Exchange rate systems
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
How will quantitative easing affect the exchange rate of a currency?
Quantitative easing involves the central bank creating new money. This will increase the supply of the currency and cause a depreciation of its exchange rate.
What are the three exchange rate systems?
fixed exchange rates
managed exchange rates
floating exchange rates
What is a fixed exchange rate?
Fixed exchange rates fix the value of one currency (like the Argentinian peso) to the value of another (like the Dollar).
So 1 dollar= 1 Peso
How can the central bank manage the exchange rate of a currency in two ways?
change the interest rate to shift the supply and demand of the currency, OR
they can use foreign currency transactions
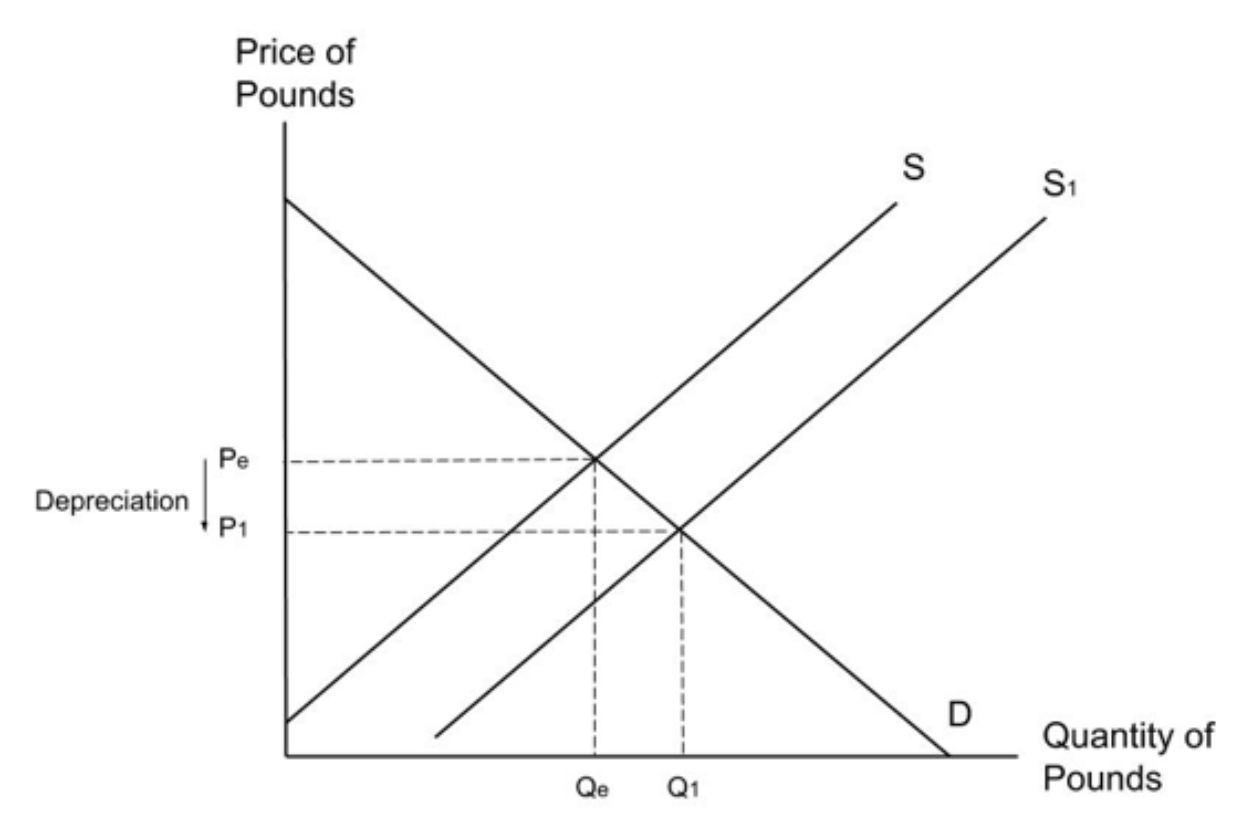
The Central Bank of Argentina uses foreign currency transactions to sell their own currency on the currency market. What is a diagram to show this?
If the Central Bank of Argentina sells Argentine pesos on the currency market, the supply of pesos will increase. This will shift the supply curve to the right and cause a decrease (a depreciation) in the exchange rate.
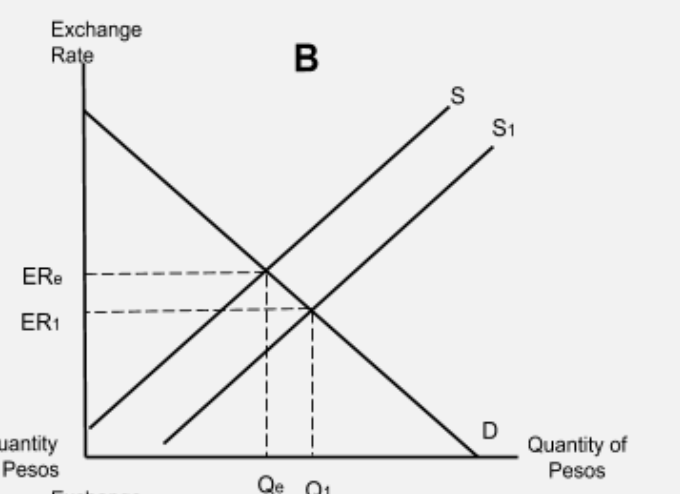
The Central Bank of Argentina increases its interest rate. What is a diagram to show this?
If the Central Bank of Argentina increases its interest rate, the demand for Argentine pesos will increase.This is because hot money investors searching for a high interest rate will be incentivised to save in Argentina. To do so they must purchase pesos and this will shift demand for the peso to the right and cause an increase (an appreciation) in the exchange rate.
