinic) karetosis
what pathology is
- Slow growing
- Rarely metastasizes
- and is caused by Loss of function mutation in PTCH1
basal cell carcinoma
T or F: basal cell carcinoma rarely metastasizes
TRUE
basal cell carcinoma is caused by what genetic component?
loss of function mutation in PTCH1
what is the greatest risk factor for basal cell carcinoma?
chronic sun exposure
how is basal cell carcinoma treated?
local excision
what is the probability that someone who has developed a basal cell carcinoma previously will develop another within 5 years?
40%
_____% of basal cell carcinoma patients develop another basal cell within 5 years
40%
Systemic lupus (SLE) Affects many organ systems including the skin in a disease called...
lupus erythematosus
Discoid rash: erythematous raised patches with adherent keratotic scaling and follicular plugging
this describes what pathology?
lupus erythematosus
T or F: only one factor plays a role in pathogenesis of lupus erythematosus
FALSE
- many factors
T or F: UV light exacerbates lupus erythematosus in many patients?
True
is lupus erythematosus autoimmune?
YES
what pathology can present as Malar rash (fixed erythema, flat or raised, over the malar eminences), photosensitivity?
lupus erythematosus
what pathology is a Form of rosacea?
Rhinophyma
what is the predilection of rhinophyma
common in men (12-30:1 ratio)
• Hypertrophy, follicular dilation, hyperplasia of sebaceous glands
• Fibrosis
• Increased vascularity
the above are characteristics of what pathology?
rhinophyma
Inflammation of the nasal cavity =
rhinitis
inflammation of the sinuses =
sinusitis
inflammation of both the nasal cavity and the sinuses =
rhinosinusitis
infectious rhinitis is also known as...
common cold
T or F: infectious rhinitis is only caused by one virus
FALSE
- can be caused by one or more
adenoviruses, echoviruses, and rhinoviruses are usually involved in what pathology?
infectious rhinitis
what sign will you expect to see in infectious rhinitis?
excessive nasal discharge
Clear nasal discharge, sneezing, itching after exposure to allergen is characteristic of...
allergic rhinitis
Repeated attacks of acute rhinitis is...
chronic rhinitis
- can be allergic or microbial
chronic microbial rhinitis may result from...
polyps or deviated septum
nasal polyps are most often associated with what?
- allergic rhinitis
Infections, asthma, aspirin intolerance, cystic fibrosis, diabetes are other causes
nasal polyps are most often associated with allergic rhinitis, what are other causes?
Infections, asthma, aspirin intolerance, cystic fibrosis, diabetes are other causes
epistaxis is commonly known as...
nosebleeds
- highly vascular nasal submucosa
• Trauma
• Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT)
• Hypertension
• Thrombocytopenia
• Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
• Sarcoidosis
• Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis)
• Hemangioma
the above are all etiologies of what?
epistaxis
loss of smell is also known as...
anosmia
the are 2 categories of anomsia:
obstructive
sensorineural
what 4 pathologies can cause obstructive anosmia?
• Rhinitis
• Sinusitis
• Nasal polyps
• Tumors
what 2 pathologies can cause sensorineural anosmia?
- trauma
- tumors
what precedes acute maxillary sinusitis?
acute or chronic rhinitis
what can result from periapical infection?
acute maxillary sinusitis
thickened, acutely inflamed sinus membranes is characteristic of...
acute maxillary sinusitis
can there be secondary bacterial infections in acute maxillary sinusitis?
YES
what is important to note about drainage in the case of acute maxillary sinusitis?
Drainage cannot occur due to inflammatory edema
- can occur at ostia
Severe infections in what pathology can involve ethmoid and frontal sinuses and meninges of brain?
acute maxillary sinusitis
what Results from recurring episodes of acute sinusitis or symptomatic disease lastinglonger than 3 months?
chronic maxillary sinusitis
chronic maxillary sinusitis is caused by?
drainage failure of acute inflamed sinus
what can be mistaken for a painful, abscessed tooth?
chronic maxillary sinusitis
T or F: chronic maxillary sinusitis can be caused by fungal infection
TRUE
Mucormycosis is seen in what groups?
immunocompromised like uncontrolled diabetics
what are other factors that can cause chronic maxillary sinusitis?
