Functional Groups
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Functional Group
the arrangement of a group of atoms within a molecule that imparts distinct chemical reactivity to the compound
Alkanes
saturated hydrocarbons of single bonded hydrocarbons. The molecular formula for is CnH2n+2
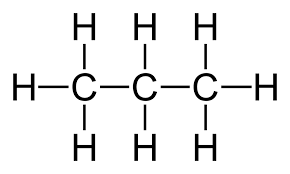
Three carbons with single bonds
Propane
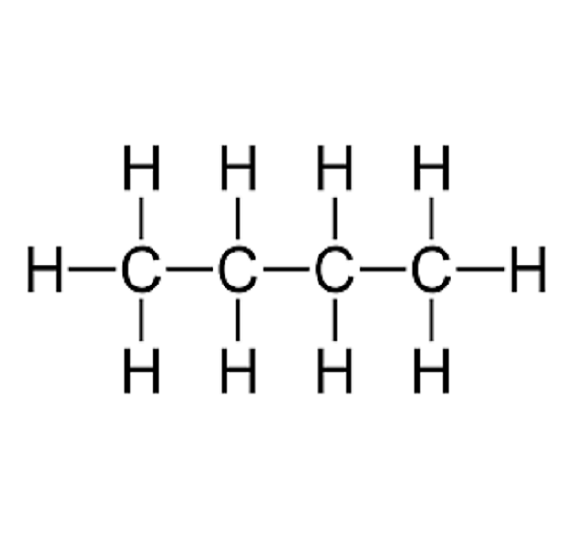
four carbons with single bonds
Butane
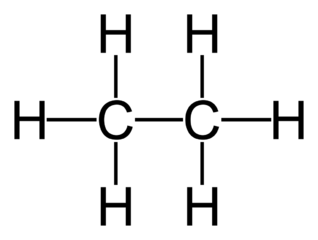
two carbons with single bonds
Ethane
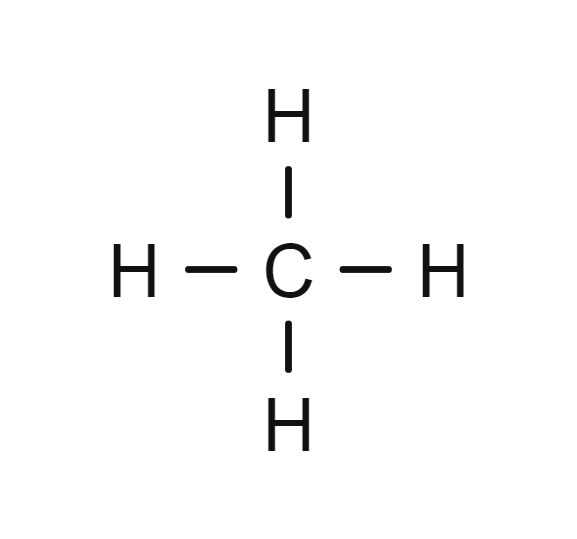
one carbon with single bonds
Methane
Physical Properties of Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes
They are non polar and therefore are hydrophobic
Boiling point increases with increasing molecular weight
They have a faint smell and are colorless
Chemical Properties of Alkanes
they react with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water and heat.
They undergo substitution reaction.
Alkyl groups Formula
CnH2n+1
Alkenes
Unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. Their general formula is CnH2n
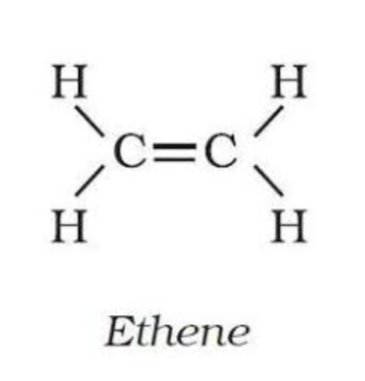
two carbons with at least one double bond
Ethene
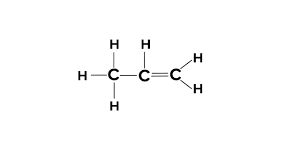
three carbons with at least one double bond
propene
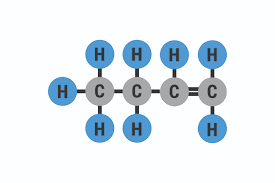
four carbons with at one double bond
Butene
Alkyne
they are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. they have the molecular formula CnH2n-2.
