Introduction to Materials Science and Engineering Principles
1/536
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
537 Terms
Materials
Substances with mass that occupy space.
Natural materials
Derived from animals, plants, and rocks.
Manufactured materials
Created from natural materials via chemical processes.
Engineering materials
Materials used in engineering and daily applications.
Material engineers
Professionals who develop and test new materials.
Advanced materials
New or modified materials for superior performance.
Functional materials
Materials performing specific functions in systems.
Shape memory alloys
Materials that return to original shape when heated.
Nanomaterials
Materials with structures at the nanoscale.
Supermaterials
Innovative materials like graphene and aerogel.
Graphene
One-atom-thick material stronger than steel.
Physical properties
Characteristics like melting point and density.
Chemical properties
Reactivity with substances like water and acids.
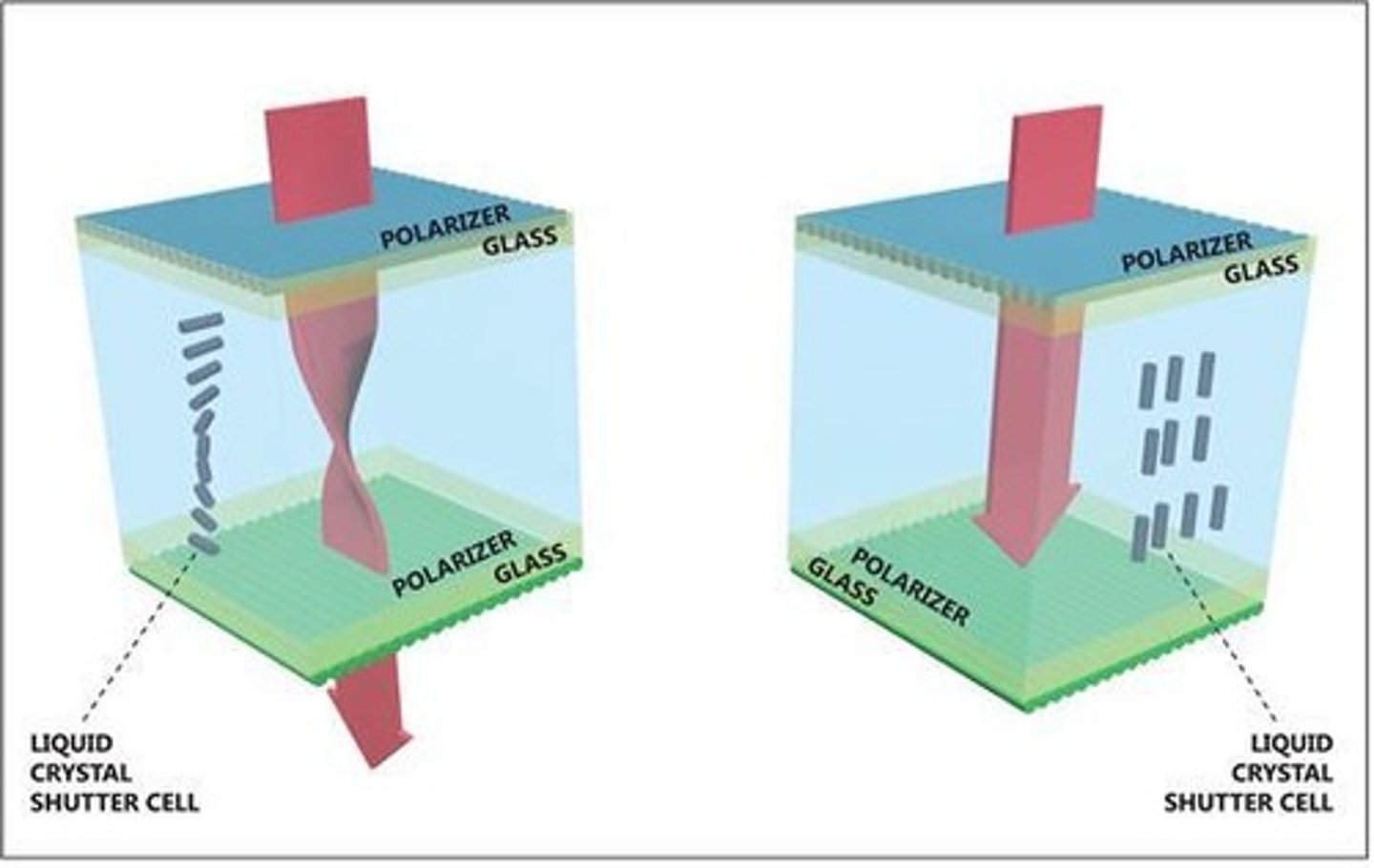
Intelligent structures
Materials designed to perform complex functions.