• Cigarette smoke
• Allergies
• Deviated nasal septum
• Nasal polyps
is malignant transformation possible in Fungiform and inverted papillomas?
YES
• Hamartoma, usually at septum
• Epistaxis
are characteristics of what pathology?
hemangioma (vascular malformation)
Fungiform and inverted papillomas contain...
respiratory epithelium
• Papillary appearance
• HPV
these are characteristics of what pathology?
squamous papilloma
hamartomas in hemangioma (vascular malformation) are usually where?
nasal septum
what pathology is a vascular tumor that exclusively affects adolescent males and young men, may mimic malignancy and presents with epistaxis?
nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
what is a vascular tumor that may mimic malignancy?
nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
what malignant tumor affects the paranasal sinuses?
squamous cell carcinoma
what pathology?
• Causes erosion
• Maxillary sinus most often affected
squamous cell carcinoma
malignant tumor of the paranasal sinus
what sinus is most often affected in squamous cell carcinoma?
maxillary sinus
what malignant tumor of the nasopharynx is caused by Epstein-barr virus (EBV)?
nasopharyngeal carcinoma
what pathology?
• Caused by Epstein-barr virus (EBV)
• Prevalent in China, Southeast Asia and East Africa (Smoking, Salted fish, Pickled food)
• Early metastasis, late detection
nasopharyngeal carcinoma
the following is the clinical presentation of what pathology?
• Nasal obstruction
• Epistaxis
• Cervical lymph node metastasis
nasopharyngeal carcinoma
what pathology is prevalent in China, SW Asia and East Africa?
nasopharyngeal carcinoma
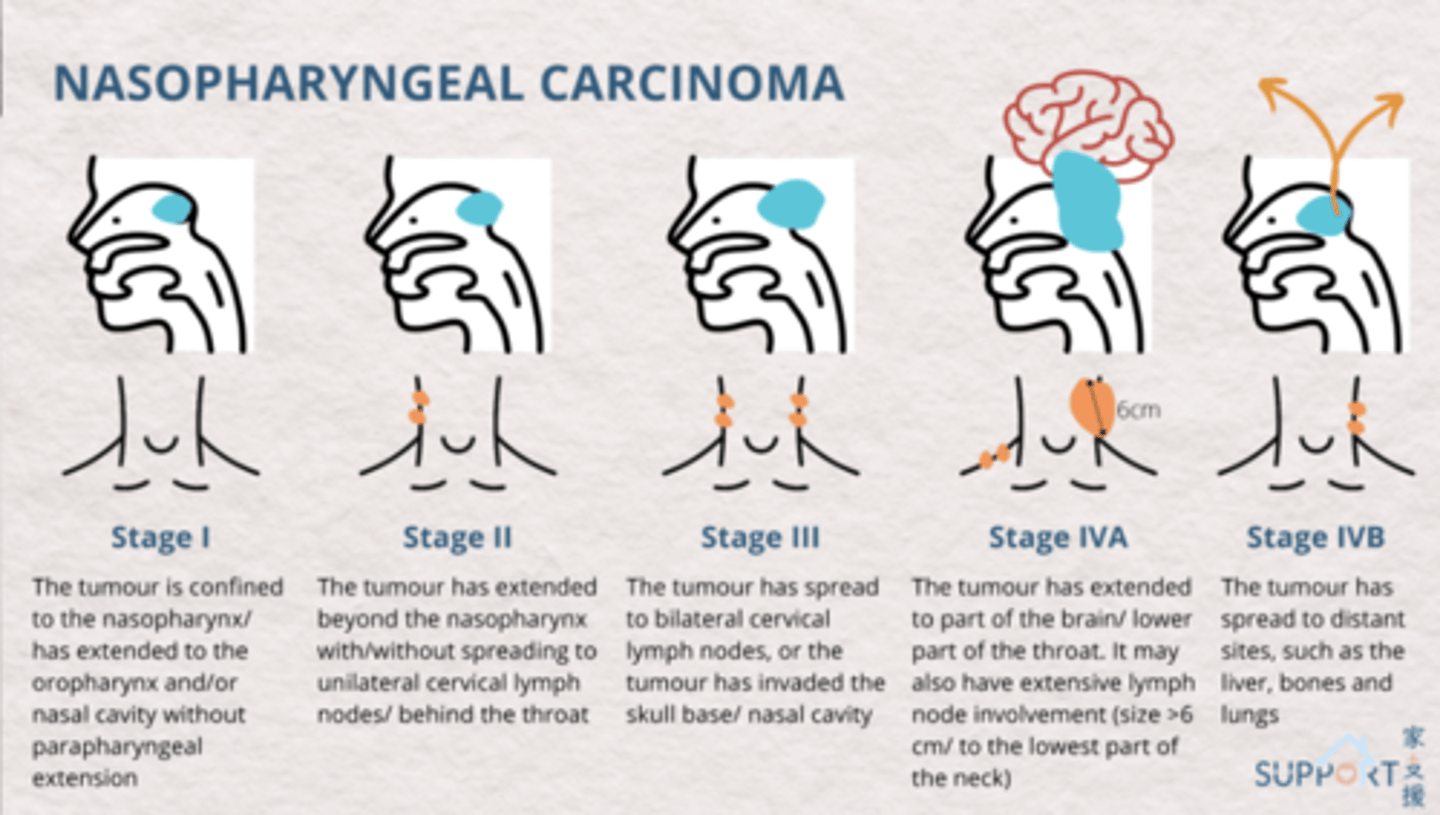
what stage of nasopharyngeal carcinoma?
the tumor is confined to the nasopharynx/has extended to the oropharynx and/or nasal cavity without parapharyngeal extension
stage 1
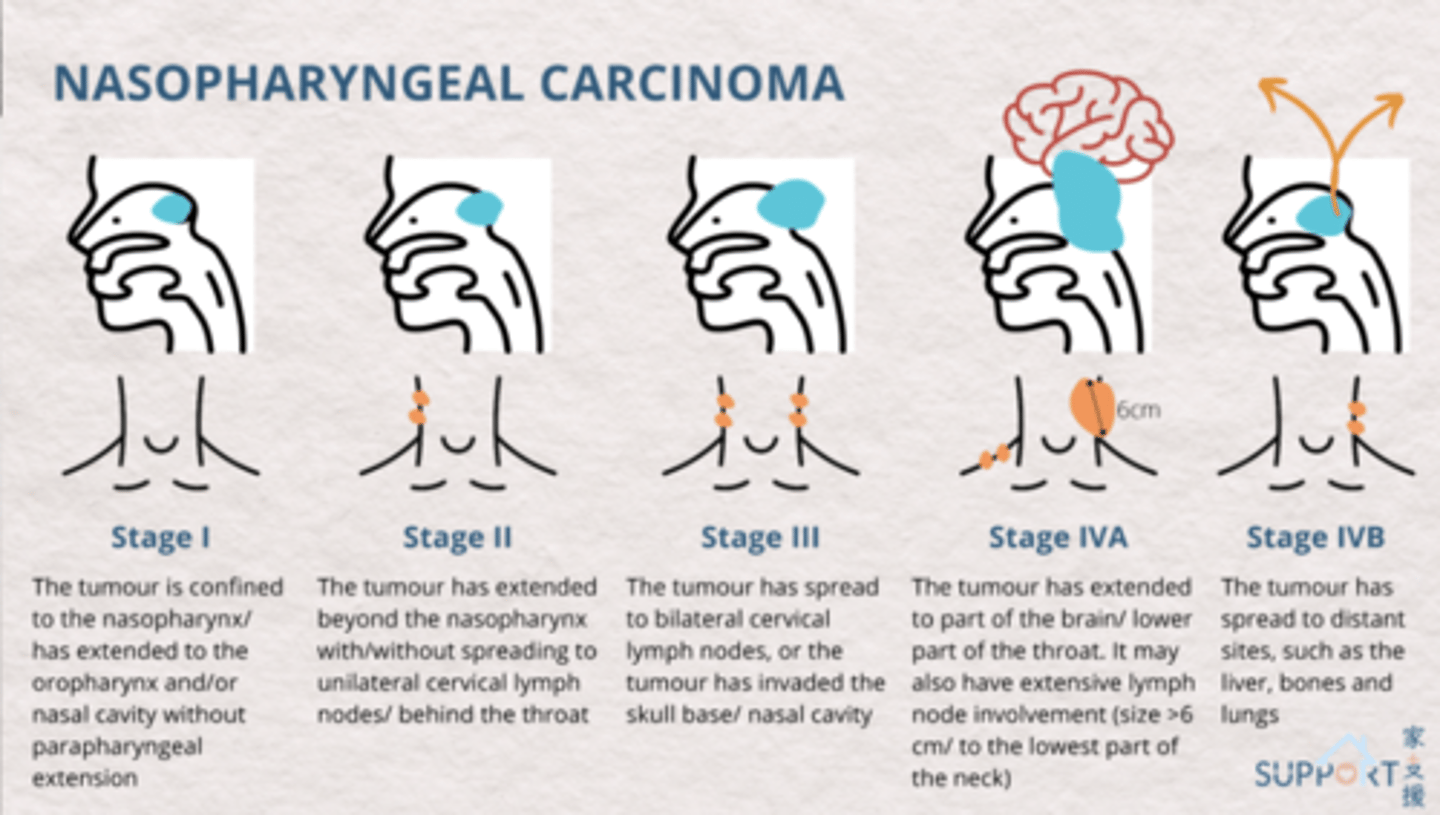
what stage of nasopharyngeal carcinoma?