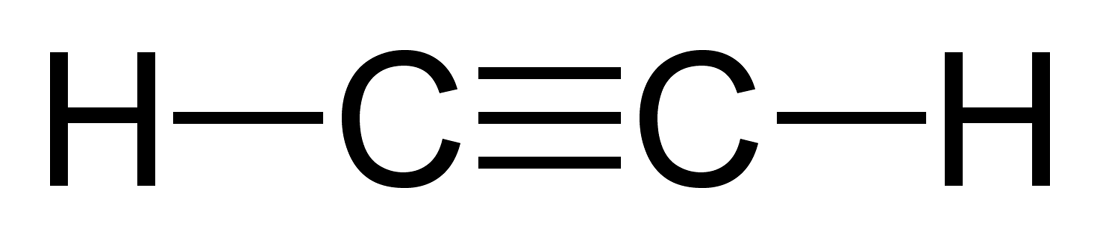
two carbons with at least one triple bond
Ethyne

three carbons with at least one triple bond
Propyne
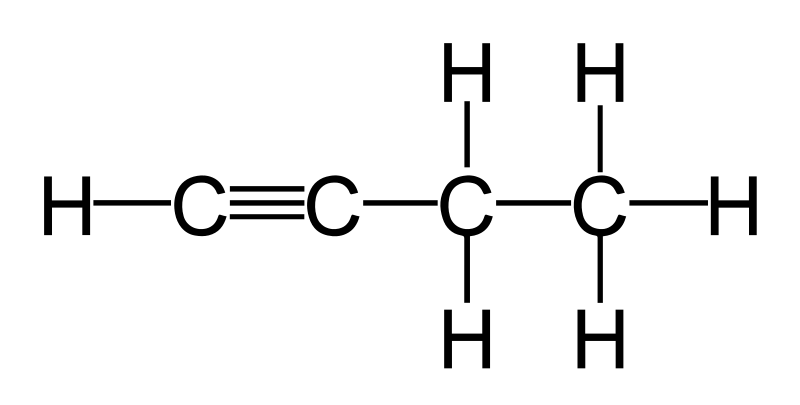
four carbons with at least one triple bond
Butyne
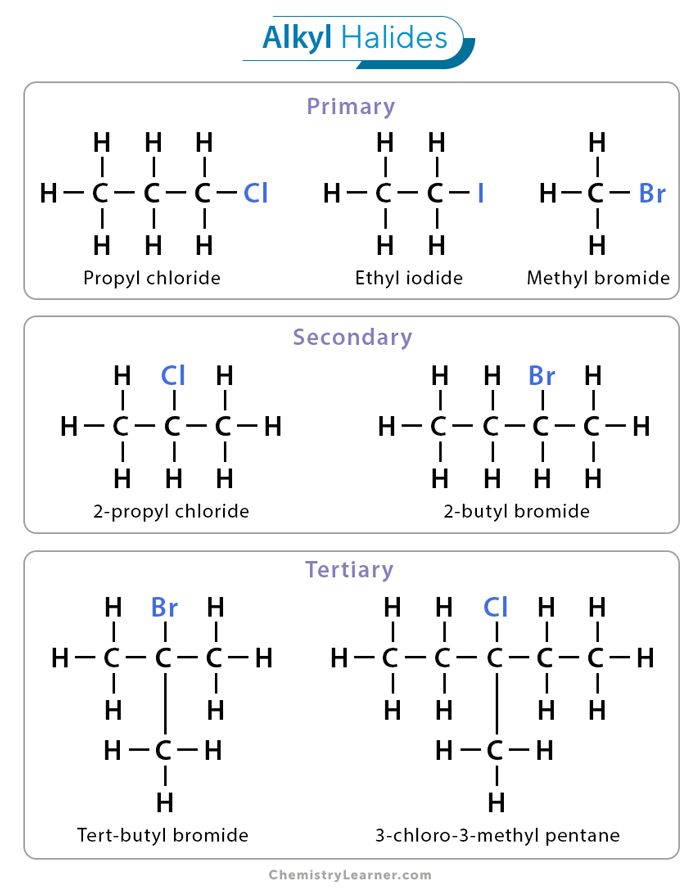
Primary Alkyl Halide
this compound is formed when the carbon atom that bears the halogen is attached to only one other carbon