Modern materials
Used in manufacturing across various industries.
Densest crystal packing
Maximum density arrangement of atoms in a crystal.
Intermolecular attractions
Forces holding molecules together in materials.
Thermal conductor
Material that efficiently conducts heat.
Electrical insulator
Material that resists electrical flow.
Viscosity
Resistance of a fluid to flow.
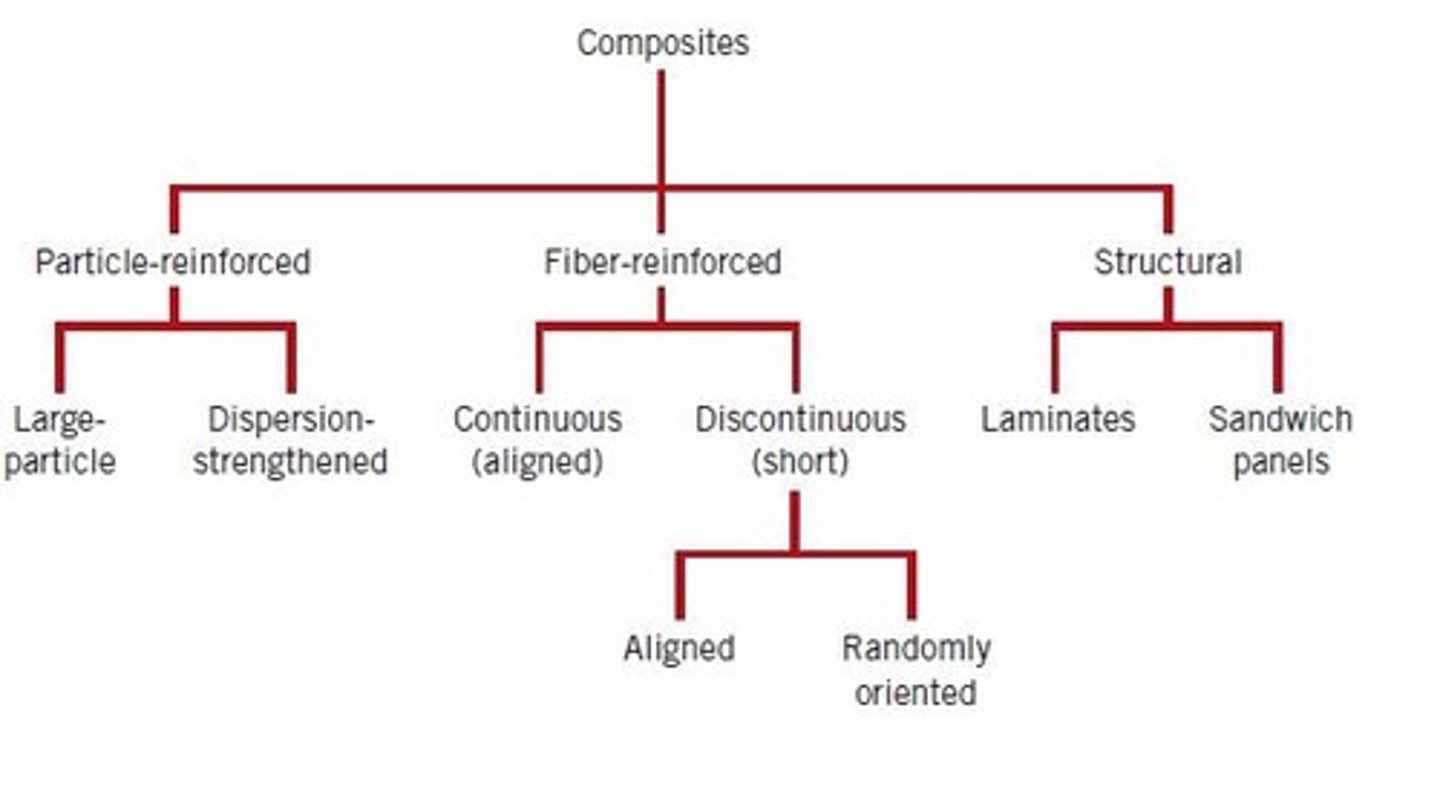
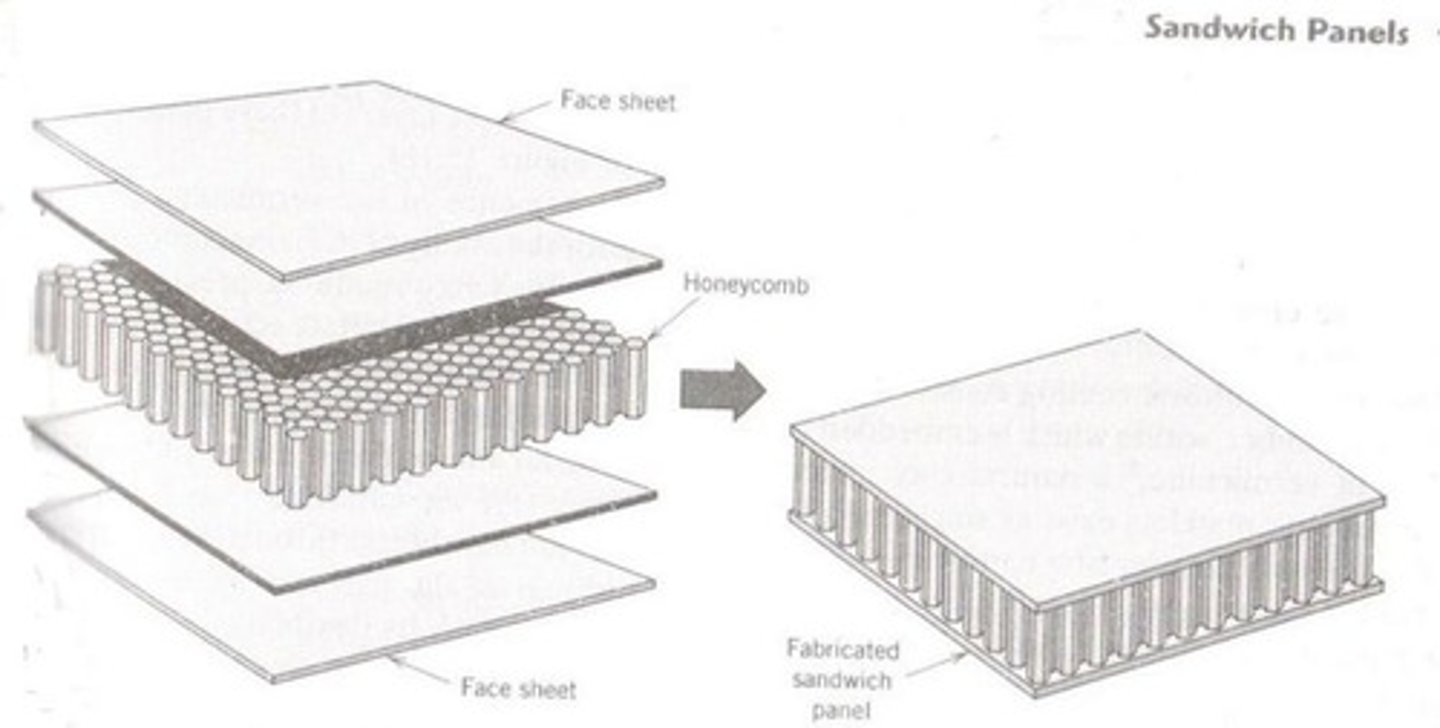
Composites
Materials made from two or more constituent materials.
Functional smart materials
Materials that respond to environmental changes.
Societal impact of materials science
Advancements improving quality of life through materials.
Material Science
Study of materials' structure and properties.
Structure-Property Relationship
Connection between material structure and its properties.
Materials Technology
Application of materials in manufacturing products.
Plastics
Synthetic materials used in various applications.
Metals
Elements like iron and aluminum for structures.
Concrete
Primary material for civil construction projects.
Building Materials
Materials used in construction, structural or decorative.
Appropriate Technology
Local resources used for local needs.
Rubber
Elastic material used in footwear and tires.
Plaster of Paris
Material that hardens when mixed with water.