How can a country change the value of their fixed exchange rates?
Revaluing or devaluing the currency
What is revalutation?
When a country raises their fixed exchange rate
What is devalutation?
When a country lowers their fixed exchange rate.
When will the government or central bank only intervene in a managed exchange rate system?
to keep the exchange rate in a certain range
How does a reduction in imports affect the value of the UK’s exchange rate?
In order to buy imports, consumers must purchase foreign currency. To do so they must sell (or supply) pounds. This means that a decrease in imports will lead to a decrease in the supply of pounds which in turn will lead to an appreciation of the pound.
What is a floating exchange rate?
With a floating exchange rate, the government or central bank does not intervene to manage their exchange rate at all. The exchange rate is simply determined by the supply and demand for the domestic currency.
What are the two types of exchange rates?
Nominal and real
What is a nominal exchange rate?
The nominal exchange rate tells us the price of one currency in terms of another.
What is a real exchange rate?
the product of the nominal exchange rate (the dollar cost of a euro, for example) and the ratio of prices between the two countries.
How can you calculate the real exchange rate?
Real ER = (Nominal ER x Domestic Price)/Foreign Price
What does a price level tell us?
A price level tells us the average price of a basket of goods and services in an economy.
floating exchange rate positives: Monetary Policy Autonomy
greater flexibility in conducting an independent monetary policy
they can adjust interest rates and the size of quantitative easing to address domestic economic conditions such as growth, inflation and unemployment without being constrained by exchange rate considerations
floating exchange rate positives: Shock Absorption
If a country faces an economic crisis, such as a recession, the exchange rate can act as a shock absorber by helping to rebalance the economy
For example, a recession might cause the exchange rate to depreciate which acts as a boost to export businesses and domestic firms facing import competition.
floating exchange rate positives: Reduced Speculative Attacks
Since exchange rates are determined by market forces, speculative attacks on a currency are less likely although not impossible
Traders and investors are less likely to attempt coordinated efforts to manipulate the exchange rate for short-term gains
floating exchange rate positives: Trade Balance Adjustment
can help correct trade imbalances over time
If a country is running a large trade deficit, its currency's depreciation can eventually make its exports more price competitive and imports more expensive, leading to a narrowing of the deficit
This depends on the price elasticities of demand for exports and imports along with the elasticity of supply of domestic firms
floating exchange rate positives: Currency reserves
the central bank does not need to hold large foreign currency reserves because there is no specific currency target, financial capital can flow freely across countries seeking the best returns
floating exchange rate negatives: Exchange Rate Volatility
Currencies can experience rapid and unpredictable fluctuations, which can introduce uncertainty for businesses engaged in international trade and investment.
floating exchange rate negatives: Currency risk
The volatility of exchange rates introduces currency risk for businesses and investors.
floating exchange rate negatives: Inflation pass through
Exchange rate fluctuations can lead to changes in import prices, which can impact domestic inflation. A significant depreciation of the currency can contribute to imported inflation and erode real purchasing power.
floating exchange rate negatives: Loss of Exchange Rate as a Policy Tool
While countries gain monetary policy autonomy, they lose the ability to manage the exchange rate as a deliberate policy tool. This can limit the direct influence of exchange rates on trade and competitiveness.
fixed exchange rate positives: Price stability
A fixed exchange rate system provides a high degree of price stability since fluctuations in the exchange rate are minimized. This stability can help control inflation and provide a predictable environment for businesses and consumers.
fixed exchange rate positives: Trade confidence
Businesses can plan for transactions without worrying about sudden currency value changes, making cross-border trade more predictable and manageable.
fixed exchange rate positives: Reduced Exchange Rate Risk
Fixed exchange rates eliminate the currency risk associated with fluctuating exchange rates. This stability can be particularly beneficial for companies engaged in long-term contracts, investments, and trade.
fixed exchange rate positives: Foreign investment
A stable exchange rate can attract foreign investment. Investors may be more inclined to invest in a country with predictable currency values, reducing the risk associated with currency fluctuations.
fixed exchange rate negatives: Lack of flexibility
One of the main drawbacks of a fully fixed exchange rate system is the lack of flexibility in responding to external economic shocks. Countries cannot independently adjust their exchange rates to address changing economic conditions.
fixed exchange rate negatives: Loss of Monetary Policy Autonomy
The country may be forced to adopt monetary policies that are not necessarily suited to its specific economic circumstances.
fixed exchange rate negatives: Balance of Payments Issues
In a fixed exchange rate system, a country's balance of payments must be maintained through other means, such as fiscal policy or controls on capital flows. Persistent imbalances can lead to pressures on the currency peg.
fixed exchange rate negatives: Speculative attacks
Fixed exchange rate systems can be vulnerable to speculative attacks if investors believe that the currency is overvalued or if there are concerns about the country's ability to maintain the peg.
fixed exchange rate negatives: Dependence on Reserves
To maintain a fixed exchange rate, a country needs to have sufficient foreign exchange reserves. If reserves are inadequate, the country might struggle to defend the peg during times of market stress.
Managed exchange rate positives: Flexibility
Allows the currency to respond to market conditions while preventing extreme volatility.
Managed exchange rate positives: Policy independence
Countries can pursue independent monetary policies suited to domestic conditions, unlike fixed rate systems.
Managed exchange rate positives: Controlled speculation
Interventions can discourage excessive speculative movements against the currency.
Managed exchange rate negatives: Uncertainty
Some level of uncertainty remains for businesses due to potential government interventions.
Managed exchange rate negatives: Resource intensive
Frequent interventions require significant reserves and can be resource-intensive.
Managed exchange rate negatives: Lack of full control
Although more flexible than a fixed rate, governments do not have full control over the currency value.