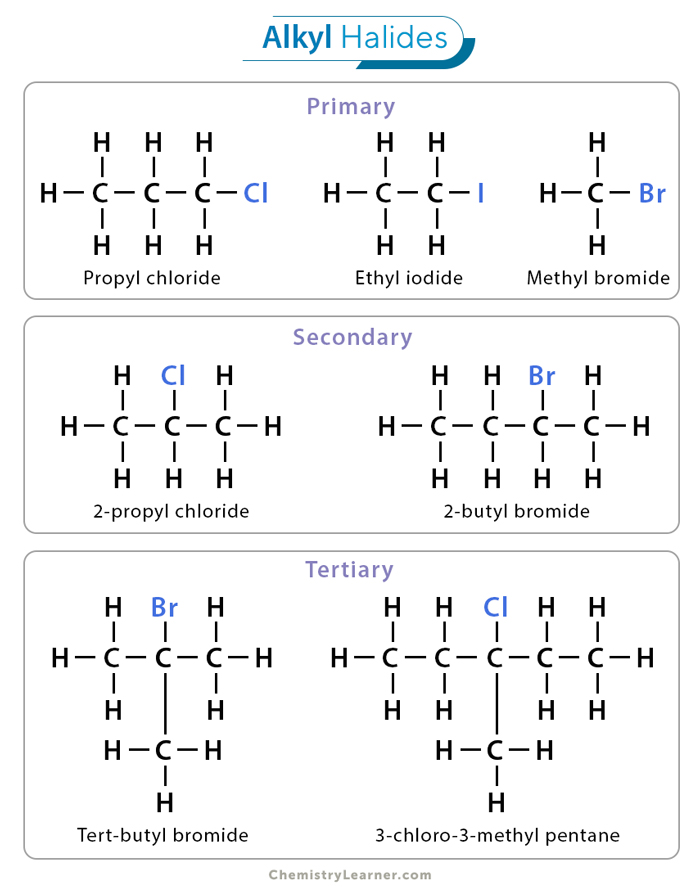
Secondary Alkyl Halide
this compound is formed when the carbon that bears the halogen is itself attached to two other carbon atoms
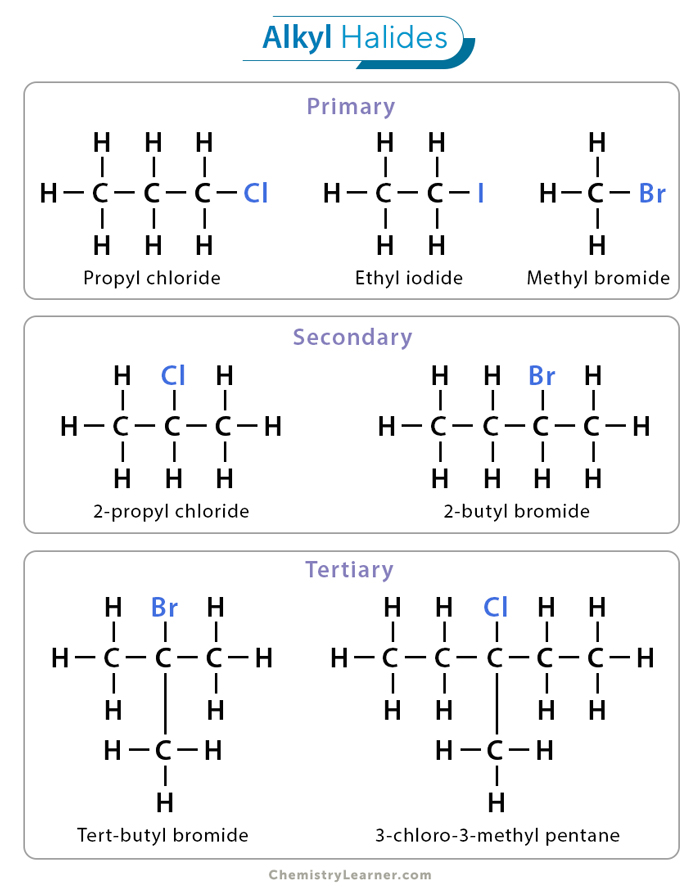
Tertiary Alkyl Halide
This compound is formed when the carbon that is bonded to the halogen is attached to three other carbon atoms
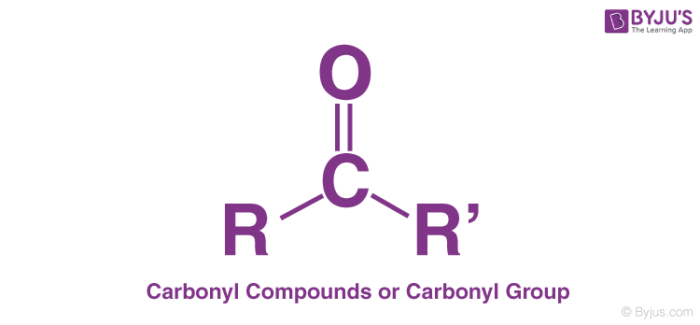