Thin-Film Materials
Used in sensors and solar cells.
Nano-Scale Effects
Altered properties at molecular levels.
Biocompatibility
Compatibility of materials with biological systems.
Smart Features
Innovative technology integration in materials engineering.
Physical Properties
Characteristics like hardness and thermal conductivity.
Chemical Properties
Reactivity and interactions of materials with substances.
Defect Structure
Imperfections in material phases affecting properties.
Residual Stress
Internal stresses remaining in materials after processing.
Mechanical Properties
Strength, hardness, and elasticity of materials.
Thermal Properties
Material behavior under temperature changes.
Electrical Properties
Conductivity and response to electric fields.
Optical Properties
Interaction of materials with light.
Thermodynamic Properties
Energy changes and equilibrium in materials.
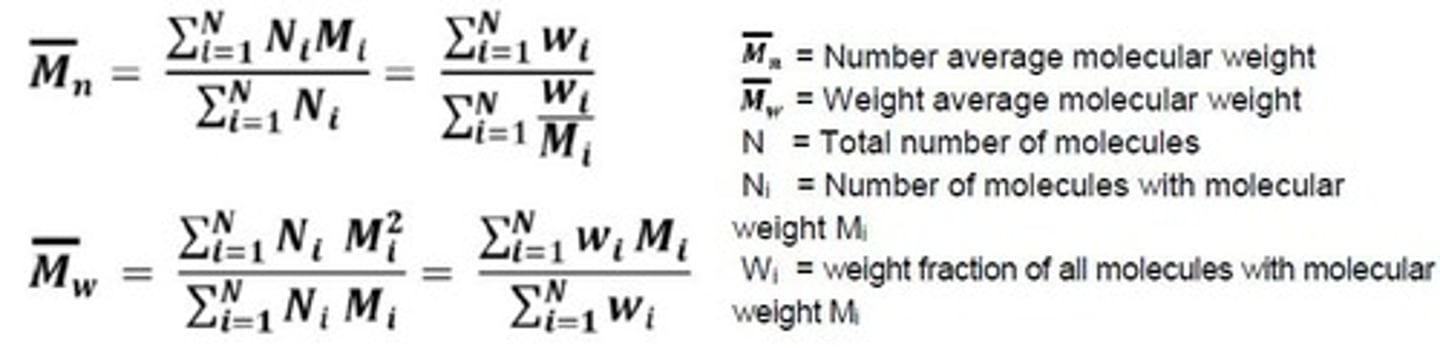
Properties of Materials
Depend on components' size, shape, and bonding.
Materials Science Goal
Design materials with predetermined properties and performance.
Microstructure
Arrangement of particles affecting material properties.
Materials Classification
Six categories: pure, alloys, polymers, ceramics, composites, miscellaneous.
Pure Substances
Elements like Cu, Ni, Fe used in engineering.
Alloys
Metal mixtures like brass and NiAl.
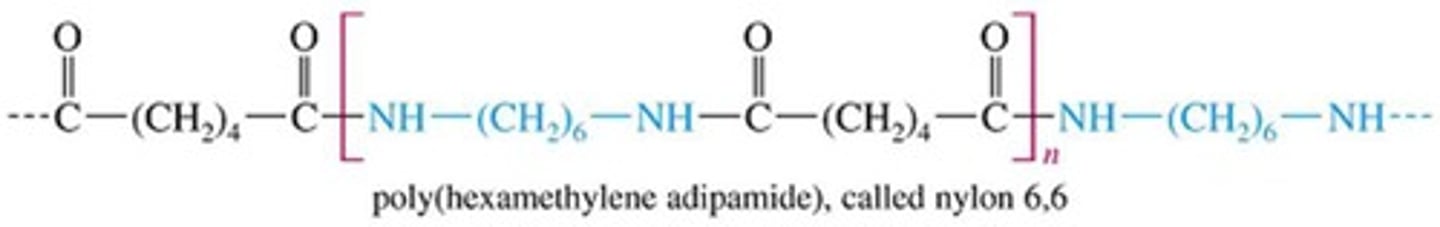
Polymers
Long-chain molecules like polyethylene and PVC.
Ceramics
Inorganic materials like alumina and glass.
Composites
Materials made from two or more constituents.
Miscellaneous Materials
Includes lime, gypsum, and tiles.