the tumor has extended beyond the nasopharynx with/without spreading to unilateral cervical lymph nodes/behind the throat
stage 2
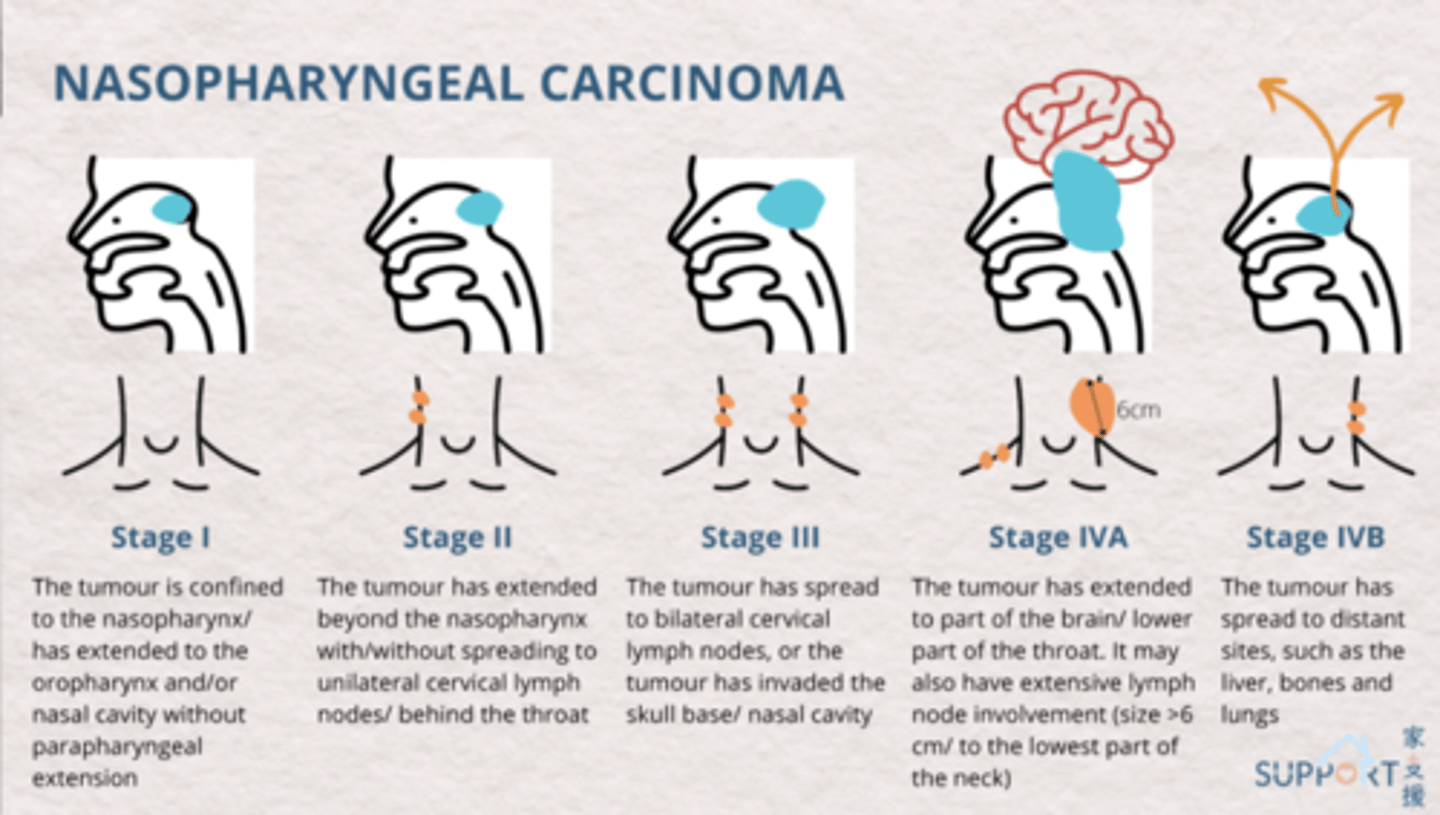
what stage of nasopharyngeal carcinoma?