Carbonyl group
An organic functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom
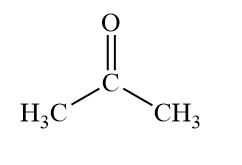
Ketone
organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group that is within the chain
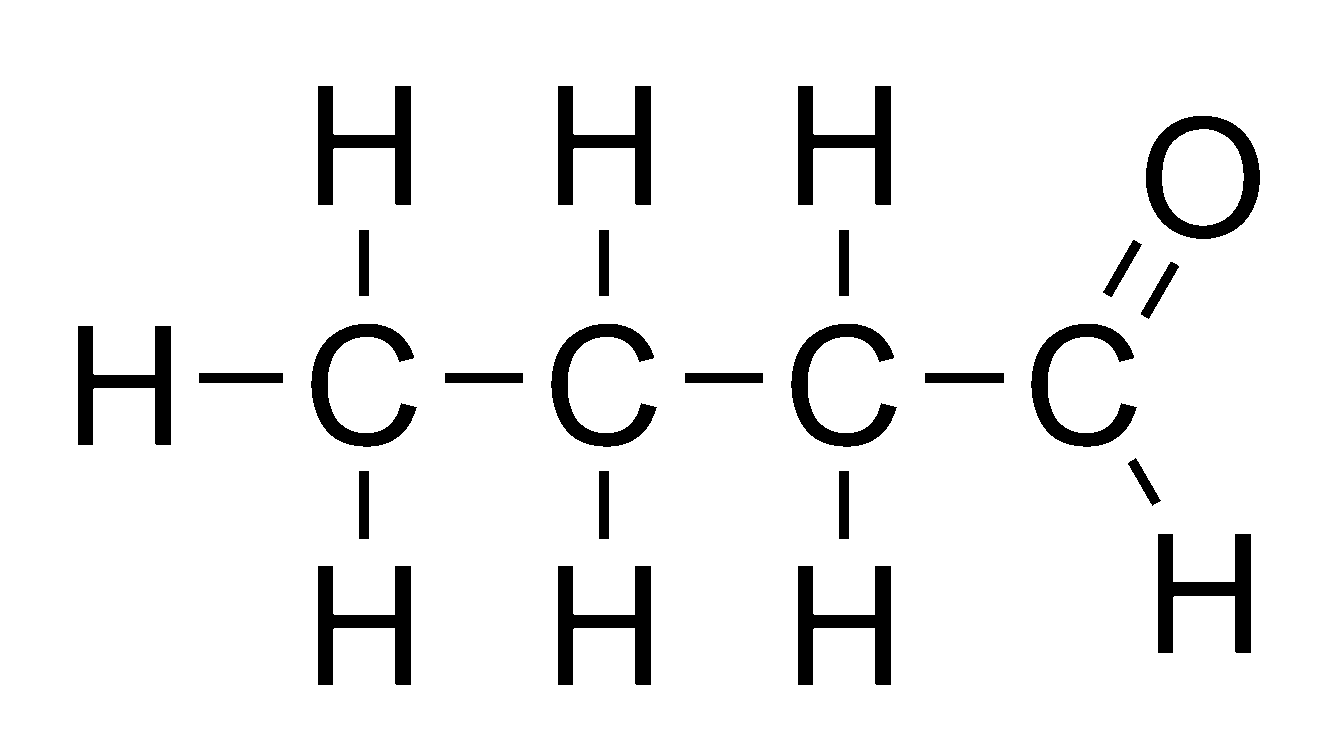
Aldehyde
organic compounds in which the carbonyl group is located at the end of the carbon chain.