States of Matter
Materials classified as gases, liquids, or solids.
Crystalline State
Particles arranged in a nearly perfect order.
Amorphous Materials
Lack a defined crystalline structure, like glass.
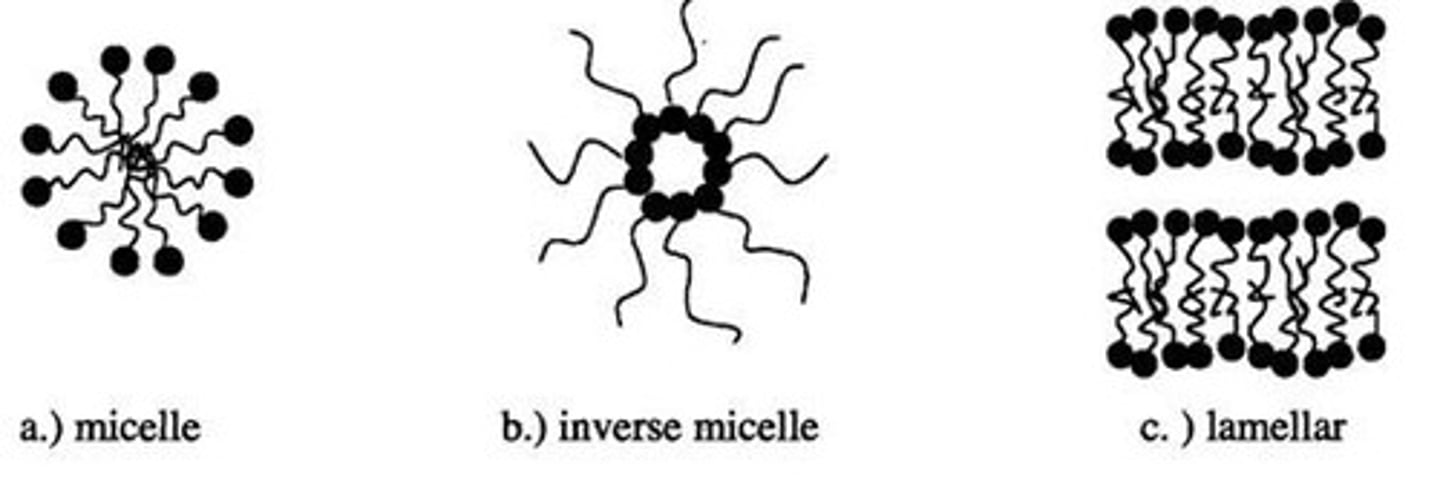
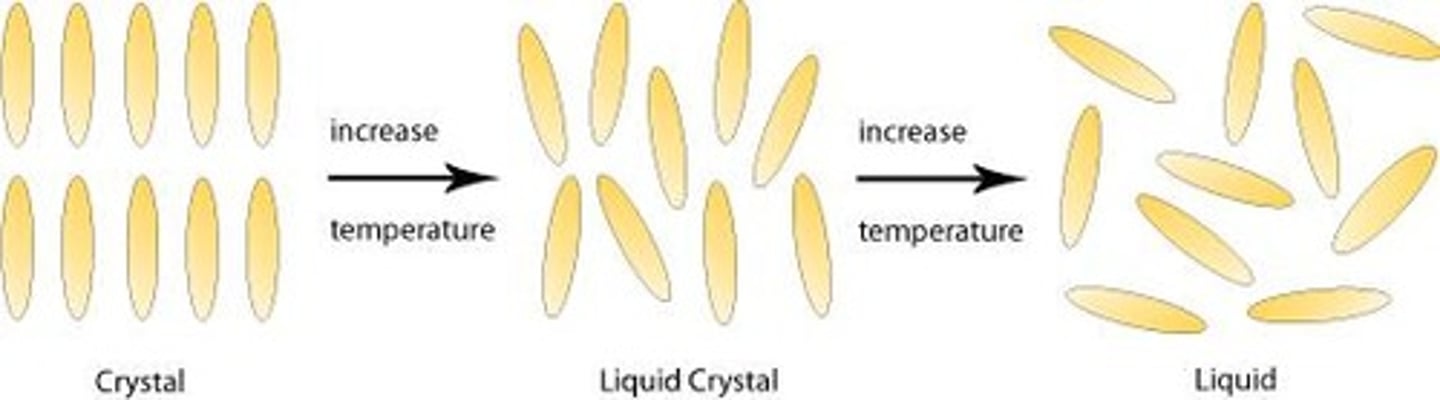
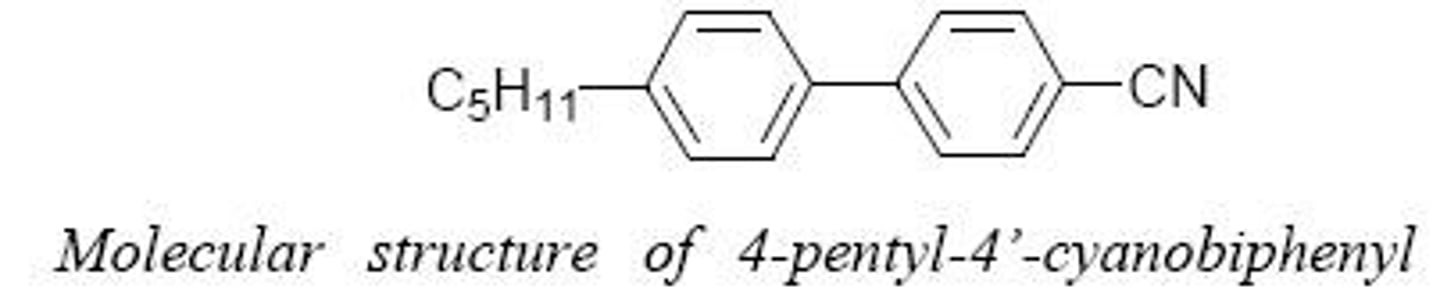
Liquid Crystals
Exhibit properties between liquids and solids.
Supercritical Fluids
Have properties between liquids and gases.
Homogeneous Materials
Uniform composition, includes pure substances and solutions.
Heterogeneous Materials
Can be mechanically separated into components.
Magnetic Materials
Classified as paramagnetic, diamagnetic, ferromagnetic, etc.
Electrical Conductors
Materials like Cu, Al, and Ag that conduct electricity.
Semiconductors
Materials like Ge and Si with intermediate conductivity.
Insulators
Materials like Al2O3 that resist electrical flow.
Ductility
Materials classified as ductile (metals) or brittle (ceramics).
Acoustic Conductors
Materials like bronze that transmit sound effectively.
Light Interaction
Materials categorized as transparent, translucent, or opaque.
Bonding Types
Classified into ionic, molecular, covalent, and metallic.
Chemical Classifications
Includes bulk, fine, and specialty chemicals.
Ferrous Metals
Contain iron, examples include steel and cast iron.
Non-Ferrous Metals
Do not contain iron, like aluminum and copper.
Thermoplastics
Plastics that can be remolded with heat.
Thermosets
Plastics that cannot be remolded after curing.
Elastomers
Flexible materials that can stretch significantly.
Linear Plastics
Polymers with a straight-chain molecular structure.
Branched Plastics
Polymers with side chains off the main chain.
Cross-linked Plastics
Polymers with interconnected molecular chains.
Natural Plastics
Plastics derived from natural sources.
Synthetic Plastics
Plastics made from synthetic materials.
Addition Plastics
Plastics formed by adding monomers together.
Condensation Plastics
Plastics formed by eliminating small molecules.
Ceramic Materials
Inorganic materials that are brittle and heat-resistant.
Matrix Material
Base material in composite structures.
Liquid Crystalline Materials
Materials with properties between liquids and solids.
Smart Materials
Materials that respond to external stimuli.
Biomaterials
Materials compatible with biological systems.
Superconductors
Materials that conduct electricity without resistance.
Type-I Superconductors
Soft superconductors that exhibit complete expulsion of magnetic fields.
Type-II Superconductors
Hard superconductors that allow partial magnetic field penetration.
Hazardous Materials
Substances posing risks to health or safety.
Material Design Qualities
Factors influencing successful material development.
World-class materials
High-quality materials produced through expertise and experience.
Systematic planning
Organized approach to achieve predictable outcomes.
Atomic structure
Arrangement of atoms in a material affecting properties.
Nature of bonding
Type of atomic interactions influencing material characteristics.
Chemical bond
Force holding atoms together in stable arrangements.
Ionic bond
Electrostatic attraction between cations and anions.