the tumor has spread to bilateral cervical lymph nodes or the tumor has invaded the skull base/nasal cavity
stage 3
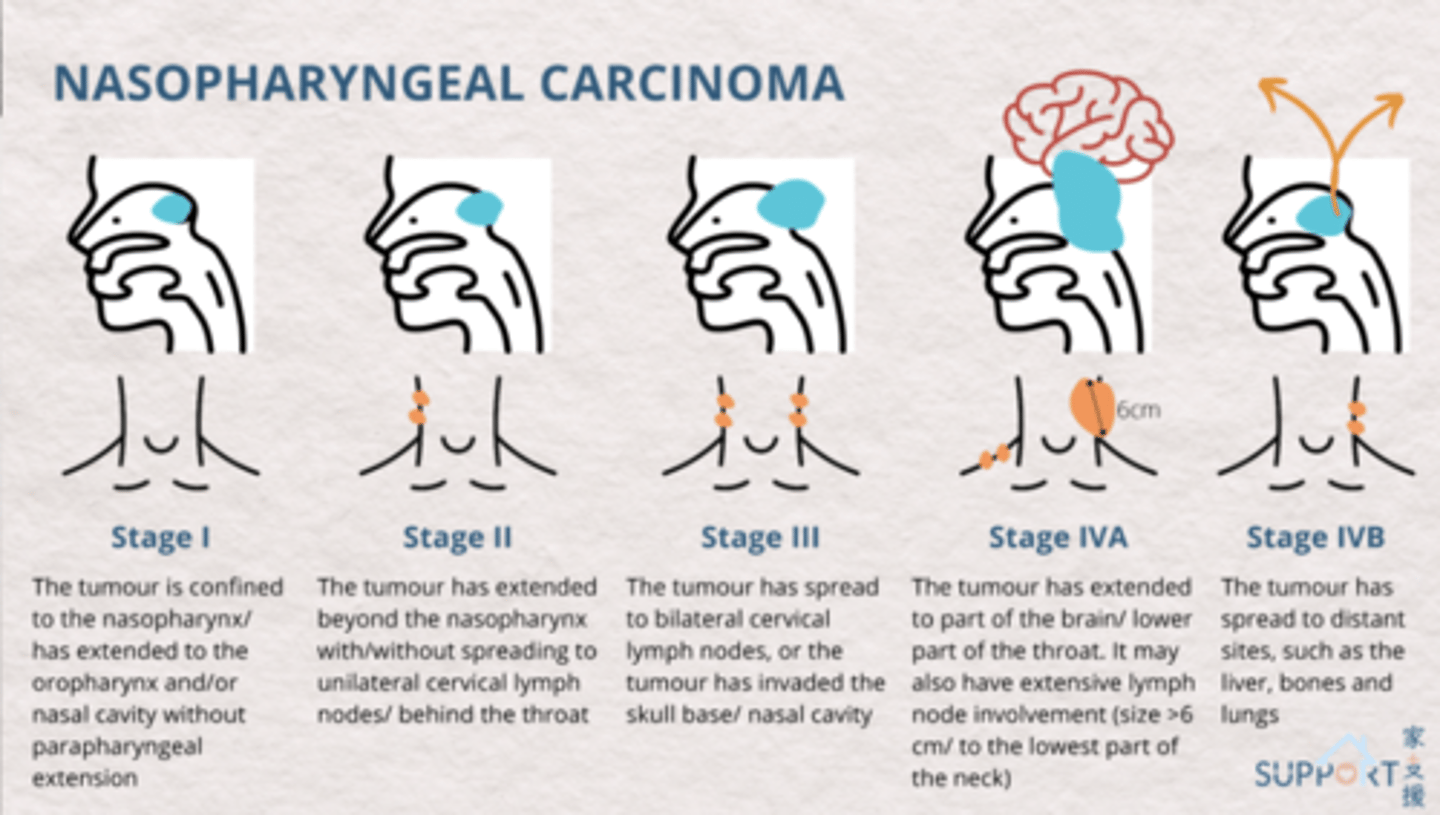
what stage of nasopharyngeal carcinoma?
the tumor has extended to part of the brain/lower part of the throat. It may also have extensive lymph node involvement (size>6 cm/to the lowest part of the neck)
stage 4A
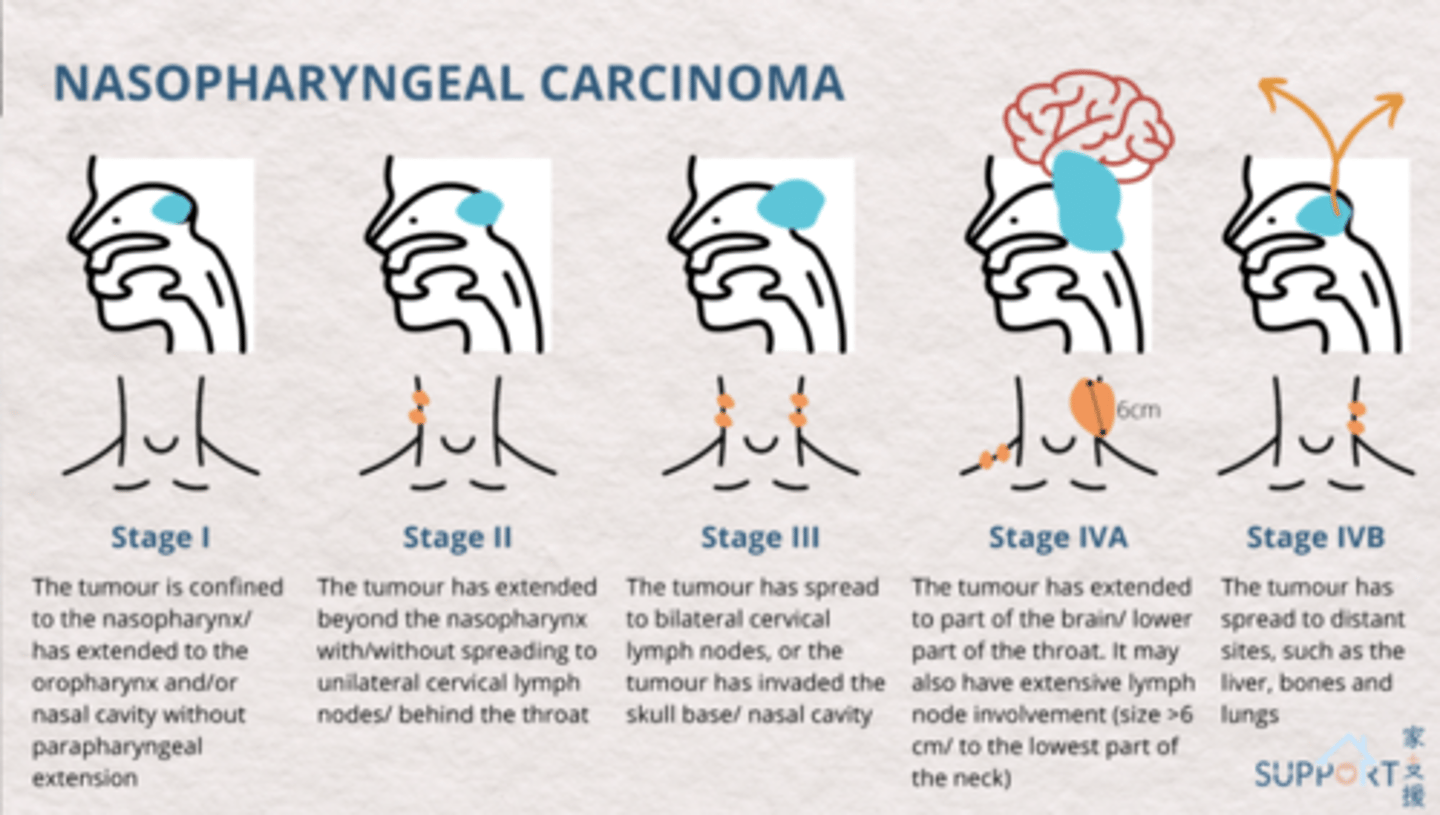
what stage of nasopharyngeal carcinoma?
the tumor has spread to distant sites such as the liver, bones and lungs
stage 4B
these 4 strictures form what?
• Palatine tonsils (tonsils)
• Nasopharyngeal tonsils (adenoids)
• Lingual tonsils
• Tubal tonsils (Eustachian)
Waldeyer's ring
• Common cold
• Influenza
• Mononucleosis (caused by EBV)
• Other viral respiratory tract infections
these are common infections of what part of the body?
the oropharynx
what is the most common cause of tonsillar enlargement
reactive lymphoid hyperplasia
what is the most common pharyngitis that also usually accompanies a cold?
mild pharyngitis
these are characteristics of what?
• Can accompany β-hemolytic streptococcal and adenovirus infection
• Potential for peritonsillar abscess "Quinsy"
• Acute rheumatic fever
• Acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
more severe pharyngitis and tonsillitis
what is caused by Corynebacterium diphtheria?
Diphtheria
what pathogens usually discovered in individuals that have contact with farm animals or dairy products?
diphtheria
what pathology includes a bacterial infection (Corynebacterium diphtheria) that is transmitted via contact with infected person or carrier through respiratory droplets
diphtheria
what pathology results in obstructive asphyxia due to a pseudomembrane produced on soft palate and pharynx?
diphtheria
diphtheria symptoms:
fever, malaise, sore throat, neck swelling
what pathology/infection involves produces an exotoxin that causes necrosis and affects heart and nerves
diphtheria caused by Corynebacterium diphtheria
Corynebacterium diphtheria produces a exotoxin does what and affects what organs?
causes necrosis and affects the heart and nerves
does Corynebacterium diphtheria produce an endotoxin or exotoxin?
exotoxin
T or F: diphtheria is common
FALSE
- rare occurrence since vaccine was developed
the epiglottis, false cords, ventricles, saccules are all in what region of the larynx?
supraglottis
the true vocal cords, ant. & post.commissures, vocal processes of arytenoids are all in what region of the larynx?
glottis
below true vocal cords to lower border of cricoid cartilage describes what region of the larynx?
subglottis
what is caused by inhaling irritants, allergic reaction, or common cold and results in hoarseness and/or temporary loss of voice?
acute laryngitis
diphtheria laryngitis produces?
what exotoxins and pseudomembrane
tuberculosis laryngitis results from
infected, coughed-up sputum
croup is also known as...
laryngotracheobronchitis
the following are characteristics of what pathology?
• Harsh persistent cough
• Caused by parainfluenza virus
• Affects children
• Self-limiting
• Respiratory failure can occur- laryngeal inflammation narrows airway
Croup (laryngotracheobronchitis)
Acute toxic laryngitis is caused by...
toxic fumes
Chronic toxic laryngitis is caused by...
results from cigarettes, premalignant
Angioedema is the result of...
type 1 hypersensitivity reaction
in the case of polyps, chronic irritation is usually caused by what?
heavy smokers
the following is the clinical presentation of what
• Unilateral
• Smooth and round
• Can be sessile or pedunculated
polyps (on vocal cords)
what is caused by chronic irritation and strain, affects true vocal cords with progressive hoarseness and presents as bilateral lesions?
Singer's nodules (vocal cord nodules)
treatment for Singer's nodules (vocal cord nodules)
• Voice or speech therapy
• Behavior modification
what is human papillomavirus (HPV)
squamous papilloma of the larynx
where does squamous papilloma of the larynx occur?
true vocal cords
what pathology present solitarily in adults but with multiple in children?
squamous papilloma of the larynx