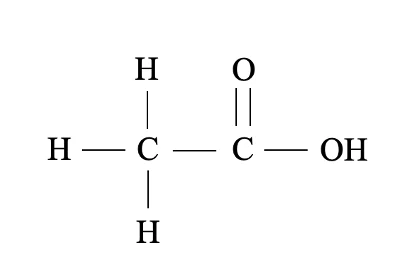
Carboxylic acid
Organic compounds that contain the carboxyl group (COOH)
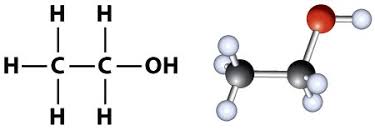
Alcohol
Organic compounds that contain a hydroxyl (OH) functional group.
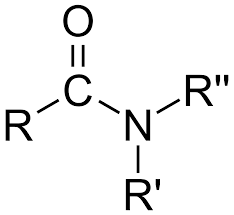
Amides
Organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group linked to a nitrogen atom.
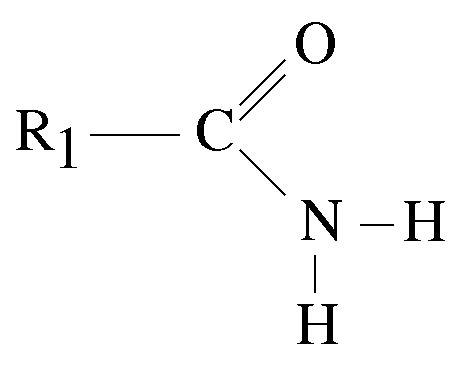
Primary Amides
Amides that have one carbon-containing group attached to the nitrogen atom
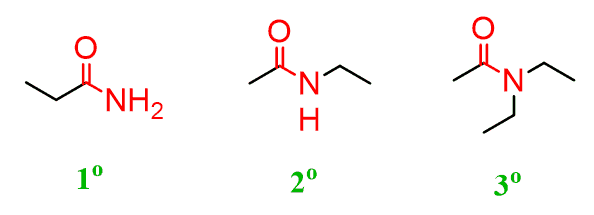
Secondary Amides
Amides that have two carbon-containing group attached to the nitrogen atom
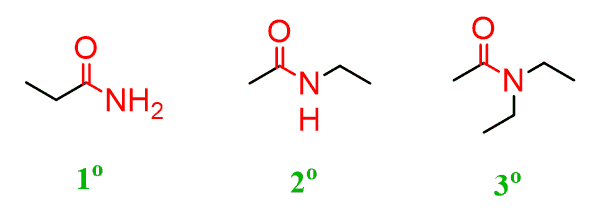
Tertiary Amides
Amides that have three carbon-containing groups attached to the nitrogen
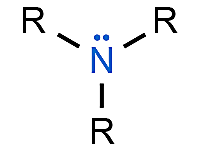
Amines
Organic compounds that contain a central nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons
Ester
Organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group bonded to an alkoxyl group
Chemical property of Esters
reacts with water to produce alcohol and organic or inorganic acid.
Chemical Formula for Esters
RCOOR’
R’ can never be a hydrogen atom
Nitrile
Any organic compound which contains a carbon triple bonded to a nitrogen
Ether
any of a class of organic compounds characterized by an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups.